Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Roles of Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factors
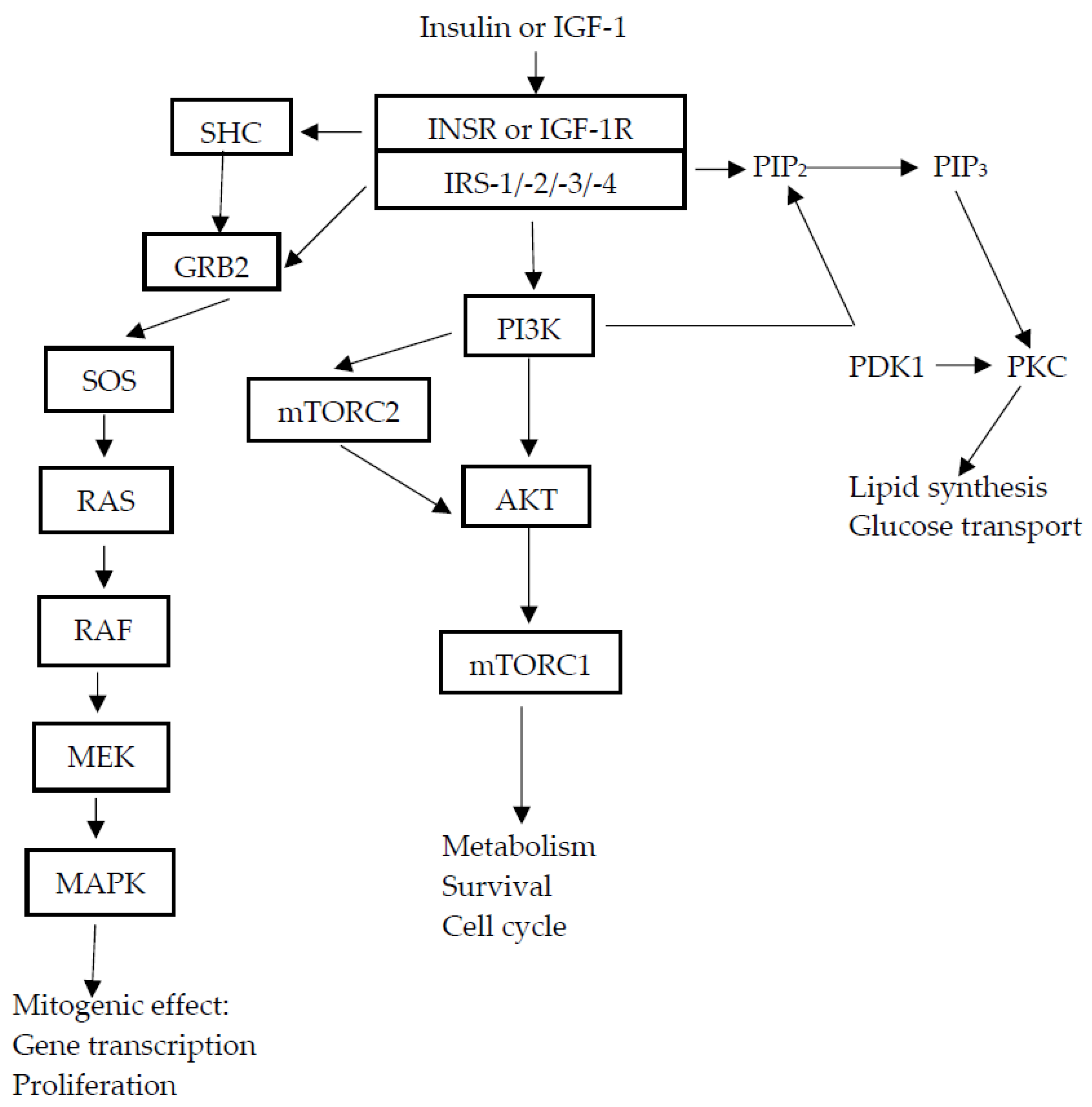
Insulin and IGF Cellular Signaling Pathways
3. Insulin Resistance and Its Pathogeny
3.1. Genetic Factors
3.1.1. Mutations in the Insulin Gene
3.1.2. Mutations in the Intracellular Insulin Signaling System
3.2. Autoimmune Factor
3.3. Environmental Factors
3.3.1. Obesity
3.3.2. Aging
3.3.3. Diseases and Drugs
4. Insulin Resistance and Cancer Mechanisms
4.1. Factors of Insulin Resistance and Selected Cancers
4.1.1. Insulin and IGFs
4.1.2. Obesity
| Factor | Effects of IR |
|---|---|
| Insulin and IGFs | Cancer progression and promotion [1,2], growth stimulus in preneoplastic and neoplastic cells [28], stimulation of cancer growth, and development of solid cancers [122,128,129]. |
| Obesity | There are many controversial results and differences between obtained results, which are still not fully understood. |
| Hyperinsulinemia | Increased cancer cell survival, proliferation, invasion, differentiation, and metastasis [141]. |
4.1.3. Cancers Associated with Obesity
Breast Cancer
Thyroid Cancer (TC)
Colon Cancer
Liver Cancer
Prostate Cancer
4.1.4. Diabetes Mellitus
4.1.5. Cancers Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Pancreatic Cancer
Thyroid Cancer
Breast Cancer
Endometrial Cancer
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC)
Cervical Cancer
Vulvar Cancer
4.1.6. Hyperinsulinemia
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Magrill, J.; de Winter, T.J.J.; Hu, X.; Skovsø, S.; Schaeffer, D.E.; Kopp, J.L.; Johnson, J.D. Endogenous hyperinsulinemia contributes to pancreatic cancer development. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Mao, Y. Daily insulin dose and cancer risk among patients with Type 1 diabetes. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. International Agency for Research on Cancer Handbook Working Group. Body fatness and cancer-viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, B.P.; Siebel, S.; Akingbesote, N.B.; Zhang, X.; Perry, R.J. Insulin and cancer: A tangled web. Biochim. J. 2022, 479, 583–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, C. Identification and validation of MSMB as a critical gene for prostate cancer development in obese people. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanović, M.; Kovačević, S.; Brkljačić, J.; Djordjevic, A. Oxidative stress linking obesity and cancer: Is obesity a “radical trigger” to cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larssen, S.C.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Body fatness associations with cancer: Evidence from recent epidemiological studies and future directions. Metabolism 2022, 137, 155326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidossis, A.; Lan, F.Y.; Hershey, M.S.; Hadkhale, K.; Kales, S.N. Cancer and potential prevention with life style among career firefighters: A narrative review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson-Stuttard, J.; Zhou, B.; Kontis, V.; Bentham, J.; Gunter, M.J. Worldwide burden of cancer attribute to diabetes and high body-mass index: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabet. Endocrinol. 2018, 6, e6–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Knezetic, J.A.; Strömmer, L.; Perment, J.; Larsson, J.; Adrian, T.E. The intracellular mechanism of insulin resistance in pancreatic cancer patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-Yu, E.; Graber, J.M.; Lu, S.-E.; Lin, Y.; Lu-Yao, G.; Tan, X.-L. Effect of metformin and statin use on survival in pancreatic cancer patients: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2595–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.-K.; Su, T.-T.; Si, J.-M.; Sun, L.-M. Metformin is associated with slightly reduced risk of colorectal cancer and moderate survival benefits in diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Buniato, D.; Zambon, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Corrao, G. Cancer risk for patients using thiazolidinediones for Type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Oncologist 2013, 18, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonagiri, P.R.; Shubrook, J.H. Review of associations between Type 2 diabetes and cancer. Clin. Diabet. J. 2020, 38, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallhager, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Hyperinsulinemia in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, L.D.; Mortimer, J.E.; Natarajan, R.; Dietze, E.C.; Seewaldt, V.L. Metabolic health, insulin, and breast cancer: Why oncologists should care about insulin. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, W.; Kulahin, N.; Schluckebier, G.; Ribel, U.; Henderson, H.R.; Tatar, M.; Hansen, B.F.; Svendsen, H.R.; Kiselyov, V.V.; Norgaard, P.; et al. Structural and biological properties of the Drosophila insulin-like peptide 5 show evolutionary conservation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen-Cody, S.O.; Pottohoff, M.J. Hepatokines and metabolism: Deciphering communication from the liver. Mol. Metab. 2020, 44, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Heald, A.H.; Gibson, J.M.; Cruickshauk, J.K.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 and development of glucose intolerance: A prospective observational study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, D.R. The relative roles of growth hormone and IGF-1 in controlling insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Lawrence, M.C.; Sciacca, L.; Frasca, F.; Morrione, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms in physiology and disease: An update view. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 379–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denley, A.; Wallace, J.C.; Cosgrove, L.J.; Forbes, B.E. The insulin receptor isoform exon 11 (IR-A) in cancer and other diseases. A review. Horm. Metabol. Res. 2003, 35, 778–785. [Google Scholar]
- Escribano, O.; Beneit, N.; Rubio-Longás, C.; López-Pastor, A.R.; Gómez-Hernández, A. The role of insulin receptor isoforms in diabetes and its metabolism and vascular complications. J. Diab. Res. 2017, 2017, 1403206. [Google Scholar]
- Djiogue, S.; Nwaba Kamdje, A.H.N.; Vecchio, L.; Kipanyula, M.J.; Farahna, M.; Aldebasi, Y.; Etet, P.F.S. Insulin resistance and cancer: The role of insulin and IGFs. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R1–R17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeldi, A.M.; Filippaios, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Severe insulin resistance syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriaans, G.; de Jong, S.; Gietema, J.A.; Lefrandt, J.D.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Jalving, M. Cancer-drug induced insulin resistance: Innocent bystander or unusual. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, R.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, P. Rethinking the relationship between insulin and cancer. Trends. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, C.-S. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, V.; Milluzzo, A.; Scalisi, N.M.; Vigneri, P.; Sciacca, L. Insulin receptor isoforms in cancer. Int. J. Med. 2018, 19, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallhager, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Minireview: IGF, insulin and cancer. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2546–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Cai, W.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Steger, M.; Batista, T.M.; Pan, H.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Mann, M.; Kahn, C.R. Distinct signaling by insulin and IGF-1 receptors and their extra- and intracellular domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019474118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Yee, D. Disrupting insulin and IGF receptor function in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancaro, A. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga, M.; Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y.; Blithe, D.L.; White, M.F.; Kahn, C.R. Characterization of the insulin receptor kinase purified from human placental membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 10973–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailes, E.M.; Navé, B.T.; Soos, M.A.; Orr, S.R.; Hayward, A.C.; Siddle, K. Insulin receptor/IGF-I receptor hybrids are widely distributed in mammalian tissues: Quantitation of individual receptor species by selective immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Biochem. J. 1997, 327, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, D.; Halje, M.; Nordin, M.; Engström, W. Insulin-like growth factor 2 in development of disease: A mini review. Gerontology 2013, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Song, B.; Cui, Z.; Chen, G.; Yu, Z.; Song, B. Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) in fibrosis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Jones, E.Y.; Forbes, B.E. Interactions of IGF-II with the IGF2R/cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor mechanism and biological outcomes. Vit. Hormon 2009, 80, 699–719. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.; Park, S.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.I. Association between insulin resistance and luminal B subType breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Medicine 2016, 95, e2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.M.; Pennings, N. Insulin Resistance; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.J.; Huang, K.; Xu, B.; Hu, S.-Q.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.-C.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Diabetes-associated mutations in human insulin: Crystal structure and photo-cross-linking studies of A-chain variant insulin Wakayama. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataul Islam, M.; Bhayye, S.; Adeniyi, A.A.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Pillay, T.S. Diabetes mellitus caused by mutations in human insulin: Analysis of impaired receptor binding of insulins Wakayama, Los Angeles and Chicago using pharmacoinformatics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.J.; Hammer, R.E.; Chan, S.J.; Swift, H.H.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Steiner, D.F. A mutant human proinsulin is secreted from islets of Langerhans in increased amounts via an upregulated pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8943–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, F. Case report: A Chinese family of Type A insulin resistance syndrome with diabetes mellitus, with a novel heterozygous missensemutation of the insulin receptor gene. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 895424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, R.K.; Savage, D.B.; Cochran, E.K.; Gorden, P.; O’Rahilly, S. Genetic syndromes of severe insulin resistance. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 498–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bock, M.; Hayes, I.; Semple, R. Donohue syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1416–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosavi, S.; Sangamesh, S.; Rao, A.S.; Patel, S.; Hodigere, V.C. Insulin, insulin everywhere: A rare case report of Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome. Cureus 2021, 13, e13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakura, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Kuzuya, T. Hyperinsulinemia, acanthosis nigricans and normal insulin binding in young women—Evidence for familial occurrence of post-binding defect in insulin action. J. Japan Diab. Soc. 1988, 31, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, F.; Taira, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Makino, H.; Sasaki, N. Familial Type C syndrome of insulin resistance and short stature with possible autosomal dominant transmission. Endocrinol. Japon 1989, 36, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, D.L.; Stevenson, M.; Steenkamp, D. Type B insulin resistance syndrome. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 23, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioglu, E.; Andewelt, A.; Diabo, C.; Bell, M.; Taylor, S.I.; Garden, P. Clinical course of the syndrome of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor (Type B insulin resistance): A 28-year perspective. Medicine 2002, 81, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flier, J.S.; Bar, R.S.; Muggeo, M.; Kahn, C.R.; Roth, J.; Gorden, P. The involving clinical course of patients with insulin receptor autoantibodies: Spontaneous remission or receptor proliferation with hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 1978, 47, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, C.R.; Wang, G.; Lee, K.Y. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3990–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.H.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosslink. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Hudis, C.A.; Dannenberg, A.J. Obesity and cancer: Local and systemic mechanisms. Ann. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.M.; Halter, J.B. Aging and insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E7–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.J.; Viljoen, A.; Sinclair, A. Insulin resistance: A risk marker for disease and disability in the older person. Diabetes Med. 2013, 30, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Befroy, D.; Dufour, S.; Dziura, J.; Ariyan, C.; Rothman, D.L.; DiPietro, L.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science 2003, 300, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, H.A.; Kahn, C.R. New mechanisms of glucocorticoids-induced insulin resistance: Make no bones about it. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3854–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; An, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, H.; Lian, F. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1149239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Støy, J.; De Franco, E.; Ye, H.; Park, S.-Y.; Bell, G.I.; Hattersley, A.T. In celebration of a century with insulin—Update of insulin gene mutations in diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushi, R.; Hirota, Y.; Ogawa, W. Insulin resistance and exaggerated insulin sensitivity triggered by single gene mutations in insulin signaling pathway. Diabetol. Intern. 2021, 12, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.F.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin action at a molecular level—100 years of progress. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine Genetics Home Reference. Type A Insulin Resistance Syndrome. 2019. Available online: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov//condition/type-a-insulin-resistance-syndrome#statistics. (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Yoshimasa, Y.; Seino, S.; Whittaker, J.; Takako, O.; Kosaki, A.; Kuzuya, H.; Imura, H.; Bell, G.I.; Steiner, D.F. Insulin-resistant diabetes due to a point mutation that prevents insulin proreceptor processing. Science 1988, 240, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Bevins, C.L.; Cama, A.; Ojomaa, K.; Marcus-Samuek, B.; Kadowaki, H.; Beitz, C.; McKeon, C.; Taylor, S.J. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in patients with extreme insulin resistance. Science 1988, 240, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, C.; Fang, T.; Chen, D.; Chen, K.; Quan, H. Type A insulin resistance syndrome misdiagnosed as polycystic ovary syndrome: A case report. J. Mol. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, A.V.; Scaglia, P.; Gryngarten, M.G.; Gutiérez, M.; Arcari, A.J.; Suarez, L.; Ballerini, M.G.; Valinotto, L.; Natale, M.I.; Del Toro Camargo, K.Y.; et al. Type A Insulin Resistance Syndrome—Novel insulin receptor gene mutation and familiar phenotypic variability. Int. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 5, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, W.L.; Uchida, J. Leprechaunism: A euphemism for a rare familial disorder. J. Pediatr. 1954, 45, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Utsunomiya, A.; Kagawa, R.; Funata, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Hamaki, K.; Kanzaki, S. Leprechaunism (Donohue syndrome): A case bearing novel compound heterozygous mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perge, K.; Massoud, M.; Gauthier-Moulinier, H.; Lascols, O.; Pangaud, N.; Villanueva, C.; Pons, L. Intrauterine growth restriction and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy as prenatal ultrasound findings in a case of leprechaunism. Mol. Syndromol. 2020, 11, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirel, B.; Bozdaǧ, Ö.; Köşger, P.; Aydoǧdu, S.D.; Alincak, E.; Tekin, N. A case of Donohue syndrome “Leprechaunism” with a novel mutation in the insulin receptor gene. Turk. Pediatri Ars. 2017, 52, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanfa, D.; Mohamadi, F.; Moskapil, S.R. Rabson Mendenhall syndrome; a case report and review of literature. Int. J. Environ. Chem. 2020, 4, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, W.F.; Rizza, R.A.; Mandarino, L.J.; Gerich, J.E.; Hayles, A.B.; Haymond, M.W. Familial insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Presence of a postbinding defect. Diabetes 1986, 35, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, D.E.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Azziz, R. Severe insulin-resistance hyperandrogenic syndromes. In Androgen Excess Disorders in Women. Contemporary Endocrinology; Azziz, R., Nestler, D., Eds.; Human Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Winkelmann, R.K. Acanthosis nigricans: A study of 90 cases. Medicine 1968, 47, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flier, J.S.; Eastman, R.C.; Minaker, K.L.; Matteson, D.; Rowe, J.W. Acanthosis nigricans in obese women with hyperandrogenism: Characterization of an insulin-resistant state distinct from the Type A and Type B syndromes. Diabetes 1985, 34, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łebkowska, A.; Krentowska, A.; Adamska, A.; Lipińska, D.; Piasecka, B.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Górska, M.; Semple, R.K.; Kowalska, I. Type B insulin resistance syndrome associated with connective tissue disease and psoriasis. Endocrinol. Diabet. Metab. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, 20–0027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, E.C.; Chavez, T.A.; Seewaldt, V.L. Obesity and triple-negative breast cancer: Disparities, controversies, and biology. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallhager, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and diabetes: The increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G. Insulin resistance, obesity, and liver cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001, 414, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front. Med. 2013, 2, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, A.Z.; Dasari, S.; Johnson, M.L.; Robinson, M.M.; Konopka, A.R.; Distelmaier, K.; Port, J.D.; Glavin, M.T.; Esponda, R.R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Predictors of whole-body insulin sensitivity across ages and adiposity in adult humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Kader, S.M.; Al-Jiffri, O.H. Impact of weight reduction on insulin resistance, adhesive molecules and adipokines dysregulation among obese Type 2 diabetic patients. Afr. Health Sci. 2018, 18, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gancheva, S.; Jelenik, T.; Alvarez-Hernández, E.; Roden, M. Interorgan metabolic crosstalk in human insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1371–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirosumi, J.; Tuncman, G.; Chang, L.; Görgün, C.Z.; Uysal, K.T.; Maeda, K.; Karin, M.; Hotomisligil, G. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Etiology of insulin resistance. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119 (Suppl. S1), S10–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.-P.G.; Kursawe, R.; Titchenell, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Perry, C.J.; Jurczak, M.J.; Abudukadier, A.; Han, M.S.; Zhang, X.-M.; et al. Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Cell 2015, 160, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.; Saberi, M.; Olefsky, J.M. Insulin sensitivity modulation by nutrients and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.S.; Jung, D.Y.; Morel, C.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kim, J.K.; Flovell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Science 2013, 339, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Makayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, F.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lisanti, M.P. Mitochondrial oxidative stress drives tumor progression and metastasis: Should we use antioxidants as a key component of cancer treatment and prevention. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, I.; Ma, X.H.; Yang, X.M.; Atzmon, G.; Rajda, M.W.; Berg, A.H.; Scherer, P.; Rossetti, L.; Barzilai, N. Removal of visceral fat prevents insulin resistance and glucose intolerance of aging an adipokine mediated process? Diabetes 2002, 51, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowell, B.B.; Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction and Type 2 diabetes. Science 2005, 307, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira-Lara, M.A.; Dommerholt, M.B.; Zhang, W.; Blankstijn, M.; Wolters, J.C.; Abegaz, F.; Gerding, A.G.; van der Veen, Y.T.; Thomas, R.; van Os, R.P.; et al. Age-related susceptibility to insulin resistance arises from a combination of CPTTB decline and lipid overload. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, F.V.C.; Pitta, F.; Hermandes, N.A.; Bertolini, G.L. Physiopathological relationship between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and insulin resistance. Endocrine 2018, 61, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coslo, F.G.; Kudva, Y.; van der Velde, M.; Larson, T.S.; Textor, S.C.; Griffin, M.D.; Stegall, M.D. New onset hyperglycemia and diabetes are associated with increased cardiovascular risk after kidney transplantation. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2415–2421. [Google Scholar]
- Porrini, E.; Delgado, P.; Bigo, C.; Alvarez, A.; Cobo, M.; Checa, M.D.; Hortal, L.; Fernández, A.; García, J.J.; Velázquez, S.; et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on graft function and survival after cadaveric renal transplantation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.C.; Fuhrmann, A.; Carvalho, F.; Sereno, J.; Santos, M.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W.; Reis, F.; Carvalho, E. Cyclosporine enhances gluconeogenesis while sirolimus impairs insulin signaling in peripheral tissues after 3 weeks of treatment. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, R.A.; Mandarino, L.J.; Gerich, J.E. Cortisol-induced insulin resistance in man: Impaired suppression of glucose production and stimulation of glucose utilization due to postreceptor defect of insulin action. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1982, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäcke, H.; Döcke, W.D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafacho, A.; Ortsäter, H.; Nadal, A.; Quesada, I. Glucocorticoid treatment and endocrine pancreas function: Implication for glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 3, R49–R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Uribe, K.B.; Siddigi, H.; Ostolaza, H.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martin, C. Statin treatment-induced development of Type 2 diabetes: From clinical evidence to mechanistic insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Màrmol, J.M.; Carlsson, M.; Raun, S.H.; Grand, M.K.; Sørensen, J.; Lang Lehrskov, L.; Richter, E.A.; Norgaard, O.; Sylow, L. Insulin resistance in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2023, 62, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Capuano, A.; Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and endometrial cancer: Meta-analysis. Endocrine 2014, 45, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Colao, A.; Lenzi, A.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Capuano, A.; Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Parretta, E.; Lenzi, A.; Giugliano, D. Effect of metabolic syndrome and its components on prostate cancer risk: Meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2013, 36, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinjuvadia, R.; Patel, S.; Liangpunsakul, S. The association between metabolic syndrome and hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowey, S.; Hardy, R.W. The metabolic syndrome: A high risk state for cancer? Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1505–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Song, Q.; Xu, X.; Cao, D. Insulin promotes progression of colon cancer by upregulation of ACAT1. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, A.J.; Kirk, N.S.; Forbes, B.E. Understanding IGF-II action through insight into receptor binding and activation. Cells 2020, 9, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Gupta, K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Gopinath, P.; Kumar, B.; Manvati, S.; Chaman, N.; Bamezai, R.N.K. Insulin enhances metabolic capacities of cancer cells by dual regulation of glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Alalem, M.; Ray, B.K. Insulin signaling network in cancer. Indian. J. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 51, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giorgino, F.; Belfore, A.; Milazzo, G.; Costantino, A.; Maddeux, B.; Whittaker, J.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R. Overexpression of insulin receptors in fibroblast and ovary cells induces a ligand mediated transformed phenoType. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Grisouard, J.; Ehemann, V.; Hermani, A.; Enzmann, H.; Mayer, D. Analysis of signaling pathway related to cell proliferation stimulated by insulin in human mammary epithelial cell lines. Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brismar, K.; Fernqvist-Forbes, E.; Wahren, J.; Hall, K. Effect of insulin on the hepatic production of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1), IGFB-3 and IGF-1 in insulin dependent diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 79, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaaks, R.; Lukanova, A. Energy balance and cancer: The role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Canc 2008, 8, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, P.; Frasca, F.; Sciacca, L.; Pandini, G.; Vigneri, R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocrinol. Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 1103–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiakono, B.; Iiritano, S.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Nevolo, M.T.; Ventura, V.; Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, A. Insulin resistance and cancer risk: An overview of the pathogenic mechanisms. Expt. Diab. Res. 2012, 2012, 789174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcavallo, A.; Gaspari, M.; Pandini, G.; Palummo, A.; Cuda, G.; Larsen, M.R.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Research rescue: New and diverse substrate for the insulin receptor isoform a revealed by quantitative proteomics after stimulation with IGF-II or insulin. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.J.; Resnik, J.L.; Reichart, D.B.; Struss, B.; Haas, M.; Seely, B.L. Repression of the insulin receptor promoter by the tumor suppressor gene product p53: A possible mechanism for receptor overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2781–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, H.; Maor, S. The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor gene: A downstream target for oncogene and tumor suppressor action. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, R.R.; Vanhaese, B.; Semple, R.K. Cancer-associated PI3K mutations in overgrowth disorders. Trends. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Medarde, A.; Santos, E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes. Cancer 2011, 2, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B. Insulin and cancer. Integr. Cancer. Therap 2003, 2, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatseba, T. Study of insulin resistance in patients with cancer. Arch. Clin. Med. 2020, 26, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Petrelli, J.M.; Rodriguez, C.; Heath, C.W., Jr. Body mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of US adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 341, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, J. Body mass index, prostate cancer-specific mortality, and biochemical recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prevent. Res. 2011, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabek, T.; Bukowczan, J.; Chlosta, P.; Powroznik, J.; Dobruch, J.; Borowska, A. Obesity and prostate cancer incidence and mortality: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies. Urol. Int. 2014, 92, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discacciati, A.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Body mass index and incidence of localized and advanced prostate cancer-a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Hunter, D.J.; Manson, J.E.; Rosner, B.; Speizer, F.E.; Haukinson, S.E. Waist circumference, waist hip ratio, and risk of breast cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, M.; Hooper, L.; Howell, A.H. Central obesity and breast cancer risk: A systematic review. Obesity Rev. 2003, 4, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, G.C.; Kim, M.; Hunt, J.R.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Rohan, T.E. Body mass index and waist circumference in relation to lung cancer risk in the Women’s Health Initiative. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanistic links between obesity, insulin, and cancer. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugane, S.; Inoue, M. Insulin resistance and cancer: Epidemiological evidence. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Insulin-PI3K signaling: An evolutionarily insulated metabolic driver of cancer. Natl. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundaktepe, B.P.; Durmus, S.; Cengiz, M.; Kundaktepe, F.O.; Sozer, V.; Papila, C.; Gelisgen, R.; Uzun, H. The significance of insulin resistance in nondiabetic breast cancer patients. J. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2021, 11, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Park, M.J.; Park, S.J.; Moon, W.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. Insulin resistance is associated with early gastric cancer: A prospective multicenter case control study. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Nelson, R.A.; Wacławski-Wende, J.; Lee, D.J.; Manson, J.A.; Aragaki, A.K.; Mortimer, J.E.; Philips, L.S.; Rohan, T.; Ho, G.Y.F.; et al. Insulin resistance and all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women: The Women’s Health Initiate. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Arzoun, H.G.K.L.B.; Thangarai, S.R. A systematic review: Does insulin resistance affect the risk of survival outcome of breast cancer in women? Cureus 2022, 14, e21712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connoly, B.S.; Barnett, C.; Vogt, K.N.; Li, T.; Stone, N.F.; Boyd, N.F. A meta-analysis of published literature on waist-to-hip ratio and risk of breast cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2002, 44, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daling, J.R.; Malone, K.E.; Doody, D.R.; Johnson, L.G.; Grawlow, J.R.; Porter, P.L. Relation of body mass index to tumor markers and survival among young women with invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer 2001, 92, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankester, K.J.; Philips, J.E.; Lawton, P.A. Weight gain during adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: An audit of 100 women receiving FEC or CMF chemotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 14, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, C.L.; Denmark-Wahnefried, W. Nutrition and survival after the diagnosis of the evidence. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3302–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.B.; Cantor, A.; Allen, K.; Cox, C.E. Android obesity at diagnosis and breast carcinoma survival: Evaluation of the effects of anthropometric variables and diagnosis including body composition and body fat distribution and weight gain during life span, and survival from breast carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 88, 2751–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.D.; Folsorn, A.R. International weight loss and incidence of obesity-related cancers: The Iowa Women’s Healthy Study. Int. J. Obesity Related Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.; Welch, H.G. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc 2006, 295, 2164–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, S.D.; Jackson, L.N.; Riall, T.S.; Uchida, T.; Thomas, R.P.; Qiu, S.; Evers, B.M. Increased evidence of well-differentiated thyroid cancer associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis and the role of the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2007, 204, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevallos, J.P.; Hartman, C.M.; Kramer, J.R.; Sturgis, E.M.; Chiao, E.Y. Increased thyroid cancer incidence corresponds to increased use of thyroid ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration: A study of the veterans affairs health care system. Cancer 2015, 121, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.G.T.; Myssiorek, D. Improved detection does not fully explain the rising incidence of well-differentiated thyroid cancer: A population-based study. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 200, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishna, A.; Ishak, A.; Ellinides, A.; Saad, R.; Christodoulou, H.; Spartalis, E.; Paschou, S.A. The impact of obesity and insulin resistance on thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Maturitas 2019, 125, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.-T.; He, H.; Yu, K.; Xie, J.; Lei, M.; Ma, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. The association between thyroid cancer and insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and its components: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 57, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Ricci, C.; Behrens, G.; Leitzmann, M.F. Adiposity and risk of thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberman, B.; Khaku, A.; Camachov, F.; Goldenberg, D. Relationship between obesity, diabetes and the risk of thyroid cancer. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2015, 36, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, A.; Tretli, S.; Akslen, L.A.; Bjørge, T. Body size and thyroid cancer in two million Norwegian men and women. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, C.M.; Platz, E.A.; Freeman, L.B.; Hsing, A.W.; Linet, M.S.; Park, Y.; Schairer, C.; Schatzkin, A.; Shikany, J.M.; de González, A.B. Obesity and thyroid cancer risk among U.S. men and women: A pooled analysis of 5 prospective studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.Y.; Jee, Y.H.; Cho, E.R. Body mass index and incidence of thyroid cancer in Korea: The Korean Cancer Prevention Study—II. J. Canc. Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, N.; Greenwood, D.C.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, R.; Aune, D.; Ju, W.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.L. Adult weight gain and adiposity-related cancers: A dose response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscemi, S.; Massenti, F.M.; Vasto, S.; Buscemi, C.; Corleo, D.; Barille, A.M.; Rosafio, G.; Rini, N.; Giordano, C. Association of obesity and diabetes with thyroid nodules. Endocrine 2018, 60, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Ye, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, H. Obesity and risk of thyroid cancer: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 observational studies. Med. Sci. Mon. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Bai, X.; Ge, H.; Cui, H.; Wei, Z.; Han, G. Meta-analysis in the association between obesity and risk of thyroid cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5268–5274. [Google Scholar]
- Paes, J.E.; Hua, K.; Nagy, R.; Kloos, R.T.; Jarjoura, D.; Ringe, M.D. The relationship between body mass index and thyroid cancer pathology features and outcomes a clinicopathological cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.P.; Chi, C.W.; Tzen, C.Y.; Yang, T.L.; Lee, J.J.; Liu, T.P.; Liu, C.L. Clinicopathologic significance of leptin and leptin receptor expressions in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 2010, 147, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platz, E.A.; Willet, W.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Rimm, E.B.; Spigelman, D.; Giovannucci, E. Proportion of colon cancer risk that might be preventable in a cohort of middle-aged US men. Cancer Causes Control 2000, 11, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.K.; Calle, E.E.; Rodriquez, C.; Kahn, H.S.; Thun, M.J. Body mass index and colon cancer in a large prospective study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardou, M.; Barkun, A.N.; Martel, M. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomain, E.S.; Waldman, S.A. Does obesity promote the development of colorectal cancer? Expert. Rev. Anticanc. Ther. 2016, 16, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colditz, G.A.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Frazier, A.L. Physical activity and reduced risk of colon cancer: Implications for prevention. Cancer Causes Control 1997, 4, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Orenstein, M.R. Physical activity evidence and biological mechanisms. J. Nutr. 2002, 132 (Suppl. S11), 3456S–3464S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, D.; Thune, I. Does physical activity prevent cancer? Evidence suggests protection against colon and probably breast cancer. BMJ 2000, 321, 1424–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, A.; Entezari, A.A.; Crutcher, M.; Snook, A.E.; Waldman, S.A. Guanyl cyclase C as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Per. Med. 2022, 19, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.J.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Edwards, S.; Caan, B.J.; Potter, J.D. Body mass index and colon cancer: An evaluation of the modifying effects of estrogen (United States). Cancer Causes Control 2003, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Obesity and risk of liver cancer: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, T.; Tateishi, R.; Sato, T.; Masuzaki, R.; Imamura, J.; Goto, T.; Yamashiki, N.; Yoshida, H.; Kanai, F.; Kato, N.; et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic hepatitis C patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascha, M.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Lopez, R.; Abu-Rajab Tamini, T.; Fedelstein, A.F.; Zein, N.N. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Yang, H.J.; Su, J.; Brenner, D.; Iloeje, U.; Chen, C.-J. Obesity and alcohol synergize to increase the risk of incident hepatocellular carcinoma in situ. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, M.W.; Park, C.H.; Yon, S.K. Obesity and the risk of primary liver cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Shen, F.; Fan, J.; Cao, H. Body mass index and risk of primary liver cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Oncologist 2012, 17, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Hepatocellular carcinoma and obesity, Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease: Causing factors, molecular links and treatment options. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 808526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, G.D.; Shipley, M.J.; Jarrett, R.J.; Breeze, E.; Marmot, M.G.; Smith, G.D. Obesity and overweight in relation to organ specific cancer mortality in London (UK): Findings from the original Whitehall study. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Petrick, J.L.; Kelly, S.P.; Graubard, B.I.; Freedman, N.D.; McGlynn, K.A. Adiposity across the adult life course and incidence of primary liver cancer: The NIH-AARP cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, J.L.; Thistle, J.E.; Zeleniuch Jacquatte, A.; Zhang, X.; Wacławski-Wende, J.; Van Dyke, A.L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Sinha, R.; Sesso, H.D.; Schairer, C.; et al. Body mass index, diabetes and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma risk: The Liver Cancer Pooling Project and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitta, C.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G. Obesity and liver cancer. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyad, M.A. Is obesity a risk factor for prostate cancer, and does it even matter? A hypothesis and different perspective. Urology 2002, 59 (Suppl. S1), 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.; Patel, A.V.; Calle, E.E.; Jacobs, E.J.; Chao, A.; Thum, M.J. Body mass index, height, and prostate cancer mortality in two large cohorts of adult men in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2001, 10, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, S.O.; Wolk, A.; Bergström, R.; Adami, H.O.; Engholm, G.; Englund, A.; Nyrén, O. Body size and prostate cancer: A 20-year follow-up study among 135006 Swedish construction workers. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 1997, 89, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Deng, J.; Seseterhenn, I.A.; Mostofi, F.K.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Benichou, J.; Xie, T.; Gao, Y.T. Body size and prostate cancer. A population-based study case-control study in China. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2000, 12, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Hsing, A.W.; Gao, Y.T.; Chua, S., Jr.; Deng, J.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Insulin resistance and prostate cancer risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amling, C.L.; Kane, C.J.; Riffenburgh, R.H.; Ward, J.F.; Roberts, J.L.; Lance, R.S.; Friedrichs, P.A.; Moul, J.W. Relationship between obesity and race in predicting adverse pathologic variables in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Urology 2001, 58, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mydlo, J.H.; Tieng, N.L.; Volpe, M.A.; Chaiken, R.; Kral, J.G. A pilot study analyzing PSA, serum testosterone, lipid profile, body mass index and race in a small sample of patients with and without carcinoma of the prostate. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2001, 4, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maynard, G.D. A statistical study in cancer death-rates. Biometrika 1910, 7, 276–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulds, M.H.; Dahlman-Wright, K. Metabolic diseases and cancer risk. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, V.A.; Becker, S.; Kaaks, R. Diabetes mellitus Type 2—An independent risk factor for cancer. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2010, 118, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, U.; Gale, E.M. Cancer and diabetes: Are we ready for prime time? Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.A.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Yee, D. Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, B.B.; Yeh, H.C.; Snyder, C.F.; Peairs, K.S.; Stein, K.B.; Derr, R.L.; Wolff, A.C.; Brancati, F.L. Postoperative mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Zendehdel, K.; Nyren, O.; Ostenson, C.G.; Adami, H.O.; Ekbom, A.; Ye, W. Cancer incidence in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study in Sweden. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2003, 95, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Li, X.; Sundquist, K.; Hemminki, K. Cancer risk among patients hospitalized for Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study in Sweden. Diabetic Med. 2010, 27, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, A.J.; Laing, S.P.; Qiao, Z.; Slater, S.D.; Burden, A.C.; Botha, J.L.; Waugh, N.R.; Morris, A.D.; Gatling, W.; Gale, E.A.; et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes: A UK cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscombe, L.L.; Goodwin, P.J.; Zinman, B.; McLaughlin, J.R.; Hux, J.E. The impact of diabetes on survival following breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 109, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chan, A.T.; Ng, K.; Chan, J.A.; Wu, K.; Pollak, M.N.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S. Insulin, the insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Jiménez, C.; Gutiérrez-Salmeron, M.; Chocarro-Calvo, A.; Garcia-Martinez, J.M.; Castaño, A.; De la Vieja, A. From obesity to diabetes and cancer: Epidemiological links and role of therapies. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Nowlin, S.; Palu, S. Cancer incidence in the National Health and Nutrition Survey I. Follow-up data: Diabetes, cholesterol, pulse and physical activity. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 1995, 4, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michels, K.B.; Solomon, C.G.; Hu, F.B.; Rosner, B.A.; Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Manson, J.E. Nurses’ Health Study. Type 2 diabetes and subsequent incidence of breast cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hao, L.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, S. Long-term diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Ranson, J.; de Andrade, M.; Peterson, G.M. Probability of pancreatic cancer following diabetes: A population-based study. Gastroenetrology 2005, 129, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, P.; Hoorn, S.V.; Christophi, C.; Nikfarjam, M. Association of diabetes mellitus and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis of 88 studies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, H.; Hassan, M.M.; Holly, E.A.; Bracci, P.M.; Silverman, D.T. Diabetes and risk of pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis of three large case-control studies. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-X.; Zhu, H.-H.; Zhu, Y.-M. Diabetes and cancer: Associations, mechanisms, and implications for medical practice. World J. Diabet. 2014, 5, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.K.; Korc, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Eibl, G.; Li, D.; Rickels, M.R.; Chari, S.T.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Diabetes, pancreatogenic diabetes, and pancreatic cancer. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, G.; Ramachandran, V.; Javeed, N.; Arumugam, T.; Dutta, S.; Klee, G.G.; Klee, E.W.; Smyrk, T.C.; Bamlet, W.; Han, J.J.; et al. Adrenomedullin is up-regulated in patients with pancreatic cancer and causes insulin resistance in β cells and mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, E.; Surazynski, A.; Orłowski, K.; Łaszkiewicz, J.; Puchalski, Z.; Nawrat, P.; Pałka, J. Serum and tissue levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I binding protein as an index of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2002, 83, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Datta, K.; Neid, M.; Li, J.; Parangi, S.; Mukhopadyay, D. Requirement of different signaling pathways mediated by the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor for proliferation, invasion, and VPF/VEGF expression in a pancreatic carcinoma cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.Z.; Fehsenfeld, D.M.; Murphy, L.O.; Perment, J.; Adrian, T.E. Physiological concentrations of insulin augment pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and glucose utilization by activating MAP kinase, PI3 kinase, and enhancing GLUT1 expression. Pancreas 2000, 21, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, R.J.; Pollak, M. Insulin-like growth factor-I antagonizes the antiproliferative effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7372–7376. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, K.A.; Karl, R.C.; Naidu, K.A.; Coppola, D. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effect of ascorby stearate in human pancreatic cancer cells: Association with decreased expression of insulin-like growth factor receptor. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschou, S.A.; Vryonidou, A.; Goulis, D.G. Thyroid nodules: A guide to assessment, treatment and follow-up. Mauritius 2017, 96, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H. Metformin reduces thyroid cancer risk in Taiwanese patients with Type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, S.; Renko, K.; Derwahl, M. Metformin inhibits growth of thyroid carcinoma cells, suppresses self-renewal of derived cancer stem cells, and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E510–E520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R.; Bodmer, M. No evidence for a decreased risk of thyroid cancer in association with use of metformin or other antidiabetic drugs: A case-control study. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Philips, L.; Liu, S.; Wacławski-Wende, J.; Margolis, K.I. Diabetes, diabetes treatment, and risk of thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykholat, T.; Lykholat, O.; Antonyuk, S. Immunohistochemical and biochemical analysis of mammary gland tumours of different age patients. Cytol. Genet. 2016, 50, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, K.M.J.; Arends, L.R.; Hansen, B.E.; Leeflang, S.; Ruiter, R.; van Eijck, C.H.J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality in breast and colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Wolk, A. Diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Association between diabetes mellitus and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of the literature. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, C.; Xia, J. Influence of diabetes mellitus on mortality in breast cancer patients. ANZ J. Surg. 2015, 85, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-B.; Ren, G.S. Diabetes mellitus and prognosis in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity, diabetes and increased cancer progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatseba, T.S. Influence of pathogenic factors of Type 2 diabetes on activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and on the development of endometrial and breast cancer. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2019, 10, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, P.F.; Msaouel, P.; Koutsiliers, M. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Preti, E.; Landoni, F.; Carinelli, S.; Colombo, A.; Marini, C.; Sessa, C.; ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Endometrial cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, vi33–vi38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristofano, A.; Ellenson, L.H. Endometrial carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2007, 2, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasi, E.; Filardi, T.; Tartaglione, S.; Lenzi, A.; Angeloni, A.; Morano, S. Linking Type 2 diabetes and gynecological cancer: An introductory overview. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, E.; Orsini, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Wolk, A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Beresford, S.; Chen, C.; Chlebowski, R.; Garcia, L.; Kuller, L.; Regier, M.; Wacławski-Wende, J.; Margolis, K.L. Association between diabetes, diabetes treatment and risk of developing endometrial cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Su, P.-Y.; Hao, J.-H.; Sun, Y.-H. The role of preexisting diabetes mellitus on incidence and mortality of endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Zhang, D.; Mungo, C.; Tompkins, D.A.; Zeidan, A.M. Is diabetes mellitus associated with increased incidence and disease-specific mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, L.; Varse, F.; Baradaran, H.R.; Moradi, Y.; Khateri, S.; Friberg, E.; Khazaei, Z.; Gharahjeh, S.; Tehrani, S.; Sioofy-Knojine, A.B.; et al. The effect of diabetes on the risk of endometrial cancer: An update a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, K.; Cvancarova, M.; Eskild, A. Body mass index, diabetes and survival after diagnosis of endometrial cancer: A report from the HUNT-Survey. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 139, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, Z.; Hu, N.; Ying, J.; Soisson, P.; Dodson, M.; Gaffney, D.K. Impact of comorbid conditions on survival in endometrial cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Gapstur, S.M.; Patel, A. Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of one million U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folson, A.R.; Anderson, K.E.; Sweeney, C.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Diabetes as a risk factor for death following endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 94, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, K.H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Ku, B.J. The association between Type 2 diabetes mellitus and women cancer: The epidemiological evidences and putative mechanisms. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 920618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchim, I.; Sarfstein, R.; Werner, H. The IGF hormonal network in endometrial cancer: Functions, regulation, and targeting approaches. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih, I.M. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: A proposed unifying theory. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piek, J.M.; van Diest, P.J.; Zweemer, R.P.; Kenemans, P.; Verheijen, R.H. Tubal ligation and risk of ovarian cancer. Lancet 2001, 358, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piek, J.M.; Verheijen, R.H.; Kenemans, P.; Massuger, L.F.; Bulten, H.; van Diest, P.J. BRCA1/2-related ovarian cancers are tubal origin: A hypothesis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 90, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapstur, S.M.; Patel, A.V.; Diver, W.R.; Hildebrand, J.S.; Gaudet, M.M.; Jacobs, E.J.; Campbell, P.T. Type II diabetes mellitus and the incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer in the cancer prevention study-II nutrition cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 21, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeon, I.; Kim, J.W.; Song, Y.S.; Yoon, J.M.; Park, S.M. Diabetes mellitus and ovarian cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhara, A.; Buckanovich, R.; Griggs, J. The impact of diabetes on survival in women with ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, M.I.; Kannan, A.; Pawar, S.; Haschek, W.M.; Bagchi, M.K.; Bagchi, I.C. Dysregulated estrogen receptor signaling in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis leads to ovarian epithelial tumorigenesis in mice. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminki, X.; Li, X.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. Risk of cancer following hospitalization for Type 2 diabetes. Oncologist 2010, 15, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachamp, M.C.; Yasmeen, A.; Knafo, A.; Gotlieb, W.H. Targeting insulin and insulin-like growth factor pathways in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 257058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2016 Atlanta. 2016. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2016.html (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Choi, J.; Chang, H.K.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, K.H.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H. Does diabetes mellitus have an impact on the prognosis for patients with cervical cancer? Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 139, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Ju, W.; Kum, K.H. Plasma levels of insulin like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor-1 binding protein-3 in women with cervical neoplasia. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 21, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.Y.; Lin, Z.Z.; Kuo, R.; Shau, W.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Shao, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.; Cheng, W.F.; Cheng, A.L.; et al. The prognostic impact of Type 2 diabetes mellitus in early cervical cancer in Asia. Oncologist 2015, 20, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Shen, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Surgery 2013, 153, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkatout, I.; Schubert, M.; Garbecht, N.; Weigel, M.T.; Jonat, W.; Mundhenke, C.; Günther, V. Vulvar cancer: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and management options. Int. J. Women’s Health 2015, 7, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allbritton, J. Vulvar neoplasms, benign and malignant. Obst. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 44, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suglyama, V.E.; Chan, J.K.; Shin, J.Y.; Berek, J.S.; Osann, K.; Kapp, D.S. Vulvar melanoma: A multivariable analysis of 644 patients. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 110, 226–301. [Google Scholar]
- Brinton, L.A.; Thistle, J.E.; Liao, L.M.; Trabert, B. Epidemiology of vulvar neoplasia in the NIH-AARP Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 145, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinten, F.; van den Einden, L.C.G.; Hendriks, J.C.M.; van der Zee, A.G.J.; Bulten, J.; Massuger, L.F.A.G.; van de Nieuwenhof, H.P.; de Hullu, H.P. Risk factors for short- and long-term complications after groin surgery in vulvar cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchini, C.; Nottegar, A.; Solmi, M.; Sergi, G.; Manzato, E.; Capelli, P.; Scarpa, A.; Veronese, N. Prognostic implications of extranodal extension in node-positive squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 25, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerf, M.E. Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Xiong, Q.-Y.; Lu, L.; Duan, P.; Yang, Q.O.; Zhou, P.; Tu, J.-H. miR-29a regulated ER-positive breast cancer cell growth and invasion and is involved in the insulin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32566–32575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, G.C.; Kim, M.Y.; Lane, D.S.; Zaslavsky, O.; Ho, G.Y.F.; Luo, J.; Nicholson, W.K.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Barrington, W.E.; Vitolins, M.Z.; et al. Serum glucose and insulin and risk of cancers of the breast, endometrium, and ovary in postmenopausal women. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, D.R.; Mittal, A.; Sathin, B.; Bhatta, B. Role of hyperinsulinemia in increased risk of prostate cancer: A case control study from Kathmandu valley. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, N.H.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.R.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.J. Glycemic status, insulin resistance, and risk of pancreatic cancer mortality in individuals with and without diabetes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Mortimer, J.E.; Gunter, M.J.; Rohan, T.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Adams-Campbell, L.L.; Ho, G.Y.F.; Cheng, T.-Y.D.; Nelson, R.A. Insulin resistance and breast cancer incidence and mortality in postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer 2020, 126, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargny, M.; Balkau, B.; Lange, C.; Charles, M.-A.; Giral, P.; Simon, D. Association of fasting serum insulin and cancer mortality in a healthy population—28-year follow-up to the French TELECOM study. Diabet. Metab. 2018, 44, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors and colon cancer: A review of the evidence. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3109S–3120S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misnikova, I.V. Diabetes and cancer. RMJ 2016, 20, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, M.A.; Wadea, F.M.; Hussein, N.M.M.; Elnagar, A.-E.M.A. Insulin resistance, resistin hormone and hepatocellular carcinoma interplay: A review article. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 90, 2041–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Pasupuleti, V.; Benites-Zapata, V.A.; Thota, P.; Deshpande, A.; Perez-Lopez, F.R. Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkau, B.; Kahn, H.S.; Courbon, D.; Eschwège, E.; Ducimetière, P.; Paris Prospective Study. Hyperinsulinemia predicts fatal liver cancer but is inversely associated with fatal cancer at some other sites: The Paris Prospective Study. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.L.; Duggan, C.; Wang, C.Y.; Smith, A.W.; McTieman, A.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Bernstein, L.; Ballard-Barbash, R. Fasting C-peptide levels and death resulting from all causes and breast cancer: The health eating, activity, and lifestyle study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheus, M.; Peeters, P.H.; Rinaldi, S.; Dossus, L.; Biessy, C.; Olsen, A.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Jeppesen, M.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Serum C-peptide levels and breast cancer risk: Results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autier, P.; Koechlin, A.; Boniol, M.; Mullie, P.; Bolli, G.; Rosenstock, J.; Boyle, P. Serum insulin and C-peptide concentration and breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, H.; Giovannucci, E.; Mucci, L.; Qiu, W.; Nguyen, P.L.; Gaziano, J.M.; Pollak, M.; Stampfer, M.J. Prediagnostic body-mass index, plasma C-peptide concentration, and prostate cancer-specific mortality in men with prostate cancer: A long-term survival analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, V.L.; Jacobs, E.J.; Sun, J.; Gapstur, S.M. No association of plasma levels of adiponectin and C-peptide with risk of aggressive prostate cancer in the Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 890–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walraven, I.; van’t Rief, E.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Polak, B.C.P.; Moll, A.C.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G. Fasting proinsulin levels are significantly associated with 20 year cancer mortality rates. The Hoorn Study. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Organ/Tissue | Effect of Insulin | |
|---|---|---|
| Stimulation | Inhibition | |
| Brain | Hunger | Production of hepatic glucose, production of lipoprotein |
| Liver | Synthesis of glycogen, accumulation of lipids, inflammation | Synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis), release of glucose |
| Peripheral muscle | Metabolism of glucose, uptake of glucose, synthesis of glycogen, muscle mass, mitochondrial dysfunction | |
| Adipose tissue | Metabolism of glucose, uptake of glucose, storage of fat (lipogenesis), transport of fatty acids from the blood stream | Fat breakdown (lipolysis) |
| Factors | Cause | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | ||
| Mutations in insulin gene | ValA3→Asp | Insulin Wakuama. Decreased binding of insulin to INSR [42]. |
| PheB24→Ser | Insulin Los Angeles. Decreased insulin bioactivity [43]. | |
| PheB25→Leu | Insulin Chicago. Decreased insulin bioactivity [43]. | |
| HisB10→Asp | Mutation in proinsulin. Hyperproinsulinemia [44]. | |
| Mutations in the insulin signaling pathway | Autosomal dominant or recessive mutations in INSR gene. | TAIRS [45]. Donohue syndrome, also known as leprechaunism [46,47]. |
| Autosomal recessive mutations in INSR. | RMS [48]. | |
| Autosomal dominant mutations in INSR gene or in postreceptor proteins. | Type C insulin resistance is a variant of TAIRS, also called HAIR-AN syndrome [49,50]. | |
| Autoimmune factor | TBIRS due to circulating anti-INSR antibodies, usually immunoglobulin G [51,52] | IR or hyperglycemia, dependent on levels of autoantibodies [53]. |
| Environmental factor | Obesity | IR, impaired insulin action, metabolic abnormalities, disturbances in release and signaling of hormones, adipokines, growth factors, free fatty acids. Inflammation and increased levels of pro-inflammatory mediators [54,55,56]. |
| Aging | Decreased insulin secretion and glucose tolerance. IR, sarcopenia, excess adiposity, osteoporosis [57,58]. Oxidative stress, disturbances in mitochondrial function [59]. | |
| Diseases and drugs | IR [60]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szablewski, L. Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 998-1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31020075
Szablewski L. Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(2):998-1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31020075
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzablewski, Leszek. 2024. "Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers" Current Oncology 31, no. 2: 998-1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31020075
APA StyleSzablewski, L. (2024). Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers. Current Oncology, 31(2), 998-1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31020075




