Determinants of SME Internationalisation: An Empirical Assessment of Born Global Firms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Early Internationalization in Born Global Firms
2.2. Pull Factors Among Born Globals (PLFs)
2.3. Push Factors Among Born Globals (PUFs)
2.4. Recent Developments in Born Global Internationalization
2.5. Internal Firm-Specific Factors (IFCs)
3. Conceptual Model
4. Methods
5. Results
5.1. Methods of Data Analysis
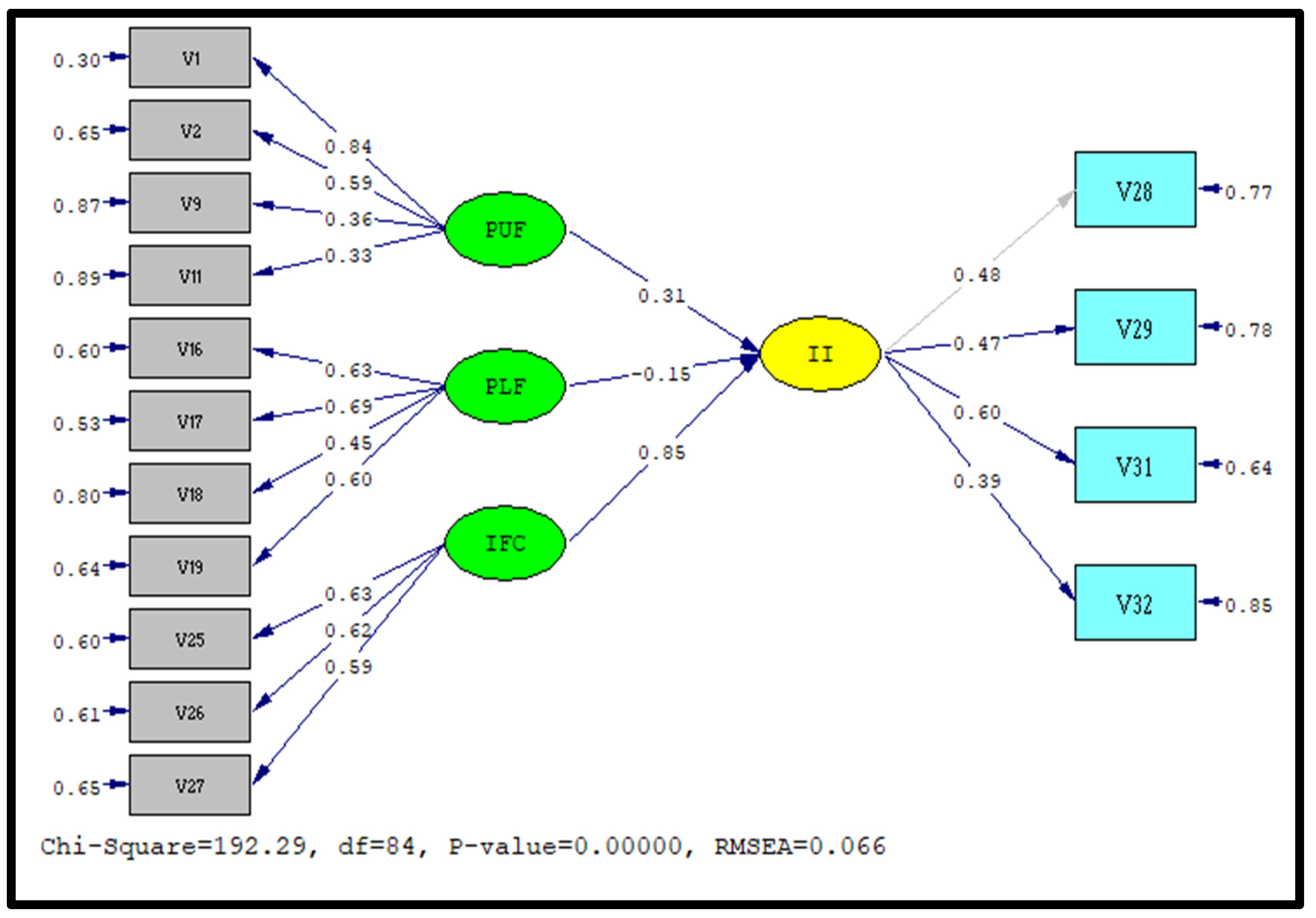
5.2. Measurement Model
5.3. Evaluation of Structural Model
6. Discussion
7. Implications of the Study
8. Conclusions
Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardito, L., Raby, S., Albino, V., & Bertoldi, B. (2021). The duality of digital and environmental orientations in the context of SMEs: Implications for innovation performance. Journal of Business Research, 123, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpa, C., Tiernan, S., & O’Dwyer, M. (2012). Entrepreneurial orientation, market orientation and internationalisation in born global small and micro-businesses. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business, 16(4), 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W., & Johanson, M. (2018). International opportunity networks. Industrial Marketing Management, 70, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barłożewski, K., & Trąpczyński, P. (2021). Internationalisation motives and the multinationality-performance relationship: The case of Polish firms. Entrepreneurial Business and Economics Review, 9(2), 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, A., Kamboj, S., Sharma, N., Pereira, V., Salwan, P., Chavan, M., & Pathak, A. A. (2023). Linking dynamic absorptive capacity and service innovation for born global service firms: An organization innovation lens perspective. Journal of International Management, 29(4), 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembom, M., & Schwens, C. (2018). The role of networks in early internationalizing firms: A systematic review and future research agenda. European Management Journal, 36(6), 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, G. R. G., Petersen, B., & Welch, L. S. (2011). Mode combinations and international operations. Management International Review, 51(6), 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, G. R. G., Petersen, B., & Welch, L. S. (2015). Towards more realistic conceptualisations of foreign operation modes. International Business Strategy: Theory and Practice, 40, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérard, C., & Delerue, H. (2010). A cross-cultural analysis of intellectual asset protection in SMEs: The effect of environmental scanning. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 17(2), 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıçakcıoğlu-Peynirci, N. (2023). Internationalization of emerging market multinational enterprises: A systematic literature review and future directions. Journal of Business Research, 164, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, T. K., Chew, T. C., Purohit, S., & Moser, R. (2024). International business entry modes and consumer ethnocentrism: A multi country perspective. Thunderbird International Business Review, 66(3), 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneel, J., Yli-Renko, H., & Clarysse, B. (2010). Learning from experience and learning from others: How congenital and interorganizational learning substitute for experiential learning in young firm internationalization. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 4(2), 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, N., & Villarreal, O. (2019). Internationalization as process of value distribution through innovation: Polyhedral diagnosis of a ‘born global’ firm. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 34(3), 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canabal, A., & White, G. O. (2008). Entry mode research: Past and future. International Business Review, 17(3), 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J., Moreira, A. A., & Sheng, H. H. (2022). Influences of foreign and domestic venture capitalists on internationalisation of small firms. BAR-Brazilian Administration Review, 19(1), e200105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casallas, R., González, O., & López, N. (2007). Dealing with scalability in an event-based infrastructure to support global software development. In Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics) (Vol. 4473, pp. 100–111). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavusgil, S. T., & Knight, G. (2015). The born global firm: An entrepreneurial and capabilities perspective on early and rapid internationalization. Journal of International Business Studies, 46(1), 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S., & Wang, L. (2012). The long-term sustenance of sustainability practices in mncs: A dynamic capabilities perspective of the role of R&D and internationalization. Journal of Business Ethics, 110(2), 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T., Pugh, D. S., & Mallory, G. (1997). The process of internationalization in the operating firm. International Business Review, 6(6), 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J. E. (2020). Applied structural equation modeling using AMOS (1st ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, J. M., Crick, D., & Chaudhry, S. (2020). Entrepreneurial marketing decision-making in rapidly internationalising and de-internationalising start-up firms. Journal of Business Research, 113, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyert, R. M., & March, J. G. (1965). A behavioral theory of the firm. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 60(309), 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, G., & Paul, J. (2021). CB-SEM vs PLS-SEM methods for research in social sciences and technology forecasting. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 173, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, Y. S., & Olive-Tomas, A. (2020). International entrepreneurship in the video game industry in barcelona. In Cases on internationalization challenges for SMEs (pp. 99–128). IGI Global. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A. V., & Guimarães-Iosif, R. M. (2013). The internationalization of higher education in Brazil: A marketing policy. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Education, 8(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S. P., & Craig, C. S. (2010). Global marketing strategy: Perspectives and approaches. In Wiley international encyclopedia of marketing. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J. H., & Lundan, S. M. (1998). The geographical sources of competitiveness of multinational enterprises: An econometric analysis. International Business Review, 7(2), 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J. H., & Lundan, S. M. (2008). Multinational enterprises and the global economy (2nd ed.). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Efrat, K., & Shoham, A. (2012). Born global firms: The differences between their short- and long-term performance drivers. Journal of World Business, 47(4), 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, S., Khan, F. M., Tabash, M. I., Ahmad, G., Akhter, J., & Al-Absy, M. S. M. (2023). Financial distress in the banking industry: A bibliometric synthesis and exploration. Cogent Economics & Finance, 11(2), 2253076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahat, M., Knight, G., & Alon, I. (2018). Orientations and capabilities of born global firms from emerging markets. International Marketing Review, 35(6), 936–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahat, M., Senik, Z. C., Lee, Y. Y., & Migin, M. W. (2023). The impact of ecosystem on the speedy internationalisation of born global firms in emerging markets. European Journal of International Management, 21(3), 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T., & Phan, P. (2007). International new ventures: Revisiting the influences behind the ‘born-global’ firm. Journal of International Business Studies, 38(7), 1113–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C. I., Ferreira, J. J., Lobo, C. A., & Raposo, M. (2020). The impact of market orientation on the internationalisation of SMEs. Review of International Business and Strategy, 30(1), 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernhaber, S. A., & Li, D. (2013). International exposure through network relationships: Implications for new venture internationalization. Journal of Business Venturing, 28(2), 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsson, M., & Kirpalani, V. H. M. (2012). Handbook of research on born globals (pp. 1–417). Edward Elgar. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Babin, B. J., & Krey, N. (2017). Covariance-based structural equation modeling in the Journal of Advertising: Review and recommendations. Journal of Advertising, 46(1), 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, A. (2018). Acculturation of halal food to the american food culture through immigration and globalization: A literature review. Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Studies, 5(2), 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashai, N., & Almor, T. (2004). Gradually internationalizing ‘born global’ firms: An oxymoron? International Business Review, 13(4), 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, E. B., & Thiel, J. (2000). The cultural economy of cities: A comparative study of the audiovisual sector in Hamburg and Lisbon. European Urban and Regional Studies, 7(3), 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Rowe, G. W. (2005). Strategic leadership: Strategy, resources, ethics and succession. In Handbook on responsible leadership and governance in global business (pp. 19–41). Elgaronline. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Y., & Hsieh, M. H. (2013). The accelerated internationalization of born global firms: A knowledge transformation process view. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 7(3), 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J., & Mattsson, L. (1988). Internationalisation in industrial systems—A network approach. In Knowledge, networks and power (pp. 287–314). Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J. E. (1977). The internationalization process of the firm—A model of knowledge development and increasing foreign market commitments. Journal of International Business Studies, 8(1), 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J. E. (2015). The Uppsala internationalization process model revisited: From liability of foreignness to liability of outsidership. International Business Strategy: Theory and Practice, 40, 33–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G., & Pitelis, C. (2015). Entrepreneurial imagination and a demand and supply-side perspective on the MNE and cross-border organization. Journal of International Management, 21(4), 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K. G., & Sörbom, D. (1990). Model search with TETRAD II and LISREL. Sociological Methods & Research, 19(1), 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinic, I., & Brouthers, K. D. (2022). Entrepreneurial orientation, export channel selection, and export performance of SMEs. International Business Review, 31(1), 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacı, A. (2021). Entrepreneurship in cross-border investments: Cases of emerging multinationals’ strategic asset-seeking internationalisation. In Contemporary entrepreneurship issues in international business (pp. 115–138). World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F. M., Anas, M., & Uddin, S. M. F. (2023). Anthropomorphism and consumer behaviour: ASPAR-4-SLRprotocol compliant hybrid review. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 48(1), e12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F. M., & Azam, M. K. (2023). Chatbots in hospitality and tourism: A bibliometric synthesis of evidence. Journal of the Academy of Business and Emerging Markets, 3(2), 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F. M., Khan, A., Ahmed, S. S., Naz, A., Salim, M., Zaheer, A., & Rashid, U. (2025a). The machiavellian, narcissistic, and psychopathic consumers: A systematic review of dark triad. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 49(2), e70018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F. M., Uddin, S. M. F., Anas, M., Kautish, P., & Thaichon, P. (2025b). Personal values and sustainable consumerism: Performance trends, intellectual structure, and future research fronts. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 24(2), 734–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A. N., Danis, W. M., & Cavusgil, S. T. (2012). International entrepreneurship research in emerging economies: A critical review and research agenda. Journal of Business Venturing, 27(2), 266–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G., & Khan, H. (2024). Born global firms. In Encyclopedia of international strategic management (pp. 14–17). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G. A., & Cavusgil, S. T. (2004). Innovation, organizational capabilities, and the born-global firm. Journal of International Business Studies, 35(2), 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G. A., & Liesch, P. W. (2016). Internationalization: From incremental to born global. Journal of World Business, 51(1), 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. (2017). Born global firms’ growth and collaborative entry mode: The role of transnational entrepreneurs. International Marketing Review, 34(1), 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, C. A., Fernandes, C., Ferreira, J., Veiga, P. M., & Gerschewski, S. (2023). The determinants of international performance for family firms: Understanding the effects of resources, capabilities, and market orientation. Entrepreneurship Research Journal, 13(3), 773–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, T. K. (2014). Internationalization processes of professional service firms. In Research handbook on export marketing (pp. 132–144). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, G., & Zucchella, A. (2019). Coping with uncertainty in the internationalisation strategy: An exploratory study on entrepreneurial firms. International Marketing Review, 36(1), 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N. K. (2020). Marketing research: An applied orientation (7th ed.). Pearson Education Limited. [Google Scholar]
- Manohar, A., Lioliou, E., Prevezer, M., & Saridakis, G. (2025). Explaining differences in internationalization between emerging and developed economy born global firms: A systematic literature review and the way forward. International Journal of Management Reviews, 27(1), 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S. L., & Javalgi, R. G. (2018). Epistemological foundations of international entrepreneurship. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 14(3), 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M., & Somaya, D. (2020). Born globals from emerging economies: Reconciling early exporting with theories of internationalization. Global Strategy Journal, 10(2), 251–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, P. P., Oviatt, B. M., & Shrader, R. C. (2003). A comparison of international and domestic new ventures. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 1(1), 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, P. P., Shane, S., & Oviatt, B. M. (1994). Explaining the formation of international new ventures: The limits of theories from international business research. Journal of Business Venturing, 9(6), 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S. R., Lavie, D., & Delios, A. (2016). International intensity, diversity, and distance: Unpacking the internationalization–performance relationship. International Business Review, 25(4), 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moed, H. F., Glänzel, W., & Schmoch, U. (Eds.). (2005). Handbook of quantitative science and technology research. Springer Science + Business Media, Inc. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, Ø., Falahat, M., & Lee, Y. (2022). Are born global firms really a “new breed” of exporters? Empirical evidence from an emerging market. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 20(1), 157–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, K., Sethi, D., Weber, T., & Wu, J. (2014). The smirk of emerging market firms: A modification of the dunning’s typology of internationalization motivations. Journal of International Management, 20(3), 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Martínez, P., & Del Pozo-Rubio, R. (2021). The financing of SMEs in the Spanish tourism sector at the onset of the 2008 financial crisis: Lessons to learn? Tourism Economics, 27(7), 1323–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, R. (2012). Do we need different frameworks to explain infant MNEs from developing countries? Global Strategy Journal, 2(3), 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A. R., de Sousa-Filho, J. M., Leocádio, Á. L., & Nascimento, J. C. H. B. D. (2020). Internationalization of cultural products: The influence of soft power. International Journal of Market Research, 62(3), 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, S., & Gbadamosi, A. (Eds.). (2020). Entrepreneurship marketing (2nd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L. (2019). Internationalization effects on financial performance: The case of Portuguese industrial SMEs. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 29(3), 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, L., & Tavares, F. (2017). Capital structure determinants of hospitality sector SMEs. Tourism Economics, 23(1), 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J., & Gupta, P. (2014). Process and intensity of internationalization of IT firms—Evidence from India. International Business Review, 23(3), 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J., & Rosado-Serrano, A. (2019). Gradual Internationalization vs Born-Global/International new venture models: A review and research agenda. International Marketing Review, 36(6), 830–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, U., Abdullah, M., Tabash, M. I., Khan, F. M., Naaz, I., & Akhter, J. (2025). Unlocking the synergy between capital structure and corporate sustainability: A hybrid systematic review and pathways for future research. International Journal of Organizational Analysis. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M., Lashgari, M., & Farsi, J. Y. (2019). International entrepreneurial alertness in opportunity discovery for market entry. Journal of Research in Marketing and Entrepreneurship, 21(2), 76–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rialp, A., Rialp, J., & Knight, G. A. (2005). The phenomenon of early internationalizing firms: What do we know after a decade (1993–2003) of scientific inquiry? International Business Review, 14(2), 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, L. A., & Gillespie, K. (2003). Information sources for new ventures in the turkish clothing export industry. Small Business Economics, 20(1), 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riefler, P. (2012). Why consumers do (not) like global brands: The role of globalization attitude, GCO and global brand origin. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 29(1), 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, C. (2020). What affects the export entrepreneurship of SMEs? Review of International Business and Strategy, 30(2), 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B., Zhang, T., Xu, X., Chan, H., & Choi, T. (2022). Preordering in luxury fashion: Will additional demand information bring negative effects to the retailer? Decision Sciences, 53(4), 681–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdu, I., Greve, H. R., & Benito, G. R. G. (2021). Back to basics: Behavioral theory and internationalization. Journal of International Business Studies, 52(6), 1047–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M., Jack, R., Madsen, T., & Alam, M. (2021). The nature of service characteristics and their impact on internationalization: A multiple case study of born global firms. Journal of Business Research, 132, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza, E. J., & Jaramillo, E. (2016). Marketing internacional. INNOVA Research Journal, 1(1), 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Li, X., Zhu, H., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Influencing factors of livestream selling of fresh food based on a push-pull model: A two-stage approach combining structural equation modeling (SEM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Expert Systems with Applications, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A. M., & Shaw, G. (2011). Internationalization and innovation in tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 38(1), 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. M., Li, T., & Wang, Y. (2020). What explains the degree of internationalization of early-stage entrepreneurial firms? A multilevel study on the joint effects of entrepreneurial self-efficacy, opportunity-motivated entrepreneurship, and home-country institutions. Journal of World Business, 55(6), 101114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, S., Yeniyurt, S., Uslay, C., & Cavusgil, E. (2018). The role of market orientation, relational capital, and internationalization speed in foreign market exit and re-entry decisions under turbulent conditions. International Business Review, 27(6), 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalan, T. (2018). Born global on blockchain. Review of International Business and Strategy, 28(1), 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., He, X., Wang, T., & Wang, K. (2022). Institutional distance and the international market entry mode: A meta-analysis. Journal of International Management, 29(1), 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S.No. | Factors | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Push Factors (PUFs) | Domestic market saturation, risk diversification, government policies, and unfavorable legal and political environments. |
| 2 | Pull Factors (PLFs) | Formal and informal contact networks, geographic closeness to new markets, and cultural and linguistic proximity (Miller et al., 2016). |
| 3 | Internal Firm-Specific Characteristics (IFCs) | Includes particular employee abilities, personnel experience abroad, and a strong inclination towards entrepreneurship and risk-taking among employees and the firm’s management (Pacheco, 2019). |
| 4 | Internationalization Index (II) | The degree to which a company relies on sales in overseas markets as opposed to its home market is referred to as its internationalization index, which is used as a dependent variable in this study (Chakrabarty & Wang, 2012). We adopted Yang et al.’s (2020) recommendation to use a percentage measure to evaluate the degree of internationalization. |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 3.386 | 14.720 | 14.720 | 3.386 | 14.720 | 14.720 | 2.602 | 11.313 | 11.313 |
| 2 | 2.417 | 10.510 | 25.230 | 2.417 | 10.510 | 25.230 | 1.818 | 7.902 | 19.215 |
| 3 | 1.575 | 6.848 | 32.078 | 1.575 | 6.848 | 32.078 | 1.788 | 7.775 | 26.991 |
| 4 | 1.360 | 5.913 | 37.991 | 1.360 | 5.913 | 37.991 | 1.634 | 7.105 | 34.095 |
| 5 | 1.264 | 5.496 | 43.487 | 1.264 | 5.496 | 43.487 | 1.597 | 6.945 | 41.040 |
| 6 | 1.223 | 5.319 | 48.805 | 1.223 | 5.319 | 48.805 | 1.338 | 5.817 | 46.857 |
| 7 | 1.153 | 5.014 | 53.820 | 1.153 | 5.014 | 53.820 | 1.312 | 5.703 | 52.561 |
| 8 | 1.048 | 4.559 | 58.378 | 1.048 | 4.559 | 58.378 | 1.215 | 5.281 | 57.842 |
| 9 | 1.029 | 4.475 | 62.854 | 1.029 | 4.475 | 62.854 | 1.153 | 5.012 | 62.854 |
| Constructs | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|
| PUF | −0.213 | −0.114 |
| PLF | −0.220 | −0.432 |
| IFC | −0.342 | −0.622 |
| II | −0.547 | 0.821 |
| Constructs | Std. Loadings Range | Cronbach Alpha | CR | AVE | T-Values | GFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUF | 0.36–0.87 | 0.765 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 3.45–5.65 | 0.90 |
| PLF | 0.45–0.69 | 0.871 | 0.7 | 0.76 | 2.33–6.66 | 0.90 |
| IFC | 0.59–0.63 | 0.754 | 0.6 | 0.87 | 4.56–10.77 | 0.91 |
| II | 0.39–0.60 | 0.712 | 0.5 | 0.65 | 5.33–11.66 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chishty, S.K.; Sayari, S.; Mohamed, A.H.; Inkesar, A.; Mallick, M.F.; Khan, N. Determinants of SME Internationalisation: An Empirical Assessment of Born Global Firms. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2025, 18, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040199
Chishty SK, Sayari S, Mohamed AH, Inkesar A, Mallick MF, Khan N. Determinants of SME Internationalisation: An Empirical Assessment of Born Global Firms. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2025; 18(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleChishty, Syed Khusro, Sonia Sayari, Amani Hamza Mohamed, Asra Inkesar, Mohammed Faishal Mallick, and Nusrat Khan. 2025. "Determinants of SME Internationalisation: An Empirical Assessment of Born Global Firms" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 18, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040199
APA StyleChishty, S. K., Sayari, S., Mohamed, A. H., Inkesar, A., Mallick, M. F., & Khan, N. (2025). Determinants of SME Internationalisation: An Empirical Assessment of Born Global Firms. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 18(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040199







