Emerging Trends in the Use of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
Abstract
1. Introduction: The Human Skin and Fungal Infections
2. Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
2.1. Setting the Scene: The Need for Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
2.2. The Diversity and Use of Existing Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
2.3. Emerging Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations: Rationale and Formulation Design
2.4. Choosing a Topical Vehicle Formulation for the Delivery of Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
2.4.1. Creams
2.4.2. Ointments
2.4.3. Gels
2.5. Misuse of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
3. Miconazole and Terbinafine: Contributions to Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
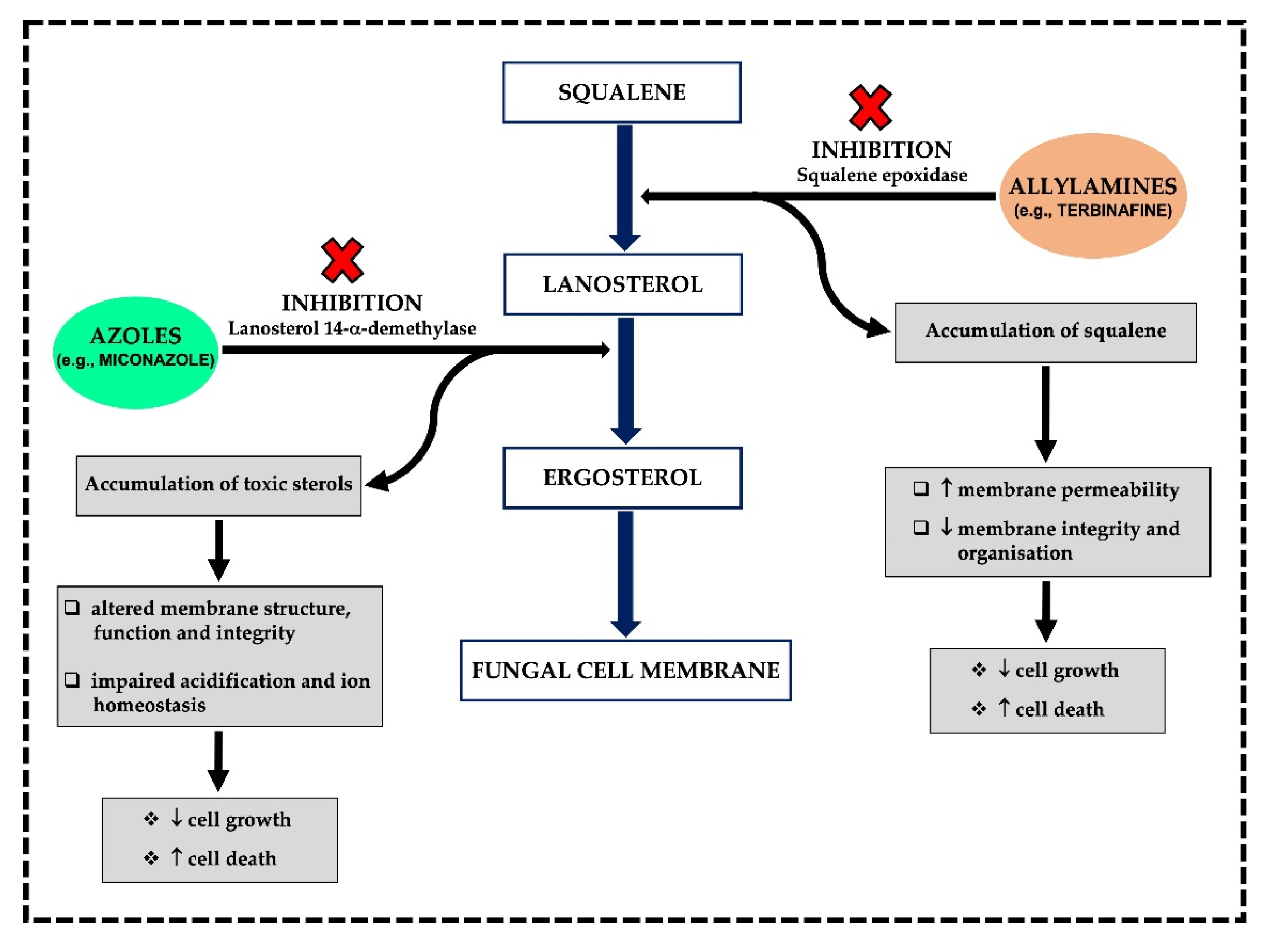
3.1. MoA and Spectrum of Activity
3.1.1. Azoles
3.1.2. Allylamines
3.2. Miconazole and Terbinafine: Formulation Availability, Clinical Indications and Potential Risks
3.2.1. Miconazole
3.2.2. Terbinafine
3.3. Antifungal Resistance and Alternatives to Conventional Antifungal Treatment Strategies
4. The Contributions of Corticosteroids to Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations
4.1. Potency Ratings/Classification
4.2. Selecting Formulations, Clinical Indications and Potential Risks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdo, J.M.; Sopko, N.A.; Milner, S.M. The applied anatomy of human skin: A model for regeneration. Wound Med. 2020, 28, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre-Utile, A.; Braun, C.; Haftek, M.; Aubin, F. Five functional aspects of the epidermal barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaney, M.H.; Kalan, L.R. Living in your skin: Microbes, molecules, and mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00695-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarsick, P.A.J.; Kolarsick, M.A.; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and physiology of the skin. J. Dermatol. Nurses Assoc. 2011, 3, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Geyer, S.; Weninger, W.; Guimberteau, J.C.; Wong, J.K. The dynamic anatomy and patterning of skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.V.; Soulika, A.M. The Dynamics of the skin’s immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, L.; Grice, E.A. The skin microbiota: Balancing risk and reward. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxberger, M.; Cenizo, V.; Cassir, N.; La Scola, B. Challenges in exploring and manipulating the human skin microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiew, P.Y.; Mac Aogain, M.; Ali, N.A.B.M.; Thng, K.X.; Goh, K.; Lau, K.J.X.; Chotirmall, S.H. The mycobiome in health and disease: Emerging concepts, methodologies and challenges. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Kong, F.-Q.; Galzote, C.; Quan, Z.-X. Dynamics of skin mycobiome in infants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, K.; Bauza-Kaszewska, J.; Kraszewska, Z.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Radtke, L.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Human skin microbiome: Impact of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on skin microbiota. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrestein, P.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Knight, R. Microbial skin inhabitants: Friends forever. Cell 2016, 165, 771–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limon, J.J.; Skalski, J.H.; Underhill, D.M. Commensal fungi in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriu, P.A.; Iker, B.; Malik, K.; Leung, H.; Mohn, W.W.; Hillebrand, G.G. New insights into the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that shape the human skin microbiome. mBio 2019, 10, e00839-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.C.; Findley, K.; Dawson, T.L., Jr.; Scheynius, A.; Boekhout, T.; Cuomo, C.A.; Xu, J.; Saunders, C.W. Fungi on the skin: Dermatophytes and Malassezia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a019802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaga, K.; Krzyściak, P. Non-lipophilic mycobiota of human skin. Acta Micol. 2015, 50, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hilles, A.R.; Mahmood, S.; Kaderi, M.A.; Hashim, R. Review of fungal skin infections and their invasion. Fungal Territory 2019, 2, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rubio, R.; de Oliveira, H.C.; Rivera, J.; Trevijano-Contador, N. The fungal cell wall: Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus species. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Lemetais, G.; Ferreira, T.; Cayot, P.; Gervais, P.; Beney, L. Ergosterol biosynthesis: A fungal pathway for life on land? Evolution 2012, 66, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Gharti Magar, D.; Thapa, S.; Nayak, N.; Talwar, O.P. Histopathology of important fungal infections–a summary. J. Pathol. Nepal 2019, 9, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Ćirić, A.; Stojković, D. Emerging antifungal targets and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, M.; Zhang, L.-J. Keratin 6, 16 and 17-critical barrier alarmin molecules in skin wounds and psoriasis. Cells 2019, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridzuan, P.M.; Nazira, C.M.; Ruth, M.; Abdul Rassip, C.N.; Nur Raihan, M.H.; Ismail, S.A.; Rahman, N.I.; Suzima, E.A.; Azhan, H. Mini review on dermatomycosis. J. Sci. Math. Lett. 2019, 8, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Bains, A.; Kaushik, R.; Dhull, S.B.; Melinda, F.; Chawla, P. A Review on antifungal efficiency of plant extracts entrenched polysaccharide-based nanohydrogels. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jartarkar, S.R.; Patil, A.; Goldust, Y.; Cockerell, C.J.; Schwartz, R.A.; Grabbe, S.; Goldust, M. Pathogenesis, immunology and management of dermatophytosis. J. Fungi 2021, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Pujalte, G.G.; Reese, S.T. Superficial fungal infections. Prim. Care 2015, 42, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovitwanichkanont, T.; Chong, A.H. Superficial fungal infections. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 48, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Santos, G.C.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Lopes, A.J.O.; de Sousa Cartágenes, M.D.S.; Filho, A.K.D.B.; do Nascimento, F.R.F.; Ramos, R.M.; Pires, E.R.R.B.; de Andrade, M.S.; Rocha, F.M.G.; et al. Candida infections and therapeutic strategies: Mechanisms of action for traditional and alternative agents. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans biofilms and human disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Ortiz, M.A.; Gabaldón, T. Fungal evolution: Cellular, genomic and metabolic complexity. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 1198–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayba, J.N.; Gooderham, M.J. A guide to topical vehicle formulations. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 22, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, T.M.; Mijaljica, D.; Townley, J.P.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. Vehicles for drug delivery and cosmetic moisturizers: Review and comparison. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Shah, A.H.; Rawal, M.K. Antifungals: Mechanism of action and drug resistance. In Yeast Membrane Transport: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Ramos, J., Sychrová, H., Kschischo, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 892, pp. 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gintjee, T.J.; Donnelley, M.A.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd. Aspiring antifungals: Review of current antifungal pipeline developments. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, J.D.; Last, A.R. Choosing topical corticosteroids. Am. Fam. Phys. 2009, 79, 135–140. Available online: https://www.aafp.org/afp/2009/0115/p135.html (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Mehta, A.B.; Nadkarni, N.J.; Patil, S.P.; Godse, K.V.; Gautam, M.; Agarwal, S. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.; Aung, S.T. Selection of an effective topical corticosteroid. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2021, 50, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.; Friedrich, M.; Papini, M.; Pujol, R.M.; Veraldi, S. Topical antifungal-corticosteroid combination therapy for the treatment of superficial mycoses: Conclusions of an expert panel meeting. Mycoses 2016, 59, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Madhu, R. The great Indian epidemic of superficial dermatophytosis: An appraisal. Indian J. Dermatol. 2017, 62, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Ghadlinge, M.; Roy, V. Topical antifungal-corticosteroid fixed-drug combinations: Need for urgent action. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2021, 53, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.P.; Spada, F. Breaking the itch-scratch cycle: Topical options for the management of chronic cutaneous itch in a dermatitis. Medicines 2019, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, D.K.; Stewart, C.S. Keratin hydrolysis by dermatophytes. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, V.L.; Beccacece, I.; Guasconi, L.; Mena, C.J.; Cervi, L.; Chiapello, L.S. Skin immunity to dermatophytes: From experimental infection models to human disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, M.; van Zuuren, E.J.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Burgess, H.; Doney, L.; Stuart, B.; Moore, M.; Little, P. Topical antifungal treatments for Tinea cruris and Tinea corporis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 8, CD009992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenane, P.; Macarthur, C.; Parkin, P.C.; Krafchik, B.; DeGroot, J.; Khambalia, A.; Pope, E. Clobetasol propionate, 0.05%, vs hydrocortisone, 1%, for alopecia areata in children: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, R.L.; Morias, J.; Verhamme, G. A double-blind study comparing Daktacort, miconazole and hydrocortisone in inflammatory skin infections. Dermatologica 1976, 15, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, F.; Hollis, S. Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 3, CD001434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, J.F.; Verweij, P.E. Current management of fungal infections. Drugs 2001, 61, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Falson, P. Multidrug resistance ATP-binding cassette membrane transporters as targets for improving oropharyngeal candidiasis treatment. Adv. Cell. Mol. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2, 23955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, F.; Barnes, T.M.; Greive, K.A. Comparative safety and efficacy of topical mometasone furoate with other topical corticosteroids. Aust. J. Dermatol. 2018, 59, e168–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Patent Office. Topical Composition Comprising Terbinafine and Hydrocortisone. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP1656125A2/en (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Carlos, G.; Uribe, P.; Fernandez-Penas, P. Rational use of topical corticosteroids. Aust. Prescrib. 2013, 36, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.P.; Spada, F. Hydrogels for atopic dermatitis and wound management: A superior drug delivery vehicle. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryczyk-Poprawa, A.; Kwiecień, A.; Opoka, W. Photostability of topical agents applied to the skin: A review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Sorrell, T.C. Antifungal agents. Med. J. Aust. 2007, 187, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.D.; Perfect, J.R. Use of antifungal combination therapy: Agents, order, and timing. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2010, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, L.; Abreu, P.A.; Teixeira, V.L.; Paixão, I.C.P.; Pereira, R.; Leal, B.; Lourenço, A.L.; Rampelotto, P.H.; Castro, H.C. Mycoses and antifungals: Reviewing the basis of a current problem that still is a biotechnological target for marine products. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.F.; Bernardes-Filho, F.; Quaresma-Santos, M.V.; Amorim, A.G.; Schechtman, R.C.; Azulay, D.R. Treatment of superficial mycoses: Review. Part II. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.K.; Singh, P.; Yadav, R.K.; Pandey, S.; Bhunia, S.S. Past, present, and future of antifungal drug development. In Communicable Diseases of the Developing World; Saxena, A.K., Ed.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 29, pp. 125–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.J.; Hitchcock, C.A.; Sibley, C.M. Current and emerging azole antifungal agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 40–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.C.; Keniya, M.V. Roles for structural biology in the discovery of drugs and agrochemicals targeting sterol 14α-demethylases. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, M.; Posteraro, B.; Lass-Flörl, C. Antifungal drug resistance among Candida species: Mechanisms and clinical impact. Mycoses 2015, 58 (Suppl. 2), 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Yarden, O.; Li, S. Abnormal ergosterol biosynthesis activates transcriptional responses to antifungal azoles. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Gamarra, S.; Garcia-Effron, G.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S.; Rao, R. Requirement for ergosterol in V-ATPase function underlies antifungal activity of azole drugs. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durdu, M.; Ilkit, M.; Tamadon, Y.; Tolooe, A.; Rafati, H.; Seyedmousavi, S. Topical and systemic antifungals in dermatology practice. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Rice, L.B. Antifungal agents: Mode of action, mechanisms of resistance, and correlation of these mechanisms with bacterial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, D.G.; Tupe, S.G.; Ramana, C.V.; Deshpande, M.V. Fungal cell membrane-promising drug target for antifungal therapy. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, N.S.; Wagner, S.; Leitner, I. In vitro activities of terbinafine against cutaneous isolates of Candida albicans and other pathogenic yeasts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, S.; Erdal, M.S.; Aksu, B. New formulation strategies in topical antifungal therapy. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2013, 3, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barasch, A.; Griffin, A.V. Miconazole revisited: New evidence of antifungal efficacy from laboratory and clinical trials. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhry, S.; Gupta, S.; D’souza, P. Topical antifungals used for treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. J. Bacteriol. Mycol. 2017, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sahni, K.; Singh, S.; Dogra, S. Newer topical treatments in skin and nail dermatophyte infections. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 9, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R. Therapy of skin, hair and nail fungal infections. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poojary, S.A. Topical antifungals: A review and their role in current management of dermatophytoses. Clin. Dermatol. Rev. 2017, 1, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fothergill, A.W. Miconazole: A historical perspective. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2006, 4, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balfour, J.A.; Faulds, D. Drug evaluation terbinafine a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in superficial mycoses. Drugs 1992, 43, 259–284. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/00003495-199243020-00010 (accessed on 20 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Newland, J.G.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M. Update on terbinafine with a focus on dermatophytoses. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 2, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, K.; Gupta, A.K.; Versteeg, S.; Mays, R.; Villanueva, E.; John, D. Topical and device-based treatments for fungal infections of the toenails. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD012093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Rashed, A.; Rathi, D.G.; Ahmad Nasir, N.A.H.; Abd Rahman, A.Z. Antifungal properties of essential oils and their compounds for application in skin fungal infections: Conventional and nonconventional approaches. Molecules 2021, 26, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyigit, T.; Ozer, O. Corticosteroids for skin delivery: Challenges and new formulation opportunities. In Glucocorticoids-New Recognition of Our Familiar Friend; Qian, X., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, E.; Rademaker, M.; Dailey, R.; Daniel, B.S.; Drummond, C.; Fischer, G.; Foster, R.; Grills, C.; Halbert, A.; Hill, S.; et al. Adverse effects of topical corticosteroids in paediatric eczema: Australasian consensus statement. Aust. J. Dermatol. 2015, 56, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Cunill, A.; Lazaro, M.; Herráez, L.; Quiñones, M.D.; Moro-Moro, M.; Sanchez, I.; Skin Allergy Committee of Spanish Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (SEAIC). Basic skin care and topical therapies for atopic dermatitis: Essential approaches and beyond. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.C.; Stoughton, R.B. Correlation of the vasoconstriction assay and clinical activity in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 1985, 121, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, S.K.; D’Souza, P. Rational and ethical use of topical corticosteroids based on safety and efficacy. Indian J. Dermatol. 2012, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvidzayi, M.; Rath, S.; Bon, C.; Abboo, S.; Kanfer, I. A novel approach to assess the potency of topical corticosteroids. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, K.; Rees, J.L. Variation in epidermal morphology in human skin at different body sites as measured by reflectance confocal microscopy. Acta. Derm. Venereol. 2010, 90, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Évora, A.S.; Adams, M.J.; Johnson, S.A.; Zhang, Z. Corneocytes: Relationship between structural and biomechanical properties. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coondoo, A.; Phiske, M.; Verma, S.; Lahiri, K. Side-effects of topical steroids: A long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Pimpinelli, N.; Ricceri, F.; Bagnoni, G.; Bartoli, L.; Bellini, M.; Brandini, L.; Caproni, M.; Castelli, A.; Fimiani, M.; et al. Treatment of psoriasis with topical agents: Recommendations from a Tuscany Consensus. Dermatol. Therapy 2017, 30, e12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greive, K.A.; Barnes, T.M. Increased bioavailability of hydrocortisone dissolved in a cream base. Aust. J. Dermatol. 2015, 56, e30–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mijaljica, D.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. Emerging Trends in the Use of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080812
Mijaljica D, Spada F, Harrison IP. Emerging Trends in the Use of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(8):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080812
Chicago/Turabian StyleMijaljica, Dalibor, Fabrizio Spada, and Ian P. Harrison. 2022. "Emerging Trends in the Use of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 8: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080812
APA StyleMijaljica, D., Spada, F., & Harrison, I. P. (2022). Emerging Trends in the Use of Topical Antifungal-Corticosteroid Combinations. Journal of Fungi, 8(8), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080812