Transoral Approach to Parapharyngeal Space Tumours: Preliminary Reports from a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
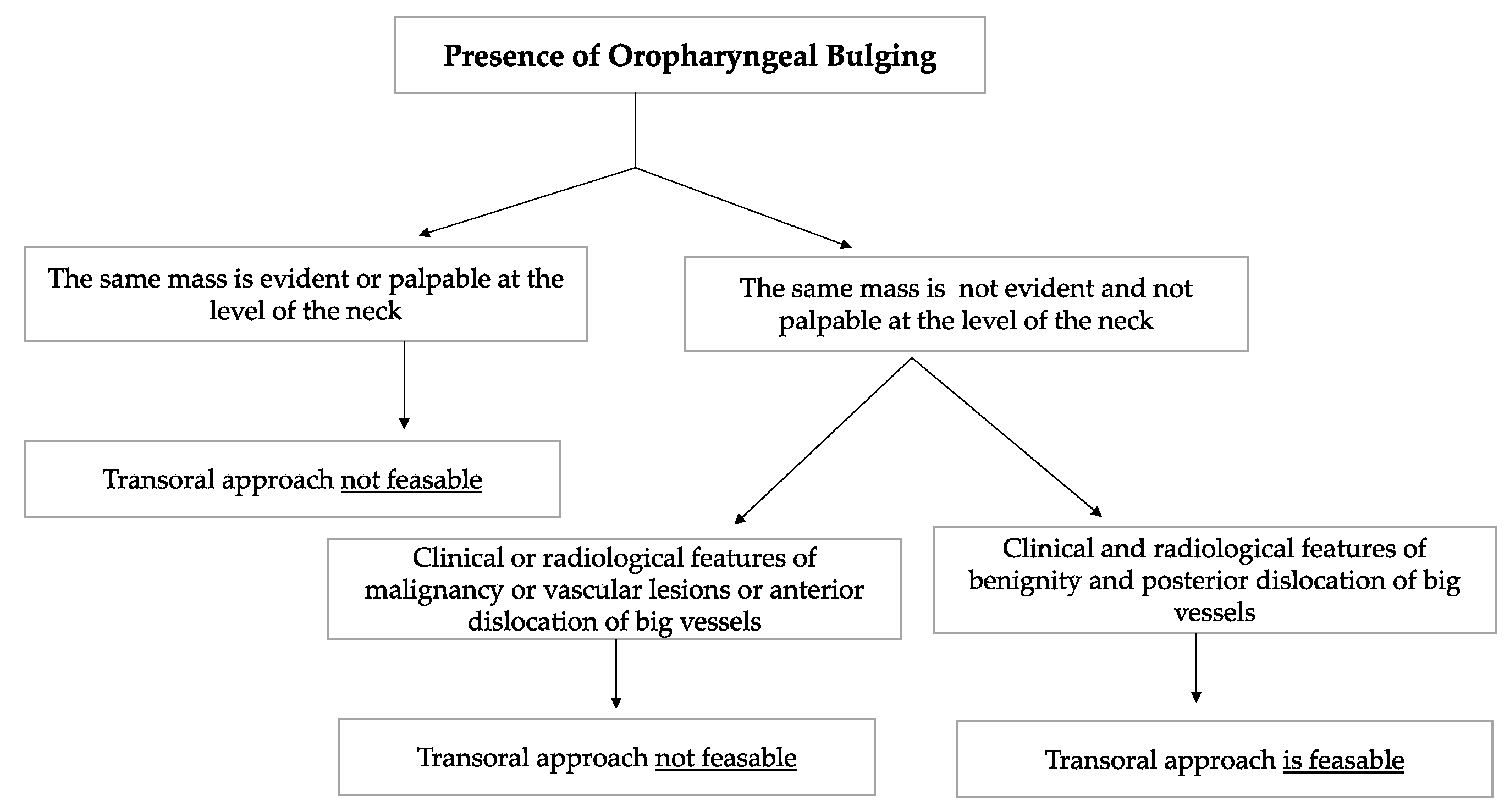
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- Five pleomorphic adenomas that arose from minor salivary glands in three cases and from the deep lobe of the parotid gland in two cases. All of these tumours were situated in the true PPS, medially with respect to the great vessels. In all the patients, no complications were observed during and after surgery. Hospitalisation time was two days for three patients, three days for one patient and four days for the other patient. No tumour recurrence was observed after sixteen, nine, eight and seven years for the first four patients. Evaluating the recurrence in the last patient is still not possible due to the short follow-up period, since the patient underwent surgery in 2021.
- One lipoma arose from the true parapharyngeal space. The patient underwent surgery in 2012 and had no intraoperative and no postoperative complications. No recurrence was observed after ten years. The hospitalisation time was two days.
- One ectopic thyroid arose from the right true parapharyngeal space. This was the only case in which a fine needle aspiration citology (FNAC) was performed, and the results were inconclusive. The patient underwent surgery in 2003 with no intraoperative or postoperative complications. The hospitalisation time was three days. No recurrence observed after eighteen years.
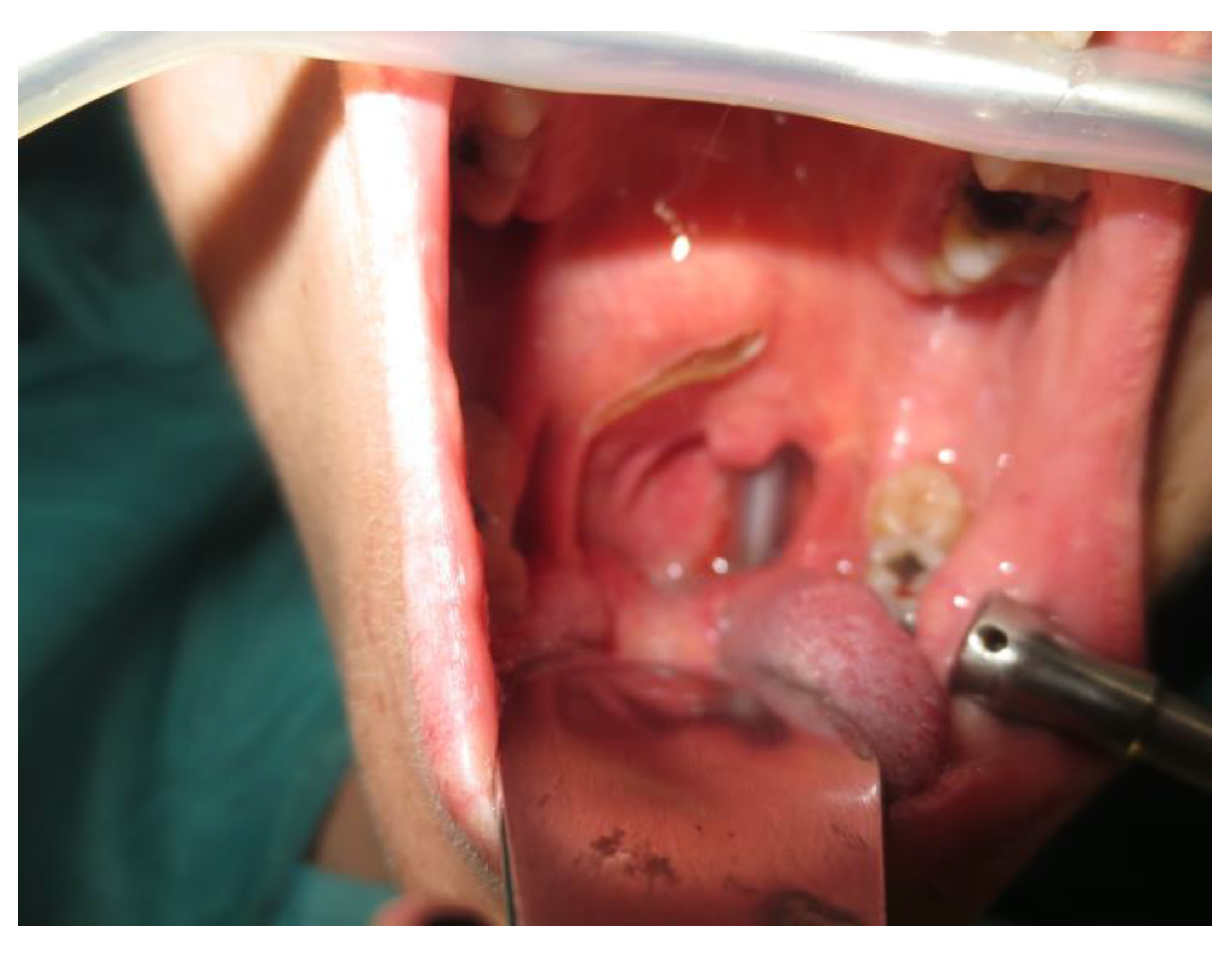
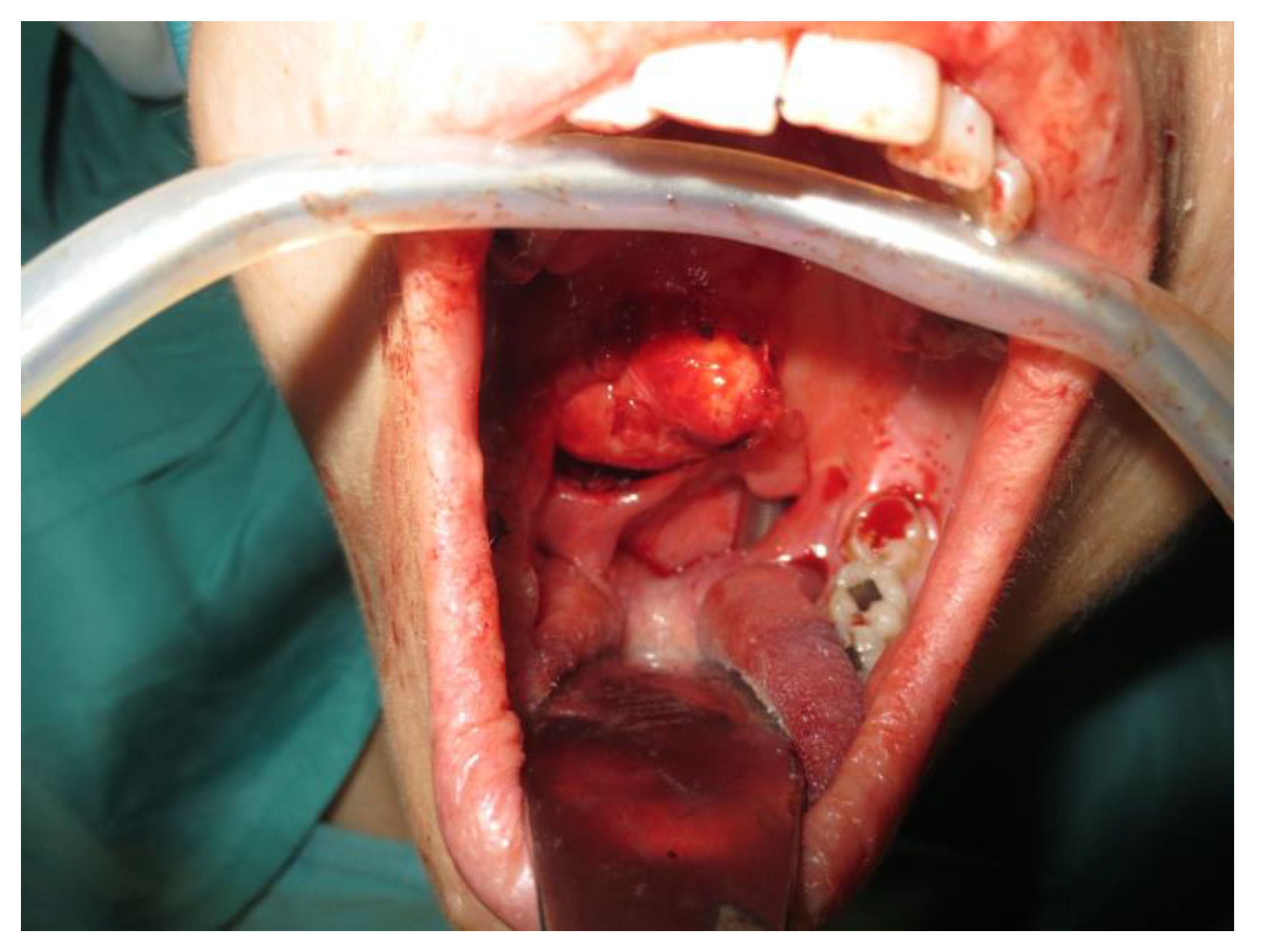
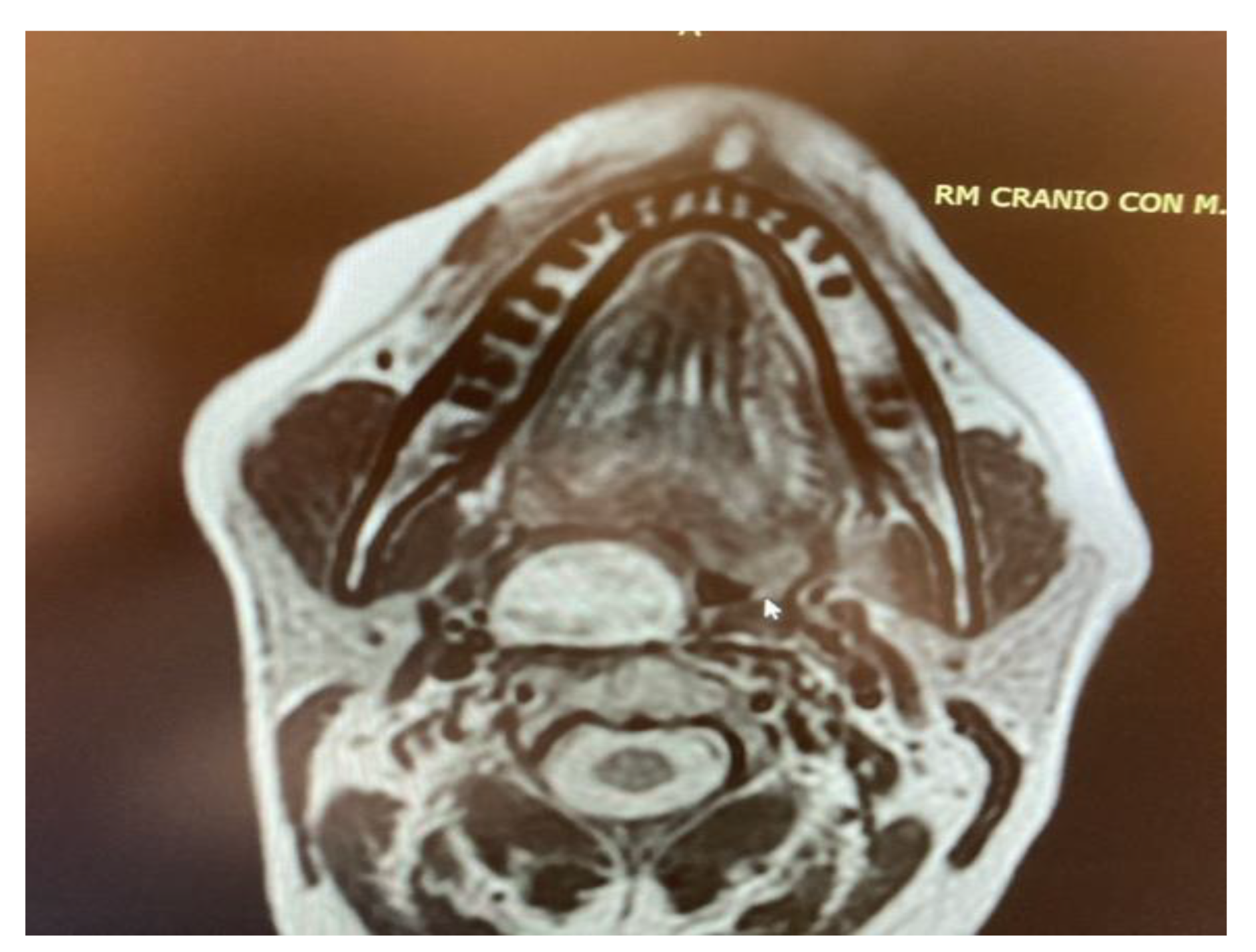
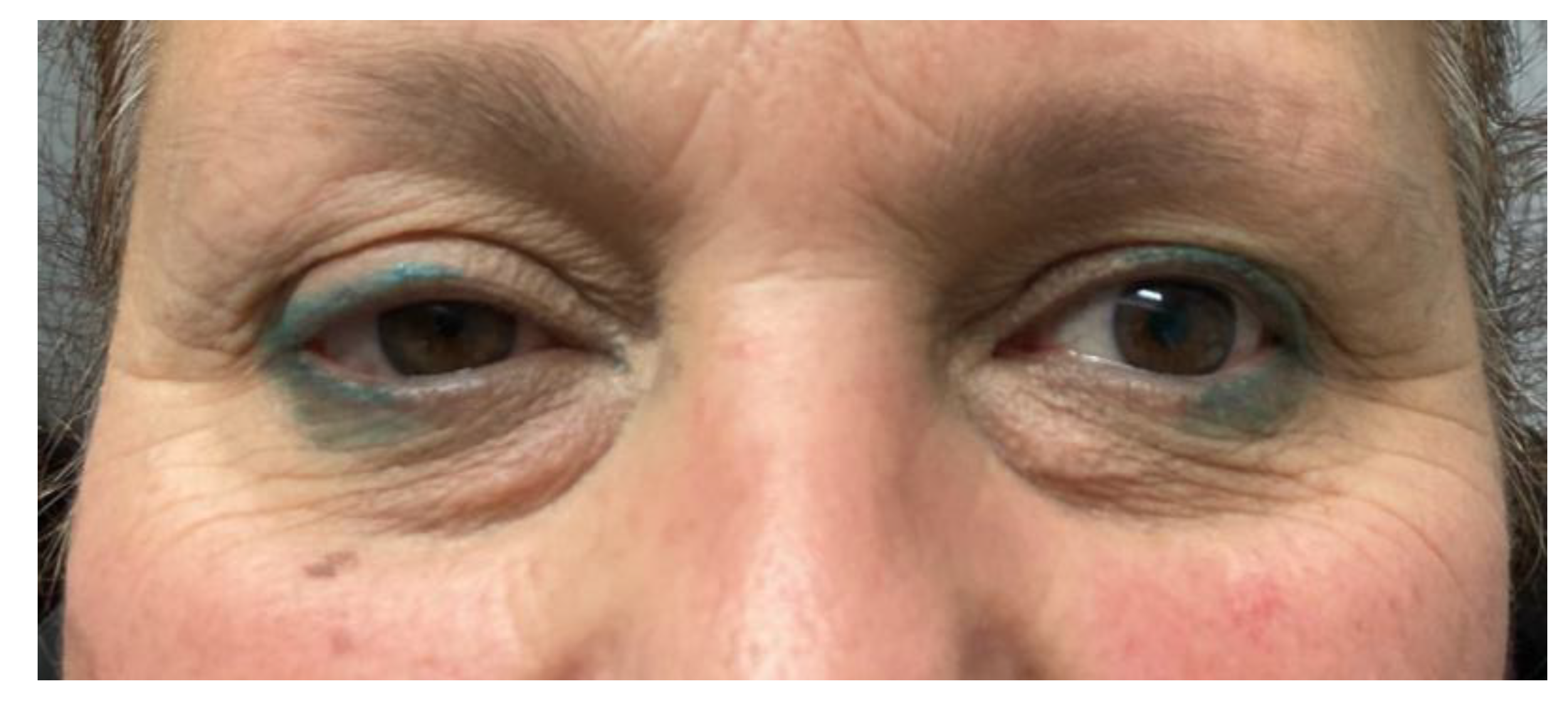
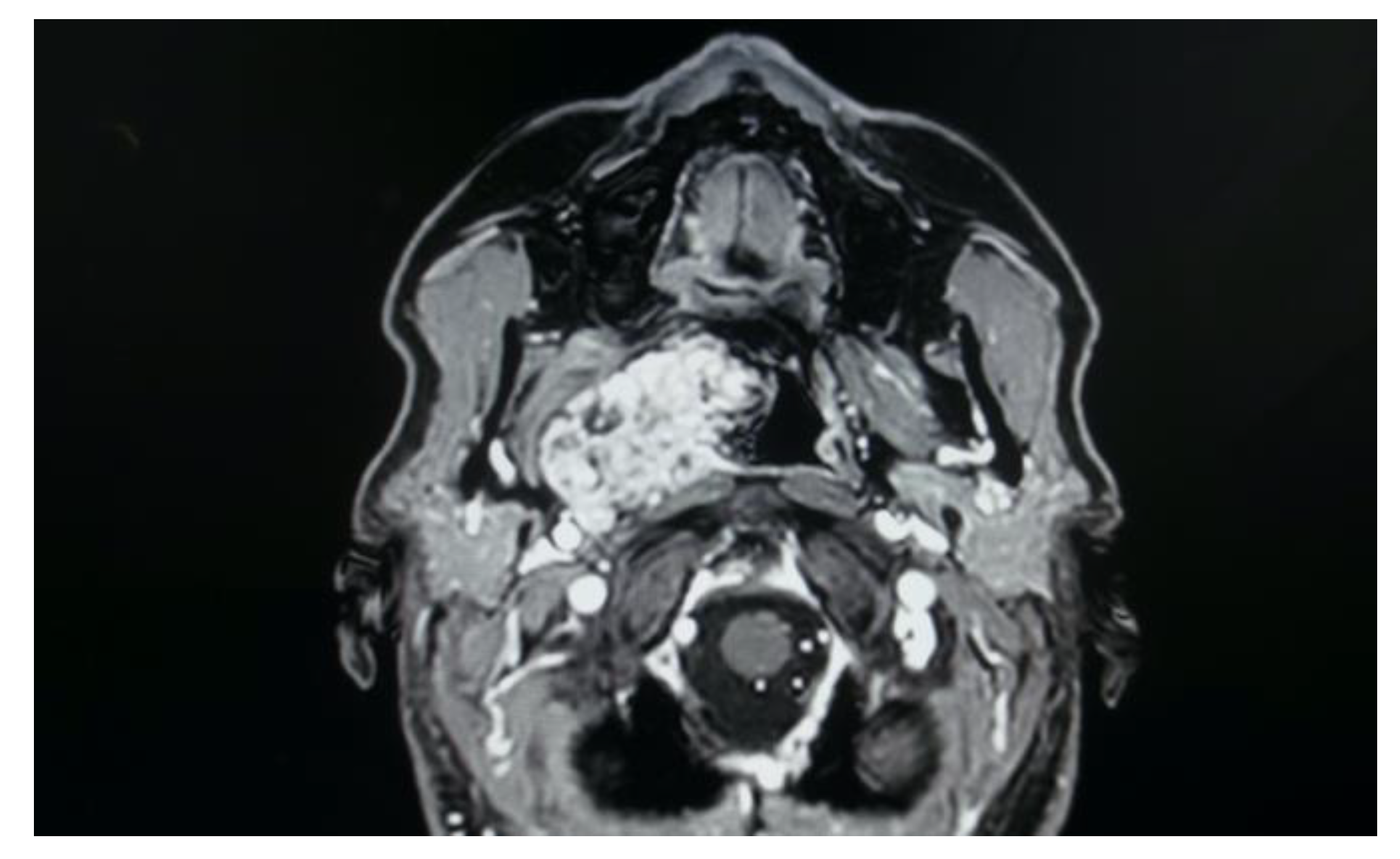
- Two schwannomas (Figure 5) originating from the cervical sympathetic chain and that arose in the superomedial aspect of the PPS, medially to the carotid sheath. The first patient underwent surgery in 2008, the second in 2019. No complications were observed during surgery and no tumour recurrence has been observed after 14 and 4 years, respectively. The only long-term complication observed was Horner syndrome (Figure 6), despite the continuity of the nerve not being interrupted. The hospitalisation time was three days for both patients.
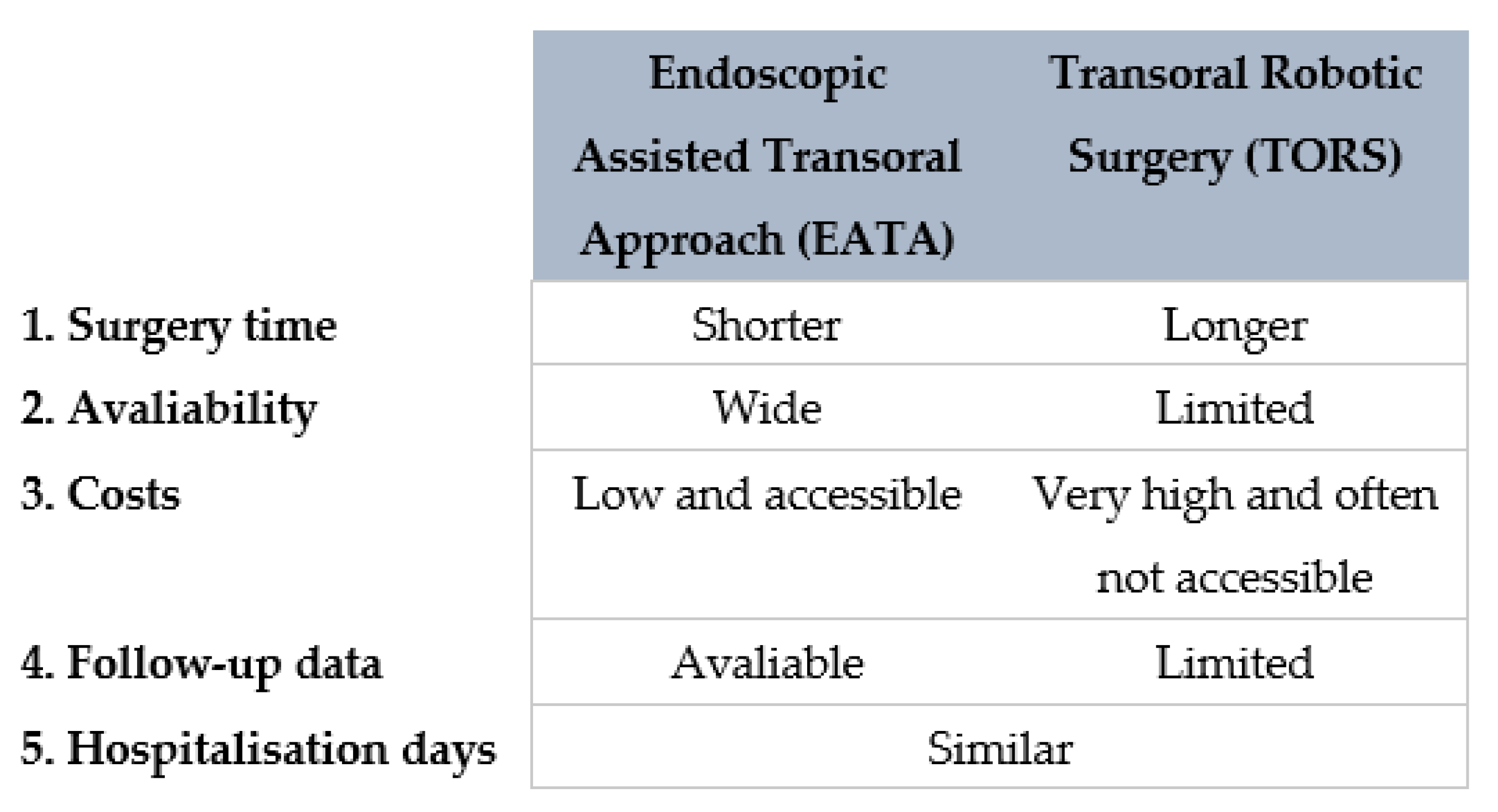
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bootz, F.; Greschus, S.; Van Bremen, T. Therapie parapharyngealer Tumoren [Diagnosis and treatment of parapharyngeal space tumors]. HNO 2016, 64, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Lorenzi, A.; Borello, A.; Albera, A.; Canale, A.; Pecorari, G. Transoral Approach to Parotid Tumors: A Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 9416–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, F.; Suarez, C.; Vander Poorten, V.; Mäkitie, A.; Nixon, I.J.; Strojan, P.; Hanna, E.Y.; Rodrigo, J.P.; de Bree, R.; Quer, M.; et al. Contemporary management of primary parapharyngeal space tumors. Head Neck 2019, 41, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaran, B.; Polat, B.; Unsaler, S.; Ulusan, M.; Aslan, I.; Hafiz, G. Parapharyngeal space tumors: The efficiency of a transcervical approach without mandibulotomy through review of 44 cases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Presutti, L.; Molteni, G.; Malvè, L.; Marchioni, D.; Ghidini, A.; Tassi, S.; Chiarini, L.; Alicandri-Ciufelli, M. Parapharyngeal space tumors without mandibulotomy: Our experience. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2012, 269, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.L.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, S.H.; Bao, Y.Y.; Shang, D.S.; Ruan, L.X. Excision of tumors in the parapharyngeal space using an endoscopically assisted transoral approach: A casa series and literature review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.R.; Ryan, W.R. Transoral Excision of Parapharyngeal Space Tumors. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 54, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, W.P.; Han, P.S.; Lee, N.H.; Gilde, J.E.; Inman, J.C. Transoral Excision of Parapharyngeal Tumors. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP454–NP458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducic, Y.; Oxford, L.; Pontius, A.T. Transoral approach to the superomedial parapharyngeal space. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseri, M.; Ozturk, M.; Kara, A.; Ucar, S.; Aydin, O.; Keskin, G. Endoscope-assisted transoral approach to parapharyngeal space tumors. Head Neck 2015, 37, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallan, I.; Fiacchini, G.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Seccia, V.; Battaglia, P.; Casani, A.P.; Cristofani-Mencacci, L.; Sellari-Franceschini, S. Endoscopic-assisted transoral transpharyngeal approach to parapharyngeal space and infratemporal fossa: Focus on feasibility and lessons learned. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3965–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Fan, S.; Huang, Z.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Endoscopy-assisted transoral versus endoscopy-assisted transcervical minimal incision plus mandibular osteotomy approach in resection of large parapharyngeal space tumors. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Tagliabue, M.; Giugliano, G.; Calabrese, L.; Preda, L.; Ansarin, M. From transmandibular to transoral robotic approach for parapharyngeal space tumors. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 38, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffat, F.; Dwivedi, R.C.; Palme, C.; Fish, B.; Jani, P. A systematic review of 1143 parapharyngeal space tumors reported over 20 years. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadogeorgakis, N.; Petsinis, V.; Goutzanis, L.; Kostakis, G.; Alexandridis, C. Parapharyngeal space tumors: Surgical approaches in a series of 13 cases. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrijevic, M.V.; Jesic, S.D.; Mikic, A.A.; Arsovic, N.A.; Tomanovic, N.R. Parapharyngeal space tumors: 61 case reviews. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Yan, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, W.; Cao, S.; Liu, D.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Lei, D. Surgical management of primary parapharyngeal space tumors in 103 patients at a single institution. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante-Cossio, P.; González-Cardero, E.; González-Pérez, L.M.; Leopoldo Rodado, M.; Garcia-Perla, A.; Esteban, F. Management of parapharyngeal giant pleomorphic adenoma. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 15, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimilla, E.; Motta, G.; Magaldi, M.; Montella, M.; Messina, G.; Testa, D.; Cantone, E.; Motta, G. Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallan, I.; Seccia, V.; Muscatello, L.; Lenzi, R.; Castelnuovo, P.; Bignami, M.; Montevecchi, F.; Tschabitscher, M.; Vicini, C. Transoral endoscopic anatomy of the parapharyngeal space: A step-by-step logical approach with surgical considerations. Head Neck 2011, 33, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhong, Q.; Fang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Early experience in endoscopic transoral resection for parapharyngeal space tumors. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018, 97, E5–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaslikaya, S.; Koca, C.F.; Toplu, Y.; Kizilay, A.; Akpolat, N. Endoscopic transoral resection of parapharyngeal osteoma: A case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 2329.e1–2329.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yan, B.; Truong, H.; Borghei-Razavi, H.; Snyderman, C.; Fernandez-Miranda, J. A comparative analysis of endoscopic-assisted transoral and transnasal approaches to parapharyngeal space: A cadaveric study. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2017, 79, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chen, M.-K. Minimally invasive endoscope-assisted trans-oral excision of huge parapharyngeal space tumors. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.-J.; Zhen, H.-T. Transoral and endoscope-assisted transoral approaches to resecting benign tumours of the parapharyngeal space located in the medial portion of the carotid sheaths and extending toward the skull base: Our experience. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2018, 132, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliai, B.R.; Sheth, S.; Burroughs, F.H.; Ali, S.Z. “Parapharyngeal space” tumors: A cytopathological study of 24 cases on fine-needle aspiration. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2005, 32, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.J.; Bradley, P.T.; Olsen, K.D. Update on the management of parapharyngeal tumours. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 19, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, K.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Ji, Q.; Shen, Q.; Sun, T.; Xiang, J.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Extracranial schwannoma in the carotid space: A retrospective review of 91 cases. Head Neck 2017, 39, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakura, S.; Tsunoda, A.; Akita, K.; Sumi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Kishimoto, S. Parapharyngeal space tumors: Anatomical and image analysis findings. Auris Nasus Larynx 2010, 37, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.J.; Curry, J.M.; Luginbuhl, A.; Cognetti, D. Transoral robotic approach to parapharyngeal space tumors: Case series and technical limitations. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Rege, S. Horner’s Syndrome due to Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannoma: A Rare Presentation and Review of Literature. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2021, 14, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.Y.; Tsang, R.K.; Eisele, D.W.; Richmon, J.D. Transoral robotic surgery of the parapharyngeal space: A case series and systematic review. Head Neck 2015, 37, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, A.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, W.S.; Byeon, H.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.H. Transoral robotic surgery for the resection of parapharyngeal tumour: Our experience in ten patients. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2012, 37, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, A.; Costantino, A.; Mercante, G.; Di Maio, P.; Iocca, O.; Spriano, G. Trans-oral robotic surgery in the management of parapharyngeal space tumors: A systematic review. Oral Oncol. 2020, 103, 104581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Age | Sex | Signs | Symptoms | Location | Surgery Time | Intraoperative Complications | Tumour Size (cm) | Histological Diagnosis | Hospitalization Days | Post-Operative Sequalae | Follow Up (Years) | Recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 86 | Male | Oropharyngeal mass | Dyspnea, dysphagia | True PPS | 60 min | None | 435.2 | Benign thyroid tissue | 3 | None | 19 | No |
| 75 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Dysphagia | Carotid space | 70 min | None | 343 | Schwannoma | 3 | Horner Syndrome | 14 | No |
| 53 | Male | Oropharyngeal mass | Asymptomatic | True PPS | 20 min | None | 42.53 | Lipoma | 2 | None | 10 | No |
| 56 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Dysphagia, Foreign body sensation | True PPS | 40 min | None | 53.34.2 | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 2 | None | 9 | No |
| 59 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Dysphagia, Foreign body sensation | True PPS | 50 min | None | 533.3 | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 2 | None | 7 | No |
| 57 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass, snoring | Dysphagia, Foreign body sensation | Carotid space | 120 min | None | 2.62.62.2 | Schwannoma | 3 | Horner Syndrome | 4 | No |
| 49 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Dysphagia, dysphonia Foreign body sensation | True PPS | 50 min | None | 63.44.5 | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 3 | None | 1 | No |
| 55 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Foreign body sensation, | True PPS | 40 min | None | 422 | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 2 | None | 16 | No |
| 36 | Female | Oropharyngeal mass | Asymptomatic | True PPS | 30 min | None | 322.2 | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 4 | None | 8 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motta, G.; Testa, D.; Donadio, A.; Ricciardiello, F.; Cavaliere, M.; Massimilla, E.A.; Motta, G. Transoral Approach to Parapharyngeal Space Tumours: Preliminary Reports from a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3927-3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040297
Motta G, Testa D, Donadio A, Ricciardiello F, Cavaliere M, Massimilla EA, Motta G. Transoral Approach to Parapharyngeal Space Tumours: Preliminary Reports from a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(4):3927-3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040297
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotta, Giovanni, Domenico Testa, Anna Donadio, Filippo Ricciardiello, Michele Cavaliere, Eva Aurora Massimilla, and Gaetano Motta. 2023. "Transoral Approach to Parapharyngeal Space Tumours: Preliminary Reports from a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis" Current Oncology 30, no. 4: 3927-3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040297
APA StyleMotta, G., Testa, D., Donadio, A., Ricciardiello, F., Cavaliere, M., Massimilla, E. A., & Motta, G. (2023). Transoral Approach to Parapharyngeal Space Tumours: Preliminary Reports from a Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Current Oncology, 30(4), 3927-3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040297







