Clinical Effects of RUNX1 Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Detection of RUNX1 Mutations
2.3. Transplant Protocols
2.4. Definitions and End-Points
2.5. Statistical Analysis
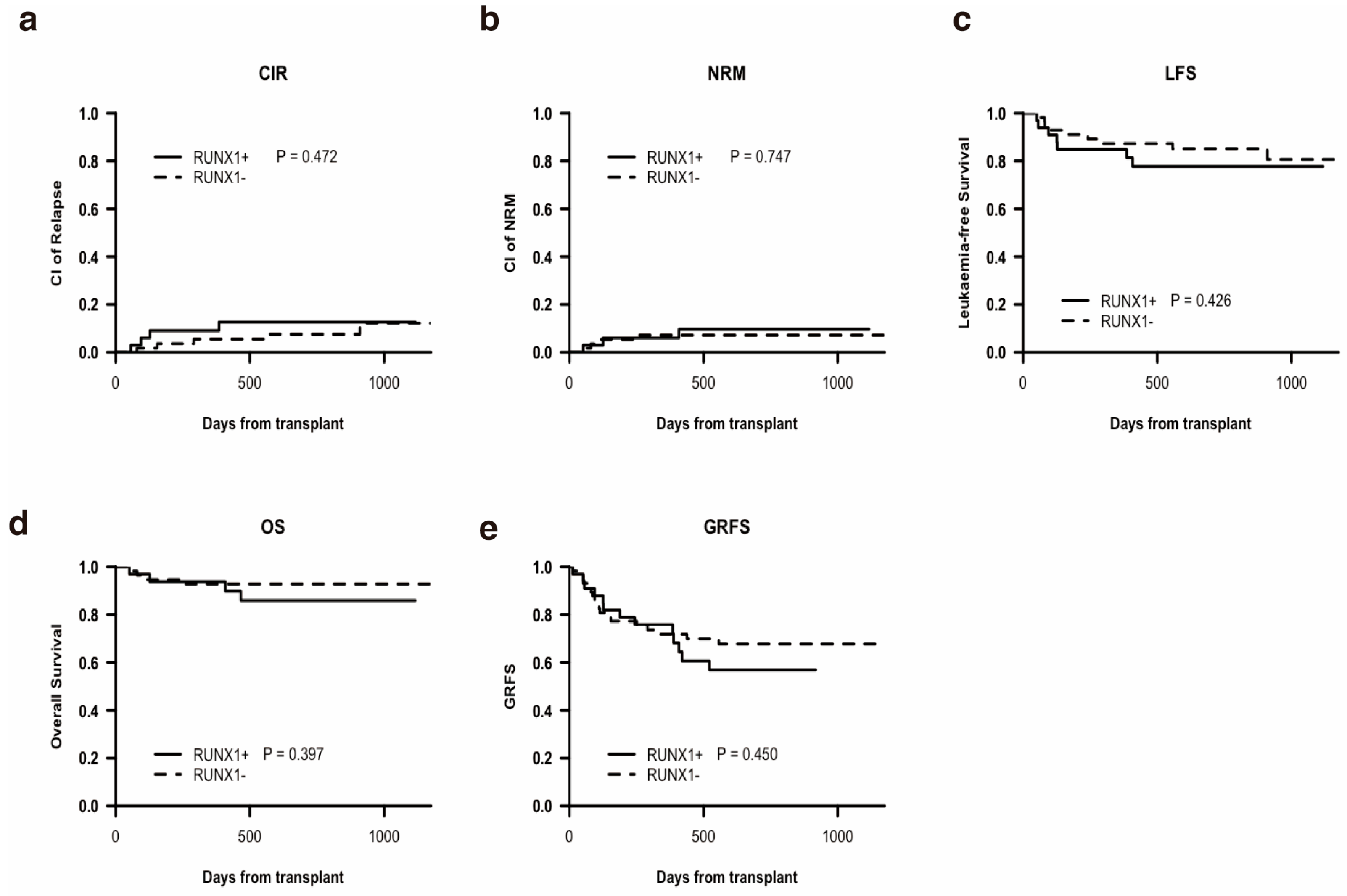
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Transplantation Outcomes and Univariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CR | Complete remission |
| LFS | Leukemia-free survival |
| allo-HSCT | Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| Haplo-HSCT | Haploidentical HSCT |
| NRM | Non-relapse mortality |
| CIR | Cumulative incidence of relapse |
| GRFS | GvHD-free/relapse-free survival |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| CK | Complex karyotype |
| HCT-CI | Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Comorbidity Index |
| HLA | Human leucocyte antigen |
| MRD | Minimal residual disease |
References
- Sood, R.; Kamikubo, Y.; Liu, P. Role of RUNX1 in Hematological Malignancies. Blood 2017, 129, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Bae, S.-C.; Chuang, L.S.H. The RUNX Family: Developmental Regulators in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-L.; Hou, H.-A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Chou, W.-C.; Tseng, M.-H.; Huang, C.-F.; Lee, F.-Y.; Liu, M.-C.; Yao, M.; et al. AML1/RUNX1 Mutations in 470 Adult Patients with de Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognostic Implication and Interaction with Other Gene Alterations. Blood 2009, 114, 5352–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greif, P.A.; Konstandin, N.P.; Metzeler, K.H.; Herold, T.; Pasalic, Z.; Ksienzyk, B.; Dufour, A.; Schneider, F.; Schneider, S.; Kakadia, P.M.; et al. RUNX1 Mutations in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia Are Associated with a Poor Prognosis and Up-Regulation of Lymphoid Genes. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidzik, V.I.; Bullinger, L.; Schlenk, R.F.; Zimmermann, A.S.; Röck, J.; Paschka, P.; Corbacioglu, A.; Krauter, J.; Schlegelberger, B.; Ganser, A.; et al. RUNX1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results From a Comprehensive Genetic and Clinical Analysis From the AML Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittger, S.; Dicker, F.; Kern, W.; Wendland, N.; Sundermann, J.; Alpermann, T.; Haferlach, C.; Haferlach, T. RUNX1 Mutations Are Frequent in de Novo AML with Noncomplex Karyotype and Confer an Unfavorable Prognosis. Blood 2011, 117, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2022 Recommendations from an International Expert Panel on Behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendler, J.H.; Maharry, K.; Radmacher, M.D.; Mrózek, K.; Becker, H.; Metzeler, K.H.; Schwind, S.; Whitman, S.P.; Khalife, J.; Kohlschmidt, J.; et al. RUNX1 Mutations Are Associated With Poor Outcome in Younger and Older Patients With Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia and With Distinct Gene and MicroRNA Expression Signatures. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 Revision to the World Health Organization Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, R.; Stevenson, K.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Galili, N.; Nilsson, B.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Raza, A.; Levine, R.L.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Clinical Effect of Point Mutations in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Arismendy, J.; Arroyave, J.C.; Röthlisberger, S. Molecular Biomarkers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidzik, V.I.; Teleanu, V.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Weber, D.; Paschka, P.; Hahn, J.; Wallrabenstein, T.; Kolbinger, B.; Köhne, C.H.; Horst, H.A.; et al. RUNX1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Are Associated with Distinct Clinico-Pathologic and Genetic Features. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, O.; Talati, C.; Asghari, H.H.; Song, J.; Hussaini, M.; Kuykendall, A.T.; Sallman, D.A.; Padron, E.; Komrokji, R.S.; List, A.F.; et al. RUNX1 Mutation Is Associated with Poor Outcome in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Receiving Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Blood 2019, 134, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, M.G.; Gallì, A.; Bacigalupo, A.; Zibellini, S.; Bernardi, M.; Rizzo, E.; Allione, B.; van Lint, M.T.; Pioltelli, P.; Marenco, P.; et al. Clinical Effects of Driver Somatic Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients With Myelodysplastic Syndromes Treated With Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidhauser, J.; Labopin, M.; Esteve, J.; Kröger, N.; Cornelissen, J.; Gedde-Dahl, T.; Van Gorkom, G.; Finke, J.; Rovira, M.; Schaap, N.; et al. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for AML Patients with RUNX1 Mutation in First Complete Remission: A Study on Behalf of the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-C.; Tang, J.-L.; Hou, H.-A.; Chou, W.-C.; Hu, F.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yao, M.; Ko, B.-S.; Huang, S.-Y.; Tsay, W.; et al. Prognostic Implication of Gene Mutations on Overall Survival in the Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Receiving or Not Receiving Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantations. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poiré, X.; Labopin, M.; Maertens, J.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Blaise, D.; Ifrah, N.; Socié, G.; Gedde-Dhal, T.; Schaap, N.; Cornelissen, J.J.; et al. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia and 17p Abnormalities in First Complete Remission: A Study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canichella, M.; Molica, M.; Mazzone, C.; De Fabritiis, P. Maintenance Therapy Post-Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 6050–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Fei, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. Comparison Analysis between Haplo Identical Stem Cell Transplantation and Matched Sibling Donor Stem Cell Transplantation for High-Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chang, Y.-J.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, F.-R.; et al. Dynamic Immune Profiling Identifies the Stronger Graft-versus-Leukemia (GVL) Effects with Haploidentical Allografts Compared to HLA-Matched Stem Cell Transplantation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.-F.; Wu, D.-P.; Xu, Z.-L.; Han, T.-T.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Huang, F.; Fan, Z.-P.; Xu, N.; Chen, F.; et al. Mini-Dose Methotrexate Combined with Methylprednisolone for the Initial Treatment of Acute GVHD: A Multicentre, Randomized Trial. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, T.; Fan, Z.; Lin, R.; Xu, N.; Xuan, L.; Ye, J.; et al. Haploidentical Transplantation Might Have Superior Graft-versus-Leukemia Effect than HLA-Matched Sibling Transplantation for High-Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission: A Prospective Multicentre Cohort Study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyridonidis, A. How I Treat Measurable (Minimal) Residual Disease in Acute Leukemia after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2020, 135, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, G.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Huang, X. The Effect of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation on Comutations Based on Next-generation Sequencing in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients with the FLT3-ITD Mutation. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.; Han, M.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Lai, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Q.; et al. Consensus on the Monitoring, Treatment, and Prevention of Leukaemia Relapse after Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in China: 2024 Update. Cancer Lett. 2024, 605, 217264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.H.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Burnett, A.K.; Dombret, H.; Fenaux, P.; Grimwade, D.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Adults: Recommendations from an International Expert Panel, on Behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010, 115, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przepiorka, D.; Weisdorf, D.; Martin, P.; Klingemann, H.G.; Beatty, P.; Hows, J.; Thomas, E.D. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995, 15, 825–828. [Google Scholar]
- Filipovich, A.H.; Weisdorf, D.; Pavletic, S.; Socie, G.; Wingard, J.R.; Lee, S.J.; Martin, P.; Chien, J.; Przepiorka, D.; Couriel, D.; et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. Diagnosis and Staging Working Group Report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005, 11, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Maris, M.B.; Storb, R.; Baron, F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maloney, D.G.; Storer, B. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT)-Specific Comorbidity Index: A New Tool for Risk Assessment before Allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005, 106, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtan, S.G.; DeFor, T.E.; Lazaryan, A.; Bejanyan, N.; Arora, M.; Brunstein, C.G.; Blazar, B.R.; MacMillan, M.L.; Weisdorf, D.J. Composite End Point of Graft-versus-Host Disease-Free, Relapse-Free Survival after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2015, 125, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, W.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Quantification of Minimal Residual Disease Pre- and Post-Unmanipulated Haploidentical Allograft by Multiparameter Flow Cytometry in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2020, 98, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wang, Z.-L.; Wang, X.-J.; Gale, R.P.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Wu, L.-X.; Liao, M.-Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.-Y.; et al. Measurable Residual Disease Testing by next Generation Sequencing Is More Accurate Compared with Multiparameter Flow Cytometry in Adults with B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Lett. 2024, 598, 217104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, Y.; Phan, M.; Bambace, N.; Bernard, L.; Cohen, S.; Delisle, J.-S.; Kiss, T.; Lachance, S.; Roy, D.-C.; Sauvageau, G.; et al. Donor Age and Non-Relapse Mortality: Study of Their Association after HLA-Matched Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5955–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschka, P.; Schlenk, R.F.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Herzig, J.K.; Aulitzky, T.; Bullinger, L.; Spath, D.; Teleanu, V.; Kundgen, A.; Kohne, C.-H.; et al. ASXL1 Mutations in Younger Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Study by the German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group. Haematologica 2015, 100, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Kern, W.; Meggendorfer, M.; Nadarajah, N.; Perglerovà, K.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Number of RUNX1 Mutations, Wild-Type Allele Loss and Additional Mutations Impact on Prognosis in Adult RUNX1-Mutated AML. Leukemia 2018, 32, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.-M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating Morphologic, Clinical, and Genomic Data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, X.C.-H.; Sun, K.-J.; Lo, M.-Y.; Tien, F.-M.; Kuo, Y.-Y.; Tseng, M.-H.; Peng, Y.-L.; Chuang, Y.-K.; Ko, B.-S.; Tang, J.-L.; et al. Poor Prognostic Implications of Myelodysplasia-Related Mutations in Both Older and Younger Patients with de Novo AML. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardin, C.; Pautas, C.; Fournier, E.; Itzykson, R.; Lemasle, E.; Bourhis, J.-H.; Adès, L.; Marolleau, J.-P.; Malfuson, J.-V.; Gastaud, L.; et al. Added Prognostic Value of Secondary AML-like Gene Mutations in ELN Intermediate-Risk Older AML: ALFA-1200 Study Results. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All | RUNX1+ | RUNX1− | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | n = 91 | n = 33 | n = 58 | |
| Age at HSCT, years, median (range) | 38 (6–64) | 44 (14–60) | 35.5 (6–64) | 0.086 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.639 | |||
| Male | 58(63.7) | 20 (60.6) | 38 (65.5) | |
| female | 33(36.3) | 13 (39.4) | 20 (34.5) | |
| Donor type | 0.42 | |||
| haplo | 73 (80.2) | 25 (75.8) | 48 (82.8) | |
| MSD/MUD | 18 (19.8) | 8 (24.2) | 10 (17.2) | |
| Transplantation, n (%) | 0.783 | |||
| CR1 | 65 (71.4) | 23 (69.7) | 42 (72.4) | |
| Non-CR1 | 26 (28.6) | 10 (30.3) | 16 (27.6) | |
| Donor-recipient blood type match, n (%) | 0.112 | |||
| Matched | 54 (59.3) | 16 (48.5) | 38 (65.5) | |
| Mismatched | 37 (40.3) | 17 (51.5) | 20 (34.5) | |
| Time from diagnosis to HSCT, median, range (range) | 211 (62–1079) | 29 (87.9) | 220.5 (62–679) | 0.509 |
| Sex match, n (%) | 0.456 | |||
| Male recipient–female donor | 16 (17.6) | 4 (12.1) | 12 (20.7) | |
| Any other | 75 (82.4) | 29 (87.9) | 46 (79.3) | |
| HCT-CI, n (%) | 0.487 | |||
| 0–2 | 81 (89.0) | 28 (84.8) | 53 (91.4) | |
| >3 | 10 (11.0) | 5 (15.2) | 5 (8.6) | |
| Pre-MRD, n(%) | 0.358 | |||
| Positive | 20 (30.0) | 9 (27.3) | 11 (19) | |
| Negative | 71 (70.0) | 24 (72.7) | 47 (81) | |
| CK, n (%) | 0.745 | |||
| NO | 74 (81.3) | 25 (83.3) | 49 (87.5) | |
| CK | 13 (14.3) | 5 (16.7) | 7 (12.5) | |
| Missing | NA = 5 | NA = 3 | NA = 2 | |
| HLA, n (%) | 0.593 | |||
| 3/6, 5/10 | 53 (58.2) | 17 (51.5) | 36 (62.1) | |
| 4/6, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10 | 20 (30.0) | 8 (24.2) | 12 (20.7) | |
| 6/6, 10/10 | 18 (11.8) | 8 (24.2) | 10 (17.2) | |
| Disease type, n% | 0.519 | |||
| denovo | 80 (87.9) | 28 (84.8) | 52 (89.7) | |
| secondary | 11 (12.1) | 5 (15.2) | 6 (10.3) | |
| Cytogenetic risk-2022ELN | 0.161 | |||
| favorable | 9 (9.9) | 1 (3.3) | 8 (14.3) | |
| intermediate | 63 (69.2) | 22 (73.3) | 41 (73.2) | |
| poor | 14 (15.4) | 7 (23.3) | 7 (12.5) | |
| Missing | NA = 5 | NA = 3 | NA = 2 |
| Common Molecular Mutation (%) | All | RUNX1+ | RUNX1− | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KMT2A-PTD | 0.198 | |||
| positive | 9 (9.9) | 1 (3.0) | 8 (13.8) | |
| negative | 82 (90.1) | 32 (97.0) | 50 (86.2) | |
| FLT3-ITD | 0.358 | |||
| positive | 20 (30.0) | 9 (27.3) | 11 (19) | |
| negative | 71 (70.0) | 24 (72.7) | 47 (81) | |
| ASXL1 | 0.859 | |||
| positive | 13 (14.3) | 5 (15.2) | 8 (13.8) | |
| negative | 78 (85.7) | 28 (84.8) | 50 (86.2) | |
| CEBPA | 0.198 | |||
| positive | 9 (9.9) | 1 (3.0) | 8 (13.8) | |
| negative | 82 (90.1) | 32 (97.0) | 50 (87.2) | |
| NRAS | 0.577 | |||
| positive | 9 (9.9) | 2 (6.1) | 7 (12.1) | |
| negative | 82 (90.1) | 31 (93.9) | 51 (87.9) | |
| BCORL1 | 0.264 | |||
| positive | 4 (4.4) | 3 (9.1) | 1 (1.7) | |
| negative | 87 (95.6) | 30 (90.9) | 57 (98.3) | |
| SRSF-2 | 0.017 | |||
| positive | 7 (7.7) | 6 (18.8) | 1 (1.8) | |
| negative | 80 (87.9) | 26 (81.2) | 54 (98.2) | |
| Missing | NA = 4 | NA = 1 | NA = 3 | |
| DNMT3A | 0.963 | |||
| positive | 14 (15.4) | 5 (15.2) | 9 (15.5) | |
| negative | 77 (84.6) | 28 (84.8) | 49 (84.5) | |
| IDH1 | >0.99 | |||
| positive | 6 (6.6) | 2 (6.1) | 4 (6.9) | |
| negative | 85 (93.4) | 31 (93.9) | 54 (93.1) | |
| IDH2 | 0.041 | |||
| positive | 6 (6.6) | 5 (15.2) | 1 (1.7) | |
| negative | 85 (93.4) | 28 (84.8) | 57 (98.3) | |
| NPM1 | 0.198 | |||
| positive | 9 (9.9) | 1 (3) | 8 (13.8) | |
| negative | 82 (90.1) | 32 (97) | 50 (86.2) | |
| TP53 | 0.041 | |||
| positive | 6 (6.6) | 5 (15.2) | 1 (1.7) | |
| negative | 85 (93.4) | 28 (84.8) | 57 (98.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, W.-J.; Xu, L.-P.; Zhang, X.-H.; Chang, Y.-J.; Mo, X.-D.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Huang, X.-J.; Wang, Y. Clinical Effects of RUNX1 Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060294
Ran W-J, Xu L-P, Zhang X-H, Chang Y-J, Mo X-D, Sun Y-Q, Huang X-J, Wang Y. Clinical Effects of RUNX1 Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(6):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060294
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Wei-Jie, Lan-Ping Xu, Xiao-Hui Zhang, Ying-Jun Chang, Xiao-Dong Mo, Yu-Qian Sun, Xiao-Jun Huang, and Yu Wang. 2025. "Clinical Effects of RUNX1 Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation" Current Oncology 32, no. 6: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060294
APA StyleRan, W.-J., Xu, L.-P., Zhang, X.-H., Chang, Y.-J., Mo, X.-D., Sun, Y.-Q., Huang, X.-J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Clinical Effects of RUNX1 Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. Current Oncology, 32(6), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32060294






