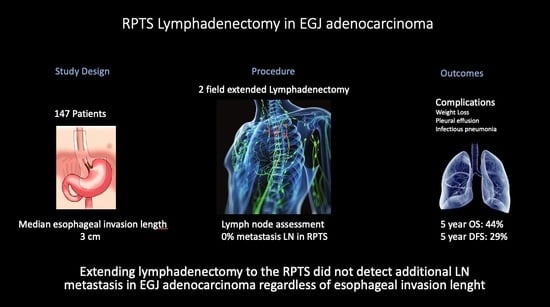
The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Data and Study Objectives
2.3. Surgery
2.4. Lymphadenectomy
2.5. Management of Postoperative Complications
2.6. Objectives
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Pathology Lymph Node Staging, RPTS Status, and Outcomes
3.3. Postoperative Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgian Cancer Registry. Cancer Incidence in Belgium 2024; Belgian Cancer Registry: Brussels, Belgium, 2024; Available online: https://kankerregister.org/ (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Zhang, Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlenhopp, D.; Then, E.O.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermannová, R.L.; Leong, T. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline interim update on the treatment of locally advanced oesophageal and oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma and metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma. ESMO Open 2025, 10, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, B. Respiratory Complication of Trans-Thoracic Esophagectomies for Cancer. Master’s Thesis, Université de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France, 2004. Available online: https://dumas.ccsd.cnrs.fr/dumas-01085942 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Mariette, C.; Piessen, G.; Briez, N.; Triboulet, J. The Number of Metastatic Lymph Nodes and the Ratio Between Metastatic and Examined Lymph Nodes Are Independent Prognostic Factors in Esophageal Cancer Regardless of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation or Lymphadenectomy Extent. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerut, T.; Coosemans, W.; Decker, G.A.; De Leyn, P.; Moons, J.; Nafteux, P.; Van Raemdonck, D. Surgical techniques. J. Surg. 2005, 92, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Hiki, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kutsukake, K.; Ito, Y.; Ohi, M.; Wada, N.; Takiguchi, S.; Mine, S.; Hasegawa, S.; et al. Mediastinal lymph node metastasis and recurrence in adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. Surgery 2015, 157, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Doki, Y.; Mine, S.; Terashima, M.; Yasuda, T.; Yasuda, K.; Hiroyuki, D.; Shinichi, S.; Takushi, Y.; et al. Mapping of Lymph Node Metastasis from Esophagogastric Junction Tumors. Ann. Surg. 2019, 274, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Ishikawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Oyama, T.; Oyama, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Kawakubo, H.; Kawachi, H.; et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2022 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: Part 2. Esophagus 2023, 20, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.; Berlth, F.; Hadzijusufoviç, E.; Tagkalos, E.; Uzun, E.; Codony, C.; Lang, H.; Grimminger, P.P. Extended lower paratracheal lymph node resection during esophagectomy for cancer—Safety and necessity. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderegg, M.; Lagarde, S.M.; Jagadesham, V.P.; Gisbertz, S.S.; Immanuel, A.; Meijer, S.L.; Hulshof, M.C.C.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Griffin, S.M.; et al. Prognostic significance of the location of lymph node metastases in patients with adenocarcinoma of the distal esophagus or gastroesophageal junction. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, S.; Sano, T.; Hiki, N.; Yamada, K.; Nunobe, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Lymphadenectomy around the left renal vein in Siewert type II adenocarcinoma of the oesophagogastric junction. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 100, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kutsukake, K.; Misawa, K.; Ohi, M.; Mine, S.; Hiki, N.; Takeuchi, H. Clinicopathologicalcharacteristics and prognostic factors of patients with Siewert type II esophagogastric junction carcinoma: A retrospective multicenter study. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Kang, X.; Qin, J.; Qi, X.; Li, Y. Lymph node metastases in middle and upper mediastinum of Siewert type II adenocarcinoma: A real-world retrospective study. Cancer 2024, 13, e6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Seto, Y.; Sano, T.; Makuuchi, H.; Ando, N.; Sasako, M. Results of a nationwide retrospective study of lymphadenectomy for esophagogastric junction carcinoma. Gastric Cancer 2016, 20 (Suppl. S1), 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, K.; Haverkamp, L.; Bruijnen, R.; Siersema, P.D.; Ruurda, J.P.; Van Hillegersberg, R. Surgical treatment of adenocarcinomas of the gastro-esophageal junction. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 22, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagens, E.R.C.; Kingma, B.F.; Van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Borggreve, A.S.; Ruurda, J.P.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; Gisbertz, S.S. The Impact of Paratracheal Lymphadenectomy on Survival After Esophagectomy: A Nationwide Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Journo, X.B.; Doddoli, C.; Michelet, P.; Loundou, A.; Trousse, D.; Giudicelli, R.; Fuentes, P.A.; Thomas, P.A. Transthoracicesophagectomy for adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus: Standard versus extended two-field mediastinal lymphadenectomy? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac Surg. 2005, 27, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulscher, J.B.F.; Van Sandick, J.W.; De Boer, A.G.E.M.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Tijssen, J.G.P.; Fockens, P.; Stalmeier, P.F.M.; ten Kate, F.J.W.; van Dekken, H.; Obertop, H.; et al. Extended Transthoracic Resection Compared with Limited Transhiatal Resection for Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| n = 147 | |
|---|---|
| Age, yr Median (range) | 69.0 (64.0–75.0) |
| Sex Male Female | 129 (87.8%) 18 (12.2%) |
| Tumor size *, cm Median (range) | 2.7 (1.8–4.5) |
| Length of the esophageal involvement *, cm at endoscopy Median (range) | 3.0 (1.5–5.0) |
| Patients with esophageal length involvement <4 cm ≥4 cm Unknown | 53 (36.1%) 38 (25.9%) 56 (38.1%) |
| Tumor epicenter Siewert I Siewert II Siewert III Unknown | 55 (37.4%) 43 (29.3%) 9 (6.1%) 40 (27.2%) |
| Clinical Tumor stage (cT) Tx T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 | 2 (1.4%) 0 (0.0%) 17 (11.6%) 29 (19.7%) 96 (65.3%) 3 (2.0%) |
| Clinical Node stage (cN) Nx N0 N1 N2 N3 | 11 (7.5%) 47 (32.0%) 74 (50.3%) 13 (8.8%) 2 (1.4%) |
| Clinical Metastasis stage (cM) Mx M0 M1 | 106 (72.1%) 41 (27.9%) 0 (0.0%) |
| Neoadjuvant treatment Yes No | 118 (80.3%) 29 (19.7%) |
| TRG (patients with neoadjuvant treatment) Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Not assessed | 15 (10.2%) 18 (12.2%) 26 (17.7%) 31 (21.1%) 7 (4.8%) 21 (14.3%) |
| Invasion at pathology Lymphatic Vascular Nerve Unknown | 56 (38.1%) 22 (15.0%) 36 (24.5%) 33 (22.4%) |
| Surgical techniques Two-field: Laparo-thoracic approach Three-field: Laparo-thoraco-cervical approach | 140 (95.2%) 7 (4.8%) |
| Type of resection R0 R1 R2 Unknown | 127 (86.4%) 19 (12.9%) 0 (0.0%) 1 (0.7%) |
| Pathological T stage (pT) Tx T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 | 2 (1.4%) 0 (0.0%) 42 (28.6%) 24 (16.3%) 65 (44.2%) 14 (9.5%) |
| Pathological N stage (pN) Nx N0 N1 N2 N3 | 2 (1.4%) 76 (51.7%) 32 (21.8%) 19 (12.9%) 18 (12.2%) |
| Pathological M stage (pM) M0 ** M1 | 144 (98.0%) 3 (2.0%) |
| Number of retrieved Lymph Nodes on operative specimen * Median (range) | 26.0 (20.0–32.0) |
| Adjuvant treatment Yes No Unknown | 57 (38.8%) 74 (50.3%) 16 (10.9%) |
| Total Patients n = 147 | pN0 n = 77 (52.4%) | pN+ n = 70 (47.6%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
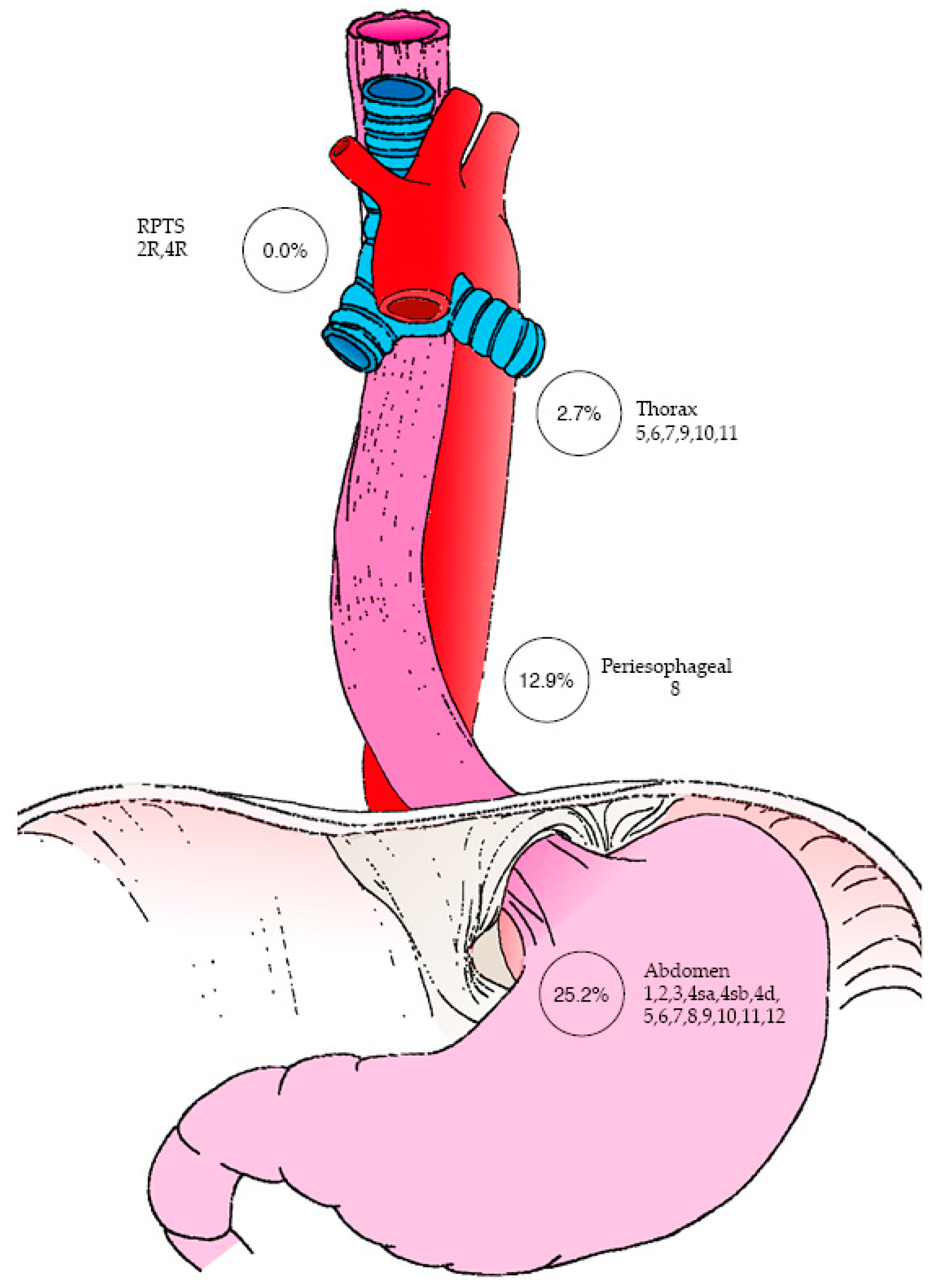
| Specified LN stations in pathology report | 145 (98.6%) | 75 (51.0%) | 70 (47.6%) |
| Thoracic nodes | |||
| Subaortic (st. 5) Para-aortic (st. 4) Subcarinal (st. 7) Triangular ligament (st. 9) Hilar (st. 10) Interlobar (st. 11) | 125 (85.0%) | 4 (2.7%) | |
| Peri-esophagus (st. 8) | 64 (43.5%) | 19 (12.9%) | |
| RPTS (st 2R, 4R) | 108 (73.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Abdominal nodes | |||
| Perigastric(st. 1, 2, 3, 4sa, 4sb, 4d, 5, 6, 7) Common-hepatic artery (st. 8) Celiac (st. 9) Splenic hilum and splenic-artery (st. 10,11) Hepatoduodenal ligament (st. 12) | 51 (34.7%) | 37 (25.2%) | |
| Unspecified LN stations in pathology report | 2 (1.36%) | 2 (1.36%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Esophageal Invasion Length < 4 cm (n = 53) | Esophageal Invasion Length ≥ 4 cm (n = 38) | Missing or Uncertain Data (n = 56) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total lymph nodes * | 26.5 | 26.2 | 26.1 |
| Metastatic lymph nodes * mean | 2.7 | 2.1 | 2.6 |
| LNR | 10.3% | 7.9% | 10% |
| 5-year OS | 43% | 53% | 40% |
| 5-year DFS | 31% | 21% | 17% |
| 5-year OS | 44% | ||
| 5-year DFS | 29% | ||
| n = 147 | |
|---|---|
| Postoperative Complications Yes No Type of postoperative complication Weight loss ≥ 10% Pleural effusion Infectious pneumonia Anastomotic leak Acute respiratory distress syndrome Atelectasis Empyema Chylothorax Hemothorax Cardiac arrest Conduit ischemia Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis | 61 (41.5%) 86 (58.5%) 43 (29.2%) 31 (21.1%) 29 (19.7%) 18 (12.2%) 15 (10.2%) 10 (6.8%) 7 (4.8%) 3 (2.0%) 3 (2.0%) 2 (1.4%) 0 (0.0%) 0 (0.0%) |
| Clavien–Dindo Classification 1 2 3a 3b 4a 4b 5 | 8 (5.4%) 11 (7.5%) 13 (8.8%) 16 (10.9%) 2 (1.4%) 2 (1.4%) 9 (6.1%) |
| Pleural drainage | 19 (12.9%) |
| Surgical reintervention Yes No | 16 (10.9%) 131 (89.1%) |
| Readmission to ICU Yes No | 19 (12.9%) 128 (87.1%) |
| CU stay duration (days), Median | 1.2 (0–34) |
| 30-day mortality | 5 (3.4%) |
| 90-day mortality | 9 (6.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yazidi, D.; Vander Kuylen, M.; Ennaji, M.; Charara, F.; El Nakadi, I.; Moreau, M.; Gomez, M.G.; Verset, L.; Liberale, G. The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110609
Yazidi D, Vander Kuylen M, Ennaji M, Charara F, El Nakadi I, Moreau M, Gomez MG, Verset L, Liberale G. The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(11):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110609
Chicago/Turabian StyleYazidi, Dina, Maarten Vander Kuylen, Meriem Ennaji, Fadi Charara, Issam El Nakadi, Michel Moreau, Maria Galdon Gomez, Laurine Verset, and Gabriel Liberale. 2025. "The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study" Current Oncology 32, no. 11: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110609
APA StyleYazidi, D., Vander Kuylen, M., Ennaji, M., Charara, F., El Nakadi, I., Moreau, M., Gomez, M. G., Verset, L., & Liberale, G. (2025). The Relevance of Lymphadenectomy Extension to the Right Paratracheal Space in the Treatment of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Bicentric Study. Current Oncology, 32(11), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110609