Impact of Multileaf Collimator Width and Normal Tissue Objective on Radiation Dose Distribution in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using HyperArc for Single Brain Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Patient Selection
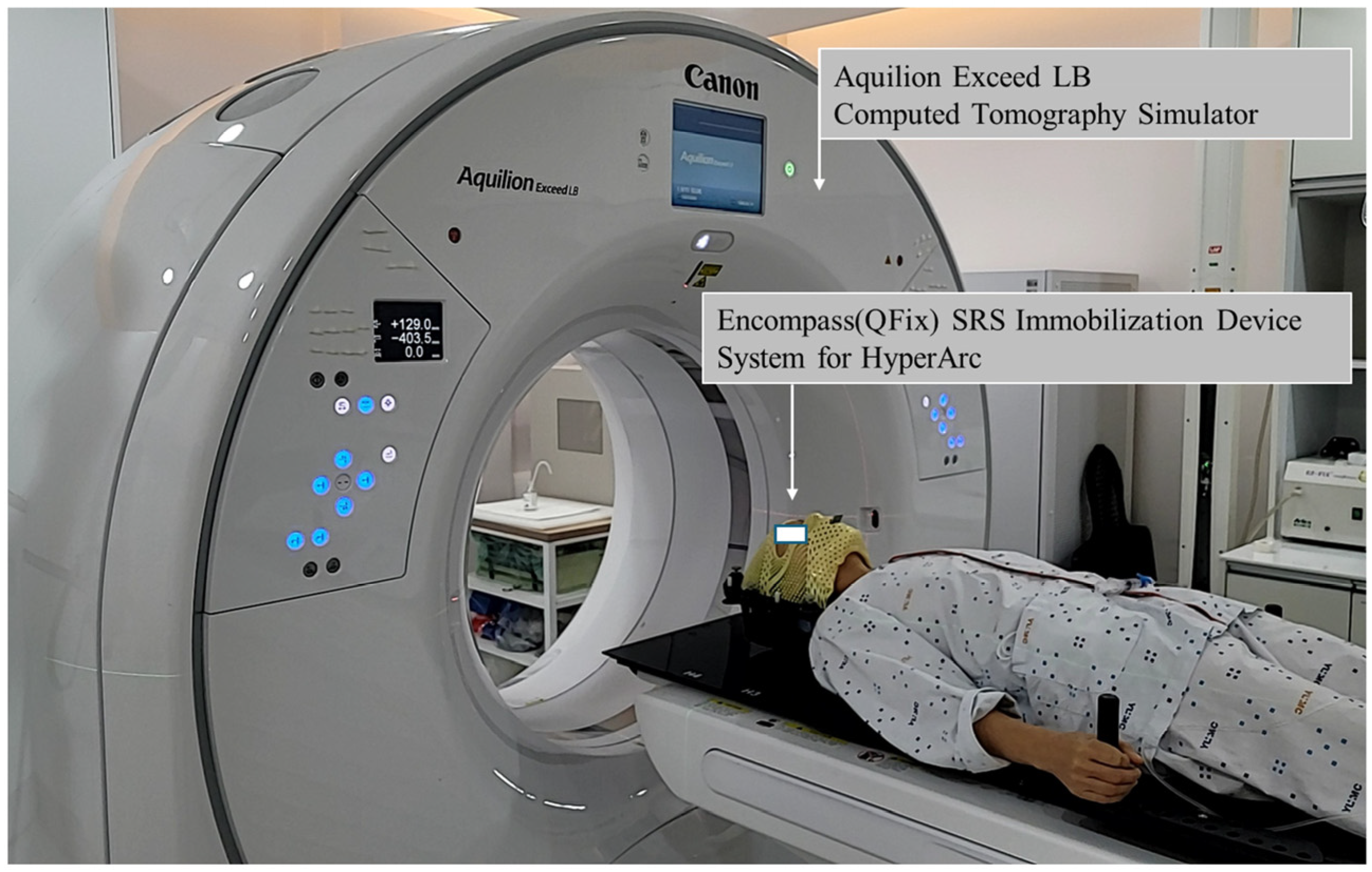
2.3. Immobilization and Computed Tomography (CT) Simulations
2.4. Target Delineation
2.5. Treatment Planning
2.6. Comparative Dosimetric Evaluation of Target and Normal Brain Tissues
2.7. Statistical Analysis of HASH, HAAH, and HAAM Plans
3. Results
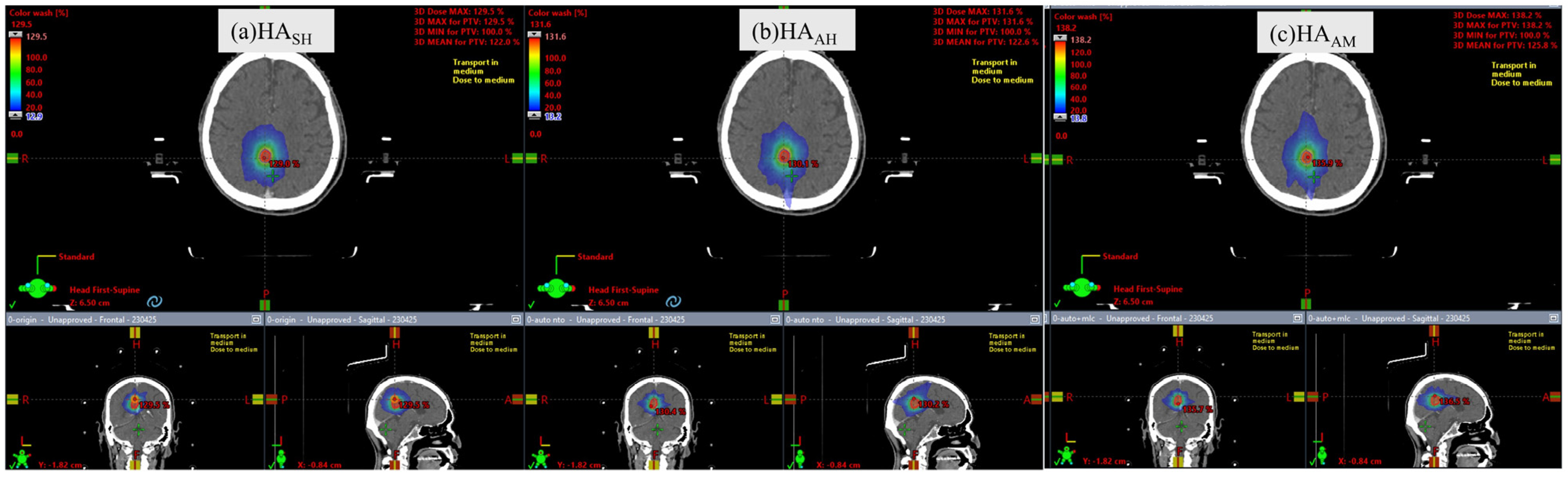
3.1. Plan Comparison of HASH and HAAH
3.2. Plan Comparison of HAAH and HAAM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Conformity index |
| CK | CyberKnife |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DVH | Dose volume histogram |
| GI | Gradient index |
| GTV | Gross target volume |
| HI | Homogeneity index |
| IMRT | Intensity-modulated radiotherapy |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| MLC | Multileaf collimator |
| MU | Monitor units |
| NTO | Normal tissue objective |
| PTV | Planning target volume |
| SRS | Stereotactic radiosurgery |
| VMAT | Volumetric modulated arc therapy |
References
- Garsa, A.; Jang, J.K.; Baxi, S.; Chen, C.; Akinniranye, O.; Hall, O.; Larkin, J.; Motala, A.; Hempel, S. Radiation therapy for brain metastases: A systematic review. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miccio, J.A.; Tian, Z.; Mahase, S.S.; Lin, C.; Choi, S.; Zacharia, B.E.; Sheehan, J.P.; Brown, P.D.; Trifiletti, D.M.; Palmer, J.D.; et al. Estimating the risk of brain metastasis for patients newly diagnosed with cancer. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.W.; Patel, A.J. Review of current principles of the diagnosis and management of brain metastases. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 857622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the metropolitan detroit cancer surveillance system. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G. Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumor. Ewha Med. J. 2021, 44, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-W.; Yang, C.-C.; Lin, H.-M.; Chen, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-W. The new SRS/FSRT technique HyperArc for benign brain lesions: A dosimetric analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celen, Y.Y.; Dinç, Ö.; Arslan, N.D.; Dağ, S.; Doğan, A.K.; Günenç, S. HyperArc VMAT and VMAT planning for stereotactic radiosurgery in multiple brain metastases. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2023, 16, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.; Ueda, Y.; Akino, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Masaoka, A.; Hirata, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Koizumi, M.; Teshima, T. HyperArc VMAT planning for single and multiple brain metastases stereotactic radiosurgery: A new treatment planning approach. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, T.; Ueda, Y.; Tsuru, H.; Kamima, T.; Ohira, S.; Tamura, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Monzen, H.; Konishi, K. Dosimetric potential of knowledge-based planning model trained with HyperArc plans for brain metastases. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalasova, I.; Liu, H.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Nie, K.; Shi, W.; Teo, B.-K.K.; Yu, Y.; Yue, N.J. Multi-institutional dosimetric evaluation of modern day stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) treatment options for multiple brain metastases. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Xu, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Guan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, E. Dosimetric quality of HyperArc in boost radiotherapy for single glioblastoma: Comparison with CyberKnife and manual VMAT. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, D.; Mallory, R.; Bush, M.; Clair, W.S.; Bernard, M.E. Feasibility study of stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of glomus jugulare tumors via HyperArc VMAT. Med. Dosim. 2022, 47, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.; Park, J.W.; Yea, J.W.; Oh, S.A. A comparison between portal dosimetry and Mobius3D results for patient-specific quality assurance in radiotherapy. Prog. Med. Phys. 2021, 32, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.; Park, J.W.; Yea, J.W. Clinical performance of FractionLab in patient-specific quality assurance for intensity-modulated radiotherapy: A retrospective study. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2022, 39, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yea, J.W.; Park, J.W.; Oh, S.A. Evaluation of the setup discrepancy between 6D ExacTrac and cone beam computed tomography in spine stereotactic body radiation therapy. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.; Ueda, Y.; Kanayama, N.; Isono, M.; Inui, S.; Komiyama, R.; Washio, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Koizumi, M.; Teshima, T. Impact of multileaf collimator width on dose distribution in HyperArc fractionated stereotactic irradiation for multiple (-) brain metastases. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.C.; Cunningham, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Dolan, J.; Wen, N.; Chetty, I.J.; Shah, M.M.; Siddiqui, S.M. Dosimetric evaluation of fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for skull base meningiomas using HyperArc and multicriteria optimization. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, S.H.; Yenice, K.M.; Followill, D.; Galvin, J.M.; Hinson, W.; Kavanagh, B.; Keall, P.; Lovelock, M.; Meeks, S.; Papiez, L. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM task group 101. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4078–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuvret, L.; Noël, G.; Mazeron, J.-J.; Bey, P. Conformity index: A review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Chen, J.; Wong, E.; Van Dyk, J.; Perera, F. A Treatment planning study comparing whole breast radiation therapy against conformal, IMRT and tomotherapy for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 82, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Choi, N.; Jang, N.Y. Dosimetric evaluations of HyperArc and RapidArc in stereotactic radiosurgery for a single brain metastasis. Prog. Med. Phys. 2024, 35, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasocki, A.; Sia, J.; Stuckey, S.L. Improving the diagnosis of radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery to intracranial metastases with conventional MRI features: A case series. Cancer Imaging 2022, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, U.; Patel, A.; Cobb, C.; Benkers, T.; Vermeulen, S. The management of brain necrosis as a result of SRS treatment for intra-cranial tumors. Trans. Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonigen, B.J.; Steinmetz, R.D.; Levin, L.; Lamba, M.A.; Warnick, R.E.; Breneman, J.C. Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Characteristics | |
| Number of patients | N = 21 |
| Median age (range) | 66 (47–85) |
| Gender (%) | |
| Female | 6 (28.6) |
| Male | 15 (71.4) |
| Radiation Treatment Characteristics | |
| Dose of prescriptions (%) | |
| 20 Gy | 21 (100) |
| Number of fractions (%) | |
| 1 | 21 (100) |
| Size of volume (cc) | |
| GTV | 1.18 (0.03–12.00) |
| Planning target volume (PTV) | 2.04 (0.10–21.20) |
| Normal brain (cc) | 1443.8 (1190.8–1679.8) |
| Parameters | HASH | HAAH | HAAM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | Mean ± Standard Deviation | Mean ± Standard Deviation | HASH vs. HAAH | HAAH vs. HAAM | ||
| Target | MU | 7206.37 ± 1102.81 | 5798.04 ± 1511.99 | 5835.41 ± 1536.52 | <0.001 * | 0.434 |
| Max of PTV | 125.70 ± 5.21 | 122.39 ± 5.23 | 124.38 ± 6.11 | 0.010 * | 0.033 * | |
| Mean of PTV | 116.18 ± 4.50 | 113.37 ± 4.69 | 114.53 ± 5.17 | 0.003 * | 0.032 * | |
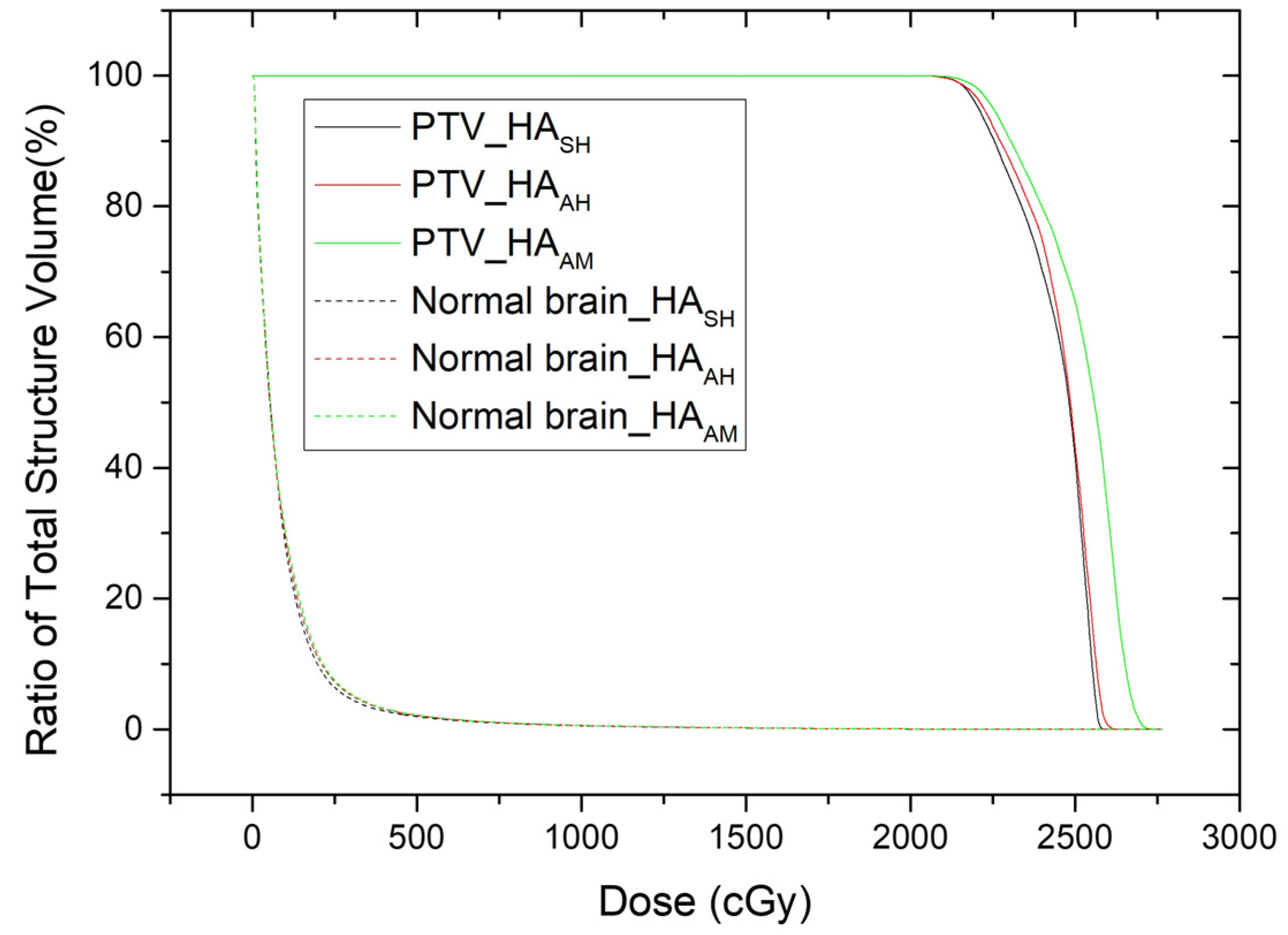
| CI | 0.49 ± 0.19 | 0.50 ± 0.20 | 0.47 ± 0.19 | 0.784 | 0.083 | |
| rDHI | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 0.82 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 0.010 * | 0.046 * | |
| mDHI | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 0.848 | 0.122 | |
| GI | 3.87 ± 1.44 | 5.52 ± 2.27 | 5.90 ± 2.78 | <0.001 * | 0.033 * | |
| Normal brain | V2Gy (%) | 3.43 ± 4.81 | 4.27 ± 4.55 | 4.64 ± 4.26 | 0.001 * | 0.006 * |
| V10Gy (%) | 0.25 ± 0.27 | 0.33 ± 0.29 | 0.38 ± 0.32 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| V12Gy (%) | 0.18 ± 0.19 | 0.22 ± 0.20 | 0.26 ± 0.22 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| V18Gy (%) | 0.05 ± 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.07 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| V10Gy (cc) | 3.63 ± 4.21 | 4.74 ± 4.44 | 5.47 ± 4.91 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| V12Gy (cc) | 2.57 ± 2.88 | 3.26 ± 3.02 | 3.82 ± 3.46 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.A.; Park, J.W.; Yea, J.W.; Park, J.; Jo, Y.Y. Impact of Multileaf Collimator Width and Normal Tissue Objective on Radiation Dose Distribution in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using HyperArc for Single Brain Lesions. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050272
Oh SA, Park JW, Yea JW, Park J, Jo YY. Impact of Multileaf Collimator Width and Normal Tissue Objective on Radiation Dose Distribution in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using HyperArc for Single Brain Lesions. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(5):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050272
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Se An, Jae Won Park, Ji Woon Yea, Jaehyeon Park, and Yoon Young Jo. 2025. "Impact of Multileaf Collimator Width and Normal Tissue Objective on Radiation Dose Distribution in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using HyperArc for Single Brain Lesions" Current Oncology 32, no. 5: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050272
APA StyleOh, S. A., Park, J. W., Yea, J. W., Park, J., & Jo, Y. Y. (2025). Impact of Multileaf Collimator Width and Normal Tissue Objective on Radiation Dose Distribution in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using HyperArc for Single Brain Lesions. Current Oncology, 32(5), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050272





