Successful Treatment with Brigatinib after Alectinib-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma—A Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
2.1. Patient 1
2.2. Patient 2
2.3. Patient 3
2.4. Patient 4
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pennell, N.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Gandara, D.R.; West, H. Biomarker Testing for Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Issues and Tough Choices. ASCO Educ. Book 2019, 39, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Han, C. Recent Progress in Rare Oncogenic Drivers and Targeted Therapy For Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 10343–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.A.; Hughes, B.G. Targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and the promise of the future. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramagopalan, S.; Leahy, T.P.; Ray, J.; Wilkinson, S.; Sammon, C.J.; Subbiah, V. Association between improvements in survival of metastatic NSCLC patients and targeted- and immuno-therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.; Camidge, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Rosell, R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Kim, D.-W.; Pérol, M.; Ou, S.-H.; Ahn, J.; Shaw, A.; et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Y. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for solid tumors in the past 20 years (2001–2020). J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W. Safety and efficacy of anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.F.; Tai, Y.H.; Gao, H.J. ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.Y.L.; Wan, H.; Shi, G.; Niu, W. Clinicopathological and Demographical Characteristics of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with ALK Rearrangements: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Bai, Z.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Kelly, S.; Chen, L.; Skidmore, B.; Yousef, S.; Zheng, C.; Stewart, D.; Wells, G. ALK inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Braud, F.G.; Niger, M.; Damian, S.; Bardazza, B.; Martinetti, A.; Marrapese, G.P.; Palmeri, L.; Cerea, G.; Valtorta, E.; Veronese, S.; et al. Alka-372-001: First-in-human, phase I study of entrectinib—An oral pan-trk, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor–in patients with advanced solid tumors with relevant molecular alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Infante, J.R.; Reckamp, K.L.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Leal, T.A.; Waqar, S.N.; Gitlitz, B.J.; Sanborn, R.E.; Whisenant, J.G.; Du, L.; et al. Ensartinib (X-396) in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from a First-in-Human Phase I/II, Multicenter Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Gitlitz, B.; Sanborn, R.; Whisenant, J.; Du, L.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.-J.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Bu, L.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated Asian patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ALESIA): A randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazières, J.; Oh, I.J.; De Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, Å.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Dhillon, S. Alectinib: A Review in Advanced, ALK-Positive NSCLC. Drugs 2018, 78, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullapalli, V.; Xu, W.; Lewis, C.R.; Anazodo, A.; Gerber, G.K. A multi-centre case series of alectinib-related erythrocyte membrane changes and associated haemolysis. J. Hematopathol. 2021, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzich, J.A.; Heynemann, S.; Geoghegan, N.; Evelyn, C.; O’Mahoney, S.; Wilson, S.; Campbell, J.; Rogers, K.; Solomon, B.; Westerman, D.; et al. Alectinib induces marked red cell spheroacanthocytosis in a near-ubiquitous fashion and is associated with reduced eosin-5-maleimide binding. Pathology 2021, 53, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.; Low, M.S.Y. Spheroacanthocytes secondary to novel tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 1, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun Bhuyan, A.; Lang, F. Inhibition of Erythrocyte Cell Membrane Scrambling Following Energy Depletion and Hyperosmotic Shock by Alectinib. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, R.S.; Kuo, K.H.M. Hemolytic Anemia Excluding Hemoglobinopathies. In Chapter 8—American Society of Hematology Self-Assessment Program, 7th ed.; Cuker, A., Altman, J.K., Gerds, A.T., Wun, T., Eds.; FACP: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garratty, G. Drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2009, 1, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, A. [Drug-induced hemolytic anemia]. Nihon Rinsho. 1996, 54, 2534–2538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, B.; Bartolmäs, T.; Yürek, S.; Salama, A. Variability of Findings in Drug-Induced Immune Haemolytic Anaemia: Experience over 20 Years in a Single Centre. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2015, 42, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, J.; Nagababu, E.; Rifkind, J. Red blood cell oxidative stress impairs oxygen delivery and induces red blood cell aging. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packman, C.H. The Clinical Pictures of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Transfus Med. Hemother. 2015, 42, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lavallade, H.; Khoder, A.; Hart, M.; Sarvaria, A.; Sekine, T.; Alsuliman, A.; Mielke, S.; Bazeos, A.; Stringaris, K.; Ali, S.; et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors impair B-cell immune responses in CML through off target inhibition of kinases important for cell signaling. Blood 2013, 122, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, N.; Plana, M. Immunomodulatory Activity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Elicit Cytotoxicity Against Cancer and Viral Infection. Front Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.G.; Cardiel, M.H.; Cornejo, H.; Viveros, M.E. Prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in 3 groups of healthy individuals: Blood donors, hospital personnel, and relatives of patients with autoimmune diseases. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 15, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaolalla, A.; Sollie, S.; Rislan, A.; Josephs, D.H.; Hammar, N.; Walldius, G.; Garmo, H.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Association between serum markers of the humoral immune system and inflammation in the Swedish AMORIS study. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segel, G.B.; Lichtman, M.A. Direct antiglobulin ("Coombs") test-negative autoimmune hemolytic anemia: A review. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2014, 52, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrith, B.; Sharma, M.; Jain, P.; Joga, S.; Bothra, S.; Jajodia, A.; Sood, R.; Pasricha, S.; Batra, U. PD-L1 expression in ALK rearranged NSCLC: All questions answered? Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ix170–ix171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.-C.; Yang, T.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Hsu, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Su, K.-Y.; Yu, S.-L.; Tseng, J.-S. ALK variants, PD-L1 expression, and their association with outcomes in ALK-positive NSCLC patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, Y.; Koh, J.; Jeon, Y.K.; Heo, D.S. Alterations in PD-L1 Expression Associated with Acquisition of Resistance to ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostova, E.B.; Beuger, B.M.; Klei, T.R.; Halonen, P.; Lieftink, C.; Beijersbergen, R.; Berg, T.K.V.D.; van Bruggen, R. Identification of signalling cascades involved in red blood cell shrinkage and vesiculation. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guihard, S.; Clay, D.; Cocault, L.; Saulnier, N.; Opolon, P.; Souyri, M.; Pagès, G.; Pouysségur, J.; Porteu, F.; Gaudry, M. The MAPK ERK1 is a negative regulator of the adult steady-state splenic erythropoiesis. Blood 2010, 115, 3686–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.L.; Takakuwa, Y.; Nunomura, W.; Manno, S.; Mohandas, N. Modulation of band 3-ankyrin interaction by protein 4.1. Functional implications in regulation of erythrocyte membrane mechanical properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33187–33191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, M.A.; de la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; López-Grueso, M.J.; Navarro-Villarán, E.; Requejo-Aguilar, R.; Castejón-Vega, B.; Negrete, M.; Gallego, P.; Vega-Ochoa, Á.; Victor, V.M.; et al. Integrated molecular signaling involving mitochondrial dysfunction and alteration of cell metabolism induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Redox. Biol. 2020, 36, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Akimoto, K.; Sato, H.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Homma, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; et al. Brigatinib and Alectinib for ALK Rearrangement-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With or Without Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcereny, E.; Fernández-Nistal, A.; López, A.; Montoto, C.; Naves, A.; Segú-Vergés, C.; Coma, M.; Jorba, G.; Oliva, B.; Mas, J.M. Head to head evaluation of second generation ALK inhibitors brigatinib and alectinib as first-line treatment for ALK+ NSCLC using an in silico systems biology-based approach. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores, G.M.; Nayernama, A.; Cheng, C.; Moureaud, C.; Jones, S.C. Hemolytic anemia following alectinib reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E129–E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
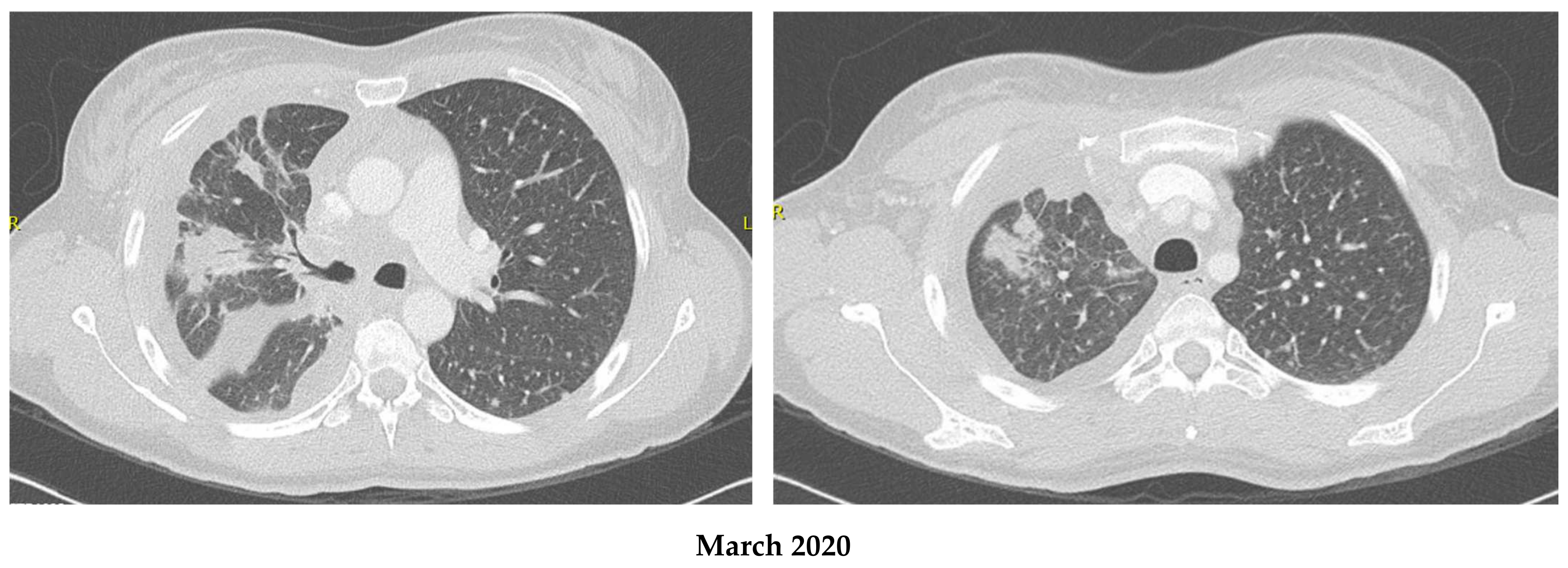
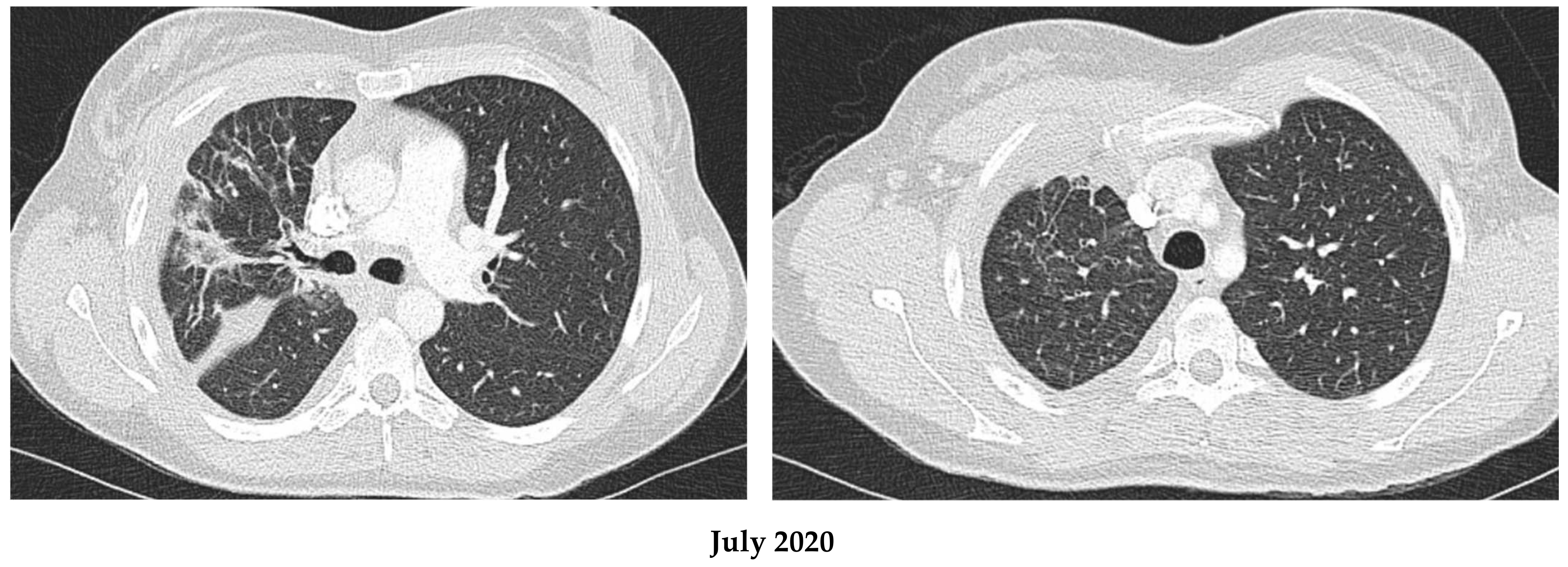

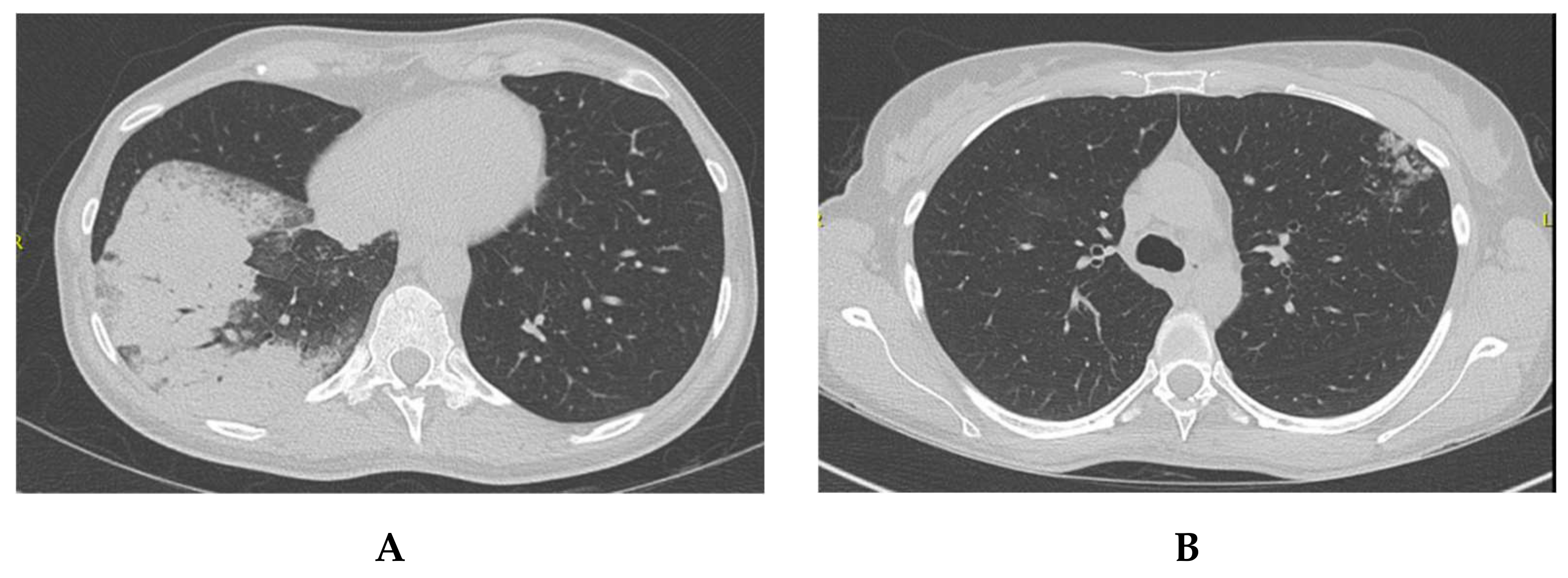

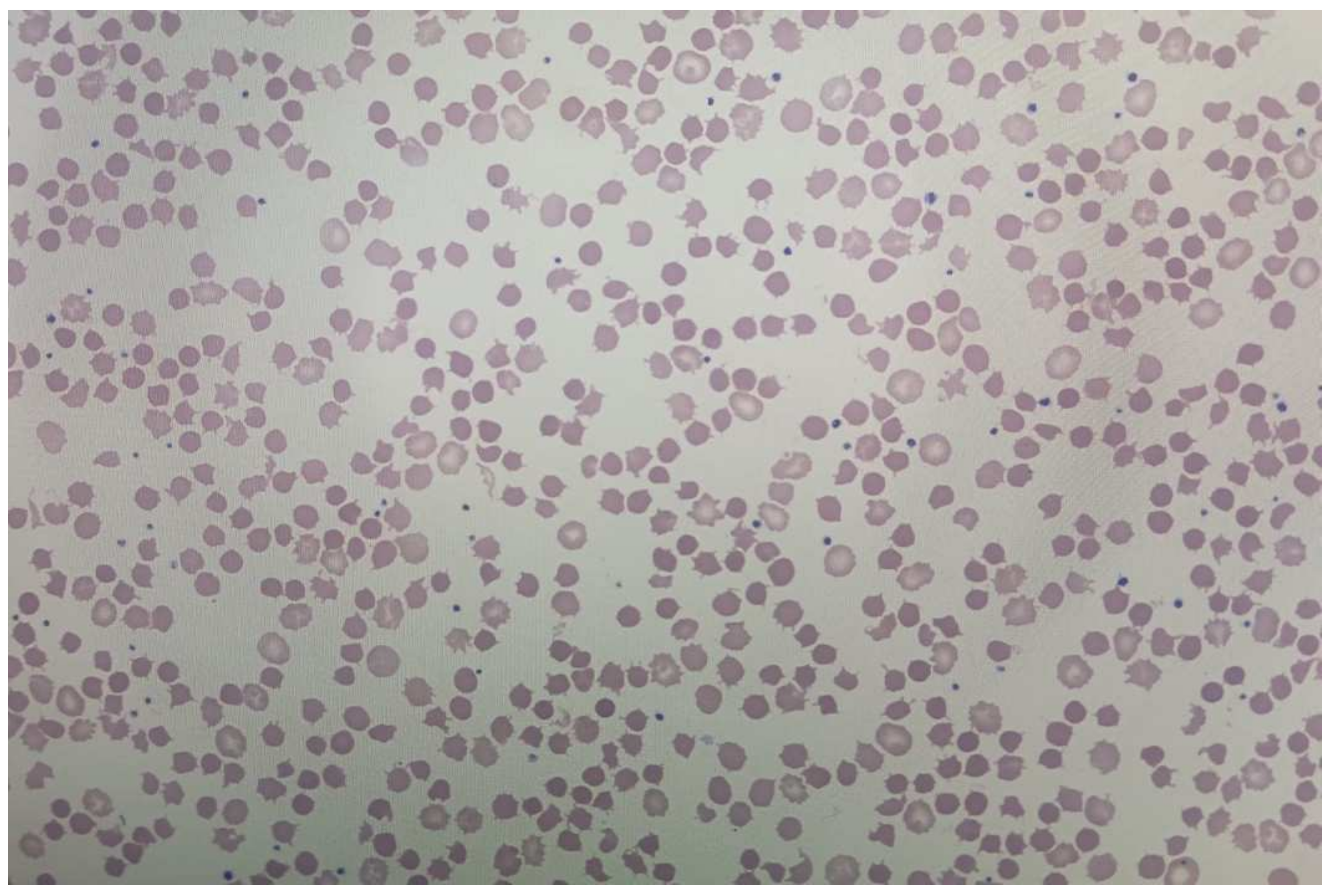
| Date | Alectinib | Hb (g/L) | MCV (fL) | PLT (×109/L) | LDH (U/L) | Bil T (μmol/L) | Bil I (μmol/L) | Haptoglobin (g/L) | Retic (×109/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019–10 (early) | (baseline) | 106 | 84 | 322 | Not done | 16 | Not done | Not done | Not done |
| 2019–10 (late) | 600 mg BID | 67 | 83 | 181 | 361 | 21 | Not done | 1.57 | 124 |
| 2019–11 | 600 mg BID | 80 | 91 | 247 | 363 | 26 | 16.7 | 0.37 | 143 |
| 2019–12 | 600 mg BID | 101 | 99 | 365 | 371 | 31 | 21 | <0.3 | 118 |
| 2020–01 | 600 mg BID | 89 | 99 | 308 | 306 | 32 | 20.6 | <0.3 | 134 |
| 2020–03 (late) | 450 mg BID | 95 | 99 | 321 | 325 | 34 | 22.5 | Not done | Not done |
| 2020–04 | Stopped | 128 | 98 | 310 | 388 | 52 | 25 | 0.38 | 305 |
| 2020–06 | Stopped | 133 | 98 | 350 | 378 | 24 | 13.2 | 1.23 | Not done |
| 2020–07 | 450 mg BID | 83 | 98 | 381 | 401 | 33 | 14.3 | 0.37 | 265 |
| 2020–08 | Stopped | 123 | 100 | 265 | 302 | 13 | Not done | 0.99 | 49.8 |
| 2020–09 | Replaced by Brigatinib | 133 | 94.7 | 207 | 389 | 5 | Not done | 2.22 | 22.7 |
| Hb (g/L) | MCV (fL) | Plt (×109/L) | LDH (U/L) | Bil I (T) (μmol/L) | Haptoglobin (g/L) | Reticulocytes (×109/L) | Coombs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 112 | 92 | 306 | 575 | 31 (65) | <0.3 | 105.8 | negative |
| Patient 2 | 67 | 84 | 234 | 361 | 25 (52) | <0.3 | 142 | negative |
| Patient 3 | 114 | 94 | 349 | 285 | 26 (39) | 0.08 | 110 | negative |
| Patient 4 | 101 | 80 | 414 | 298 | 21 (27) | <0.3 | 230 | negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Sayed, R.; Tehfe, M.; Blais, N. Successful Treatment with Brigatinib after Alectinib-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma—A Case Series. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 518-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010041
El Sayed R, Tehfe M, Blais N. Successful Treatment with Brigatinib after Alectinib-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma—A Case Series. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(1):518-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Sayed, Rola, Mustapha Tehfe, and Normand Blais. 2023. "Successful Treatment with Brigatinib after Alectinib-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma—A Case Series" Current Oncology 30, no. 1: 518-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010041
APA StyleEl Sayed, R., Tehfe, M., & Blais, N. (2023). Successful Treatment with Brigatinib after Alectinib-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma—A Case Series. Current Oncology, 30(1), 518-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010041





