Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma and Associated Risk Factors: A Retrospective Chart Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Disease and Patients’ Characteristics
2.2. Statistical Analyses
2.3. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
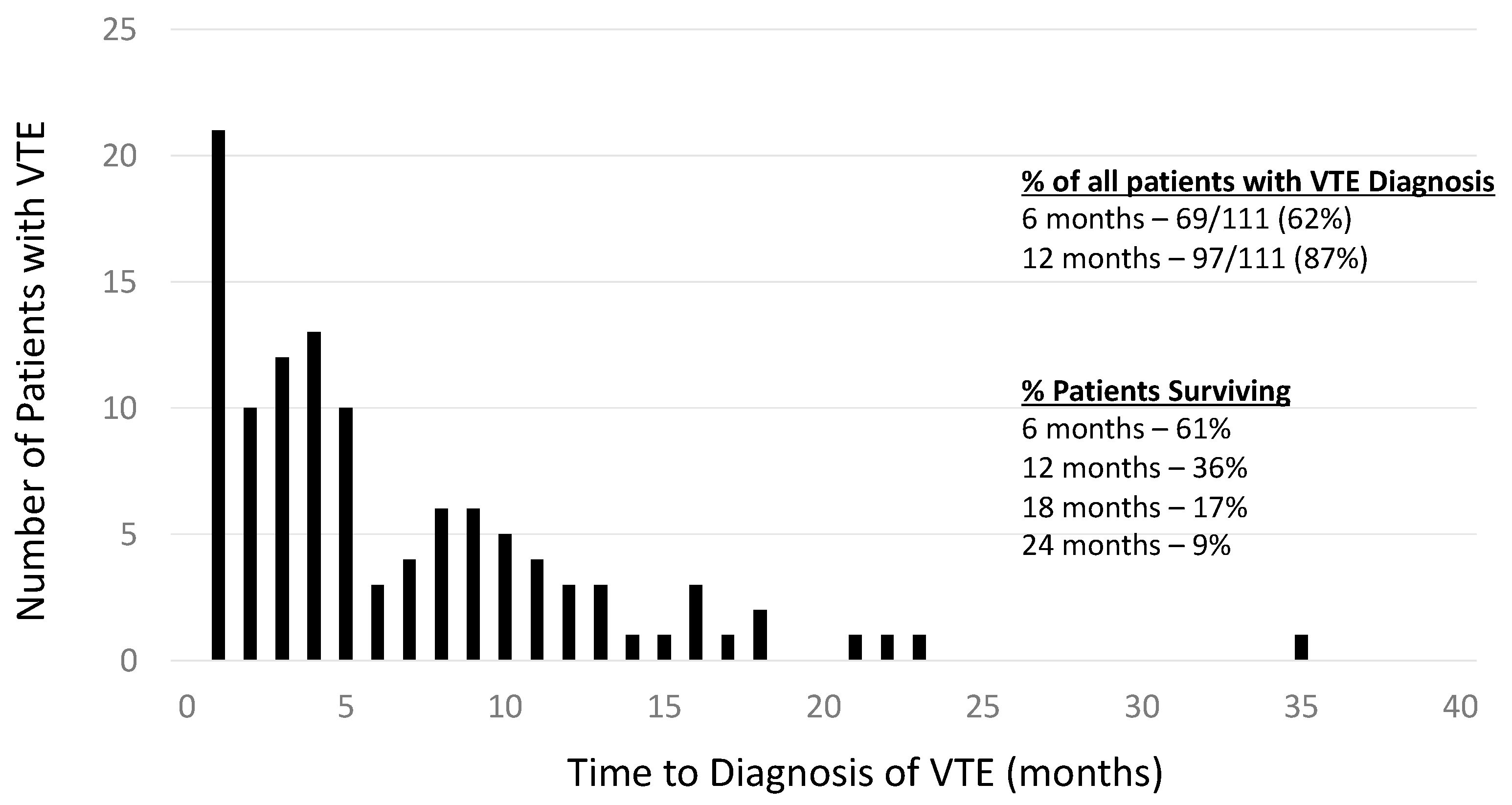
3.2. Characterization of the VTE Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GB | Glioblastoma |
| JCC | Juravinski Cancer Centre |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DVT | Deep venous thrombosis |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| KPS | Karnofsky performance status |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| RP | Recurrence/progression |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| LMWH | Low-molecular-weight heparin |
| DOAC | Direct oral anti-coagulant |
| ICH | Intracranial hemorrhage |
References
- Marras, L.C.; Geerts, W.H.; Perry, J.R. The risk of venous thromboembolism is increased throughout the course of malignant glioma: An evidence based review. Cancer 2000, 89, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, D.E.; Grossman, S.A.; Streiff, M.D. Management of venous thromboembolism in patients with primary and metastatic brain tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, N.C.; Khoury, M.N.; Sohal, D.; McCrae, K.R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khorana, A.A. Recurrent venous thromboembolism in glioblastoma. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semrad, T.J.; O’Donnell, R.; Wun, T.; Chew, H.; Harvey, D.; Zhou, H.; White, R.H. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in 9489 patients with malignant glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Culakova, E.; Lyman, G.H.; Francis, C.W. Development and validation of a predictive model for chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Blood 2008, 111, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, A.A.; Scelzi, E.; Salmistraro, G.; Ermani, M.; Carollo, C.; Berti, F.; Zampieri, P.; Baiocchi, C.; Fiorentino, M.V. Incidence and risk of thromboembolism during treatment of high-grade gliomas: A prospective study. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdett, K.B.; Unruh, D.; Drumm, M.; Steffens, A.; Lamano, J.; Judkins, J.; Schwartz, M.; Javier, R.; Amidei, C.; Lipp, E.S.; et al. Determining venous thromboembolism risk in patients with adult-type diffuse glioma. Blood 2023, 141, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, R.; Ay, C. Venous Thromboembolism in Brain Tumors: Risk Factors, Molecular Mechanisms, and Clinical Challenges. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, J.; de La Rocha, I.V.; Font, L.; Braester, A.; Madridano, O.; Peromingo, J.A.D.; Apollonio, A.; Pagán, B.; Bascuñana, J.; Monreal, M. Venous thromboembolism in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Findings of the RIETE registry. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.; Ho, C.; Urgoti, G.R.; Leugner, D.; Easaw, J. Risk of venous thromboembolism in glioblastoma patients. Cureus 2018, 10, e2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.R. Thromboembolic disease in patients with high-grade glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14 (Suppl. 4), iv73–iv80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsumeda, M.; Uzuka, T.; Watanabe, J.; Fukuda, M.; Akaiwa, Y.; Hanzawa, K.; Okada, M.; Oishi, M.; Fujii, Y. High incidence of deep vein thrombosis in the perioperative period of neurosurgical patients. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e103–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Diaz, M.; Horbinski, C.; Mackman, N.; Bagley, S.; Broekman, M.; Rak, J.; Perry, J.; Pabinger, I.; Key, N.S.; et al. Epidemiology, biology, and management of venous thromboembolism in gliomas: An interdisciplinary review. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.; Jo, J.; Smolkin, M.; Ratcliffe, S.J.; Schiff, D. Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Grade II–IV Gliomas as a Function of Molecular Subtype. Neurol 2021, 96, e1063–e1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.K.; Anjum, Z.; Mahmoud, A.; Joshi, U.; Kouides, P. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation and risk of venous thromboembolism in glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2022, 219, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, R.; Vormittag, R.; Hassler, M.; Roessler, K.; Schwarz, M.; Zielinski, C.; Pabinger, I.; Marosi, C. Venous thromboembolism and survival in patients with high-grade glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 9, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, N.; Cote, D.J.; Hulou, M.M.; Alghamdi, A.; Alshahrani, A.; Mekary, R.A.; Smith, T.R. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in brain tumor patients undergoing craniotomy: A meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 130, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.R.; Julian, J.A.; Laperriere, N.J.; Geerts, W.; Agnelli, G.; Rogers, L.R.; Malkin, M.G.; Sawaya, R.; Baker, R.; Falanga, A.; et al. PRODIGE: A randomized placebo-controlled trial of dalteparin low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed malignant glioma. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1959–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, M.; Abou-Nassar, K.; Mallick, R.; Tagalakis, V.; Shivakumar, S.; Schattner, A.; Kuruvilla, P.; Hill, D.; Spadafora, S.; Marquis, K.; et al. Apixaban to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskob, G.E.; Van Es, N.; Verhamme, P.; Carrier, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Garcia, D.; Grosso, M.A.; Kakkar, A.K.; Kovacs, M.J.; Mercuri, M.F.; et al. Edoxaban for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; Thirlwall, J.; Chapman, O.; Lokare, A.; Hill, C.; Hale, D.; Dunn, J.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Hutchinson, C.; et al. Comparison of an oral factor Xa inhibitor with low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer with venous thromboembolism: Results of a randomized trial (SELECT-D). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; McNamara, M.G.; Kakkar, A.K.; Streiff, M.B.; Riess, H.; Vijapurkar, U.; Kaul, S.; Wildgoose, P.; Soff, G.A.; on behalf of the CASSINI Investigators. Assessing full benefit of rivaroxaban prophylaxis in high-risk ambulatory patients with cancer: Thromboembolic events in the randomized CASSINI Trial. TH Open 2020, 4, e107–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinski, D.; Won, S.Y.; Voss, M.; Keil, F.; Miesbach, W.; Behmanesh, B.; Dosch, M.; Baumgarten, P.; Bernstock, J.D.; Seifert, V.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus low-molecular-weight heparin for pulmonary embolism in patients with glioblastoma. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.A.; Wright, H.; Chan, K.; Ross, H.; Prasad, P.; Goodwin, A.; Holmes, C.E. Safety of apixaban for venous thromboembolic primary prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed malignant glioma. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 53, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Number Assessed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Median (range) | 528 | 65 (17, 90) |
| Gender | 528 | N (%) | |
| Female | 230 (43.6) | ||
| Male | 298 (56.4) | ||
| BMI * | Median (interquartile range) | 489 | 27.2 (24.4–31.1) |
| KPS ** | 525 | N (%) | |
| 30 | 78 (14.9) | ||
| 40 | 27 (5.1) | ||
| 50 | 34 (6.5) | ||
| 60 | 39 (7.4) | ||
| 70 | 82 (15.6) | ||
| 80 | 118 (22.5) | ||
| 90 | 144 (27.4) | ||
| 100 | 3 (0.6) | ||
| Weakness | 514 | N (%) | |
| 1—unilateral upper | 9 (1.8) | ||
| 2—unilateral lower | 11 (2.1) | ||
| 3—bilateral upper | 1 (0.2) | ||
| 4—bilateral lower | 8 (1.6) | ||
| 5—hemiplegia/paresis | 98 (19.1) | ||
| 6—generalized | 80 (15.6) | ||
| 7—no weakness | 307 (59.7) | ||
| Location | 523 | N (%) | |
| Brainstem | 9 (1.7) | ||
| Frontal | 158 (30.2) | ||
| Occipital | 23 (4.4) | ||
| Parietal | 63 (12.1) | ||
| Temporal | 141 (27.0) | ||
| Multiple Lobes | 129 (24.7) | ||
| Number of Lesions | 519 | N (%) | |
| Unifocal | 410 (79.0) | ||
| Multifocal | 109 (21.0) | ||
| Median (interquartile range) | 495 | 4.4 (3.3–5.4) | |
| Surgery | 521 | N (%) | |
| Biopsy | 103 (19.8) | ||
| Gross total resection | 181 (34.7) | ||
| Subtotal resection | 237 (45.5) | ||
| Treatment | 528 | N (%) | |
| Chemoradiation + temozolomide | 204 (38.6) | ||
| Chemoradiation | 175 (33.1) | ||
| Radiation alone | 12 (2.3) | ||
| Temozolomide alone | 31 (5.9) | ||
| Missing treatment information | 12 (2.3) | ||
| Bevacizumab | 51 (9.7) | ||
| No treatment | 89 (16.9) |
| Variable | Number Assessed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| VTE | 528 | N (%) | |
| Yes | 111 (21.0) | ||
| No | 413 (78.2) | ||
| Missing information | 4 (0.8) | ||
| Site | 111 | N (%) | |
| Arterial thrombosis | 1 (0.9) | ||
| Bilateral lower extremity | 8 (7.2) | ||
| Unilateral lower extremity | 39 (35.1) | ||
| Unilateral upper extremity | 8 (7.2) | ||
| Pulmonary embolism | 30 (27.0) | ||
| Deep venous thrombosis + pulmonary embolism | 25 (22.5) | ||
| Intravenous catheter | 106 | N (%) | |
| Yes | 4 (3.8) | ||
| Intra-venacaval filter | 106 | N (%) | |
| Yes | 8 (7.6) | ||
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 109 | N (%) | |
| Yes | 9 (8.3) | ||
| Other bleeding | 105 | N (%) | |
| Gastro-intestinal | 2 (1.9) | ||
| Hematuria | 1 (1.0) | ||
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 4 (3.8) | ||
| Epistaxis | 2 (1.9) | ||
| Minor bleed | 1 (1.0) | ||
| No bleeding | 95 (90.5) | ||
| Steroids | Yes (%) | 510 | 488 (95.7) |
| Anticoagulation | Yes (%) | 500 | 73 (14.6) |
| Antiplatelet agents | Yes (%) | 503 | 56 (11.1) |
| Survival | 528 | % (95% CI) | |
| 6-months | 73.7 (69.6, 77.4) | ||
| 1-year | 53.9 (49.3, 58.3) | ||
| 2-year | 26.3 (22.1, 30.8) | ||
| 5-year | 8.5 (5.0, 13.0) | ||
| Cumulative Incidence of VTE | N (%) Events | ||
| Total | 528 | 111 (21.0) | |
| 6-months | 13.5 (10.7, 16.6) | ||
| 1-year | 18.8 (15.5, 22.4) | ||
| 2-year | 23.2 (19.5, 27.1) |
| Variable | Comparator | n | Hazards Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | /year | 528 | 1.00 (0.99, 1.02) | 0.98 |
| Sex | Female versus Male | 528 | 0.89 (0.61, 1.30) | 0.56 |
| KPS * | /10 units | 525 | 0.96 (0.88, 1.05) | 0.41 |
| Weakness | None versus any | 514 | 0.72 (0.49, 1.04) | 0.080 |
| Diabetes | Yes versus No | 528 | 0.80 (0.46, 1.38) | 0.43 |
| Hypertension | Yes versus No | 528 | 0.96 (0.66, 1.40) | 0.82 |
| Dyslipdemia | Yes versus No | 528 | 1.15 (0.78, 1.72) | 0.48 |
| History of VTE | Yes versus No | 528 | 0.61 (0.16, 2.36) | 0.48 |
| Active Smoker | Yes versus No | 528 | 0.88 (0.47, 1.62) | 0.67 |
| History of Cancer | Yes versus No | 528 | 1.33 (1.01, 1.75) | 0.045 |
| Number of Lesions | Multifocal versus unifocal | 519 | 0.70 (0.42, 1.17) | 0.18 |
| Surgery | Gross Total Resection versus other | 528 | 1.24 (0.86, 1.80) | 0.25 |
| RP ** | Yes versus No | 528 | 1.61 (1.11, 2.36) | 0.013 |
| Bevacizumab | Yes versus No | 528 | 1.22 (0.71, 2.10) | 0.47 |
| Khorana Score | ≥3 versus 2 | 470 | 0.78 (0.53, 1.15) | 0.20 |
| Platelets (109/L) | ≥350 versus <350 | 505 | 0.35 (0.11, 1.13) | 0.079 |
| Hb (g/L) | <10 versus ≥10 | 505 | 0.89 (0.32, 2.43) | 0.81 |
| WBC (109/L) | >11 versus ≤11 | 504 | 0.85 (0.58, 1.24) | 0.39 |
| BMI *** | ≥35 versus <35 | 489 | 1.17 (0.65, 2.13) | 0.60 |
| Multivariable | ||||
| RP ** | Yes versus No | 528 | 1.61 (1.11, 2.36) | 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Binjabal, D.; Al Majarafi, N.; Pond, G.R.; Hirte, H. Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma and Associated Risk Factors: A Retrospective Chart Review. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080449
Binjabal D, Al Majarafi N, Pond GR, Hirte H. Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma and Associated Risk Factors: A Retrospective Chart Review. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(8):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080449
Chicago/Turabian StyleBinjabal, Duaa, Nasser Al Majarafi, Gregory R. Pond, and Hal Hirte. 2025. "Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma and Associated Risk Factors: A Retrospective Chart Review" Current Oncology 32, no. 8: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080449
APA StyleBinjabal, D., Al Majarafi, N., Pond, G. R., & Hirte, H. (2025). Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma and Associated Risk Factors: A Retrospective Chart Review. Current Oncology, 32(8), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080449





