Resistance Mutation Profiles Associated with Current Treatments for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
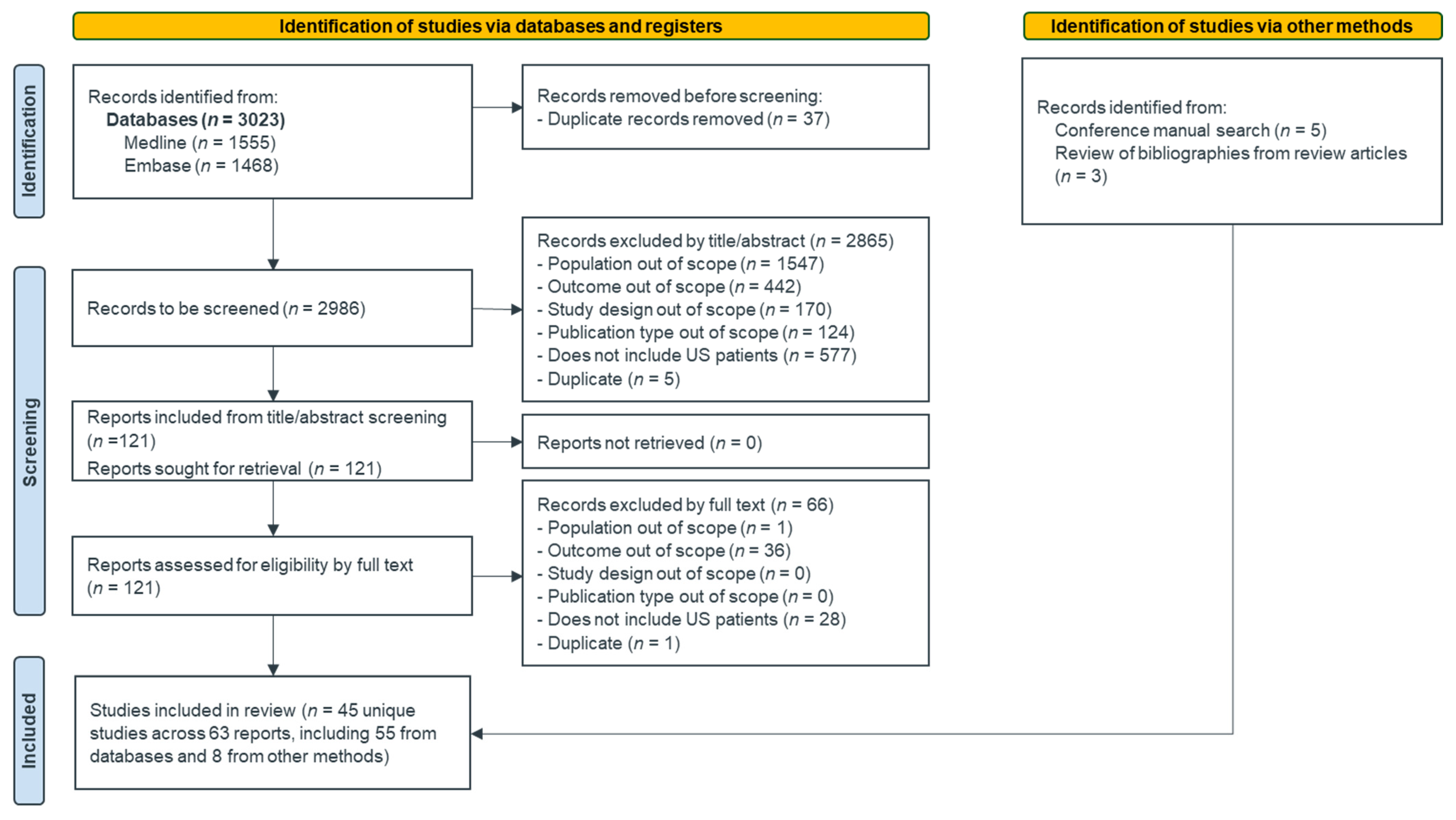
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study and Patient Characteristics
3.3. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
3.4. Outcomes
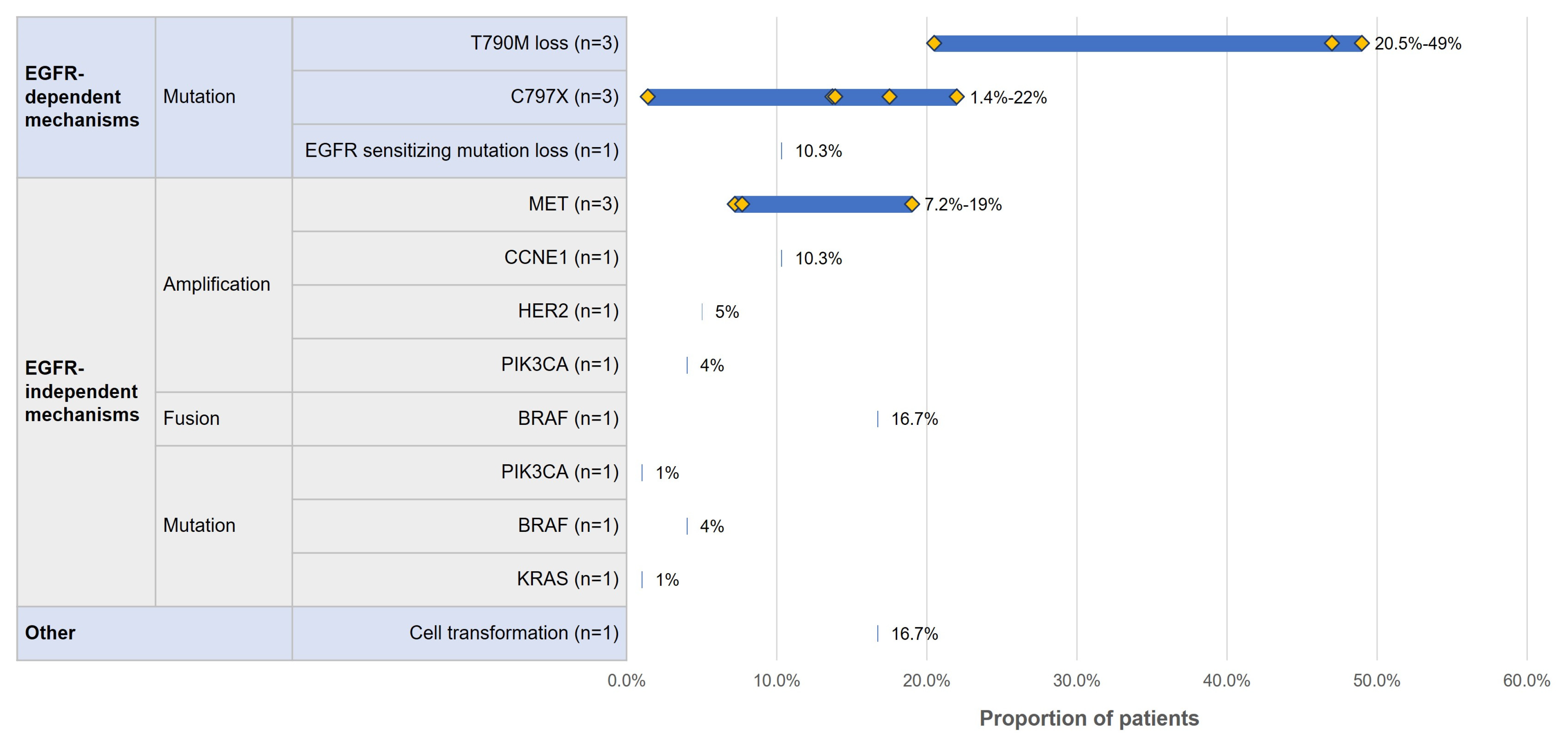
3.4.1. Acquired Resistance Mutation Profile by Line of Therapy
- First-Line osimertinib
- Second-Line osimertinib
- Resistance mutation profile for patients who received other lines of osimertinib
- Resistance mutation profile for patients who received other treatments
3.4.2. Impact of Acquired Resistance on Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of incidence, prevalence, survival, and initial treatment in patients with non–small cell lung cancer in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non–small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Society, A.C. Can Lung Cancer Be Found Early? Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/detection.html (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Jordan, E.J.; Kim, H.R.; Arcila, M.E.; Barron, D.; Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Chang, M.T.; Ni, A.; Kundra, R.; Jonsson, P. Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and emerging therapies. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 596–609. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 321–346. [Google Scholar]
- Tulpule, A.; Bivona, T.G. Acquired resistance in lung cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2020, 4, 279–297. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.-H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouris, A.; Tsagkaris, C.; Corriero, A.C.; Metro, G.; Mountzios, G. Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: From mechanisms to new therapeutic strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 6.3. 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses; Ottawa Hospital Research Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Tho, L.; Chik, Y.; Lee, W.; Yang, T.; Le, X.; Eisert, A.; Himpe, U.; De Bondt, C.; Mazieres, J. 364P Tepotinib with an EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in patients with EGFR-mutant MET-amplified NSCLC: A case series. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauml, J.; Mick, R.; Mccoach, C.; Weiss, J.; Marrone, K.; Nieva, J.; Villaruz, L.; Levy, B.; Moreno, R.; Murkherji, R. FP14. 06 multicenter analysis of mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib (O) in EGFR mutated NSCLC: An ATOMIC registry study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S229–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, A.F.; Ruiz-Patiño, A.; Recondo, G.; Martín, C.; Raez, L.; Samtani, S.; Minata, J.N.; Blaquier, J.B.; Enrico, D.; Burotto, M. Mechanisms of resistance to first-line osimertinib in Hispanic patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer (FRESTON-CLICaP). Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.C.; Fernandes, A.W.; Pavilack, M.; Wu, J.W.; Laliberté, F.; Duh, M.S.; Chehab, N.; Subramanian, J. EGFR mutation testing and treatment decisions in patients progressing on first-or second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaut, D.; Sim, M.S.; Yue, Y.; Wolf, B.R.; Abarca, P.A.; Carroll, J.M.; Goldman, J.W.; Garon, E.B. Clinical implications of the T790M mutation in disease characteristics and treatment response in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e19–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.E.; Montesion, M.; Young, L.; Suh, J.; Greenbowe, J.; Kennedy, M.; Giaccone, G.; Akerley, W.L.; Dowlati, A.; Creelan, B.C. Multiple configurations of EGFR exon 20 resistance mutations after first-and third-generation EGFR TKI treatment affect treatment options in NSCLC. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, N.; Hu, Y.; Feeney, N.; Kuang, Y.; Plagnol, V.; Jones, G.; Howarth, K.; Beeler, J.; Paweletz, C.; Oxnard, G. Amplicon-based next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA for detection of driver and resistance mutations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, E.; Nguyen, M.; Karlovich, C.A.; Despain, D.; Choquette, A.K.; Spira, A.I.; Helena, A.Y.; Camidge, D.R.; Harding, T.C.; Lanman, R.B. Cell-free DNA next-generation sequencing prediction of response and resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitor. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 518–530.e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.-T.; Soo, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Gucalp, R.; Halmos, B.; Wang, L.; Golembesky, A. Sequential treatment with afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: An observational study. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2861–2874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.K.; Madison, R.; Venstrom, J.M.; Schrock, A.B.; Oxnard, G.R. Incidence and heterogeneity of C797S and other EGFR resistance mutations on routine comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Bao, H.; Le, X.; Fan, X.; Tang, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, J.; Lou, G. P1.14-17 Genomic Evolution During TKI Treatment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients With or Without Acquired T790M Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S559. [Google Scholar]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.; Boyle, T.; Hicks, J.K.; Lovinger, K.L.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W. Landscape of EGFR-dependent and-independent resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and continuation therapy beyond progression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Janku, F.; Jung, B.; Hou, C.; Madwani, K.; Alden, R.; Razavi, P.; Reis-Filho, J.; Shen, R.; Isbell, J. Ultra-deep next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in patients with advanced lung cancers: Results from the Actionable Genome Consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.M.; Yang, S.; Lim, S.; Heo, S.G.; Daniel, S.; Markovets, A.; Rafati, M.; Park, C.; Yun, J.; Pyo, K. P76.18 Tissue-and Plasma-Based Landscape of Resistance to Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S593–S594. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, P.C.; Banks, K.C.; Espenschied, C.R.; Burich, R.A.; Zill, O.A.; Lee, C.E.; Riess, J.W.; Mortimer, S.A.; Talasaz, A.; Lanman, R.B. Spectrum of driver mutations and clinical impact of circulating tumor DNA analysis in non–small cell lung cancer: Analysis of over 8000 cases. Cancer 2020, 126, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar]
- Mambetsariev, I.; Arvanitis, L.; Fricke, J.; Pharaon, R.; Baroz, A.R.; Afkhami, M.; Koczywas, M.; Massarelli, E.; Salgia, R. Small cell lung cancer transformation following treatment in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondaca, S.; Offin, M.; Borsu, L.; Myers, M.; Josyula, S.; Makhnin, A.; Shen, R.; Riely, G.J.; Rudin, C.M.; Ladanyi, M. Lessons learned from routine, targeted assessment of liquid biopsies for EGFR T790M resistance mutation in patients with EGFR mutant lung cancers. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M–positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib. Jama Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, T.; Dimou, A.; Pacheco, J.; Smith, D.; Aisner, D.; Merrick, D.; Rusthoven, C.; Kavanaugh, B.; Miller, R.; Schenk, E. P1. 01-87 Osimertinib Acquired Resistance Mechanisms and Post-Progression Outcomes in Stage IV EGFR Positive Non-Small Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S394. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, T.; Mushtaq, R.; Marsh, S.; Azelby, C.; Pujara, M.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Purcell, W.T.; Schenk, E.L.; Pacheco, J.M. Clinicopathologic Characteristics, Treatment Outcomes, and Acquired Resistance Patterns of Atypical EGFR Mutations and HER2 Alterations in Stage IV Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e191–e204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Isozaki, H.; Lennerz, J.K.; Gainor, J.F.; Lennes, I.T.; Zhu, V.W.; Marcoux, N.; Banwait, M.K.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Su, W. Landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant NSCLC and clinical validation of combined EGFR and RET inhibition with osimertinib and BLU-667 for acquired RET fusion. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Piper-Vallillo, A.; Banwait, M.; Hung, Y.P.; Rao, R.; Muzikansky, A.; Meador, C.B.; Hata, A.N.; Sequist, L.V. Complete evaluation of resistance mechanisms to first-line osimertinib requires tissue biopsy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e21154. [Google Scholar]
- Raez, L.E.; Baca, Y.; Nieva, J.J.; Mamdani, H.; Lopes, G.; Borghaei, H.; Socinski, M.A.; Nabhan, C.; Wozniak, A.J.; Vanderwalde, A.M. Acquired EGFR-resistant mutations in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9113. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.; Zhang, N.; Yu, J.; Espenschied, C.; Green, T.; Infantine, J.; Mar, B. MA07. 03 Real-world Landscape of EGFR C797X Mutation as a Resistance Mechanism to Osimertinib in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S67–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Robichaux, J.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.; Hicks, K.; Elamin, Y.; Tran, H.; Varghese, S.; He, J.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L. MA13. 07 Structural Classification of Atypical EGFR Mutations Identifies 4 Major Subgroups With Distinct Patterns of Drug Sensitivity. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S183–S184. [Google Scholar]
- Rotow, J.; Patel, J.; Hanley, M.; Yu, H.; Goldman, J.; Nechustan, H.; Scheffler, M.; Awad, M.; Clifford, S.; Santucci, A. FP14. 07 combination osimertinib plus selpercatinib for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with acquired RET fusions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S230. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Rizvi, H.; Rekhtman, N.; Daneshbod, Y.; Kubota, D.; Chang, J.C.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M.; Somwar, R. Tissue-based molecular and histological landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib given initially or at relapse in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9028. [Google Scholar]
- Schrock, A.B.; Zhu, V.W.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Madison, R.; Creelan, B.; Silberberg, J.; Costin, D.; Bharne, A.; Bonta, I.; Bosemani, T. Receptor tyrosine kinase fusions and BRAF kinase fusions are rare but actionable resistance mechanisms to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Strohbehn, G.; Szeto, L.; Beach, B.; Edgington, K.; Lugtu, K.; Segal, J.; Ritterhouse, L.; Bestvina, C.; Vokes, E.; Patel, J. P2. 14-12 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance Mechanisms in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer: The University of Chicago Experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S833–S834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suero-Abreu, G.A.; Gonzalez Velez, M.; Proverbs-Singh, T.A.; Gutierrez, M. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) for genomic profiling of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Experience in a large community-based cancer center. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 36, e24026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Schuler, M.; Popat, S.; Miura, S.; Park, K.; Passaro, A.; De Marinis, F.; Solca, F.; Märten, A.; Kim, E. 1212P Afatinib for the treatment of NSCLC with uncommon EGFR mutations: An updated database of 1023 cases. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, X.; Zeng, A.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Xia, X. RET fusion in first/third-generation EGFR-TKIs resistance in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e20634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bazhenova, L.; Gold, K.; Tran, L.; Hilburn, V.; Vu, P.; Patel, S.P. Clinicopathologic and molecular characteristics of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small cell lung cancer after TKI therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 452. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, R.; Lin, G.; Liu, L.; Zhu, C.; Liang, N.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.X.; Dai, P. Landscape of osimertinib resistant mutations between the two common subtypes of EGFR 19del or L858R in NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 12108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, R.; Lin, G.; Ai, X.; Sheng, W.; Ji, Y.; Fan, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Q. Next generation sequencing (NGS) based mutation profiling and heterogeneity of resistance mechanisms to AZD9291. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 9068. [Google Scholar]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Robichaux, J.P.; Carter, B.W.; Altan, M.; Tran, H.; Gibbons, D.L.; Heeke, S.; Fossella, F.V.; Lam, V.K.; Le, X. Poziotinib for EGFR exon 20-mutant NSCLC: Clinical efficacy, resistance mechanisms, and impact of insertion location on drug sensitivity. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 754–767.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Dong, X.; Yang, C.; Song, Y.; Chang, G.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Chiu, C. 1208P Final results of APOLLO study: Overall survival (OS) of aumolertinib in patients with pretreated EGFR T790M-positive locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoach, C.E.; Yu, A.; Gandara, D.R.; Riess, J.W.; Vang, D.P.; Li, T.; Lara, P.N.; Gubens, M.; Lara, F.; Mack, P.C. Phase I/II study of capmatinib plus erlotinib in patients with MET-positive non–small-cell lung cancer. Jco Precis. Oncol. 2021, 1, 177–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.-W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y. Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauml, J.; Cho, B.C.; Park, K.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Haura, E.B.; Sabari, J.K.; Sanborn, R.E. Amivantamab in combination with lazertinib for the treatment of osimertinib-relapsed, chemotherapy-naïve EGFR mutant (EGFRm) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and potential biomarkers for response. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Baik, C.; Su, W.-C.; Johnson, M.L.; Hayashi, H.; Nishio, M.; Kim, D.-W.; Koczywas, M.; Gold, K.A.; Steuer, C.E. Efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR inhibitor–resistant, EGFR-mutated non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovets, A.; Han, J.-Y.; Cho, B.C.; Cantarini, M.; Janne, P.A.; Hartmaier, R. Acquired resistance in patients with EGFRm NSCLC following treatment with osimertinib plus savolitinib in the Ph1b TATTON study Parts B and D. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, CT024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, N.; Brown, A.-L.; Wei, J.S.; Pack, S.; Trindade, C.; Kim, C.; Restifo, O.; Gao, S.; Sindiri, S.; Mehrabadi, F. Clonal evolution and heterogeneity of osimertinib acquired resistance mechanisms in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Wu, Y.-L.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ramalingam, S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.-H.; Bulusu, K.; Laus, G. Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.P.; Boyle, T.A.; Hicks, J.K.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; Glisson, B.S.; et al. Landscape of EGFR-dependent and independent mechanisms of osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.; Robichaux, J.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; Glisson, B.; Zhang, J.; Heymach, J.V. Mechanisms of resistance for osimertinib for patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer: MD Anderson Cancer Center single institution experience with osimertinib resistance. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Baik, C.S.; Gold, K.; Hayashi, H.; Johnson, M.; Koczywas, M.; Murakami, H.; Nishio, M.; Steuer, C.; Su, W.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan (U3-1402), a novel HER3 directed antibody drug conjugate, in patients (pts) with EGFR-mutated (EGFRm) NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1189–S1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; Todd, A. LBA8—Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S9), ix177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. LBA50—Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S8), viii740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Su, W.-C.; Kowalski, D.; et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet. Oncol. 2020, 21, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmos, B.; Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.T.; Soo, R.A.; Yang, J.C.H.; Gucalp, R.; Wang, L.; Marten, A.; et al. Afatinib followed by osimertinib in EGFR mutation-positive (EGFRM+) advanced NSCLC: Subgroup analyses of the giotag study by ECOG PS, age, and ethnicity. Jnccn J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 30, v629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.T.; Soo, R.; Yang, J.C.H.; Gucalp, R.; Halmos, B.; Wang, L.; Golembesky, A.; et al. Afatinib followed by osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive (EGFRm+) advanced NSCLC: Updated data from the GioTag real-world study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.T.; Soo, R.A.; Yang, J.C.H.; Gucalp, R.; Halmos, B.; Wang, L.; Golembesky, A. Afatinib followed by osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC: A real-world study (GioTag). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, ix176–ix177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Morabito, A.; Hao, D.; Yang, C.; Soo, R.; Yang, J.C.; Gucalp, R.; Halmos, B.; Golembesky, A.; Marten, A.; et al. Afatinib Followed by Osimertinib in Real-World Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced NSCLC: The Giotag Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S1045. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Xi, L.; Cultraro, C.M.; Pham, T.H.T.; Shafei, A.; Roper, N.; Bagheri, M.; Beeler, J.; Jones, G.; Raffeld, M.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis for Predicting Response to Osimertinib and Disease Progression in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13 (Suppl. S10), S478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Roper, N.; Hoang, C.; Wisch, L.; Connolly, M.; Chou, H.C.; Wei, J.; Tyagi, M.; Cultraro, C.M.; Xi, L.; et al. Local ablative therapy for oligoprogressive, EGFR-mutant, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after treatment with osimertinib. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, CT106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Xi, L.; Cultraro, C.; Wei, F.; Cheng, J.; Shafiei, A.; Pham, T.; Roper, N.; Akoth, E.; Strom, C.; et al. P1.01-27 Serial Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) Analysis of Blood and Saliva Predicts Osimertinib Response and Resistance in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S366. [Google Scholar]
- Vaclova, T.; Grazini, U.; Ward, L.; O’Neill, D.; Markovets, A.; Huang, X.; Chmielecki, J.; Hartmaier, R.; Thress, K.S.; Smith, P.D.; et al. Clinical impact of subclonal EGFR T790M mutations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, Y.; Robichaux, J.; Carter, B.; Altan, M.; Gibbons, D.; Fossella, F.; Simon, G.; Lam, V.; Blumenschein, G.; Tsao, A.; et al. MA09.03 Identification of Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Poziotinib in EGFR Exon 20 Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S282–S283. [Google Scholar]
- Haura, E.B.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Sanborn, R.E.; Govindan, R.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, S.W.; Reckamp, K.L.; Sabari, J.K. JNJ-61186372 (JNJ-372), an EGFR-cMet bispecific antibody, in EGFR-driven advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9009. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Bao, H.; Le, X.; Fan, X.; Tang, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; et al. Distinct resistant mechanism and genomic evolution during TKI treatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients with or without acquired T790M mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e20603. [Google Scholar]
- Raez, L.E.; Baca, Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Nieva, J.; Mandani, H.; Wanderwalde, A.; Borghaei, H.; Naban, C.; Langer, C.; Socinsky, M.A.; et al. Developing of EGFR resistant mutations to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKI) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S597. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Katakura, S.; Kamimaki, C.; Somekawa, K.; Fukuda, N.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, K.; Horita, N.; Hara, Y.; Piao, H. Resistance mechanisms of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar]

| Author Year; Country | LoT; Treatment | Study Design | Study Period | N | Sex, Male % | Age, Years-Median (Range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | ||||||
| Cardona 2022; international [18] | 1L; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 94 | 54.3% | 59.0 (31.0–84.0) |
| Piotrowska 2022; US [37] | 1L; osimertinib | RWE/observational | November 2016–January 2022 | 54 | 29.6% | 61.0 |
| Ramalingam 2018; international [54] | 1L; osimertinib | Single-arm clinical trial | 4 March 2013–30 December 2022 | 60 | 25.0% | 63.5 (38.0–91.0) |
| Bauml -a 2021; US, Canada [17] | 1L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 799 | 32.3% | 63.0 (30.0–95.0) |
| Le 2018; US [27,60,61] | 1L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | January 2011–February 2018 | 118 | 28.0% | 63.0 (36.0–88.0) |
| Patil 2019; US [34] | 1L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 95 | 33.7% | NR |
| Schoenfeld 2019; US [42] | 1L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | January 2016–December 2018 | 71 | NR | NR |
| Ramalingam 2022; US [39] | 1L or 2L; osimertinib | RWE/observational | July 2014–June 2021 | 2050 | NR | NR |
| Oxnard 2018; US [33] | 2L-3L; osimertinib | RWE/observational | November 2017 | 151 | 47.0% | NR |
| Lim 2021; US, Korea [29] | 2L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 55 | NR | NR |
| Zhao 2018; US, China [50] | 2L+; osimertinib | RWE/observational | January 2017–October 2017 | 293 | NR | NR |
| Guibert 2018; US [22] | Unspecified; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 46 | NR | NR |
| Janne 2021; US [25,62] | Unspecified; osimertinib | RWE/observational | December 2014–November 2020 | 755 | NR | NR |
| Strohbehn 2019; US [44] | Unspecified; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 28 | NR | NR |
| Zhang 2018; US, China [49] | Unspecified; osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 110 | NR | NR |
| Osimertinib included as one treatment option among patients treated with TKIs | ||||||
| Mondaca 2019; US [32] | 1L; erlotinib, afatinib, gefitinib, osimertinib, rociletinib, and nazartinib | RWE/observational | January 2016–August 2017 | 177 | 35.0% | 66.0 (38.0–91.0) |
| Robichaux 2021; US [40] | 1L; EGFR TKIs (osimertinib and other TKIs) | RWE/observational | NR | 16,715 | NR | NR |
| Soria 2018; international [8,63,64] | 1L; osimertinib and SoC (gefitinib and erlotinib) | Randomized clinical trial | 3 December 2014–30 December 2022 | 556 | 37.1% | 64.0 (2.06–93.0) |
| Le 2022; international [16] | 1L+; tepotinib + osimertinib, and/or gefitinib | RWE/observational | NR | 12 | 25.0% | 69.5 (47.0–86.0) |
| Markovets 2021; international [57,65] | 1L+; osimertinib + savolitinib | Non-randomized clinical trial | 5 August 2014–30 December 2022 | 180 | 41.1% | 61.0 (28.0–92.0) |
| Piotrowska 2018; US [36] | 1L+; osimertinib and BLU667 + osimertinib | RWE/observational | July 2014–August 2018 | 41 | 37.0% | 64.0 (40.0–87.0) |
| Hochmair 2018; international [24,66,67,68,69] | 1L and 2L; afatinib and osimertinib | RWE/observational | 28 December 2017–31 May 2018 | 204 | 46.1% | 60.0 (30.0–86.0) |
| Rotow 2021; US [41] | 2L+; osimertinib + selpercatinib | RWE/observational | NR | 12 | NR | NR |
| Goldberg 2018; US [21] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs (afatinib, osimertinib, gefitinib, erlotinib, and rociletinib) | RWE/observational | NR | 29 | 37.9% | 60.0 (38.0–87.0) |
| Mack 2020; US [30] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs (erlotinib, afatinib, gefitinib, osimertinib, rociletinib, and others) | RWE/observational | June 2014–October 2016 | 8388 | 43.0% | NR |
| Yang 2021; international [46] | Unspecified; afatinib post-osimertinib | RWE/observational | NR | 1023 | NR | NR |
| Yao 2019; US [47] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs (gefitinib, osimertinib, Lenvatinib, or other EGFR TKIs) | RWE/observational | 2016–2018 | 3600 | NR | NR |
| Yu 2022; US [48] | Unspecified; gefitinib, afatinib, erlotinib, or osimertinib | RWE/observational | 1 August 2005–1 August 2020 | 9 | 44.4% | 60.0 |
| Osimertinib included as one treatment option in patients treated with TKIs and/or non-TKIs | ||||||
| Mambetsariev 2022; US [31] | 1L+; erlotinib, osimertinib, afatinib, carboplatin/pemetrexed, and carboplatin/pemetrexed/pembrolizumab | RWE/observational | 2014–2021 | 9 | 44.4% | 60.0 (35.0–72.0) |
| Roper 2020; US [58,70,71,72] | 1L or 2L; osimertinib and local ablative therapy (LAT) | Non-randomized clinical trial | 13 April 2016–20 September 2022 | 34 | NR | NR |
| Papadimitrakopoulou 2018; international [59,73] | 2L; osimertinib and platinum-based doublet chemotherapy | Randomized clinical trial | 4 August 2014–15 April 2016 | 419 | 35.8% | Mean (SD): 61.7 (11.7) |
| Patil 2020; US [35] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs: erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib, dacomitinib, and osimertinib Immune checkpoint inhibitors: pembrolizumab, nivolumab, or atezolizumab as single agents or in combination with chemotherapy | RWE/observational | June 2009–March 2019 | 570 | NR | NR |
| Schrock 2018; US [43] | Unspecified; with or without EGFR TKIs (erlotinib, ASP8273 or afatinib + cetuximab or afatinib or erlotinib, and osimertinib) | RWE/observational | June 2012–October 2017 | 31 | 38.7% | 64.0 (46.0–77.0) |
| Other TKIs | ||||||
| Elamin 2022; US [51,74] | 1L+; poziotinib | Single-arm clinical trial | 17 March 2017–1 March 2023 | 50 | 40.0% | 62.0 (29.0–77.0) |
| Helman 2018; international [23] | 1L+; rociletinib | RWE/observational | Enrolled as of 1 July 2015 | 77 | 28.6% | 61.0 (37.0–82.0) |
| Lu 2021; US [52] | 1L+; aumolertinib | Single-arm clinical trial | 8 May 2017–November 2022 | 244 | NR | NR |
| McCoach 2021; US [53] | Unspecified; capmatinib + erlotinib | Single-arm clinical trial | 2013 to 2020 | 35 | 40.0% | 65.0 (39.0–89.0) |
| Other TKIs with non-TKIs | ||||||
| Bauml-b 2021; international [55,75] | 2L and 3L; amivantamab + lazertinib | Non-randomized clinical trial | 24 May 2016–26 January 2024 | 161 | NR | NR |
| Non-TKIs | ||||||
| Janne 2022; international [56] | 1L+; patritumab deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) | Non-randomized clinical trial | 30 October 2017–31 December 2023 | 81 | 35.8% | 64 (40–80) |
| Treatment/therapy name unspecified | ||||||
| Gaut 2018; US [20] | 1L or 2L; TKIs and chemotherapy | RWE/observational | April 2012–October 2016 | 97 | 28.9% | Mean: 66.7 |
| Chiang 2020; US [19] | 1L or 2L+; 1st- and 2nd-generation EGFR TKIs | RWE/observational | 1 November 2015-30 September 2017 | 782 | 36.4% | 69.0 |
| Jin 2019; international [26,76] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs | RWE/observational | NR | 64 | NR | NR |
| Li 2019; US [28] | Unspecified; NR | RWE/observational | January 2015–December 2015 | 136 | 85.5% | 68.0 (23.0–85.0) |
| Raez 2022; US [38,77] | Unspecified; EGFR TKIs | RWE/observational | NR | 3223 | NR | NR |
| Suero-Abreu 2018; US [45] | Unspecified; NR | RWE/observational | September 2015–January2018 | 115 | 43.0% | 68.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadagam, P.; Waters, D.; Bhagat, A.; Kuang, Y.; Uyei, J.; Vanderpoel, J. Resistance Mutation Profiles Associated with Current Treatments for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040191
Vadagam P, Waters D, Bhagat A, Kuang Y, Uyei J, Vanderpoel J. Resistance Mutation Profiles Associated with Current Treatments for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(4):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040191
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadagam, Pratyusha, Dexter Waters, Anil Bhagat, Yuting Kuang, Jennifer Uyei, and Julie Vanderpoel. 2025. "Resistance Mutation Profiles Associated with Current Treatments for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review" Current Oncology 32, no. 4: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040191
APA StyleVadagam, P., Waters, D., Bhagat, A., Kuang, Y., Uyei, J., & Vanderpoel, J. (2025). Resistance Mutation Profiles Associated with Current Treatments for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: A Systematic Literature Review. Current Oncology, 32(4), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040191





