Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
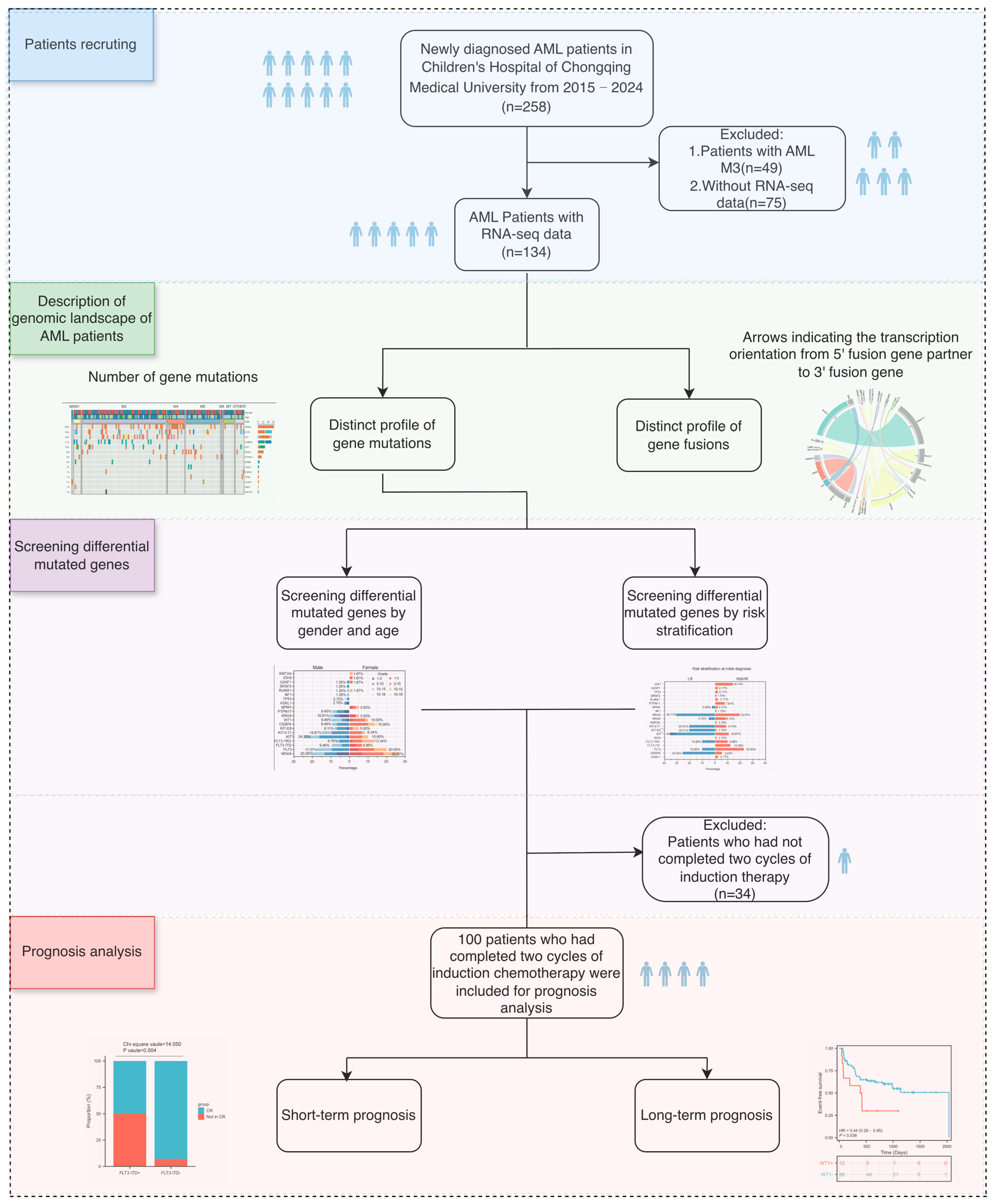
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
2.2. Classic Cytogenetic and Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) Analysis
2.3. Risk Stratification of pAML Patients
2.4. Treatment Protocol
2.5. Definition and Outcome
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and Analysis
2.7. Classification Criteria for Level 1–3 Fusion Genes and Mutated Genes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Gene Fusions Identified in Pediatric AML Patients
3.3. Gene Mutation Landscape in Pediatric AML Patients
3.3.1. Summary Mutation Profile
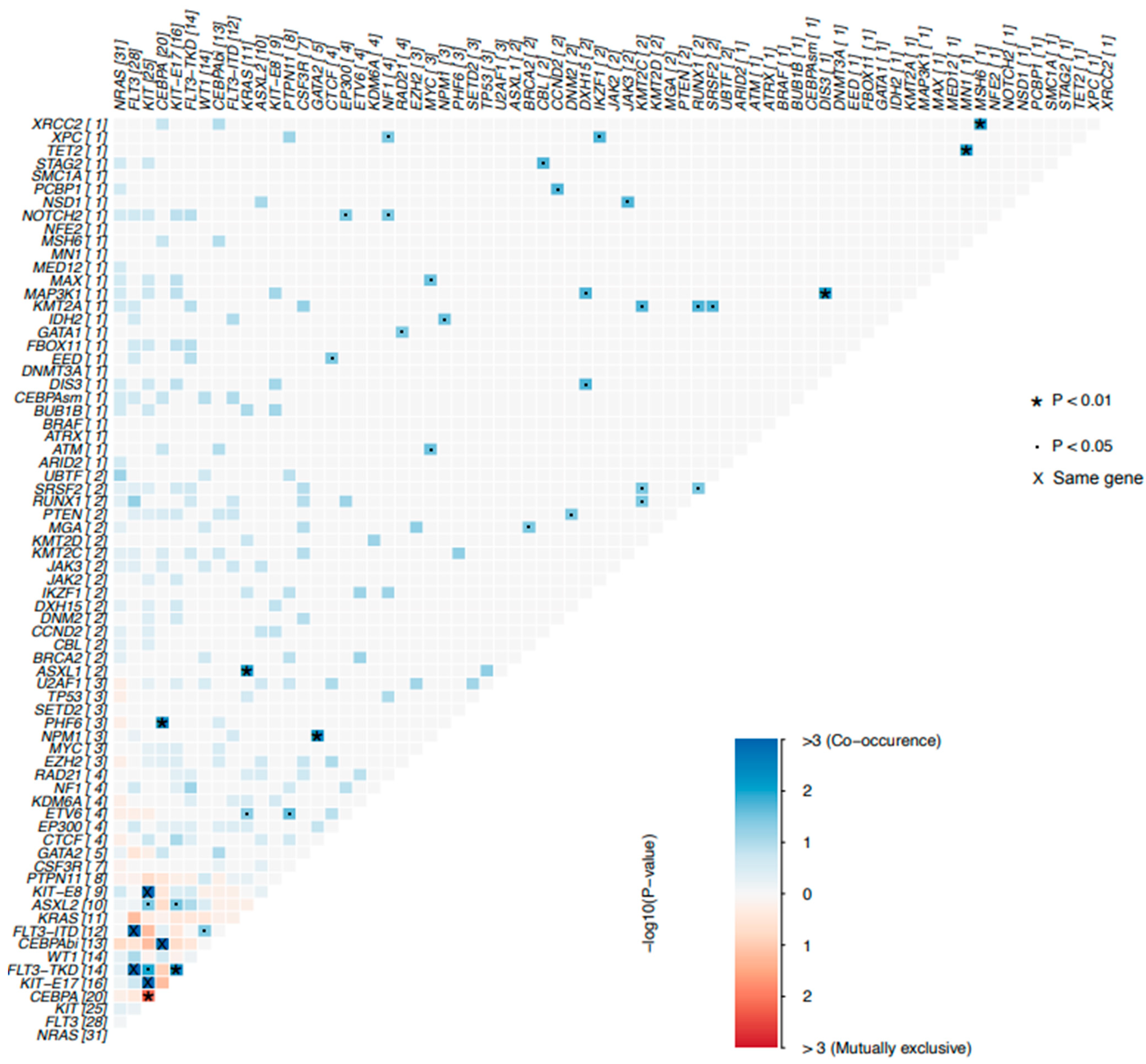
3.3.2. Co-Mutation Profiles in Pediatric AML Patients
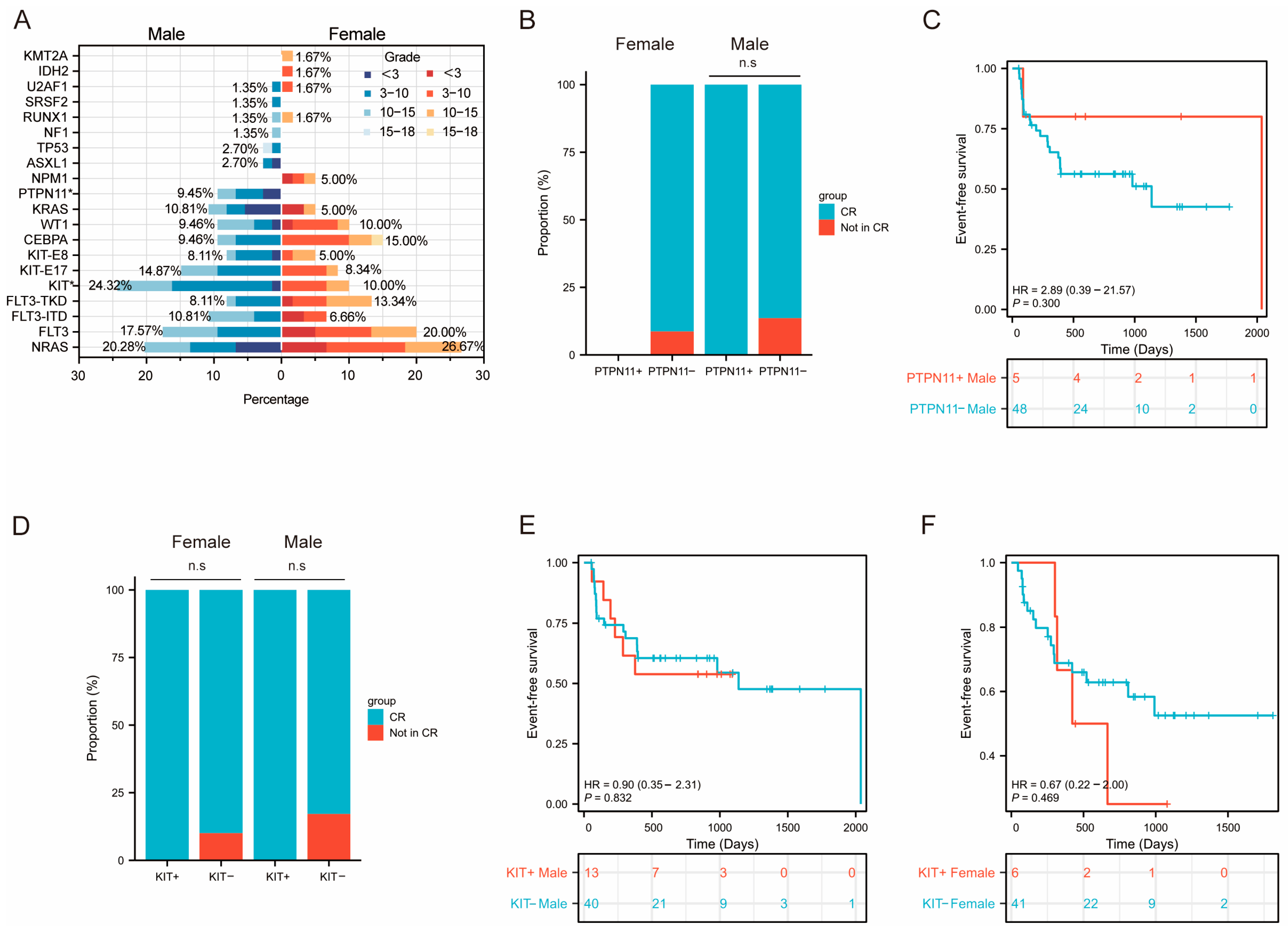
3.3.3. Sex-Related and Risk-Stratification-Related Mutational Profile
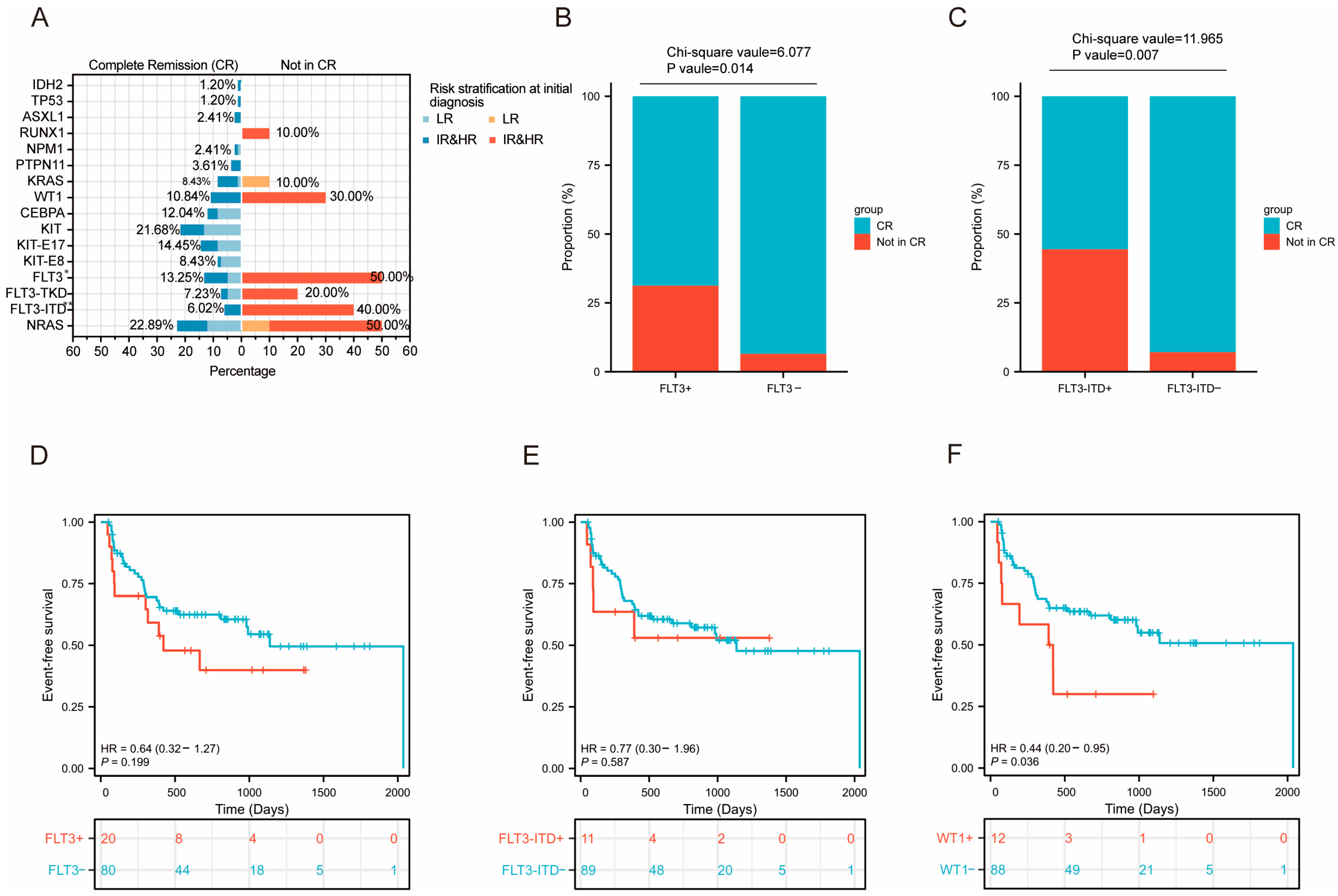
3.3.4. Prognosis Analysis of Differentially Mutated Genes
3.4. Prognosis Analysis of Level 1 Mutated Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmeister, L.M.; Suttorp, J.; Walter, C.; Antoniou, E.; Behrens, Y.L.; Göhring, G.; Awada, A.; von Neuhoff, N.; Reinhardt, D.; Schneider, M. Panel-Based RNA Fusion Sequencing Improves Diagnostics of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, G.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Socioeconomic Inequalities in Cancer Incidence and Access to Health Services among Children and Adolescents in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet 2022, 400, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, G.; Tasian, S.K. Relapsed Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: State-of-the-Art in 2023. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizsán, S.; Péterffy, B.; Egyed, B.; Nagy, T.; Sebestyén, E.; Hegyi, L.L.; Jakab, Z.; Erdélyi, D.J.; Müller, J.; Péter, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing–Based Genomic Profiling of Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 25, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gawad, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Rusch, M.C.; John, E.; et al. Pan-Cancer Genome and Transcriptome Analyses of 1,699 Paediatric Leukaemias and Solid Tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri, H.; Farrar, J.E.; Triche, T.; Ries, R.E.; Lim, E.L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Ma, Y.; Moore, R.; Mungall, A.J.; Marra, M.A.; et al. The Molecular Landscape of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Reveals Recurrent Structural Alterations and Age-Specific Mutational Interactions. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, Z.J.; Chen, X.; Gedman, A.L.; Boggs, K.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Radtke, I.; Chao, J.R.; Walsh, M.P.; Song, G.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Core-Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemias. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Gönen, M.; Figueroa, M.E.; Fernandez, H.; Sun, Z.; Racevskis, J.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Dolgalev, I.; Thomas, S.; Aminova, O.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Integrated Genetic Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Rao, J.; Hu, W.; Cui, B.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Distinct Genomic Landscape of Chinese Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Impacts Clinical Risk Classification. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, R.J.; Moore, S.; Chia, N. ISCN 2024—An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (2024). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2024, 164, 1–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Toruner, G.A.; Tang, G.; Cameron Yin, C.; Wang, W.; Hu, S.; Thakral, B.; Wang, S.A.; Miranda, R.N.; Khoury, J.D.; et al. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with Insertion-Derived BCR-ABL1 Fusion: Redefining Complex Chromosomal Abnormalities by Correlation of FISH and Karyotype Predicts Prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.J.; Bagg, A.; Cooley, L.D.; Dewald, G.W.; Hirsch, B.A.; Jacky, P.B.; Rao, K.W.; Rao, P.N. Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Committee; American College of Medical Genetics Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee Guidance for Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization Testing in Hematologic Disorders. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Diagnosis and Management of Adult Central Nervous System Leukemia. Blood Sci. 2023, 5, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, A.; Liu, W.; Xiong, H.; Liang, C.; Fang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Shao, J.; Yu, H.; et al. Homoharringtonine-Based Induction Regimen Improved the Remission Rate and Survival Rate in Chinese Childhood AML: A Report From the CCLG-AML 2015 Protocol Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4881–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrums, E.J.M.; Smith, J.L.; Harmon, L.; Ries, R.E.; Wang, Y.C.J.; Alonzo, T.A.; Menssen, A.J.; Chisholm, K.M.; Leonti, A.R.; Tarlock, K.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular and Clinical Characterization of NUP98 Fusions in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2044–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T.A.; Larson Gedman, A.; Zhang, J.; Koss, C.S.; Marada, S.; Ta, H.Q.; Chen, S.C.; Su, X.; Ogden, S.K.; Dang, J.; et al. An Inv(16)(P13.3q24.3)-Encoded CBFA2T3-GLIS2 Fusion Protein Defines an Aggressive Subtype of Pediatric Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshinchi, S.; Stirewalt, D.L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Zhang, Q.; Sweetser, D.A.; Woods, W.G.; Bernstein, I.D.; Arceci, R.J.; Radich, J.P. Activating Mutations of RTK/Ras Signal Transduction Pathway in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2003, 102, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rau, R.; Brown, P. Nucleophosmin (NPM1) Mutations in Adult and Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: Towards Definition of a New Leukaemia Entity. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 27, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Xing, H.; Sun, H.; Sun, L.; Wan, D.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; et al. Gene Mutational Analysis by NGS and Its Clinical Significance in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Dan, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, H.; He, R.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, N.; Niu, B.; Xu, S.; et al. Genomic Mutation Patterns and Prognostic Value in de Novo and Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Multicenter Study from China. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 155, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, C.; Teichler, S.; Millahn, A.; Stiewe, T.; Krause, M.; Stabla, K.; Ross, P.; Huynh, M.; Illmer, T.; Mernberger, M.; et al. Oncogenic NRAS Primes Primary Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells for Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaburagi, T.; Yamato, G.; Shiba, N.; Yoshida, K.; Hara, Y.; Tabuchi, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ohki, K.; Sotomatsu, M.; Arakawa, H.; et al. Clinical Significance of RAS Pathway Alterations in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2022, 107, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, T.J.; Ding, L.; Walter, M.J.; McLellan, M.D.; Lamprecht, T.; Larson, D.E.; Kandoth, C.; Payton, J.E.; Baty, J.; Welch, J.; et al. DNMT3A Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Loghavi, S. Acute Myeloid Leukemia with RUNX1::CBFA2T3 Fusion. Blood 2025, 145, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Beà, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Gutiérrez-Abril, J.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Pérez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-Coding Recurrent Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Frameshift Mutations of a Tumor Suppressor Gene ZNF292 in Gastric and Colorectal Cancers with High Microsatellite Instability. Apmis 2016, 124, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrejon Chavez, F.; Luo, H.; Cifani, P.; Pine, A.; Chu, K.L.; Joshi, S.; Barin, E.; Schurer, A.; Chan, M.; Chang, K.; et al. RNA Binding Protein SYNCRIP Maintains Proteostasis and Self-Renewal of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.P.; Prieto, C.; Amin, E.M.; Chhangawala, S.; Krivtsov, A.; Nieves Calvo-Vidal, M.; Chou, T.; Chow, A.; Minuesa, G.; Mi Park, S.; et al. Functional Screen of MSI2 Interactors Identifies an Essential Role for SYNCRIP in Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells HHS Public Access Author Manuscript. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhu, G.; Wang, C.; Johnson, N.A.; Zhang, Z.; Tirado, C.R.; Xu, Y.; Metang, L.A.; et al. Loss of SYNCRIP Unleashes APOBEC-Driven Mutagenesis, Tumor Heterogeneity, and AR-Targeted Therapy Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1427–1449.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ryu, H.G.; Kang, M.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, D.; Chung, C.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, W.; et al. SYNCRIP Promotes Cell Cycle Progression and Lung Tumorigenesis by Modulating AURKB Translation. Cancer Commun. 2025, 45, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviraghi, M.; Vivori, C.; Pareja Sanchez, Y.; Invernizzi, F.; Cattaneo, A.; Santoliquido, B.M.; Frenquelli, M.; Segalla, S.; Bachi, A.; Doglioni, C.; et al. Tumor Suppressor PNRC 1 Blocks r RNA Maturation by Recruiting the Decapping Complex to the Nucleolus. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e99179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, M.; Nicolet, D.; Mrózek, K.; Yilmaz, A.S.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Larkin, K.T.; Blachly, J.S.; Oakes, C.C.; Buss, J.; Walker, C.J.; et al. Sex-Associated Differences in Frequencies and Prognostic Impact of Recurrent Genetic Alterations in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Alliance, AMLCG). Leukemia 2024, 38, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, M.; Cordeddu, V.; Chang, H.; Shaw, A.; Kalidas, K.; Crosby, A.; Patton, M.A.; Sorcini, M.; Van Der Burgt, I.; Jeffery, S.; et al. Report Paternal Germline Origin and Sex-Ratio Distortion in Transmission of PTPN11 Mutations in Noonan Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Ramos, C.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Kuijjer, M.L.; Paulson, J.N.; Sonawane, A.R.; Fagny, M.; Platig, J.; Glass, K.; Quackenbush, J.; DeMeo, D.L. Sex Differences in Gene Expression and Regulatory Networks across 29 Human Tissues. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, A.M.; Bertrums, E.J.M.; van Roosmalen, M.J.; Hofman, D.A.; Oka, R.; Verheul, M.; Manders, F.; Ubels, J.; Belderbos, M.E.; van Boxtel, R. Mutation Signatures of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Normal Blood Progenitors Associated with Differential Patient Outcomes. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czogała, M.; Czogała, W.; Pawińska-Wąsikowska, K.; Książek, T.; Bukowska-Strakova, K.; Sikorska-Fic, B.; Łaguna, P.; Fałkowska, A.; Drabko, K.; Muszyńska-Rosłan, K.; et al. Characteristics and Outcome of FLT3-ITD-Positive Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Experience of Polish Pediatric Leukemia and Lymphoma Study Group from 2005 to 2022. Cancers 2023, 15, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Ren, J.-G.; Han, X.; Gui, J.; Gong, C.; Tong, W. Depalmitoylation Rewires FLT3-ITD Signaling and Exacerbates Leukemia Progression. Blood 2021, 138, 2244–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollink, I.H.I.M.; Van Den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Zimmermann, M.; Balgobind, B.V.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.C.J.M.; Alders, M.; Willasch, A.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Trka, J.; Baruchel, A.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Wilms Tumor 1 Gene Mutations in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 5951–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Underwood, L.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Wilms’ Tumor (WT1) Gene Mutations Occur Mainly in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and May Confer Drug Resistance. Blood 1998, 91, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampal, R.; Figueroa, M.E. Wilms Tumor 1 Mutations in the Pathogenesis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, T.; Shi, J.; Kang, Y.; Xi, J.; Wang, M.; et al. Dynamic Changes in the Level of WT1 as an MRD Marker to Predict the Therapeutic Outcome of Patients with AML with and without Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Indicators | N (%) | Indicators | N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | AGE | ||
| Female | 60 (44.78) | P50 (P25, P75) | 5.96 (3.42, 11.48) |
| Male | 74 (55.22) | <3 | 32 (23.88%) |
| 3–10 | 60 (44.78%) | ||
| WBC count (× 109/L) | 10–18 | 42 (31.34%) | |
| P50 (P25, P75) | 13.88 (5.55, 46.79) | ||
| 0–50 | 102 (76.12) | FAB classification | |
| 50–100 | 18 (13.43) | M0 | 2 (1.49) |
| ≥100 | 14 (10.45) | M1 | 5 (3.73) |
| M2 | 68 (50.75) | ||
| CNSL | M4 | 14 (10.45) | |
| CNSL1 | 123 (91.79) | M5 | 28 (20.90) |
| CNSL2 | 4 (2.99) | M6 | 1 (0.75) |
| CNSL3 | 7 (5.22) | M7 | 9 (6.72) |
| NA | 7 (5.22) | ||
| Chromosome karyotype | |||
| normal | 34 (25.37) | Number of fusions | |
| abnormal | 89 (66.42) | Level 1 | 5 (7.46) |
| NA | 11 (8.21) | Level 2 | 8 (11.94) |
| Structural chromosomal abnormalities | Level 3 | 54 (80.60) | |
| t(8;21)(q22;q22) | 30 (33.71) | ||
| inv(16)(p13q22) | 7 (7.87) | Number of mutations | |
| t(9;11)(p21;q23) | 7 (7.87) | Level 1 | 16 (2.88) |
| t(6;9)(p23;q34) | 1 (1.12) | Level 2 | 58 (10.45) |
| Other * | 2 (2.25) | Level 3 | 481 (86.67) |
| Risk stratification at initial diagnosis | Final risk stratification | ||
| LR | 39 (29.10) | LR | 14 (10.45) |
| IR | 51 (38.06) | IR | 27 (20.15) |
| HR | 40 (29.85) | HR | 69 (51.49) |
| NA | 4 (2.99) | NA | 24 (17.91) |
| HSCT | |||
| YES | 21 (15.67) | First event | |
| NO | 113 (84.33) | Alive | 66 (49.25) |
| FAB classification of transplanted patients | Relapse | 22 (16.42) | |
| M2 | 9 (42.86) | Death | 9 (6.72) |
| M5 | 9 (42.86) | Failure of induction chemotherapy | 12 (8.96) |
| M7 | 2 (9.52) | Therapy-Related Malignancy | 1 (0.75) |
| NA | 1 (4.76) | NA | 24 (17.91) |
| Numbers | Age (Years), P50 (P25, P75) | Male | FAB (N) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEVEL1 | ||||
| RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | 32 | 6.96 (4.65, 11.77) | 21 | M2(32) |
| KMT2A rearrangement | 29 | 3.5 (2.08, 7.42) | 13 | M2(5), M5(20), M4(3), NA (1) |
| CBFB::MYH11 | 13 | 10.33 (7.42, 12) | 7 | M2(2), M4(9), NA (2) |
| DEK::NUP214 | 1 | 5.67 | 0 | M2(1) |
| NUP98::KDM5A | 1 | 2.67 | 1 | M7(1) |
| LEVEL2 | ||||
| CBFA2T3::GLIS2 | 4 | 1.83 (1.39, 3.31) | 2 | M7(4) |
| FUS::ERG | 4 | 3.21 (2.04, 6.48) | 2 | M5(3), M2(1) |
| NUP98::NSD1 | 2 | 3.38 (1.33, 5.42) | 1 | M2(1), M4(1) |
| DDX3X::MLLT10 | 2 | 7.25 (0.83, 13.67) | 0 | M1(1), M5(1) |
| FUS::FEV | 1 | 3.75 | 1 | M5(1) |
| ZEB2::BCL11B | 1 | 8.08 | 1 | M5(1) |
| PICALM::MLLT10 | 1 | 9.33 | 1 | M0(1) |
| TBC1D15::RAB21 | 1 | 3.58 | 10 | M2(1) |
| Numbers | Age, P50 (P25, P75), /Years | Male | FAB (N) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEVEL1 | ||||
| NRAS | 31 | 7.42 (2.67, 10.88) | 15 | M1(1), M2(15), M4(10), M5(2), M7(1), NA (2) |
| FLT3 | 25 | 9.42 (5.25, 12.33) | 13 | M1(2), M2(12), M4(5), M5(4), NA (2) |
| FLT3-ITD | 12 | 7.58 (5.04, 11.98) | 8 | M1(2), M2(5), M4(1), M5(2), NA (2) |
| FLT3-TKD | 14 | 9.13 (5.42, 12.33) | 6 | M2(7), M4(4), M5(3) |
| KIT | 24 | 9.5 (5.73, 11.69) | 18 | M2(19), M4(5) |
| KIT-E17 | 16 | 9.5 (5.73, 12.35) | 11 | M2(9), M4(2) |
| KIT-E8 | 9 | 8.50 (3.83, 10.92) | 6 | M2(6), M4(3) |
| CEBPA | 14 | 7.88 (5.54, 12.17) | 6 | M1(2), M2(12) |
| CEBPAbi | 13 | 8.08 (6.42,13.42) | 5 | M1(1), M2(12) |
| CEBPAsm | 1 | 5.25 | 1 | M1(1) |
| WT1 | 13 | 7.42 (4.67, 11.58) | 7 | M1(2), M2(7), M4(1), M5(2), NA (1) |
| KRAS | 11 | 2.58 (1.83, 8.63) | 8 | M2(3), M4(2), M5(5),NA(1) |
| PTPN11 | 7 | 5.42 (2.83, 9.08) | 7 | M0(1), M2(2), M5(3), M6(1) |
| NPM1 | 3 | 9.67 (6.25, 11.79) | 0 | M1(1), M2(2) |
| RUNX1 | 2 | 13.67 (12.58, 14.75) | 1 | M2(1), NA (1) |
| U2AF1 | 2 | 6.38 (3.42, 9.33) | 1 | M5(1), M0(1) |
| ASXL1 | 2 | 3.96 (1.67, 6.25) | 2 | M5(2) |
| TP53 | 2 | 11.09 (6.25, 15.92) | 2 | M5(1), NA (1) |
| IDH2 | 1 | 9.67 | 0 | M1(1) |
| KMT2A | 1 | 14.75 | 0 | M2(1) |
| SRSF2 | 1 | 9.83 | 1 | M2(1) |
| NF1 | 1 | 12.75 | 1 | M0(1) |
| LEVEL2 | ||||
| ASXL2 | 10 | 5.25 (4.35, 9.54) | 5 | M2(10) |
| CSF3R | 7 | 12.67 (7, 12.83) | 3 | M2(7) |
| CEBPA | 6 | 11.46 (4.56, 13.23) | 1 | M1(2), M2(1), NA (3) |
| GATA2 | 5 | 8.08 (7.67, 13.92) | 1 | M2(4), M5(1) |
| EP300 | 4 | 13.33 (11.65, 14.35) | 3 | M2(2), M4(1), NA (1) |
| RAD21 | 4 | 4.38 (2.85, 6.65) | 3 | M2(3), M7(1) |
| CTCF | 4 | 4.17 (3.75, 6.54) | 3 | M2(2), M5(2) |
| ETV6 | 4 | 3.42 (2.96, 4.17) | 3 | M2(2), M5(1), M6(1) |
| KDM6A | 4 | 6.71 (4.83, 9.48) | 3 | M5(2), M2(2) |
| FLT3 | 4 | 8.29 (3.21, 12.90) | 1 | M5(3), NA (1) |
| SETD2 | 3 | 3.42 (3.08 5.42) | 0 | M5(3) |
| MYC | 3 | 8.42 (5.25, 9.13) | 2 | M2(1), M4(1), M7(1) |
| PHF6 | 3 | 13.67 (10.04, 14.58) | 1 | M1(1), M2(2) |
| EZH2 | 3 | 7.42 (6.67, 9.92) | 2 | M2(3) |
| NF1 | 3 | 12.33 (10.58, 14.13) | 3 | M4(2), NA2(1) |
| DXH15 | 2 | 8 (3.67, 12.33) | 1 | M2(2) |
| IKZF1 | 2 | 7.67 (2.58, 12.75) | 1 | M0(1), M2(1) |
| JAK2 | 2 | 7.67 (0.92, 14.42) | 2 | M2(1), M7(1) |
| JAK3 | 2 | 3.34 (2.42, 4.25) | 0 | M2(1), NA (1) |
| DNM2 | 2 | 8.25 (3.83, 12.67) | 1 | M2(2) |
| CBL | 2 | 8.17 (5.25, 11.08) | 2 | M2(2) |
| UBTF | 2 | 12.25(11.17, 13.33) | 2 | M2(2) |
| PTEN | 2 | 8.96 (3.83, 14.08) | 2 | M2(2) |
| CCND2 | 2 | 7.08 (3.83, 10.33) | 2 | M2(2) |
| KMT2D | 2 | 12.05 (11.67, 12.42) | 1 | M2(1), M5(1) |
| KMT2C | 2 | 10.59 (6.42, 14.75) | 1 | M2(2) |
| MGA | 2 | 5.79 (5.67, 5.92) | 0 | M2(2) |
| BRCA2 | 2 | 5.54 (5.42, 5.67) | 1 | M2(1), M6(1) |
| MN1 | 1 | 1.25 | 1 | M2(1) |
| TET2 | 1 | 1.25 | 1 | M2(1) |
| ATM | 1 | 8.42 | 0 | M2(1) |
| MAP3K1 | 1 | 3.67 | 0 | M2(1) |
| NSD1 | 1 | 4.25 | 0 | M2(1) |
| NOTCH2 | 1 | 8.83 | 1 | M4(1) |
| ARID2 | 1 | 2.75 | 1 | M4(1) |
| XPC | 1 | 12.75 | 1 | M0(1) |
| DIS3 | 1 | 3.67 | 0 | M2(1) |
| DNMT3A | 1 | 3.58 | 0 | M5(1) |
| EED | 1 | 3.75 | 1 | M5(1) |
| BRAF | 1 | 3.83 | 1 | M2(1) |
| BUB1B | 1 | 2.58 | 1 | M4(1) |
| MED12 | 1 | 2.08 | 1 | M4(1) |
| MSH6 | 1 | 8.33 | 0 | M1(1) |
| NFE2 | 1 | 3.50 | 0 | M2(1) |
| ATRX | 1 | 10.08 | 0 | NA (1) |
| FBOX11 | 1 | 5.42 | 1 | M2(1) |
| GATA1 | 1 | 2.17 | 1 | M7(1) |
| MAX | 1 | 9.83 | 1 | M4(1) |
| PCBP1 | 1 | 10.33 | 1 | M2(1) |
| STAG2 | 1 | 5.25 | 1 | M2(1) |
| SMC1A | 1 | 4.33 | 1 | M5(1) |
| XRCC2 | 1 | 8.33 | 0 | M1(1) |
| U2AF1 | 1 | 12.42 | 1 | M2(1) |
| PTPN11 | 1 | 9.33 | 1 | M0(1) |
| SRSF2 | 1 | 14.75 | 0 | M2(1) |
| TP53 | 1 | 2.08 | 0 | M2(1) |
| WT1 | 1 | 9.33 | 1 | M0(1) |
| KIT | 1 | 5.25 | 1 | M2(1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Peng, X.; Shu, W.; Shi, H.; Xiao, L.; Liu, T.; Xiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, J.; et al. Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110605
Huang L, Peng X, Shu W, Shi H, Xiao L, Liu T, Xiang Y, Guo Y, Guan X, Li J, et al. Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(11):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110605
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lan, Xingyu Peng, Wenjing Shu, Hui Shi, Li Xiao, Tao Liu, Yan Xiang, Yuxia Guo, Xianmin Guan, Jiacheng Li, and et al. 2025. "Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China" Current Oncology 32, no. 11: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110605
APA StyleHuang, L., Peng, X., Shu, W., Shi, H., Xiao, L., Liu, T., Xiang, Y., Guo, Y., Guan, X., Li, J., & Yu, J. (2025). Unveiling the Genetic Mosaic of Pediatric AML: Insights from Southwest China. Current Oncology, 32(11), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110605





