Molecular Characterization and Prognosis of Lactate-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Resources
2.2. Mutation, CNV, Expression, and Survival of LRGs in LUAD
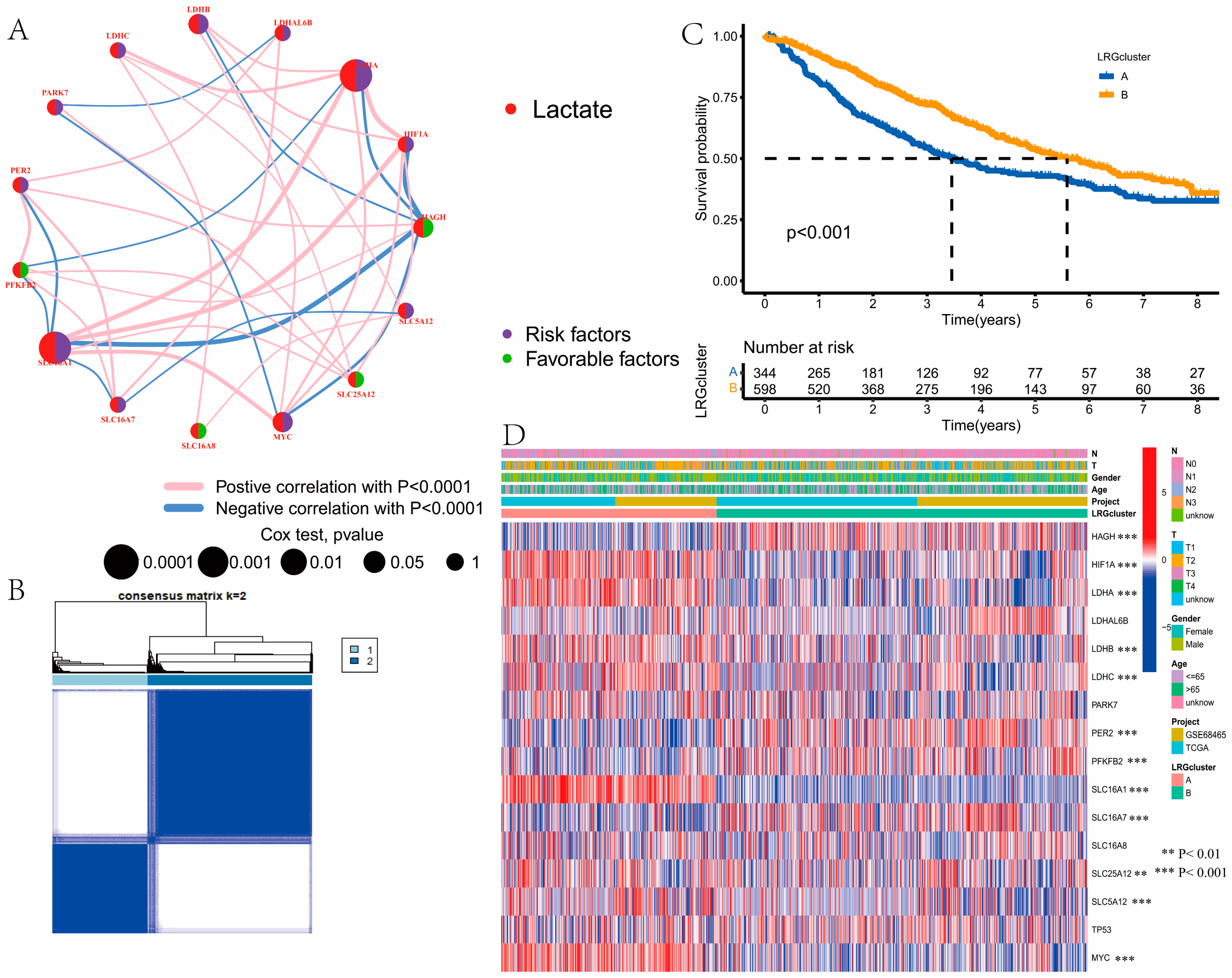
2.3. Consensus Clustering for LRGs
2.4. LRGs-Related Genes Identification and Function
2.5. Development and Validation of the Prognostic Model
2.6. Development and Validation of the Nomogram
2.7. Landscape of TME Cell Infiltration between Low- and High-Risk Groups
2.8. Mutation and Drug Susceptibility Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mutation, CNV, Expression, and Survival of LRGs in LUAD
3.2. Identification of Lactate Clusters in LUAD
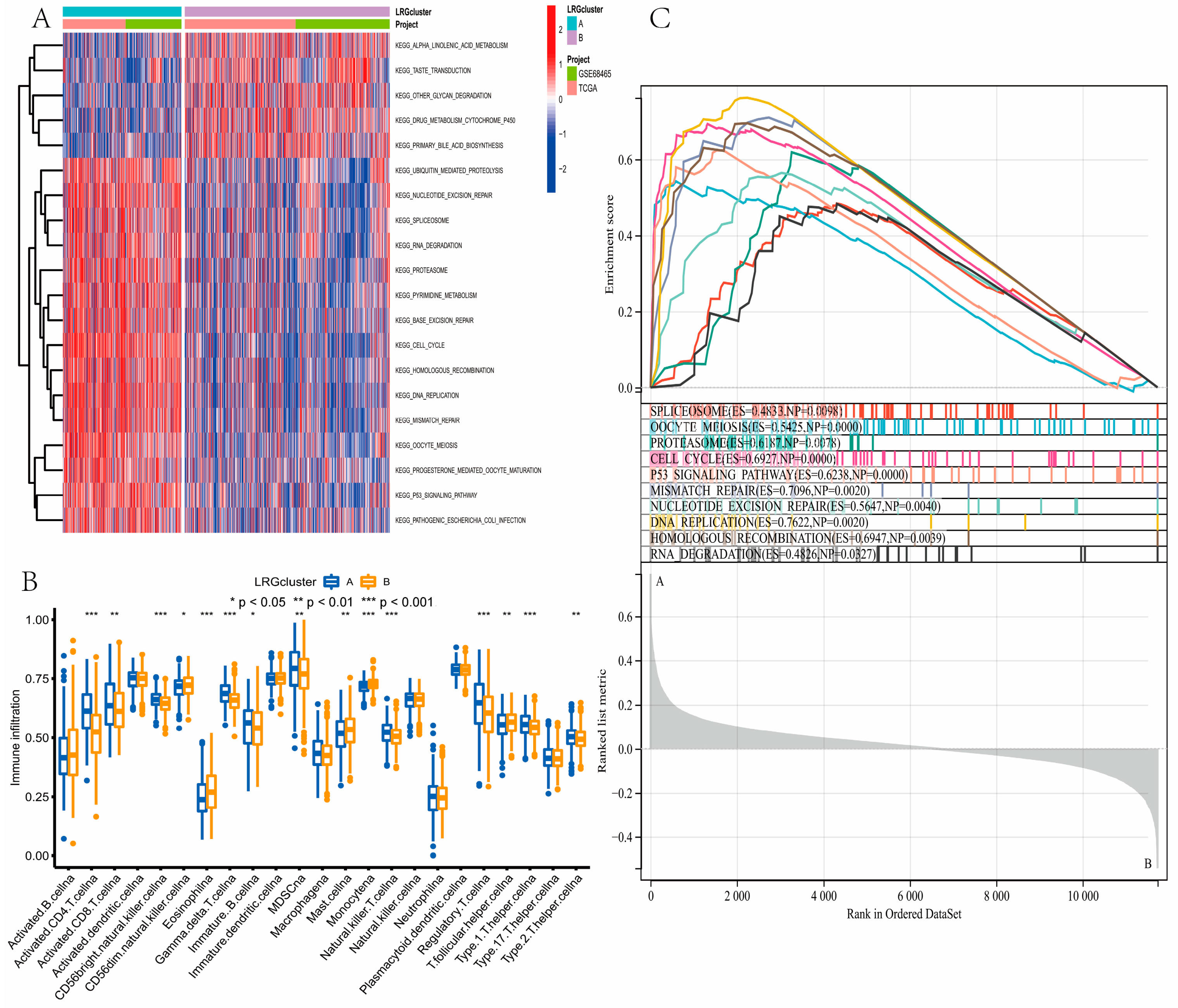
3.3. Gene Function Analysis for LRGs
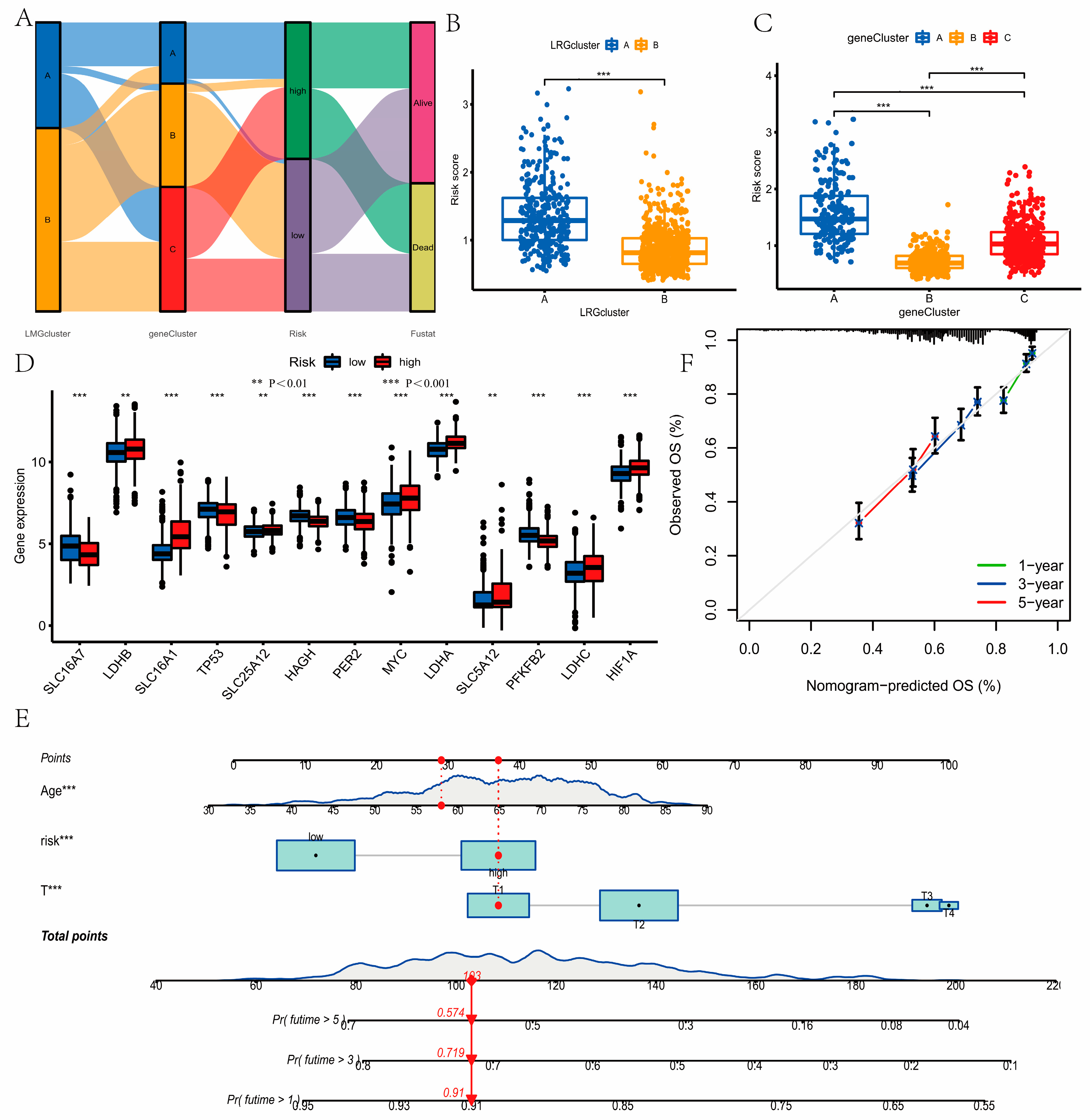
3.4. Identification of Gene Clusters
3.5. Construction and Validation of the Prognostic Model
3.6. Development of a Nomogram to Predict Survival
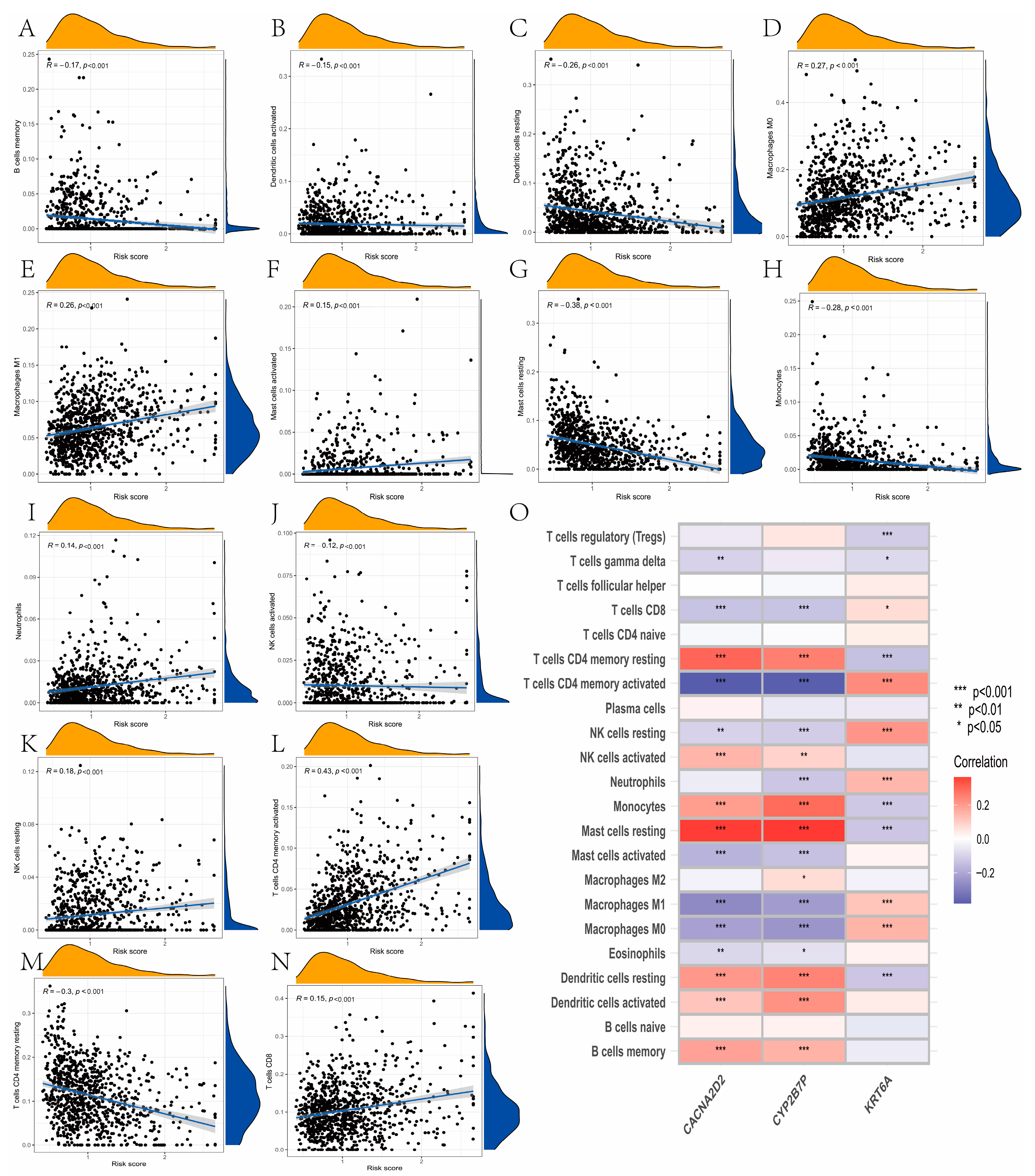
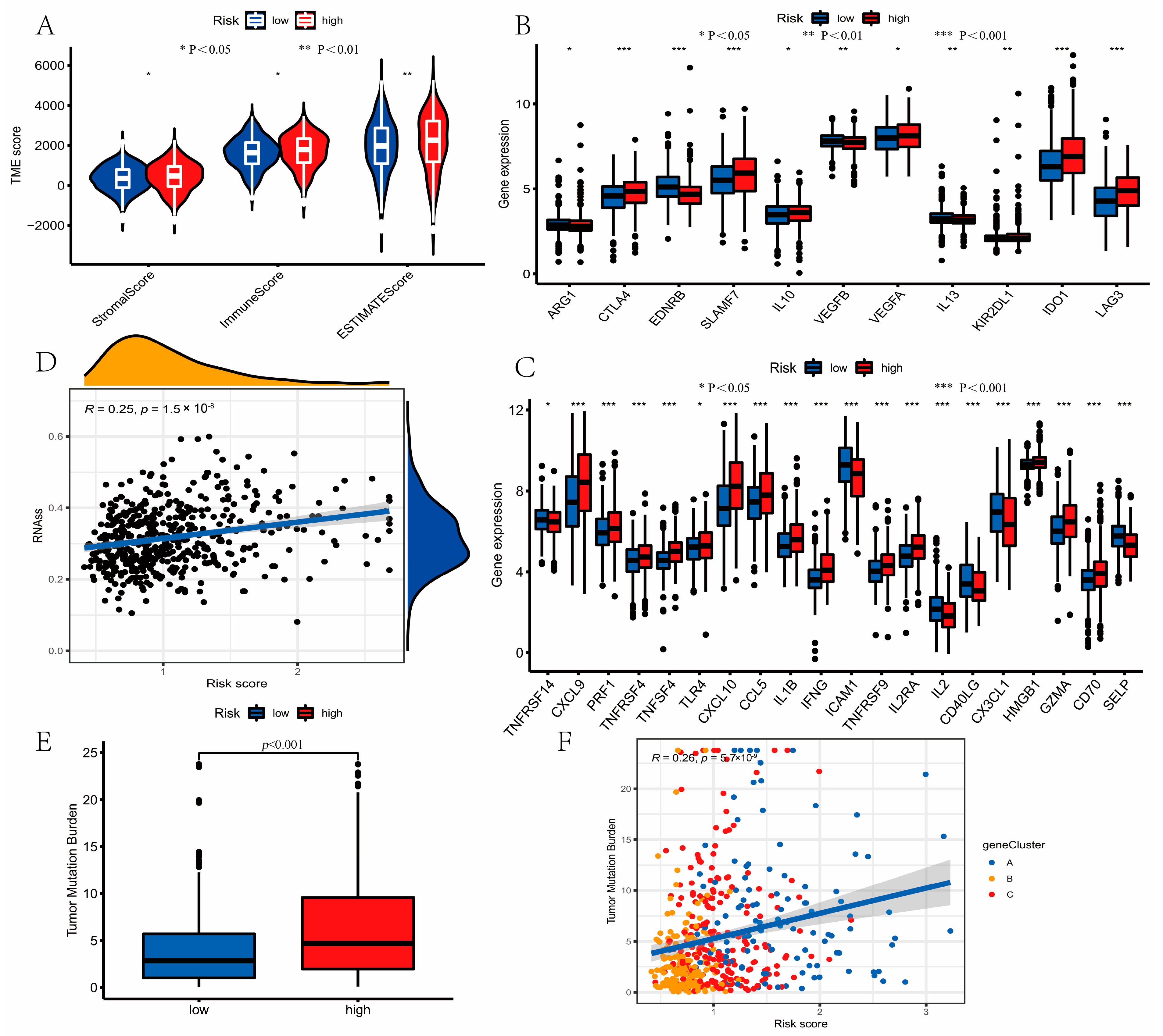
3.7. Evaluation of TME Cell Infiltration between the High- and Low-Risk Groups
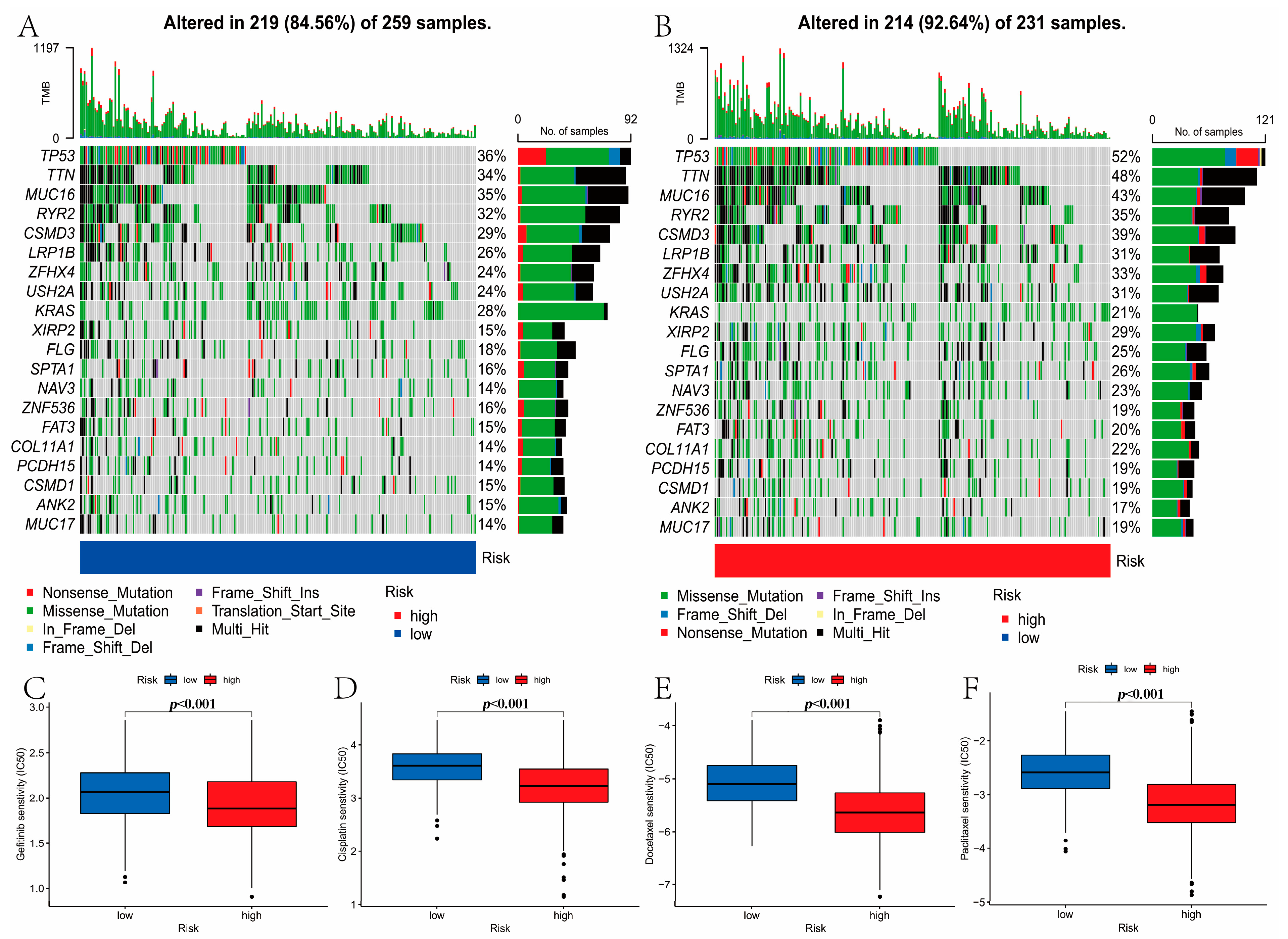
3.8. Mutation and Drug Susceptibility Analysis
3.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Cardarella, S.; Lydon, C.A.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jackman, D.M.; Jänne, P.A.; Johnson, B.E. Five-Year Survival in EGFR-Mutant Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma Treated with EGFR-TKIs. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmani, L.; Askin, F.; Gabrielson, E.; Li, Q.K. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Ma, D.; Hao, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Shan, L.; Xin, T.; Liang, L.; et al. Efficacy of Crizotinib for Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastasis: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study in China. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Lung Cancers: Molecular Characterization, Clonal Heterogeneity and Evolution, and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Shi, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhao, T.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Tumor-derived lactate induces M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the ERK/STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S. Lactic acid promotes macrophage polarization through MCT-HIF1α signaling in gastric cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 388, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xiang, H.; Pang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Dai, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T. Association between lactate dehydrogenase levels and oncologic outcomes in metastatic prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7341–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedden, K.; Taylor, J.M.; Enkemann, S.A.; Tsao, M.S.; Yeatman, T.J.; Gerald, W.L.; Eschrich, S.; Jurisica, I.; Giordano, T.J.; Misek, D.E.; et al. Gene expression-based survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma: A multi-site, blinded validation study. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, F.; Chai, L.; Jia, J. The Pyroptosis-Related Signature Predicts Prognosis and Indicates Immune Microenvironment Infiltration in Gastric Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 676485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, M.S.; Shukla, S.A.; Wu, C.J.; Getz, G.; Hacohen, N. Molecular and genetic properties of tumors associated with local immune cytolytic activity. Cell 2015, 160, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iasonos, A.; Schrag, D.; Raj, G.V.; Panageas, K.S. How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830.e814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geeleher, P.; Cox, N.; Huang, R.S. pRRophetic: An R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Sattler, U.G.; Mueller-Klieser, W. Lactate: A metabolic key player in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6921–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, S.K.; Chiche, J.; Pouysségur, J. Disrupting proton dynamics and energy metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halestrap, A.P. Monocarboxylic acid transport. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1611–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, S.; Tavares-Valente, D.; Queirós, O.; Baltazar, F. Value of pH regulators in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 43, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Escuredo, J.; Van Hée, V.F.; Sboarina, M.; Falces, J.; Payen, V.L.; Pellerin, L.; Sonveaux, P. Monocarboxylate transporters in the brain and in cancer. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, L.; Roche, M.; Domingo-Vidal, M.; Tanson, K.; Philp, N.; Curry, J.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U. Metabolic coupling and the Reverse Warburg Effect in cancer: Implications for novel biomarker and anticancer agent development. Semin. Oncol. 2017, 44, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubert, B.; Li, K.Y.; Cai, L.; Hensley, C.T.; Kim, J.; Zacharias, L.G.; Yang, C.; Do, Q.N.; Doucette, S.; Burguete, D.; et al. Lactate Metabolism in Human Lung Tumors. Cell 2017, 171, 358–371.e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Nunes, A.; Afonso, J.; Granja, S.; Baltazar, F. Lactate and Lactate Transporters as Key Players in the Maintenance of the Warburg Effect. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1219, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarsky, L.; Bill, R.; Fagiani, E.; Dimeloe, S.; Goosen, R.W.; Hagmann, J.; Hess, C.; Christofori, G. Targeting Metabolic Symbiosis to Overcome Resistance to Anti-angiogenic Therapy. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, C.; Garcia, E.A.; Morais-Santos, F.; Moreira, M.A.; Almeida, F.M.; Jubé, L.F.; Queiroz, G.S.; Paula, É.C.; Andreoli, M.A.; Villa, L.L.; et al. Reprogramming energy metabolism and inducing angiogenesis: Co-expression of monocarboxylate transporters with VEGF family members in cervical adenocarcinomas. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Guo, L.; Kang, E.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Niu, H.T. Monocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 are independent prognostic biomarkers for the survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and those receiving therapy targeting angiogenesis. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 311.e315–311.e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, V.L.; Mina, E.; Van Hée, V.F.; Porporato, P.E.; Sonveaux, P. Monocarboxylate transporters in cancer. Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, T.W.; Schuurbiers, O.C.; Kaanders, J.H.; Looijen-Salamon, M.G.; de Geus-Oei, L.F.; Verhagen, A.F.; Lok, J.; van der Heijden, H.F.; Rademakers, S.E.; Span, P.N.; et al. Differences in metabolism between adeno- and squamous cell non-small cell lung carcinomas: Spatial distribution and prognostic value of GLUT1 and MCT4. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrail, D.J.; Pilié, P.G.; Rashid, N.U.; Voorwerk, L.; Slagter, M.; Kok, M.; Jonasch, E.; Khasraw, M.; Heimberger, A.B.; Lim, B.; et al. High tumor mutation burden fails to predict immune checkpoint blockade response across all cancer types. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2021, 32, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Wan, J. Identification of prognostic immune-related genes in the tumor microenvironment of endometrial cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 3371–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Mora, F.; Locke, W.J.; Bandrés, E.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; Cejas, P.; García-Cabezas, M.A.; Colino-Sanguino, Y.; Feliú, J.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Lacal, J.C. Clinical relevance of the transcriptional signature regulated by CDC42 in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26755–26770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Kong, F.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X. LncRNA MIR210HG promotes proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating methylation of CACNA2D2 promoter via binding to DNMT1. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 3779–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, B.; Luo, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y. Identification of key pseudogenes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on RNA-Seq analysis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, G.; Xu, E.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q. Identification of SRXN1 and KRT6A as Key Genes in Smoking-Related Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer through Bioinformatics and Functional Analyses. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 810301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, D.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Li, B.; Xu, T.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Lu, Z.; Gu, X. KRT6A Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion Through MYC-Regulated Pentose Phosphate Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 694071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Hu, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.-P.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Hu, W. Molecular Characterization and Prognosis of Lactate-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2845-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030217
Guo Z, Hu L, Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu X-P, Chen C, Li S, Hu W. Molecular Characterization and Prognosis of Lactate-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):2845-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030217
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zixin, Liwen Hu, Qingwen Wang, Yujin Wang, Xiao-Ping Liu, Chen Chen, Sheng Li, and Weidong Hu. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Prognosis of Lactate-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 2845-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030217
APA StyleGuo, Z., Hu, L., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, X.-P., Chen, C., Li, S., & Hu, W. (2023). Molecular Characterization and Prognosis of Lactate-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Current Oncology, 30(3), 2845-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030217




