Safety of CDK4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
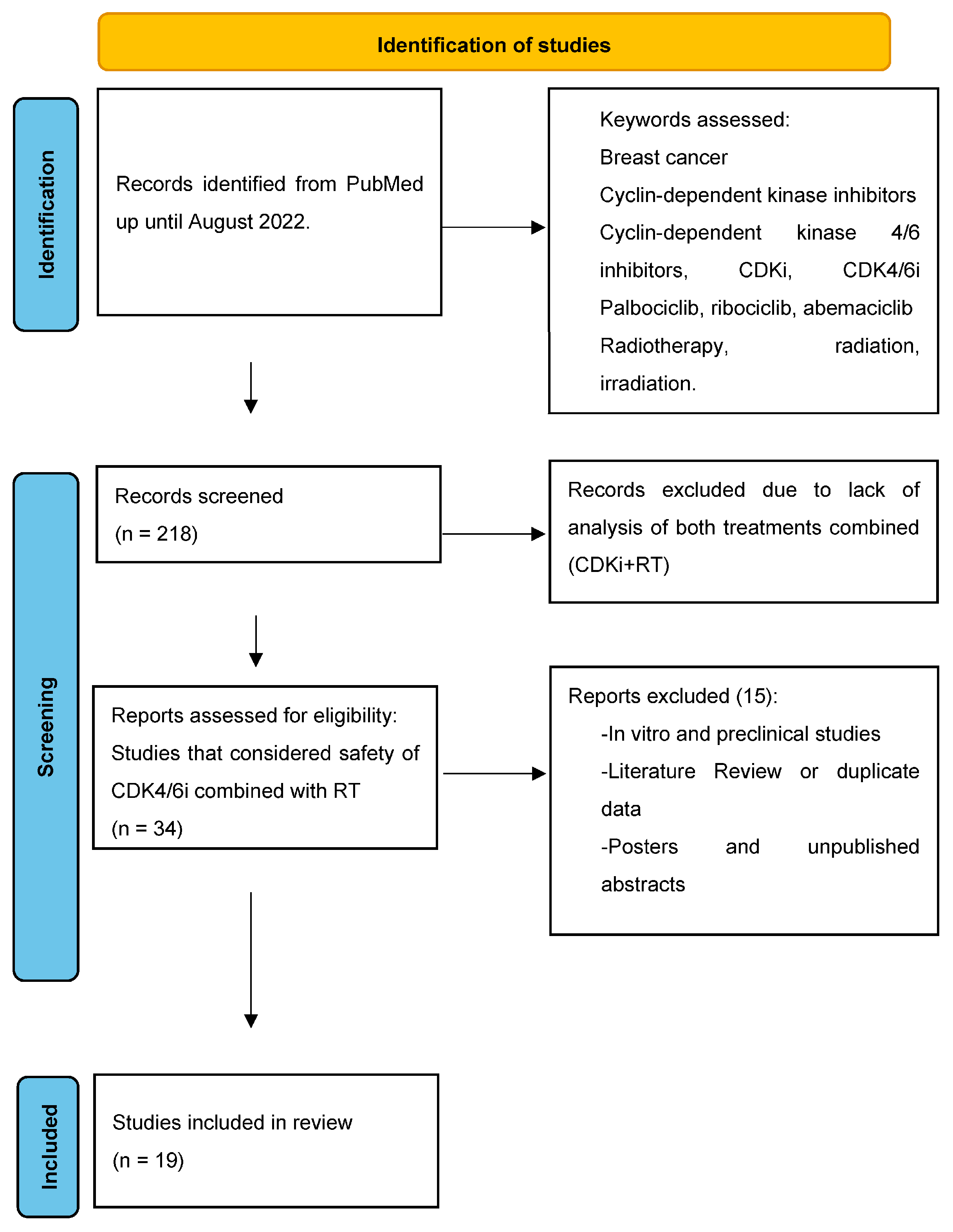
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy—MONARCH 2: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.-A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Esteva, F.J.; Martin, M.; et al. Overall survival results of the phase III MONALEESA-3 trial of postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor negative advanced breast cancer treated with fulvestrant and ribociclib. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. 5), 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Turner, N.C.; Bondarenko, I.; Ro, J.; Im, S.-A.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; et al. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALO-MA-3): Final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomized controlled trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2016, 17, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.-A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Esteva, F.J.; Martín, M.; et al. Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Sun, T.; Yin, Y.M.; Li, H.P.; Yan, M.; Tong, Z.S.; Oppermann, C.P.; Liu, Y.P.; Costa, R.; Li, M.; et al. MONARCH plus: Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer: The multinational randomized phase III study. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920963925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braal, C.L.; Jongbloed, E.M.; Wilting, S.M.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Jager, A. Inhibiting CDK4/6 in Breast Cancer with Palbociclib, Ribociclib, and Abemaciclib: Similarities and Differences. Drugs 2021, 81, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Mei, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Yu, X. CDK4/6 inhibitors: A novel strategy for tumor radiosensitization. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, K.; Solomon, D.A.; Oermann, E.; Kim, J.-S.; Zhong, W.-Z.; Prados, M.D.; Ozawa, T.; James, C.D.; Waldman, T. Pharmacologic Inhibition of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 Arrests the Growth of Glioblastoma Multiforme Intracranial Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S.; Madani, D.; Joshi, S.; Chung, S.; Johns, T.; Day, B.; Khasraw, M.; McDonald, K.L. Combination of palbociclib and radiotherapy for glioblastoma. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-L.; Oh, P.; Xu, E.S.; Ma, Y.; Kim, Y.; Daniel, A.R.; Kirsch, D.G. Blocking cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 during single dose versus fractionated radiation therapy leads to opposite effects on acute gastrointestinal toxicity in mice. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Shah, P.; Clark, A.; Freedman, G.M.; Dastgheyb, S.; Barsky, A.R.; Dreyfuss, A.D.; Taunk, N.K. Safety of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor combined with palliative radiotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast 2021, 60, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figura, N.B.; Potluri, T.K.; Mohammadi, H.; Oliver, D.E.; Arrington, J.A.; Robinson, T.J.; Etame, A.B.; Tran, N.D.; Liu, J.K.; Soliman, H.; et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitors and stereotactic radiation in the management of hormone receptor positive breast cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, E.; Greco, C.; Silipigni, S.; Dell’aquila, E.; Petrianni, G.M.; Tonini, G.; Fiore, M.; D’Angelillo, R.M.; Ramella, S. Concurrent radiotherapy with palbociclib or ribociclib for metastatic breast cancer patients: Preliminary assessment of toxicity. Breast 2019, 46, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerini, A.E.; Pedretti, S.; Salah, E.; Simoncini, E.L.; Maddalo, M.; Pegurri, L.; Pedersini, R.; Vassalli, L.; Pasinetti, N.; Peretto, G.; et al. A single-center retrospective safety analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors concurrent with radiation therapy in metastatic breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, M.; Sen, N.; Chowdhary, A.; Usha, L.; Cobleigh, M.A.; Wang, D.; Patel, K.R.; Barry, P.N.; Rao, R.D. Safety and Efficacy of Palbociclib and Radiation Therapy in Patients with Met-astatic Breast Cancer: Initial Results of a Novel Combination. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddok, A.; Xu, H.P.; Henry, A.A.; Porte, B.; Fourquet, A.; Cottu, P.; Kirova, Y. Concurrent use of palbociclib and radiation therapy: Single-centre experience and review of the literature. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, H.; Lee, K.T.; Stearns, V.; Alcorn, S.R.; Mangini, N.S. Incidence and Severity of Myelosuppression with Palbociclib After Palliative Bone Radiation in Advanced Breast Cancer: A Single Center Experience and Review of Literature. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 22, e65–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratosa, I.; Orazem, M.; Scoccimarro, E.; Steinacher, M.; Dominici, L.; Aquilano, M.; Cerbai, C.; Desideri, I.; Ribnikar, D.; Marinko, T.; et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashdan, A.; Quirk, S.; Roumeliotis, M.; Abedin, T.; Amaro, C.P.; Barbera, L.; Lupichuk, S.; Cao, J.Q. Radiation Therapy with Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors: A Mul-ti-institutional Safety and Toxicity Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messer, J.A.; Ekinci, E.; Patel, T.A.; Teh, B.S. Enhanced dermatologic toxicity following concurrent treatment with palbociclib and radiation therapy: A case report. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2019, 24, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjan, A.; Dayyat, A. Ribociclib-Induced Radiation Recall Dermatitis Following Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: Case Report and Literature Review. Hematol. Stem Cell Ther. 2020, 14, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Sahgal, A.; Warner, E.; Czarnota, G.J. Safety of palbociclib concurrent with palliative pelvic radiotherapy: Discussion of a case of increased toxicity and brief review of literature. J. Med Radiat. Sci. 2020, 68, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, U.M.; Mozeika, A.M.; Sayan, M.; Jan, I.; Kowal, N.; Haffty, B.; Ahlawat, S.; Kothari, N. Severe Gastrointestinal Mucositis Following Concurrent Palbociclib and Palliative Radiation Therapy. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 5291–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Ho, G.; Day, D.; Harris, M.; Tan, J.; Goel, S.; Hanna, G.G.; Srivastava, R.; Kruss, G.; McDowell, L.; et al. Enhanced toxicity with CDK 4/6 inhibitors and palliative radiotherapy: Non-consecutive case series and review of the literature. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 14, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meattini, I.; Desideri, I.; Scotti, V.; Simontacchi, G.; Livi, L. Ribociclib plus letrozole and concomitant palliative radiotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. Breast 2018, 42, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aken, E.S.M.; Beeker, A.; Houtenbos, I.; Pos, F.J.; Linn, S.C.; Elkhuizen, P.H.M.; de Jong, M.C. Unexpected toxicity of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib and radiotherapy. Cancer Rep. 2021, 18, e1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, S.; Cottu, P.; Kirova, Y.M. Preliminary results of the association of Palbociclib and radiotherapy in metastatic breast cancer patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 126, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Shikama, N.; Sasai, K. Severe acute radiation-induced enterocolitis after combined palbociclib and palliative radiotherapy treatment. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 131, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, S.; Harvey-Jones, E.; Smith, D.; Ahmad, S.; Goldsmith, C.; Sawyer, E.; Castell, F.; Swampillai, A.; Mullassery, V. Does Concurrent Use of CDK4/6 Inhibitors During Palliative Radiotherapy In-crease Toxicity in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer? Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, R.; Zhang, A.; Mueller, S.; Prados, M.D.; Lulla, R.R.; Goldman, S.; Saratsis, A.M.; Mazar, A.P.; Stegh, A.H.; Cheng, S.-Y.; et al. Inhibition of DNA damage repair by the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib delays irra-diated intracranial atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor and glioblastoma xenograft regrowth. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M.; Sotillo, R.; Santamaría, D.; Galán, J.; Cerezo, A.; Ortega, S.; Dubus, P.; Barbacid, M. Mammalian Cells Cycle without the D-Type Cyclin-Dependent Kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell 2004, 118, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheicher, R.; Hoelbl-Kovacic, A.; Bellutti, F.; Tigan, A.-S.; Prchal-Murphy, M.; Heller, G.; Schneckenleithner, C.; Salazar-Roa, M.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Zuber, J.; et al. CDK6 as a key regulator of hematopoietic and leukemic stem cell activation. Blood 2015, 125, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Guzmán, R.; Calsina, B.; Hermoso, A.; Baquero, C.; Alvarez, B.; Amat, J.; McNulty, A.M.; Gong, X.; Boehnke, K.; Du, J.; et al. Preclinical characterization of abemaciclib in hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69493–69507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Bartlett, C.H.; Schnell, P.; DeMichele, A.M.; Loi, S.; Ro, J.; Colleoni, M.; Iwata, H.; Harbeck, N.; Cristofanilli, M.; et al. Palbociclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with hormone recep-tor-positive/HER2-negative advanced metastatic breast cancer: Detailed safety analysis from a multicenter, randomized, placebo controlled, phase III study (PALOMA-3). Oncologist 2016, 21, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Blackwell, K.L.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugo, H.; Diéras, V.; Gelmon, K.; Finn, R.; Slamon, D.; Martin, M.; Neven, P.; Shparyk, Y.; Mori, A.; Lu, D.; et al. Impact of palbociclib plus letrozole on patient-reported health-related quality of life: Results from the PALOMA-2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohdy, K.S.; Lasheen, S.; Kassem, L.; Abdel-Rahman, O. Gastrointestinal adverse effects of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors in breast cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2017, 8, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, A.; Chow, E.; Zhang, L.; Wong, R.; Wu, J.; Sinclair, E.; Danjoux, C.; Tsao, M.; Barnes, E.; Loblaw, A. Determining the Incidence of Pain Flare Following Palliative Radiotherapy for Symptomatic Bone Metastases: Results from Three Canadian Cancer Centers. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 75, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, J.A.; Callahan, J.W.; Herschtal, A.; Everitt, S.; Binns, D.S.; Hicks, R.J.; Mac Manus, M. Distribution of Proliferating Bone Marrow in Adult Cancer Patients Determined Using FLT-PET Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 79, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Toya, R.; Matsuyama, T.; Semba, A.; Oya, N. Dosimetric predictors of treatment-related lymphopenia induced by palliative radio-therapy: Predictive ability of dose volume parameters based on body surface contour. Radiol. Oncol. 2017, 51, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sini, C.; Fiorino, C.; Perna, L.; Chiorda, B.N.; Deantoni, C.L.; Bianchi, M.; Sacco, V.; Briganti, A.; Montorsi, F.; Calandrino, R.; et al. Dose–volume effects for pelvic bone marrow in predicting hematological toxicity in prostate cancer radiotherapy with pelvic node irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 118, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Aroca, D.; Roche, O.; Sabater, S.; Pascual-Serra, R.; Ortega-Muelas, M.; Pérez, I.S.; Belandia, B.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, M.; Sánchez-Prieto, R. P53 pathway is a major determinant in the radiosensitizing effect of Palbociclib: Implication in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 451, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, P.G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): A randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AUTHOR | STUDY DESIGN | PATIENTS (N) | CDKI4/6 AGENT | CDKI4/6 COMBINED WITH | RT SITE | TECHNIQUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al., 2021 [13] | Retrospective analysis | 30 | Palbociclib (34) | Fulvestrant (13) | Brain (5) | 3D-CRT (29) |
| Abemaciclib (2) | AI (12) | Bone-spine (19) | IMRT (2) | |||
| TMX (3) | Bone-pelvis (9) | VMAT (4) | ||||
| Alone (8) | Bone-other (6) | SBRT (7) | ||||
| Other (4) | Electron (1) | |||||
| David S et al., 2020 [26] | Case series | 5 | Palbociclib (5) | AI (5) | Mediastinal nodes (1) | N/A |
| Right breast (1) | ||||||
| Bone-spine (3) | ||||||
| Hans et al., 2018 [29] | Letter to the editor | 5 | Palbociclib (5) | Fulvestrant | Bone-pelvis (1) | |
| Bone-spine (2) | ||||||
| Bone-scapula/humerus (1) | Unknown (4) | |||||
| Liver (1) | SBRT (1) | |||||
| Kawamoto et al., 2019 [30] | Letter to the editor | 1 | Palbociclib | Fulvestrant | Bone-pelvis | 3D-CRT |
| Figura et al., 2019 [14] | Retrospective analysis | 15 | Palbociclib (10) | AI (16) | Brain (15) | SBRT (26) |
| Abemaciclib (5) | Fulvestrant (20) | FSRT (16) | ||||
| Ippolito et al., 2019 [15] | Retrospective analysis | 16 | Palbociclib (13) | N/A | Bone-pelvis (6) | 3D-CRT (19) |
| Ribociclib (3) | Bone-spine (4) | IMRT (2) | ||||
| Bone-others (4) | VMAT (3) | |||||
| Chest wall-skin (1) | ||||||
| Nodal (1) | ||||||
| Guerini et al., 2020 [16] | Retrospective analysis | 18 | Palbociclib (9) | Fulvestrant (10) | Bone-spine (11) | 3D-CRT (29) |
| Ribociclib (6) | AI (8) | Bone-pelvis (9) | VMAT (2) | |||
| Abemaciclib (3) | Ribs (4) | Tomotherapy (1) | ||||
| Skull (1) | ||||||
| Sternum (2) | ||||||
| Bone-extremities (1) | ||||||
| Messer et al., 2019 [22] | Case report | 1 | Palbociclib | Fulvestrant | Supraclavicular node | 3D-CRT |
| Chowdhary et al., 2019 [17] | Retrospective analysis | 16 | Palbociclib (16) | Fulvestrant (6) | Bone-spine (11) | 3D-CRT (18) |
| AI (10) | Bone-pelvis (4) | IMRT (2) | ||||
| Bone-extremities (3) | SBRT (2) | |||||
| Brain (4) | FSRS (1) | |||||
| Mediastinum (1) | ||||||
| Beddock et al., 2020 [18] | Retrospective analysis | 30 | Palbociclib (30) | Fulvestrant (9) | Bone-spine (17) | 3D-CRT (24) |
| AI (21) | Bone-extremities (7) | IMRT (10) | ||||
| Choroidal (1) | SBRT (1) | |||||
| Brain (1) | ||||||
| Locoregional breast RT (9) | ||||||
| Meattini et al., 2018 [27] | Case series | 5 | Ribociclib (5) | AI | Bone-spine (2) | 3D-CRT (4) |
| Bone-extremities (2) | VMAT (1) | |||||
| Bone-hip (1) | ||||||
| Howlett et al., 2021 [31] | Letter to the editor | - | Palbociclib (28) | - | Bone-spine (23) | - |
| Ribociclib (N/A) | Bone-others (16) | |||||
| Abemaciclib (N/A) | Brain (2) | |||||
| Norman et al., 2022 [19] | Retrospective analysis | 47 | Palbociclib (47) | Fulvestrant (20) | Bone-pelvis (21) | 3D-CRT (38) |
| AI (27) | Bone-spine (12) | SBRT (5) | ||||
| Spine + pelvis (4) | IMRT (3) | |||||
| Bone-extremities (10) | Unknown (1) | |||||
| Ratosa et al., 2020 [20] | Retrospective analysis | 46 | Palbociclib (30) | AI (14) | Bone-pelvis (11) | 3D-CRT (41) |
| Ribociclib (15) | TMX/LHRH (15) | Bone-spine (31) | IMRT (1) | |||
| Abemaciclib (1) | Fulvestrant (3) | Bone-others (8) | Tomotherapy (2) | |||
| Visceral/nodes mets (7) | SBRT (7) | |||||
| Brain (3) | 2D-RT (11) | |||||
| Locoregional breast RT (2) | ||||||
| Erjan et al., 2021 [23] | Case report | 1 | Ribociclib | AI (1) | Chest wall | SBRT |
| van Aken et al., 2021 [28] | Case series | 3 | Palbociclib | AI (1) | Bone-pelvis (3) | 3D-CRT (3) |
| Fulvestrant (2) | Mediastinal nodes | VMAT (1) | ||||
| Dasgputa et al., 2021 [24] | Case report | 1 | Palbociclib | AI | Bone-pelvis and proximal femur | 3D-CRT |
| Nasir et al., 2020 [25] | Case report | 1 | Palbociclib | AI | Bone-pelvis | 3D-CRT |
| Bone-spine (T10) | ||||||
| Al-Rashdan et al., 2022 [21] | Retrospective analysis | 132 | Palbociclib (124) | AI (157) | Bone-pelvis (191) | 3D-CRT (274) |
| Ribociclib (8) | Fulvestrant/leuprolide (28) | Bone-other (61) | IMRT (18) | |||
| Brain (20) | SBRT (28) | |||||
| Liver (1) | ||||||
| Lung (8) | ||||||
| Locorregional breast RT (39) |
| MOST COMMON TOXICITIES | GRADE 2 | GRADE 3 | GRADE 4 | CASES (N) | % (Number) of TOTAL POPULATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEUTROPENIA | 14 | 48 | 3 | 65 | 43.9% (N = 148) |
| LEUKOPENIA | 28 | 16 | 0 | 44 | 29.7% (N = 148) |
| ANEMIA | 9 | 4 | 0 | 13 | 8.7% (N = 149) |
| THROMBOCYTOPENIA | 4 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 4% (N = 150) |
| DERMATITIS | 14 | 9 | 1 | 24 | 6.4% (N = 375) |
| DIARRHEA | 15 | 3 | 2 | 20 | 5.8% (N = 345) |
| ESOPHAGITIS | 11 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 4% (N = 375) |
| COLITIS | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.8% (N = 375) |
| TOXICITY | GRADE | AUTHOR | CDKI4/6 AGENT | RT SITE | DELIVERED DOSE (Gy) | FRACTIONS (N) | TECHNIQUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermatitis | G3 | David S et al., 2021 [26] | Palbociclib | Right breast | 36 | 12 | N/A |
| Messer et al., 2019 [22] | Palbociclib | Supraclavicular node | 60 | 30 | 3D-CRT | ||
| Beddock et al., 2020 [18] | Palbociclib | LR | 50.4 | 28 | N/A | ||
| Howlett et al., 2021 [31] | NID | NID | NID | NID | NID | ||
| Norman et al., 2022 [19] | Palbociclib | NID | NID | NID | NID | ||
| Ratosa et al., 2020 [20] | NID | NID | NID | NID | NID | ||
| Al-Rashdan et al., 2022 [21] | Palbociclib | Sternum | 32 | 4 | SBRT | ||
| Diarrhea | G3 | Guerini et al., 2020 [16] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis | 30 | 10 | 3D-CRT |
| Ratosa et al., 2020 [20] | NID | NID | 30 | 10 | NID | ||
| van Aken et al., 2021 [28] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis | 20 | 5 | N/A | ||
| Diarrhea | G4 | Meattini et al., 2018 [27] | Ribociclib | Bone-hip | 20 | 5 | N/A |
| Al-Rashdan et al., 2022 [21] | Ribociclib | Bone | 20 | 5 | 3D-CRT | ||
| Colitis | G3 | Kawamoto et al., 2019 [30] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis | 30 | 10 | 3D-CRT |
| van Aken et al., 2021 [28] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis | 20 | 5 | 3D-CRT | ||
| Dasgputa et al., 2021 [24] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis and proximal femur | 30 | 10 | 3D-CRT | ||
| Guerini et al., 2020 [16] | Palbociclib | Bone-pelvis | 30 | 10 | 3D-CRT | ||
| Esophagitis | G3 | Messer et al., 2019 [22] | Palbociclib | Supraclavicular node | 60 | 30 | 3D-CRT |
| Nasir et al., 2020 [25] | Palbociclib | Bone-spine | 20 | 5 | 3D-CRT | ||
| David S et al., 2021 [26] | Palbociclib | Bone-spine | 30 | 10 | N/A | ||
| Palbociclib | Bone-spine | 20 | 5 | N/A | |||
| Pneumonitis | G5 | David S et al., 2021 [26] | Palbociclib | Mediastinal node | 20 | 5 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, R.; Cao, J.Q.; Yassa, M.; Hijal, T. Safety of CDK4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5485-5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060415
Franco R, Cao JQ, Yassa M, Hijal T. Safety of CDK4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of the Literature. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(6):5485-5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060415
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Rejane, Jeffrey Q. Cao, Michael Yassa, and Tarek Hijal. 2023. "Safety of CDK4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of the Literature" Current Oncology 30, no. 6: 5485-5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060415
APA StyleFranco, R., Cao, J. Q., Yassa, M., & Hijal, T. (2023). Safety of CDK4/6 Inhibitors Combined with Radiotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of the Literature. Current Oncology, 30(6), 5485-5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060415





