The Unmet Diagnostic and Treatment Needs in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Is LCNEC a Rare Type of Cancer?
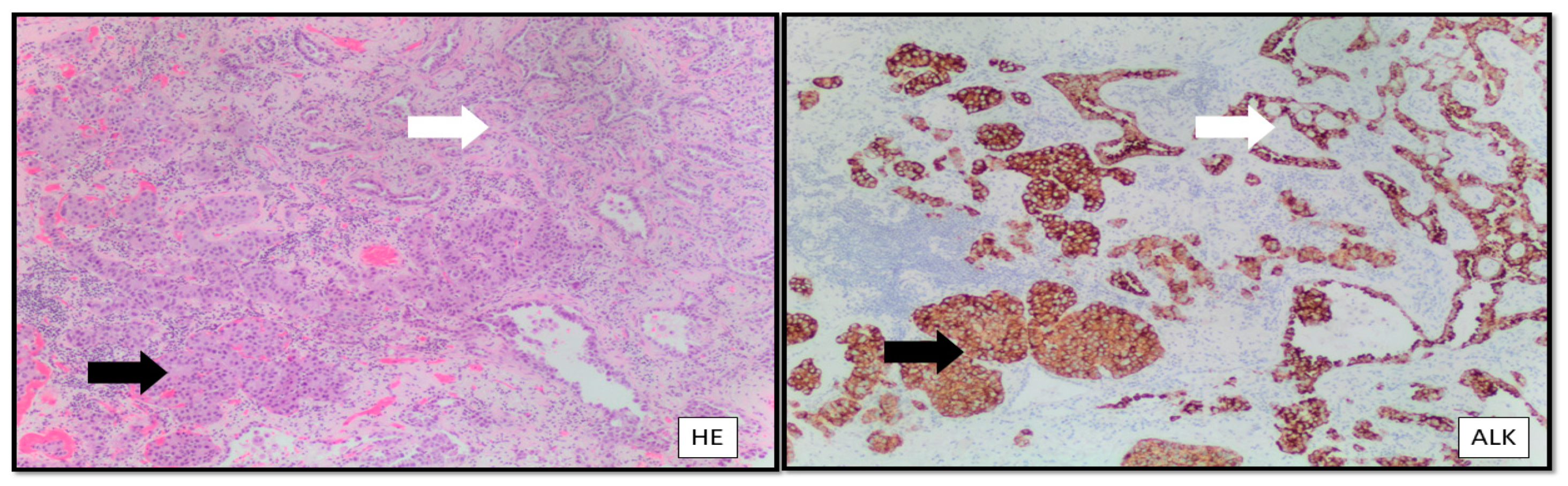
3. Pathologic Diagnosis of LCNEC and Its Limitations
4. Molecular Subtypes of LCNEC
5. Role of Surgery
6. Role of Chemotherapy in Advanced Stages
7. Role of Radiotherapy
8. Role of Immunotherapy
9. Role of Targeted Therapy
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrara, M.G.; Stefani, A.; Simbolo, M.; Pilotto, S.; Martini, M.; Lococo, F.; Vita, E.; Chiappetta, M.; Cancellieri, A.; D’argento, E.; et al. Large Cell Neuro-Endocrine Carcinoma of the Lung: Current Treatment Options and Potential Future Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 650293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, M.; Della Corte, C.M.; Papaccio, F.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: From Epidemiology to Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, C.R.; Shaw, E.C.; Moore, D.A.; Rassl, D.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Steele, N.; Naheed, S.; Dick, C.; Taylor, F.; Adderley, H.; et al. Large cell neuroendocrine lung carcinoma: Consensus statement from The British Thoracic Oncology Group and the Association of Pulmonary Pathologists. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2022; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2022.html (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Thoracic Tumours. WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2021; Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Who-Classification-Of-Tumours/Thoracic-Tumours-2021 (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Rekhtman, N.; Montecalvo, J.; Chang, J.C.; Alex, D.; Ptashkin, R.N.; Ai, N.; Sauter, J.L.; Kezlarian, B.; Jungbluth, A.; Desmeules, P.; et al. SMARCA4-Deficient Thoracic Sarcomatoid Tumors Represent Primarily Smoking-Related Undifferentiated Carcinomas Rather Than Primary Thoracic Sarcomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 15, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, J.; Fujii, T.; Shih, J.H.; Dracheva, T.; Meerzaman, D.; Player, A.; Hong, K.; Settnek, S.; Gupta, A.; Buetow, K.; et al. Chromatin Remodeling Factors and BRM/BRG1 Expression as Prognostic Indicators in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4314–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhtman, N. Lung neuroendocrine neoplasms: Recent progress and persistent challenges. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Walter, V.; Peifer, M.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Seidel, D.; Leenders, F.; Maas, L.; Müller, C.; Dahmen, I.; Delhomme, T.M.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas reveals distinct subtypes of high-grade neuroendocrine lung tumors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Umemura, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Mimaki, S.; Tada, S.; Makinoshima, H.; Ishii, G.; Udagawa, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, Z.-W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.-T.; Bao, B.; Liu, Y.-P. Clinicopathological characteristics, treatment and survival of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A SEER population-based study. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorn, F.; Dienemann, H.; Muley, T.; Warth, A.; Hoffmann, H. Predictors of Survival After Operation Among Patients With Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 99, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, A.; Hiroshima, K.; Moriya, Y.; Takiguchi, Y.; Sekine, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Kimura, H.; Nakatani, Y.; Fujisawa, T. Prospective Study of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, A.; Hiroshima, K.; Moriya, Y.; Iwadate, Y.; Takiguchi, Y.; Uno, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Yoshino, I. Postoperative recurrence and the role of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeam, E.; Adibfar, A.; Stokes, S.; Leighl, N.B.; Giuliani, M.E.; Varghese, T.K.; Darling, G.E. Defining the role of adjuvant therapy for early-stage large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 159, 2043–2054.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Cao, H.; You, Y.; He, W.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Xia, L. Optimal Surgery Type and Adjuvant Therapy for T1N0M0 Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 591823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Uchino, K.; Ohbayashi, C.; Maniwa, Y.; Nishio, W.; Nakao, A.; Yoshimura, M. Immunohistochemical studies of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A possible association between staining patterns with neuroendocrine markers and tumor response to chemotherapy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 145, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Sakai, Y.; Nishio, W.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Nishikubo, M.; Nishioka, Y.; Tane, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Sudo, T.; Sakuma, T.; et al. DLL3expression is a predictive marker of sensitivity to adjuvant chemotherapy for pulmonaryLCNEC. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Treut, J.; Sault, M.C.; Lena, H.; Souquet, P.J.; Vergnenegre, A.; Le Caer, H.; Berard, H.; Boffa, S.; Monnet, I.; Damotte, D.; et al. Multicentre phase II study of cisplatin–etoposide chemotherapy for advanced large-cell neuroendocrine lung carcinoma: The GFPC 0302 study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ahn, J.S.; Um, S.-W.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Han, J.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O.J.; et al. Chemotherapy for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: Similar to that for small cell lung cancer or non-small cell lung cancer? Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.L.; jan van Suylen, R.; Thunnissen, E.; den Bakker, M.A.; Groen, H.J.; Smit, E.F.; Damhuis, R.A.; van den Broek, E.C.; Speel, E.M.; Dingemans, A.C. Chemotherapy for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: Does the regimen matter? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.; Guan, Y.; Yang, X.; Hong, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, R.; Abbas, H.A.; Chang, L.; Gong, Y.; et al. The Prognostic and Therapeutic Role of Genomic Subtyping by Sequencing Tumor or Cell-Free DNA in Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Sekine, I.; Tsuta, K.; Horinouchi, H.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kubota, K.; Tamura, T. Amrubicin Monotherapy for Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Large-cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 41, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, V.; Jawitz, O.K.; Yang, C.-F.J.; Voigt, S.L.; Tong, B.C.; D’amico, T.A.; Harpole, D.H. Outcomes for Surgery in Large Cell Lung Neuroendocrine Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.S.; Kinslow, C.J.; Adams, C.; Saqi, A.; Shu, C.A.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Wang, T.J.C.; Cheng, S.K. Outcomes for localized treatment of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung in the United States. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limonnik, V.; Abel, S.; Finley, G.G.; Long, G.S.; Wegner, R.E. Factors associated with treatment receipt and overall survival for patients with locally advanced large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: A National Cancer Database analysis. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Gong, D.; Wang, Y.; Chi, B.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Min, L. The demographic and treatment options for patients with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2979–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Niho, S.; Ishii, G.; Hishida, T.; Yoshida, J.; Nishimura, M.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K.; Ohmatsu, H.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Clinical features of unresectable high-grade lung neuroendocrine carcinoma diagnosed using biopsy specimens. Lung Cancer 2012, 75, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinslow, C.J.; May, M.S.; Saqi, A.; Shu, C.A.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Wang, T.J.; Cheng, S.K. Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung: A Population-Based Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 21, e99–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, F.; Harms, A.; Warth, A.; Muley, T.; Winter, H.; Eichhorn, M. PD-L1 expression in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpin, D.; Charpentier, M.-C.; Bernardi, M.; Monnet, I.; Boni, A.; Watkin, E.; Goubin-Versini, I.; Lamy, R.; Gérinière, L.; Geier, M.; et al. PD-L1-expression patterns in large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: Potential implications for use of immunotherapy in these patients: The GFPC 03-2017 “EPNEC” study. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920937972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G., Jr.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; Ock, C.-Y.; Moon, J.-W.; Yoo, C.W.; Lee, G.K.; Han, J.-Y. Association of PD-L1 Expression with Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Mutation Burden in High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, B.; Derks, J.; Thunnissen, E.; van Suylen, R.; Bakker, M.D.; Groen, H.J.; Smit, E.; Damhuis, R.; Broek, E.V.D.; Stallinga, C.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in molecular subtypes of metastatic large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC). Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, T.; Ravindra, N.; Powell, E. Role of Immunotherapy in Stage IV Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudnik, E.; Kareff, S.; Moskovitz, M.; Kim, C.; Liu, S.V.; Lobachov, A.; Gottfried, T.; Urban, D.; Zer, A.; Rotem, O.; et al. Real-world survival outcomes with immune checkpoint inhibitors in large-cell neuroendocrine tumors of lung. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; McGrath, J.E.; Xiu, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Ma, P.C.; Nieva, J.J.; Lopes, G.; Borghaei, H.; Ikpeazu, C.; Owonikoko, T.K.; et al. Genomic and immunologic characterization of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Cao, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, G.; Zhu, B.; Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of the Genomic Landscape in Chinese Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors Reveals Prognostic and Therapeutic Markers (CSWOG-1901). Oncol. 2022, 27, e116–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M.; Jin, Y.; Shen, X.; Shan, L.; Shen, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. ALK-rearrangement neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: A comprehensive study of a rare case series and review of literature. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 4991–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omachi, N.; Shimizu, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tezuka, K.; Kanazu, M.; Tamiya, A.; Asami, K.; Okishio, K.; Kitaichi, M.; Atagi, S. A Case of Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Harboring an EML4–ALK Rearrangement with Resistance to the ALK Inhibitor Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, e40–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Z.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Identified a Novel Crizotinib-Sensitive PLB1-ALK Rearrangement in Lung Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 22, e366–e370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.A.; Banyi, N.; Tucker, T.; Ionescu, D.N.; Melosky, B. A Case of ALK-Rearranged Combined Lung Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Carcinoma with Diffuse Bone Metastasis and Partial Response to Alectinib. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.H.; Ma, S.; Zhou, J. A marked response to icotinib in a patient with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma harboring an EGFR mutation: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uprety, D.; Remon, J.; Adjei, A.A. All That Glitters Is Not Gold: The Story of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helleday, T. Homologous recombination in cancer development, treatment and development of drug resistance. Carcinog. 2010, 31, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, A.; Pothuri, B.; Vergote, I.; DePont Christensen, R.; Graybill, W.; Mirza, M.R.; McCormick, C.; Lorusso, D.; Hoskins, P.; Freyer, G.; et al. Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, L.; Volante, M.; Rapa, I.; Tavaglione, V.; Inzani, F.; Pelosi, G.; Papotti, M. Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling activation patterns in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2010, 17, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christopoulos, P.; Engel-Riedel, W.; Grohé, C.; Kropf-Sanchen, C.; von Pawel, J.; Gütz, S.; Kollmeier, J.; Eberhardt, W.; Ukena, D.; Baum, V.; et al. Everolimus with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment for metastatic large-cell neuroendocrine lung carcinoma: A multicenter phase II trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, R.A.E.; García-Talavera, P.; Martin, M.N.; López, B.P.; Muñoz, M.G.; Alonso, M.P.T.; Hernández, J.J.C. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung with atypical evolution and a remarkable response to lutetium Lu 177 dotatate. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odate, S.; Nakamura, K.; Onishi, H.; Kojima, M.; Uchiyama, A.; Nakano, K.; Kato, M.; Tanaka, M.; Katano, M. TrkB/BDNF signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013, 79, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NCT Number | Drug and Condition | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 03901378 | Pembrolizumab in GI-tract and LCNEC of the lung | Withdrawn |
| 03976518 | Atezolizumab in NSCLC: rare histologies | Recruiting |
| 03728361 | Nivolumab and temozolomide in refractory SCLC or advanced neuroendocrine cancer | Active, not recruiting |
| 03305133 | Evaluation of PD-L1 expression in LCNEC | Completed |
| 03591731 | Nivolumab ± ipilimumab in advanced/refractory GI-tract and LCNEC of the lung | Active, not recruiting |
| 02834013 | Nivolumab and ipilimumab in rare tumors (including LCNEC of the lung) | Recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buium, C.; Negru, S.; Ionescu, D.N.; Dediu, M. The Unmet Diagnostic and Treatment Needs in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7218-7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080523
Buium C, Negru S, Ionescu DN, Dediu M. The Unmet Diagnostic and Treatment Needs in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(8):7218-7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080523
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuium, Catalin, Serban Negru, Diana N. Ionescu, and Mircea Dediu. 2023. "The Unmet Diagnostic and Treatment Needs in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung" Current Oncology 30, no. 8: 7218-7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080523
APA StyleBuium, C., Negru, S., Ionescu, D. N., & Dediu, M. (2023). The Unmet Diagnostic and Treatment Needs in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Current Oncology, 30(8), 7218-7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080523





