A Population Survival Kinetics Assessment of Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rationale for Maintenance Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Studies Included
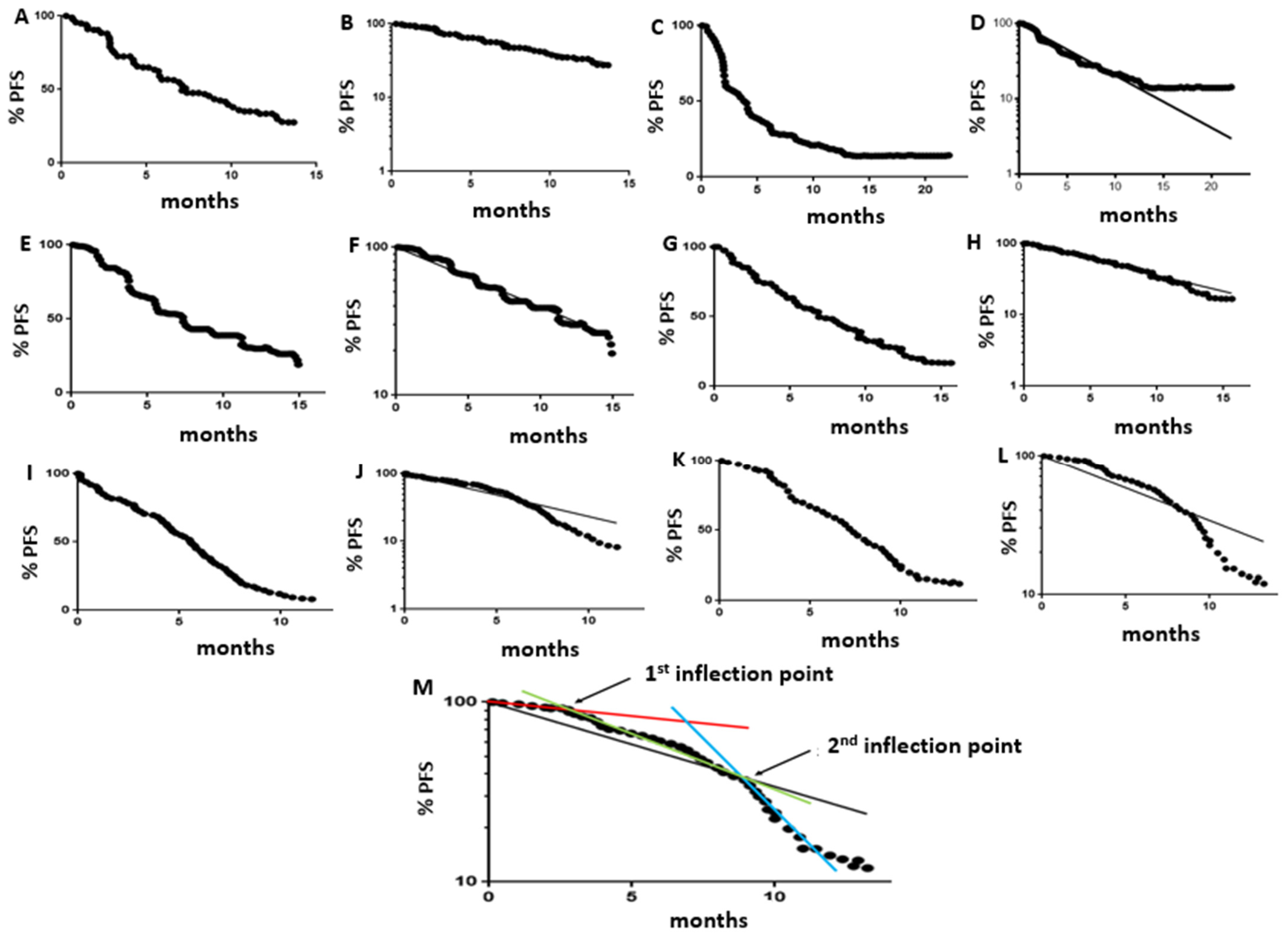
3.2. Population Kinetics Characteristics of PFS Curves
3.3. Optimal Frequency of Follow-Up Scans
3.4. Population Kinetics Characteristics of Overall Survival Curves
3.5. PFS and Overall Survival Curve Characteristics for SCLC vs. Other Tumor Types
3.6. PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiro, S.G. Chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Br. Med. J. Clin. Res. Ed. 1985, 290, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, A.; Carillio, G.; Daniele, G.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Montanino, A.; Costanzo, R.; Sandomenico, C.; Giordano, P.; Normanno, N.; Perrone, F.; et al. Treatment of small cell lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 91, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veslemes, M.; Polyzos, A.; Latsi, P.; Dimitroulis, J.; Stamatiadis, D.; Dardoufas, C.; Rasidakis, A.; Katsilambros, N.; Jordanoglou, J. Optimal duration of chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer: A randomized study of 4 versus 6 cycles of cisplatin-etoposide. J. Chemother. 1998, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, M.; Morgan, D.; Gregory, W.; Robinson, M.; Cox, D.; McGivern, D.; Ward, M.; Richards, M.; Stableforth, D.; Macfarlane, A.; et al. Maintenance chemotherapy for anaplastic small cell carcinoma of the bronchus: A randomised, controlled trial. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1986, 17, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccone, G.; Dalesio, O.; McVie, G.J.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Postmus, P.E.; Burghouts, J.T.; Bakker, W.; Koolen, M.G.; Vendrik, C.P.; Roozendaal, K.J.; et al. Maintenance chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: Long-term results of a randomized trial. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleehen, N.M.; Fayers, P.M.; Girling, D.J.; Stephens, R.J. Controlled trial of twelve versus six courses of chemotherapy in the treatment of small-cell lung cancer. Report to the Medical Research Council by its Lung Cancer Working Party. Br. J. Cancer 1989, 59, 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Ozguroglu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J.; Bosse, D.; Goss, G.; Hilton, J.F.; Jonker, D.; Fung-Kee-Fung, M. A novel, more reliable approach to use of progression-free survival as a predictor of gain in overall survival: The Ottawa PFS Predictive Model. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 148, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J.; Macdonald, D.B.; Awan, A.A.; Thavorn, K. Optimal frequency of scans for patients on cancer therapies: A population kinetics assessment. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6871–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J.; Behrens, C.; Roth, J.; Wistuba, I.I. Exponential decay nonlinear regression analysis of patient survival curves: Preliminary assessment in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 71, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J.; Bosse, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Ong, M.; Fung-Kee-Fung, M.; Brule, S.Y.; Hilton, J.F.; Ocana, A. Potential insights from population kinetic assessment of progression-free survival curves. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 153, 103309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.J.; Cole, K.; Bosse, D.; Brule, S.; Fergusson, D.; Ramsay, T. Population Survival Kinetics Derived from Clinical Trials of Potentially Curable Lung Cancers. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 1600–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, L.K.J.; Wouters, P.; Slooter, G.D.; de Hingh, I. Cancer Survival Data Representation for Improved Parametric and Dynamic Lifetime Analysis. Healthcare 2019, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.J.; Maziak, D.; Moore, S.; Brule, S.Y.; Gomes, M.; Sekhon, H.; Dennie, C.; Lo, B.; Sekhon, H.; Lo, B.; et al. The need for speed in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A population kinetics assessment. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 9040–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csoszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belani, C.P.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Rudin, C.M.; Fleisher, M.; Chen, H.X.; Takebe, N.; Velasco, M.R., Jr.; Tester, W.J.; Sturtz, K.; Hann, C.L.; et al. Vismodegib or cixutumumab in combination with standard chemotherapy for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E1508). Cancer 2016, 122, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sandler, A.B.; Dowlati, A.; Moore, D.F.; Murren, J.R.; Schiller, J.H. Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6006–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.I.; Lavin, P.; Lo, G.; Lebel, F.; Einhorn, L. Carboplatin and Etoposide With or Without Palifosfamide in Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter, Adaptive, Randomized Phase III Study (MATISSE). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.; Kim, H.K.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Irinotecan Plus Cisplatin versus Etoposide Plus Cisplatin in Chemotherapy-Naive Korean Patients with Extensive-Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niell, H.B.; Herndon, J.E.; Miller, A.A., 2nd; Watson, D.M.; Sandler, A.B.; Kelly, K.; Marks, R.S.; Perry, M.C.; Ansari, R.H.; Otterson, G.; et al. Randomized phase III intergroup trial of etoposide and cisplatin with or without paclitaxel and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 9732. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sica, G.L.; Wagner, L.I.; Wade, J.L., 3rd; Srkalovic, G.; Lash, B.W.; Leach, J.W.; Leal, T.B.; Aggarwal, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide in Combination with Veliparib or Placebo for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ECOG-ACRIN 2511 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R.; Ramlau, R.A.; Schuette, W.; Zatloukal, P.; Ferreira, I.; Lillie, T.; Vansteenkiste, J.F. Safety and efficacy of darbepoetin alpha in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with platinum plus etoposide. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2342–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Luft, A.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Kim, S.W.; Akerley, W.; Pietanza, M.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Zielinski, C.; Thomas, M.; et al. Phase III Randomized Trial of Ipilimumab Plus Etoposide and Platinum Versus Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, K.M., Jr.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Shaw, E.G.; Maksymiuk, A.W.; Kuross, S.A.; Jung, S.H.; Kugler, J.W.; Tschetter, L.K.; Ghosh, C.; Schaefer, P.L.; et al. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of cisplatin and etoposide plus megestrol acetate/placebo in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: A North Central Cancer Treatment Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckl, M.J.; Ottensmeier, C.H.; Cullen, M.; Schmid, P.; Ngai, Y.; Muthukumar, D.; Thompson, J.; Harden, S.; Middleton, G.; Fife, K.M.; et al. Multicenter, Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pravastatin Added to First-Line Standard Chemotherapy in Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LUNGSTAR). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Kaye, F.J.; Spigel, D.R.; Kudrik, F.J.; Ponce, S.; Ellis, P.M.; Majem, M.; Lorigan, P.; Gandhi, L.; Gutierrez, M.E.; et al. Phase 1/2 Study of the CD56-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate Lorvotuzumab Mertansine (IMGN901) in Combination with Carboplatin/Etoposide in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Extensive-Stage Disease. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 68–76e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Smit, E.F.; Lorigan, P.; Konduri, K.; Reck, M.; Szczesna, A.; Blakely, J.; Serwatowski, P.; Karaseva, N.A.; Ciuleanu, T.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin compared with etoposide plus carboplatin in chemotherapy-naive patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4787–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Townley, P.M.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Fang, L.; Adiguzel, I.; Huang, J.E.; Karlin, D.A.; Faoro, L.; Scappaticci, F.A.; Socinski, M.A. Randomized phase II study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Results from the SALUTE trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, M.; Boni, L.; Ambrosio, F.; Camerini, A.; Baldini, E.; Cinieri, S.; Brighenti, M.; Zanelli, F.; Defraia, E.; Chiari, R.; et al. Italian, Multicenter, Phase III, Randomized Study of Cisplatin Plus Etoposide With or Without Bevacizumab as First-Line Treatment in Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The GOIRC-AIFA FARM6PMFJM Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viren, M.; Liippo, K.; Ojala, A.; Helle, L.; Hinkka, S.; Huovinen, R.; Jakobsson, M.; Jarvinen, M.; Paloheimo, S.; Salmi, R.; et al. Carboplatin and etoposide in extensive small cell lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 1994, 33, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisson, B.; Besse, B.; Dols, M.C.; Dubey, S.; Schupp, M.; Jain, R.; Jiang, Y.; Menon, H.; Nackaerts, K.; Orlov, S.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1b/2 Study of Rilotumumab or Ganitumab in Combination with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 615–625e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J.; Albert, I.; Ross, H.J.; Kovacs, P.; Blakely, L.J.; Pajkos, G.; Somfay, A.; Zatloukal, P.; Kazarnowicz, A.; Moezi, M.M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of carboplatin and etoposide with or without obatoclax mesylate in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Ponce-Aix, S.; Navarro, A.; Riera-Knorrenschild, J.; Schmidt, M.; Wiegert, E.; Kapp, K.; Wittig, B.; Mauri, C.; Domine Gomez, M.; et al. Immunotherapeutic maintenance treatment with toll-like receptor 9 agonist lefitolimod in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Results from the exploratory, controlled, randomized, international phase II IMPULSE study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2076–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J. Tumor and host factors that may limit efficacy of chemotherapy in non-small cell and small cell lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2010, 75, 173–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Hansen, H.; Dombernowsky, P.; Gamucci, T.; Kaplan, S.; Postmus, P.; Giaccone, G.; Schaefer, B.; Wanders, J.; Verweij, J. Topotecan, a new active drug in the second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: A phase II study in patients with refractory and sensitive disease. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Early Clinical Studies Group and New Drug Development Office, and the Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.W.; Su, A.; Liang, X.J.; Pai-Panandiker, A.; Gottesman, M.M. Reduced expression of small GTPases and hypermethylation of the folate binding protein gene in cisplatin-resistant cells. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Cross-resistance to methotrexate and metals in human cisplatin-resistant cell lines results from a pleiotropic defect in accumulation of these compounds associated with reduced plasma membrane binding proteins. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Gladkov, O.; Ramlau, R.; Serwatowski, P.; Milanowski, J.; Tomeczko, J.; Komarnitsky, P.B.; Kramer, D.; Krzakowski, M.J. Cyclophosphamide and tucotuzumab (huKS-IL2) following first-line chemotherapy in responding patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, R.E.; Patel, J.D.; Masters, G.A.; Jayaram, N.; Stephens, A.; Guarino, M.; Misleh, J.; Wu, J.; Hanna, N. A randomized, double-blind, phase 2 trial of platinum therapy plus etoposide with or without concurrent vandetanib (ZD6474) in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: Hoosier Cancer Research Network LUN06-113. Cancer 2017, 123, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.M.; Seymour, L.; Smylie, M.; Ding, K.; Ung, Y.; Findlay, B.; Lee, C.W.; Djurfeldt, M.; Whitehead, M.; Ellis, P.; et al. Phase II study of vandetanib or placebo in small-cell lung cancer patients after complete or partial response to induction chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy: National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.20. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4278–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Woll, P.J.; Rudd, R.; Ferry, D.; O’Brien, M.; Middleton, G.; Spiro, S.; James, L.; Ali, K.; Jitlal, M.; et al. Anti-angiogenic therapy using thalidomide combined with chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Luft, A.; Serwatowski, P.; Barlesi, F.; Chacko, R.; Sebastian, M.; Lu, H.; Cuillerot, J.M.; Lynch, T.J. Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in extensive-disease-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.T.; Lim, K.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.S. Randomized phase II study of maintenance irinotecan therapy versus observation following induction chemotherapy with irinotecan and cisplatin in extensive disease small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.G.; Min, Y.J.; Yi, S.Y.; Yun, H.J.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Pazopanib maintenance after first-line etoposide and platinum chemotherapy in patients with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled Phase II study (KCSG-LU12-07). Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, N.E.; Pang, H.H.; Gu, L.; Otterson, G.A.; Thomas, S.P.; Miller, A.A.; Baggstrom, M.; Masters, G.A.; Graziano, S.L.; Crawford, J.; et al. Chemotherapy With or Without Maintenance Sunitinib for Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study-CALGB 30504 (Alliance). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarogoulidis, K.; Ziogas, E.; Papagiannis, A.; Charitopoulos, K.; Dimitriadis, K.; Economides, D.; Maglaveras, N.; Vamvalis, C. Interferon alpha-2a and combined chemotherapy as first line treatment in SCLC patients: A randomized trial. Lung Cancer 1996, 15, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummarello, D.; Graziano, F.; Mari, D.; Cetto, G.; Pasini, F.; Antonio, S.; Isidori, P.; Gasparini, S. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): A randomized trial of cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine plus etoposide (CAV-E) or teniposide (CAV-T) as induction treatment, followed in complete responders by alpha-interferon or no treatment, as maintenance therapy. Anticancer Res. 1994, 14, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Beith, J.M.; Clarke, S.J.; Woods, R.L.; Bell, D.R.; Levi, J.A. Long-term follow-up of a randomised trial of combined chemoradiotherapy induction treatment, with and without maintenance chemotherapy in patients with small cell carcinoma of the lung. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Finkelstein, D.M.; Abeloff, M.D.; Ruckdeschel, J.C.; Aisner, S.C.; Eggleston, J.C. A randomized comparison of standard chemotherapy versus alternating chemotherapy and maintenance versus no maintenance therapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: A phase III study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, L.H.; Tulloh, M.; Weiss, R.B.; Blom, J.; Leone, L.; Glidewell, O.; Pajak, T.F. A randomized combined modality trial in small cell carcinoma of the lung: Comparison of combination chemotherapy-radiation therapy versus cyclophosphamide-radiation therapy effects of maintenance chemotherapy and prophylactiv whole brain irradiation. Cancer 1980, 45, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.H.; Adak, S.; Cella, D.; DeVore, R.F., 3rd; Johnson, D.H. Topotecan versus observation after cisplatin plus etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: E7593—A phase III trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.H.; Sandier, A.B.; Loehrer, P.J.; Sr Ansari, R.; Jung, S.H.; Lane, K.; Einhorn, L.H. Maintenance daily oral etoposide versus no further therapy following induction chemotherapy with etoposide plus ifosfamide plus cisplatin in extensive small-cell lung cancer: A Hoosier Oncology Group randomized study. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuleanu, T.; Brodowicz, T.; Zielinski, C.; Kim, J.H.; Krzakowski, M.; Laack, E.; Wu, Y.L.; Bover, I.; Begbie, S.; Tzekova, V.; et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.J. Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Maintenance Oral Etoposide Daily for 6 Days Every 3-4 Weeks Until Tumor Progression: EP.13B.14. J. Thoracic Oncol. 2024, 19, S669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Vicente, D.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Gettinger, S.; Peters, S.; Horn, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Pardo Aranda, N.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Second-line nivolumab in relapsed small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 331. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Bendell, J.; Ott, P.A.; Taylor, M.; Eder, J.P.; Jager, D.; Pietanza, M.C.; Le, D.T.; de Braud, F.; et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ready, N.E.; Ott, P.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Hann, C.L.; de Braud, F.; Antonia, S.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Moreno, V.; Atmaca, A.; et al. Nivolumab Monotherapy and Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the CheckMate 032 Randomized Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Elez, E.; Hiret, S.; Kim, D.W.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; Mehnert, J.M. Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.C.; Sequist, L.V.D.; Gilbert, J.; Conkling, P.; Thompson, D.; Marcoux, J.P.; Gettinger, S.; Kowanetz, M.; Molinero, L.; O’Hear, C.; et al. Clinical Activity and Safety of Atezolizumab in a Phase 1 Study of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 455–463.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Park, E.M.; Diao, L.; Groves, S.M.; Heeke, S.; Nabet, B.Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis, L.M.; Lu, W.; et al. Patterns of transcription factor programs and immune pathway activation define four major subtypes of SCLC with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 346–360.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Platinum | Targeted Agent | No. Patients | No. Cycles | Median PFS (Months) | Median OS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belani [17] | cisplatin | vismodegib | 52 | 4 | 4.4 | 9.8 |
| Belani [17] | cisplatin | cixutumumab | 52 | 4 | 4.6 | 10.1 |
| Glisson [32] | cis- or carboplatin | 61 | 6 | 5.4 | 10.8 | |
| Glisson [32] | cis- or carboplatin | ganitumumab | 62 | 6 | 5.5 | 10.7 |
| Glisson [32] | cis- or carboplatin | rolitumumab | 62 | 6 | 5.4 | 12.2 |
| Horn [7] | carboplatin | atezolizumab | 201 | 4 | 5.2 | 12.3 |
| Horn [18] | cisplatin | bevacizumab | 63 | 4 | 4.7 | 10.9 |
| Horn [7] | carboplatin | 202 | 4 | 4.3 | 10.3 | |
| Jalal [19] | carboplatin | 94 | 4–6 | Not reported | 10.4 | |
| Kim [20] | cisplatin | 189 | 6 | 5.8 | 10.3 | |
| Langer [33] | carboplatin | 82 | 6 | 5.2 | 9.8 | |
| Langer [33] | carboplatin | obatoclax | 83 | 6 | 5.8 | 10.5 |
| Niell [21] | cisplatin | 282 | 6 | 5.9 | 9.9 | |
| Owonikoko [22] | cisplatin | veliparib | 52 | 4 | 6.1 | 10.3 |
| Paz-Ares [8] | cis- or carboplatin | 269 | 4 | 5.4 | 10.3 | |
| Paz-Ares [8] | cis- or carboplatin | durvalumab | 268 | 4 | 5.1 | 13 |
| Pirker [23] | cis- or carboplatin | darbepoetin | 298 | 6 | 5.5 a | 9.2 |
| Pirker [23] | cis- or carboplatin | 298 | 6 | 5.5 a | 9.2 | |
| Reck [24] | cis- or carboplatin | 476 | 4 | 4.4 | 10.9 | |
| Reck [24] | cis- or carboplatin | ipilimumab | 478 | 4 | 4.6 | 11 |
| Rowland [25] | cisplatin | 121 | 4 | 7.2 | 10 | |
| Rowland [25] | cisplatin | megesterol | 122 | 4 | 6.1 | 8.2 |
| Seckl [26] | cis- or carboplatin | pravastatin | 239 | 6 | Not reported | 9.1 |
| Seckl [26] | cis- or carboplatin | 243 | 6 | Not reported | 8.8 | |
| Socinski [27] | carboplatin | lorvotuzumab mertansine | 94 | 6 | 6.2 | 10.1 |
| Socinski [28] | carboplatin | 455 | 6 | 5.4 | 10.6 | |
| Spigel [29] | cis- or carboplatin | 50 | 4 | 4.4 | 10.9 | |
| Thomas [34] | cis- or carboplatin | lefitolimod | 62 | 4 | 3.0 | 9.2 |
| Spigel [29] | cis- or carboplatin | bevacizumab | 52 | 4 | 5.5 | 9.4 |
| Tiseo [30] | cisplatin | bevacizumab | 101 | 6 | 6.7 | 9.8 |
| Tiseo [30] | cisplatin | 103 | 6 | 5.7 | 8.9 | |
| Viren [31] | carboplatin | 56 | 6 | 4.6 a | 4.6 | |
| Median | 5.4 | 10.2 |
| Author a | No. Cycles | PFS Curve Shape b | PFS t1/2 d | LCI e | UCI f | R2 g | 1st Inflec h | 1st Inflec from End Rx i | 1st Inflec % Left j | 2nd Inflec k | 2nd Inflec % Left l | PFS t1/2 on Rx m | PFS t1/2 Post Rx n | PFS t1/2 Post 2nd Inflec o |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belani (vism) [17] | 4 | high conv | 5.0 | 4.4 | 5.7 | 0.74 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 81% | 4.2 | 64% | 11.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Belani (cixut) [17] | 4 | high conv | 5.4 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 0.59 | 2.7 | −0.1 | 93% | 4.0 | 83% | 37.7 | 2.2 | 1.0 |
| Glisson [32] | 6 | high conv | 5.2 | 4.7 | 5.6 | 0.84 | 3.6 | −0.6 | 80 | 5.4 | 55% | 11.9 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| Glisson (ganit) [32] | 6 | high conv | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.9 | 0.82 | 2.7 | −1.5 | 85 | 5.5 | 52% | 9.3 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Glisson (rolit) [32] | 6 | high conv | 5.7 | 5.2 | 6.3 | 0.78 | 3.8 | −0.4 | 81 | 5.4 | 49% | 12.4 | 1.9 | 1.7 |
| Horn (atezo) [7] | 4 | high conv c | 4.9 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 0.88 | 2.7 | −0.1 | 86% | 4.0 | 76% | 16.1 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| Horn (bev) [18] | 4 | high conv | 4.9 | 4.3 | 5.7 | 0.82 | 3.8 | 1.0 | 75% | 3.8 | 75% | 8.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Horn [7] | 4 | high conv | 4.1 | 3.7 | 4.5 | 0.83 | 2.7 | −0.1 | 91% | 3.8 | 75% | 17.1 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| Jalal [19] | 4–6 | |||||||||||||
| Kim [20] | 6 | mod conv | 4.7 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 0.93 | 4.1 | −0.1 | 66% | 7.0 | 32% | 6.6 | 2.6 | 1.8 |
| Langer [33] | 6 | mod conv | 4.1 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 0.91 | 3.8 | −0.4 | 64% | 5.3 | 49% | 5.5 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| Langer (obat) [33] | 6 | high conv | 4.9 | 4.4 | 5.3 | 0.84 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 67% | 6.8 | 33% | 10.4 | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| Niell [21] | 6 | mod conv | 5.2 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 0.91 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 68% | 6.4 | 46% | 9.6 | 2.6 | 2.1 |
| Owonikoko (vel) [22] | 4 | high conv | 6.6 | 5.7 | 7.7 | 0.69 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 92% | 5.7 | 67% | 27.9 | 3.4 | 1.1 |
| Paz-Ares [8] | 4 | high conv | 5.3 | 4.8 | 5.8 | 0.82 | 4.6 | 1.8 | 73% | 6.3 | 44% | 13.5 | 3.1 | 1.7 |
| Paz-Ares (durv) [8] | 4 | high conv c | 5.6 | 5.3 | 6.1 | 0.90 | 4.5 | 1.7 | 73% | 6.7 | 41% | 15.0 | 3.7 | 7.3 |
| Pirker (darb) [23] | 6 | |||||||||||||
| Pirker [23] | 6 | |||||||||||||
| Reck [24] | 4 | high conv c | 4.4 | 3.9 | 4.9 | 0.77 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 92% | 4.0 | 77% | 84.5 | 1.9 | 1.1 |
| Reck (ipil) [24] | 4 | high conv c | 4.6 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 0.83 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 94% | 3.9 | 77% | 79.7 | 2.2 | 1.4 |
| Rowland [25] | 4 | high conv | 6.4 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 0.88 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 88% | 8.9 | 37% | 19.2 | 4.4 | 2.0 |
| Rowland (meg) [25] | 4 | mod conv | 5.9 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 0.96 | 5.3 | 2.5 | 60% | 8.2 | 37% | 7.2 | 4.6 | 3.2 |
| Secki (prav) [26] | 6 | |||||||||||||
| Secki [26] | 6 | |||||||||||||
| Socinski (lorv) [27] | 6 | high conv c | 6.5 | 5.9 | 7.1 | 0.84 | 3.2 | −1.0 | 87% | 4.5 | 73% | 16.2 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Socinski [28] | 6 | high conv | 6.0 | 5.5 | 6.6 | 0.87 | 1.4 | −2.8 | 93% | 4.5 | 73% | 11.8 | 2.9 | 2.7 |
| Spigel [29] | 4 | high conv | 5.5 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 0.78 | 1.3 | −1.5 | 90% | 3.9 | 71% | 9.9 | 2.5 | 1.0 |
| Spigel (bev) [29] | 4 | mod conv | 6.5 | 5.9 | 7.1 | 0.84 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 77% | 5.4 | 58% | 9.6 | 3.3 | 1.9 |
| Thomas (lefi) [34] | 4 | high conv | 3.1 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 0.84 | 1.6 | −1.2 | 87% | 3.6 | 44% | 4.4 | 1.8 | 1.2 |
| Tiseo (bev) [30] | 6 | high conv | 6.7 | 6.0 | 7.5 | 0.89 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 76% | 5.9 | 62% | 12.0 | 3.6 | 3.0 |
| Tiseo [30] | 6 | high conv | 5.5 | 4.9 | 6.3 | 0.89 | 2.7 | −1.5 | 82% | 4.6 | 70% | 9.4 | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| Viren [31] | 6 | |||||||||||||
| Medians | 5.4 | 4.8 | 5.9 | 0.84 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 82% | 5.4 | 60% | 11.9 | 2.6 | 1.7 |
| Interval (Weeks) Between Follow-Up Scans | |||||
| 3 weeks | 6 weeks | 9 weeks | 12 weeks | 18 weeks | |
| Proportion of remaining patients progressing since previous scan | |||||
| During 1st-line therapy (PFS t1/2 11.9 months/ 51.6 weeks) | 4% | 8% | 11% | 15% | 21% |
| After 1st-line therapy completion (PFS t1/2 2.6 months/11.3 weeks) | 17% | 31% | 42% | 51% | 67% |
| After 2nd PFS curve inflection point (PFS t1/2 1.7 months/7.4 weeks) | 24% | 43% | 57% | 67% | 81% |
| Author a | No. Cycles | OS Curve Shape b | OS t1/2 d | LCI e | UCI f | R2 g | PPS h | 1st Inflec i | 1st Inflec from End Rx j | 1st Inflec % Left k | 2nd Inflec l | 2nd Inflec % Left m | OS t1/2 on Rx n | OS t1/2 Post Rx o |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belani (vism) [17] | 4 | high conv | 9.9 | 9.3 | 10.5 | 0.92 | 4.9 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 96% | 8.2 | 66% | 33.7 | 7.3 |
| Belani (cixut) [17] | 4 | high conv | 10.4 | 9.5 | 11.4 | 0.83 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 2.5 | 88% | 11.8 | 42% | 53.6 | 7.5 |
| Glisson [32] | 6 | high conv | 10.2 | 9.4 | 11.1 | 0.82 | 5.0 | 3.6 | −0.6 | 93% | 9.0 | 68% | 27.9 | 8.2 |
| Glisson (ganit) [32] | 6 | mod conv | 10.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 0.93 | 4.7 | 7.1 | 2.9 | 73% | 13.6 | 39% | 16.5 | 7.3 |
| Glisson (rolit) [32] | 6 | mod conv | 11.0 | 10.6 | 11.5 | 0.93 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 82% | 13.1 | 45% | 25.0 | 8.4 |
| Horn (atezo) [7] | 4 | mod conv | 14.4 | 13.7 | 15.1 | 0.90 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 2.5 | 90% | 10.2 | 61% | 39.9 | 11.0 |
| Horn (bev) [18] | 4 | high conv | 10.4 | 9.3 | 11.5 | 0.87 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 2.7 | 83% | 11.5 | 86% | 25.3 | 7.8 |
| Horn [7] | 4 | high conv | 10.7 | 10.0 | 11.4 | 0.86 | 6.6 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 91% | 6.5 | 79% | 26.8 | 8.0 |
| Jalal [19] | 4–6 | high conv | 10.9 | 9.8 | 12.2 | 0.89 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 89% | 12.8 | 44% | 36.2 | 7.1 | |
| Kim [20] | 6 | mod conv | 9.5 | 8.9 | 10.1 | 0.91 | 4.8 | 6.6 | 2.4 | 74% | 11.5 | 43% | 17.7 | 6.7 |
| Langer [33] | 6 | mod conv | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 0.96 | 4.5 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 77% | 10.0 | 47% | 9.2 | 7.1 |
| Langer (obat) [33] | 6 | high conv | 10.7 | 10.4 | 11.2 | 0.94 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 2.0 | 79% | 15.8 | 34% | 17.8 | 8.3 |
| Niell [21] | 6 | mod conv | 9.5 | 9.0 | 10.1 | 0.93 | 4.3 | 6.1 | 1.9 | 78% | 12.8 | 35% | 21.0 | 6.5 |
| Owonikoko (vel) [22] | 4 | high conv | 11.9 | 10.4 | 13.6 | 0.74 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 2.8 | 90% | 7.8 | 76% | 85.6 | 7.4 |
| Paz-Ares [8] | 4 | mod conv | 10.0 | 9.5 | 10.6 | 0.94 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 86% | 6.3 | 75% | 18.0 | 7.9 |
| Paz-Ares (durv) [8] | 4 | mod conv | 12.8 | 12.3 | 13.3 | 0.96 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 3.0 | 80% | 14.1 | 49% | 19.7 | 11.2 |
| Pirker (darb) [23] | 6 | mod conv c | 8.2 | 7.8 | 8.5 | 0.97 | 6.4 | 2.2 | 66% | 13.0 | 26% | 10.8 | 6.4 | |
| Pirker [23] | 6 | mod conv | 8.1 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 0.96 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 78% | 7.7 | 57% | 10.7 | 5.9 | |
| Reck [24] | 4 | mod conv | 9.9 | 9.1 | 10.7 | 0.85 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 2.7 | 89% | 8.8 | 65% | 233.5 | 7.3 |
| Reck (ipil) [24] | 4 | mod conv c | 10.3 | 9.7 | 10.9 | 0.89 | 5.7 | 6.3 | 3.5 | 84% | 9.6 | 59% | 154.7 | 7.6 |
| Rowland [25] | 4 | mod conv | 8.3 | 7.7 | 9.0 | 0.89 | 1.9 | 4.9 | 2.1 | 81% | 9.1 | 56% | 16.9 | 6.7 |
| Rowland (meg) [25] | 4 | mod conv | 7.0 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 0.97 | 1.1 | 6.3 | 3.5 | 61% | 8.4 | 47% | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| Secki (prav) [26] | 6 | mod conv | 8.1 | 7.4 | 8.9 | 0.94 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 74% | 7.8 | 60% | 13.7 | 5.5 | |
| Secki [26] | 6 | high conv | 9.6 | 8.6 | 10.7 | 0.86 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 84% | 6.6 | 70% | 16.8 | 5.4 | |
| Socinski (lorv) [27] | 6 | high conv c | 12.9 | 11.9 | 14.1 | 0.85 | 6.4 | 5.2 | 1.0 | 88% | 7.6 | 74% | 43.9 | 7.9 |
| Socinski [28] | 6 | high conv c | 11.1 | 10.4 | 11.9 | 0.89 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 83% | 10.0 | 53% | 21.2 | 7.3 |
| Spigel [29] | 4 | mod conv | 13.9 | 12.6 | 15.5 | 0.88 | 8.4 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 92% | 6.3 | 79% | 36.2 | 9.6 |
| Spigel (bev) [29] | 4 | high conv c | 11.0 | 10.0 | 12.1 | 0.84 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 88% | 8.7 | 63% | 14.1 | 8.3 |
| Thomas (lefi) [34] | 4 | high conv | 9.1 | 8.4 | 9.9 | 0.89 | 6.0 | 5.6 | 2.8 | 79% | 9.0 | 54% | 30.9 | 6.6 |
| Tiseo (bev) [30] | 6 | mod conv c | 9.5 | 9.0 | 10.1 | 0.94 | 2.8 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 75% | 8.9 | 59% | 15.2 | 7.1 |
| Tiseo [30] | 6 | high conv | 8.3 | 7.6 | 9.1 | 0.91 | 2.8 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 74% | 7.6 | 65% | 12.4 | 5.6 |
| Viren [31] | 6 | high conv | 5.0 | 4.7 | 5.5 | 0.77 | 3.5 | −0.7 | 74% | 4.5 | 60% | 7.3 | 1.0 | |
| Medians | 10.1 | 9.3 | 10.7 | 0.90 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 1.7 | 83% | 9.0 | 59% | 20.4 | 7.3 |
| Extensive SCLC Treated with Platinum–Etoposide | Other Advanced Cancers/Therapy Types [9,10,12] | p (SCLC vs. Others) a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. evaluable PFS curves | 26 | 888 | |
| No. (%) PFS curves highly convex | 21 (81%) | 35 (4%) | <0.0001 |
| No. (%) PFS curves highly or moderately convex | 26 (100%) | 186 (21%) | <0.0001 |
| Total No. evaluable OS curves | 32 | 363 | |
| No. (%) OS curves highly convex | 15 (47%) | 15 (4%) | <0.0001 |
| No. (%) OS curves highly or moderately convex | 32 (100%) | 87 (24%) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stewart, D.J.; Cole, K.; Brule, S. A Population Survival Kinetics Assessment of Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rationale for Maintenance Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050258
Stewart DJ, Cole K, Brule S. A Population Survival Kinetics Assessment of Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rationale for Maintenance Therapy. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(5):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050258
Chicago/Turabian StyleStewart, David J., Katherine Cole, and Stephanie Brule. 2025. "A Population Survival Kinetics Assessment of Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rationale for Maintenance Therapy" Current Oncology 32, no. 5: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050258
APA StyleStewart, D. J., Cole, K., & Brule, S. (2025). A Population Survival Kinetics Assessment of Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rationale for Maintenance Therapy. Current Oncology, 32(5), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32050258






