Crack Cocaine Smoke Induces Tissue Degeneration in Rat Submandibular Glands by Toll-like Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Illicit Drug
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Histomorphometric Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Western Blot—Toll-like Pathway
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histopathology
3.2. Histomorphometry
3.3. Immunohistochemistry BCL-2, P16 and Ki67
3.4. Toll-like Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, D.M.; Huang, J.P.; Jara-Muñoz, O.A.; Madriñá, N.S.; Ree, R.H.; Mason-Gamer, R.J. The Origins of Coca: Museum Genomics Reveals Multiple Independent Domestications from Progenitor Erythroxylum gracilipes. Syst. Biol. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacca, J.J.; Botelho, E.D.; Vieira, M.L.; Almeida, F.L.; Ferreira, L.S.; Maldaner, A.O. Brazilian Federal Police drug chemical profiling—The PeQui project. Sci. Justice 2014, 54, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, A.Q.C.; Madruga, C.S.; Simões, V.; Yamauchi, R.; da Silva, C.J.; Abdalla, R.R.; McDonell, M.; McPherson, S.; Roll, J.M.; Mari, J.J.; et al. Crack cocaine users views regarding treatment with contingency management in Brazil. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2018, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrenoud, L.O.; Oikawa, K.F.; Williams, A.V.; Laranjeira, R.; Fischer, B.; Strang, J.; Ribeiro, M. Factors associated with crack-cocaine early initiation: A Brazilian multicenter study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spezzia, S. Oral manifestations from crack consumption. J. Oral Investig. 2020, 9, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, A.T.; Bhatt, A.A. Review of the Major and Minor Salivary Glands, Part 1: Anatomy, Infectious, and Inflammatory Processes. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2018, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibly, A.M.; Aure, M.H.; Patel, V.N.; Hoffman, M.P. Salivary gland function, development, and regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1495–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, T.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Zakheim, D.R.; Harrington, D.A.; Witt, R.L.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X.; Pradhan-Bhatt, S. Bottom-up assembly of salivary gland microtissues for assessing myoepithelial cell function. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiben, C.L.; Batista, T.B.D.; Penteado, C.A.S.; Barbosa, M.C.M.; Ventura, T.M.O.; Dionizio, A.; Rosa, E.A.R.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Azevedo-Alanis, L.R. Salivary proteome analysis of crack cocaine dependents. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 121, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniazzi, R.P.; Sari, A.R.; Casarin, M.; Moraes, C.M.B.; Feldens, C.A. Association between crack cocaine use and reduced salivary flow. Braz. Oral Res. 2017, 3, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.S.; Melo, I.S.; Silva, N.K.G.T.; Souza, F.M.A.; Santos-Neto, J.G.; Pacheco, A.L.D.; Cavalcante, C.M.B.; Freitas-Santos, J.; Ferreira-Rodrigues, A.K.B. Crack cocaine inhalation induces cardiacatrophy and facilitates limbic-motor seizures in mice submitted to subconvulsive dose of pilocarpine. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Manag. 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, D.; Rosarioa, B.; Casagrandea, B.; Viana, M.; Estadella, D.; Peres, R.; Seabra Pereira, C.D.; Peres, R. Histopathological and inflammatory response in multiple organs of rats exposed to crack. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aguiar, G.C.; Souza, A.C.F.; de Souza, D.V.; Neto, M.M.; Le Sueur-Maluf, L.; de Moraes Malinverni, A.C.; Antunes, H.K.M.; Ribeiro, D.A. Degenerative changes induced by paradoxical sleep deprivation in rat sublingual glands. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 4261–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Queiroz Constantino Miguel, A.; Sandi Madruga, C.; Simões, V.; Yamauchi, R.; da Silva, C.J.; McDonell, M.; McPherson, S.; Roll, J.; Laranjeira, R.R.; de Jesus Mari, J. Contingency management is effective in promoting abstinence and retention in treatment among crack cocaine users with a previous history of poor treatment response: A crossover trial. Psicol. Reflex. Crit. 2019, 32, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidonja Uzelac, T.; Tatalović, N.; Mijović, M.; Miler, M.; Grahovac, T.; Oreščanin Dušić, Z.; Nikolić-Kokić, A.; Blagojević, D. Ibogaine Induces Cardiotoxic Necrosis in Rats—The Role of Redox Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, R.C.; Ferraz, P.; Chaiben, C.L.; Fernandes, Â.; Grégio, A.T.; Machado, M.N.; Azevedo-Alanis, L.R.; de Lima, A.S. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Potential of Smoke Crack Cocaine on the Epithelium of the Human Oral Mucosa. J. Dent. Indones. 2016, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes Pinto, T.; Viana, M.B.; Cury, P.R.; Martins, M.D.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Ribeiro, D.A. Are Cytomorphogenetic Events Correlated with Oral Mucosal Lesions Induced by Crack Cocaine Use? A Systematic Review. Pathophysiology 2023, 30, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, H.; Miskovic, M.; Buxton, J.A.; Holland, S.P.; Strike, C. Smoke Gets in the Eye: A systematic review of case reports of ocular complications of crack cocaine use. Drug Alcohol. Rev. 2022, 41, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujra, V.Q.; Moretti, E.G.; Claudio, S.R.; Silva, M.J.; Oliveira, F.d.; Oshima, C.T.; Ribeiro, D.A. Genotoxicity and mutagenicity induced by acute crack cocaine exposure in mice. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 39, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, T.A.; Palazzo, R.P.; de Andrade, F.M.; Reichert, C.L.; Pechansky, F.; Kessler, F.; de Farias, C.B.; de Andrade, G.G.; Leistner-Segal, S.; Maluf, S.W. Genomic instability in human lymphocytes from male users of crack cocaine. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 10003–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalaxmi; Cao, Y.; Scarfi, M.R. Adaptive response in mammalian cells exposed to non-ionizing radiofrequency fields: A review and gaps in knowledge. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2014, 760, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozorgi, S.S.; Proctor, G.B.; Carpenter, G.H. Rapamycin delays salivary gland atrophy following ductal ligation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.; Tennavan, A.; Saraswathy, S.; Sekhri, T.; Singh, A.K.; Nair, V. Acute Radiation-Induced Changes in Sprague-Dawley Rat Submandibular Glands: A Histomorphometric Analysis. World J. Oncol. 2017, 8, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonosova, E.; Chinnadurai, G. BH3-only proteins in apoptosis and beyond: An overview. Oncogene 2008, 27 (Suppl. S1), S2–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangkhoee, H.; Cross, K.M.; Koljonen, V.; Ghazarian, D.; Fish, J.S. Evaluation of Ki-67 as a histological index of burn damage in a swine model. J. Burn Care Res. 2012, 33, e55–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini Denchi, E.; Attwooll, C.; Pasini, D.; Helin, K. Deregulated E2F activity induces hyperplasia and senescence-like features in the mouse pituitary gland. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2660–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
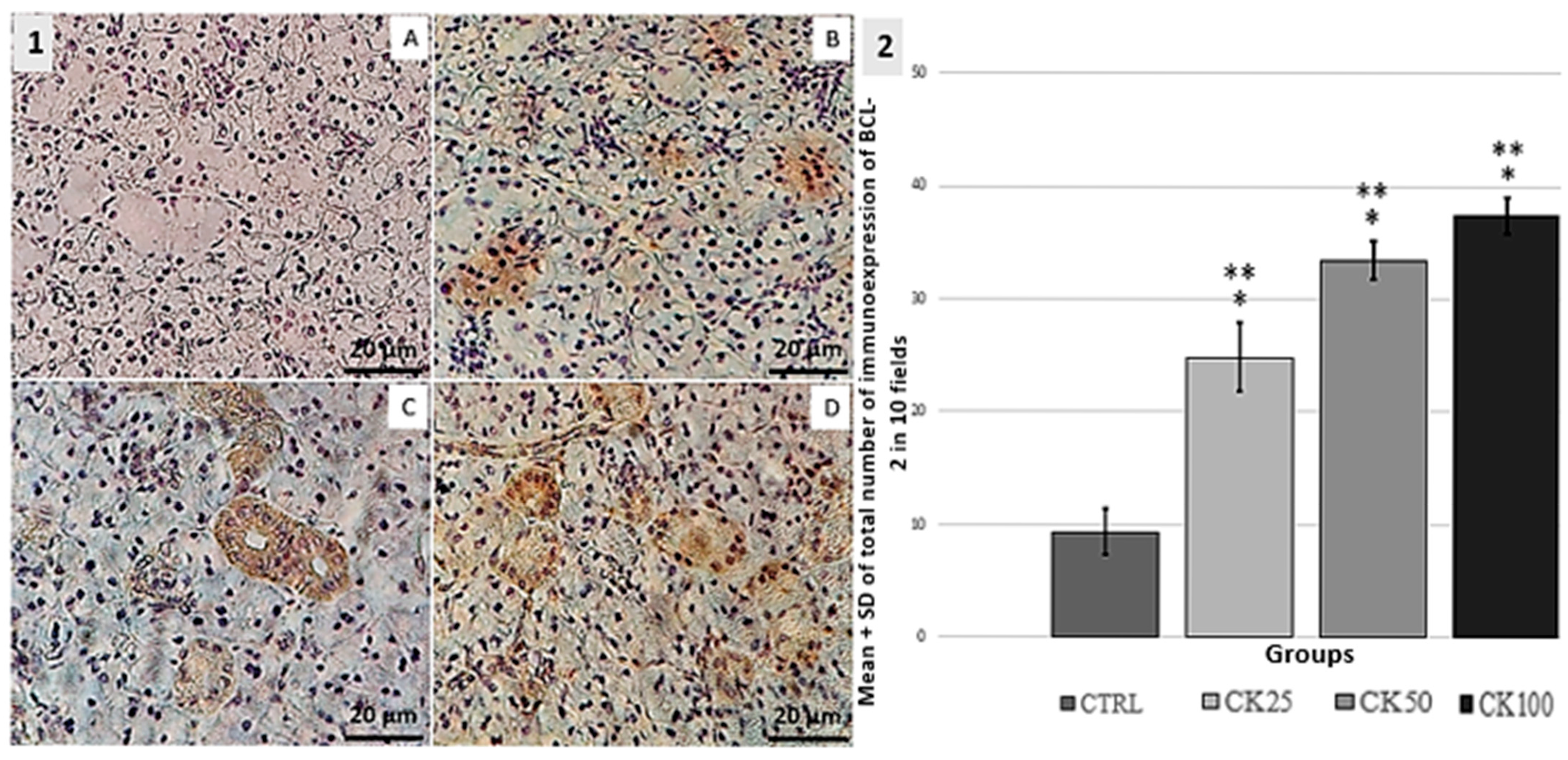
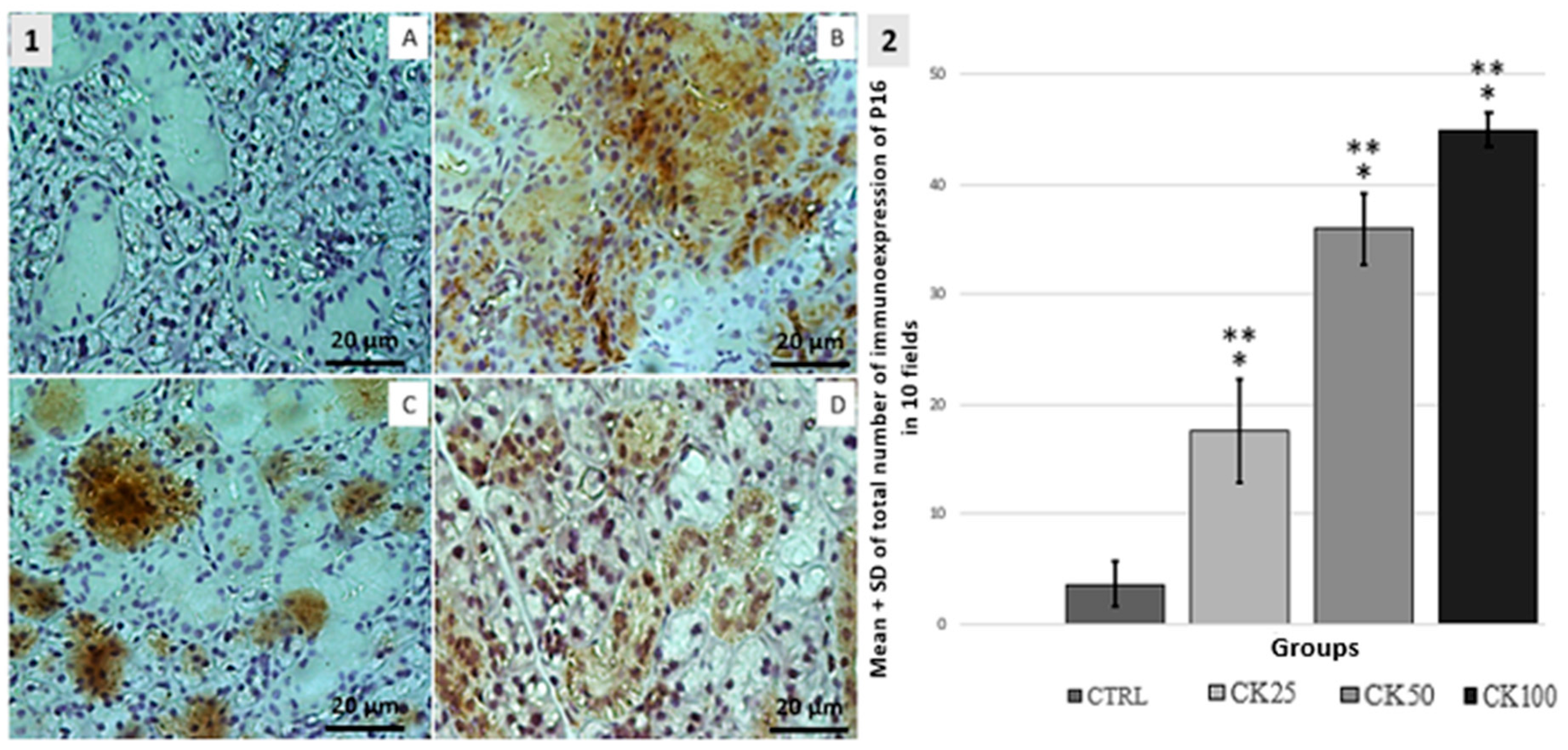
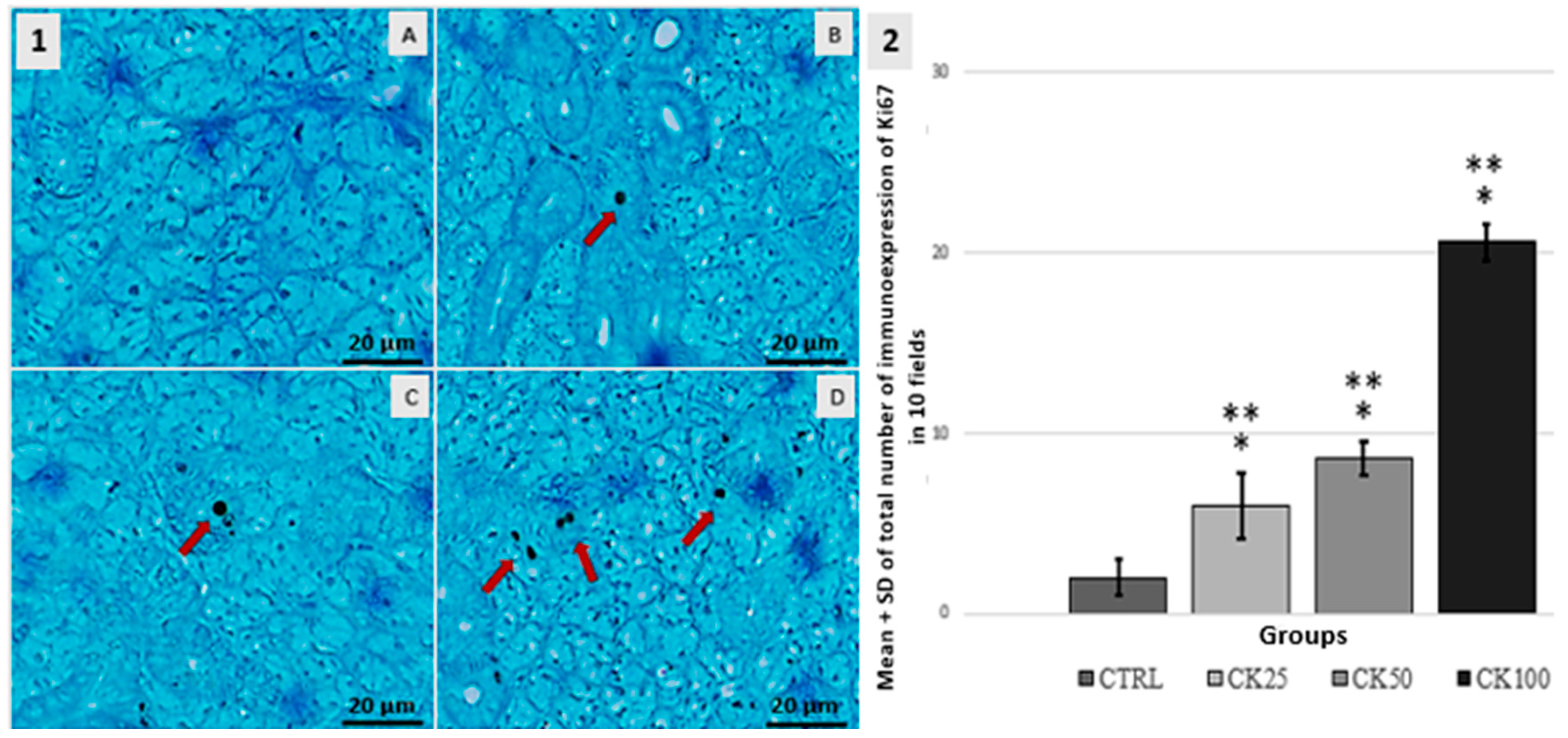

| GROUPS | n | SCORE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| CTRL | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| CK25 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | *, ** |
| CK50 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 | * |
| CK100 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 | * |
| Groups | Serous Acini Mean ± SD | Mucous Acini Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 357.8 ± 12.67 | 119.6 ± 17.24 |
| CK25 | 247.8 ± 14.06 *, ** | 166.6 ± 13.22 *, ** |
| CK50 | 298.8 ± 25.26 *, ** | 76.20 ± 24.31 *, ** |
| CK100 | 274.2 ± 6.3 * | 73.2 ± 3.49 *, ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avanci, L.d.S.; de Souza, D.V.; de Aguiar, G.C.; Guedes Pinto, T.; Rosario, B.d.A.; Viana, M.d.B.; Ferreira, Y.A.M.; Cordaro, V.C.; Pisani, L.P.; Ribeiro, D.A. Crack Cocaine Smoke Induces Tissue Degeneration in Rat Submandibular Glands by Toll-like Signaling Pathway. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32030032
Avanci LdS, de Souza DV, de Aguiar GC, Guedes Pinto T, Rosario BdA, Viana MdB, Ferreira YAM, Cordaro VC, Pisani LP, Ribeiro DA. Crack Cocaine Smoke Induces Tissue Degeneration in Rat Submandibular Glands by Toll-like Signaling Pathway. Pathophysiology. 2025; 32(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvanci, Lorrany da Silva, Daniel Vitor de Souza, Gabriel Carvalhal de Aguiar, Thiago Guedes Pinto, Barbara dos Anjos Rosario, Milena de Barros Viana, Yasmin Alaby Martins Ferreira, Viviane Carlin Cordaro, Luciana Pellegrini Pisani, and Daniel Araki Ribeiro. 2025. "Crack Cocaine Smoke Induces Tissue Degeneration in Rat Submandibular Glands by Toll-like Signaling Pathway" Pathophysiology 32, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32030032
APA StyleAvanci, L. d. S., de Souza, D. V., de Aguiar, G. C., Guedes Pinto, T., Rosario, B. d. A., Viana, M. d. B., Ferreira, Y. A. M., Cordaro, V. C., Pisani, L. P., & Ribeiro, D. A. (2025). Crack Cocaine Smoke Induces Tissue Degeneration in Rat Submandibular Glands by Toll-like Signaling Pathway. Pathophysiology, 32(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32030032






