Preclinical Synergistic Combination Therapy of Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan and 5-Fluorouracil in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. Therapeutic Agents
2.3. Cell Viability Analysis and Combination Synergy Score Analysis
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
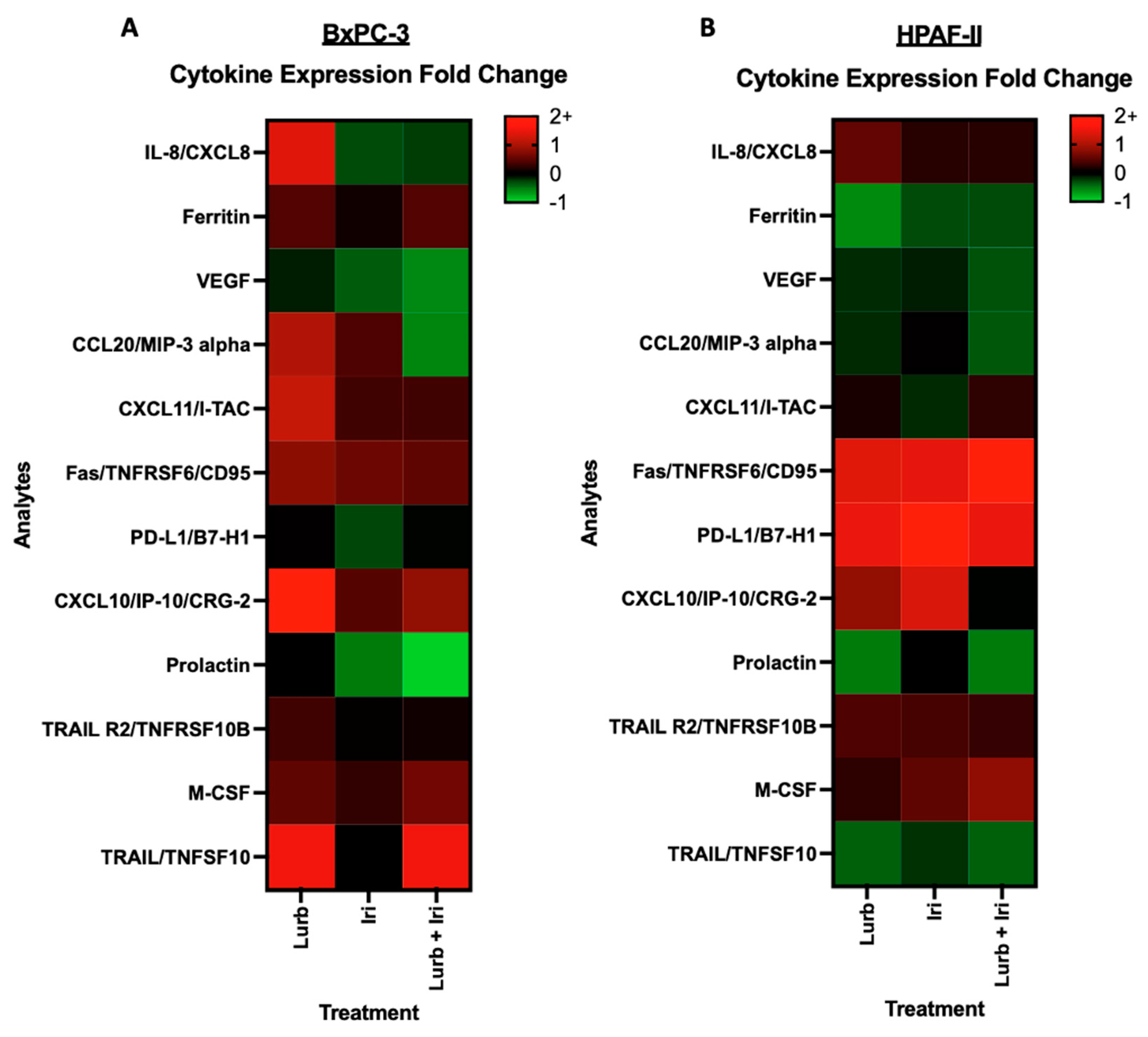
2.5. Cytokine Profiling Analysis
3. Results
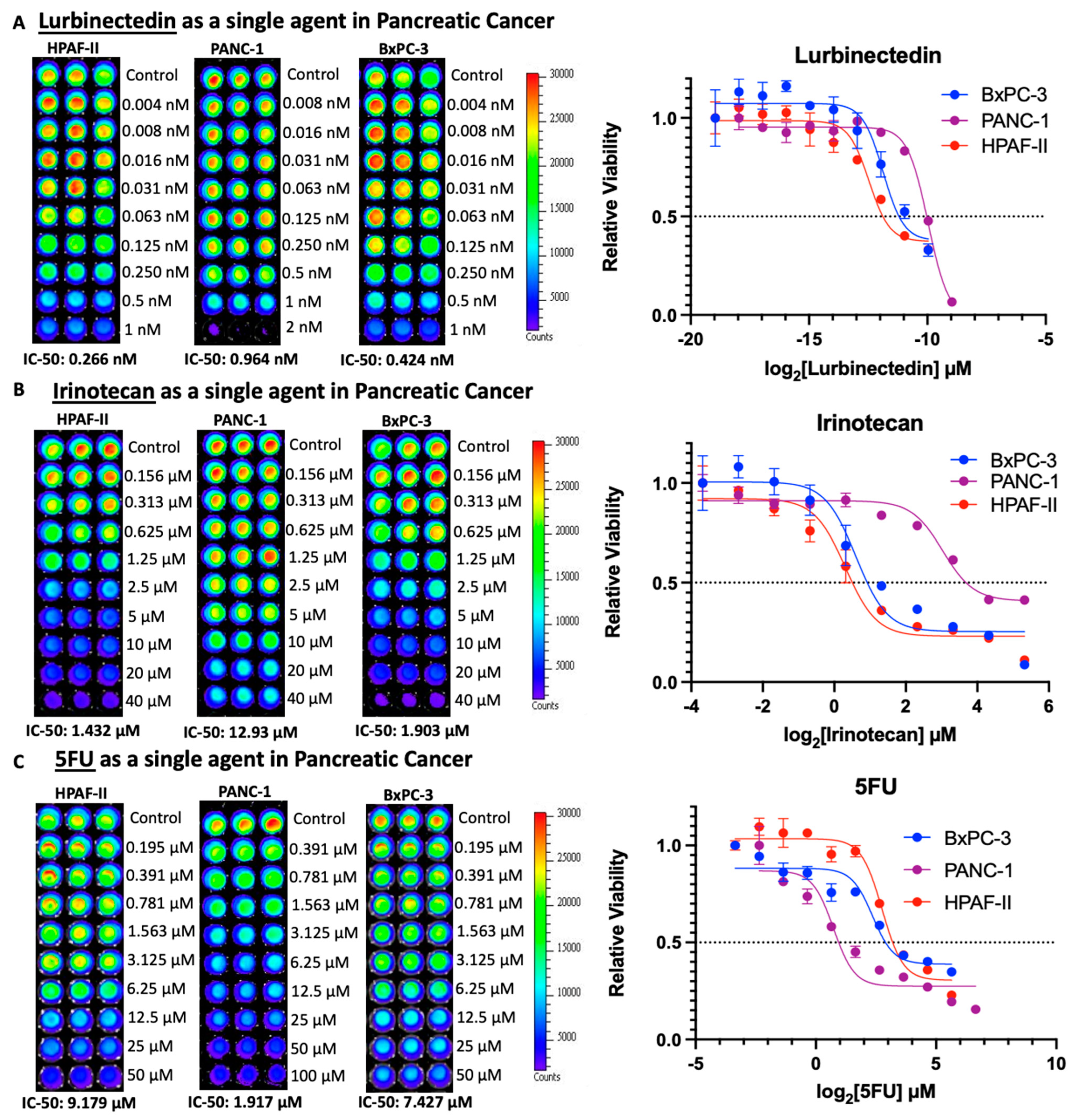
3.1. Lurbinectedin Is a Highly Potent Cytotoxic Agent in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
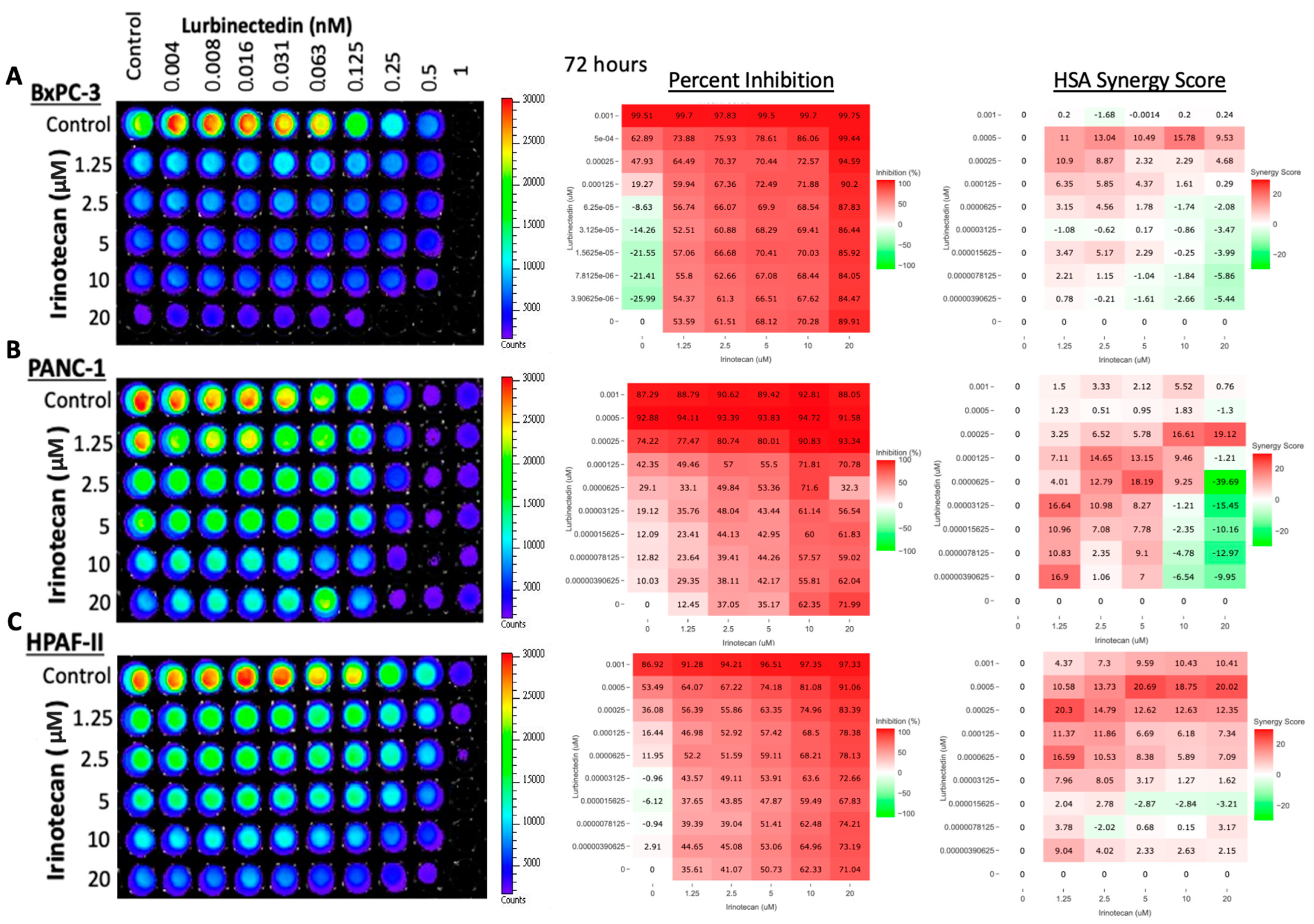
3.2. Lurbinectedin and Irinotecan Synergize in Killing Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
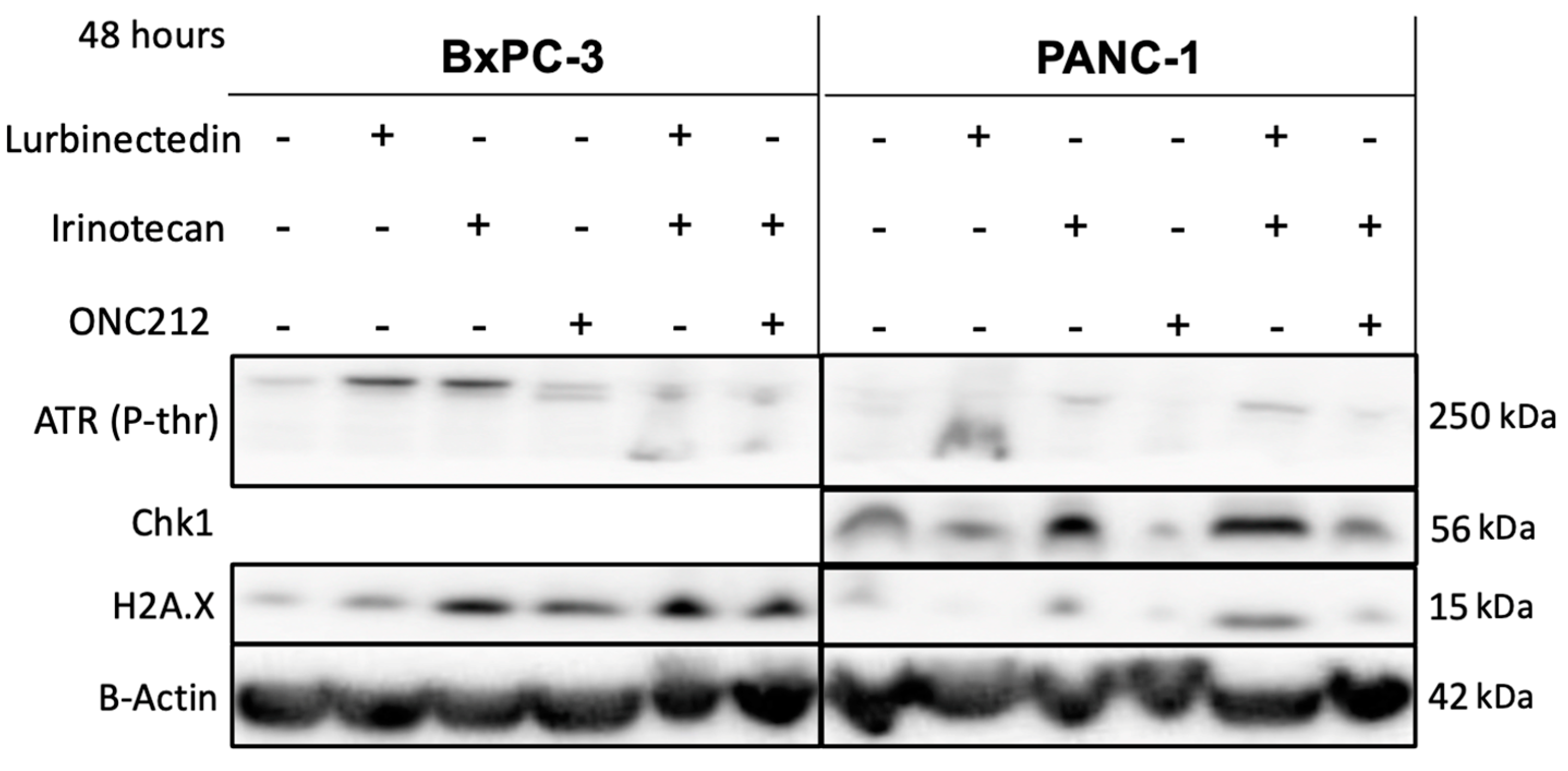
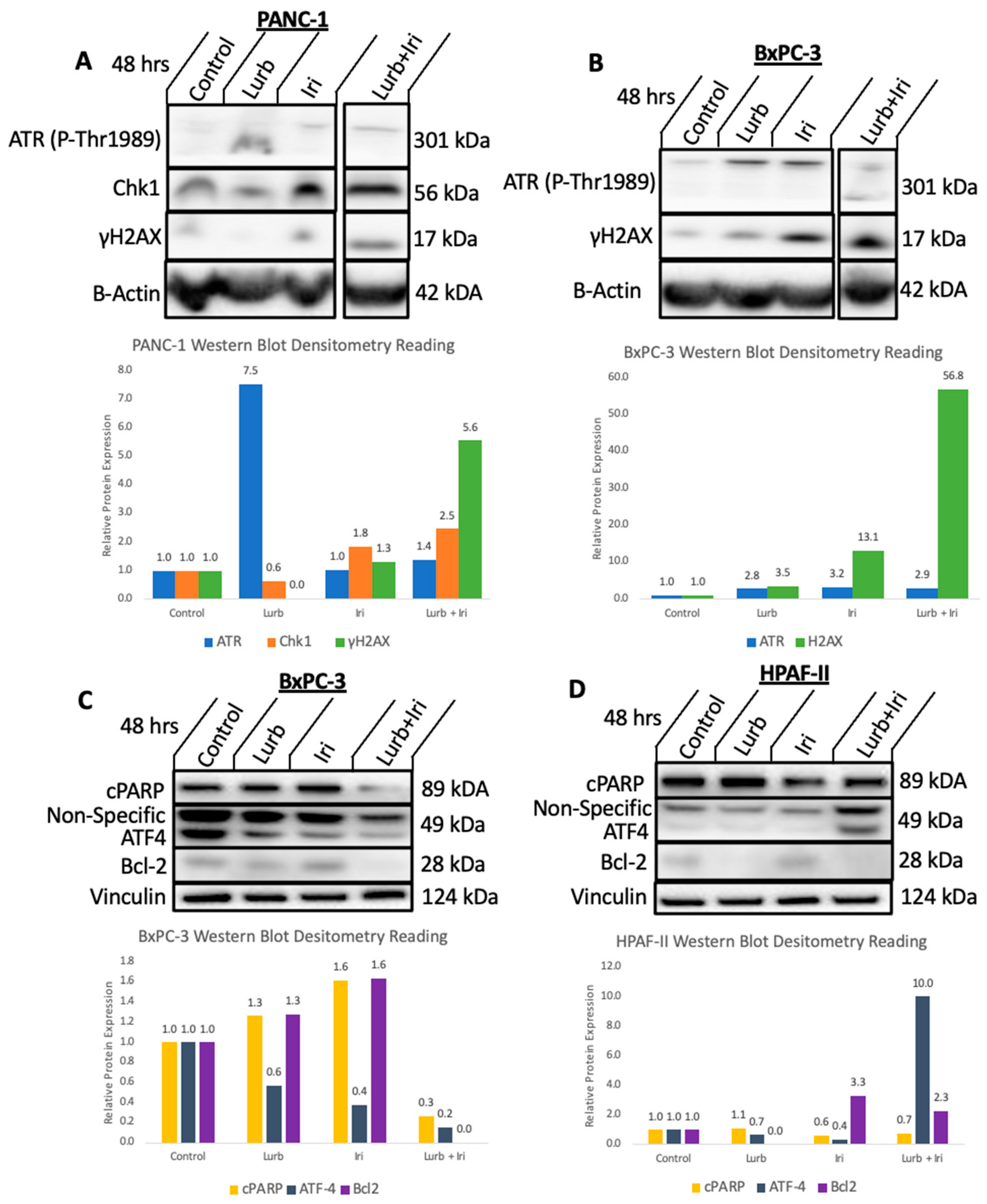
3.3. DNA Damage and Replicative Stress Likely Underlies Synergism between Lurbinectedin and Irinotecan
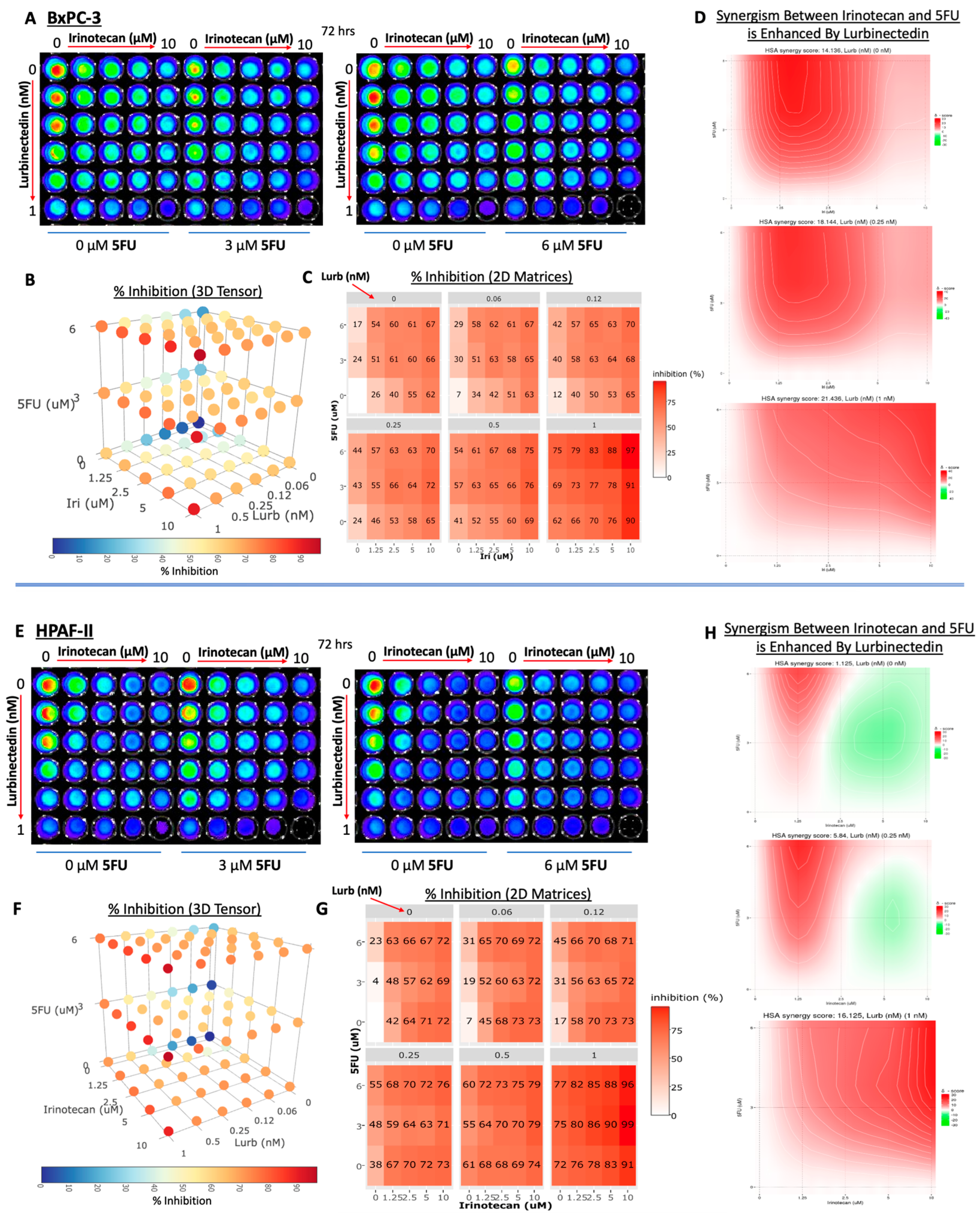
3.4. Lurbinectedin, Irinotecan, and 5-FU Are a Highly Potent Combination Therapy in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Halbrook, C.J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Pasca di Magliano, M.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Cell 2023, 186, 1729–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev, A.; Lulla, A.R.; Wagner, J.; Ralff, M.D.; Kiehl, J.B.; Zhou, Y.; Benes, C.H.; Prabhu, V.V.; Oster, W.; Astsaturov, I.; et al. Anti-pancreatic cancer activity of ONC212 involves the unfolded protein response (UPR) and is reduced by IGF1-R and GRP78/BIP. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81776–81793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyromski, N.J.; White, P.B. Pancreatic cancer in obesity: Epidemiology, clinical observations, and basic mechanisms. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manji, G.A.; Olive, K.P.; Saenger, Y.M.; Oberstein, P. Current and Emerging Therapies in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Brill, A.; Amar-Farkash, S.; Lawrence, G.; Collisson, E.A.; Aran, D. Comparison of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine Plus Nab-Paclitaxel as First-Line Chemotherapy for Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2216199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Lurbinectedin: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elez, M.E.; Tabernero, J.; Geary, D.; Macarulla, T.; Kang, S.P.; Kahatt, C.; Pita, A.S.; Teruel, C.F.; Siguero, M.; Cullell-Young, M.; et al. First-in-human phase I study of Lurbinectedin (PM01183) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, A.; Sharma, M.R.; Szyldergemajn, S.; Gore, L.; Geary, D.; Diamond, J.R.; Fernandez Teruel, C.; Soto Matos-Pita, A.; Iglesias, J.L.; Cullell-Young, M.; et al. Phase I study of lurbinectedin, a synthetic tetrahydroisoquinoline that inhibits activated transcription, induces DNA single- and double-strand breaks, on a weekly × 2 every-3-week schedule. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría Nuñez, G.; Robles, C.M.; Giraudon, C.; Martínez-Leal, J.F.; Compe, E.; Coin, F.; Aviles, P.; Galmarini, C.M.; Egly, J.M. Lurbinectedin Specifically Triggers the Degradation of Phosphorylated RNA Polymerase II and the Formation of DNA Breaks in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumini, E.; Herrera-Moyano, E.; San Martín-Alonso, M.; Barroso, S.; Galmarini, C.M.; Aguilera, A. The Antitumor Drugs Trabectedin and Lurbinectedin Induce Transcription-Dependent Replication Stress and Genome Instability. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiovine, C.; Bello, E.; Liguori, M.; Craparotta, I.; Mannarino, L.; Paracchini, L.; Beltrame, L.; Marchini, S.; Galmarini, C.M.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Lurbinectedin reduces tumour-associated macrophages and the inflammatory tumour microenvironment in preclinical models. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.P.; Smith, A.J.; Bowman, K.J.; Thomas, A.L.; Jones, G.D. Comet assay measures of DNA damage as biomarkers of irinotecan response in colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Man, F.M.; Goey, A.K.L.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Bins, S. Individualization of Irinotecan Treatment: A Review of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacogenetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1229–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer. Prescrire Int. 2010, 19, 219–224.
- Bailly, C. Irinotecan: 25 years of cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaka, T.; Taguchi, T. Timeline from discovery of 5-FU to development of an oral anticancer agent S-1 and its drug concept. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 2006, 33 (Suppl. S1), 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Diasio, R.B.; Harris, B.E. Clinical pharmacology of 5-fluorouracil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1989, 16, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Yin, Y.; Xu, S.J.; Chen, W.S. 5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies. Molecules 2008, 13, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienot, A.; Chevalier, H.; Bolognini, C.; Gherga, E.; Klajer, E.; Meurisse, A.; Jary, M.; Kim, S.; d’Engremont, C.; Nguyen, T.; et al. FOLFOXIRI vs FOLFIRINOX as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A population-based cohort study. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Lurbinectedin Monotherapy in Participants with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors (EMERGE-201). 2023. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05126433 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Pharmacokinetic Study of Lurbinectedin in Combination with Irinotecan in Patients with Selected Solid Tumors. 2022. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02611024 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Clinical Trial of Lurbinectedin as Single-Agent or in Combination with Irinotecan Versus Topotecan or Irinotecan in Patients with Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LAGOON). 2023. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05153239 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Céspedes, M.V.; Guillén, M.J.; López-Casas, P.P.; Sarno, F.; Gallardo, A.; Álamo, P.; Cuevas, C.; Hidalgo, M.; Galmarini, C.M.; Allavena, P.; et al. Lurbinectedin induces depletion of tumor-associated macrophages, an essential component of its in vivo synergism with gemcitabine, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma mouse models. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Forster, M.; Boni, V.; Szyldergemajn, S.; Corral, J.; Turnbull, S.; Cubillo, A.; Teruel, C.F.; Calderero, I.L.; Siguero, M.; et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of PM01183 (a tetrahydroisoquinoline, Lurbinectedin) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Sessa, C.; Harada, G.; de Miguel, M.; Kahatt, C.; Luepke-Estefan, X.E.; Siguero, M.; Fernandez-Teruel, C.; Cullell-Young, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Phase I study of lurbinectedin in combination with weekly paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, N.R.; Sanchez Sevilla Uruchurtu, A.; Zhang, L.; Abbas, A.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Zhou, L.; Azzoli, C.G.; El-Deiry, W.S. Preclinical studies with ONC201/TIC10 and lurbinectedin as a novel combination therapy in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Peters, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Reck, M.; Calles, A.; Califano, R.; Lopez-Vilariño, J.A.; Veramendi, S.; Kahatt, C.M.; et al. A phase III study of lurbinectedin alone or in combination with irinotecan vs investigator’s choice (topotecan or irinotecan) in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC; LAGOON trial). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Aix, S.; Coté, G.; Falcón, A.; Jimenez-Aguilar, E.; Lin, J.; Sánchez Simón, I.; Flor, M.J.; Nuñez, R.; Jimenez, A.M.; Jimenez, E.; et al. OA11.04 Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan in Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. Results From the Expansion Stage of a Phase I-II Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, A.; Oaknin, A.; Trigo, J.M.; Moreno, V.; Delord, J.P.; Boni, V.; Braña, I.; Fernández, C.; Kahatt, C.; Nieto, A.; et al. Pooled Safety Analysis of Single-Agent Lurbinectedin in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 192, 113259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deer, E.L.; González-Hernández, J.; Coursen, J.D.; Shea, J.E.; Ngatia, J.; Scaife, C.L.; Firpo, M.A.; Mulvihill, S.J. Phenotype and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 2010, 39, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 3.0: An interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W739–W743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, J.L.; Kim, W.; Wernick, M.; Nguyen, S.V.; Braquet, R.; Adamson, A.W.; Den, Z.; Batzer, M.A.; Collins, C.C.; Brown, K.D. Evidence for alternate splicing within the mRNA transcript encoding the DNA damage response kinase ATR. Gene 2001, 272, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, L.J.; El-Osta, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. gammaH2AX: A sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia 2010, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnitz, L.M.; Zou, L. Molecular Pathways: Targeting ATR in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4780–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Tho, L.M.; Xu, N.; Gillespie, D.A. The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 108, 73–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.N.; Strasser, A. The role of Bcl-2 and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. S3), 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadducci, A.; Cosio, S. Trabectedin and lurbinectedin: Mechanisms of action, clinical impact, and future perspectives in uterine and soft tissue sarcoma, ovarian carcinoma, and endometrial carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 914342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, P.; Müllbacher, A. Cell death induced by the Fas/Fas ligand pathway and its role in pathology. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1999, 77, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tummala, T.; Sevilla Uruchurtu, A.S.; Cruz, A.D.L.; Huntington, K.E.; George, A.; Liguori, N.R.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Abbas, A.E.; Azzoli, C.G.; et al. Preclinical Synergistic Combination Therapy of Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan and 5-Fluorouracil in Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9611-9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110696
Tummala T, Sevilla Uruchurtu AS, Cruz ADL, Huntington KE, George A, Liguori NR, Zhang L, Zhou L, Abbas AE, Azzoli CG, et al. Preclinical Synergistic Combination Therapy of Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan and 5-Fluorouracil in Pancreatic Cancer. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(11):9611-9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110696
Chicago/Turabian StyleTummala, Tej, Ashley Sanchez Sevilla Uruchurtu, Arielle De La Cruz, Kelsey E. Huntington, Andrew George, Nicholas R. Liguori, Leiqing Zhang, Lanlan Zhou, Abbas E. Abbas, Christopher G. Azzoli, and et al. 2023. "Preclinical Synergistic Combination Therapy of Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan and 5-Fluorouracil in Pancreatic Cancer" Current Oncology 30, no. 11: 9611-9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110696
APA StyleTummala, T., Sevilla Uruchurtu, A. S., Cruz, A. D. L., Huntington, K. E., George, A., Liguori, N. R., Zhang, L., Zhou, L., Abbas, A. E., Azzoli, C. G., & El-Deiry, W. S. (2023). Preclinical Synergistic Combination Therapy of Lurbinectedin with Irinotecan and 5-Fluorouracil in Pancreatic Cancer. Current Oncology, 30(11), 9611-9626. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110696





