The Protective Effect of Apigenin on Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats mediating Activation of the PPAR-γ Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mortality
2.2. General Observations
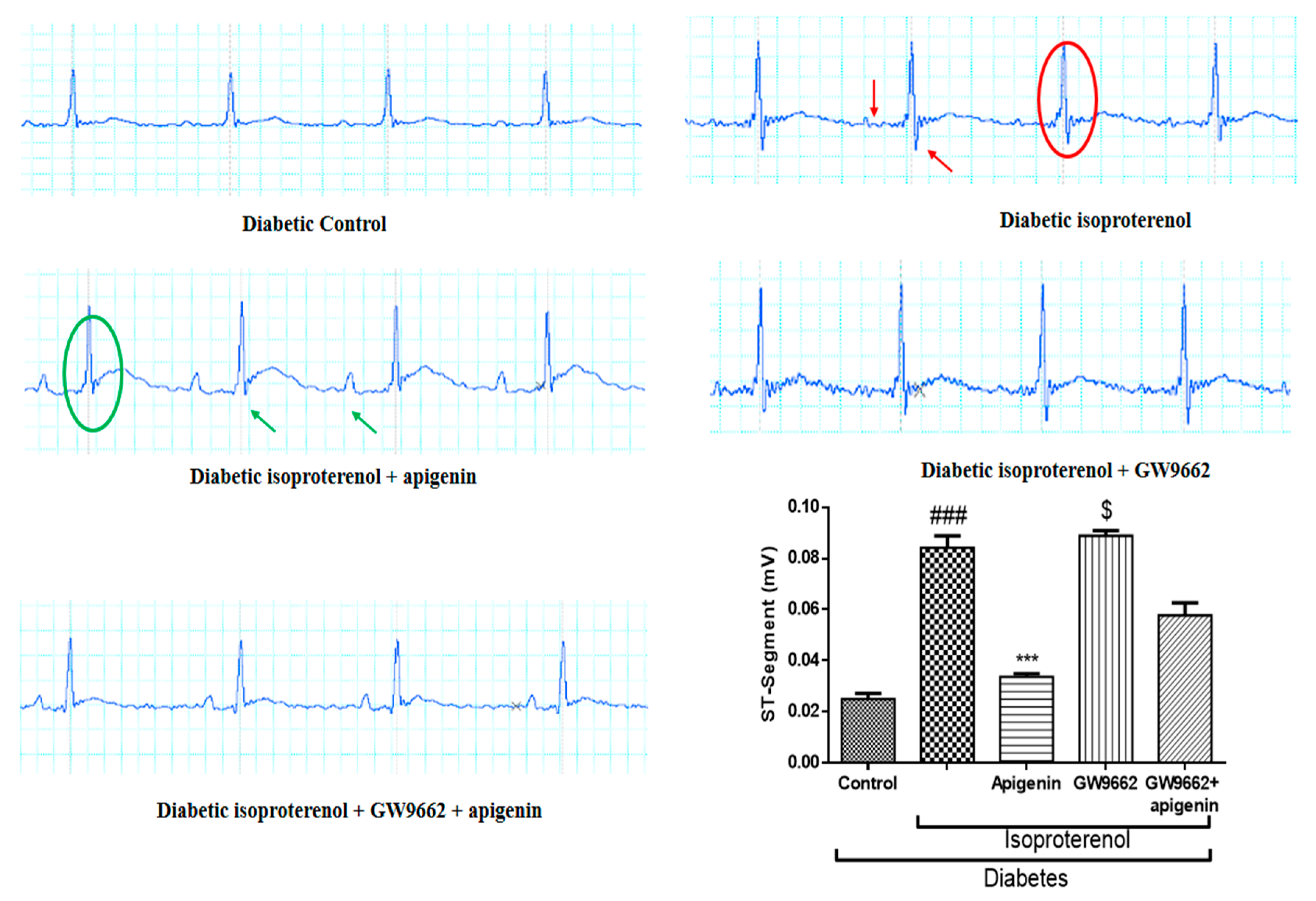
2.3. Apigenin Attenuated the Diabetes and Isoproterenol-Induced Alterations in the Electrocardiogram Pattern
2.4. Apigenin Improved the Hemodynamics and Left Ventricular Function
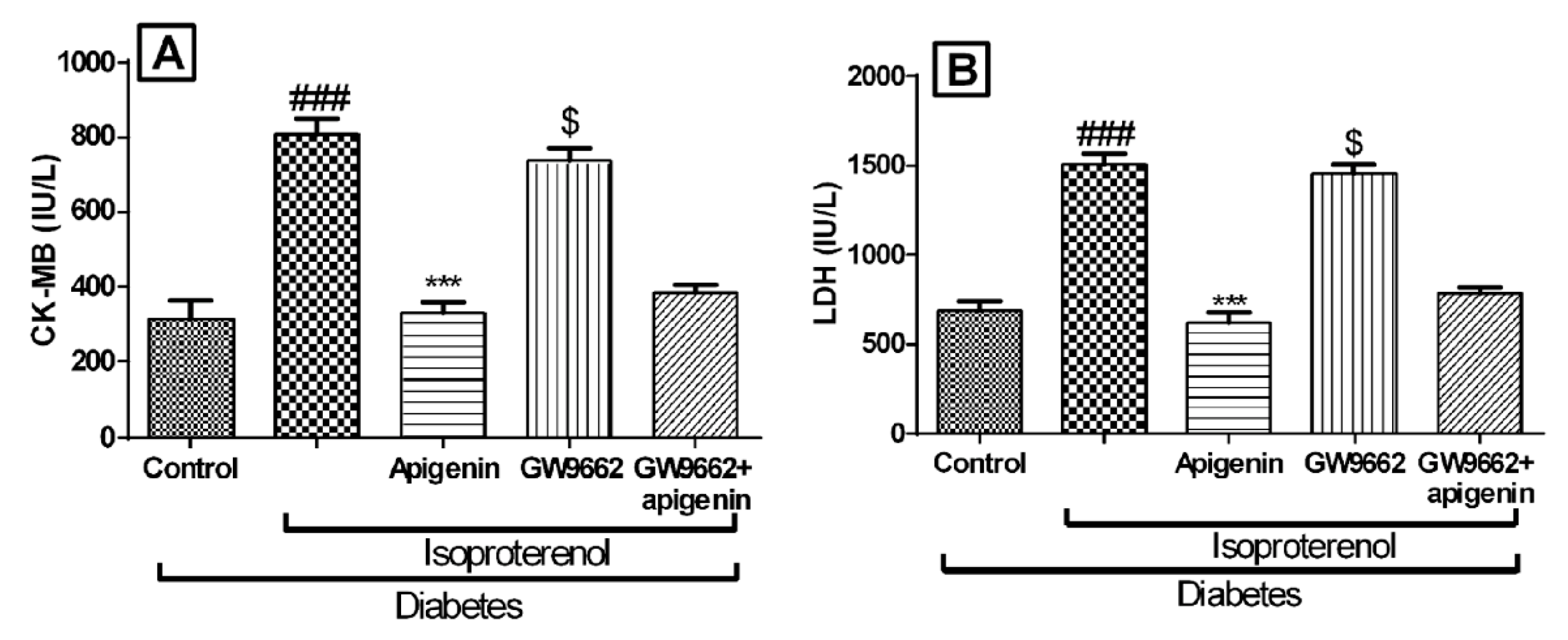
2.5. Apigenin Inhibited Diabetes and Isoproterenol Induced Cardiac Injury
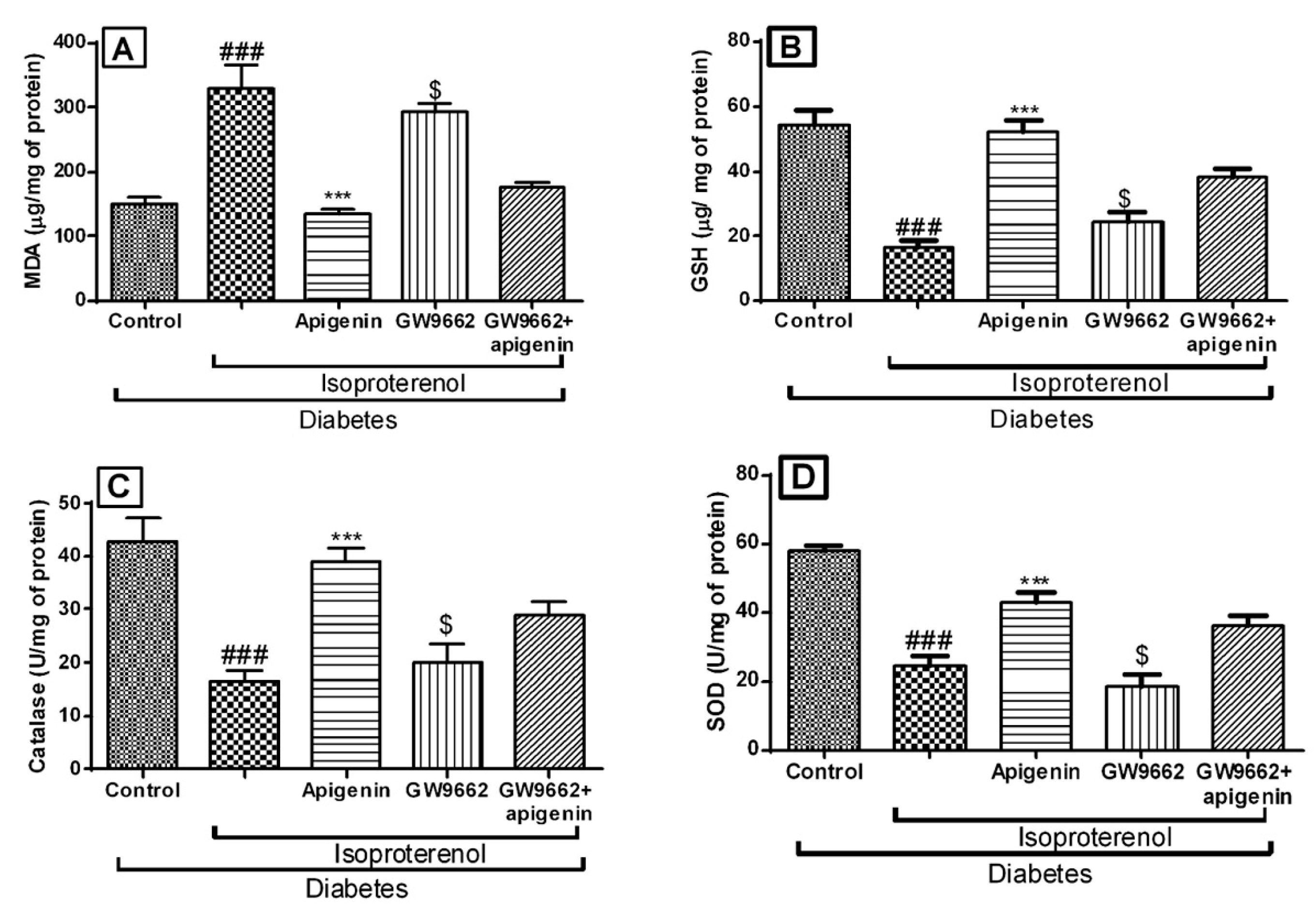
2.6. Apigenin Improved the Antioxidative Status of Rats Exposed to Diabetic Myocardial Infarction
2.7. Apigenin Reduced Bax and Increased Bcl-2 Expression in STZ–Isoproterenol-Challenged Rats
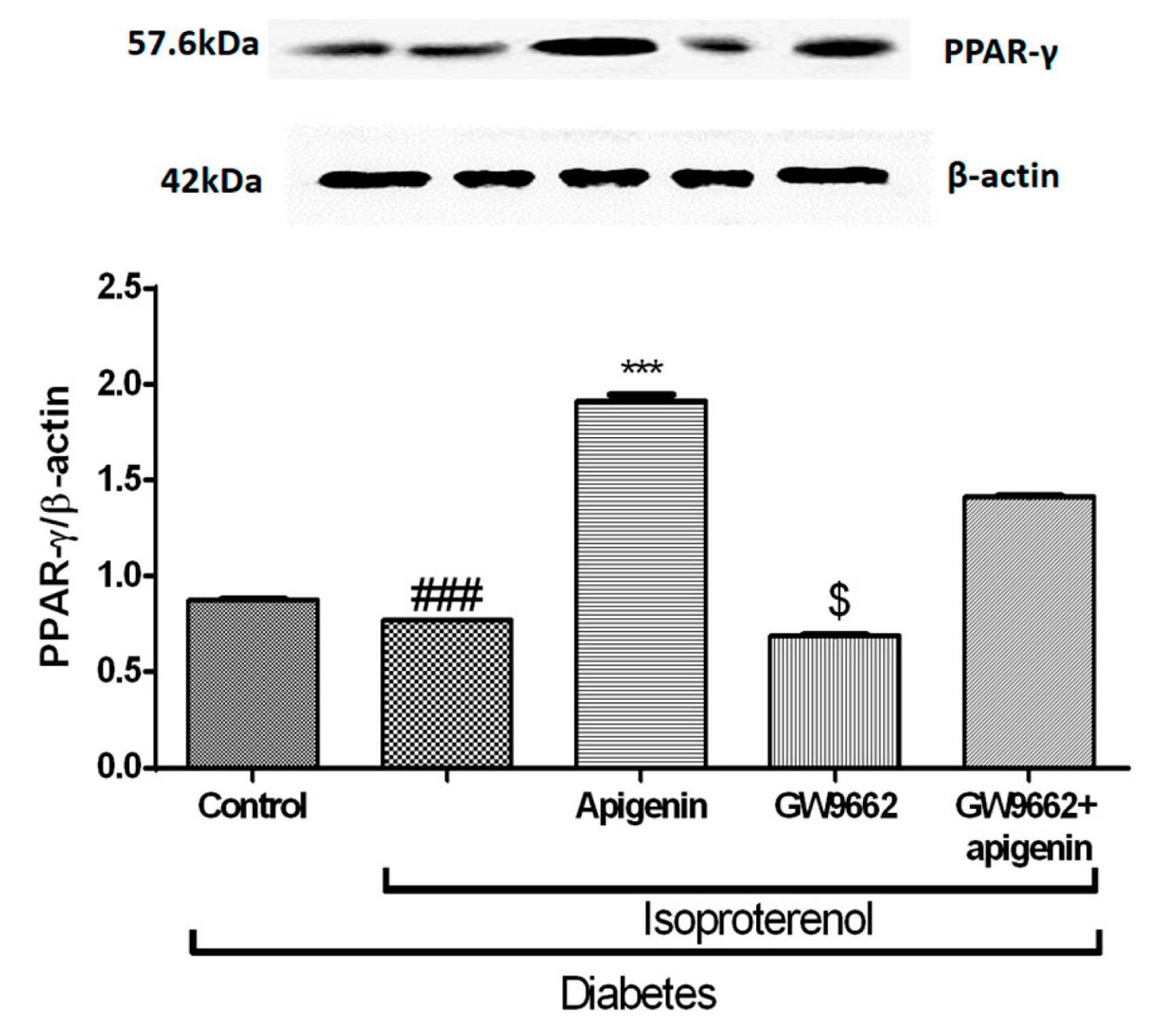
2.8. Apigenin Increased PPAR-γ Expression in STZ–Isoproterenol-Treated Rats
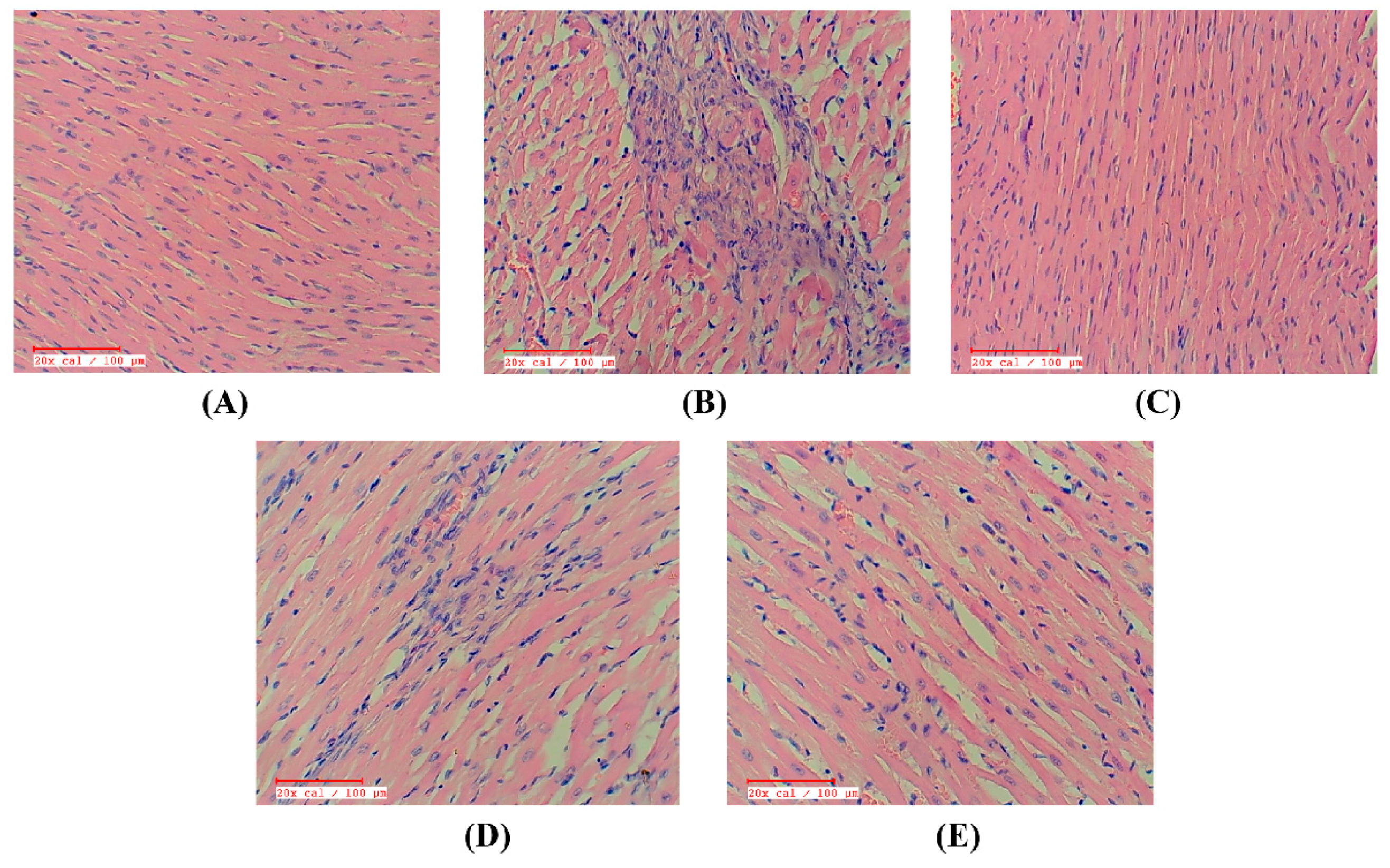
2.9. Apigenin Preserved the Myocardial Integrity in STZ–Isoproterenol-Treated Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Experimental Protocol
4.3.1. Induction of Diabetes
4.3.2. Experimental Design
- Diabetic control: This group was orally administered with distilled water as vehicle (1 mL/kg) for 14 days. On 13th and 14th days rats received 0.2 mL saline subcutaneously to serve as vehicle control for isoproterenol injection
- Diabetic isoproterenol-treated: Rats in this group were administered vehicle as above for 14 days along with subcutaneous injections of isoproterenol (100 mg/kg) on the 13th and 14th day
- Diabetic isoproterenol-treated rats administered with apigenin: This group received 75 mg/kg/day of apigenin for 14 days by oral route. On the 13th and 14th day rats were subcutaneously injected with isoproterenol (100 mg/kg)
- Diabetic isoproterenol-treated rats administered with GW9662: Rats in this group received GW9668 (1 mg/kg/day; intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection) for a period of 14 days and subcutaneous injections of isoproterenol (100 mg/kg) on the 13th and 14th days
- Diabetic isoproterenol-treated rats administered with apigenin and GW9662: For 14 days, rats in this group were orally administered with GW9662 15 min prior to the administration of apigenin (75 mg/kg). On the two terminal days of the treatment schedule, isoproterenol (100 mg/kg) was subcutaneously administered to rats in this group
4.4. Evaluation of Parameters
4.4.1. Surgical Procedures for Recording Hemodynamic Parameters
4.4.2. Estimation of the Cardiac Injury Markers and Oxidative Stress
4.4.3. Estimation of Lipid Peroxidation
4.4.4. Estimation of Glutathione Content
4.4.5. Estimation of Catalase Activity
4.4.6. Estimation of Superoxide Dismutase Activity
4.4.7. Determination of Myocardial Apoptosis
Immunohistostaining for the Expression of Bax and Bcl-2 Proteins
TUNEL Assay
4.4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.4.9. Light Microscopic Evaluation
4.4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohn, B.; Schofl, C.; Zimmer, V.; Hummel, M.; Heise, N.; Siegel, E.; Karges, W.; Riedl, M.; Holl, R.W. Achievement of treatment goals for secondary prevention of myocardial infarction or stroke in 29,325 patients with type 2 diabetes: A German/Austrian DPV-multicenter analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chi, R.F.; Qin, F.Z.; Guo, X.F. Distinct changes of myocyte autophagy during myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure: Association with oxidative stress. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Haan, M.C.; Van Zuylen, V.L.; Pluijmert, N.J.; Schutte, C.I.; Fibbe, W.E.; Schalij, M.J.; Roelofs, H.; Atsma, D.E. Discrepant results of experimental human mesenchymal stromal cell therapy after myocardial infarction: Are animal models robust enough? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, L.; Gheorghiade, M. Management of the patient with diabetes mellitus and myocardial infarction: Clinical trials update. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropea, J.; Brand, C.A.; Bohensky, M.; Van Doornum, S. Myocardial infarction and mortality following joint surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.O.; Copetti, M.; Fontana, A.; Bonis, C.; Salvemini, L.; Trischitta, V.; Menzaghi, C. Evidence of a causal relationship between high serum adiponectin levels and increased cardiovascular mortality rate in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.V.; Giricz, Z.; Liaudet, L.; Hasko, G.; Ferdinandy, P.; Pacher, P. Interplay of oxidative, nitrosative/nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadiya, J.; Mulani, H.; Shah, N. Protective effect of hesperidin on cardiovascular complication in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in diabetes in rats. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2010, 1, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suchal, K.; Malik, S.; Gamad, N.; Malhotra, R.K.; Goyal, S.N.; Ojha, S.; Kumari, S.; Bhatia, J.; Arya, D.S. Mangiferin protect myocardial insults through modulation of MAPK/TGF-β pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 776, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Hermonat, P.L.; Mehta, J.L. Anoxia-reoxygenation stimulates collagen type-I and MMP-1 expression in cardiac fibroblasts: Modulation by the PPAR-γ ligand pioglitazone. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Wang, M.; Wei, X.; Deng, S.; Fu, N.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, L.; Xie, J.; Lin, Y. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ: Master regulator of adipogenesis and obesity. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 11, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.P.; Chand, C.V.; Justin, A.; Ramanathan, M. Telmisartan mediates anti-inflammatory and not cognitive function through PPAR-γ agonism via SARM and MyD88 signaling. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 137, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Ma, Z.Q.; Du, X.H.; Yu, Q.S.; Wang, R.; Liu, L. Effect of valsartan on ACAT-1 and PPAR-γ expression in intima with carotid artery endothelial balloon injury in rabbit. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 5527–5533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Gebska, M.A.; Blokhin, I.O.; Wilson, K.M.; Ketsawatsomkron, P.; Chauhan, A.K.; Keen, H.L.; Sigmund, C.D.; Lentz, S.R. Endothelial PPAR-γ protects against vascular thrombosis by downregulating P-selectin expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygiel-Gorniak, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and clinical implications–a review. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buwa, C.C.; Mahajan, U.B.; Patil, C.R.; Goyal, S.N. Apigenin attenuates β-receptor-stimulated myocardial injury via safeguarding cardiac functions and escalation of antioxidant fefence system. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, D.J. Flavonoids for reduction of atherosclerotic risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2004, 6, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Lee, G.; Tl, O.H.; Kim, B.M.; Shim, D.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, B.O.; Lim, J.H. Inhibition of glutamine utilization sensitizes lung cancer cells to apigenin-induced apoptosis resulting from metabolic and oxidative stress. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.J.; Holder, J.C. PPAR-γ agonists: Therapeutic role in diabetes, inflammation and cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Sivarajah, A.; Thiemermann, C. Beneficial effects of PPAR-gamma ligands in ischemia-reperfusion injury, inflammation and shock. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiemermann, C.; Wayman, N.S. Menarini Academy Cardiovascular Research Awards in Basic Science 2001: Ligands of the orphan receptor peroxisome proliferator activator-gamma reduce myocardial infarct size. Med. Sci. Monit. 2001, 7, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sivarajah, A.; McDonald, M.C.; Thiemermann, C. The cardioprotective effects of preconditioning with endotoxin, but not ischemia, are abolished by a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Gao, T.; Huang, Y.; Xue, J.; Xie, M.L. Apigenin ameliorates hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy and down-regulates cardiac hypoxia inducible factor-lα in rats. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.N.; Reddy, N.M.; Patil, K.R.; Nakhate, K.T.; Ojha, S.; Patil, C.R.; Agrawal, Y.O. Challenges and issues with streptozotocin-induced diabetes—A clinically relevant animal model to understand the diabetes pathogenesis and evaluate therapeutics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 244, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.N.; Sharma, C.; Mahajan, U.B.; Patil, C.R.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Kumari, S.; Arya, D.S.; Ojha, S. Protective effects of cardamom in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27457–27469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Feng, T.; Zhu, N.; Liu, P.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Identification of a novel selective agonist of PPARγ with no promotion of adipogenesis and less inhibition of osteoblastogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Jainu, M.; Sabitha, K.; Devi, C.S. Role of mangiferin on biochemical alterations and antioxidant status in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.Q.; Chao, M.; Lu, Q.H.; Chai, W.L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.Y.; Liang, E.S.; Wang, L.B.; Tian, H.L.; Chen, Y.G. Prohibitin overexpression improves myocardial function in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheweita, S.; Mashaly, S.; Newairy, A.; Abdou, H.; Eweda, S. Changes in oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in streptozotocin-induced Diabetes mellitus in rats: Role of Alhagi maurorum extracts. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5264064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.M.; Mahajan, U.B.; Patil, C.R.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Ojha, S.; Goyal, S.N. Eplerenone attenuates cardiac dysfunction and oxidative stress in β-receptor stimulated myocardial infarcted rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.N.; Mahajan, U.B.; Chandrayan, G.; Kumawat, V.S.; Kamble, S.; Patil, P.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S. Protective effect of oleanolic acid on oxidative injury and cellular abnormalities in doxorubicin induced cardiac toxicity in rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kasala, E.R.; Bodduluru, L.N.; Dahiya, V.; Lahkar, M. Baicalein protects isoproterenol induced myocardial ischemic injury in male Wistar rats by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, D.K.; Nagarathana, P.K. Screening of cardioprotective activity of leaves of Andrographis paniculata against isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.Q.; Akhtar, M.S.; Akhtar, M.; Ansari, S.H.; Ali, J.; Haque, S.E.; Najmi, A.K. Benidipine prevents oxidative stress, inflammatory changes and apoptosis related myofibril damage in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Toxicol. Mech. Meth. 2015, 25, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, N.; Bharti, S.; Bhatia, J.; Nag, T.; Ray, R.; Arya, D.S. Chrysin, a PPAR-γ agonist improves myocardial injury in diabetic rats through inhibiting AGE-RAGE mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 250, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Groups | HW (g) | Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | BW (g) | HW/BW Ratio (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic control | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 420.8 ± 53.90 | 235 ± 3.61 | 2.72 ± 0.008 |
| Diabetic isoproterenol | 0.59 ± 0.08 | 406.5 ± 54.87 | 217 ± 3.32 | 2.71 ± 0.024 |
| Diabetic isoproterenol + apigenin | 0.61 ± 0.04 | 310.3 ± 31.24 *** | 239 ± 2.82 | 2.51 ± 0.014 |
| Diabetic isoproterenol + GW9662 | 0.56 ± 0.07 | 424.3 ± 47.24 | 209 ± 3.41 | 2.39 ± 0.020 |
| Diabetic isoproterenol + GW9662 + apigenin | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 326.7 ± 24.31 ** | 228 ± 4.21 | 2.41 ± 0.009 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahajan, U.B.; Chandrayan, G.; Patil, C.R.; Arya, D.S.; Suchal, K.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Ojha, S.; Goyal, S.N. The Protective Effect of Apigenin on Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats mediating Activation of the PPAR-γ Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040756
Mahajan UB, Chandrayan G, Patil CR, Arya DS, Suchal K, Agrawal YO, Ojha S, Goyal SN. The Protective Effect of Apigenin on Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats mediating Activation of the PPAR-γ Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahajan, Umesh B., Govind Chandrayan, Chandragouda R. Patil, Dharamvir Singh Arya, Kapil Suchal, Yogeeta O. Agrawal, Shreesh Ojha, and Sameer N. Goyal. 2017. "The Protective Effect of Apigenin on Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats mediating Activation of the PPAR-γ Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040756
APA StyleMahajan, U. B., Chandrayan, G., Patil, C. R., Arya, D. S., Suchal, K., Agrawal, Y. O., Ojha, S., & Goyal, S. N. (2017). The Protective Effect of Apigenin on Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats mediating Activation of the PPAR-γ Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040756







