Predicting Environmental Social and Governance Scores: Applying Machine Learning Models to French Companies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Determinants of ESG Scores
2.2. Critical Analysis of the Reliability of ESG Scores
2.3. Analysis of ESG Scores Using Machine Learning
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample and Data
3.2. Variables Definitions
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Independent Variables
3.3. Data Processing
3.3.1. Standardisation
3.3.2. Handling Missing Values
3.3.3. Encoding Categorical Variables
3.4. Descriptive Analysis of Variables
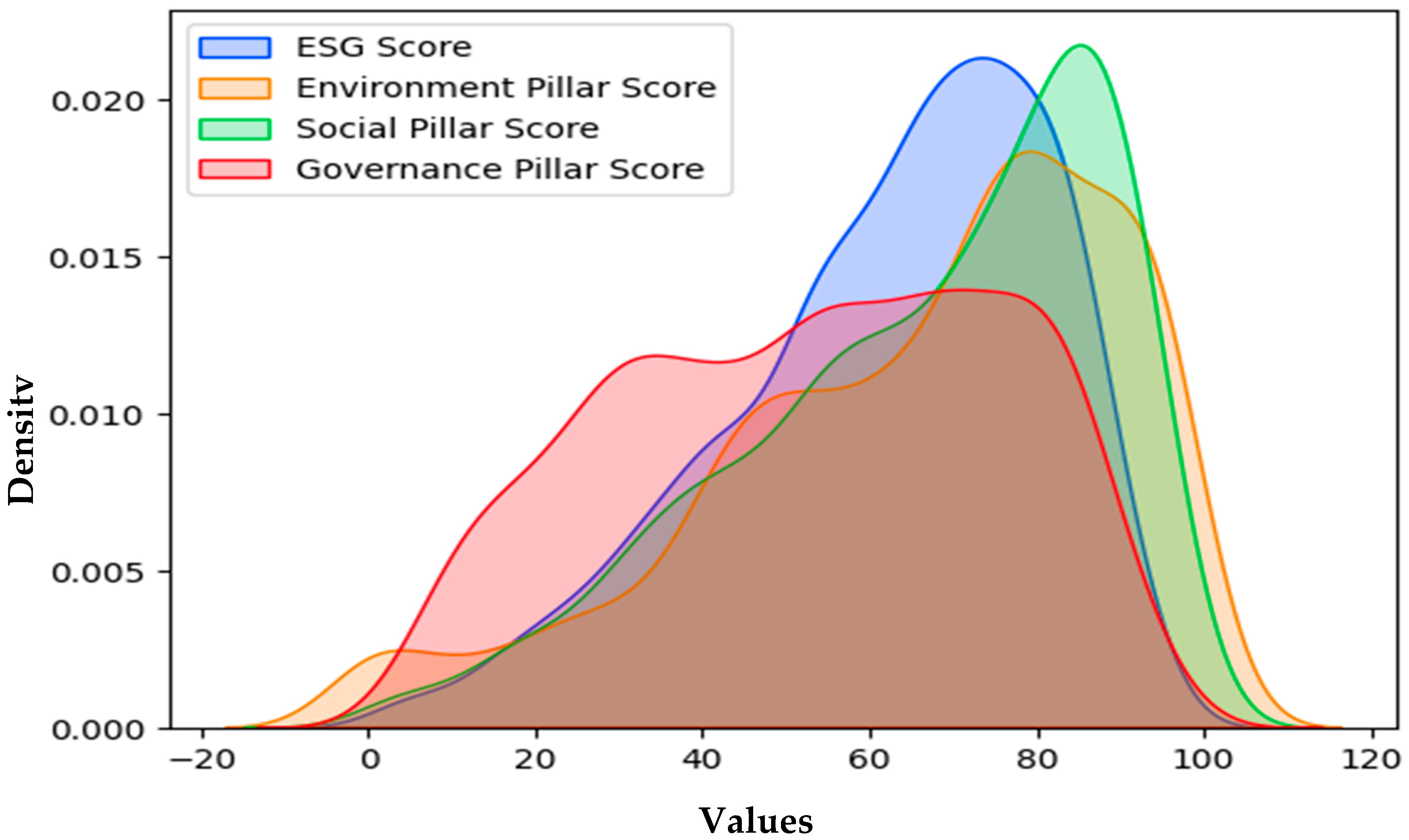
3.4.1. Descriptive Statistics
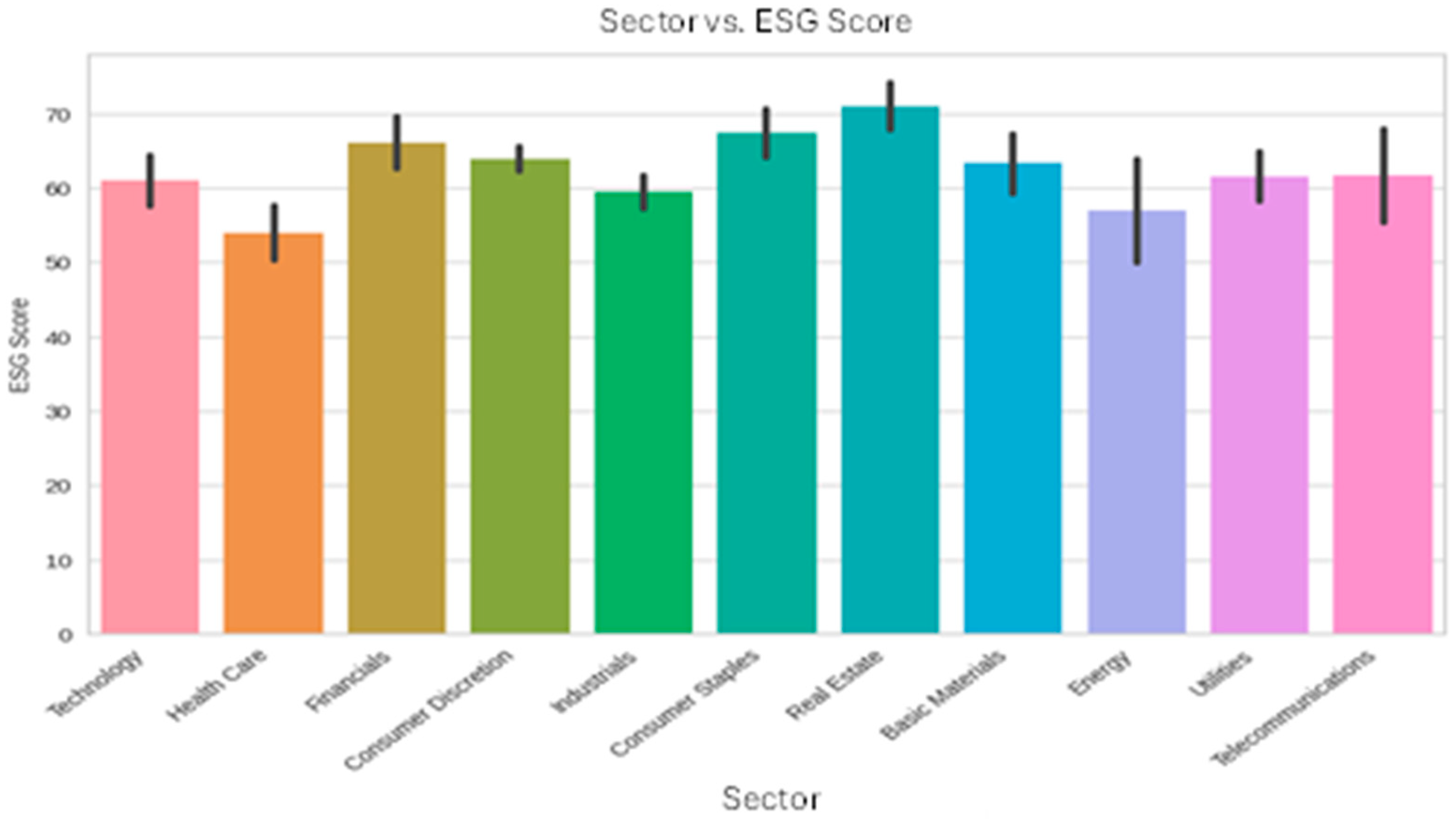
3.4.2. Analysis of ESG Scores Across Sectors
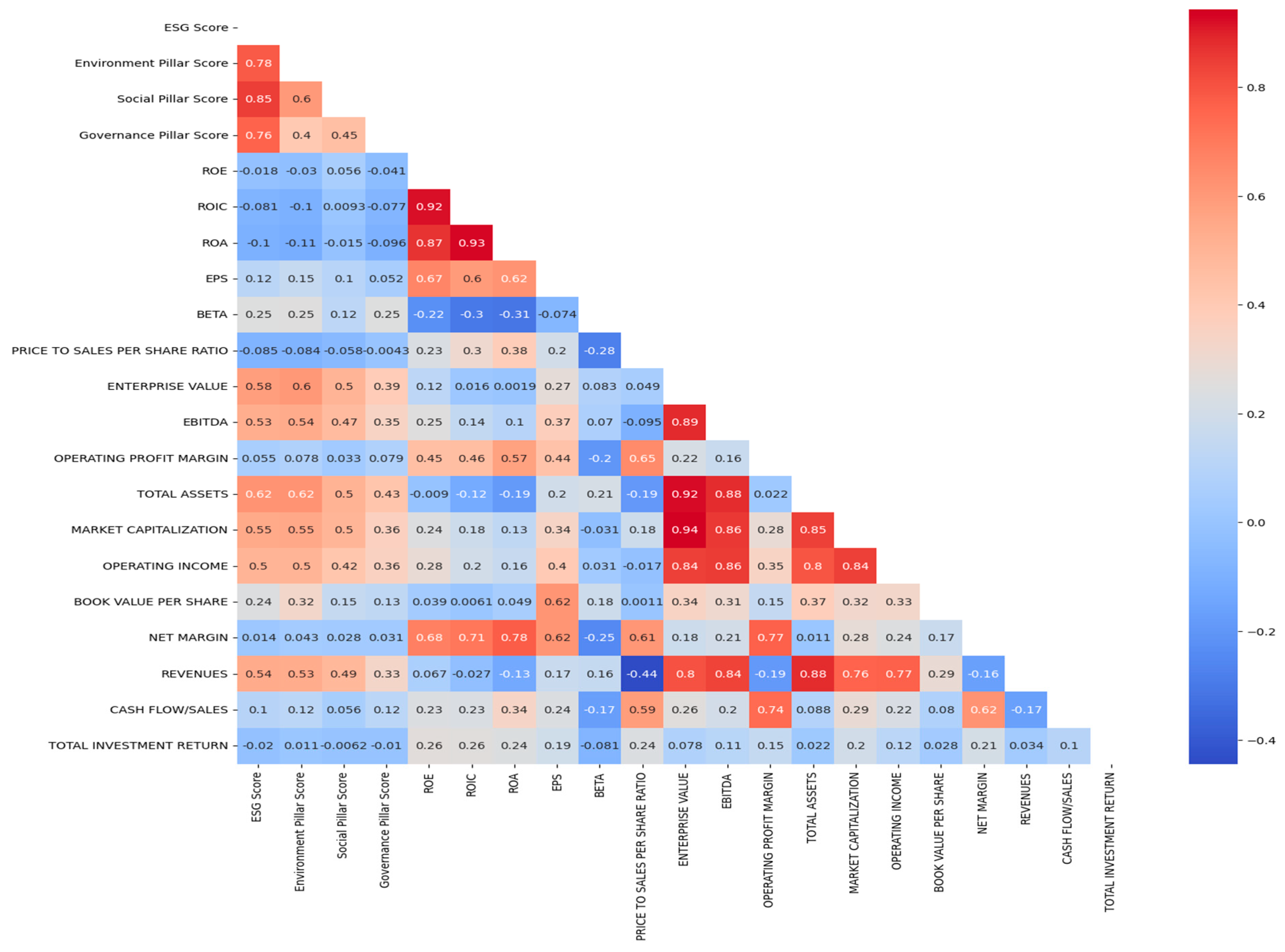
3.4.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Empirical Results and Discussion
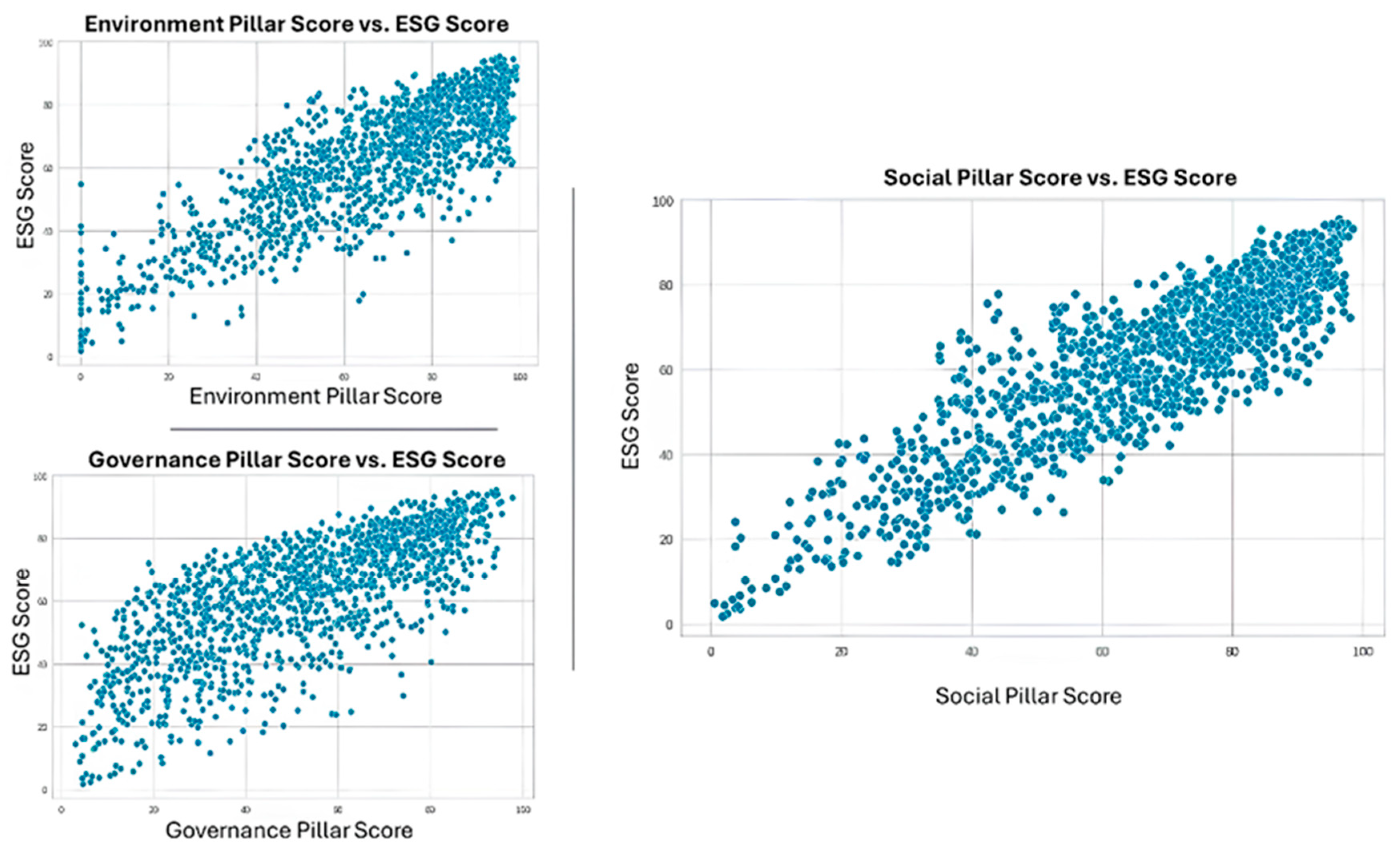
4.1. The Importance of Each Pillar in Determining the ESG Score
4.2. Modelling ESG Scores
4.2.1. Variable Selection
4.2.2. Comparative Analysis of Model Performance
4.3. Prediction of the ESG Score Using the Random Forest (RF) Algorithm: Robustness Test
4.3.1. Optimisation of Model Hyperparameters
4.3.2. Performance Evaluation of the RF Model
4.4. Discussion and Interpretation of Modelling Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Nouvelle Régulation Économique means New Economic Regulation. |
| 2 | CAC stands for Continuous Assisted Quotation. |
| 3 | Results are available on request. |
| 4 | These values and the Python code and results are available on request. |
References
- Agarwala, N., Jana, S., & Sahu, T. N. (2024). ESG disclosures and corporate performance: A non-linear and disaggregated approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 437, 140517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoraki, M. E. K., Giaka, M., Konstantios, D., & Patsika, V. (2023). Firms’ sustainability, financial performance, and regulatory dynamics: Evidence from European firms. Journal of International Money and Finance, 131, 102785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, P., & Bastani, A. F. (2023). Value-at-risk-based portfolio insurance: Performance evaluation and benchmarking against CPPI in a markov-modulated regime-switching market. arXiv, arXiv:2305.12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoncic, M. (2020). Uncovering hidden signals for sustainable investing using big data: Artificial intelligence, machine learning and natural language processing. Journal of Risk Management in Financial Institutions, 13(2), 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, M. M., Maso, L. L. D., Liberatore, G., Mazzi, F., & Terzani, S. (2018). Role of country- and firm-level determinants in environmental, social, and governance disclosure. Journal of Business Ethics, 150(1), 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Flah, I., Lajmi, A., & Hlioui, Z. (2024). How does innovation moderate the CSR impact on financial performance? An exploratory study and an empirical validation in the Tunisian context. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, F., Kölbel, J. F., & Rigobón, R. (2022). Aggregate confusion: The divergence of ESG ratings. Review of Finance, 26(6), 1315–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birindelli, G., Dell’Atti, S., Iannuzzi, A. P., & Savioli, M. (2018). Composition and activity of the board of directors: Impact on ESG performance in the banking system. Sustainability, 10, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, W., Müller, T., Rosenbach, D. J., & Salzmann, A. J. (2018). Corporate social Responsibility, investor protection, and Cost of Equity: A cross-country comparison. Journal of Banking and Finance, 96, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkham, J. (1995). Keeping Good Company: A Study of Corporate Governance in Five Countries (389p). Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji, A., Durand, R., Levine, D. I., & Touboul, S. (2015). Do ratings of firms converge? Implications for managers, investors and strategy researchers. Strategic Management Journal, 37(8), 1597–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Qian, W., & Huang, J. (2021). Motorcycle ban and traffic safety: Evidence from a quasi-experiment at Zhejiang, China. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2021, 7552180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., Song, Y., & Gao, P. (2023). Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance and financial outcomes: Analyzing the impact of ESG on financial performance. Journal of Environmental Management, 345, 118829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaibi, S., Chouaibi, J., & Rossi, M. (2022). ESG and corporate financial performance: The mediating role of green innovation: UK common law versus Germany civil law. EuroMed Journal of Business, 17(1), 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y., Geobey, S., Weber, O., & Lin, H. C. (2018). The impact of green lending on credit risk in China. Sustainability, 10(6), 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V., D’Ecclesia, R. L., & Levantesi, S. (2021a). Fundamental ratios as predictors of ESG scores: A machine learning approach. Decisions in Economics and Finance, 44(2), 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V., D’Ecclesia, R. L., & Levantesi, S. (2021b). ESG score prediction through random forest algorithm. Computational Management Science, 19(2), 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, P., Koronios, K., Thrassou, A., & Vrontis, D. (2020). Cash holdings, corporate performance and viability of Greek SMEs: Implications for stakeholder relationship management. EuroMed Journal of Business, 15(3), 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T. M. (2018). Ratings that don’t rate: The subjective world of ESG ratings agencies. ACCF. [Google Scholar]
- Drempetic, S., Klein, C., & Zwergel, B. (2019). The influence of firm size on the ESG Score: Corporate Sustainability Ratings under review. Journal of Business Ethics, 167(2), 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, B., Kölbel, J., & Rigobon, R. (2020). Aggregate confusion: The divergence of ESG ratings. Social Science Research Network, 26(6), 1315–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F., González-Bueno, J., Guijarro, F., & Javier, O. (2020). Forecasting the environmental, social, and governance rating of firms by using corporate financial performance variables: A rough set approach. Sustainability, 12(8), 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannarakis, G. (2014). The determinants influencing the extent of CSR disclosure. International Journal of Law and Management, 56(5), 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T. (2020). ESG RISK: A deep learning framework from ESG news to stock volatility prediction. arXiv, arXiv:2005.02527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. J., Kim, H. J., & Yu, J. (2016). Empirical study on relationship between corporate social responsibility and financial performance in Korea. Asian Journal of Sustainability and Social Responsibility, 1, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoepner, A. G. F., Oikonomou, I., Sautner, Z., Starks, L., & Zhou, X. (2023). ESG shareholder engagement and downside risk. Review of Finance, 28(2), 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K. H., Lin, S. J., Liu, J. Y., Chen, F. H., & Chen, S. H. (2018). The Influences of CSR’s Multi-Dimensional Characteristics on Firm Value Determination by a Fusion Approach. Sustainability, 10(11), 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, E., Krueger, P., Sautner, Z., & Starks, L. T. (2019). Institutional investors’ views and preferences on climate risk disclosure. Social Science Research Network. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S., & Yoon, A. (2023). Analyzing active fund managers’ commitment to ESG: Evidence from the United Nations principles for responsible investment. Management Science, 69(2), 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C., Zhang, L., Huang, J., Xiao, H., & Zhou, Z. (2021). Social responsibility portfolio optimization incorporating ESG criteria. Journal of Management Science and Engineering, 6(1), 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Gong, M., Zhang, X. Y., & Koh, L. (2018). The impact of environmental, social, and governance disclosure on firm value: The role of CEO power. The British Accounting Review, 50(1), 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P. C., Shih, Y. N., Wu, C. L., Zhang, X. L., & Wang, Y. (2018). Does corporate social performance pay back quickly? A longitudinal content analysis on international contractors. Journal of Cleaner Production, 170, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licari, J., Loiseau-Aslanidi, O., Piscaglia, S., & Solis Gonzalez, B. (2021). ESG score predictor: Applying a quantitative approach for expanding company coverage. Moody’s anal. Available online: https://www.moodysanalytics.com/-/media/article/2021/esg-score-predictor.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Lucia, C., Pazienza, P., & Bartlett, M. (2020). Does good ESG lead to better financial performances by firms? Machine learning and logistic regression models of public enterprises in Europe. Sustainability, 12(13), 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozes, M., Josman, Z., & Yaniv, E. (2011). Corporate social responsibility organizational identification and motivation. Social Responsability Journal, 7, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A. (2016). The tangibility of the intangibles: What drives banks’ sustainability disclosure in the emerging economies? (p. 120) GEG. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, H., Khan, M. A., Mazliham, M. S., Alam, M. M., Aman, N., & Abbas, K. (2022). Applying artificial intelligence techniques for predicting the environment, social, and governance (ESG) pillar score based on balance sheet and income statement data: A case of non-financial companies of USA, UK, and Germany. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 975487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, R., Hinze, A., & Hardeck, I. (2016). Impact of ESG factors on firm risk in Europe. Journal of Business Economics, 86(8), 867–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A., Mostovoy, J., Ding, J. B., & Seco, L. (2021). Building machine learning systems for automated ESG scoring. Journal of Impact and ESG Investing, 1(3), 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, M. (1974). Competitive and optimal responses to signals: An analysis of efficiency and distribution. Journal of Economic Theory, 7(3), 296–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, T. (1996). Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 58(1), 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, O., Koellner, T., Habegger, D., Steffensen, H., & Ohnemus, P. (2008). The relation between the GRI indicators and the financial performance of firms. Progress in Industrial Ecology, An International Journal, 5(3), 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G., Liu, Y., Cheng, W., & Lee, C. (2022, January 14–16). Data analysis of ESG stocks in the Chinese stock market based on machine learning. 2022 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X., Li, Z., Xu, J., & Shang, L. (2022). ESG disclosure and corporate financial irregularities—Evidence from Chinese listed firms. Journal of Cleaner Production, 332, 129992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W., Yin, L., Chen, X., Ma, Z., Liu, S., & Yang, B. (2021). Knowledge base graph embedding module design for visual question answering model. Pattern Recognition, 120, 108153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Accounting Indicators | Market Indicators |
|---|---|
| Return on Equity (ROE) Return on Capital Employed (ROIC) Return on Assets (ROA) Earnings per share (EPS) Operating profit margin Sales (REVENUES) Total Assets Cash-Flow/Sales Enterprise Value EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortisation) Operating Income Net Margin Total Investment Return | BETA (systematic risk factor) Market Capitalisation Price to sales per share ratio Book value per share |
| Common Indicators | |
| Activity Sector Environment Pillar Score Social Pillar Score Governance Pillar Score | |
| Variables | Observations | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESG Score | 1412 | 62.107 | 19.392 | 1.84 | 95.47 |
| Environment Pillar Score | 1412 | 65.699 | 24.403 | 0 | 99.16 |
| Social Pillar Score | 1412 | 66.494 | 21.972 | 0.45 | 98.47 |
| Governance Pillar Score | 1412 | 52.661 | 23.319 | 3.04 | 97.73 |
| ROE | 1412 | 2.132 | 15.057 | −548.997 | 47.057 |
| ROIC | 1412 | 6.454 | 17.438 | −131.94 | 358.42 |
| ROA | 1412 | 3.554 | 9.464 | −108.03 | 70.2 |
| EPS | 1412 | 3.186 | 22.018 | −60.234 | 768.921 |
| BETA | 1412 | 1.106 | 0.535 | −0.23 | 3.1 |
| PRICE TO SALES PER SHARE RATIO | 1412 | 3.059 | 18.221 | −17.29 | 549.32 |
| ENTERPRISE VALUE | 1412 | 0.762 | 2.102 | −0.407 | 18.203 |
| EBITDA | 1412 | 0.777 | 1.968 | −3.573 | 15.438 |
| OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN | 1412 | −0.566 | 9.43 | −163.97 | 15.737 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 1412 | 2.629 | 10.497 | −0.303 | 88.066 |
| MARKET CAPITALISATION | 1412 | 0.668 | 1.798 | −0.385 | 24.939 |
| OPERATING INCOME | 1412 | 0.804 | 2.125 | −4.912 | 18.627 |
| BOOK VALUE PER SHARE | 1412 | 0.298 | 3.435 | −43.668 | 74.131 |
| NET MARGIN | 1412 | −0.779 | 13.49 | −233.105 | 39.09 |
| REVENUES | 1412 | 0.702 | 1.529 | −0.261 | 9.797 |
| CASH FLOW/SALES | 1412 | −0.469 | 7.919 | −139.584 | 12.099 |
| TOTAL INVESTMENT RETURN | 1412 | 10.587 | 35.618 | −90.16 | 332.91 |
| Linear Regression | |
|---|---|
| R2 | 0.988 |
| RMSE | 2.060 |
| MAE | 1.526 |
| MSE | 4.250 |
| Coef | Std Err | T | p > |t| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Const | 0.0329 | 0.277 | 0.119 | 0.905 | −0.510 | 0.576 |
| Environment Pillar Score | 0.2724 | 0.005 | 58.235 | 0.000 | 0.263 | 0.282 |
| Social Pillar Score | 0.4017 | 0.005 | 75.848 | 0.000 | 0.391 | 0.412 |
| Governance Pillar Score | 0.3307 | 0.004 | 82.268 | 0.000 | 0.323 | 0.339 |
| Linear Regression | Random Forest (RF) | SVR | Polynomial Regression (Degree 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 16.34 | 9.96 | 17.28 | 17.7 |
| MAE | 13.66 | 7.81 | 13.96 | 14.43 |
| R2 | 23.92% | 71.60% | 16.83% | 13.24% |
| Training Sample | Test Sample | |
|---|---|---|
| MSE | 27.49 | 28.94 |
| RMSE | 5.24 | 5.37 |
| MAE | 3.90 | 4.19 |
| R2 | 92.75% | 91.75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belkhiria, S.; Lajmi, A.; Sayed, S. Predicting Environmental Social and Governance Scores: Applying Machine Learning Models to French Companies. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2025, 18, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18080413
Belkhiria S, Lajmi A, Sayed S. Predicting Environmental Social and Governance Scores: Applying Machine Learning Models to French Companies. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2025; 18(8):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18080413
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelkhiria, Sina, Azhaar Lajmi, and Siwar Sayed. 2025. "Predicting Environmental Social and Governance Scores: Applying Machine Learning Models to French Companies" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 18, no. 8: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18080413
APA StyleBelkhiria, S., Lajmi, A., & Sayed, S. (2025). Predicting Environmental Social and Governance Scores: Applying Machine Learning Models to French Companies. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 18(8), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18080413





