The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expressions in Gastric Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Won, K.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Song, M.J.; Choi, S.I.; Bae, G.E.; Lim, S.J. The expression of C-MYC in gastric adenocarcinoma is associated with PD-L1 and FOXP3 expression: C-MYC overexpression is a good prognostic factor. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, J.A.; Lee, J.; Sano, T.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Fan, D.; Song, S. Gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayapinar, A.K.; Solakoglu, D.; Bas, K.; Oymaci, E.; Isbilen, B.; Calik, B.; Diniz, G. Relationship of prognostic factors in stomach cancer with helicobacter pylori: A retrospective study. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2022, 84, 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- Usturalı Keskin, E.; Diniz, G.; Usturalı Mut, A.N.; Koca, Y.; Eryiğit Kokkoz, S.; Çakır, İ.E. Evaluation of the Relationship Between ARID1A Expression with Clinicopathologic Parameters in Gastric Carcinomas. J. Tepecik Educ. Res. Hosp. (JTERH) 2019, 29, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, S.; Kawazoe, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Kotani, D.; Kuboki, Y.; Bando, H.; Kojima, T.; Doi, T.; Ohtsu, A.; et al. Clinicopathological and molecular features of responders to nivolumab for patients with advanced gastric cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Sánchez, G.S.; Pita-Grisanti, V.; Quiñones-Díaz, B.; Gumpper, K.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E. Biological Functions and Therapeutic Potential of Lipocalin 2 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, E.; Leonardi, A.; Pacifico, F. NGAL as a Potential Target in Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candido, S.; Maestro, R.; Polesel, J.; Catania, A.; Maira, F.; Signorelli, S.S.; McCubrey, J.A.; Libra, M. Roles of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1576–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Donato, V.; Lacquaniti, A.; Fazio, M.R.; Bono, C.; Coppolino, G.; Buemi, M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human neoplasias: A new protein enters the scene. Cancer Lett. 2010, 288, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauvois, B.; Susin, S.A. Revisiting Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in Cancer: Saint or Sinner? Cancers 2018, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, D.S.; Diniz, G.; Sayhan, S.; Ersavas, S.; Ayaz, D.; Keskin, E.; Gulhan, I. Over expressions of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 in human uterine cervical neoplasms enhance tumor invasion. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2021, 42, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ersavaş, S.; Diniz, G.; Yildirim, H.T.; Koca, Y.; Kahraman, D.S.; Ayaz, D.; Demirağ, B. Expression of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 in Wilms Tumor. Turk. Patoloji Derg. 2016, 32, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bataineh, M.M.; Kinlough, C.L.; Mi, Z.; Jackson, E.K.; Mutchler, S.M.; Emlet, D.R.; Kellum, J.A.; Hughey, R.P. KIM-1-mediated anti-inflammatory activity is preserved by MUC1 induction in the proximal tubule during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F135–F148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Brooks, C.R.; Xiao, S.; Sabbisetti, V.; Yeung, M.Y.; Hsiao, L.L.; Ichimura, T.; Kuchroo, V.; Bonventre, J.V. KIM-1-mediated phagocytosis reduces acute injury to the kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakova, T.A.; Sergeeva, N.S.; Kanukoev, K.Y.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Kaprin, A.D. Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1): A Multifunctional Glycoprotein and Biological Marker. Sovrem. Tekhnologii Med. 2021, 13, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Wei, H.; Ma, J.; Du, Y. HAVCR1 expression might be a novel prognostic factor for gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J. Prognostic value of TIM-1 expression in human non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Martin, T.A.; Jiang, W.G. HAVcR-1 expression in human colorectal cancer and its effects on colorectal cancer cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.L.; Mashni, J.W.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Schworer, C.M.; Wilson, G.D.; Wolforth, S.C.; Kernen, K.M.; Seifman, B.D.; Amin, M.B.; Geddes, T.J.; et al. Urine kidney injury molecule-1: A potential non-invasive biomarker for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Rodig, S.J.; Doiron, R.; Clifton, M.C.; Kung, A.L.; Strong, R.K.; Zurakowski, D.; Moseset, M.A. Lipocalin 2 promotes breast cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3913–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, J.; Padmavathi, G.; Bordoloi, D.; Roy, N.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis and a potential target for cancer therapeutics. J. Cell Sci. Mol. Biol. 2014, 1, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Gould, M.N.; Mundhenke, C.; Maass, C.; Friedl, A. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a predictor of poor prognosis in human primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 108, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, T.; Dagher, A.; Sachdev, M.; Ebi, M.; Yamada, T.; Yamada, T.; Joh, T.; Moses, M.A. Urinary ADAM12 and MMP-9/NGAL Complex Detect the Presence of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, K.; Han, W.; Zhang, M.; Niu, H. Role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Li, Y.; Yi, J.; Jiang, H. HAVCR1 Affects the MEK/ERK pathway in gastric adenocarcinomas and influences tumor progression and patient outcome. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 6746970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.K.; Schnetz, M.; Beck, S.; Schmid, T.; Dominguez, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Daiber, A.; Brüne, B.; Jung, M. Iron-Bound Lipocalin-2 Protects Renal Cell Carcinoma from Ferroptosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakogiannis, D.; Kalogera, E.; Zagouri, F.; Zografos, E.; Balalis, D.; Bletsa, G. Determination of FABP4, RBP4 and the MMP-9/NGAL complex in the serum of women with breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.T.; Tsai, I.T.; Wu, C.C.; Hung, W.C.; Hsuan, C.F.; Yu, T.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Houng, J.Y.; Chung, F.M.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Elevated plasma level of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in patients with breast cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurozumi, S.; Alsaeed, S.; Orah, N.; Miligy, I.M.; Joseph, C.; Aljohani, A.; Toss, M.S.; Fujii, T.; Shirabe, K.; Green, A.R.; et al. Clinicopathological significance of lipocalin 2 nuclear expression in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| n | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prognosis | Survived | 78 | 45.3 |
| Exited | 94 | 54.7 | |
| Tumor Location | Cardia/Proximal stomach | 37 | 21.5 |
| Corpus/Distal stomach | 135 | 78.5 | |
| Diagnosis | Intestinal-type | 115 | 66.9 |
| Poorly adhesive/mixed | 57 | 33.1 | |
| Pathologic T stage | pT1 | 12 | 7 |
| pT2 | 22 | 12.8 | |
| pT3 | 79 | 45.9 | |
| pT4 | 59 | 34.3 | |
| Metastasis to local lymph node(s) | Present | 138 | 80.3 |
| Absent | 34 | 19.7 | |
| Distant Metastasis | Liver | 16 | 9.3 |
| Lungs | 12 | 6.9 | |
| Peritoneum | 6 | 4.3 | |
| Distant lymph nodes | 4 | 2.3 | |
| Ovaries | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | Present | 144 | 69.6 |
| Perineural invasion | Present | 104 | 75.3 |
| c-erbB2 expression (according to ASCO/CAP 2013 criteria) | Negative or 1+ | 120 | 69.7 |
| 2+ | 23 | 13.3 | |
| 3+/FISH positive | 29 | 16.9 | |
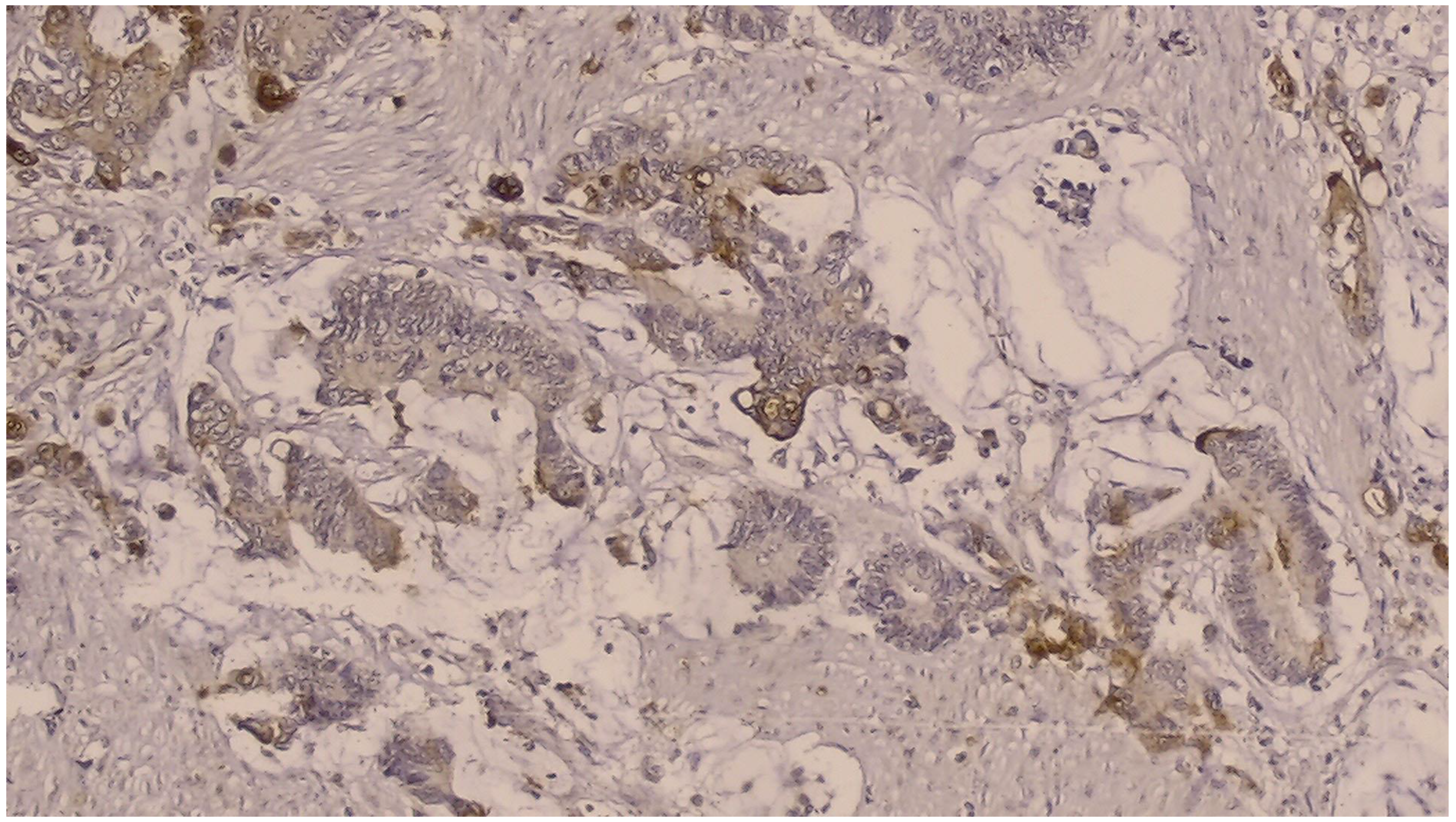
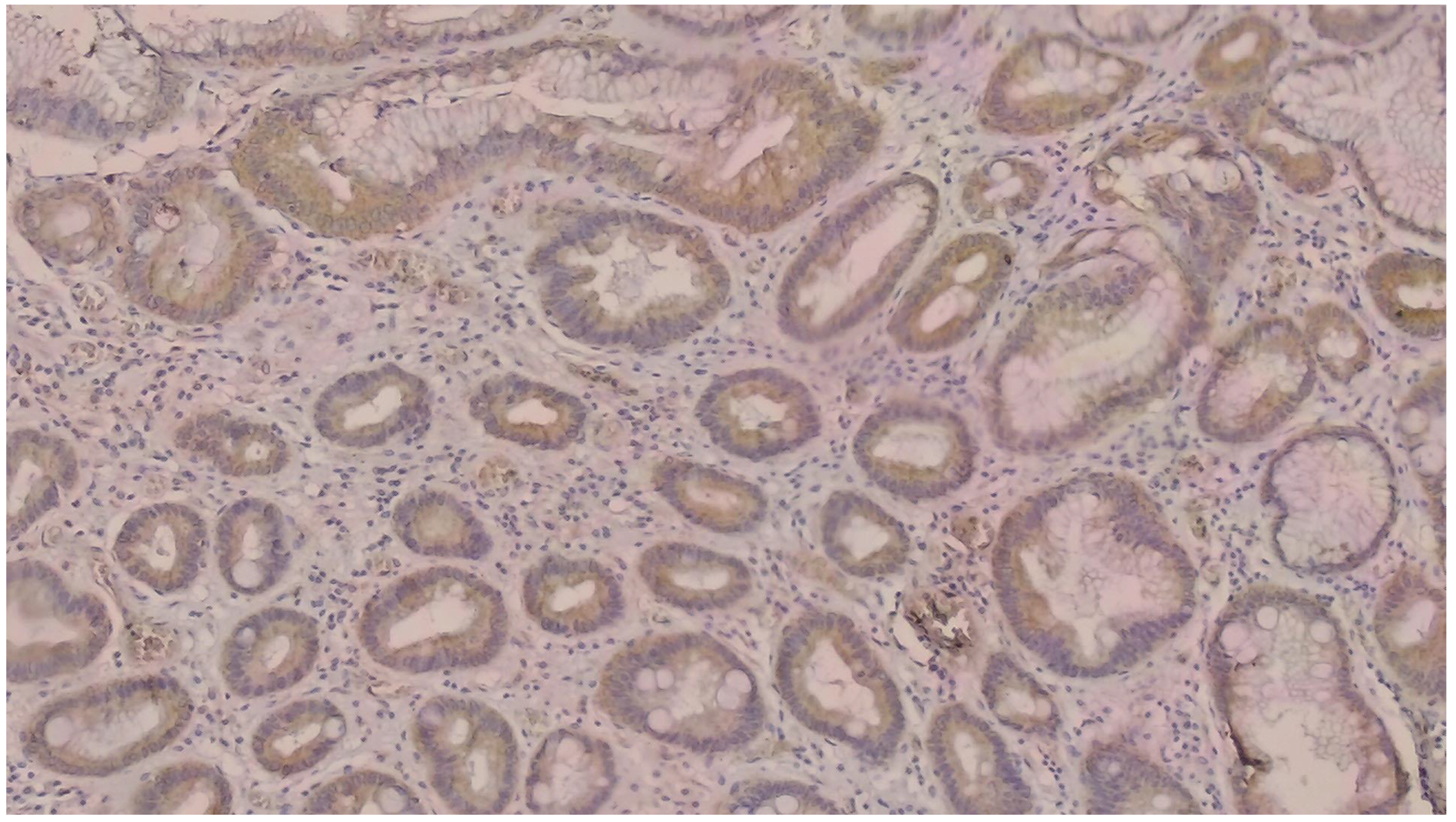
| NGAL expression | Positive in tumor cell | 54 | 31.4 |
| Positive in inflammatory cells | 23 | 13.4 | |
| KIM-1 expression | Positive in tumor cell | 54 | 31.4 |
| HER2 Positivity (*) | Absent N/% N = 143/83.1% | Present N/% N = 29/16.89% | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 95/33.6 | 20/69 | 0.792 |
| Female | 48/33.6 | 9/31 | ||
| Tumor location | Proximal Stomach | 32/22.4 | 5/17.2 | 0.529 |
| Corpus/Distal | 111/77.6 | 24/82.8 | ||
| Histological Type | Intestinal-type | 96/67.1 | 19/65.5 | 0.177 |
| Poorly adhesive/mixed | 47/32.9 | 10/34.5 | ||
| Survival status | Deceased | 75/52.4 | 19/65.5 | 0.197 |
| Lymph node metastases | Present | 116/81.2 | 22/75.9 | 0.410 |
| Location of distant metastases | Liver | 11/8.2 | 5/18.9 | 0.037 |
| Lung | 11/8.2 | 1/3.8 | ||
| Peritoneum | 3/2.9 | 3/11.4 | ||
| Ovary | 1/0.9 | 1/3.8 | ||
| Lymphovascular invasion | Present | 125/87.5 | 19/65.5 | 0.179 |
| Perineural invasion | Present | 90/62.9 | 14/48.2 | 0.007 |
| Tumor stage | Early | 28/19.6 | 7/24.1 | 0.821 |
| Late | 115/80.4 | 22/75.9 | ||
| KIM1 expression | Present | 42/29.4 | 12/41.4 | 0.204 |
| NGAL expression | Present | 46/32.2 | 9/27.6 | 0.628 |
| For Quantitative data | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p | |
| Age (year) | 64.2 ± 12.7 | 63.2 ± 10.7 | 0.199 | |
| Tumor diameter (cm) | 5.7 ± 3.2 | 6.6 ± 3.6 | 0.670 | |
| Survival (months) | 25.6 ± 21.8 | 25.2 ± 24.3 | 0.197 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayaz, D.; Diniz, G.; Pulular, A.G.; Solakoğlu Kahraman, D.; Varol, U.; Özkavruk Eliyatkın, N.; Sayhan, S.; Kayapınar, A.K. The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expressions in Gastric Carcinomas. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040190
Ayaz D, Diniz G, Pulular AG, Solakoğlu Kahraman D, Varol U, Özkavruk Eliyatkın N, Sayhan S, Kayapınar AK. The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expressions in Gastric Carcinomas. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(4):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040190
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyaz, Duygu, Gülden Diniz, Ayşe Gül Pulular, Dudu Solakoğlu Kahraman, Umut Varol, Nuket Özkavruk Eliyatkın, Sevil Sayhan, and Ali Kemal Kayapınar. 2025. "The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expressions in Gastric Carcinomas" Current Oncology 32, no. 4: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040190
APA StyleAyaz, D., Diniz, G., Pulular, A. G., Solakoğlu Kahraman, D., Varol, U., Özkavruk Eliyatkın, N., Sayhan, S., & Kayapınar, A. K. (2025). The Prognostic Role of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expressions in Gastric Carcinomas. Current Oncology, 32(4), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040190






