CKLF as a Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Differential Expression Data of CMTM Family Members in HCC
2.3. Clinicopathological Characteristics Analysis of CMTM Family Members in HCC
2.4. Survival and Prognostic Analysis of CMTM Family Members in HCC
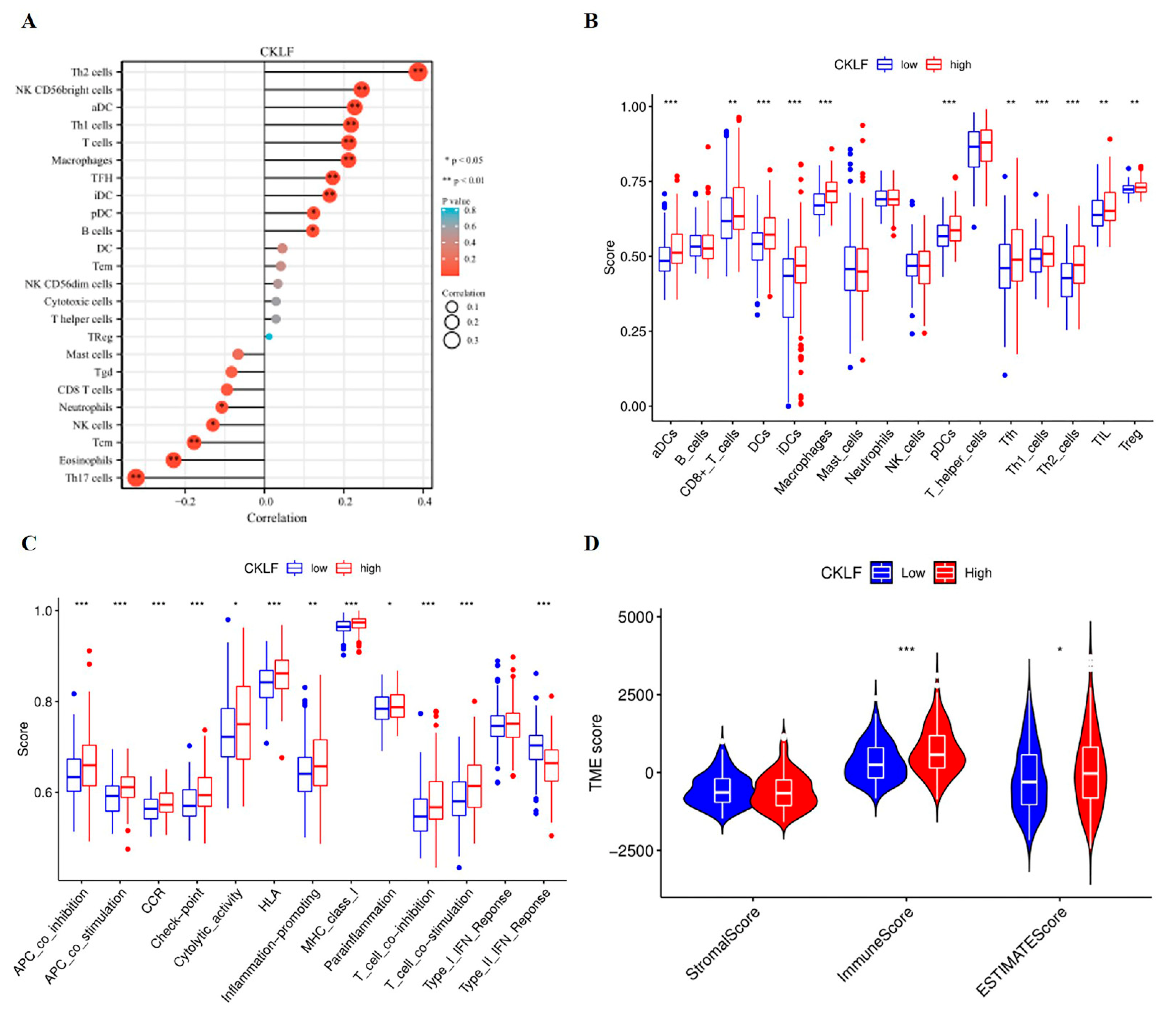
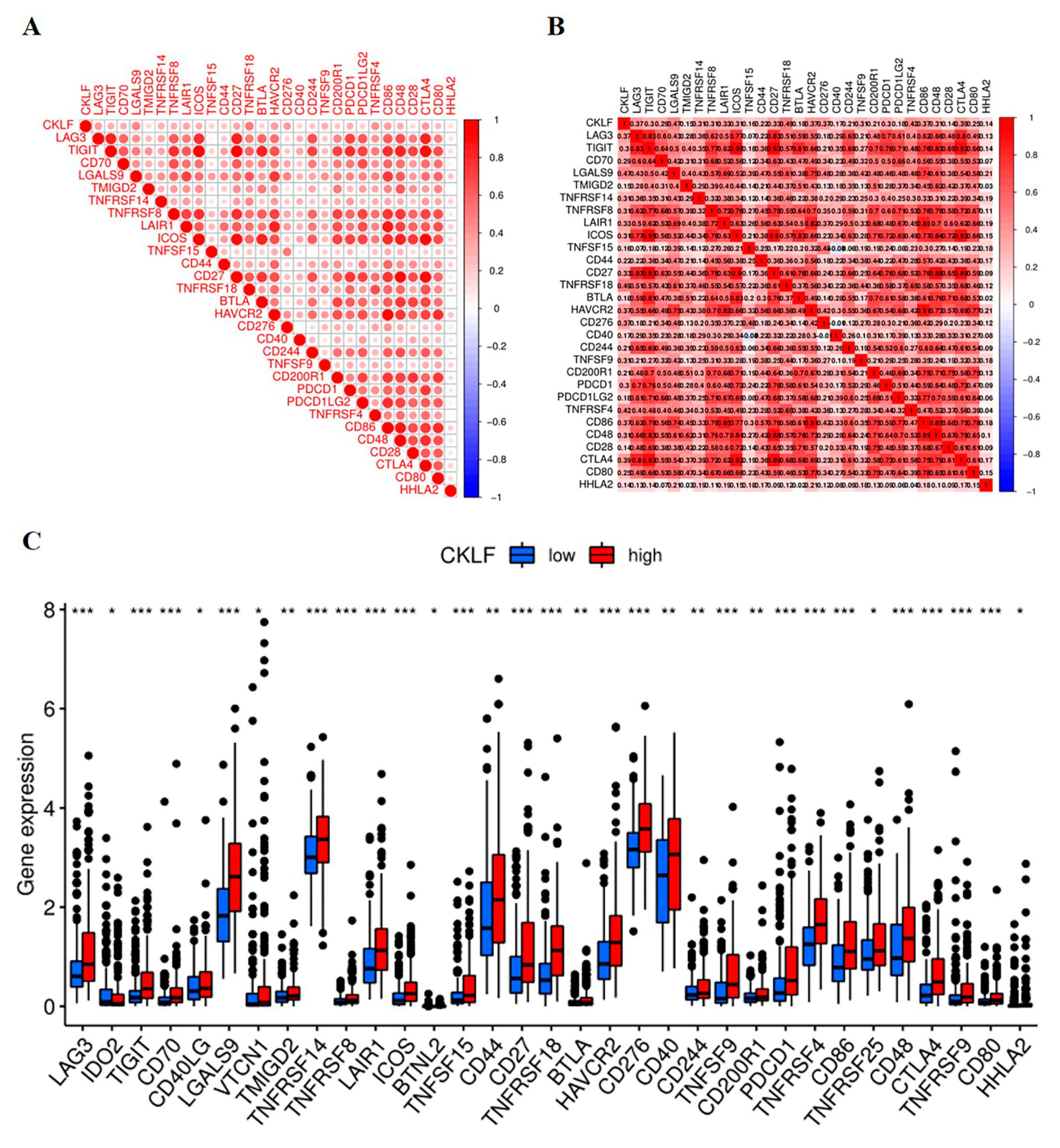
2.5. The Investigation of CMTM Family Members with Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Checkpoint Genes in HCC
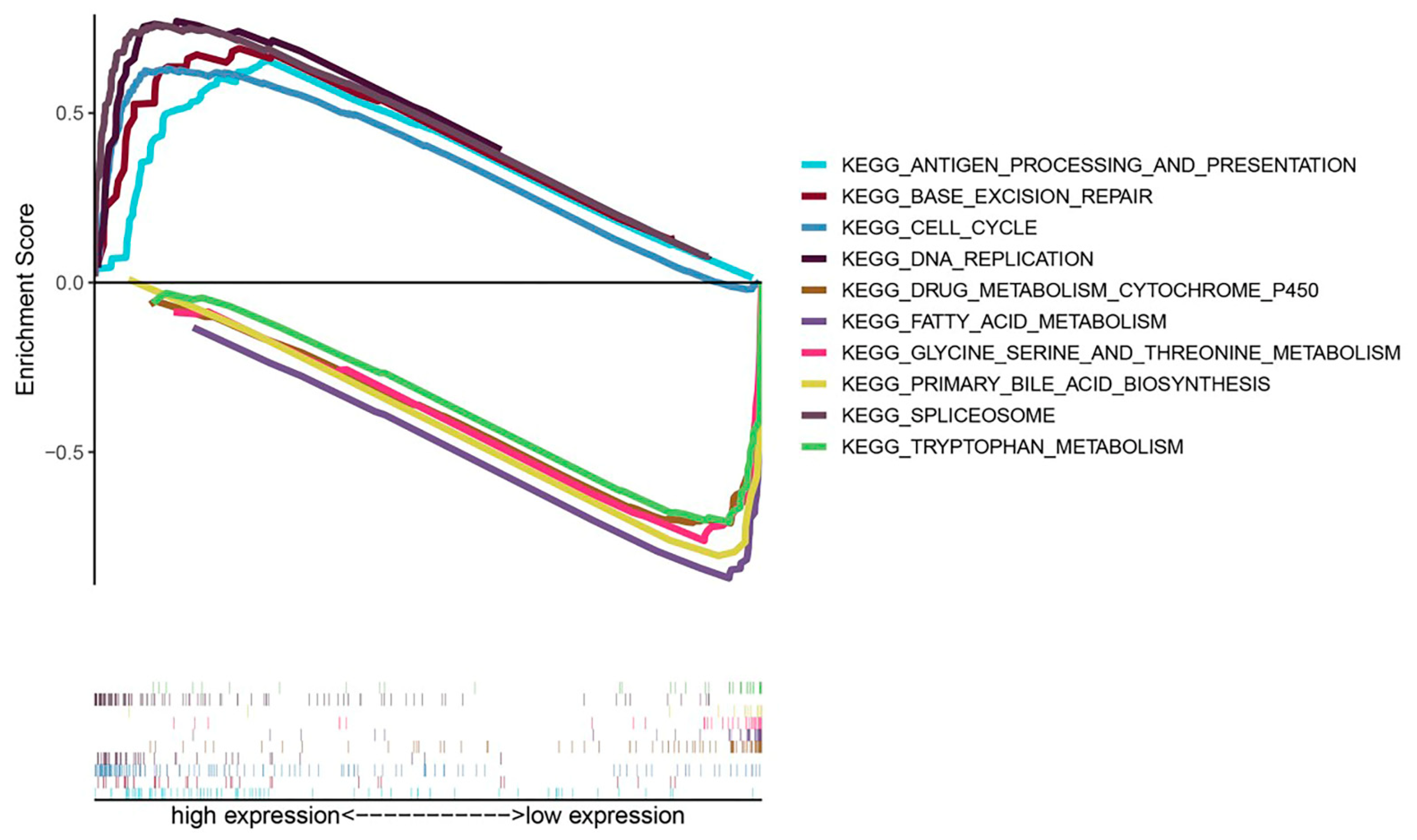
2.6. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.7. Patients and Tumor Tissues
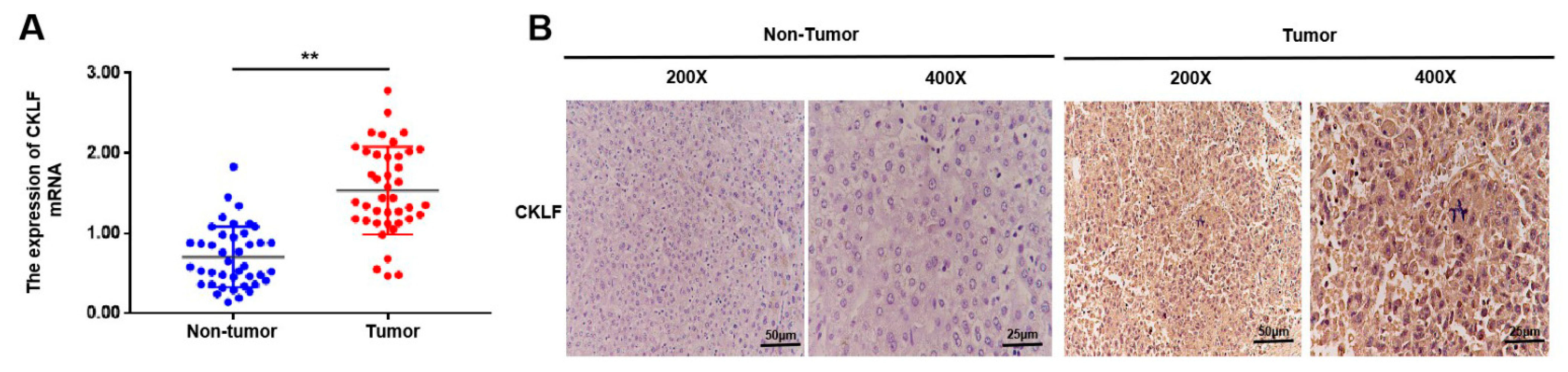
2.8. qRT-PCR
2.9. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. The Expression of CMTM Family Members in HCC
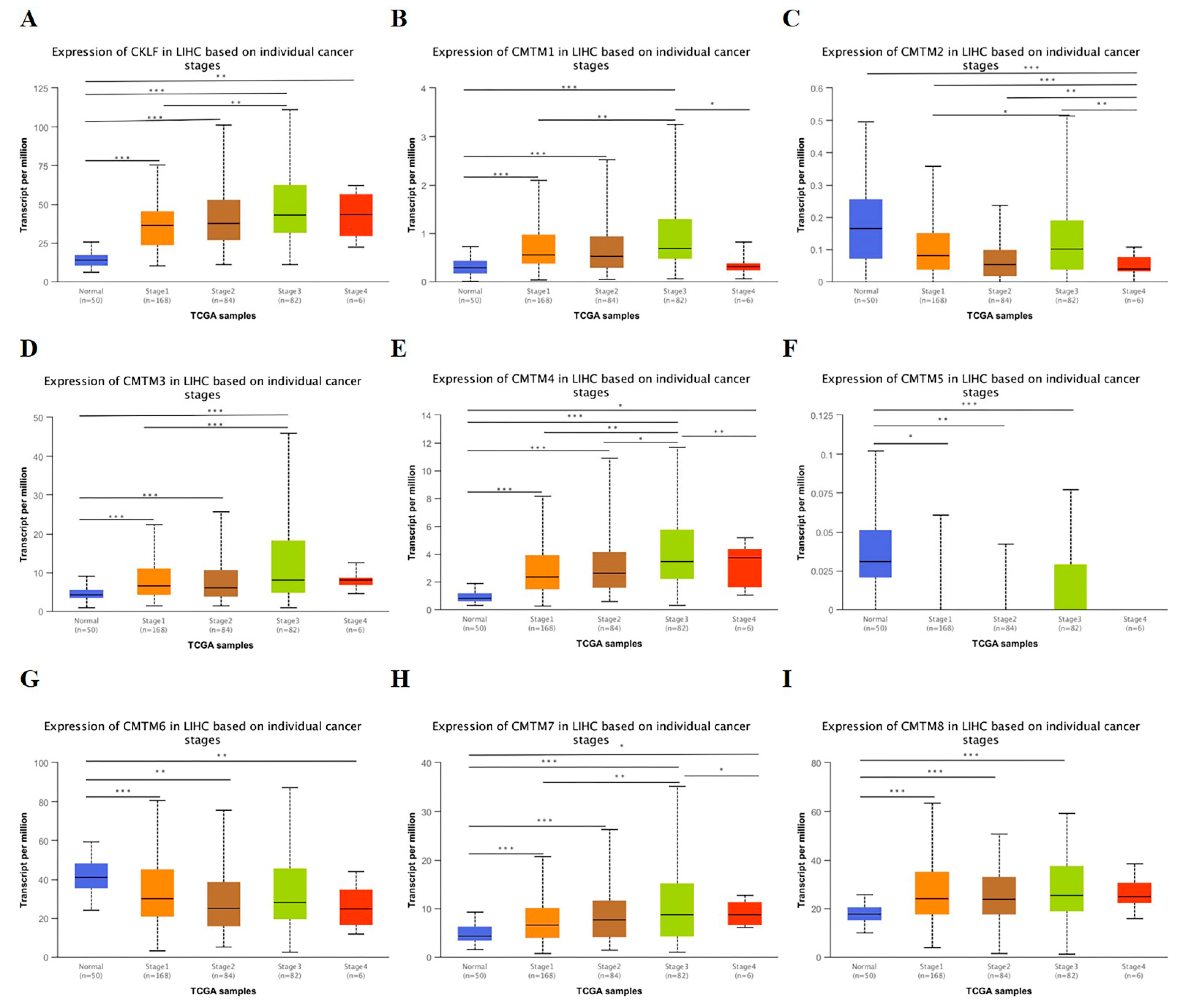
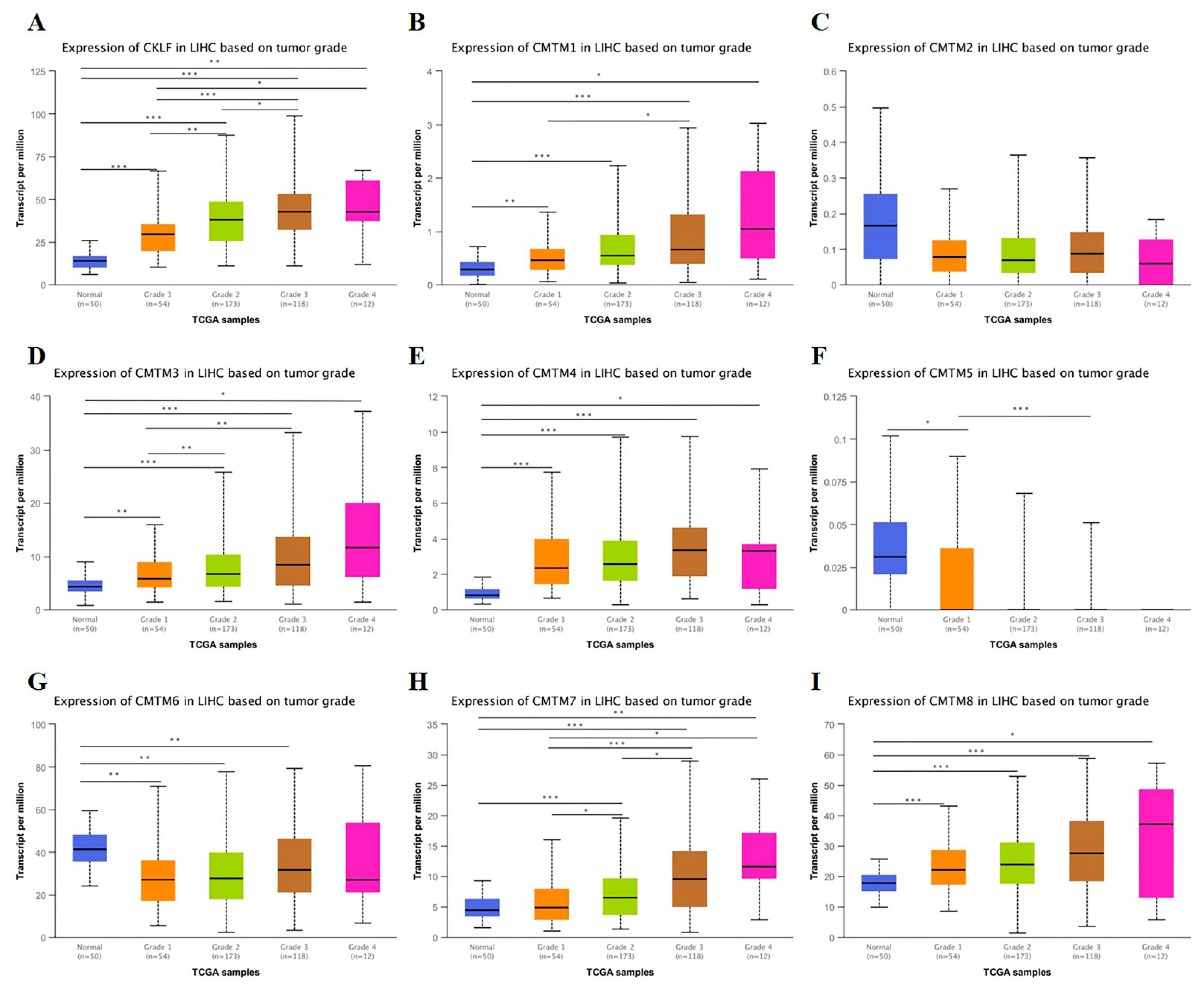
3.2. Relationship between the mRNA Expression of CMTM Family Members and Clinicopathological Parameters of HCC Patients
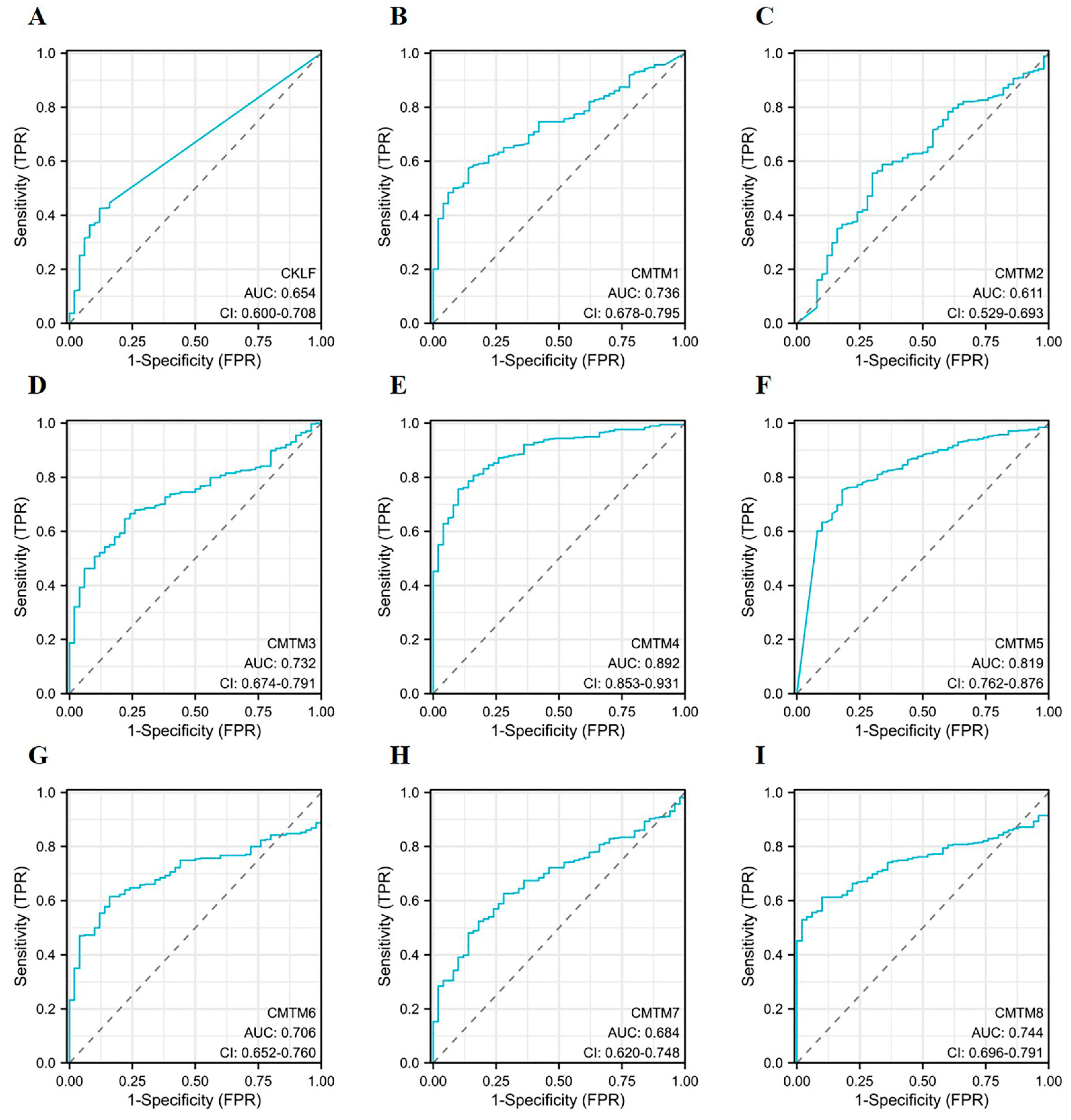
3.3. Diagnostic Capacity of CMTM Family Members in HCC
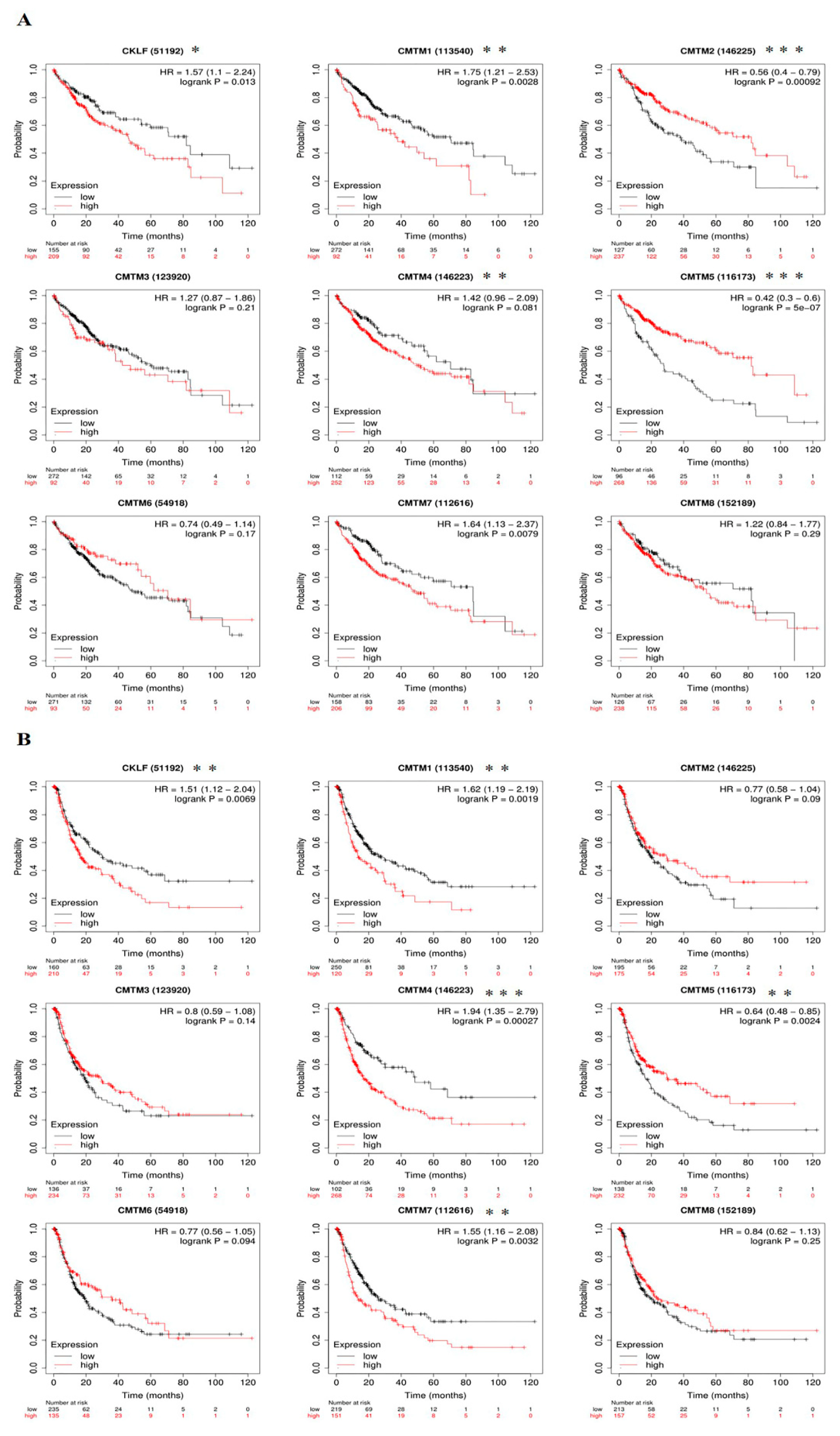
3.4. Prognostic Value of CMTM Family Members in HCC
3.5. Association of CKLF Expression with Tumor Microenvironment in HCC
3.6. Correlation Analysis of CKLF Expression with Immune Checkpoint Genes
3.7. Exploration of Molecular Mechanisms of CKLF in HCC
3.8. Experiment Validation of the mRNA Expression and Protein Levels of CKLF in HCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.J.; von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Sarcognato, S.; Villanueva, A. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, X.; Yu, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Xiu, P. Clinical applications of liquid biopsy as prognostic and predictive biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ding, P.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Rui, M.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, T.; et al. Identification of eight genes encoding chemokine-like factor superfamily members 1–8 (CKLFSF1-8) by in silico cloning and experimental validation. Genomics 2003, 81, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pulido, L.; Martín-Belmonte, F.; Valencia, A.; Alonso, M.A. MARVEL: A conserved domain involved in membrane apposition events. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.J.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Deng, X.L. Chemokine-like factor-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family in autoimmune diseases. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, B. CMTM family proteins 1-8: Roles in cancer biological processes and potential clinical value. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrifi, I.; Louzao-Martinez, L.; Brandt, M.M.; van Dijk, C.; Bürgisser, P.E.; Zhu, C.; Kros, J.M.; Verhaar, M.C.; Duncker, D.J.; Cheng, C. CMTM4 regulates angiogenesis by promoting cell surface recycling of VE-cadherin to endothelial adherens junctions. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, M.L.; Sparbier, C.E.; Chan, Y.C.; Williamson, J.C.; Woods, K.; Beavis, P.A.; Lam, E.; Henderson, M.A.; Bell, C.C.; Stolzenburg, S.; et al. CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2017, 549, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, N.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Xue, L. CMTM Family and Gastrointestinal Tract Cancers: A Comprehensive Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yan, Q.; Chen, X.; Ding, S.; Zhu, F. CKLF1 Enhances Inflammation-Mediated Carcinogenesis and Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis via IL6/STAT3 Signaling in HCC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4141–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delic, S.; Thuy, A.; Schulze, M.; Proescholdt, M.A.; Dietrich, P.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Riemenschneider, M.J. Systematic investigation of CMTM family genes suggests relevance to glioblastoma pathogenesis and CMTM1 and CMTM3 as priority targets. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, H.; Liu, C.; Gong, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hou, B. CMTM3 Overexpression Predicts Poor Survival and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5797–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzadra, R.; Sun, C.; Jae, L.T.; Gomez-Eerland, R.; de Vries, E.; Wu, W.; Logtenberg, M.; Slagter, M.; Rozeman, E.A.; Hofland, I.; et al. Identification of CMTM6 and CMTM4 as PD-L1 protein regulators. Nature 2017, 549, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, N.N.; Cheu, J.W.; Yuen, V.W.; Chiu, D.K.; Goh, C.C.; Lee, D.; Zhang, M.S.; Ng, I.O.; Wong, C.C. Inhibition of CMTM4 Sensitizes Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma to T Cell-Mediated Antitumor Immunity through PD-L1. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, H.M.; Zhang, R.X.; Pan, Z.Z.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, G.Y.; Yue, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, R.Y. CMTM6 and PD-L1 coexpression is associated with an active immune microenvironment and a favorable prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Song, X.Y.; Yang, P.F.; Ai, Q.D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Feng, X.Y.; He, X.; Chen, N.H. Progress in pharmacological research of chemokine like factor 1 (CKLF1). Cytokine 2018, 102, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Deng, J.; Ming, Q.; Cai, H.; Chen, Z. Chemokine-like factor 1: A promising therapeutic target in human diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, A68–A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Murphy, D. Application of ggplot2 to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Hübschmann, D. Make Interactive Complex Heatmaps in R. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F.; Stephens, R.M. ssGSEA score-based Ras dependency indexes derived from gene expression data reveal potential Ras addiction mechanisms with possible clinical implications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, D.; Song, M.; Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, G. Comprehensive Analysis of HOX Family Members as Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 5758601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Lei, J.; Liu, T.; et al. TAB3 upregulates PIM1 expression by directly activating the TAK1-STAT3 complex to promote colorectal cancer growth. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 391, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Tao, S.; Zhang, L.; Diao, L.T.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, S.J.; Xiao, Z.D.; Zhang, H. RNA sequencing: New technologies and applications in cancer research. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleasance, E.; Bohm, A.; Williamson, L.M.; Nelson, J.; Shen, Y.; Bonakdar, M.; Titmuss, E.; Csizmok, V.; Wee, K.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; et al. Whole-genome and transcriptome analysis enhances precision cancer treatment options. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, F.; Tian, X.; Yin, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Chemokine-Like Factor-Like MARVEL Transmembrane Domain-Containing Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Latest Advances. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 595973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, R.; Bei, C.; Zhang, H.; Kong, J.; Zheng, C.; Song, X.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Zhu, X.; et al. Down-Regulated CMTM2 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Ji, D.; Liang, N.; Li, S.; Sun, B. Up-regulation of miR-10b-3p promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting CMTM5. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3434–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, Q.C.; Li, Y.C.; Yang, L.L.; Liu, J.F.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Bu, L.L.; Zhang, W.F.; Sun, Z.J. Targeting CMTM6 Suppresses Stem Cell-Like Properties and Enhances Antitumor Immunity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Su, Y.; Li, T.; Yuan, W.; Mo, X.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Ma, D.; Han, W. CMTM7 knockdown increases tumorigenicity of human non-small cell lung cancer cells and EGFR-AKT signaling by reducing Rab5 activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41092–41107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhu, X.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Cai, J. Downregulated CMTM8 Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer Patients. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Rong, D.; Song, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, X. Targeting Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of HCC: New Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 775462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, H.; Fu, Q.; Lan, T.; Tian, X.; Wei, X. Tumor-associated neutrophils and neutrophil-targeted cancer therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Galat, V.; Galat, Y.; Lee, Y.; Wainwright, D.; Wu, J. NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: From basic biology to clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Jiang, A. Dendritic Cells and CD8 T Cell Immunity in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Cai, N.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. Tumor-associated macrophages in liver cancer: From mechanisms to therapy. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 1112–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Lou, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, W.; Huang, J.; Gui, L.; Tang, Y.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1), a novel human cytokine with unique structure and potential chemotactic activity. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.Y.; Duan, H.J.; Deng, X.L. Possible effects of chemokine-like factor-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family on antiphospholipid syndrome. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, P.; Solimando, A.G.; Fasano, R.; Argentiero, A.; Malerba, E.; Buonavoglia, A.; Lupo, L.G.; De Re, V.; Silvestris, N.; Racanelli, V. The Evolving Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment. Vaccines 2021, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Ren, Z.; Feng, Y.H.; Yau, T.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.; Bai, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, L.; Hernandez, S.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab versus Sorafenib in the Chinese Subpopulation with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Phase 3 Randomized, Open-Label IMbrave150 Study. Liver Cancer. 2021, 10, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, S.; Shen, H. From bench to bed: The tumor immune microenvironment and current immunotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimando, A.G.; Susca, N.; Argentiero, A.; Brunetti, O.; Leone, P.; De Re, V.; Fasano, R.; Krebs, M.; Petracci, E.; Azzali, I.; et al. Second-line treatments for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 22, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, B.; Heinrich, B.; Greten, T.F. Immunobiology and immunotherapy of HCC: Spotlight on innate and innate-like immune cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Crown, J. Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Immunotherapy with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, D.; Yoo, S.K.; Valero, C.; Pastore, A.; Krishna, C.; Lee, M.; Hoen, D.; Shi, H.; Kelly, D.W.; Patel, N.; et al. Improved prediction of immune checkpoint blockade efficacy across multiple cancer types. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CKLF | F: CAGCAGTATGCTGTCTTGCCGA; R: TTTTTCATGCACAGGCTTTTTCTGG |
| GADPH | F: GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT; R: GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| Characteristics | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age | ||||
| ≤60 | Reference | - | - | - |
| >60 | 1.286 (0.876–1.887) | 0.199 | - | - |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | Reference | - | - | - |
| Male | 0.816 (0.552–1.206) | 0.307 | - | - |
| Histologic grade | ||||
| G1 | Reference | - | - | - |
| G2 | 1.229 (0.668–2.261) | 0.507 | - | - |
| G3 | 1.234 (0.656–2.320) | 0.515 | - | - |
| G4 | 1.767 (0.625–4.992) | 0.283 | - | - |
| Pathologic stage | ||||
| Stage I | Reference | - | Reference | - |
| Stage II | 1.511 (0.905–2.523) | 0.114 | 1.482 (0.887–2.477) | 0.133 |
| Stage III | 2.708 (1.742–4.211) | <0.001 | 2.734 (1.756–4.255) | <0.001 |
| Stage IV | 5.612 (1.722–18.292) | 0.004 | 4.886 (1.495–15.963) | 0.009 |
| CKLF | 1.985 (1.348–2.922) | 0.001 | 1.879 (1.237–2.855) | 0.003 |
| CMTM1 | 1.047 (0.716–1.530) | 0.813 | - | - |
| CMTM2 | 1.156 (0.789–1.697) | 0.458 | - | - |
| CMTM3 | 1.053 (0.720–1.539) | 0.791 | - | - |
| CMTM4 | 1.258 (0.859–1.842) | 0.238 | - | - |
| CMTM5 | 1.124 (0.767–1.648) | 0.549 | - | - |
| CMTM6 | 1.373 (0.936–2.015) | 0.105 | - | - |
| CMTM7 | 1.659 (1.164–2.363) | 0.005 | 1.289 (0.876–1.898) | 0.198 |
| CMTM8 | 1.060 (0.725–1.550) | 0.765 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Huang, S.; Luo, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, S.; Liu, K.; Wu, J. CKLF as a Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2653-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030202
Li D, Huang S, Luo C, Xu Y, Fu S, Liu K, Wu J. CKLF as a Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):2653-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030202
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Shenglan Huang, Chen Luo, Yongkang Xu, Shumin Fu, Kan Liu, and Jianbing Wu. 2023. "CKLF as a Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 2653-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030202
APA StyleLi, D., Huang, S., Luo, C., Xu, Y., Fu, S., Liu, K., & Wu, J. (2023). CKLF as a Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Current Oncology, 30(3), 2653-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030202





