Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Cell Culture
2.2. xCELLigence System
2.3. Apoptosis Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
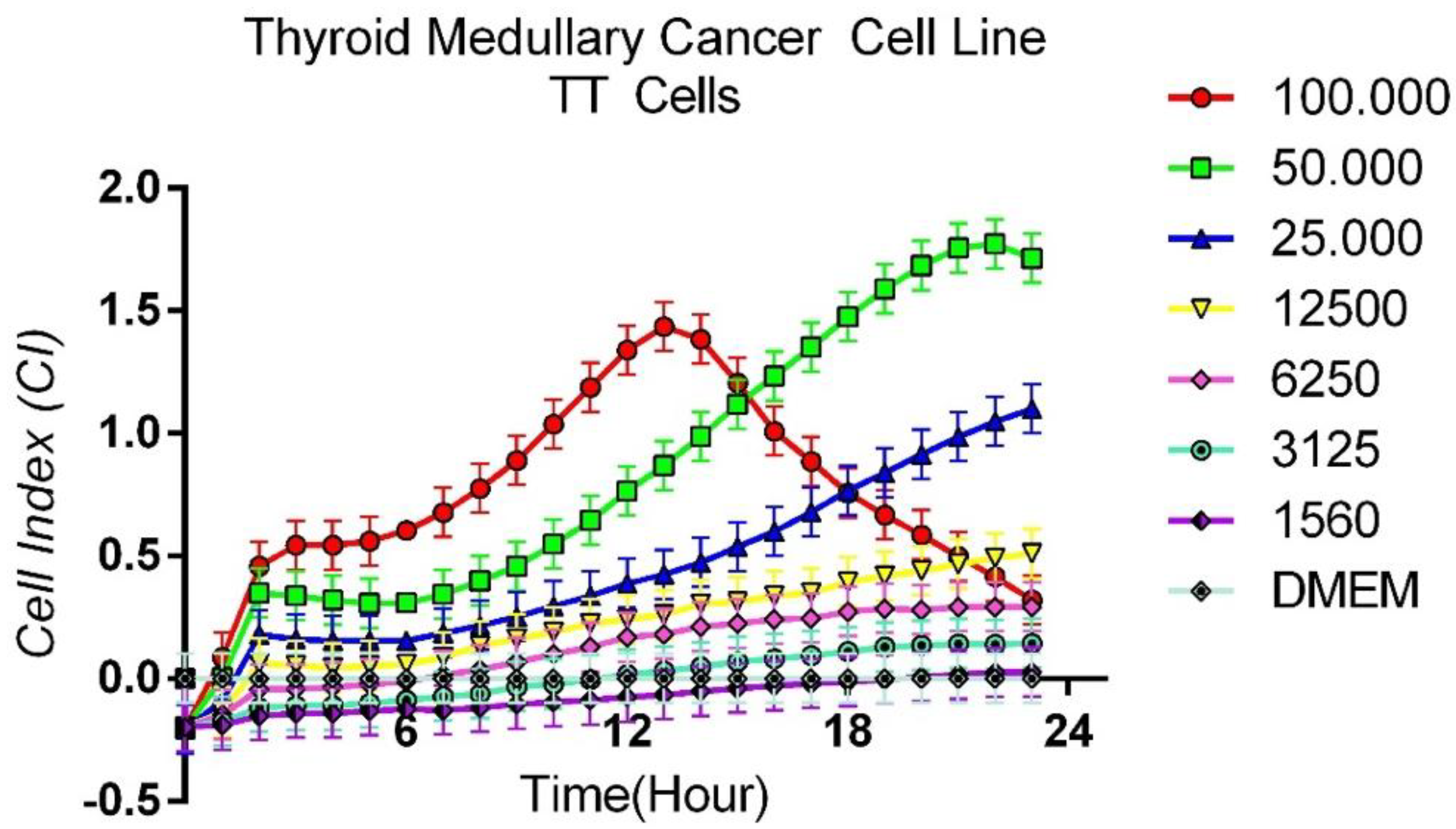
3.1. Protocol for Determining Optimum Cell Count
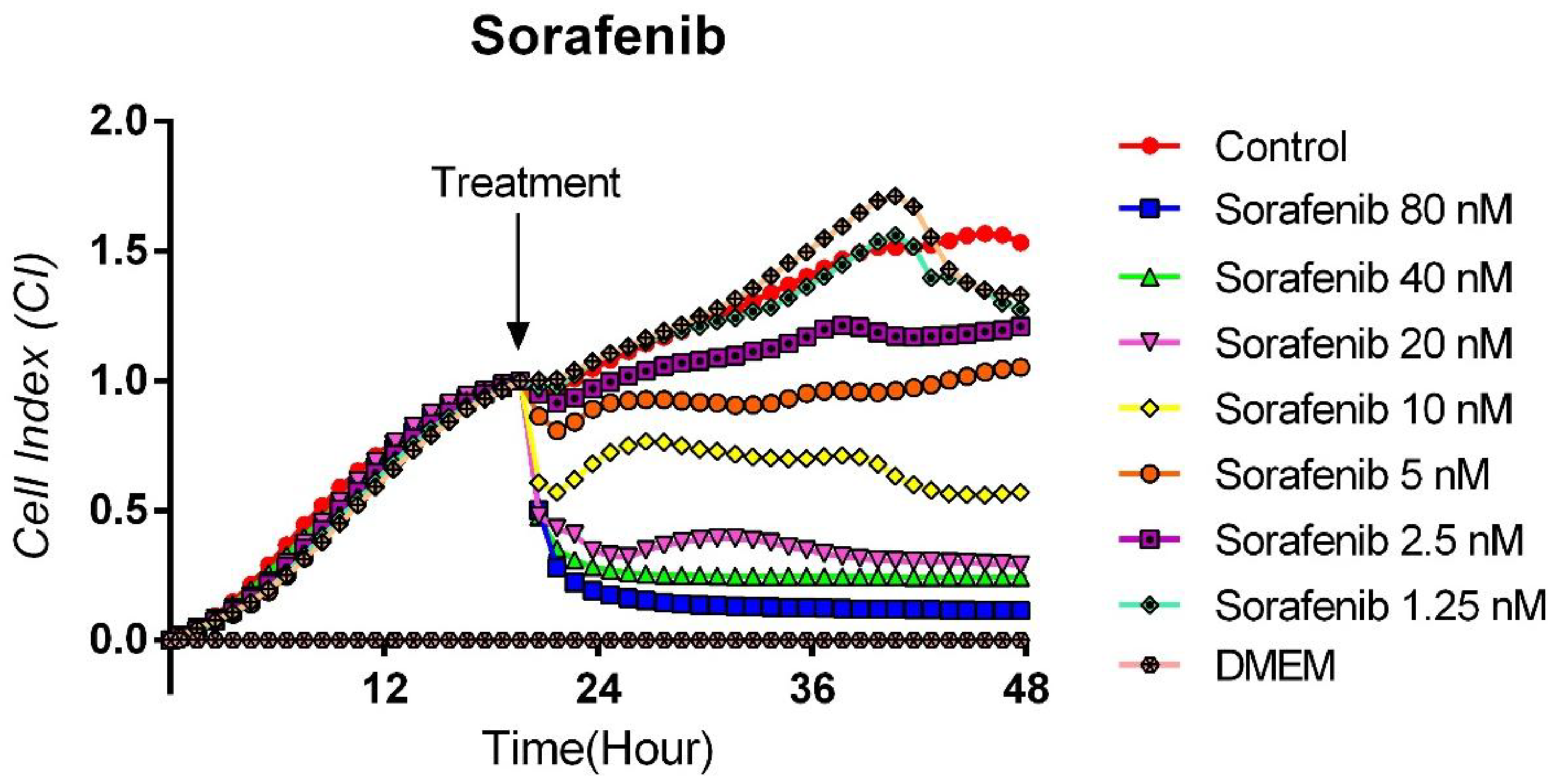
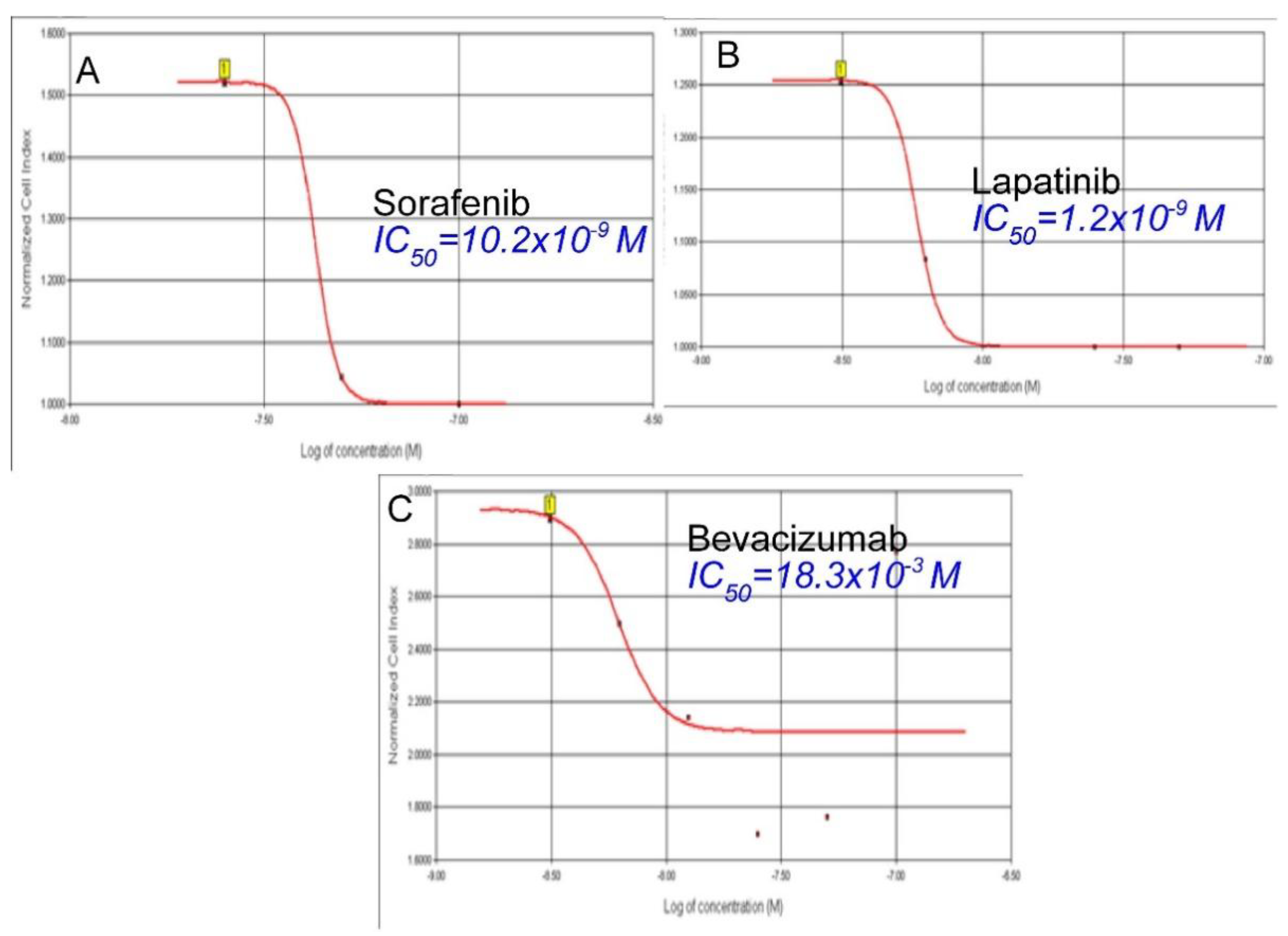
3.2. Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib on TT Cells
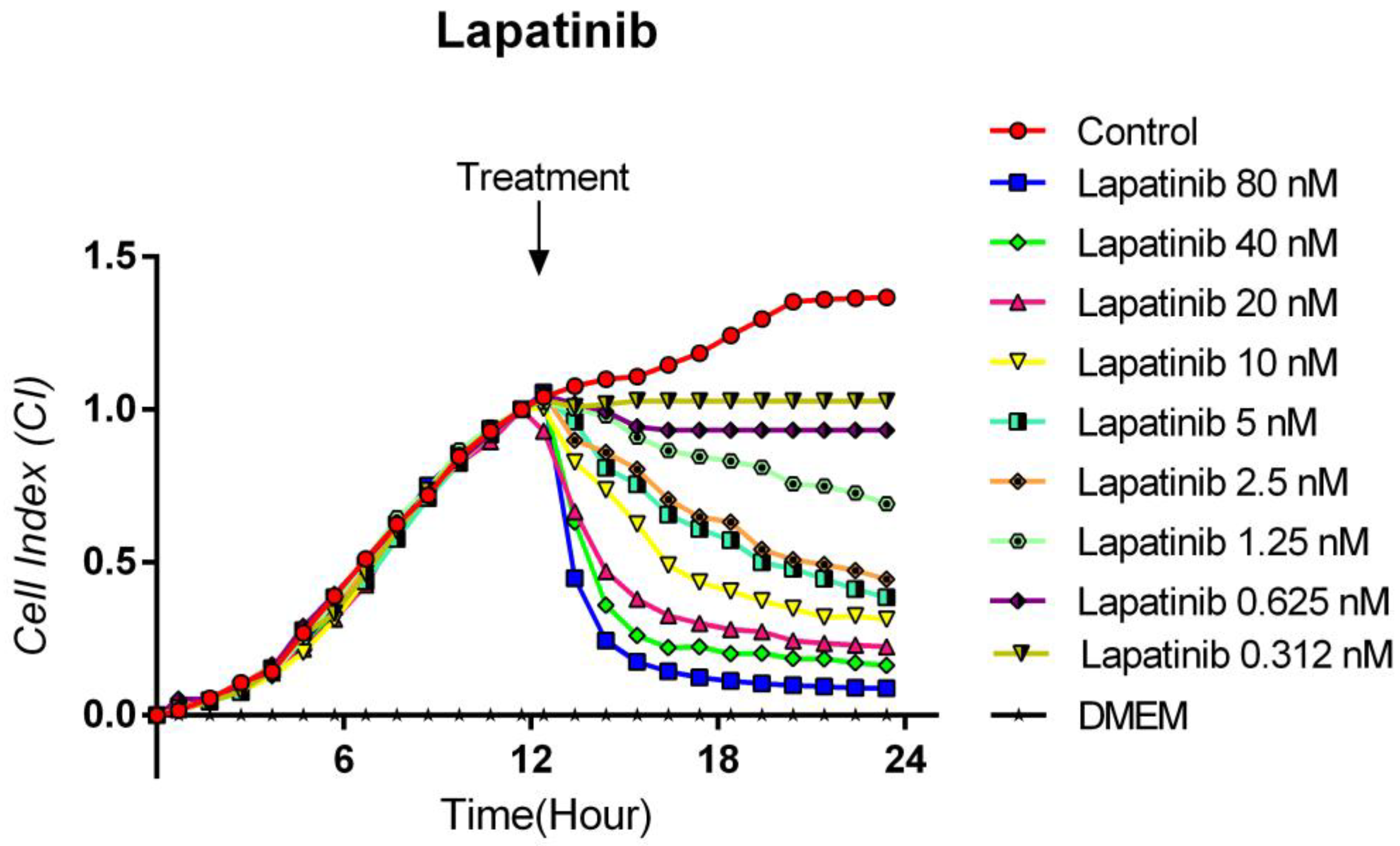
3.3. Cytotoxic Effects of Lapatinib on TT Cells
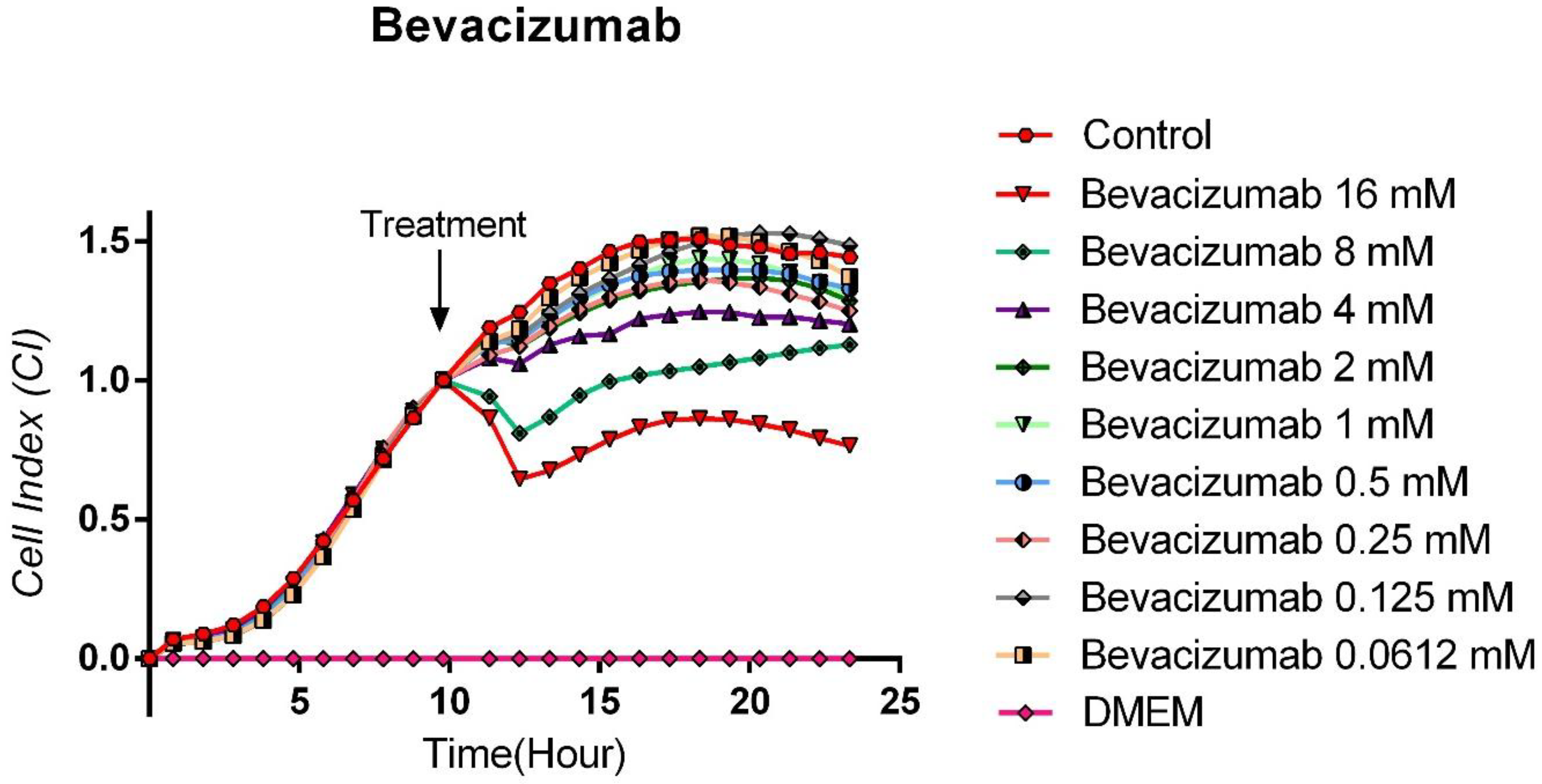
3.4. Cytotoxic Effects of Bevacizumab on TT Cells
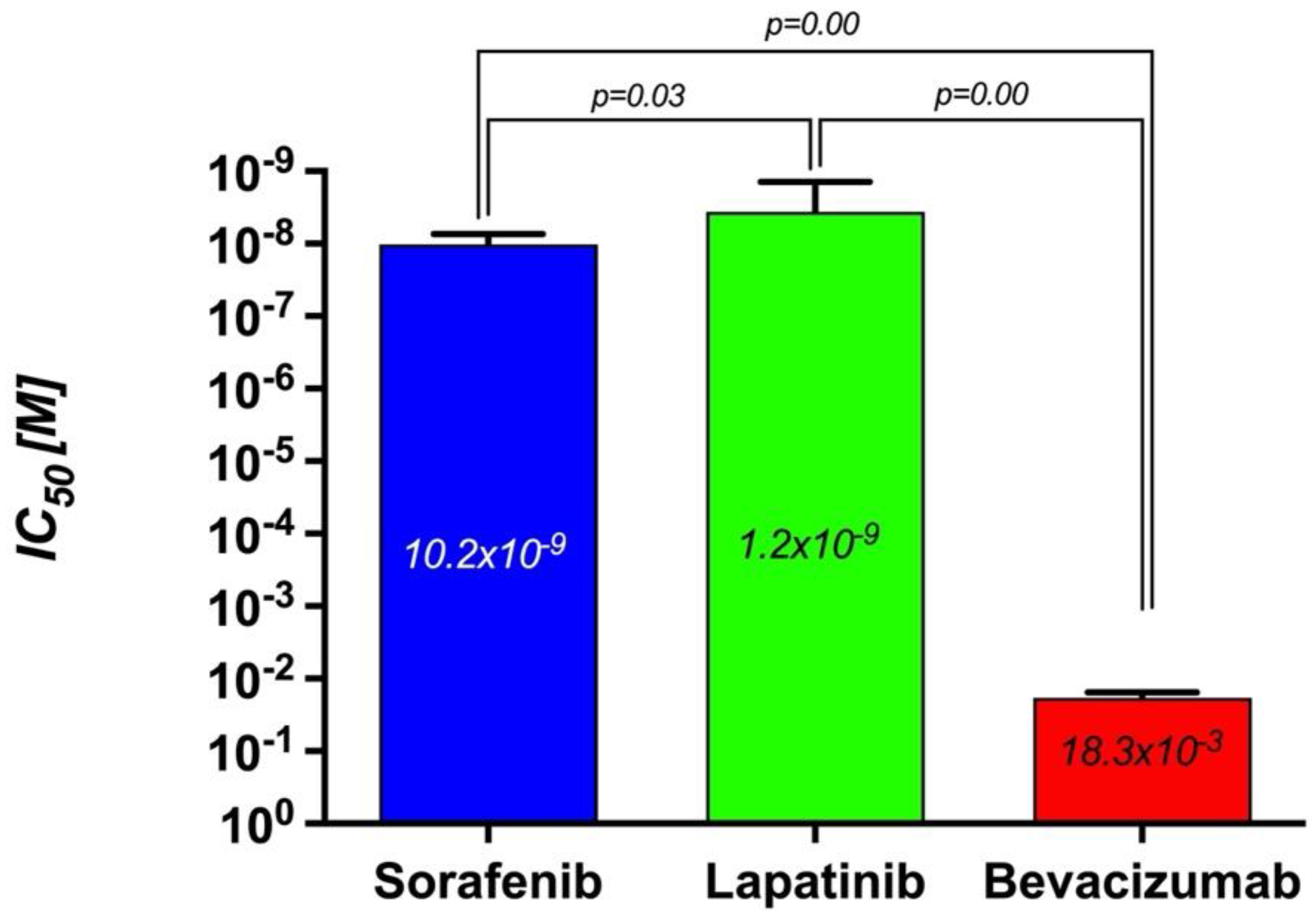
3.5. The Comparison of the Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab
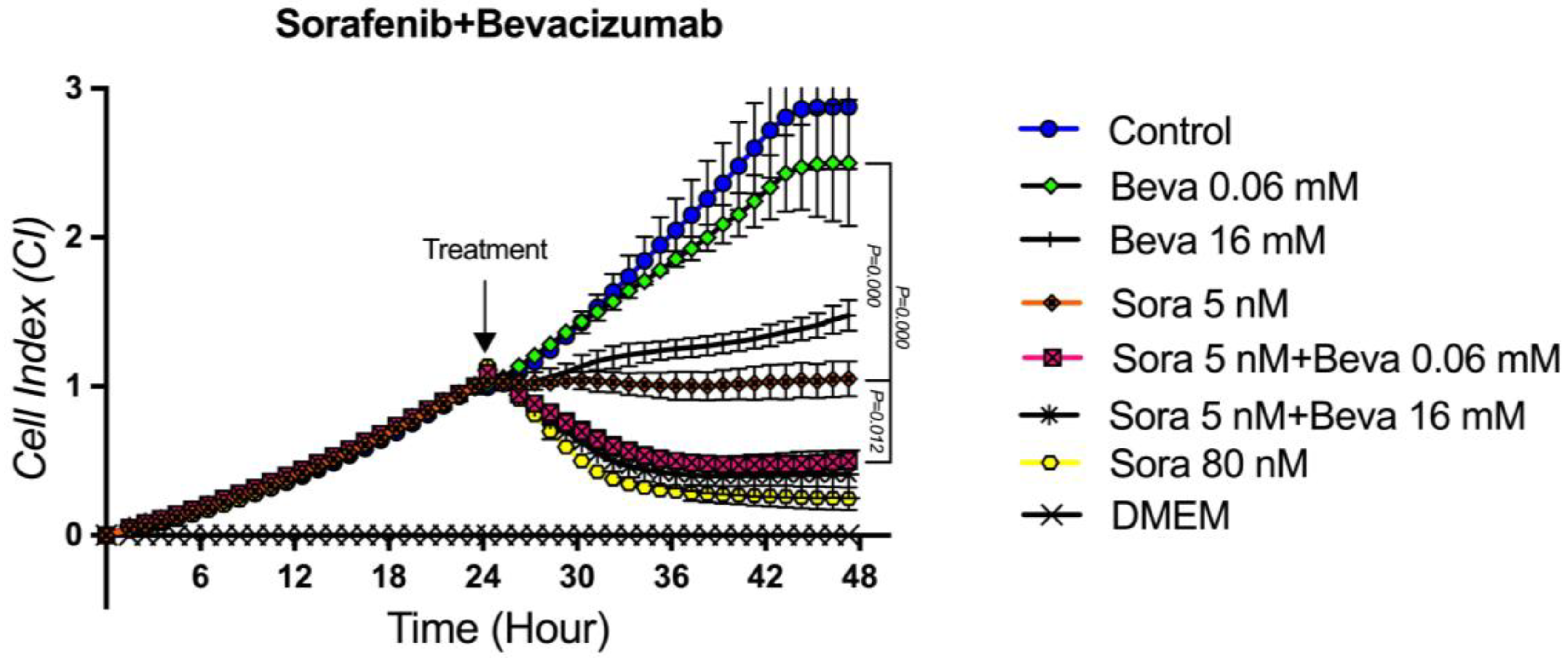
3.6. The Proliferation Analysis of the Sorafenib + Bevacizumab Combination on TT Cells
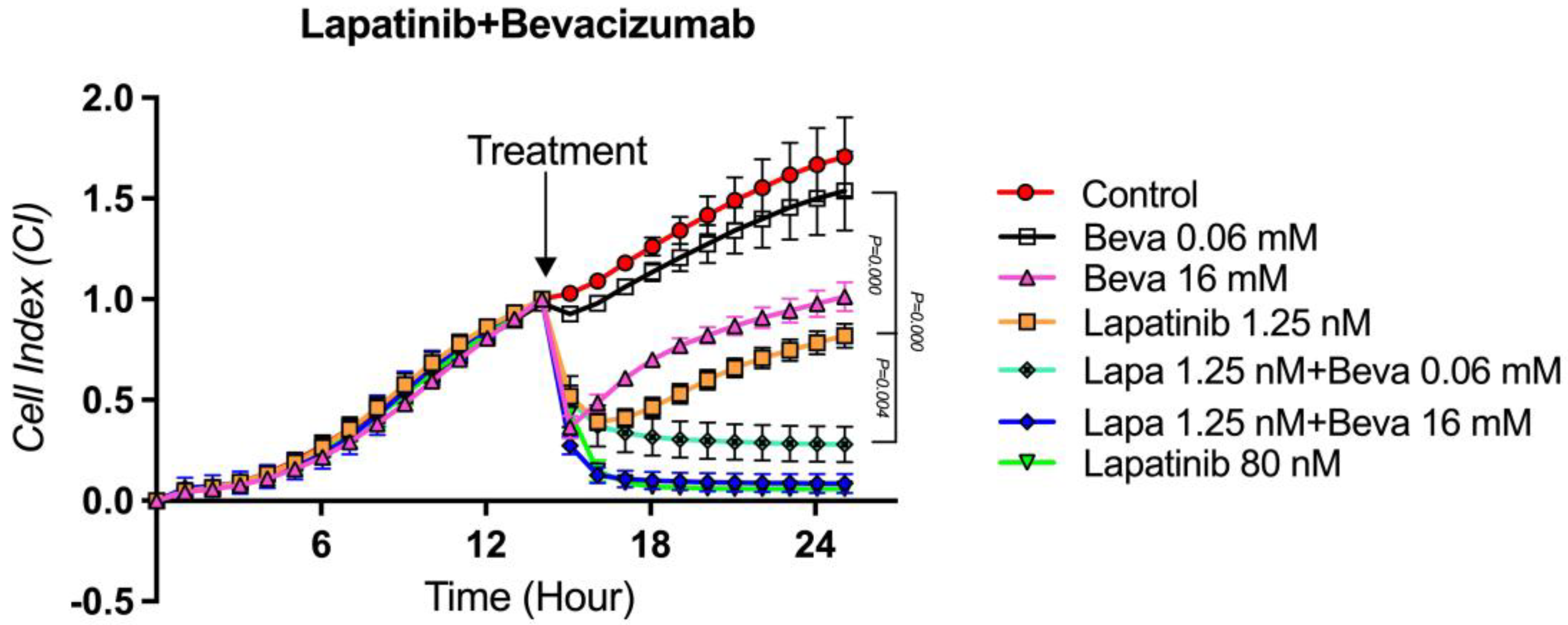
3.7. The Proliferation Analysis of the Lapatinib + Bevacizumab Combination on TT Cells
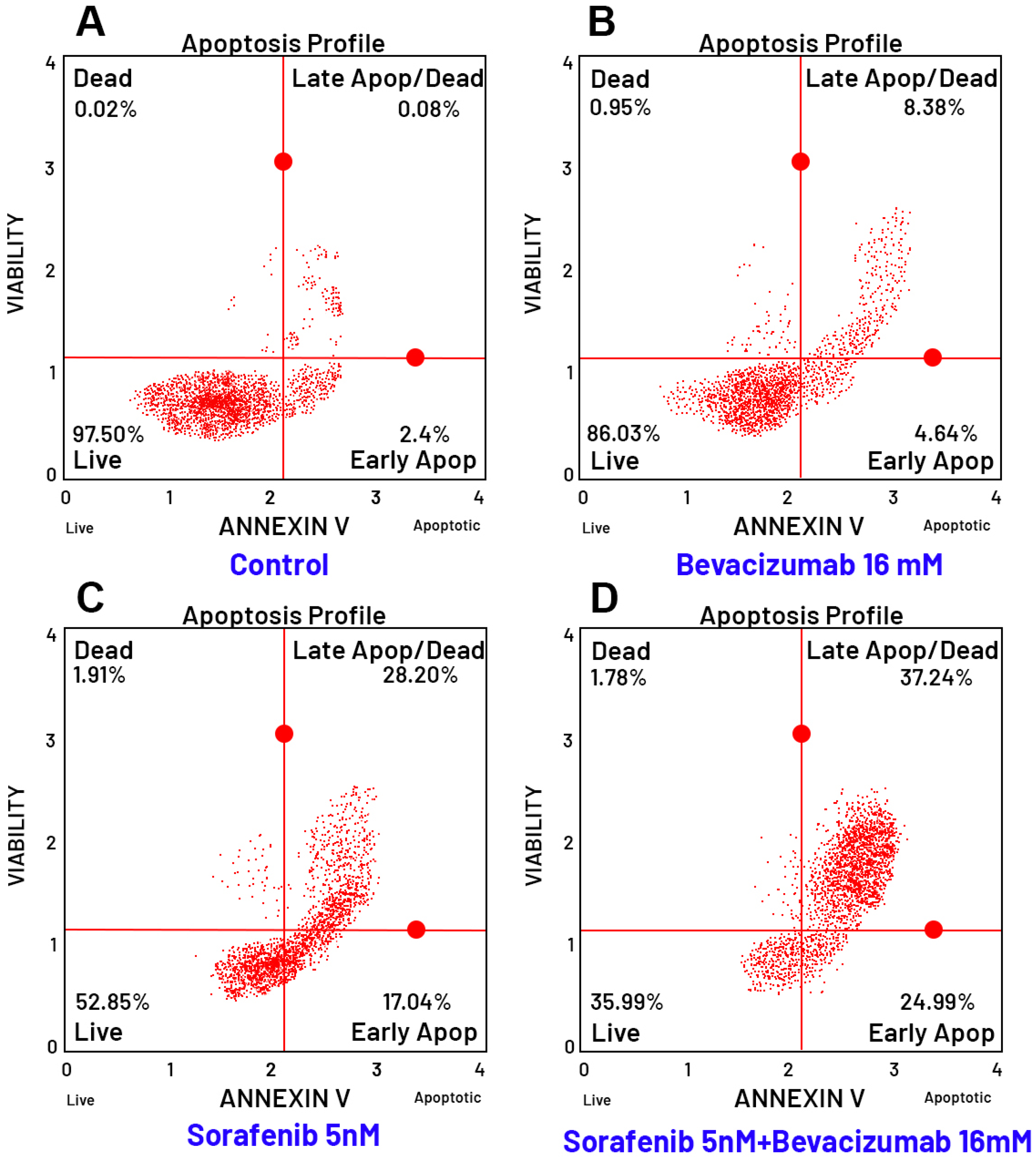
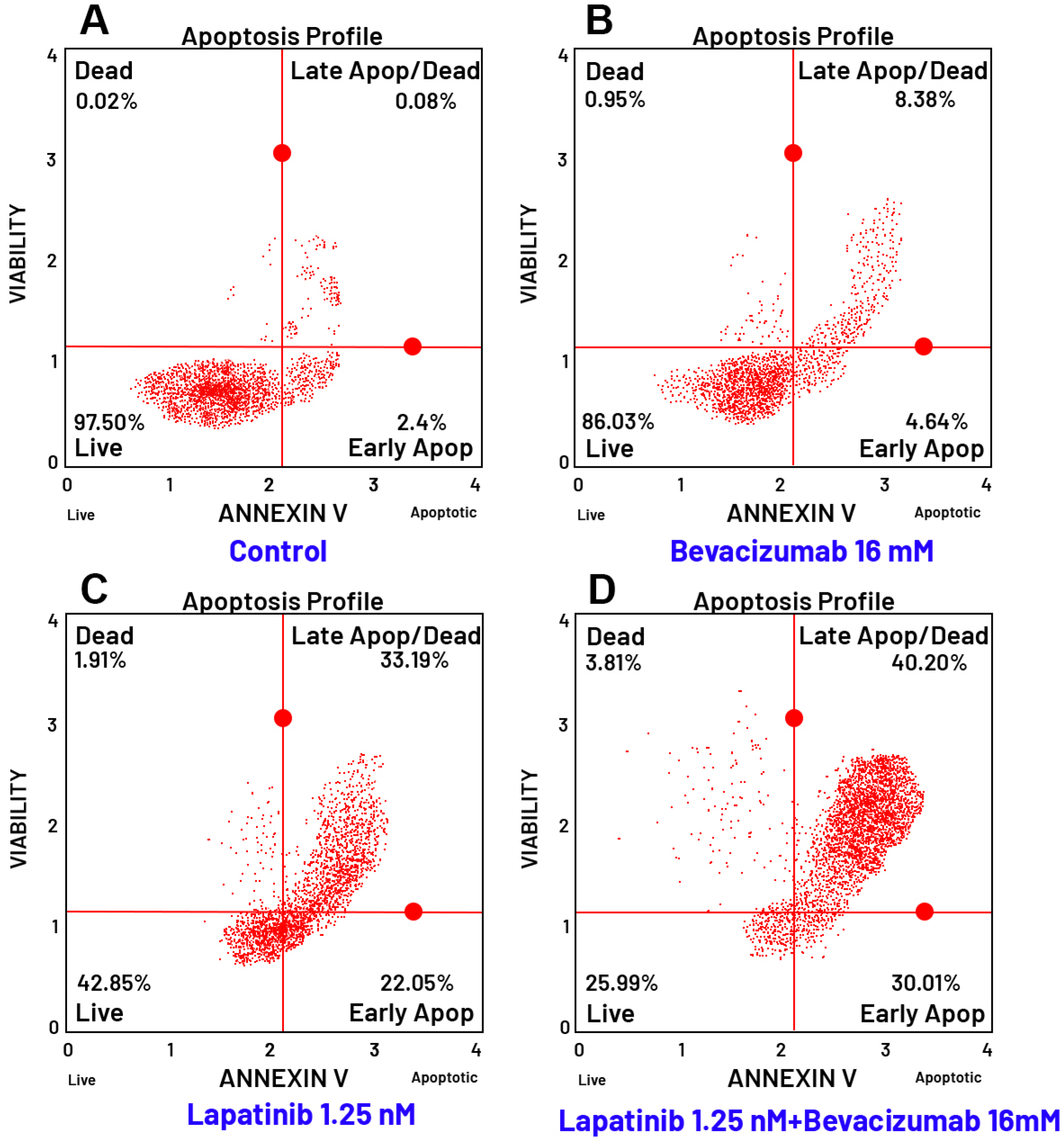
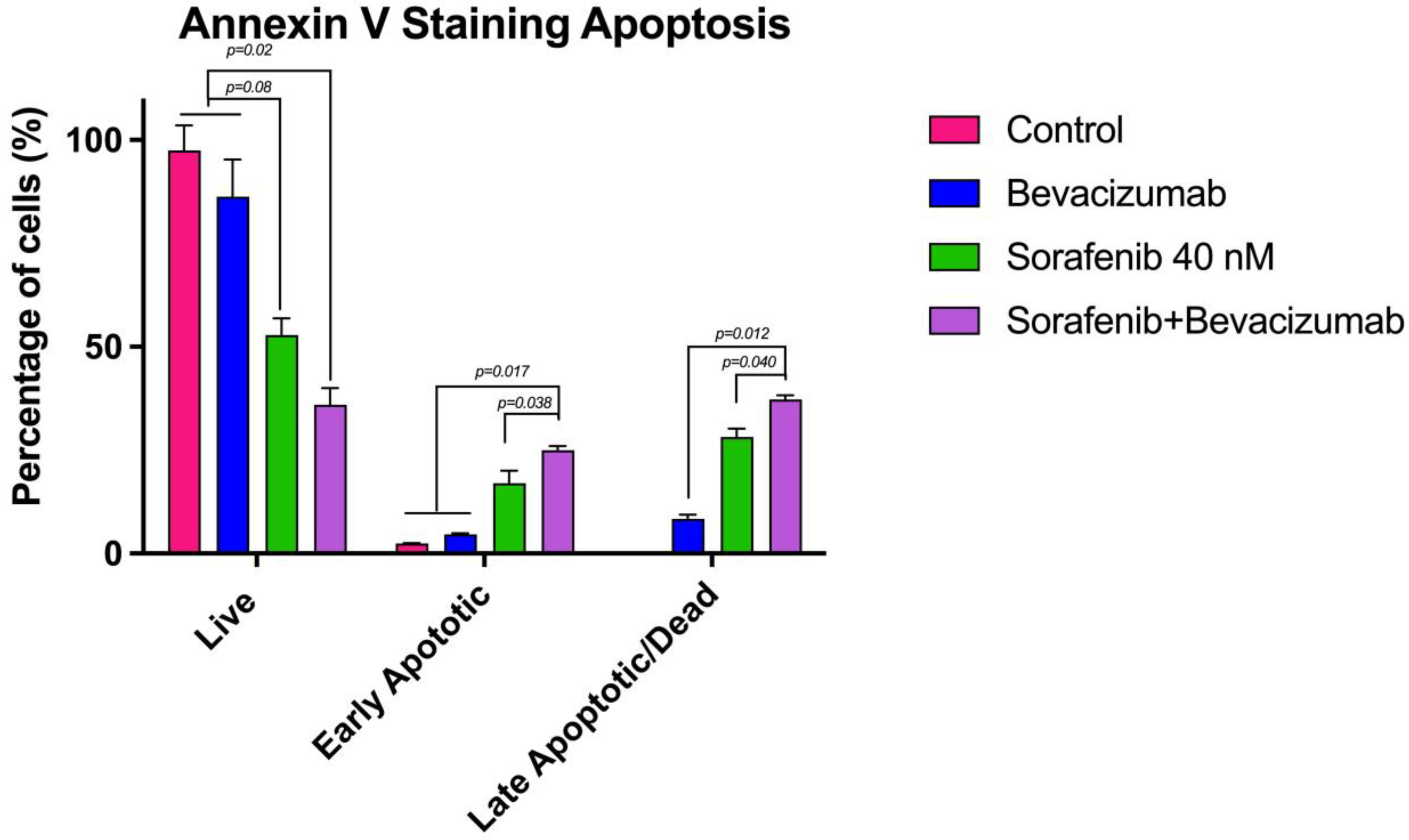
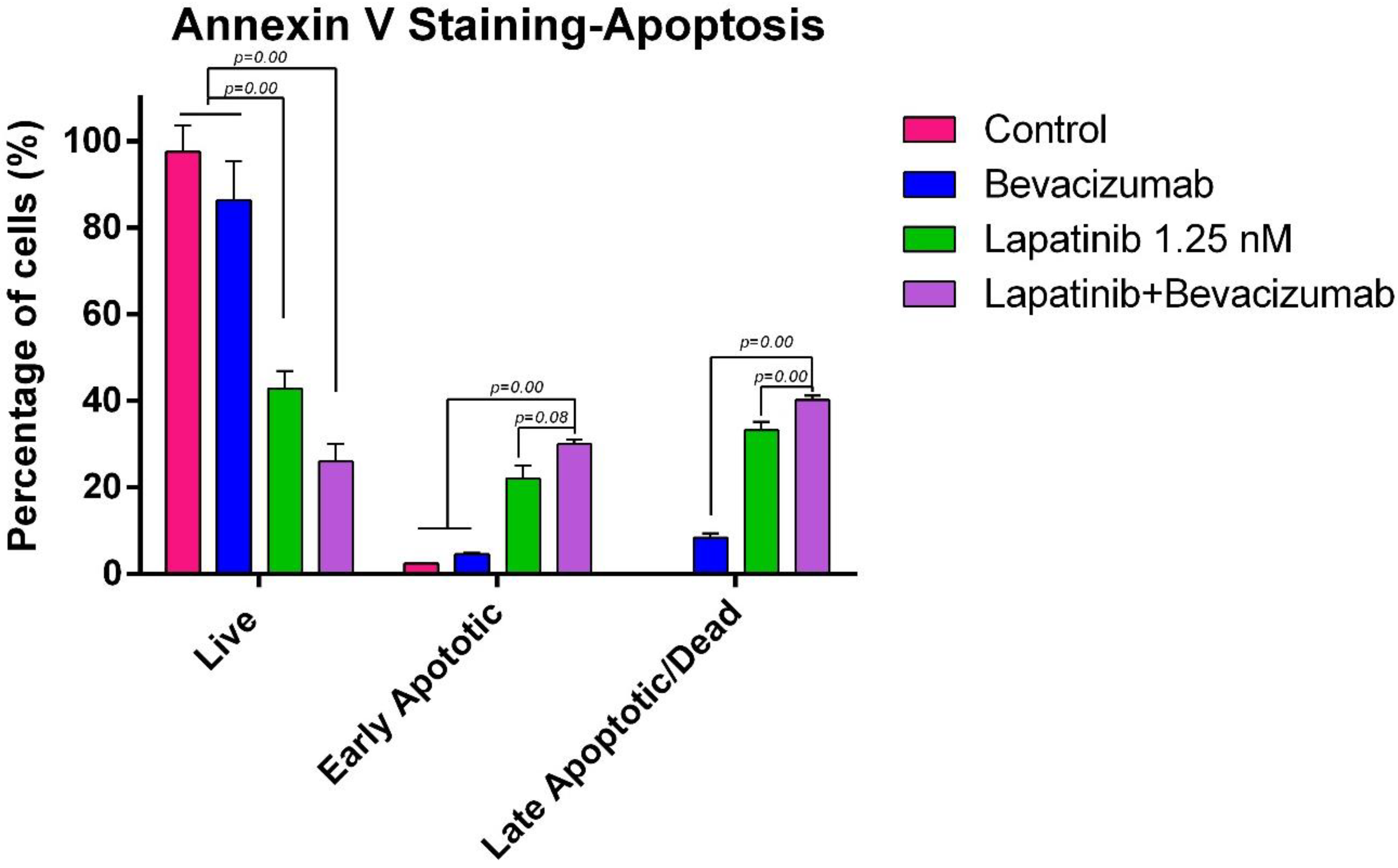
3.8. Evaluation of Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, W.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, T.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Luo, H.; Yu, L. The Burden of Thyroid Cancer and Its Association with National Development Levels in Asia: Evidence from 47 Countries (1990–2021). Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1632221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, J.; Are, C.; Wenos, C.D. Thyroid Cancer: Global Burden and Trends. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, J.D.; Donahue, R.N.; Marté, J.L.; Gramza, A.W.; Bilušić, M.; Rauckhorst, M.; Cordes, L.M.; Merino, M.J.; Dahut, W.L.; Schlom, J.; et al. A Case Report of Sequential Use of a Yeast-CEA Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine and Anti-PD-L1 Inhibitor in Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavi, B. A Prospective Study on Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid with Possible Clinical, Cytological and Histopathological Correlation. Saudi J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izenstein, B.Z. Endocrinology and Metabolism. JAMA 1996, 275, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, D.; Führer-Sakel, D.; Soares, P.; Álvarez, C.V.; Fugazzola, L.; Netea-Maier, R.T.; Jarząb, B.; Kozaric, M.; Bartès, B.; Schuster-Bruce, J.; et al. Tackling Thyroid Cancer in Europe—The Challenges and Opportunities. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakos, M.; Paraskeva, P.; Stefanaki, C.; Katsaronis, P.; Lazaris, A.C.; Safioleas, K.; Kontzoglou, K. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: The Third Most Common Thyroid Cancer Reviewed. Oncol. Lett. 2010, 2, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Du, L. A Rapidly Increasing Trend of Thyroid Cancer Incidence in Selected East Asian Countries: Joinpoint Regression and Age-Period-Cohort Analyses. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, R.; Basnayake, O.; Jayarajah, U.; Seneviratne, S. Management of Medullary Carcinoma of the Thyroid: A Review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Hu, M.I.; Gagel, R.F. Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, E.; Sapalidis, K.; Chatzinikolaou, F.; Kesisoglou, I. Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Molecular Factors, Management and Treatment. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2021, 61, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, C.; Hogan, J.; Raygada, M.; Thomas, B.J.; Akshintala, S.; Glod, J.; Rivero, J.D. Update on Targeted Therapy in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 708949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Gónzález, A.; Califano, I.; Concepción-Zavaleta, M.J.; Pitoia, F.; Salgado, S.A. Systemic Therapies for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: State of the Art. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 16, 20420188251336091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, J.; Stewart, S.D.; Mochel, J.P.; Veluvolu, S.M.; Khanna, C.; Fenger, J.M. Pharmacokinetic Exposures Associated With Oral Administration of Sorafenib in Dogs With Spontaneous Tumors. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 888483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brose, M.S.; Nutting, C.M.; Jarzab, B.; Elisei, R.; Siena, S.; Bastholt, L.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Pacini, F.; Paschke, R.; Shong, Y.K.; et al. Sorafenib in Radioactive Iodine-Refractory, Locally Advanced or Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.S.; Jesus, T.T.; Cardoso, L.; Soares, P.; Vinagre, J. Personalized Medicine in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Broad Review of Emerging Treatments. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilli, L.; Dalmiglio, C.; Pilli, T.; Barbato, F.; Maino, F.; Capezzone, M.; Cartocci, A.; Castagna, M.G. Improvement of Overall Survival Using TKIs as Salvage Therapy in Advanced Thyroid Carcinoma: Real-Life Data on a Single Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunti, S.; Antonelli, A.; Amorosi, A.; Santarpia, L. Cellular Signaling Pathway Alterations and Potential Targeted Therapies for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 803171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisby, A.; Carlson, R.D.; Baybutt, T.R.; Weindorfer, M.; Snook, A.E. Evaluation of CAR-T Cell Cytotoxicity: Real-Time Impedance-Based Analysis. Methods Cell Biol. 2022, 167, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Guo, H.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Jia, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; et al. Osimertinib in Combination with Anti-Angiogenesis Therapy Presents a Promising Option for Osimertinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, R.; Hemmatabadi, M.; Motiee-Langroudi, M.; Sohrabi, H.; Saffar, H.; Jafari, M. Association of BRAF Mutation with Treatment Response and Prognostic Factors in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, A.; Pieroni, E.; Marrama, E.; Bruschini, L.; Ferrari, M.; Scioti, G.; Aprile, V.; Guarracino, F.; Ambrosini, C.E.; Molinaro, E.; et al. Management of Patients with Extensive Locally Advanced Thyroid Cancer: Results of Multimodal Treatments. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 47, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Zhong, L. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Genetic Roles, Targeted Therapy, and Immunotherapy. Genes Dis. 2024, 12, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, L.; Matrone, A. Multikinase and Highly Selective Kinase Inhibitors in the Neoadjuvant Treatment of Patients with Thyroid Cancer. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2025, 6, 1002291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Yang, X. Exploration of the Use of Natural Compounds in Combination with Chemotherapy Drugs for Tumor Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlomagno, F.; Anaganti, S.; Guida, T.; Salvatore, G.; Troncone, G.; Wilhelm, S.M.; Santoro, M. BAY 43-9006 Inhibition of Oncogenic RET Mutants. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Whang, E.E.; Lorch, J.H.; Ruan, D.T. Autophagic Activation Potentiates the Antiproliferative Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Surgery 2012, 152, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.W.; Shah, M.H.; Agarwal, K.; McCarty, S.K.; Koo, B.S.; Brendel, V.J.; Wang, C.; Porter, K.; Jarjoura, D.; Saji, M.; et al. Sorafenib and Mek Inhibition Is Synergistic in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in Vitro. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 19, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Golubovskaya, V.M.; Conroy, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Cance, W.G. FAK Inhibition with Small Molecule Inhibitor Y15 Decreases Viability, Clonogenicity, and Cell Attachment in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines and Synergizes with Targeted Therapeutics. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7945–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Wheler, J.; Naing, A.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Ye, L.; Waguespack, S.G.; Hernandez, M.; El Naggar, A.K.; Bidyasar, S.; et al. Inhibition of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and RET Kinase Pathways with the Combination of the Multikinase Inhibitor Sorafenib and the Farnesyltransferase Inhibitor Tipifarnib in Medullary and Differentiated Thyroid Malignancies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.; Nankivell, M.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Kristensen, G.; Elit, L.; Stockler, M.; Hilpert, F.; Cervantes, A.; Brown, J.; Lanceley, A.; et al. Standard Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab in Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Quality-of-Life Outcomes from the International Collaboration on Ovarian Neoplasms (ICON7) Phase 3 Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Tan, L.; Siu, K.T.H.; Guan, X. Exploring Treatment Options in Cancer: Tumor Treatment Strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy 2024, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, T.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Bie, J.; Luo, Y. Current Status, Hotspots, and Future Directions of Research on the Treatment of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Evaluation. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benekli, M.; Yalcin, S.; Ozkan, M.; Elkiran, E.T.; Sevinc, A.; Cabuk, D.; Coskun, H.S.; Oksuzoglu, B.; Bayar, B.; Akbulat, A.; et al. Efficacy of Sorafenib in Advanced Differentiated and Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Experience in a Turkish Population. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altun, G.; Yönem, Ö. Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110607
Altun G, Yönem Ö. Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(11):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110607
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltun, Gülşah, and Özlem Yönem. 2025. "Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells" Current Oncology 32, no. 11: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110607
APA StyleAltun, G., & Yönem, Ö. (2025). Cytotoxic Effects of Sorafenib, Lapatinib, and Bevacizumab, Alone and in Combination, on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells. Current Oncology, 32(11), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110607




