Sustained Improvement in the Management of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocation: Where Are We Running?
Abstract
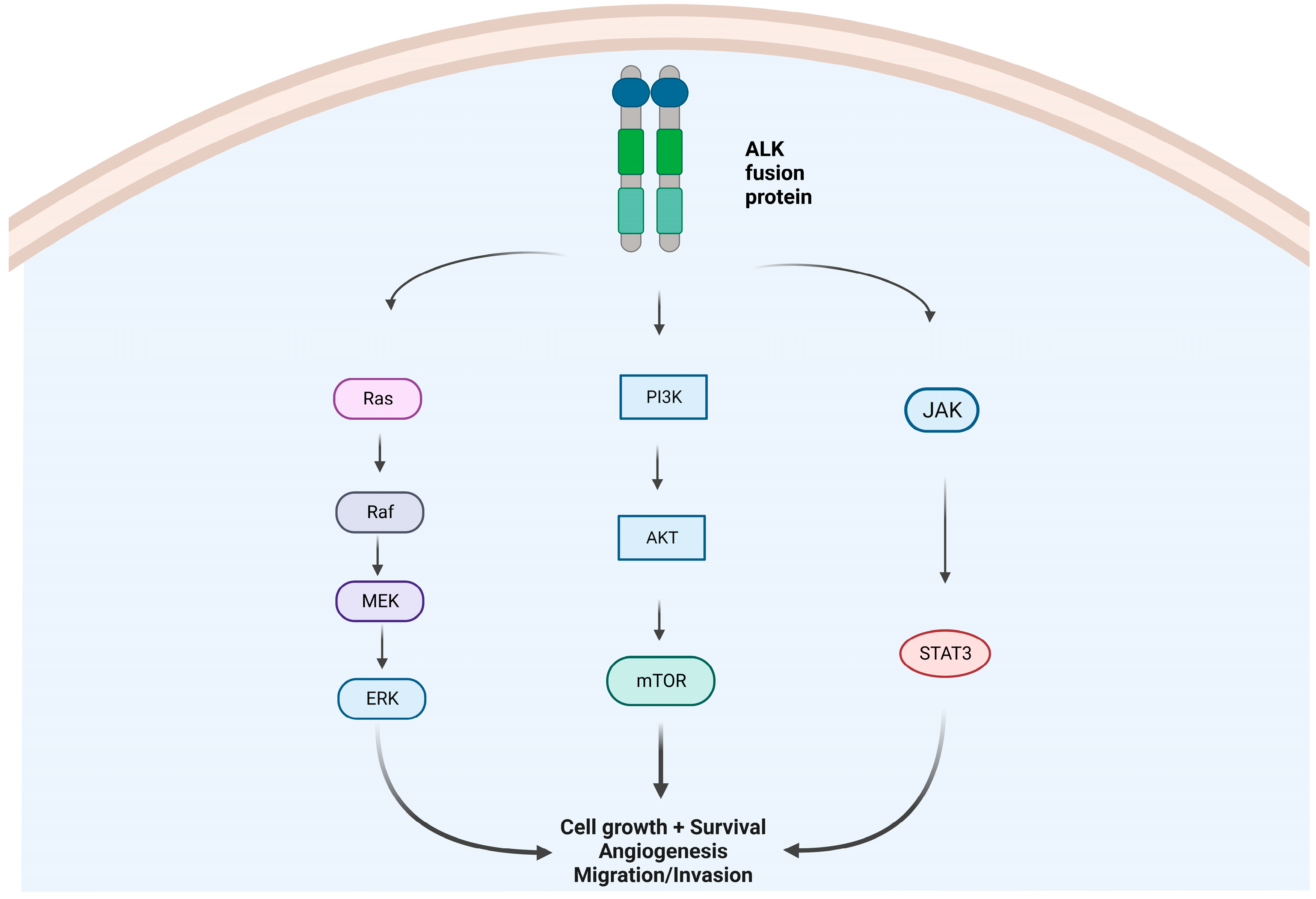
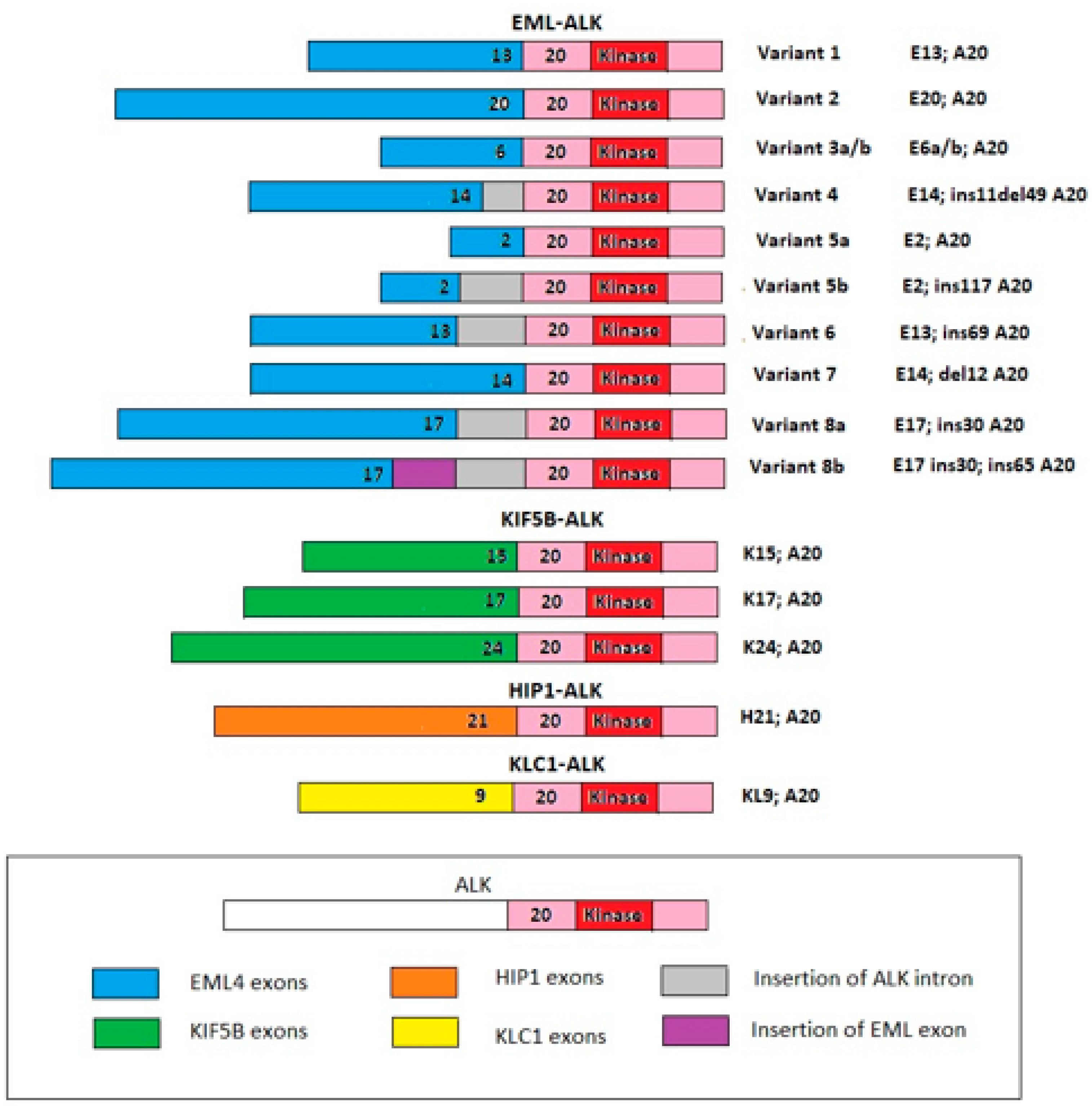
1. Introduction
2. First-Line Randomized Clinical Trials of ALK-Is
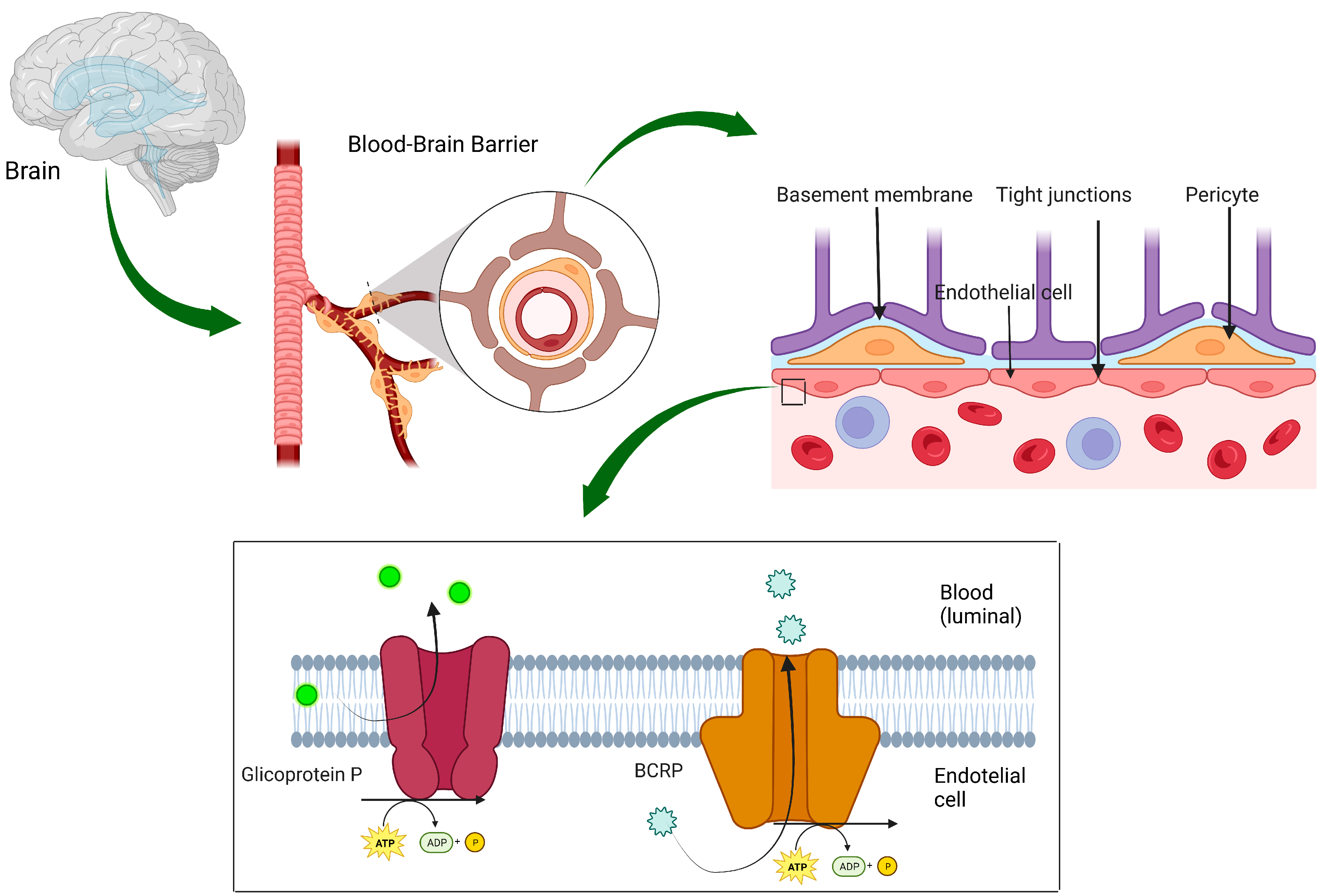
3. Management of Brain Metastases
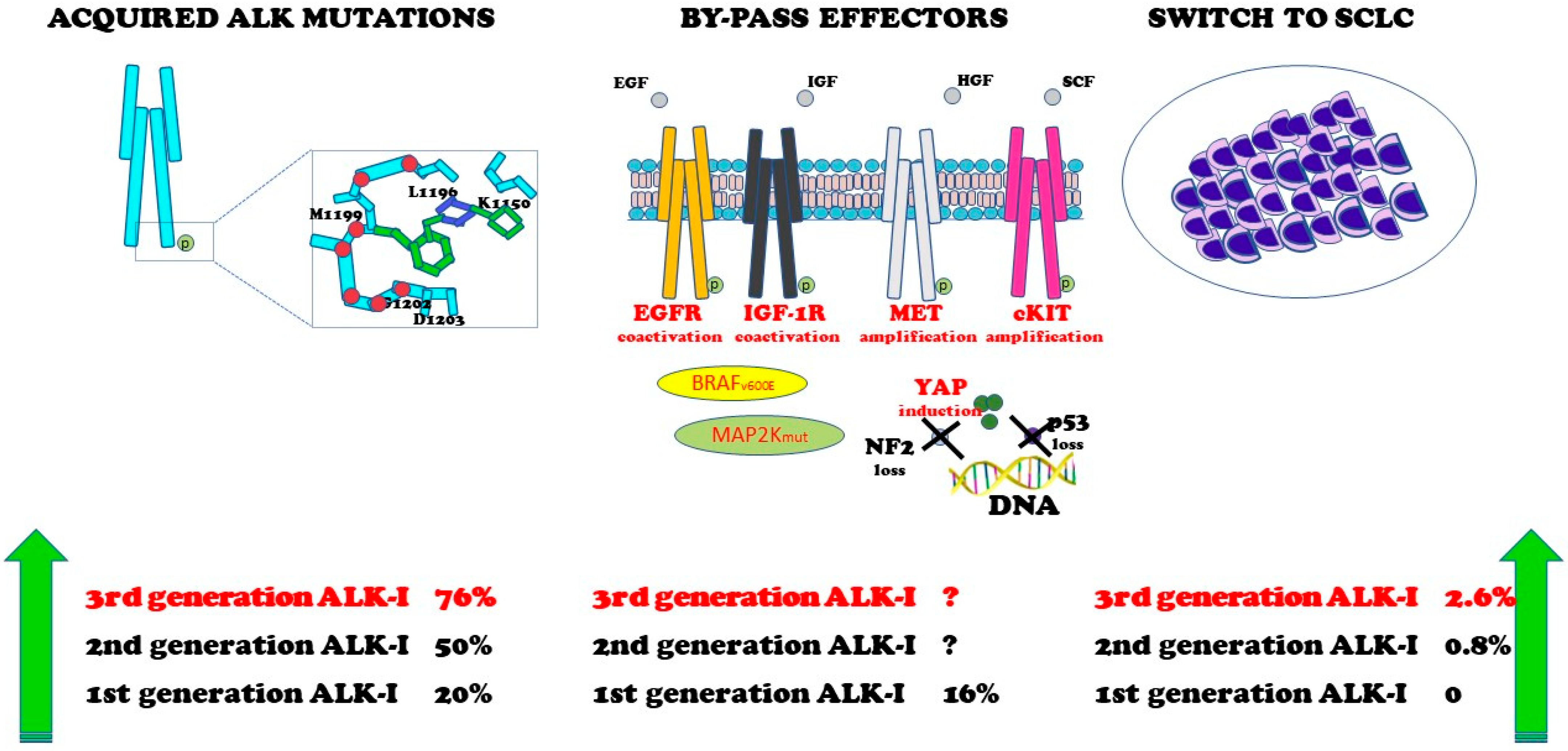
4. Resistance Mechanisms
5. Future Developments
5.1. Activity of ALK-I in Blood-Assessed ALK
5.2. New 2nd/3rd ALK-Is
5.3. Overcoming Resistance to ALK-Is
5.4. Early Stage
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.-I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4–ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernersson, E.; Khoo, N.K.; Henriksson, M.L.; Roos, G.; Palmer, R.H.; Hallberg, B. Characterization of the expression of the ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in mice. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y.; et al. Multiplex Reverse Transcription-PCR Screening for EML4-ALK Fusion Transcripts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6618–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Guo, L.; Wu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Ying, J. BIRC6-ALK, a Novel Fusion Gene in ALK Break-Apart FISH-Negative Lung Adenocarcinoma, Responds to Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, e37–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, T.C.; Gowen, K.; Ali, S.M.; Miller, V.A.; Schrock, A.B.; Lovly, C.M.; Reckamp, K.L. Variable Response to ALK Inhibitors in NSCLC with a Novel MYT1L-ALK Fusion. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e29–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Gan, J.; Hong, S.; Lu, F.; Zhang, L. MPRIP-ALK, a Novel ALK Rearrangement That Responds to ALK Inhibition in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e148–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. A novel HIP1-ALK fusion variant in lung adenocarcinoma showing resistance to Crizotinib. Lung Cancer 2021, 151, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, J.P.; Mermel, C.; Zejnullahu, K.; Murphy, C.; Lifshits, E.; Holmes, A.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.; Chiang, D.; Thomas, R.; et al. EML4-ALK Fusion Gene and Efficacy of an ALK Kinase Inhibitor in Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Costa, D.B.; Heist, R.S.; Solomon, B.; Stubbs, H.; Admane, S.; McDermott, U.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Who Harbor EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4247–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. ALK and ROS1 rearrangements, coexistence and treatment in epidermal growth factor receptor-wild type lung adenocarcinoma: A multicenter study of 732 cases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 3919–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.; Kerr, K.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.; Solomon, B.; et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Chen, X.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, C. Clinical features and therapeutic options in non-small cell lung cancer patients with concomitant mutations of EGFR, ALK, ROS1, KRAS or BRAF. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Rappa, A.; Vacirca, D.; Ranghiero, A.; Fumagalli, C.; Guarize, J.; Spaggiari, L.; de Marinis, F.; Barberis, M.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Concurrent Alterations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring Actionable Mutations. Cancers 2021, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Lu, X.; Sumey, C.; Bs, D.A.M.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Oton, A.B.; Bunn, P.A.; Barón, A.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Aisner, D.L.; et al. Oncogene status predicts patterns of metastatic spread in treatment-naive nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 4502–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lee, H.; Um, S.-W.; Kim, K.; Zo, J.I.; Shim, Y.M.; Kwon, O.J.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, H. Incidence of brain metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma at initial diagnosis on the basis of stage and genetic alterations. Lung Cancer 2019, 129, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangachari, D.; Yamaguchi, N.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Folch, E.; Mahadevan, A.; Floyd, S.R.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Wong, E.T.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Huberman, M.S.; et al. Brain metastases in patients with EGFR -mutated or ALK -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Kulig, K.; Boland, J.M.; Erickson-Johnson, M.R.; Oliveira, A.M.; Wampfler, J.; Jatoi, A.; Deschamps, C.; Marks, R.; Fortner, C.; et al. Worse Disease-Free Survival in Never-Smokers with ALK+ Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-M.; Lira, M.; Pandya, K.; Choi, Y.-L.; Ahn, J.S.; Mao, M.; Han, J.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, J. Clinical characteristics associated with ALK rearrangements in never-smokers with pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackhall, F.; Peters, S.; Bubendorf, L.; Dafni, U.; Kerr, K.M.; Hager, H.; Soltermann, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Dooms, C.; Sejda, A.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes for Patients with ALK-Positive Resected Stage I to III Adenocarcinoma: Results from the European Thoracic Oncology Platform Lungscape Project. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2780–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hei, Y.-J.; O’Malley, C.D. Survival by histologic subtype in stage IV nonsmall cell lung cancer based on data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 3, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kono, S.A.; Lu, X.; Okuyama, S.; Barón, A.E.; Oton, A.B.; Davies, A.M.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.; Doebele, R.C. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase Gene Rearrangements in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer are Associated with Prolonged Progression-Free Survival on Pemetrexed. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-O.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.; Jeon, Y.-K.; Chung, D.H.; Kim, W.-H.; Kim, Y.T.; Yang, S.-C.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Translocation: A Predictive Biomarker of Pemetrexed in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.; Varghese, A.; Solomon, B.; Costa, D.; Novello, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Awad, M.; Engelman, J.; Riely, G.; Monica, V.; et al. Pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandara, D.R.; Huang, E.; Desai, S.; Mack, P.C.; Beckett, L.; Stephens, C.; Zeger, G.; Danenberg, K.D.; Maus, M.K.H.; Li, T. Thymidylate synthase (TS) gene expression in patients with ALK positive (+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Implications for therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-W.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.-L.; Gao, W.-B.; Han, C.-J.; Gao, J.-S.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.-P.; et al. Association between EML4-ALK fusion gene and thymidylate synthase mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissues. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 2151–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crinó, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in AdvancedALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, T.M.; Crinò, L.; Gridelli, C.; Kiura, K.; Liu, G.; Novello, S.; Bearz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mok, T.; et al. Ceritinib versus chemotherapy in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously given chemotherapy and crizotinib (ASCEND-5): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazières, J.; Oh, I.-J.; de Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.; Helland, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.B.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with advanced lung cancer and oncogenic driver alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET registry. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.M.; Gao, D.; Smith, D.; Purcell, T.; Hancock, M.; Bunn, P.; Robin, T.; Liu, A.; Karam, S.; Gaspar, L.; et al. Natural History and Factors Associated with Overall Survival in Stage IV ALK-Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovitz, M.; Dudnik, E.; Shamai, S.; Rotenberg, Y.; Popovich-Hadari, N.; Wollner, M.; Zer, A.; Gottfried, M.; Mishaeli, M.; Rosenberg, S.K.; et al. ALK Inhibitors or Chemotherapy for Third Line in ALK-positive NSCLC? Real-world Data. Oncologist 2022, 27, e76–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; Tang, Y.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis From a Study Comparing First-Line Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Mutation-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.; Camidge, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Rosell, R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Kim, D.-W.; Pérol, M.; Ou, S.-H.; Ahn, J.; Shaw, A.; et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.-Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; Campelo, M.R.G.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK Inhibitor–Naive ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Second Interim Analysis of the Phase III ALTA-1L Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3592–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.; Han, J.-Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; Campelo, M.R.G.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK Inhibitor–Naive Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC: Final Results of Phase 3 ALTA-1L Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Poddubskaya, E.; Mok, T.; Reck, M.; Wakelee, H.; Chiappori, A.A.; Lee, D.H.; Breder, V.; et al. Ensartinib vs Crizotinib for Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase−Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Jassem, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated analysis of data from the phase 3, randomised, open-label CROWN study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 11, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Knetki-Wróblewska, M.; Niziński, P.; Strzemski, M.; Krawczyk, P. Effectiveness of ALK inhibitors in treatment of CNS metastases in NSCLC patients. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Felip, E.; Blackhall, F.H.; Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Mekhail, T.; Paolini, J.; et al. Intracranial Efficacy of Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from PROFILE 1014. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.; Barlesi, F.; Bertino, E.; Bent, M.V.D.; Wakelee, H.; Wen, P.; Chiu, C.-H.; Orlov, S.; Majem, M.; Chiari, R.; et al. Results of the ASCEND-7 phase II study evaluating ALK inhibitor (ALKi) ceritinib in patients (pts) with ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastatic to the brain. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. 5), v602–v660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Kim, D.-W.; Bertino, E.; Bent, M.V.D.; Wakelee, H.; Wen, P.; Lopez, P.G.; Orlov, S.; Majem, M.; McKeage, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ceritinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with leptomeningeal metastases (LM): Results from the phase II, ASCEND-7 study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. 5), v143–v158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.J.; Chiappori, A.A.; West, H.L.; Azada, M.C.; Morcos, P.N.; Lee, R.-M.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Kiura, K.; Seto, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Hida, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Harada, M.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Three-Year Follow-Up of an Alectinib Phase I/II Study in ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AF-001JP. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Shaw, A.T.; Govindan, R.; Gandhi, L.; Socinski, M.A.; Camidge, D.R.; De Petris, L.; Kim, D.-W.; Chiappori, A.; Moro-Sibilot, D.L.; et al. Pooled Analysis of CNS Response to Alectinib in Two Studies of Pretreated Patients with ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.; Kim, D.; Ou, S.; Pérol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in treatment-naive anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) non-small-cell lung cancer: CNS efficacy results from the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Jiang, G.Y.; Joshipura, N.; Ackil, J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Rincon, S.P.; Yeap, B.Y.; Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Efficacy of Alectinib in Patients with ALK-Positive NSCLC and Symptomatic or Large CNS Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.M.; Hansen, K.H.; Rodríguez, L.P.-A.; West, H.L.; Reckamp, K.L.; Leighl, N.B.; Tiseo, M.; Smit, E.F.; Kim, D.-W.; Gettinger, S.N.; et al. Brigatinib in Crizotinib-Refractory ALK+ NSCLC: 2-Year Follow-up on Systemic and Intracranial Outcomes in the Phase 2 ALTA Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Infante, J.R.; Reckamp, K.L.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Leal, T.A.; Waqar, S.N.; Gitlitz, B.J.; Sanborn, R.E.; Whisenant, J.G.; Du, L.; et al. Ensartinib (X-396) in ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from a First-in-Human Phase I/II, Multicenter Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.-C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatineni, V.; O’Shea, P.J.; Rauf, Y.; Jia, X.; Murphy, E.S.; Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; Peereboom, D.M.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Outcomes of first, second, and third-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases (NSCLCBM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 15), 2034, Abstract 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott Molecular, Inc. Vysis ALK Break Apart FISH Probe Kit. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED). 2011. Available online: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf11/P110012b.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Camidge, D.R.; Kono, S.A.; Flacco, A.; Tan, A.-C.; Doebele, R.C.; Zhou, Q.; Crino, L.; Franklin, W.A.; Varella-Garcia, M. Optimizing the detection of lung Cancer Patients Harboring Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Gene Rearrangements Potentially Suitable for ALK Inhibitor Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5581–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ho, S.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Iafrate, A.; Solomon, B.; Shaw, A.; Blackhall, F.; Mok, T.; Wu, Y.-L.; Pestova, K.; et al. Correlation of extent of ALK FISH positivity and crizotinib efficacy in three prospective studies of ALK-positive patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toruner, G.A.; Tang, Z.; Tang, G.; Medeiros, L.J.; Hu, S. Low ALK FISH positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients have shorter progression-free survival after treatment with ALK inhibitors. Cancer Genet. 2020, 241, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Noé, J.; Gadgeel, S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Kim, D.-W.; Konopa, K.; Pozzi, E.; Liu, T.; et al. Outcomes According to ALK Status Determined by Central Immunohistochemistry or Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Patients with ALK-Positive NSCLC Enrolled in the Phase 3 ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagan, J.; Van Allen, E.M. Next-generation sequencing to guide cancer therapy. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.R.; Yeoh, S.; Jackson, G.; Bayliss, R. EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients. Cancers 2017, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuckmann, J.M.; Balke-Want, H.; Malchers, F.; Peifer, M.; Sos, M.L.; Koker, M.; Meder, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Pao, W.; et al. Differential protein stability and ALK Inhibitor Sensitivity of EML4-ALK Fusion Variants. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4682–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.; Seo, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, S.; Park, K.; Song, J.; Lee, B.; Richards, M.; Bayliss, R.; Lee, D.; et al. Differential protein stability and clinical responses ofEML4-ALK fusion variants to various ALK inhibitors in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Noe, J.; Nowicka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cheema, P.; Pavlakis, N.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Updated Efficacy and Safety Data and Impact of the EML4-ALK Fusion Variant on the Efficacy of Alectinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Yoda, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Schrock, A.B.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Jessop, N.A.; Jiang, G.Y.; Le, L.P.; Gowen, K.; et al. Impact of EML4-ALK Variant on Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felip, E.; Martini, J.-F.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Shepard, D.; Polli, A.; Liu, G.; de Marinis, F.; Toffalorio, F.; Goto, Y.; et al. Resistance mechanisms to lorlatinib or crizotinib in treatment-naive patients (pts) with ALK+ advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33 (Suppl. 7), S448–S554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Deng, C.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, C.; Wu, F. The Resistance Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies for ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 713530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Greenbowe, J.; Khan, Z.U.; Azada, M.C.; Ross, J.S.; Stevens, P.J.; Ali, S.M.; Miller, V.A.; Gitlitz, B. I1171 missense mutation (particularly I1171N) is a common resistance mutation in ALK-positive NSCLC patients who have progressive disease while on alectinib and is sensitive to ceritinib. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Shao, Y.W.; Lu, S. Concomitant resistance mechanisms to multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, K.; Peters, M.L.B.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Activity of Brigatinib in the Setting of Alectinib Resistance Mediated by ALK I1171S in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, F.; Fu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Du, N.; Lizaso, A.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Acquired multiple mutations ALK I1171N, L1196M and G1202R mediate lorlatinib resistance in EML4-ALK-rearranged malignant pleural mesothelioma: A case report. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620935770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Pilling, A.B.; Aisner, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Le, A.T.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Kondo, K.L.; Linderman, D.J.; Heasley, L.E.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Crizotinib in Patients with ALK Gene Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors inALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Feng, J.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, W.; et al. Decoding the Evolutionary Response to Ensartinib in Patients with ALK-Positive NSCLC by Dynamic Circulating Tumor DNA Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Rooney, M.; Lin, J.J.; Nagy, R.J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Hubbeling, H.; Chin, E.; Ackil, J.; Farago, A.F.; Hata, A.N.; et al. Treatment with Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Fuels Plasma ALK Mutation Diversity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6662–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Mezquita, L.; Facchinetti, F.; Planchard, D.; Gazzah, A.; Bigot, L.; Rizvi, A.Z.; Frias, R.L.; Thiery, J.P.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; et al. Diverse Resistance Mechanisms to the Third-Generation ALK Inhibitor Lorlatinib in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kumagai, T.; Hida, T.; Toyozawa, R.; Shimokawaji, T.; Goto, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohe, Y.; Seto, T.; et al. Brigatinib in Japanese Patients with ALK-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated with Alectinib and Other Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Outcomes of the Phase 2 J-ALTA Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noé, J.; Lovejoy, A.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Yaung, S.; Bordogna, W.; Klass, D.M.; Cummings, C.A.; Shaw, A.T. ALK Mutation Status Before and After Alectinib Treatment in Locally Advanced or Metastatic ALK-Positive NSCLC: Pooled Analysis of Two Prospective Trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Chen, X.; Yu, R.; Bao, H.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y. Circulating tumor DNA to investigate resistance mechanism and clone evolution of ALK TKI treated lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 15), 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clancy, J.S.; Li, S.; et al. ALK Resistance Mutations and Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Khan, T.M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Solomon, B.J.; Halmos, B.; Jessop, N.A.; Wain, J.C.; Yeo, A.T.; Benes, C.; et al. Mechanisms of Acquired Crizotinib Resistance in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagitani, N.; Uchibori, K.; Koike, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Kitazono, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Horiike, A.; Ohyanagi, F.; Tambo, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; et al. Drug resistance mechanisms in Japanese anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non–small cell lung cancer and the clinical responses based on the resistant mechanisms. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Ueno, T.; Takashima, J.; Nakajima, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Hamada, T.; Haruta, H.; et al. EML4-ALK Mutations in Lung Cancer That Confer Resistance to ALK Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyokawa, G.; Inamasu, E.; Shimamatsu, S.; Yoshida, T.; Nosaki, K.; Hirai, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; Seto, T.; Takenoyama, M.; Ichinose, Y. Identification of a Novel ALK G1123S Mutation in a Patient with ALK-rearranged Non–small-cell Lung Cancer Exhibiting Resistance to Ceritinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, e55–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Koivunen, J.; Ogino, A.; Yanagita, M.; Nikiforow, S.; Zheng, W.; Lathan, C.; Marcoux, J.P.; Du, J.; Okuda, K.; et al. A Novel ALK Secondary Mutation and EGFR Signaling Cause Resistance to ALK Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, M.; Yasuda, H.; Tani, T.; Hamamoto, J.; Arai, D.; Ishioka, K.; Ohgino, K.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kawada, I.; et al. Overcoming EGFR Bypass Signal-Induced Acquired Resistance to ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK-Translocated Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Chen, H.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Heukamp, L.C.; Yan, Y.; Florin, A.; Ozretić, L.; Lim, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion–positive lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal, A.S.; Shaw, A.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Friboulet, L.; Niederst, M.J.; Lockerman, E.L.; Frias, R.L.; Gainor, J.F.; Amzallag, A.; Greninger, P.; et al. Patient-derived models of acquired resistance can identify effective drug combinations for cancer. Science 2014, 346, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Ozasa, H.; Aoki, W.; Aburaya, S.; Funazo, T.; Furugaki, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Ajimizu, H.; Okutani, R.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. Alectinib Resistance in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer by Dual Salvage Signaling in a Clinically Paired Resistance Model. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouji, T.; Takashi, S.; Mitsuhiro, T.; Yukito, I. Crizotinib Can Overcome Acquired Resistance to CH5424802: Is Amplification of the MET Gene a Key Factor? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, e27–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Filho, S.N.M.; Li, M.; Fares, A.; Weiss, J.; Pham, N.-A.; Ludkovski, O.; Raghavan, V.; Li, Q.; Ravi, D.; et al. BRAF V600E mutation and MET amplification as resistance pathways of the second-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor alectinib in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.R.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, Y.W.; Joo, H.S.; Park, C.W.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Na Kang, H.; Pyo, K.; Shin, E.J.; et al. Targeting YAP to overcome acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Langenbucher, A.; Gupta, P.; Yoda, S.; Fetter, I.J.; Rooney, M.; Do, A.; Kem, M.; Chang, K.P.; Oh, A.Y.; et al. Small cell transformation of ROS1 fusion-positive lung cancer resistant to ROS1 inhibition. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, S.; Speicher, M.R. Emerging concepts in liquid biopsies. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadziuszko, R.; Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Leighl, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Pérol, M.; Junior, G.d.C.; Nadal, E.; et al. Blood First Assay Screening Trial (BFAST) in Treatment-Naive Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC: Initial Results of the Phase 2 ALK-Positive Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?recrs=ab&cond=NSCLC&term=ALK&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Nishio, M.; Ahn, M.-J.; Mok, T.; Barlesi, F.; Zhou, C.; Felip, E.; de Marinis, F.; Kim, S.-W.; Pérol, M.; et al. Efficacy of Brigatinib in Patients with Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC Who Progressed on Alectinib or Ceritinib: ALK in Lung Cancer Trial of brigAtinib-2 (ALTA-2). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, X.; Gao, F.; et al. First-in-human phase I results of APG-2449, a novel FAK and third-generation ALK/ ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in patients (pts) with second-generation TKI-resistant ALK/ROS1+ non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Nagasaka, M.; Brazel, D.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, V.W. Will the clinical development of 4th-generation “double mutant active” ALK TKIs (TPX-0131 and NVL-655) change the future treatment paradigm of ALK+ NSCLC? Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.W.; Zhai, D.; Deng, W. TPX-0131, a potent CNS-penetrant, next-generation inhibitor of wild-type ALK and ALK-resistant mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelish, H.E.; Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Kohl, N.E.; Porter, J.R.; Shair, M.D.; Horan, J.C. Abstract 1468: NUV-655 (NVL-655) is a selective, brain-penetrant ALK inhibitor with antitumor activity against the lorlatinib-resistant G1202R/L1196M compound mutation. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04849273 (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Solomon, B.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Barlesi, F.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Nishio, M.; Shaw, A.T.; Bordogna, W.; Meyenberg, C.; Wu, Y.-L. ALINA: A phase III study of alectinib versus chemotherapy as adjuvant therapy in patients with stage IB–IIIA anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, TPS8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Bearz, A.; Martini, J.-F.; Jassem, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Chang, G.-C.; Shaw, A.T.; Shepard, D.; Dall’o, E.; Polli, A.; Thurm, H.C.; et al. Phase 3 trial of lorlatinib in treatment-naive patients (Pts) with ALK-positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Comprehensive plasma and tumor genomic analyses. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearz, A.; Felip, E.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Bauer, T.; Polli, A.; Messina, R.; Thurm, H.; Thomaidou, D.; Mok, T.; et al. 979P Long-term intracranial safety and efficacy analyses from the phase III CROWN study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33 (Suppl. 7), S998–S999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Abbattista, A.; Murphy, J.F.; Krulewicz, S.; Do, A.; Peterson, J.; Lin, J.J.; Gainor, J.F.; Messina, R.; Krueger, E.A.; et al. Factors Associated with Developing Neurocognitive Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Lorlatinib After Progression on Other Targeted Therapies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.; Bauer, T.; Mok, T.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Dvorkin, M.; et al. Abstract CT223: Updated efficacy and safety from the phase 3 CROWN study of first-line lorlatinib vs crizotinib in advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, CT223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Nagrath, S.; Ramnath, N. Immunotherapy for ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Challenges Inform Promising Approaches. Cancers 2021, 13, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Number * | Drug | Control Arm | Principal Endpoint | N. pt (FISH-) | ORR | BIRC mPFS (mos) | 2 Year OS (%) | AEs G3/4 | Discontinuation Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROFILE-1014 [26] | NCT01154140 | Crizotinib | Pem-based CT | BIRC-mPFS | 343 | 74% | 10.9 | 71.5% | 54% | 5% |
| ASCEND-4 [27] | NCT01828099 | Ceritinib | Pem-based CT | BIRC-mPFS | 373 | 73% | 16.6 | 70.6% | 78% | 2% |
| ALEX [34,35] | NCT02075840 | Alectinib | Crizotinib | mPFS | 303 (39) | 83% | 25.7 | 72.5% | 52% | 14.5% |
| ALTA-1L [36,37,38] | NCT02737501 | Brigatinib | Crizotinib | BIRC-mPFS | 275 | 74% | 24.0 | 76% | 70% | 13% |
| EXALT-3 [39] | NCT02767804 | Ensartinib | Crizotinib | BIRC-mPFS | 290 (43) | 75% | 25.8 | 78% | 50% | 9% |
| CROWN [40,41] | NCT03052608 | Lorlatinib | Crizotinib | BIRC-mPFS | 296 | 78% | NR | 88% | 72% | 11% |
| Trial | Drugs | Pts with BM | Pts with TL | Exp Arm IC-ORR | Control Arm IC-ORR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROFILE-1014 [29] | crizotinib vs. CT | 92 | 0 | NA | NA |
| ASCEND-4 [30] | ceritinib vs. CT | 121 | 44 | 72% | 27% |
| ALEX [37,38] | alectinib vs. crizotinib | 122 | 43 | 81% | 50% |
| ALTA 1-L [39,40,41] | brigatinib vs. crizotinib | 96 | 41 | 78% | 26% |
| eXalt3 [42] | ensartinib vs. crizotinib | 104 | 30 | 64% | 21% |
| CROWN [43,44] | lorlatinib vs. crizotinib | 78 | 30 | 82% | 23% |
| Drug | L1196M ^ | G1269A £ | C1156Y/T $ | E1210K & | I1171 α | I1151Ti β | S1206 µ | G1202R ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crizotinib | R | R | R | R | R | R [84] | R [84] | R [84] |
| Ceritinib | S | S | R | R | S | R | S | R |
| Alectinib | S/R | S | S | R | R | S | S | R |
| Brigatinib | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | R/S § |
| Ensartinib | S | S/R ç | S | R | S | S | S | R |
| Lorlatinib | S | S | S/R * | S | S | S | S | S |
| Trial | Phase | Pt N | Drug | Class | Setting | Principal Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03607188 | I | 18 | Alkotinib | 2nd ALK-I | Post-crizotinib | Safety |
| NCT04211922 | II | 104 | Alkotinib | 2nd ALK-I | Post-crizotinib | activity |
| NCT05441956 | I | 100 | TGRX-326 | 3rd ALK-I | Post 1st/2nd ALK-I | RP2D |
| NCT04237805 | I/II | 280 | Foritinib | 3rd ALK-I | Refractory | DLT/ORR |
| NCT05257512 | I/II | 70 | SY-3505 | 3rd ALK-I | Refractory | RP2D |
| NCT05055232 | I | 120 | XZP-3621 | 3rd ALK-I | Naïve/refractory | Safety |
| NCT05482087 | II | 190 | XZP-3621 | 3rd ALK-I | Naïve/refractory | ORR |
| NCT05204628 | RPIII | 238 | XZP-3621 | 3rd ALK-I | Naive | PFS |
| Type of Therapy | Trial Identifier | Ph. | Pt N | Drug(s) | Setting | Principal Endpoint | CNS metastasis Permitted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALK-I | ALTA-2 NCT03535740 | II | 103 | Brigatinib | Refractory | ORR | Asymptomatic BM; stable symptoms. |
| ERSGATR NCT05178511 | II | 40 | Ensartinib | Refractory | ORR | Asymptomatic BM; stable symptoms; previously treated with RT. | |
| NCT02927340 | II | 30 | Lorlatinib | Naïve/ refractory | IC-DCR | LM or CM ° | |
| ORAKLE NCT04111705 | II | 112 | Lorlatinib | Refractory | ORR | Asymptomatic BM; stable symptoms; previously treated with RT. | |
| ALKALINE NCT04127110 | II | 100 | Lorlatinib | Refractory * | PFS | Asymptomatic BM/LM; stable symptoms; previously treated with RT. | |
| NCT03917043 | I | 150 | APG-2449 (multi-TKI, 3rd ALK-I) | Refractory/naïve | MDT/RP2D | BM with controlled symptoms. | |
| ALKOVE-1 NCT05384626 | I/II | 214 | NVL-655 (4th ALK-I) | Refractory # | RP2D/ORR | NR | |
| ALK-I based combo | MASTER ALK NCT05200481 | RPII | 110 | Brigatinib +/− CT (platinum/pemetrexed) | Naïve | PFS | Symptomatic and neurologically stable BM metastases $. |
| NCT05491811 | II | 77 | Ensartinib + bevacizumab | Naïve/p53+ | 1-yr PFS rate | CNS metastases treated with RT and/or surgery. | |
| NCT03202940 | IB/II | 31 | Alectinib + cobimetinib | Refractory & | MTD | Asymptomatic BM or treated with RT. | |
| NCT04356118 | IV | 30 | RH endostatin+ IT MTX + ALK-I | Naive/ refractory | OS % | LM only. | |
| Combo without ALK-Is | NCT05266846 | II | 30 | CT+ bevacizumab + Pembrolizumab | Refractory | PFS | Treated CNS metastases. |
| NCT03991403 | RPIII | 228 | CT + bevacizumab + atezolizumab | Refractory | PFS | Asymptomatic or treated BM. | |
| GFPC 06-2018 NCT04042558 | II | 149 | CT + atezolizumab+/− bevacizumab | Refractory | ORR | Asymptomatic BM. £ | |
| NCT04425135 | II | 59 | CT+ camrelizumab + apatinib | Refractory | ORR | NA | |
| NCT04989322 | II | 46 | CT+ Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib | Refractory | ORR | Treated BM. | |
| HARMONIC NCT05456256 | II | 90 °° | CT+ LP-300 ** | Refractory | PFS/OS | Stable CNS Metastases. | |
| NCT05296278 | II | 80 | IBI-322 ## + Lenvatinib + CT | Refractory | PFS | Stable BM. | |
| NCT04777084 | Ib | 100 | IBI-318 $$ + Lenvatinib | Refractory | ORR | Asymptomatic or stable BM. | |
| NCT05681780 | I/II | 20 | CD40L-Augmented TIL+ nivolumab | Refractory | AEs | Stable or treated BM. | |
| PIKACHU NCT04322890 | Obs. | 100 | Anti-PD1 plus CT | Refractory | PFS | NA | |
| NCT05195619 | I | 16 | DC vaccines + low dose CP | Refractory | AEs | NA | |
| SNK_ASTER NCT04872634 | I/II | 24 | SNK01 NK + CT +/−cetuximab | Refractory | MTD | Treated and stable CNS metastases. | |
| NCT04880863 | II | 35 | NAP+ Docetaxel+ Obinutuzumab | Refractory | ORR | Treated and stable BM. | |
| NCT03645928 | II | 178 | Autologous TIL (LN-145) + IO | Refractory | ORR, Safety | Asymptomatic and treated BM. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spitaleri, G.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Attili, I.; Del Signore, E.; Corvaja, C.; Corti, C.; Crimini, E.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. Sustained Improvement in the Management of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocation: Where Are We Running? Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5072-5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30050384
Spitaleri G, Trillo Aliaga P, Attili I, Del Signore E, Corvaja C, Corti C, Crimini E, Passaro A, de Marinis F. Sustained Improvement in the Management of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocation: Where Are We Running? Current Oncology. 2023; 30(5):5072-5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30050384
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpitaleri, Gianluca, Pamela Trillo Aliaga, Ilaria Attili, Ester Del Signore, Carla Corvaja, Chiara Corti, Edoardo Crimini, Antonio Passaro, and Filippo de Marinis. 2023. "Sustained Improvement in the Management of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocation: Where Are We Running?" Current Oncology 30, no. 5: 5072-5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30050384
APA StyleSpitaleri, G., Trillo Aliaga, P., Attili, I., Del Signore, E., Corvaja, C., Corti, C., Crimini, E., Passaro, A., & de Marinis, F. (2023). Sustained Improvement in the Management of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocation: Where Are We Running? Current Oncology, 30(5), 5072-5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30050384





