Analysing the Factors Contributing to the Decline of Auditors Globally and Avenue for Future Research: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
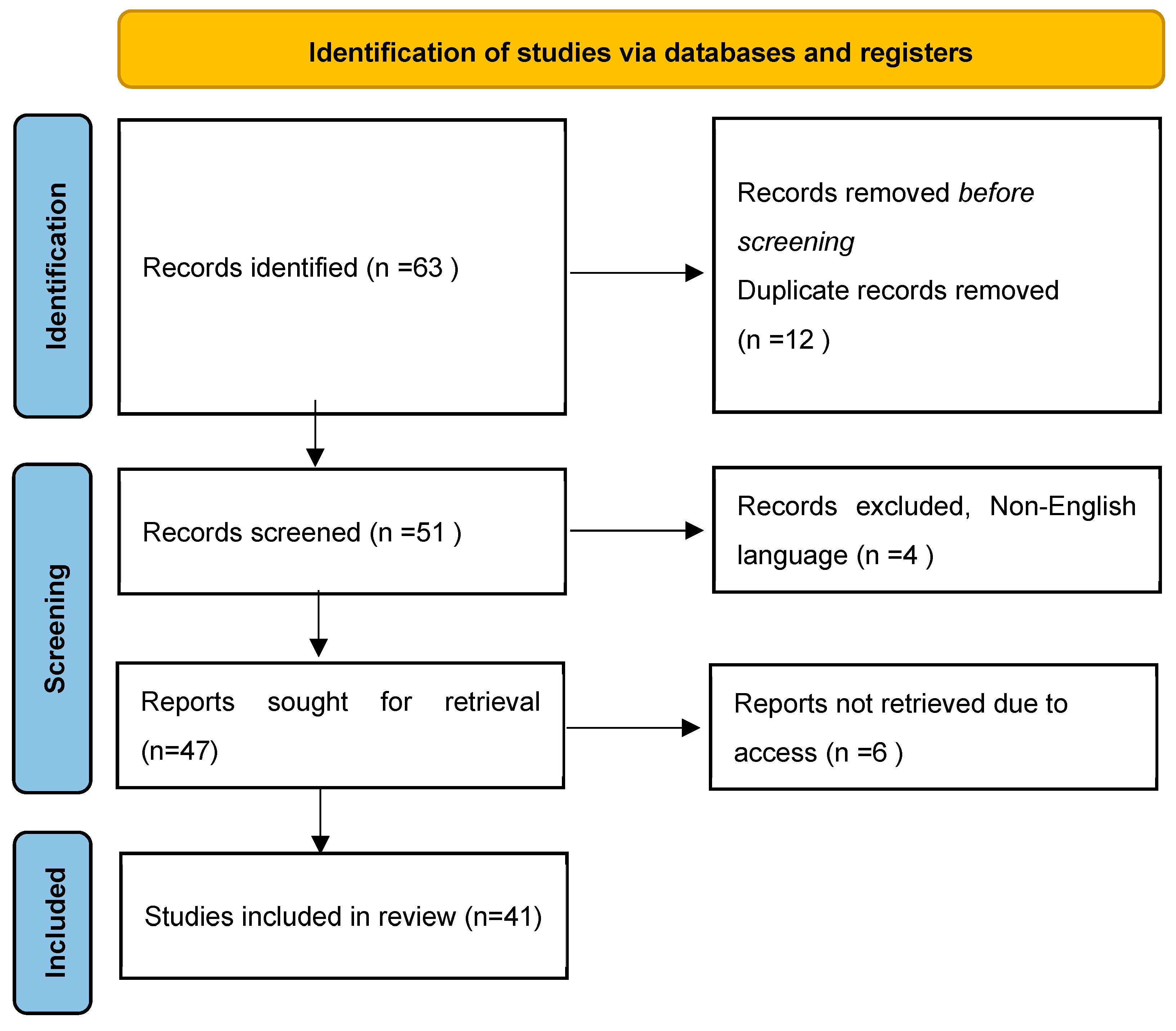
2. Methodology
- Step 1: Identify the research question.
- Step 2: Identifying relevant studies
- Step 3: Study selection using inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Step 4: Charting the data using a narrative approach to synthesize and interpret qualitative data
- Author(s) and year;
- Title;
- Source type;
- Source name;
- Summary of results and possible recommendations.
- Step 5: Collating, summarising, and reporting results
- Contributing factors;
- Consequences;
- Possible recommendations.
3. Analysis and Results
4. Findings and Gaps
- 1.
- The contributing-factor category has the following six themes identified:
- Talent pipeline and perception;
- The impact of regulation and compliance costs on the audit profession;
- Talent shortages and recruitment challenges in the industry including burnout;
- The impact of technological advancements;
- Financial pressure and profitability;
- Audit resignations and risk factors.
- 2.
- Consequences of the decline of the auditor’s category have the following three themes identified:
- Audit quality;
- Market concentration;
- Reduced public trust.
- 3.
- Possible recommendations to address the decline in the auditors category have the following three themes identified:
- Technological training and tools;
- Balance regulation with practicality;
- Strengthen talent attraction and retention.The gaps of this study are addressed at the end of each theme, where necessary.
4.1. Contributing Factors
4.1.1. Talent Pipeline and Perception
4.1.2. The Impact of Regulation and Compliance Costs on the Audit Profession
4.1.3. Talent Shortages and Recruitment Challenges in the Industry Including Burnout
4.1.4. The Impact of Technological Advancements
4.1.5. Financial Pressure and Profitability
4.1.6. Audit Resignations and Risk Factors
4.2. Consequences of the Decline of Auditors
4.2.1. Audit Quality
4.2.2. Market Concentration
4.2.3. Reduced Public Trust
4.3. Possible Recommendations to Address the Decline in Auditors
4.3.1. Technological Training and Tools
4.3.2. Balance Regulation with Practicality
4.3.3. Strengthen Talent Attraction and Retention
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, J., Hoitash, R., Hoitash, U., & Krause, E. (2024). Labor supply drought: The case of accountant talent shortage and audit outcomes. SSRN Electronic Journal. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, C. N., Albu, N., Faff, R., & Hodgson, A. (2011). Accounting competencies and the changing role of accountants in emerging economies: The case of Romania. Accounting in Europe, 8(2), 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amondarain, J., Aldazabal, M. E., & Espinosa-Pike, M. (2023). Gender differences in the auditing stereotype and their influence on the intention to enter the profession. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 37, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S., Allen, P., Peckham, S., & Goodwin, N. (2008). Asking the right questions: Scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H., & O’malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, F., Tyler, J., & Wells, P. (2015). Is audit quality impacted by auditor relationships? Journal of Contemporary Accounting & Economics, 11(2), 166–181. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, M. S., Carcello, J. V., Hermanson, D. R., & Neal, T. L. (2009). The audit committee oversight process. Contemporary Accounting Research, 26(1), 65–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennis, I., & Mouwafaq, S. (2025). Advancing AI-driven thematic analysis in qualitative research: A comparative study of nine generative models on Cutaneous Leishmaniasis data. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 25(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, B., & Yong, J. (2024). Addressing the decline in the accounting talent pipeline. International Federation of Accountants (IFAC). [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, J. F., Marcy, A. S., Boyle, D. M., & Hermanson, D. R. (2024). Accounting chairs’ perceptions of current challenges. Issues in Accounting Education, 39(4), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, J. C., Pereira, R. F., Fonseca, M., Ribeiro, R., & Bianchi, I. S. (2024). Advances in auditing and business continuity: A study in financial companies. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10(2), 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. (2023). Company auditor numbers in steady decline, ASIC data reveals. Available online: https://www.accountingtimes.com.au/profession/company-auditor-numbers-in-steady-decline-asic-data-reveals#:~:text=SMSF%20auditor%20numbers%20also%20in,to%20the%20report%20by%20ASIC (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Burke, J. A., & Polimeni, R. S. (2023). The accounting profession is in crisis. Available online: https://www.cpajournal.com/2023/12/01/the-accounting-profession-is-in-crisis/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Carey, P., & Simnett, R. (2006). Audit partner tenure and audit quality. The Accounting Review, 81(3), 653–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CaseWare. (2023). CaseWare state of accounting firms trends report. CaseWare. [Google Scholar]
- CaseWare. (2024). CaseWare state of accounting firms trends report. CaseWare. [Google Scholar]
- Church, B. K., Davis, S. M., & McCracken, S. A. (2008). The auditor’s reporting model: A literature overview and research synthesis. Accounting Horizons, 22(1), 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CK Search Global. (2024). Decline in audit firm numbers continues. Available online: https://cksearchglobal.com/decline-in-audit-firm-numbers-continues/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- CPA Ireland. (2023). Decline in the number of auditors to hit SMEs with higher costs. Available online: https://www.cpaireland.ie/Latest-News/News/News-2023/Decline-in-the-Number-of-Auditors-to-Hit-SMEs-With (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Darmawan, A. (2023). Audit quality and its impact on financial reporting transparency. Golden Ratio of Auditing Research, 3(1), 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, B. E., Dickins, D., Hatfield, R. C., & Higgs, J. L. (2012). An examination of partner perceptions of partner rotation: Direct and indirect consequences to audit quality. Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory, 31(1), 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins, M. C. (2023). Declining enrollments—A call to action! Issues in Accounting Education, 38(1), 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, F. J. (2019). Ethics and behavioural theory: How do professionals assess their mental models? Journal of Business Ethics, 157(4), 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edu, B. E., & Esang, A. E. (2008). The decline in accounting professionalism—Causes and effects. SSRN Electronic Journal. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldaly, M. K. (2012). Effects of the new regulations of the audit profession on the audit firms’ strategies. University of Bedfordshire Repository. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, L. (2022). Why so many accountants are quitting. Wall Street Journal. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/why-so-many-accountants-are-quitting-11672236016 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Filip, A., Hammami, A., Huang, Z., Jeny, A., Magnan, M., & Moldovan, R. (2017, January 18). Literature review on the effect of implementation of IFRS 13 fair value measurement [Paper presentation]. International Accounting Standard Board’s Public January 2018 Meeting and Referenced as Agenda Paper C, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Financial Reporting Council. (2024). Key facts and trends in the accountancy profession. The Financial Reporting Council Limited. [Google Scholar]
- Fülöp, M. T., & Pintea, M.-O. (2014). Effects of the new regulation and corporate governance of the audit profession. SEA-Practical Application of Science, 4, 545–554. [Google Scholar]
- Garvey, A. M., Parte, L., McNally, B., & Gonzalo-Angulo, J. A. (2021). True and fair override: Accounting expert opinions, explanations from behavioural theories, and discussions for sustainability accounting. Sustainability, 13(4), 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A., & Tang, C. Y. (2015). Auditor resignation and risk factors. Accounting Horizons, 29(3), 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold City Offshoring. (2023). Navigating the skills deficit in the audit and accounting sector: Gold city offshoring’s solution. Available online: https://goldcityoffshoring.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/1-Navigating-the-Skills-Deficit-in-the-Audit-and-Accounting-Sector-Gold-City-Offshorings-Solution.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Han, H., Shiwakoti, R. K., Jarvis, R., Mordi, C., & Botchie, D. (2023). Accounting and auditing with blockchain technology and artificial Intelligence: A literature review. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 48, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harber, M. (2018). Exploring the nature and consequences of a possible decline in the appeal of the South African audit profession. Southern African Journal of Accountability and Auditing Research, 20(1), 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, R., & Miah, M. D. (2024). Two decades of board co-option research: A scoping review. Accounting, Finance & Governance Review, 32, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hecimovic, A., Martinov-Bennie, N., & Roebuck, P. (2009). The force of law: Australian auditing standards and their impact on the auditing profession. Australian Accounting Review, 19(1), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRBA. (2023). Annual report. IRBA. [Google Scholar]
- Jahn, P., & Loy, T. (2023). Audit in Europe–A comparison of access requirements into the audit profession across the European Union. Accounting in Europe, 20(2), 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechel, W. R., Vanstraelen, A., & Zerni, M. (2015). Does the identity of engagement partners matter? An analysis of audit partner reporting decisions. Contemporary Accounting Research, 32(4), 1443–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechel, W. R., Mao, J., Qi, B., & Zhuang, Z. (2021). Is there a brain drain in auditing? The determinants and consequences of auditors leaving public accounting. Contemporary Accounting Research, 38(4), 2461–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, N., & do Céu Alves, M. (2023). Examining the fit between supply and demand of the accounting professional’s competencies: A systematic literature review. The International Journal of Management Education, 21(3), 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsch, B., & Gendron, Y. (2011). Reining in auditors: On the dynamics of power surrounding an “innovation” in the regulatory space. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 36(7), 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matshona, Z., Mabutho, S., & Phesa, M. (2024). Tax knowledge and tax behaviour of individual taxpayers in South Africa: A scoping review. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 14(5), 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, D., El Khoury, R., & Chaanine, M. (2024). Factors affecting auditor change decisions: The case of United Kingdom. Sage, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdhluli, S., Mkhize, M., & Phesa, M. (2023). Accounting and finance professionals’ perception on the current state of the accountancy profession in South Africa. International Journal of Environmental, Sustainability, and Social Science, 4(6), 1790–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkl-Davies, D. M., & Brennan, N. M. (2017). A theoretical framework of external accounting communication: Research perspectives, traditions, and theories. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 30(2), 433–469. [Google Scholar]
- Miles Education. (2024). The accountant shortage is real: Here’s what you need to know. Available online: https://www.mileseducation.com/accounting/blogs/the-accountant-shortage-is-real-heres-what-you-need-to-know (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Minutiello, V., & Tettamanzi, P. (2024). A systematic literature network analysis of the development of behavioural accounting research. International Journal of Behavioural Accounting and Finance, 7(2), 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oben, J. A. (2021). Credibility crises facing the accounting profession in South Africa. Academia. [Google Scholar]
- Olojede, P., Erin, O., Asiriuwa, O., & Usman, M. (2020). Audit expectation gap: An empirical analysis. Future Business Journal, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasewark, W. R. (2021). Preparing accountants of the future: Five ways business schools struggle to meet the needs of the profession. Issues in Accounting Education, 36(4), 119–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persellin, J. S., Schmidt, J. J., Vandervelde, S. D., & Wilkins, M. S. (2019). Auditor perceptions of audit workloads, audit quality, and job satisfaction. Accounting Horizons, 33(4), 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M. D., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Munn, Z., Tricco, A. C., & Khalil, H. (2020a). Scoping reviews. In JBI manual for evidence synthesis (Volume 10). JBI. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M. D., Marnie, C., Tricco, A. C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., McInerney, P., Godfrey, C. M., & Khalil, H. (2020b). Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 18(10), 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumlee, R. D., & Reckers, P. M. (2014). Lessons not learned: Why is there still a crisis-level shortage of accounting Ph.Ds? Accounting Horizons, 28(2), 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, B., hÓgartaigh, C. Ó., & Baskerville, R. (2012). Audit expectation-performance gap revisited: Evidence from New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Part 2: Changes in the gap in New Zealand 1989–2008 and in the United Kingdom 1999–2008. International Journal of Auditing, 16(3), 215–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W. R. (2013). Institutions and organizations: Ideas, interests, and identities. Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Sithole, N., Phesa, M., & Sibanda, M. (2024). Nexus of tax law and non-profit organizations: Incentives and challenges in compliance with tax laws by public benefit organizations in South Africa: A scoping review. International Journal of Business Ecosystem & Strategy, 6(6), 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, S. (2022). The times of India: Auditing, a serious job: Top challenges faced by auditors while auditing. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/voices/auditing-a-serious-job-top-challenges-faced-by-auditors-while-auditing/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- South African Accounting Academy. (2024). IRBA: Maximum fines for auditors—Notice of withdrawal and reissue. Available online: https://accountingacademy.co.za/news/read/irba-maximum-fines-for-auditors-notice-of-withdrawal-and-reissue (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Tarek, M., Mohamed, E. K., Hussain, M. M., & Basuony, M. A. (2017). The implication of information technology on the audit profession in developing country: Extent of use and perceived importance. International Journal of Accounting & Information Management, 25(2), 237–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tyson, J. (2023). Auditors say accountant shortage ramps up work pressure: CAQ. Available online: https://www.cfodive.com/news/auditors-say-accountant-shortage-increases-work-pressure-caq/701796/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Vien, C. (2024). Is the accounting shortage behind the drop in audit quality? Available online: https://www.cfobrew.com/stories/2024/12/09/is-the-accounting-shortage-behind-the-drop-in-audit-quality (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Yiu, E., & Zhong, J. (2023). Shortage of audit professionals will ‘affect Hong Kong’s position as a fundraising centre’, industry body says, asks government to recruit overseas auditors. Available online: https://www.scmp.com/business/article/3228197/shortage-audit-professionals-will-affect-hong-kongs-position-fundraising-centre-industry-body-says?campaign=3228197&module=perpetual_scroll_0&pgtype=article (accessed on 30 September 2023).
| No. | Authors | Title of the Study | Source Type | Source Name | Summary of the Result and/Possible Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harber (2018) | “Exploring the nature and consequences of a possible decline in the appeal of the South African audit profession” | Peer-reviewed journal | Southern African Journal of Accountability and Auditing Research | This South African study explored the decreasing appeal of the audit profession, citing overregulation, increasing liability, and career unattractiveness as core issues. A significant proportion of audit partners expressed concern over regulatory burdens such as MAFR and diminishing margins. The study also revealed that younger professionals increasingly prefer alternative career paths with better work–life balance and remuneration, raising concerns about the future talent pipeline and audit quality. |
| 2 | CaseWare (2024) | “State of Accounting Firms Trends Report 2024” | Grey literature—industry report | State of Accounting Firms Trends Report 2024 | Based on a global survey, this report highlights talent shortages, difficulty in tech adoption, and regulatory challenges as top concerns for audit and accounting firms. It identifies staff recruitment and retention as the most pressing issue, with over 90% of auditors reporting difficulties. The findings underscore a systemic strain on firms to innovate while coping with limited resources, impacting not just operational efficiency but also staff engagement and long-term audit sustainability. |
| 3 | Knechel et al. (2021) | “Is There a Brain Drain in Auditing? The Determinants and Consequences of Auditors Leaving Public Accounting” | Peer-reviewed journal | Contemporary Accounting Research | The study found that auditors who generate higher revenue are less likely to leave the profession, and these auditors tend to maintain high audit quality. Auditors who work at companies outside the Big Four and lose clients are likelier to leave the profession and have low audit quality. In turn, the clients will leave for another audit firm or want to pay less in audit fees. |
| 4 | Oben (2021) | “Credibility Crises Facing the Accounting Profession In South Africa” | Dissertation | ResearchGate | Accounting malpractices have become frequent and severe, and trust in the profession is declining, impacting the broader economic environment. The study highlights the need for stricter regulations and strong corporate governance to restore public confidence. |
| 5 | Mdhluli et al. (2023) | “Accounting and Finance Professionals’ Perception on the Current State of the Accountancy Profession in South Africa” | Peer-reviewed journal | International Journal of Environmental, Sustainability, and Social Science | The findings highlight key insights regarding ethics among South African accounting and finance professionals, including ethical knowledge, pressure to compromise ethics, the responsibility of professional members, the knowledge-ethics-pressure relationship, and the influence of accounting bodies. |
| 6 | Ghosh and Tang (2015) | “Auditor Resignation and Risk Factors” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting Horizons | The study investigates how litigation, audit, and business risks influence auditor resignation decisions. It finds that auditors often resign in anticipation of negative outcomes such as internal control failures or financial distress. These resignations are especially prevalent among Big Four firms and signal potential issues to stakeholders. The study emphasises the importance of understanding resignation patterns as indicators of engagement risk and declining audit quality. |
| 7 | Mattar et al. (2024) | “Factors Affecting Auditor Change Decisions: The Case of the United Kingdom” | Peer-reviewed journal | Sage Journals | This UK-based study explores factors influencing auditor change decisions. It identifies firm size, leverage, profitability, and governance features such as board diversity and independence as significant variables. The findings suggest that opinion shopping may still influence auditor switching, despite regulatory efforts. This challenges assumptions about auditor independence and indicates the need for stronger governance practices to reinforce audit objectivity. |
| 8 | CPA Ireland (2023) | “Decline in the Number of Auditors to Hit SMEs with Higher Costs” | Grey literature—institutional report | CPA Ireland News | This report highlights a 31% reduction in licensed audit firms in Ireland between 2014 and 2023, disproportionately affecting SMEs. The causes include talent shortages, regulatory compliance burdens, and rising operational costs. As a result, SMEs face increasing audit fees and diminished choice. The report advocates for regulatory reform and support mechanisms to sustain audit access and market diversity. |
| 9 | Blood and Yong (2024) | “Addressing the Decline in the Accounting Talent Pipeline” | Grey literature—professional body | International Federation of Accountants | This global IFAC report addresses the worsening shortage of accounting professionals. It attributes the trend to generational changes, unattractive work conditions, and declining enrolments. The report calls for coordinated action among regulators, educators, and firms to modernise certification pathways and improve career appeal to sustain the talent pipeline. |
| 10 | Burke and Polimeni (2023) | “The Accounting Profession Is in Crisis” | Grey literature—practitioner journal | The CPA Journal | Burke outlines the structural decline in the US accounting profession, citing falling CPA exam registrations, an ageing workforce, and poor adaptation to technological change. The article argues that public accounting no longer meets career expectations for younger professionals and urges reform to restore professional relevance. |
| 11 | Brownlee (2023) | “Company Auditor Numbers in Steady Decline, ASIC Data Reveals” | Grey literature—newsfeed | Accounting Times | This article documents the decline in registered company auditors in Australia, falling over 30% in the past decade. Demographic shifts, firm consolidation, and an ageing workforce are cited. The article also highlights concerns about maintaining audit independence and staff development under constrained conditions |
| 12 | Vien (2024) | “Is the Accounting Shortage Behind the Drop in Audit Quality?” | Grey literature—industry report | CFO Brew | A PCAOB study links declining audit quality to talent shortages across major firms. Interviews with audit leaders reveal that staff turnover, remote work, and outsourcing weaken training and engagement. These factors lead to higher error rates and insufficient documentation. |
| 13 | CK Search Global (2024), Financial Reporting Council (2024) | “Decline in Audit Firm Numbers Continues and Key Facts and Trends in the Accountancy Profession” | Grey literature—professional site and industry report | CK Search Global and Financial Reporting Council (FRC) | The Financial Reporting Council’s (FRC) Key Facts and Trends report tracks a continuing decline in UK and Irish audit firms. Although audit fee income continues to rise, the report notes a decrease in new accounting students and underrepresentation of women in senior roles, raising sustainability concerns. |
| 14 | Gold City Offshoring (2023) | “Navigating the Skills Deficit in the Audit and Accounting Sector: Gold City Offshoring’s Solution” | Grey literature—corporate white paper | Gold City Offshoring | This white paper outlines how offshoring from South Africa is helping address talent shortages in the UK and US. It discusses benefits and risks, including the need for quality control and cross-jurisdictional alignment, highlighting offshoring as both a strategic and logistical challenge. |
| 15 | Tyson (2023) | “Auditors Say Accountant Shortage Ramps Up Work Pressure: CAQ. CFO Dive” | Grey literature—media article | CFO Dive | A survey of 748 US audit partners reveals that staff shortages are increasing workloads and turnover. Firms are offering higher pay and more flexibility to retain staff. The article ties well-being to audit performance, calling for long-term workforce reforms. |
| 16 | Miles Education (2024) | “The Accountant Shortage Is Real: Here’s What You Need to Know” | Grey literature—education blog | Miles Education | This article highlights how the 150 h CPA requirement in the US has become a barrier to entry. It suggests alternative licensure paths and proposes curriculum updates and employer partnerships to reinvigorate student interest in accounting. |
| 17 | Edu and Esang (2008) | “The Decline in Accounting Professionalism—Causes and Effects” | Peer-reviewed journal | SSRN Electronic Journal | This study links declining professionalism in accounting to ethics erosion, corporate scandals, and regulatory gaps. It calls for stricter enforcement and ethics education reform to strengthen integrity and accountability in the profession. |
| 18 | Kroon and do Céu Alves (2023) | “Examining the fit between supply and demand of the accounting professional’s competencies: A systematic literature review” | Peer-reviewed journal | The International Journal of Management Education | This study identified several factors shaping students’ interest in accounting, including job prestige, salary, work–life balance, and societal perception. It underscores the need for long-term branding strategies and early exposure to the profession. |
| 19 | Ellis (2022) | “Why So Many Accountants Are Quitting” | Grey literature—newsfeed | The Wall Street Journal | The article highlights a 17% drop in US accounting staff from 2020–2022, attributed to burnout and low pay. Many opt for careers in finance or tech instead. Firms are increasing salaries and flexibility to retain talent. |
| 20 | South African Accounting Academy (2024) | “IRBA: Maximum Fines for Auditors—Notice of withdrawal and reissue” | Grey literature—professional body | South African Accounting Academy | This article reports on IRBA’s new fine structure in South Africa. It discusses implications for auditor morale and risk appetite and raises questions about the balance between enforcement and profession-wide support. |
| 21 | Darmawan (2023) | “Audit Quality and Its Impact on Financial Reporting Transparency” | Peer-reviewed journal | Golden Ratio of Auditing Research | This study from Indonesia links audit firm size, tenure, and specialisation to higher financial reporting transparency. It warns that reduced audit capacity could undermine credibility and regulatory compliance in emerging markets. |
| 22 | Beasley et al. (2009) | “Audit Committee Oversight Process” | Peer-reviewed journal | Contemporary Accounting Research | Explores audit committee practices in the US post-SOX. Finds that engagement varies based on member expertise, and effective committees support improved oversight of audit quality. |
| 23 | Malsch and Gendron (2011) | “Reining in auditors: On the dynamics of power surrounding an ‘innovation’ in the regulatory space” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting, Organizations and Society | Investigates Canadian audit regulation and reveals symbolic compliance by firms despite oversight. It applies institutional theory to explain regulatory capture and limited reform, which is relevant to understanding systemic legitimacy decline in auditing. |
| 24 | Porter et al. (2012) | “Audit expectation-performance gap revisited: evidence from New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Part 1: the gap in New Zealand and the United Kingdom in 2008” | Peer-reviewed journal | International Journal of Auditing | This study tracks the evolution of the audit expectation-performance gap over two decades in New Zealand and the UK. It finds that while monitoring helped narrow the performance gap in the UK, a lack of public engagement in NZ allowed the gap to widen. It recommends stakeholder education and regulatory alignment to address society’s unrealistic expectations of auditors. |
| 25 | Church et al. (2008) | “The auditor’s reporting model: A literature overview and research synthesis” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting Horizons | This article synthesises literature related to the auditor’s reporting model and its communicative limitations. The authors argue that the standard pass/fail format provides little informational value to users and contributes to the expectations gap. It calls for enhanced auditor disclosures and more nuanced reports to bridge user misunderstandings. |
| 26 | Daugherty et al. (2012) | “An Examination of Partner Perceptions of Partner Rotation: Direct and Indirect Consequences to Audit Quality” | Peer-reviewed journal | Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory | This study surveys 170 audit partners across various US firms to assess the unintended consequences of mandatory partner rotation. Findings suggest that partner rotation, while improving independence in appearance, leads to loss of client-specific knowledge and negatively impacts audit quality. |
| 27 | Ball et al. (2015) | “Is audit quality impacted by auditor relationships?” | Peer-reviewed journal | Journal of Contemporary Accounting & Economics | Examining Australian firms, the study finds that longer person-to-person relationships between audit partners and client executives reduce audit quality, while longer firm-to-client tenure enhances it. This dual effect informs debates around partner vs. firm rotation. |
| 28 | Carey and Simnett (2006) | “Audit Partner Tenure and Audit Quality” | Peer-reviewed journal | The Accounting Review | This Australian study explores whether extended audit partner tenure negatively impacts audit quality. It finds that long tenure is associated with fewer going-concern opinions for distressed companies and more cases of just meeting earnings benchmarks, suggesting compromised scepticism over time. |
| 29 | Amondarain et al. (2023) | “Gender differences in the auditing stereotype and their influence on the intention to enter the profession” | Peer-reviewed journal | Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance | Examines how gendered perceptions affect interest in audit careers among Spanish students. Found that women view auditing more favourably and are more likely to enter the profession. This has implications for diversity, inclusion, and addressing gender-related attrition in auditing. |
| 30 | Brás et al. (2024) | “Advances in auditing and business continuity: A study in financial companies” | Peer-reviewed journal | Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity | Explores how intelligent automation enhances audit processes and resilience in Portuguese banks. Highlights how tech adoption boosts auditor efficiency but may displace routine roles, adding pressure on traditional training pathways and firm models. |
| 31 | Ahn et al. (2024) | “Labor supply drought: the case of accountant talent shortage and audit outcomes” | Peer-reviewed journal | Northeastern U. D’Amore-McKim School of Business Research Paper | This study uses workforce data from Revelio Labs to examine how the decline in accounting graduates affects audit firm recruitment patterns and audit quality. It finds that although hiring volume has not dropped, firms have widened their recruitment net (hiring more from non-target schools) and reduced selectivity. These shifts are empirically associated with increased financial statement misstatements but not slower audit delivery. The effects are more pronounced in offices handling complex clients or new engagements. |
| 32 | Persellin et al. (2019) | “Auditor perceptions of audit workloads, audit quality, and job satisfaction” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting Horizons | Based on a survey of 776 current and former auditors, this study finds that excessive workloads, especially during the busy season, significantly impair audit quality and job satisfaction. Audit staff regularly work above the threshold where they perceive audit quality begins to decline. Key issues include impaired judgment, reduced scepticism, and shortcuts in documentation. Staff shortages and tight deadlines are cited as the root causes. |
| 33 | Eldaly (2012) | “Effects of the new regulations of the audit profession on the audit firms’ strategies” | Dissertation | University of Bedfordshire | Identifies strategic responses of Big Four firms to regulatory changes, including methodological reviews, conservative client acceptance, and audit quality control. Suggests that audit regulations increase operational costs, centralisation, and stress among auditors. |
| 34 | Fülöp and Pintea (2014) | “Effects of the new regulation and corporate governance of the audit profession” | Peer-reviewed journal | SEA—Practical Application of Science | This study explores the evolving role of regulation and corporate governance in shaping audit quality and public trust in the profession, particularly in post-crisis Europe. It highlights how the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB), the European Union (EU), and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) reforms aim to address audit report transparency, auditor independence, and going concern disclosure. The authors argue that enhanced governance structures, such as stronger audit committees and revised reporting standards, are crucial to restoring audit credibility and professional sustainability. |
| 35 | Hecimovic et al. (2009) | “The force of law: Australian auditing standards and their impact on the auditing profession” | Peer-reviewed journal | Australian Accounting Review | This qualitative study examines the impact of the legally enforceable Australian Auditing Standards (ASAs) on audit quality, firm behaviour, and public confidence. It finds that while regulation aimed to enhance audit credibility post-corporate collapses, most stakeholders (especially audit firms) viewed the changes as burdensome and ineffective in raising audit quality. Increased documentation, regulatory compliance costs, and talent loss were recurring concerns. The study highlights the growing expectations gap and the need for more balanced regulation. |
| 36 | Tarek et al. (2017) | “The implication of information technology on the audit profession in developing country: Extent of use and perceived importance” | Peer-reviewed journal | International Journal of Accounting & Information Management | This mixed-methods study investigates how information technology affects audit practices in Egypt. It finds that Big 4 firms are more advanced in IT adoption than smaller firms. IT use varies significantly based on firm type and client complexity, with challenges including limited standards, data security concerns, and lack of IT expertise. The authors recommend establishing national IT audit standards, improving AIS training, and developing specialised audit teams to support sustainable audit quality. |
| 37 | Albu et al. (2011) | “Accounting Competencies and the Changing Role of Accountants in Emerging Economies: The Case of Romania” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting in Europe | This country-level study highlights the decline in Romania’s audit profession, attributing it to demographic trends, low attractiveness of the profession, and inadequate regulatory support. It calls for urgent reforms in education, compensation, and public perception. |
| 38 | Jahn and Loy (2023) | “Audit in Europe—A Comparison of Access Requirements into the Audit Profession Across the European Union” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting in Europe | Through development of the Access Requirements Index (ARI), thos study exposes wide disparities in how EU states regulate access to auditing. It links stricter requirements with reduced auditor populations, suggesting occupational licensing often serves incumbent interests more than public need. |
| 39 | Plumlee and Reckers (2014) | “Lessons Not Learned: Why is There Still a Crisis-Level Shortage of Accounting Ph.D.s?” | Peer-reviewed journal | Accounting Horizons | This paper explores evolving competencies in accounting, identifying digital proficiency, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making as essential skills. It recommends redesigning education to embrace these future-focused attributes. |
| 40 | Boyle et al. (2024) | “Accounting Chairs’ Perceptions of Current Challenges” | Peer-reviewed journal | Issues in Accounting Education | Using US data, this study finds declining accounting enrolments are driven by perceptions of high workload, low pay, and poor work–life balance. It recommends strategic outreach, curriculum reform, and improved communication of career opportunities. |
| 41 | Pasewark (2021) | “Preparing Accountants of the Future: Five Ways Business Schools Struggle to Meet the Needs of the Profession” | Peer-reviewed journal | Issues in Accounting Education | This study identifies barriers in accounting education, including outdated curricula, poor assessment practices, high tuition, and weak links to practice. It recommends competency-based education, flexible learning, and stronger industry collaboration. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abrahams, T.; Phesa, M. Analysing the Factors Contributing to the Decline of Auditors Globally and Avenue for Future Research: A Scoping Review. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2025, 18, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18070363
Abrahams T, Phesa M. Analysing the Factors Contributing to the Decline of Auditors Globally and Avenue for Future Research: A Scoping Review. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2025; 18(7):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18070363
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbrahams, Thameenah, and Masibulele Phesa. 2025. "Analysing the Factors Contributing to the Decline of Auditors Globally and Avenue for Future Research: A Scoping Review" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 18, no. 7: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18070363
APA StyleAbrahams, T., & Phesa, M. (2025). Analysing the Factors Contributing to the Decline of Auditors Globally and Avenue for Future Research: A Scoping Review. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 18(7), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18070363







