Structural Basis of Native CXCL7 Monomer Binding to CXCR2 Receptor N-Domain and Glycosaminoglycan Heparin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
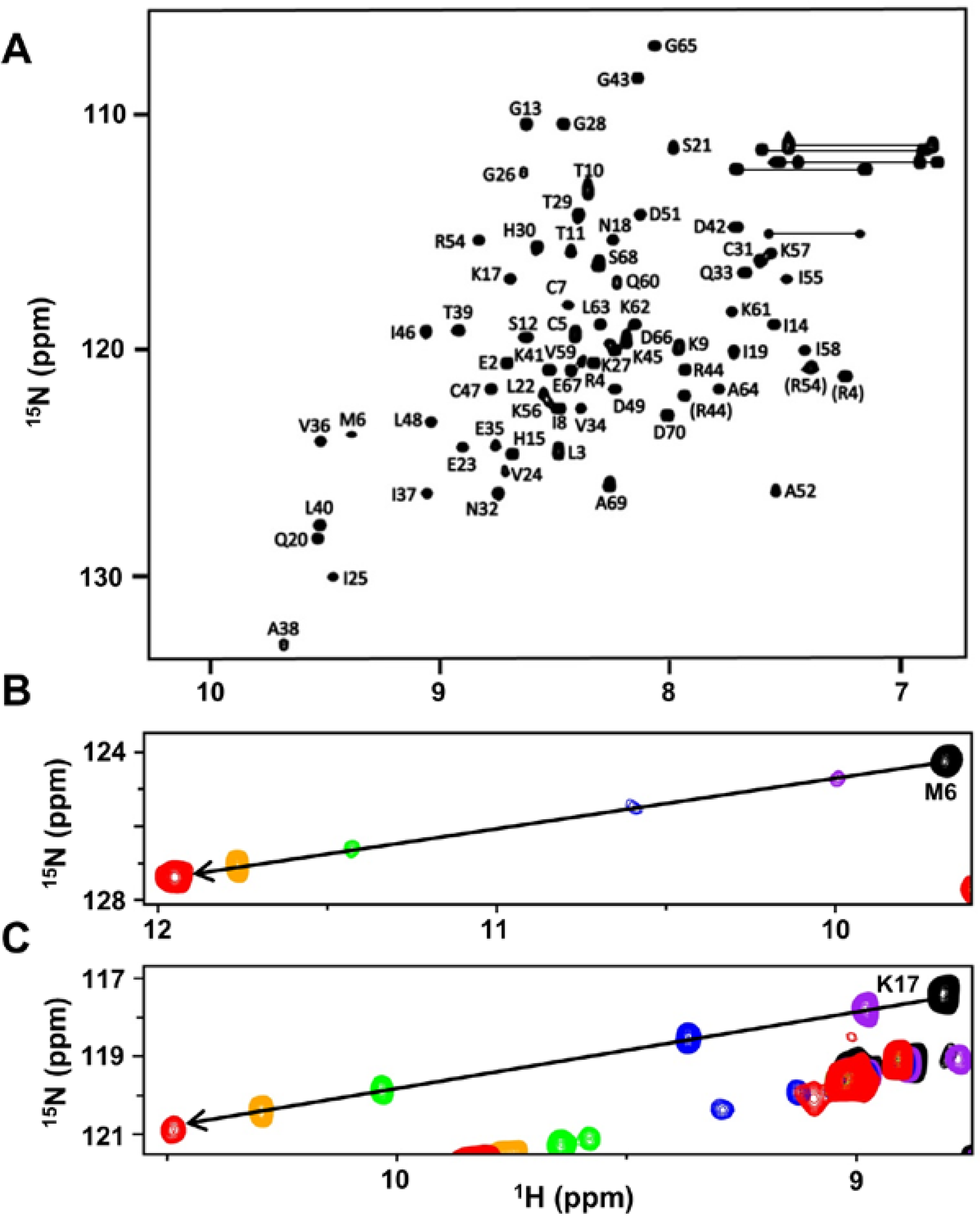
2.1. CXCL7 Monomer Chemical Shift Assignments
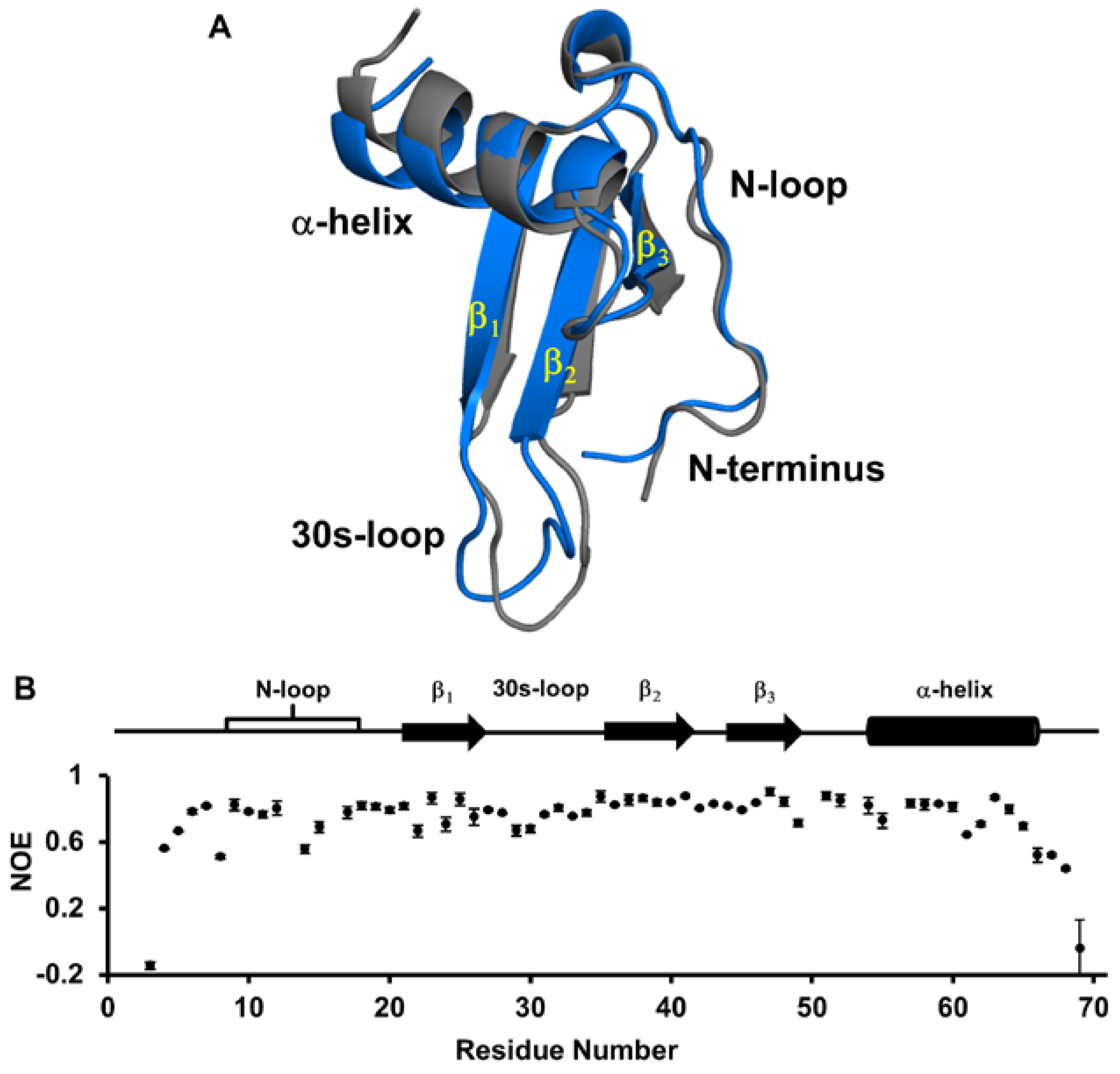
2.2. Structural Model of the Native Monomer
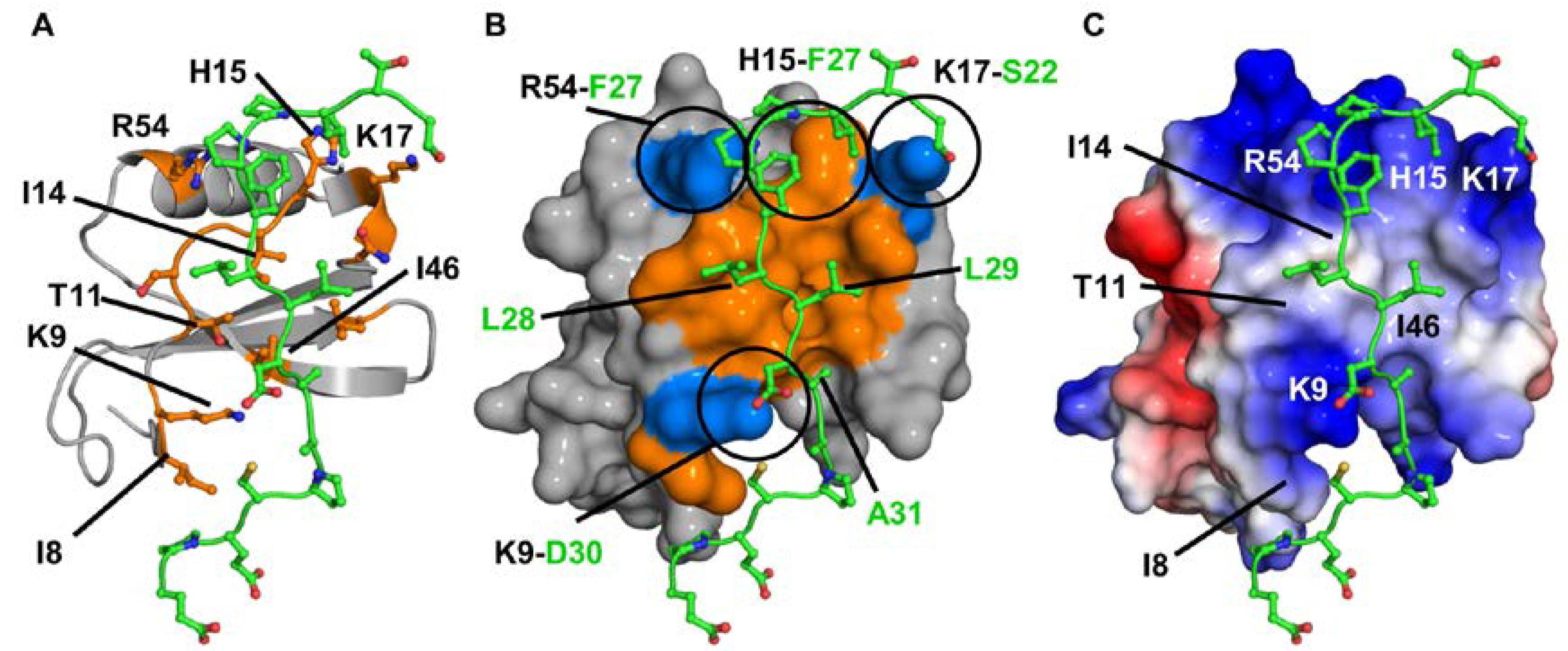
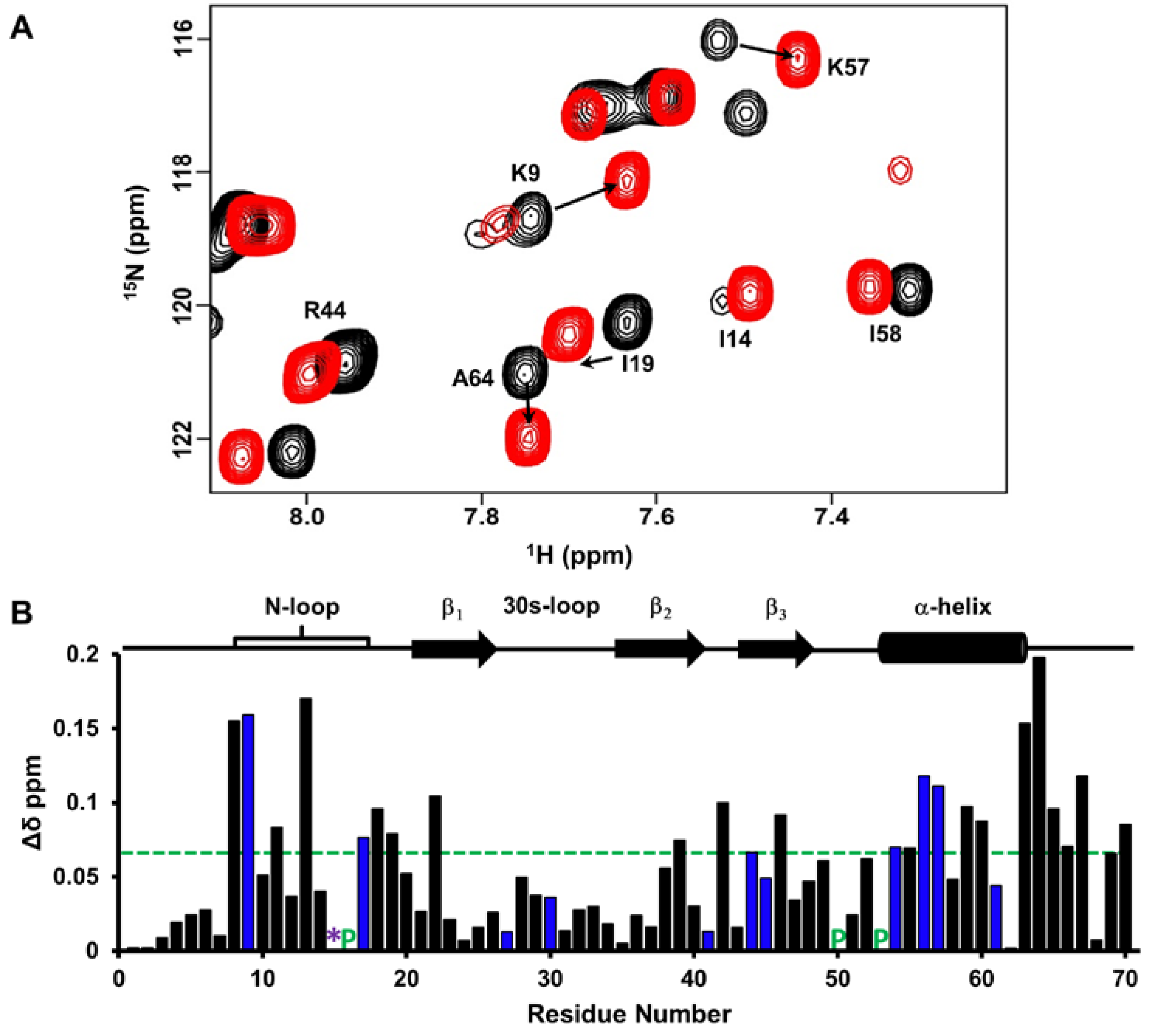
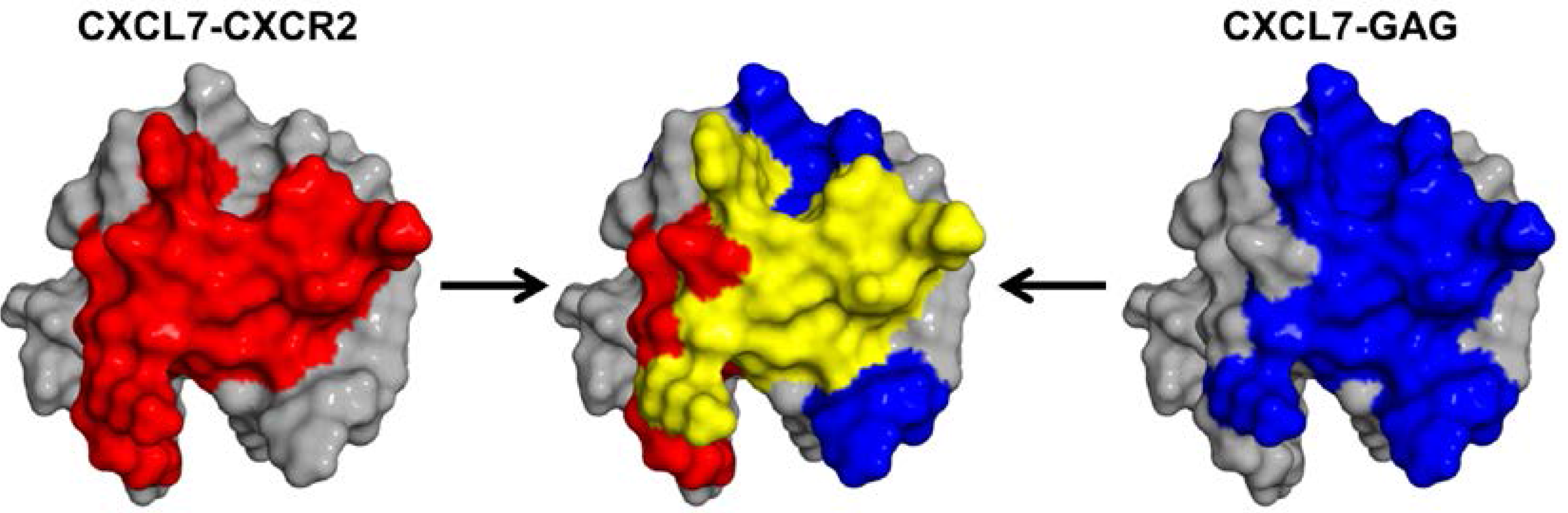
2.3. CXCL7:CXCR2 N-Domain Interactions
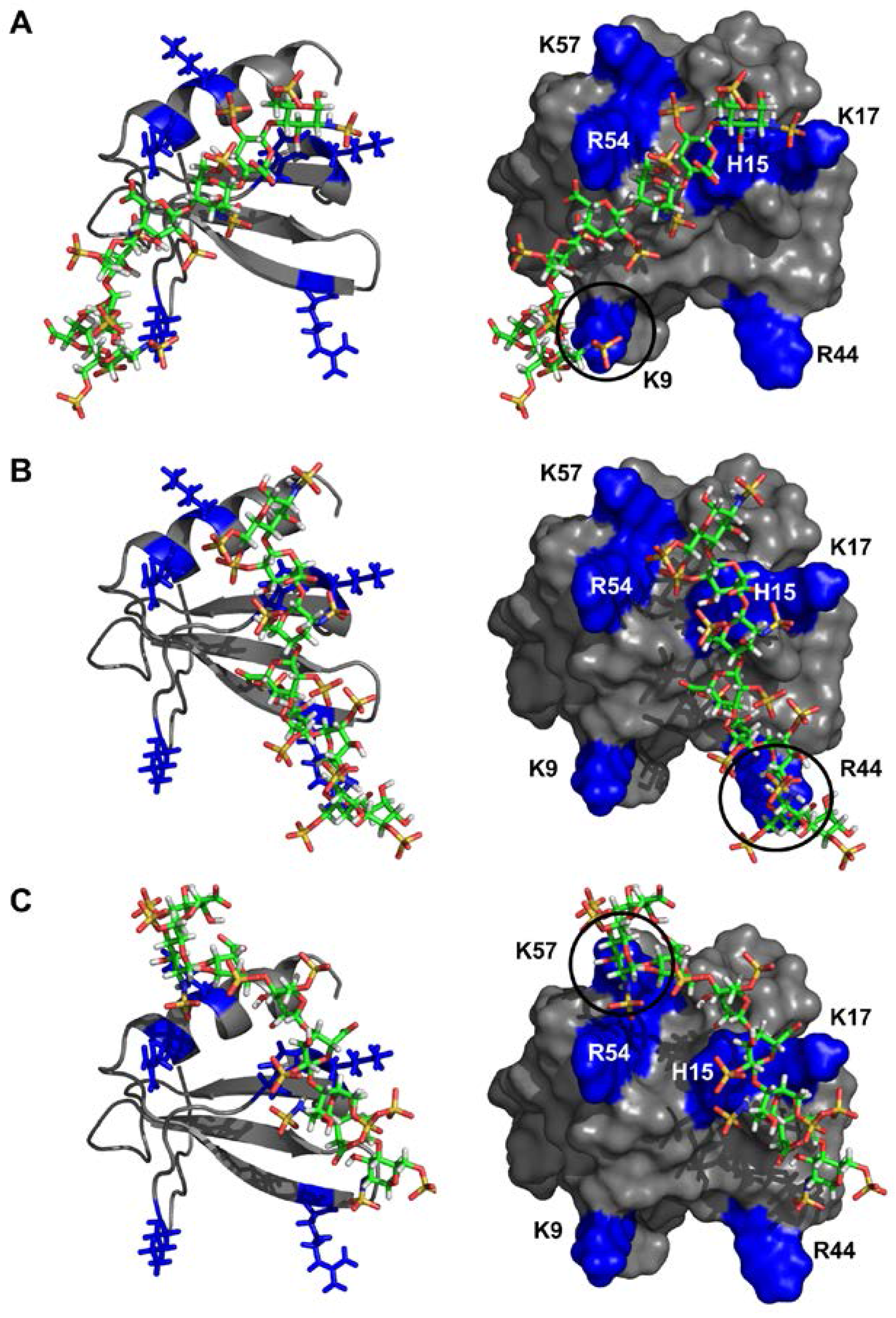
2.4. CXCL7 Monomer-Heparin dp8 Interactions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Protein Expression
4.2. Chemical Shift Assignments of the CXCL7 Monomer
4.3. NMR Titrations
4.4. Model of the Monomer Structure
4.5. Molecular Docking Using HADDOCK
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CXCL | CXC ligand |
| CXCR2 | CXC chemokine receptor 2 |
| CXCL7/NAP-2 | Neutrophil-activating peptide 2 |
| GAG | Glycosaminoglycan |
| CXCR2Nd | CXCR2 N-terminal domain |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| NAC | Neutrophil activating chemokine |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HSQC | Heteronuclear single quantum coherence |
| CSP | Chemical shift perturbation |
| NOE | Nuclear Overhauser effect |
| AIR | Ambiguous interaction restraints |
References
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonecchi, R.; Galliera, E.; Borroni, E.M.; Corsi, M.M.; Locati, M.; Mantovani, A. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: An overview. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, D.; Sobolik-Delmaire, T.; Richmond, A. Chemokines in health and disease. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanga, C.L.; Handel, T.M. Chemokine oligomerization and interactions with receptors and glycosaminoglycans: The role of structural dynamics in function. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, E.J.; Lolis, E. Structure, function, and inhibition of chemokines. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 469–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monneau, Y.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Lortat-Jacob, H. The sweet spot: How gags help chemokines guide migrating cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemzadeh, M.; Kaplan, Z.S.; Alwis, I.; Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Ashworth, K.J.; Westein, E.; Hosseini, E.; Salem, H.H.; Slattery, R.; McColl, S.R.; et al. The CXCR1/2 ligand NAP-2 promotes directed intravascular leukocyte migration through platelet thrombi. Blood 2013, 121, 4555–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeramkumar, V.; Adrover, J.M.; Ballesteros, I.; Cuartero, M.I.; Rossaint, J.; Bilbao, I.; Nácher, M.; Pitaval, C.; Radovanovic, I.; Fukui, Y.; et al. Neutrophils scan for activated platelets to initiate inflammation. Science 2014, 346, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hundelshausen, P.; Petersen, F.; Brandt, E. Platelet-derived chemokines in vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillie, R.; Farooq, S.M.; Gordon, J.R.; Stadnyk, A.W. The functional significance behind expressing two IL-8 receptor types on pmn. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Kay, C.M.; Dewald, B.; Wolf, M.; Baggiolini, M.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Sykes, B.D. Neutrophil-activating peptide-2 and melanoma growth-stimulatory activity are functional as monomers for neutrophil activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Mayo, K.H.; Daly, T.J.; Barry, J.K.; La Rosa, G.J. Subunit association and structural analysis of platelet basic protein and related proteins investigated by 1H NMR spectroscopy and circular dichroism. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20110–20118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sepuru, K.M.; Poluri, K.M.; Rajarathnam, K. Solution structure of CXCL5—A novel chemokine and adipokine implicated in inflammation and obesity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowman, H.B.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Slagle, P.H.; Kabakoff, R.; Liu, J.; Shire, S.; Hébert, C.A. Monomeric variants of IL-8: Effects of side chain substitutions and solution conditions upon dimer formation. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkowski, M.G.; Wu, J.Y.; Lazar, J.B.; Johnson, P.H.; Edwards, B.F. The crystal structure of recombinant human neutrophil-activating peptide-2 (M6L) at 1.9-a resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7077–7087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, H.; Roongta, V.; Daly, T.J.; Mayo, K.H. NMR structure and dynamics of monomeric neutrophil-activating peptide 2. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, S.K.; Murphy, P.M. The CXC chemokines growth-regulated oncogene (GRO)α, GROβ, GROγ, neutrophil-activating peptide-2, and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating peptide-78 are potent agonists for the type B, but not the type A, human interleukin-8 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20545–20550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairbrother, W.J.; Reilly, D.; Colby, T.J.; Hesselgesser, J.; Horuk, R. The solution structure of melanoma growth stimulating activity. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 242, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Sykes, B.D. 1H NMR solution structure of an active monomeric interleukin-8. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 12983–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Jerva, L.F.; West, J.; Lolis, E.; Schweitzer, B.I. Solution structure of murine macrophage inflammatory protein-2. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 8303–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.Q.; Johanson, K.O.; McDevitt, P. Nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of truncated human GROβ and its structural comparison with CXC chemokine family members GROα and IL-8. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clore, G.M.; Appella, E.; Yamada, M.; Matsushima, K.; Gronenborn, A.M. Three-dimensional structure of interleukin 8 in solution. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Sykes, B.D. Solution structure of GRO/melanoma growth stimulatory activity determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 32909–32915. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Dewald, B.; Baggiolini, M.; Sykes, B.D. 1H NMR evidence that Glu-38 interacts with the N-terminal functional domain in interleukin-8. FEBS Lett. 1996, 399, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.T.; Weber, I.T.; St Charles, R.; Xuan, J.C.; Appella, E.; Yamada, M.; Matsushima, K.; Edwards, B.F.; Clore, G.M.; Gronenborn, A.M. Crystal structure of interleukin 8: Symbiosis of NMR and crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesselgesser, J.; Chitnis, C.E.; Miller, L.H.; Yansura, D.G.; Simmons, L.C.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Kotts, C.; Wirth, C.; Gillece-Castro, B.L.; Horuk, R. A mutant of melanoma growth stimulating activity does not activate neutrophils but blocks erythrocyte invasion by malaria. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11472–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baly, D.L.; Horuk, R.; Yansura, D.G.; Simmons, L.C.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Kotts, C.; Wirth, C.M.; Gillece-Castro, B.L.; Toy, K.; Hesselgesser, J.; et al. A His19 to ALA mutant of melanoma growth-stimulating activity is a partial antagonist of the CXCR2 receptor. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4944–4949. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Sykes, B.D.; Dewald, B.; Baggiolini, M.; Clark-Lewis, I. Disulfide bridges in interleukin-8 probed using non-natural disulfide analogues: Dissociation of roles in structure from function. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7653–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Delaglio, F.; Cornilescu, G.; Bax, A. Talos+: A hybrid method for predicting protein backbone torsion angles from NMR chemical shifts. J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 44, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Bax, A. Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 56, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, C.A.; Singer, C.M.; Ermakova, E.A.; Khairutdinov, B.I.; Zuev, Y.F.; Jacobs, D.J.; Nesmelova, I.V. Dynamics and thermodynamic properties of CXCL7 chemokine. Proteins 2015, 83, 1987–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Kwakman, P.H.; Chan, D.I.; Liu, Z.; de Boer, L.; Zaat, S.A.; Vogel, H.J. Exploring platelet chemokine antimicrobial activity: Nuclear magnetic resonance backbone dynamics of NAP-2 and TC-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, L.; Rajarathnam, K. Structural basis of chemokine receptor function—A model for binding affinity and ligand selectivity. Biosci. Rep. 2006, 26, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, T.N.; Power, C.A.; Lusti-Narasimhan, M.; Hoogewerf, A.J.; Cooke, R.M.; Chung, C.W.; Peitsch, M.C.; Proudfoot, A.E. Selectivity and antagonism of chemokine receptors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P.R.; Sarmiento, J.M.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, S.T.; Garofalo, R.P.; Navarro, J.; Rajarathnam, K. Probing the role of CXC motif in chemokine CXCL8 for high affinity binding and activation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29262–29269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofuku, Y.; Yoshiura, C.; Ueda, T.; Terasawa, H.; Hirai, T.; Tominaga, S.; Hirose, M.; Maeda, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Terashima, Y.; et al. Structural basis of the interaction between chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12 and its G-protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35240–35250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P.R.; Rajarathnam, K. Solution NMR characterization of WT CXCL8 monomer and dimer binding to CXCR1 N-terminal domain. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P.R.; Sawant, K.V.; Isley, A.; Pedroza, M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Richardson, R.M.; Rajarathnam, K. Dynamic conformational switching in the chemokine ligand is essential for G-protein-coupled receptor activation. Biochem. J. 2013, 456, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, A.; Sawant, K.V.; Sarmiento, J.; Navarro, J.; Rajarathnam, K. Chemokine CXCL1 dimer is a potent agonist for the CXCR2 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12244–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldkamp, C.T.; Seibert, C.; Peterson, F.C.; De la Cruz, N.B.; Haugner, J.C., 3rd; Basnet, H.; Sakmar, T.P.; Volkman, B.F. Structural basis of CXCR4 sulfotyrosine recognition by the chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, ra4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, C.J.; Ludeman, J.P.; Canals, M.; Bridgford, J.L.; Hinds, M.G.; Clayton, D.J.; Christopoulos, A.; Payne, R.J.; Stone, M.J. Structural basis of receptor sulfotyrosine recognition by a CC chemokine: The N-terminal region of CCR3 bound to CCL11/eotaxin-1. Structure 2014, 22, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnur, E.; Kessler, N.; Zherdev, Y.; Noah, E.; Scherf, T.; Ding, F.X.; Rabinovich, S.; Arshava, B.; Kurbatska, V.; Leonciks, A.; et al. NMR mapping of RANTES surfaces interacting with CCR5 using linked extracellular domains. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2068–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, H.; Nagle, G.T.; Rajarathnam, K. Thermodynamic characterization of interleukin-8 monomer binding to CXCR1 receptor N-terminal domain. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, L.; Rajarathnam, K. Ligand selectivity and affinity of chemokine receptor CXCR1. Role of N-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30000–30008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girrbach, M.; Meliciani, I.; Waterkotte, B.; Berthold, S.; Oster, A.; Brurein, F.; Strunk, T.; Wadhwani, P.; Berensmeier, S.; Wenzel, W.; et al. A fluorescence polarization assay for the experimental validation of an in silico model of the chemokine CXCL8 binding to receptor-derived peptides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 8036–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P.R.; Mosier, P.D.; Desai, U.R.; Rajarathnam, K. Solution NMR characterization of chemokine CXCL8/IL-8 monomer and dimer binding to glycosaminoglycans: Structural plasticity mediates differential binding interactions. Biochem. J. 2015, 472, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, K.V.; Poluri, K.M.; Dutta, A.K.; Sepuru, K.M.; Troshkina, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Rajarathnam, K. Chemokine CXCL1 mediated neutrophil recruitment: Role of glycosaminoglycan interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepuru, K.M.; Rajarathnam, K. CXCL1/MGSA is a novel glycosaminoglycan (GAG)-binding chemokine: Structural evidence for two distinct non-overlapping binding domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 4247–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepuru, K.M.; Nagarajan, B.; Desai, U.R.; Rajarathnam, K. Molecular basis of chemokine CXCL5-glycosaminoglycan interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 20539–20550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Caramori, G.; Gnemmi, I.; Contoli, M.; Bristot, L.; Capelli, A.; Ricciardolo, F.L.; Magno, F.; D’Anna, S.E.; Zanini, A.; et al. Association of increased CCL5 and CXCL7 chemokine expression with neutrophil activation in severe stable COPD. Thorax 2009, 64, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Adlard, N.; Biehl, M.; Juarez, M.; Smallie, T.; Snow, M.; Buckley, C.D.; Raza, K.; Filer, A.; Scheel-Toellner, D. Expression of chemokines CXCL4 and CXCL7 by synovial macrophages defines an early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bdeir, K.; Gollomp, K.; Stasiak, M.; Mei, J.; Papiewska-Pajak, I.; Zhao, G.; Worthen, G.S.; Cines, D.B.; Poncz, M.; Kowalska, M.A. Platelet-specific chemokines contribute to the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desurmont, T.; Skrypek, N.; Duhamel, A.; Jonckheere, N.; Millet, G.; Leteurtre, E.; Gosset, P.; Duchene, B.; Ramdane, N.; Hebbar, M.; et al. Overexpression of chemokine receptor CXCR2 and ligand CXCL7 in liver metastases from colon cancer is correlated to shorter disease-free and overall survival. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grépin, R.; Guyot, M.; Giuliano, S.; Boncompagni, M.; Ambrosetti, D.; Chamorey, E.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Negrier, S.; Simonnet, H.; Pagès, G. The CXCL7/CXCR1/2 axis is a key driver in the growth of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Das, B.B.; Casagrande, F.; Tian, Y.; Nothnagel, H.J.; Chu, M.; Kiefer, H.; Maier, K.; de Angelis, A.A.; Marassi, F.M.; et al. Structure of the chemokine receptor CXCR1 in phospholipid bilayers. Nature 2012, 491, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufareva, I. Chemokines and their receptors: Insights from molecular modeling and crystallography. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, K.H.; Yang, Y.; Daly, T.J.; Barry, J.K.; La Rosa, G.J. Secondary structure of neutrophil-activating peptide-2 determined by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, A.; Joseph, P.R.; Rajarathnam, K. Structural basis for differential binding of the interleukin-8 monomer and dimer to the CXCR1 N-domain: Role of coupled interactions and dynamics. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 8795–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, T.D.; Kneller, D.G. Sparky 3; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Lange, O.; Delaglio, F.; Rossi, P.; Aramini, J.M.; Liu, G.; Eletsky, A.; Wu, Y.; Singarapu, K.K.; Lemak, A.; et al. Consistent blind protein structure generation from NMR chemical shift data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4685–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Vernon, R.; Baker, D.; Bax, A. De novo protein structure generation from incomplete chemical shift assignments. J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 43, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Darden, T.A.; Cheatham, T.E.; Simmerling, C.L.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.E.; Luo, R.; Walker, R.C.; Zhang, W.; Merz, K.M.; et al. Amber 12; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, L.; Ranjan, A.; Zhang, H.; Monzavi, H.; Boyko, R.F.; Sykes, B.D.; Wishart, D.S. Vadar: A web server for quantitative evaluation of protein structure quality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3316–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, C.; Boelens, R.; Bonvin, A.M. Haddock: A protein–protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, S.J.; van Dijk, A.D.; Krzeminski, M.; van Dijk, M.; Thureau, A.; Hsu, V.; Wassenaar, T.; Bonvin, A.M. Haddock versus haddock: New features and performance of haddock2.0 on the capri targets. Proteins 2007, 69, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulloy, B.; Forster, M.J.; Jones, C.; Davies, D.B. NMR and molecular-modelling studies of the solution conformation of heparin. Biochem. J. 1993, 293, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, A.J.; Sepuru, K.M.; Rajarathnam, K. Structural Basis of Native CXCL7 Monomer Binding to CXCR2 Receptor N-Domain and Glycosaminoglycan Heparin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030508
Brown AJ, Sepuru KM, Rajarathnam K. Structural Basis of Native CXCL7 Monomer Binding to CXCR2 Receptor N-Domain and Glycosaminoglycan Heparin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030508
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Aaron J., Krishna Mohan Sepuru, and Krishna Rajarathnam. 2017. "Structural Basis of Native CXCL7 Monomer Binding to CXCR2 Receptor N-Domain and Glycosaminoglycan Heparin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030508
APA StyleBrown, A. J., Sepuru, K. M., & Rajarathnam, K. (2017). Structural Basis of Native CXCL7 Monomer Binding to CXCR2 Receptor N-Domain and Glycosaminoglycan Heparin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030508







