Artificial Intelligence in Laryngeal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Role of AI in Medical Imaging Analysis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preregistration
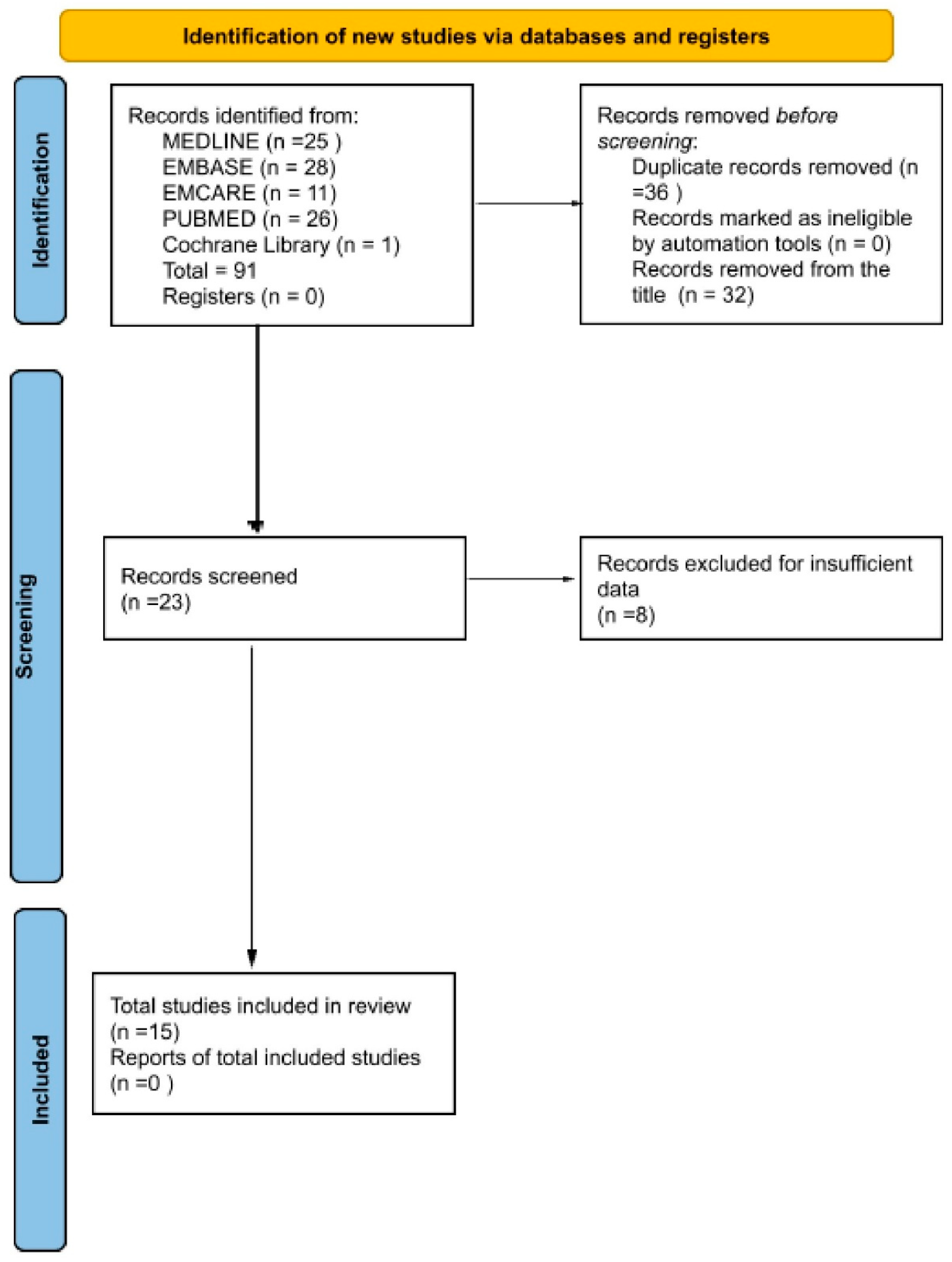
2.2. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
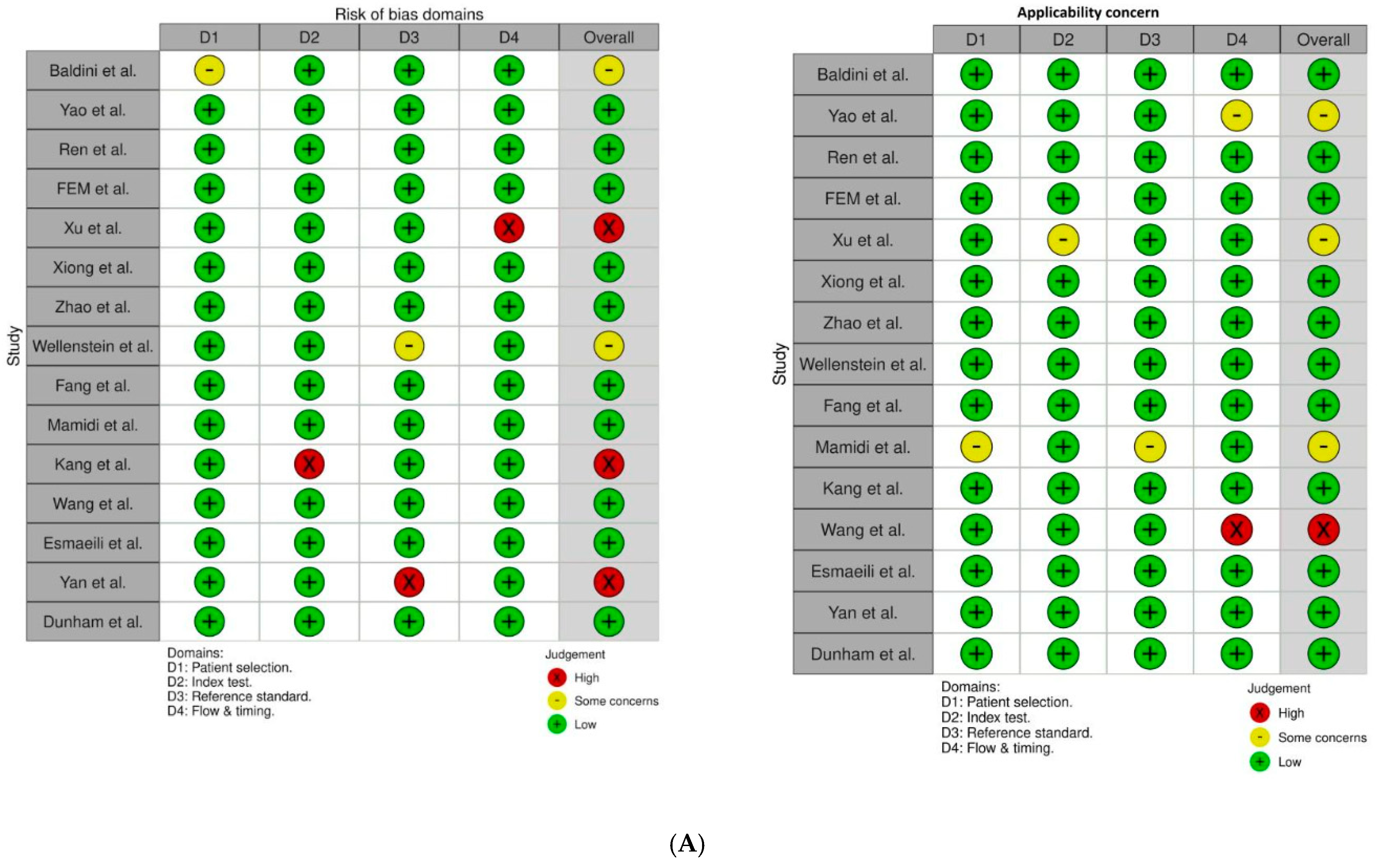
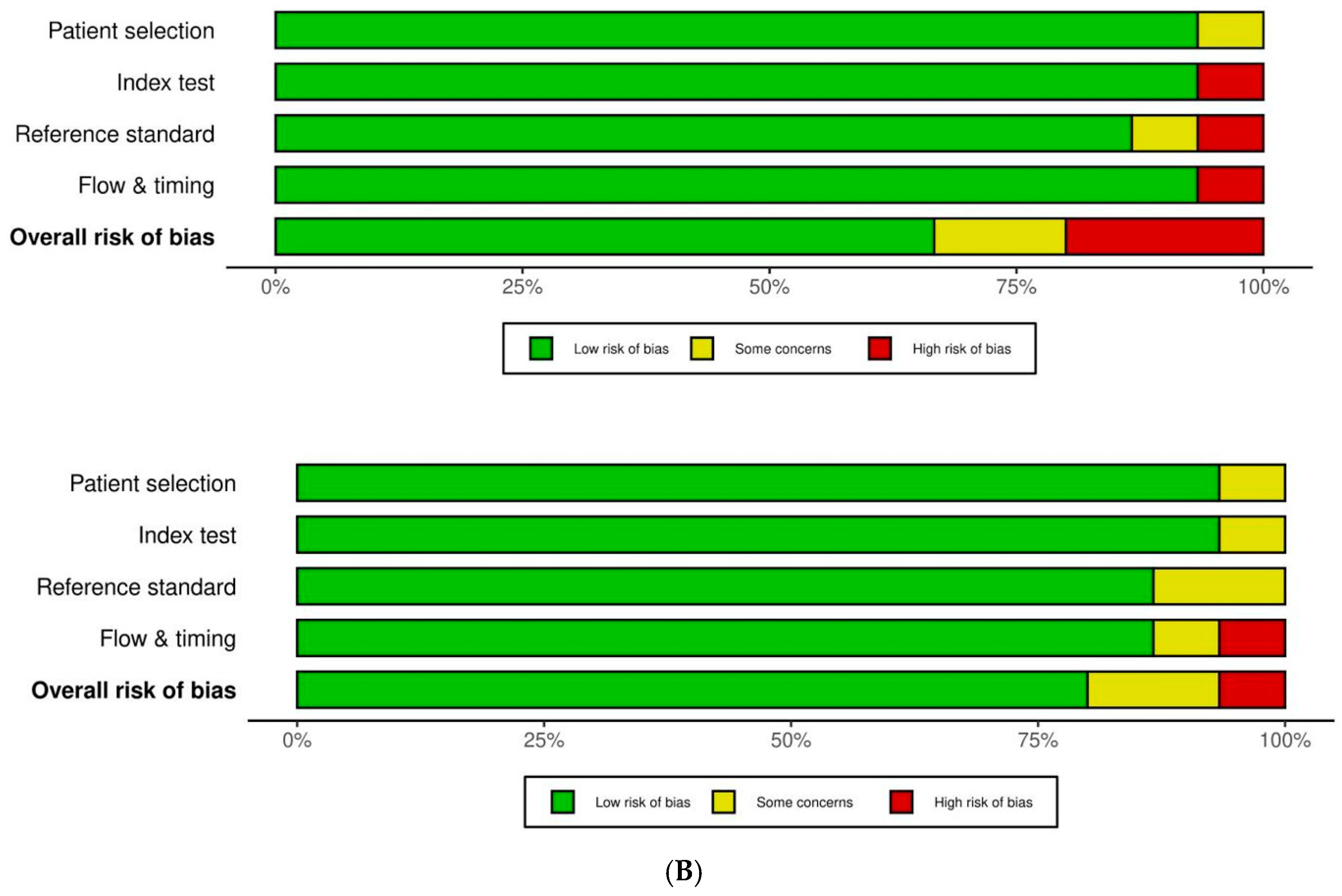
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Synthesis Methods
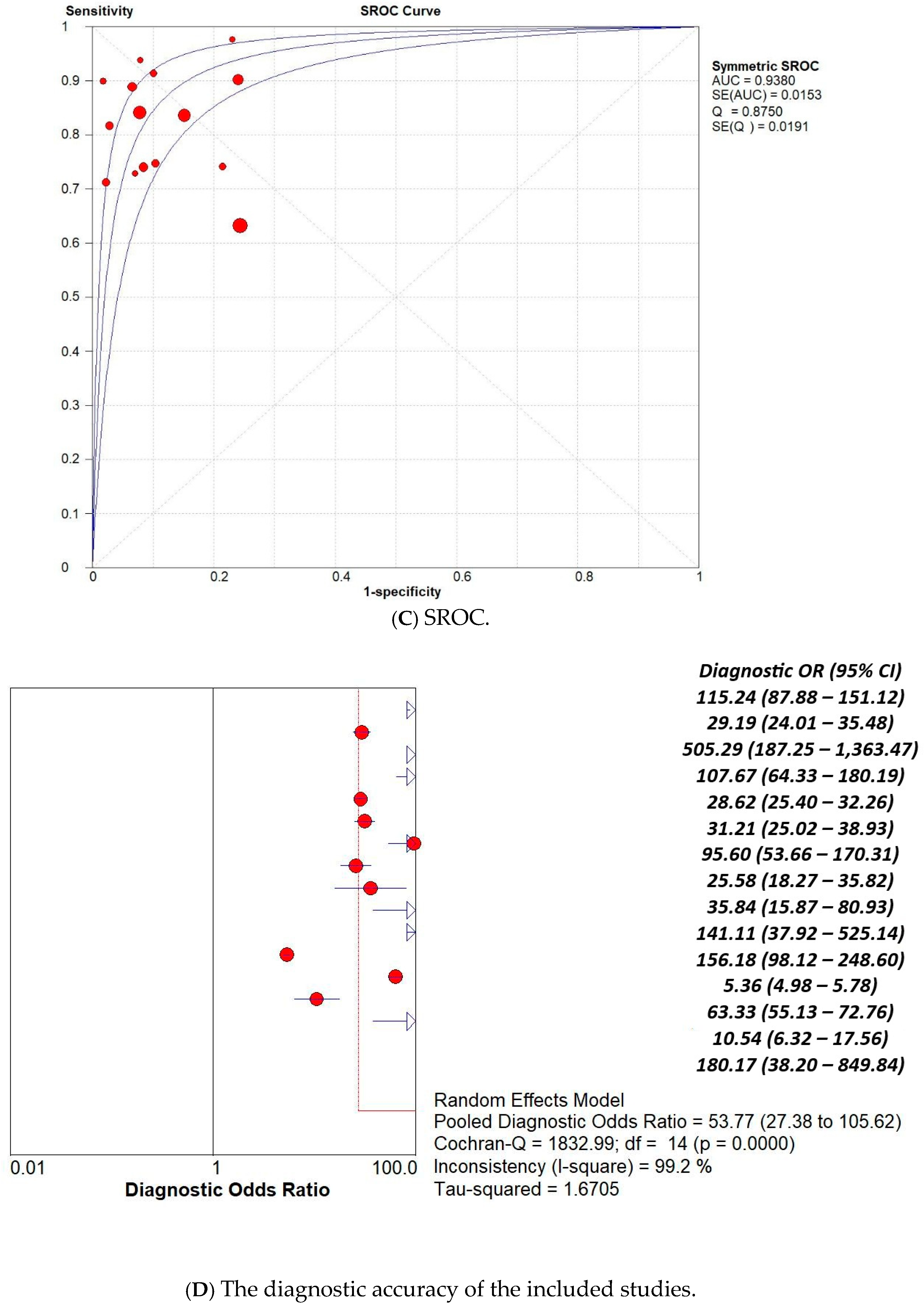
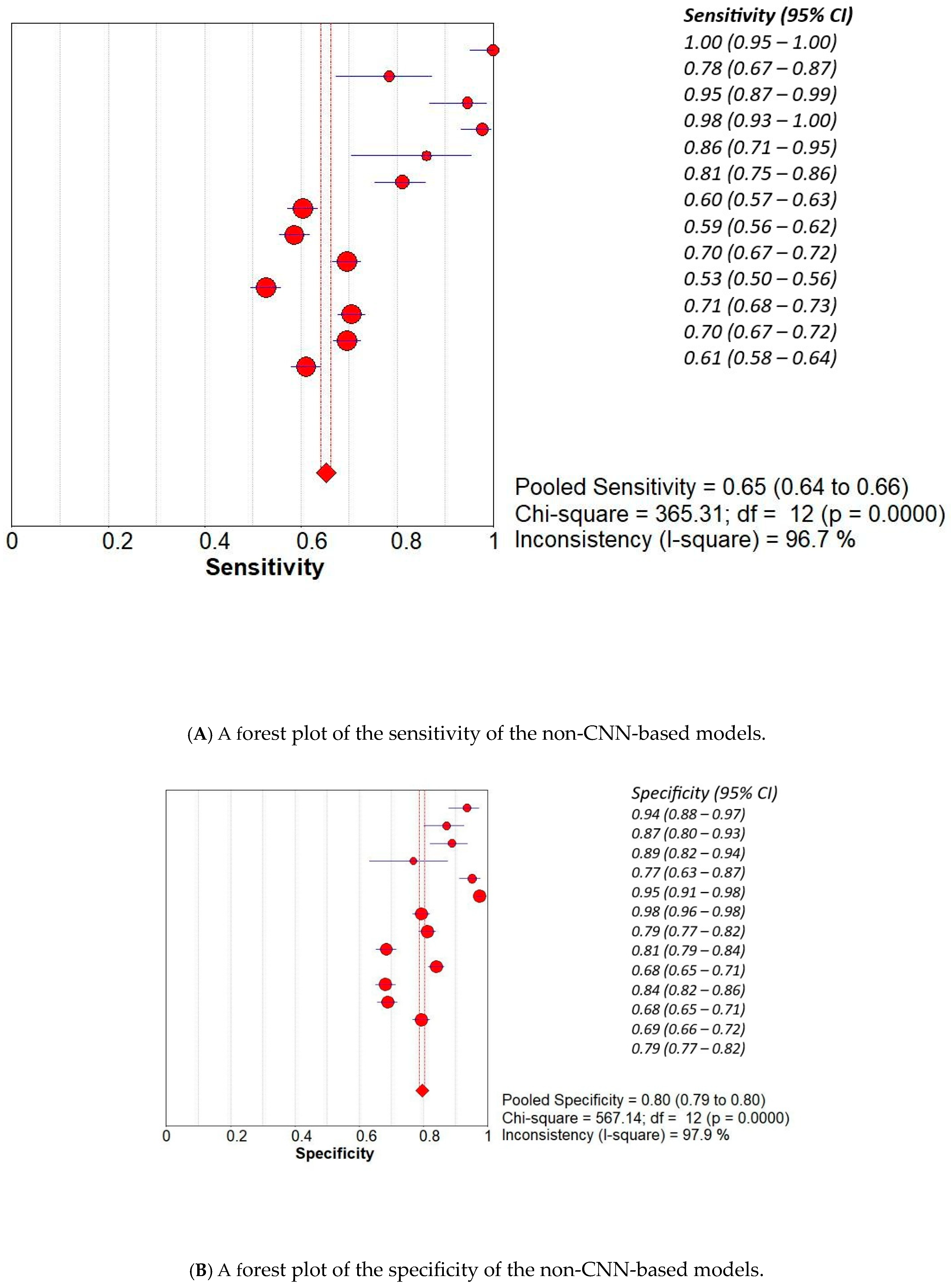
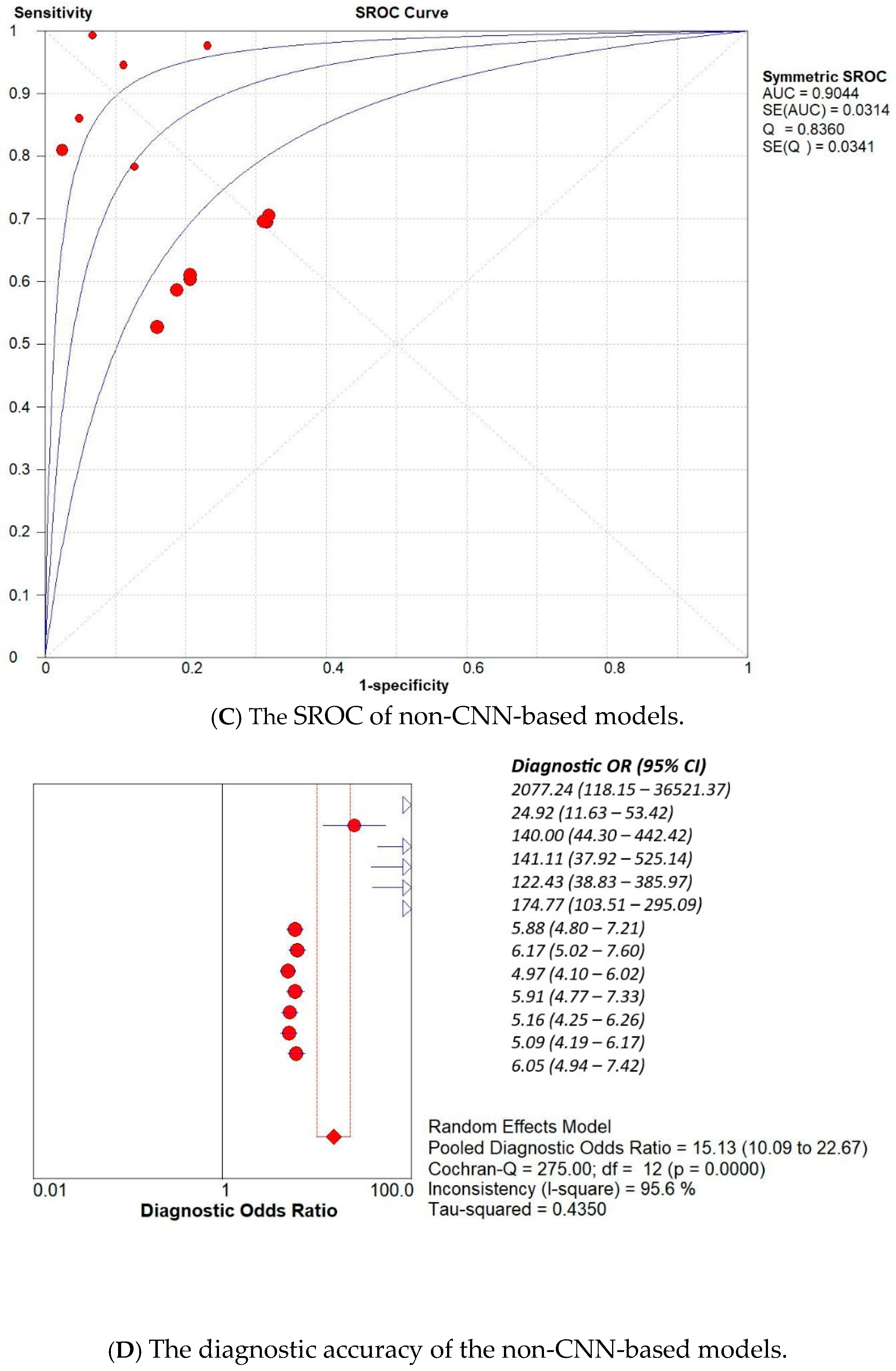
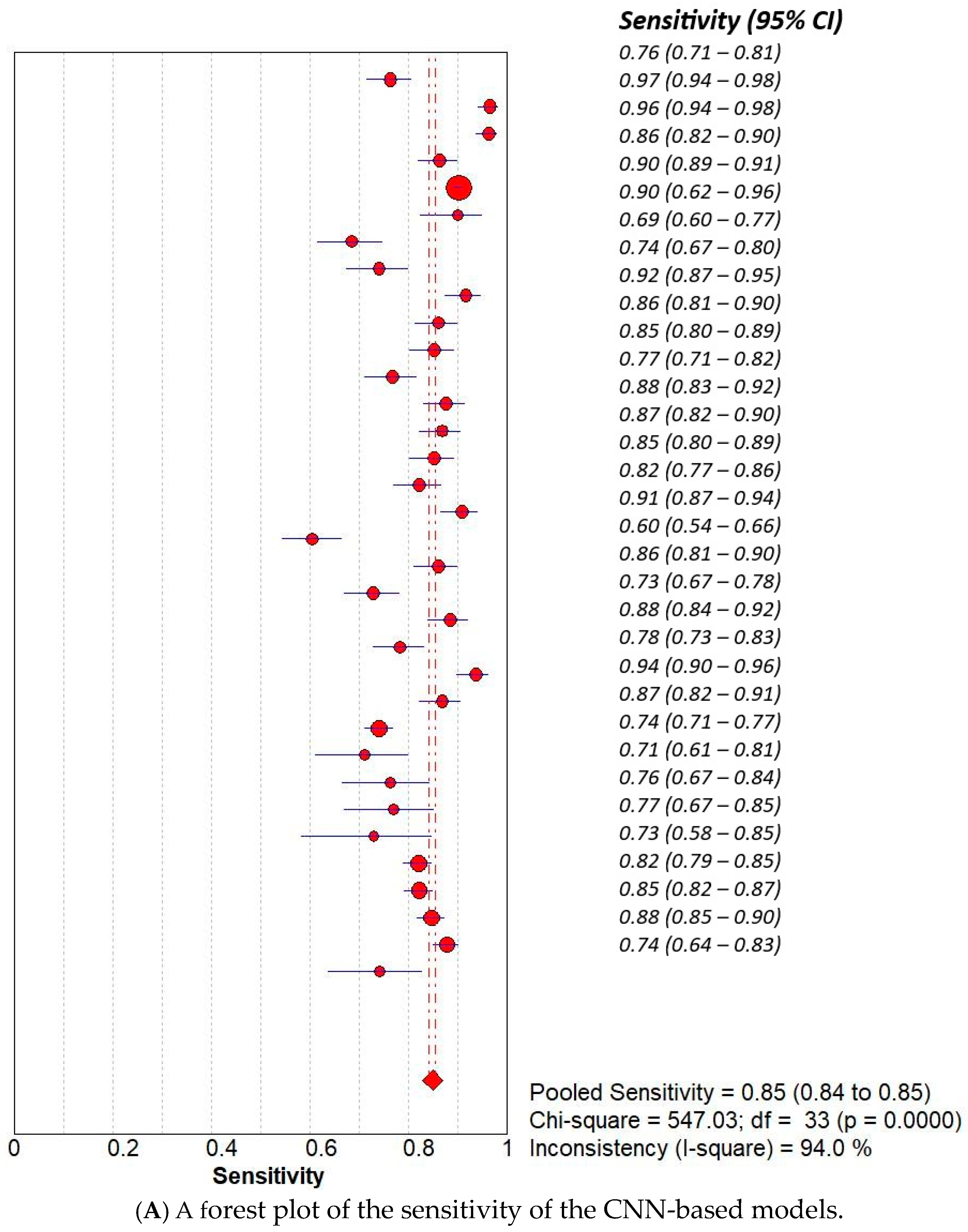
3. Results
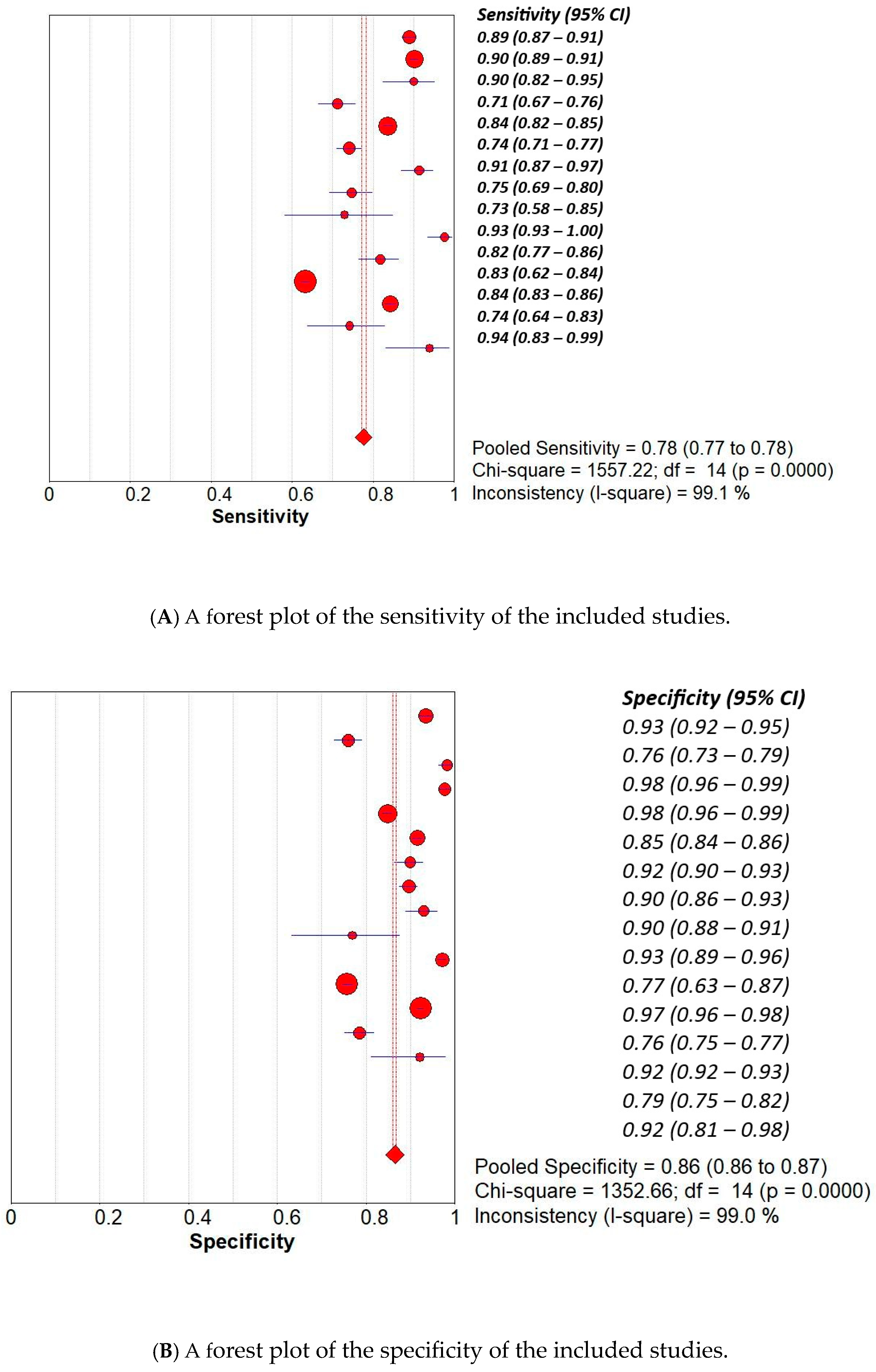
3.1. Overall Pooled Analysis
3.2. Subset Analysis: Diagnostic Accuracy of CNN-Based MODELS vs. Non-CNN Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
References
- Igissin, N.; Zatonskikh, V.; Telmanova, Z.; Tulebaev, R.; Moore, M. Laryngeal cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention: A narrative review. Iran. J. Public Health 2023, 52, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Johnson, N.W.; Kumar, N. Global epidemiology of head and neck cancers: A continuing challenge. Oncology 2016, 91, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, T.; Santos, C.P.; De Momi, E.; Moccia, S. Learned and handcrafted early-stage laryngeal SCC diagnosis features. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Lysack, J.T. Lessons Learned From Commonly Missed Head and Neck Cancers on Cross-Sectional Imaging. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2022, 73, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausert, C.R.; Olszewski, A.E.; Taylor, L.N.; McMurray, J.S.; Dailey, S.H.; Jiang, J.J. Mucosal wave measurement and visualization techniques. J. Voice 2011, 25, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Coello, P.; Rigau, D.; Sanabria, A.J.; Plaza, V.; Miravitlles, M.; Martinez, L. Quality and strength: The GRADE system for formulating recommendations in clinical practice guidelines. Arch. Bronconeumol. (Engl. Ed.) 2013, 49, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Strzelecki, M.; Piórkowski, A. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence in medical imaging and image processing—A review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Rahim, S.; Zubair, M.; Abdul-Ghafar, J. Artificial intelligence [AI] in medicine, current applications and future role with special emphasis on its potential and promise in pathology: Present and future impact, obstacles including costs and acceptance among pathologists, practical and philosophical considerations. A comprehensive review. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 16, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Coelho, L. How artificial intelligence shapes medical imaging technology: A survey of innovations and applications. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Albadawy, M. AI in diagnostic imaging: Revolutionising accuracy and efficiency. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2024, 5, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Azam, M.A.; Sampieri, C.; Ioppi, A.; Ruiz-Sevilla, L.; Vilaseca, I.; Alegre, B.; Tirrito, A.; Pennacchi, A.; Peretti, G.; et al. An automated approach for real-time informative frames classification in laryngeal endoscopy using deep learning. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 4255–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Witte, D.; Gimonet, H.; German, A.; Andreadis, K.; Cheng, M.; Sulica, L.; Elemento, O.; Barnes, J.; Rameau, A. Automatic classification of informative laryngoscopic images using deep learning. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ma, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, N.; et al. Automatic recognition of laryngoscopic images using a deep-learning technique. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E686–E693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEM, C. CARS 2023—Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Int. J. CARS 2023, 18 (Suppl. S1), S1–S123. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Fan, D.G.; Huang, J.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.Z. Computer-aided diagnosis of laryngeal cancer based on deep learning with laryngoscopic images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Lin, P.; Yu, J.G.; Ye, J.; Xiao, L.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, W.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of laryngeal cancer via deep learning based on laryngoscopic images. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhi, J.; Zheng, H.; Du, J.; Wei, M.; Lin, P.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Construction of prediction model of early glottic cancer based on machine learning. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2025, 145, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellenstein, D.J.; Woodburn, J.; Marres, H.A.; van den Broek, G.B. Detection of laryngeal carcinoma during endoscopy using artificial Intelligence. Head Neck 2023, 45, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Fu, J.; Du, C.; Lin, T.; Yan, Y. Identifying laryngeal neoplasms in laryngoscope images via deep learning based object detection: A case study on an extremely small data set. Irbm 2023, 44, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, I.S.; Dunham, M.E.; Adkins, L.K.; McWhorter, A.J.; Fang, Z.; Banh, B.T. Laryngeal cancer screening during flexible video laryngoscopy using large computer vision models. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2024, 133, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.F.; Xu, K.; Cai, L.J.; Hu, B.B.; Lu, X. Self-Attention Mechanisms-Based Laryngoscopy Image Classification Technique for Laryngeal Cancer Detection. Head Neck 2025, 47, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Tie, C.W.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, J.Q.; Chen, B.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Yang, L.; et al. Multi-instance learning based artificial intelligence model to assist vocal fold leukoplakia diagnosis: A multicentre diagnostic study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, N.; Davaris, N.; Boese, A.; Illanes, A.; Navab, N.; Friebe, M.; Arens, C. Contact Endoscopy–Narrow Band Imaging (CE-NBI) data set for laryngeal lesion assessment. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Ren, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. Automated detection of glottic laryngeal carcinoma in laryngoscopic images from a multicentre database using a convolutional neural network. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2023, 48, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, M.E.; Kong, K.A.; McWhorter, A.J.; Adkins, L.K. Optical biopsy: Automated classification of airway endoscopic findings using a convolutional neural network. Laryngoscope 2022, 132 (Suppl. S4), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur, A.M.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Kavookjian, H.; Kraft, S.; Karadaghy, O.; Farrokhian, N.; Mussatto, C.; Penn, J.; Wang, G. Interpretable computer vision to detect and classify structural laryngeal lesions in digital flexible laryngoscopic images. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2023, 169, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Migliorelli, L.; Berardini, D.; Azam, M.A.; Sampieri, C.; Ioppi, A.; Srivastava, R.; Peretti, G.; Mattos, L.S. Improving real-time detection of laryngeal lesions in endoscopic images using a decoupled super-resolution enhanced YOLO. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 260, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.A.; Sampieri, C.; Ioppi, A.; Benzi, P.; Giordano, G.G.; De Vecchi, M.; Campagnari, V.; Li, S.; Guastini, L.; Paderno, A.; et al. Videomics of the upper aero-digestive tract cancer: Deep learning applied to white light and narrow band imaging for automatic segmentation of endoscopic images. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 900451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.A.; Sampieri, C.; Ioppi, A.; Africano, S.; Vallin, A.; Mocellin, D.; Fragale, M.; Guastini, L.; Moccia, S.; Piazza, C.; et al. Deep learning applied to white light and narrow band imaging videolaryngoscopy: Toward real-time laryngeal cancer detection. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Ju, J.; Wang, J.; Mahr, J.J. Vocal cord lesions classification based on deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, S.; Vanone, G.O.; De Momi, E.; Laborai, A.; Guastini, L.; Peretti, G.; Mattos, L.S. Learning-based classification of informative laryngoscopic frames. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 158, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, F.; Brodsky, M.B.; Akst, L.M.; Ali, H. Machine learning in laryngoscopy analysis: A proof of concept observational study for the identification of post-extubation ulcerations and granulomas. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, S.L.; Ismaiel, A.; Brata, V.D.; Turtoi, D.C.; Barsan, M.; Czako, Z.; Pop, C.; Muresan, L.; Stanculete, M.F.; Dumitrascu, D.I. Artificial Intelligence and medical specialties: Support or substitution? Med. Pharm. Rep. 2024, 97, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc. J. 2019, 6, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmatko, A.; Ghaffari Laleh, N.; Gerstung, M.; Kather, J.N. Artificial intelligence in histopathology: Enhancing cancer research and clinical oncology. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
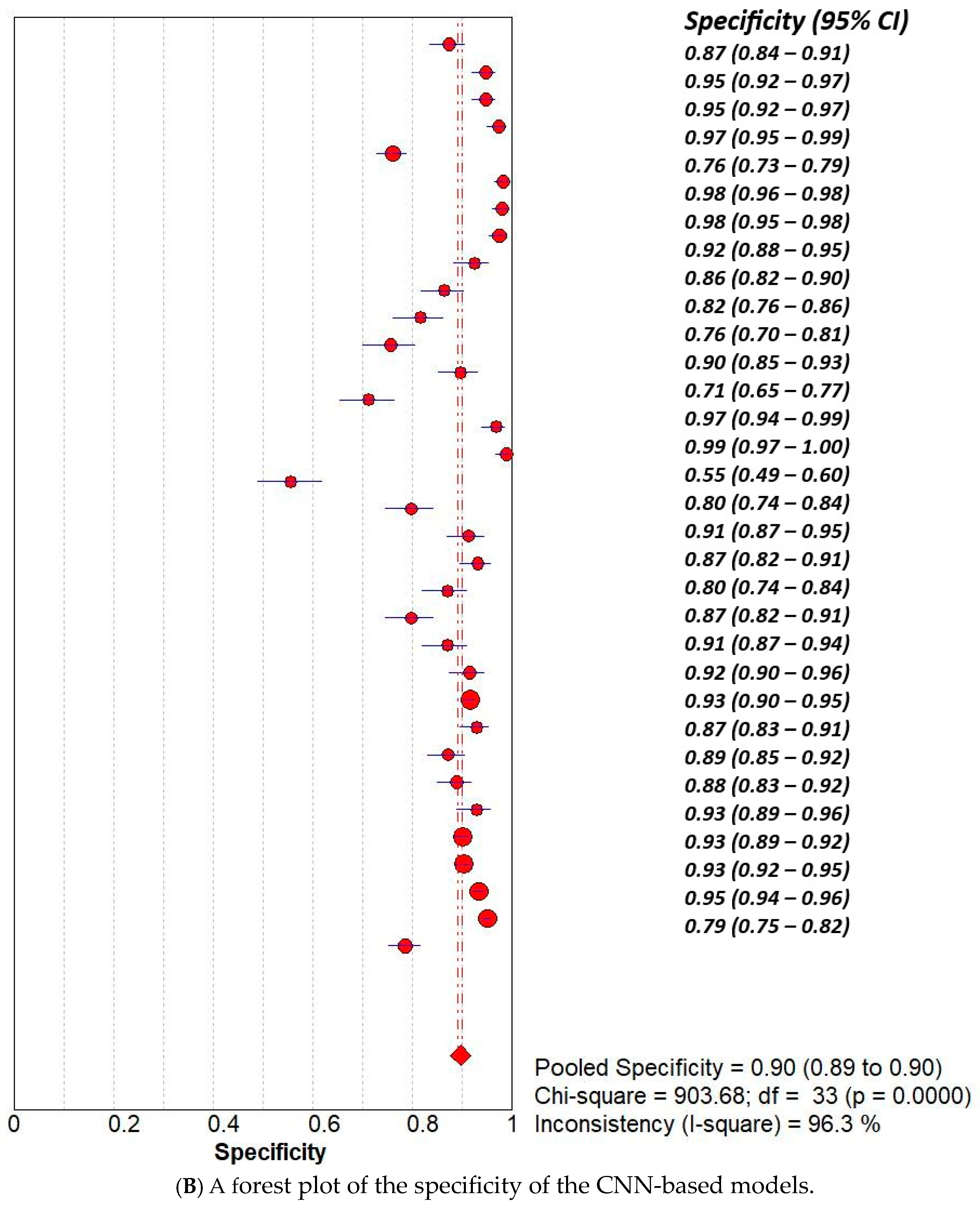
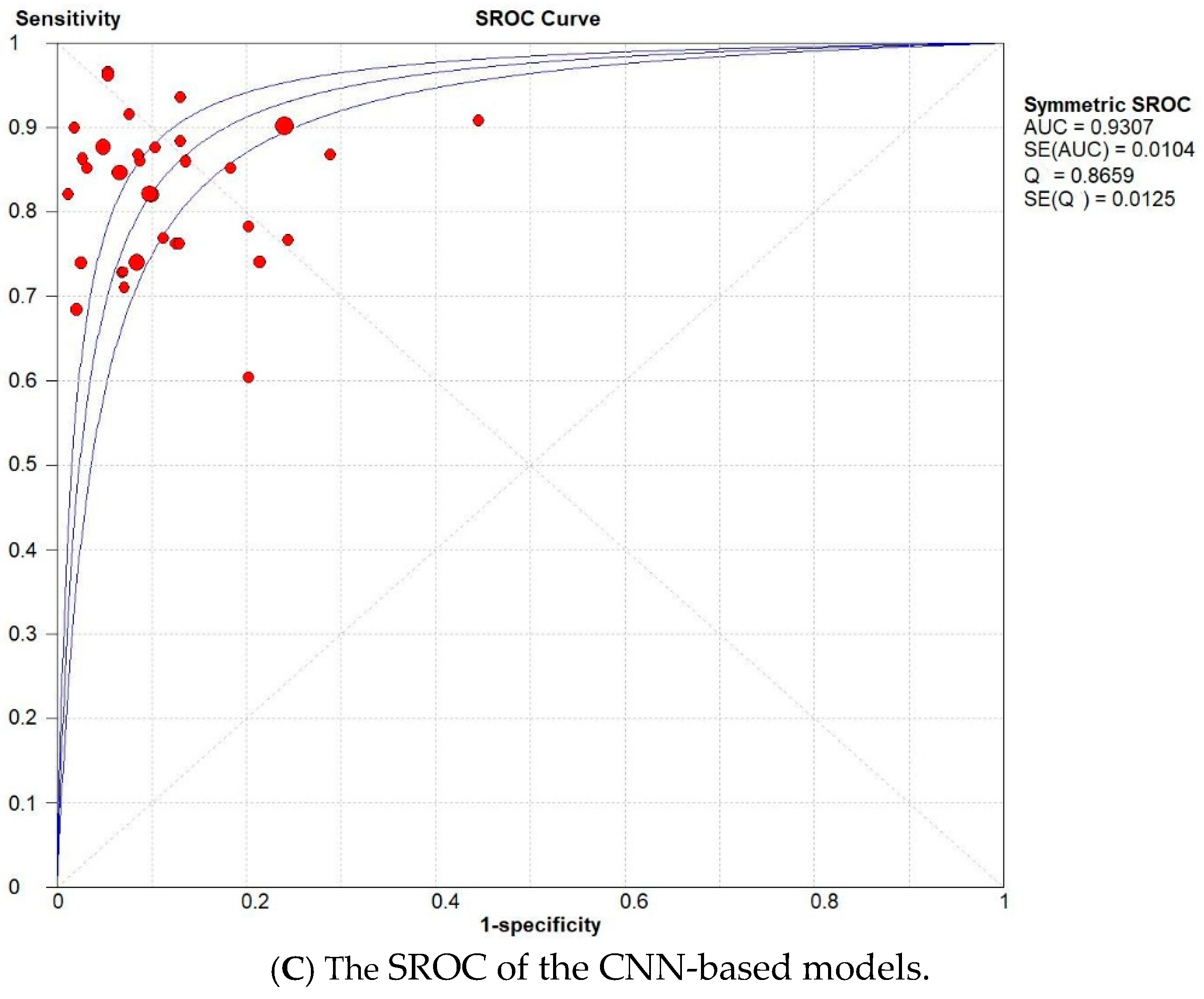
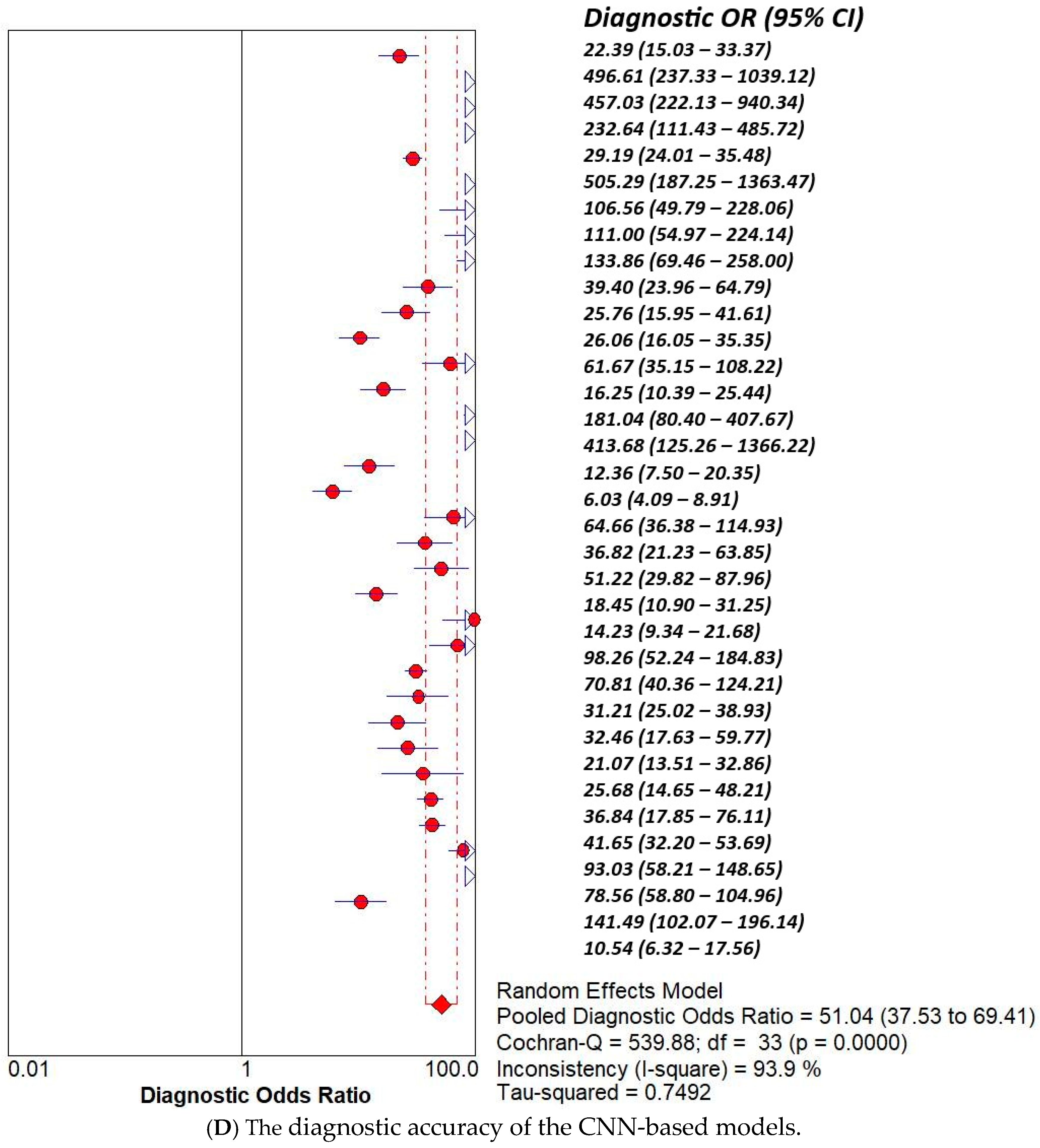
| Study | AI Model | TP | TN | FP | FN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baldini et al. [11] | Int shallow CNN | 264 | 313 | 45 | 82 |
| INT ResNet-50 | 334 | 339 | 19 | 12 | |
| INT MobileNetv2 | 333 | 339 | 19 | 13 | |
| EXT ResNet-50 | 272 | 331 | 9 | 43 | |
| Yao et al. [12] | CNN | 3277 | 612 | 193 | 356 |
| Ren et al. [13] | CNN | 90 | 393 | 7 | 10 |
| Lee et al. [14] | YOLOV5 | 137 | 392 | 8 | 63 |
| YOLOV6 | 148 | 390 | 10 | 52 | |
| Xu et al. [15] | Densenet201 INTERNAL | 230 | 220 | 18 | 21 |
| Densenet201 EXTERNAL | 222 | 230 | 36 | 36 | |
| Alexnet INTERNAL | 214 | 194 | 43 | 37 | |
| Alexnet EXTERNAL | 198 | 201 | 64 | 60 | |
| Inception v3 INTERNAL | 220 | 213 | 24 | 31 | |
| Inception v3 EXTERNAL | 224 | 189 | 76 | 34 | |
| Mnasnet INTERNAL | 214 | 231 | 7 | 37 | |
| Mnasnet EXTERNAL | 212 | 263 | 2 | 46 | |
| Mobilenet v3 INTERNAL | 228 | 132 | 105 | 23 | |
| Mobilenet v3 EXTERNAL | 156 | 212 | 53 | 102 | |
| Resnet152 INTERNAL | 216 | 217 | 20 | 35 | |
| Resnet152 EXTERNAL | 188 | 248 | 18 | 70 | |
| Squeezenet1 INTERNAL | 222 | 207 | 30 | 29 | |
| Squeezenet1 EXTERNAL | 202 | 212 | 53 | 56 | |
| Vgg19 INTERNAL | 235 | 207 | 30 | 16 | |
| Vgg19 EXTERNAL | 224 | 243 | 22 | 34 | |
| Xiong et al. [16] | DCNN | 628 | 1815 | 166 | 220 |
| Zhao et al. [17] | RF | 74 | 118 | 8 | 0 |
| DV | 58 | 110 | 16 | 16 | |
| SVM | 70 | 112 | 14 | 4 | |
| Wellenstein et al. [18] | YOLOv5s | 69 | 303 | 23 | 28 |
| YOLOv5m | 74 | 284 | 42 | 23 | |
| YOLOv5sl | 70 | 295 | 37 | 21 | |
| Fang et al. [19] | Faster R-CNN | 35 | 213 | 16 | 13 |
| Mamidi et al. [20] | [Vit] | 127 | 40 | 12 | 3 |
| Kang et al. [21] | ILCDS ex | 31 | 187 | 9.47 | 5 |
| ILCDS in | 184 | 979 | 23.97 | 43 | |
| Wang et al. [22] | LR | 627 | 723 | 187.46 | 411 |
| SVM | 609 | 740 | 170.17 | 429 | |
| RandomForest | 722 | 623 | 286.65 | 316 | |
| ExtraTrees | 548 | 765 | 144.69 | 490 | |
| XGBoost | 733 | 621 | 289.38 | 305 | |
| LightGBM | 723 | 627 | 283.01 | 315 | |
| MLP | 634 | 723 | 187.46 | 404 | |
| Esmaeili et al. [23] | DenseNet121 | 563 | 1383 | 152 | 123 |
| EfcientNetB0V2 | 564 | 1386 | 149 | 122 | |
| ResNet50V2 | 581 | 1434 | 101 | 105 | |
| Ensemble model. | 602 | 1461 | 74 | 84 | |
| Yan et al. [24] | R-CNNs | 66 | 503 | 137 | 23 |
| Dunham et al. [25]. | CNN | 46 | 47 | 4 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alabdalhussein, A.; Al-Khafaji, M.H.; Al-Busairi, R.; Al-Dabbagh, S.; Khan, W.; Anwar, F.; Raheem, T.S.; Elkrim, M.; Sahota, R.B.; Mair, M. Artificial Intelligence in Laryngeal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060338
Alabdalhussein A, Al-Khafaji MH, Al-Busairi R, Al-Dabbagh S, Khan W, Anwar F, Raheem TS, Elkrim M, Sahota RB, Mair M. Artificial Intelligence in Laryngeal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(6):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060338
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlabdalhussein, Ali, Mohammed Hasan Al-Khafaji, Rusul Al-Busairi, Shahad Al-Dabbagh, Waleed Khan, Fahid Anwar, Taghreed Sami Raheem, Mohammed Elkrim, Raguwinder Bindy Sahota, and Manish Mair. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence in Laryngeal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Current Oncology 32, no. 6: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060338
APA StyleAlabdalhussein, A., Al-Khafaji, M. H., Al-Busairi, R., Al-Dabbagh, S., Khan, W., Anwar, F., Raheem, T. S., Elkrim, M., Sahota, R. B., & Mair, M. (2025). Artificial Intelligence in Laryngeal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Current Oncology, 32(6), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060338





