Analysis of Key Factors Associated with Response to Salvage High-Dose Methotrexate Rechallenge in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with First Relapse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Clinical Information
2.3. Treatment and Response Assessment
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
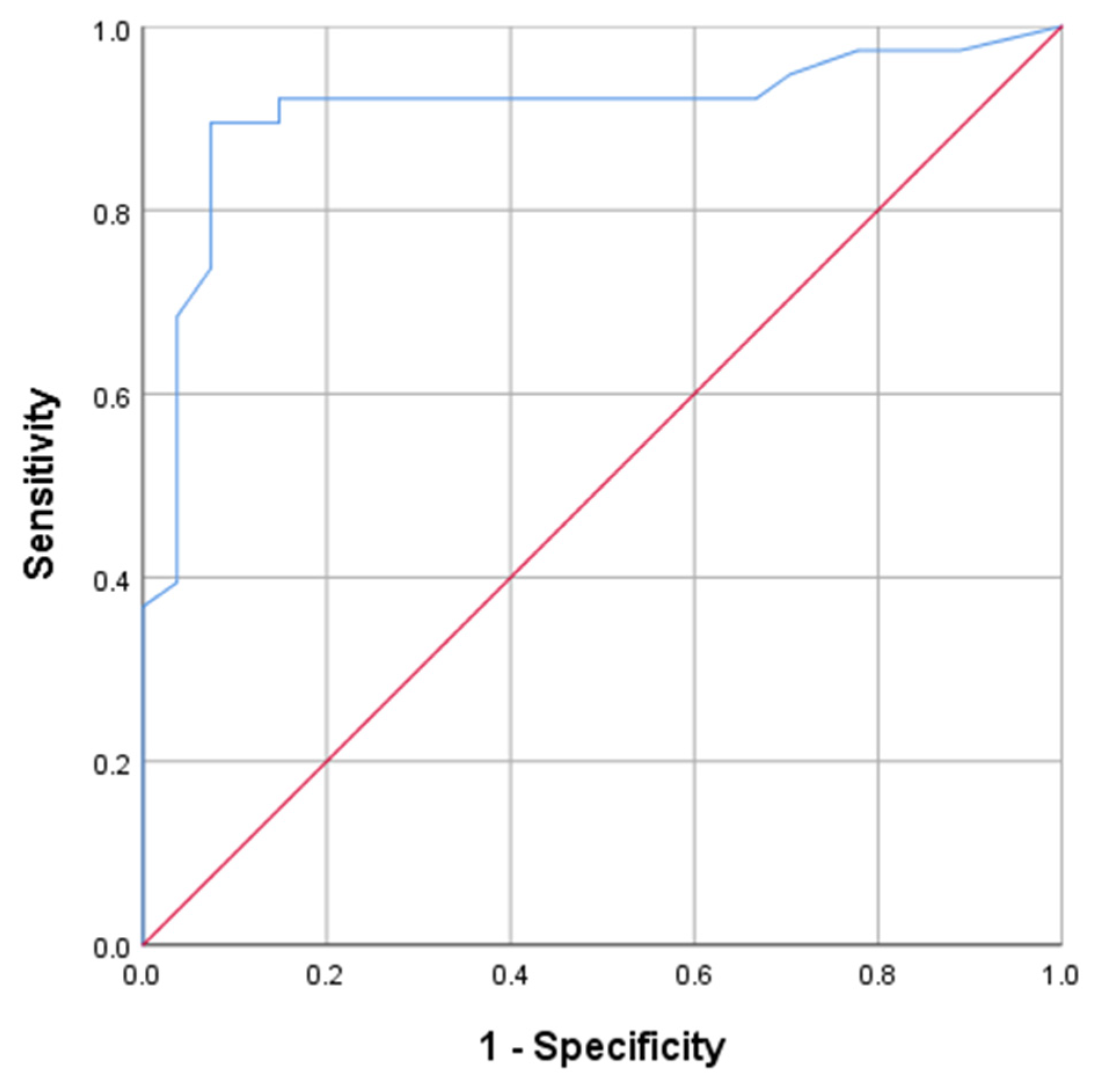
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
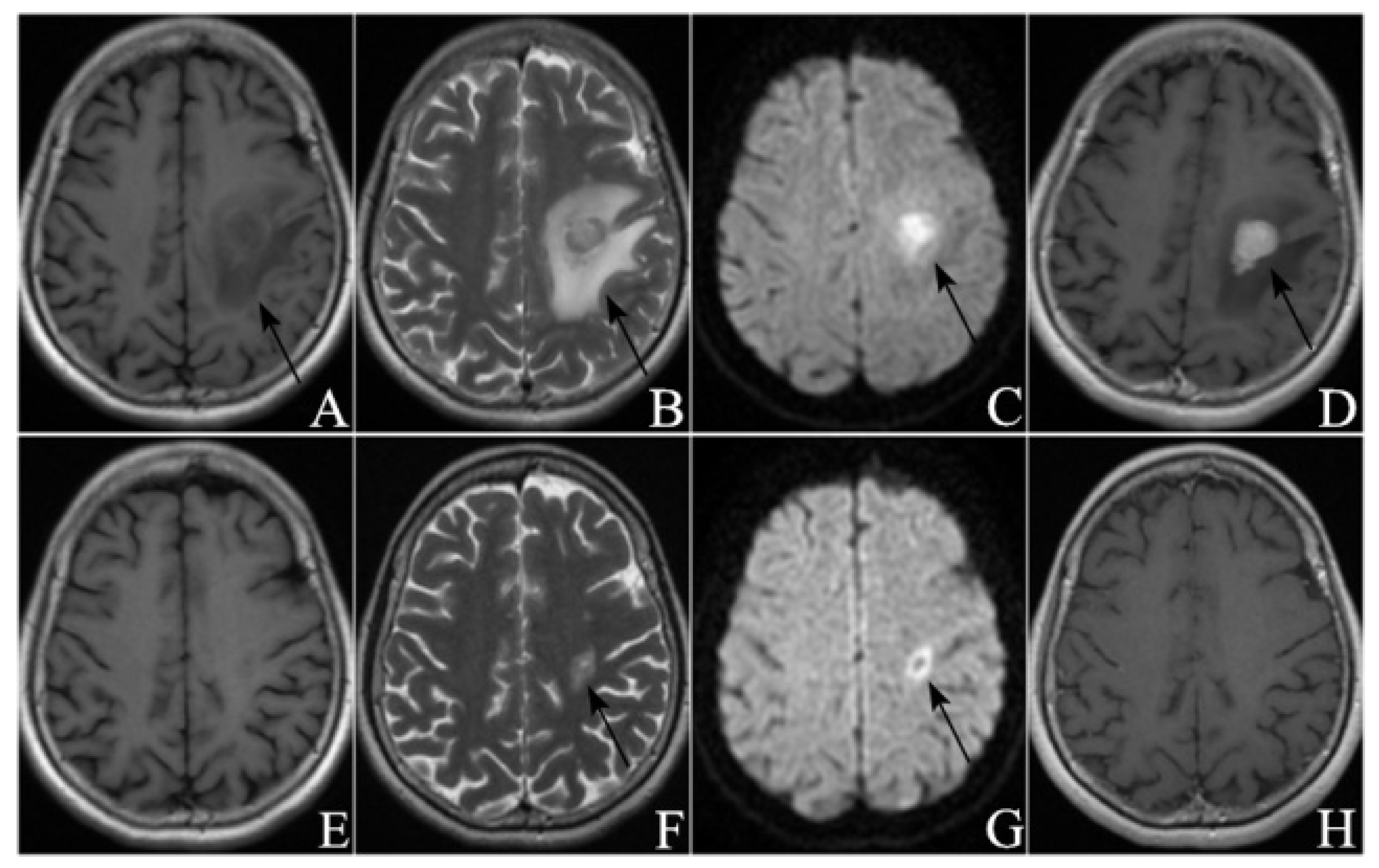
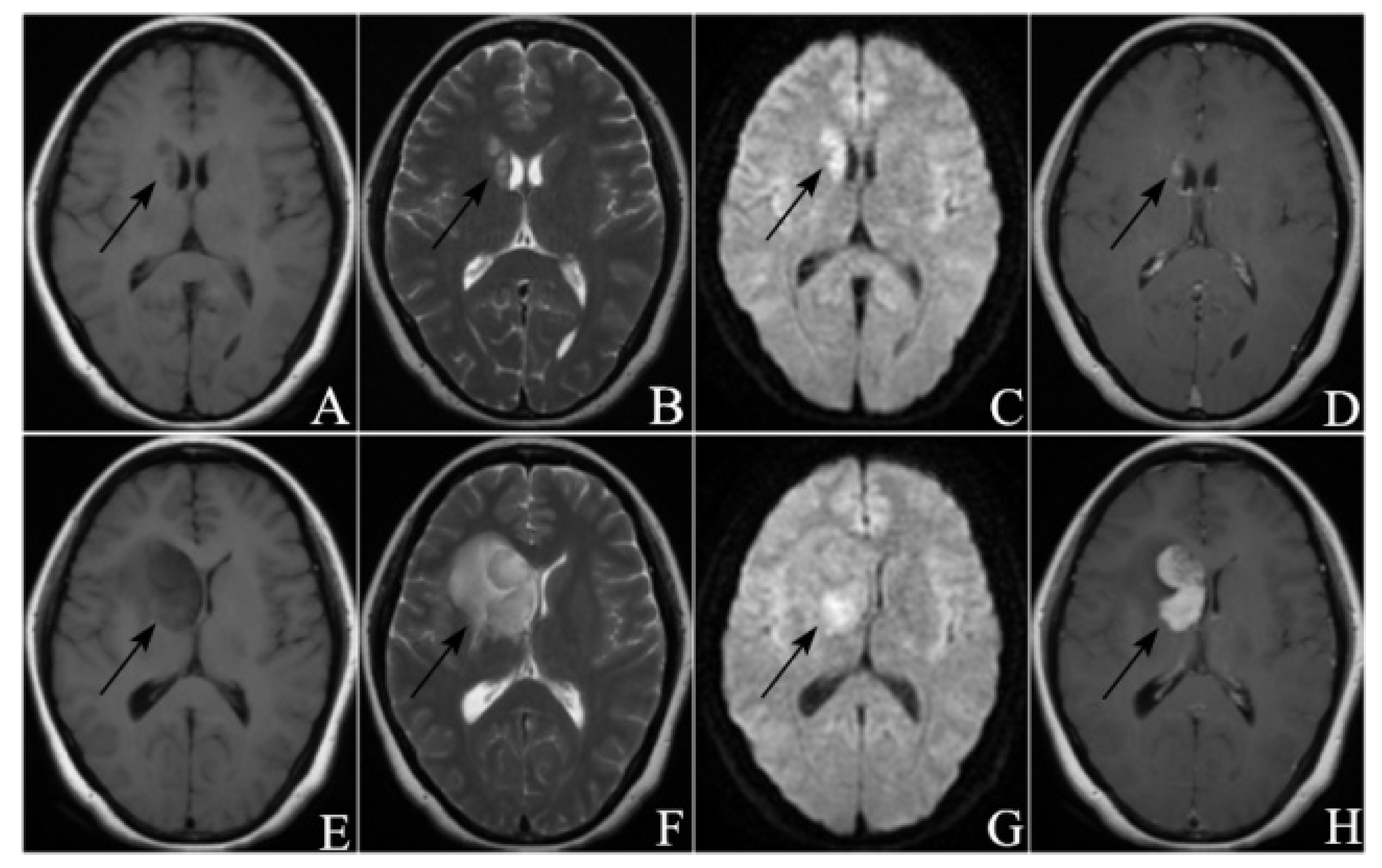
3.2. Radiological Manifestations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citterio, G.; Reni, M.; Gatta, G.; Ferreri, A. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, L.B.; Mohile, N.A. Advances in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.; Davis, M.E. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Treatment and Nursing Management of Immunocompetent Patients. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2021, 25, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, C.E.; Schaff, L.R.; Grommes, C. Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment. Cancer J. 2020, 26, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labak, C.M.; Holdhoff, M.; Bettegowda, C.; Gallia, G.L.; Lim, M.; Weingart, J.D.; Mukherjee, D. Surgical Resection for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e1436–e1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Batchelor, T.T. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Overview of current treatment strategies. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 897–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C. Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Continuum 2020, 26, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwueke, U.; Grommes, C.; Nayak, L. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovic, I.T.; Abrey, L.E. Diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdhoff, M.; Mrugala, M.M.; Grommes, C.; Kaley, T.J.; Swinnen, L.J.; Perez-Heydrich, C.; Nayak, L. Challenges in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, J.J.; Omuro, A. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Is there still a role for radiotherapy? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdhoff, M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Roschewski, M. Systemic Approach to Recurrent Primary CNS Lymphoma: Perspective on Current and Emerging Treatment Strategies. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 8323–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Bessell, E.; Bromberg, J.; Hottinger, A.F.; Preusser, M.; Rudà, R.; Schlegel, U.; Siegal, T.; Soussain, C.; Abacioglu, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: Guidelines from the European Association for Neuro-Oncology. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Campian, J.L.; Clark, S.W.; Fabiano, A.J.; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Tang, S.S.; Wolfe, J.; Kaley, T.J.; Daras, M.; Pentsova, E.I.; Piotrowski, A.F.; Stone, J.; Lin, A.; Nolan, C.P.; et al. Phase 1b trial of an ibrutinib-based combination therapy in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentsova, E.; Deangelis, L.M.; Omuro, A. Methotrexate re-challenge for recurrent primary central nervous system lymphoma. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 117, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.R.; Betensky, R.A.; Hochberg, F.H.; Grossman, S.A.; Lesser, G.J.; Nabors, L.B.; Chon, B.; Batchelor, T.T. Treatment of relapsed central nervous system lymphoma with high-dose methotrexate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5643–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.C.; McCormick, J.; Pui, C.H.; Buddington, R.K.; Harvey, R.D. Preventing and Managing Toxicities of High-Dose Methotrexate. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Spanne, O.; Mehta, M.P.; Grosu, A.L.; Geinitz, H. Presentation, patterns of care, and survival in patients with brain metastases: What has changed in the last 20 years? Cancer 2011, 117, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrey, L.E.; Batchelor, T.T.; Ferreri, A.J.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Pulczynski, E.J.; Zucca, E.; Smith, J.R.; Korfel, A.; Soussain, C.; DeAngelis, L.M.; et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize baseline evaluation and response criteria for primary CNS lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5034–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.W.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.W.; Chang, C.H.; Kim, O.L. Peritumoral brain edema in meningiomas: Correlation of radiologic and pathologic features. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2011, 49, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.T.; Stevens, G.H.; Peereboom, D.M.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Recurrent or refractory primary central nervous lymphoma: Therapeutic considerations. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2013, 13, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Reni, M.; Villa, E. Therapeutic management of primary cen-tral nervous system lymphoma: Lessons from prospective trials. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrey, L.E.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Yahalom, J. Long- term survival in primary CNS lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervin, T.; Canellos, G.P. Successful treatment of recurrent primary central nervous system lymphoma with high-dose methotrexate. Cancer 1980, 45, 1556–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reni, M.; Ferreri, A.J.; Villa, E. Second-line treatment for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, E.; Korfel, A.; Martus, P.; Kanz, L.; Griesinger, F.; Rauch, M.; Röth, A.; Hertenstein, B.; von Toll, T.; Hundsberger, T.; et al. High-dose methotrexate with or without whole brain radiotherapy for primary CNS lymphoma (G-PCNSL-SG-1): A phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Chung, D.S.; Jeun, S.S.; Hong, Y.K.; Yang, S.H. High-dose methotrexate monotherapy for newly diagnosed primary central nervous system lymphoma: 15-year multicenter experience. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. CSF, blood-brain barrier, and brain drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanswangphuwana, C.; Rojnuckarin, P.; Cherdchoo, N.; Raiyawa, T.; Uaprasert, N. Balancing relapses versus cognitive impairment in primary central nervous system lymphoma: A single-center experience. Hematology 2018, 23, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Rubenstein, J.L.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Ferreri, A.J.; Batchelor, T.T. Comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Kim, I.H.; Park, S.H.; Park, C.K.; Jung, H.W.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Heo, D.S. Low-dose whole brain radiotherapy with tumor bed boost after methotrexate-based chemotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjama, L.; Kuitunen, H.; Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Leppä, S.; Mannisto, S.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; Lehtinen, T.; Eray, M.; Vornanen, M.; et al. Constant pattern of relapse in primary central nervous lymphoma patients treated with high-dose methotrexate combinations. A Finnish retrospective study. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisselbrecht, C.; Glass, B.; Mounier, N.; Singh Gill, D.; Linch, D.C.; Trneny, M.; Bosly, A.; Ketterer, N.; Shpilberg, O.; Hagberg, H.; et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 28, 4184–4190, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Blay, J.Y.; Reni, M.; Pasini, F.; Spina, M.; Ambrosetti, A.; Calderoni, A.; Rossi, A.; Vavassori, V.; Conconi, A.; et al. Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: The International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner-Lemercier, S.; Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Soubeyran, P.; Lamy, T.; Morschhauser, F.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; et al. Primary CNS lymphoma at first relapse/progression: Characteristics, management, and outcome of 256 patients from the French LOC network. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, G.; Ferrigno, D.; Tamburini, M. Karnofsky and ECOG performance status scoring in lung cancer: A prospective, longitudinal study of 536 patients from a single institution. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, B.J.; Holland, J.M.; Kang, M.Y.; Hoffelt, S.C.; Marquez, C.M. Karnofsky Performance Status Assessment: Resident versus attending. J. Cancer Educ. 2002, 17, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.F.; Martz, K.L.; Bonner, H.; Nelson, J.S.; Newall, J.; Kerman, H.D.; Thomson, J.W.; Murray, K.J. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the brain: Can high dose, large volume radiation therapy improve survival? Re-port on a prospective trial by the radiation therapy oncology groups (RTOG): RTOG 8315. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1992, 23, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrey, L.E.; Ben-Porat, L.; Panageas, K.S.; Yahalom, J.; Berkey, B.; Curran, W.; Schultz, C.; Leibel, S.; Nelson, D.; Mehta, M.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5711–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Soubeyran, P.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Lamy, T.; Choquet, S.; Ahle, G.; Damaj, G.; et al. Management and outcome of primary CNS lymphoma in the modern era: An LOC network study. Neurology 2020, 94, e1027–e1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavizadeh, S.A.; Vossough, A.; Hajmomenian, M.; Assadsangabi, R.; Mohan, S. Neuroimaging in Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, J. Imaging features (CT, MRI, MRS, and PET/CT) of primary central nervous system lymphoma in immunocompetent patients. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küker, W.; Nägele, T.; Korfel, A.; Heckl, S.; Thiel, E.; Bamberg, M.; Weller, M.; Herrlinger, U. Primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL): MRI features at presentation in 100 patients. J. Neurooncol. 2005, 72, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.H.; Batchelor, T.T. Diagnosis and management of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer 2017, 123, 4314–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Ahn, H.J.; Yoon, D.H.; Hong, J.Y.; Yoo, C.; Kim, S.; Huh, J.; Suh, C. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: A new prognostic model for patients with diffuse large B-cell histology. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Cleveland, J.; Rubenstein, J.L. On point in primary CNS lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Age ≥ 60 | 165 (84.6) |
| Age < 60 | 30 (15.4) |
| KPS | |
| KPS ≥ 70 | 132 (67.7) |
| KPS < 70 | 63 (32.3) |
| ECOG | |
| 0 | 12 (6.2) |
| 1 | 120 (61.5) |
| 2 | 63 (32.3) |
| With clinical symptoms | |
| no | 60 (30.8) |
| yes | 135 (69.2) |
| Location of recurrence and initial lesion | |
| consistent | 69 (35.4) |
| inconsisitent | 126 (64.6) |
| Deep brain involved | |
| no | 129 (66.2) |
| yes | 66 (33.8) |
| Number | |
| single | 93 (47.7) |
| multiple | 102 (52.3) |
| Serum LDH | |
| normal | 132 (67.7) |
| abnormal increase | 63 (32.3) |
| Serum β2-MG | |
| normal | 135 (69.2) |
| abnormal increase | 60 (30.8) |
| Urine β2-MG | |
| normal | 123 (63.1) |
| abnormal increase | 72 (36.9) |
| eGFR | |
| normal | 147 (75.4) |
| abnormal | 48 (24.6) |
| CSF Pandy test | |
| positive | 96 (49.2) |
| negative | 99 (50.8) |
| CSF Protein quantification | |
| normal | 78 (40.0) |
| abnormal increase | 117 (60.0) |
| CSF Glucose | |
| normal | 126 (64.6) |
| abnormal | 69 (35.4) |
| CSF Chloride | |
| normal | 117 (60.0) |
| abnormal | 78 (40.0) |
| CSF White blood cell count | |
| normal | 129 (66.2) |
| abnormal increase | 66 (33.8) |
| Lesion removed at the initial treatment | |
| yes | 63 (32.3) |
| no | 132 (67.7) |
| WBRT after initial treatment | |
| yes | 84 (43.1) |
| no | 111 (56.9) |
| Histopathological characteristics | |
| DLBCL-non-GCB | 120 (61.5) |
| DLBCL-GCB | 69 (35.4) |
| DLBCL-unknown | 6 (3.1) |
| Variable | PFS2 < 6 Months (n = 39) | 6 Months ≤ PFS2 ≤ 12 Months (n = 39) | PFS2 > 12 Months (n = 36) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 66.770 ± 6.559 | 68.690 ± 6.550 | 67.500 ± 8.130 |
| KPS | 70.770 ± 9.541 | 73.080 ± 9.473 | 69.17 ± 9.003 |
| ECOG (0/1/2) | 3/24/12 | 3/27/9 | 0/21/15 |
| PFS1 | 12.392 ± 2.845 | 12.685 ± 2.5816 | 13.200 ± 0.9195 |
| Clinical symptoms (no/yes) | 9/30 | 15/24 | 9/27 |
| Location of recurrence (consistent/inconsisitent) | 12/27 | 18/21 | 6/30 |
| Deep brain involved (no/yes) | 30/9 | 24/15 | 24/12 |
| Number (single/multiple) | 18/21 | 21/18 | 27/9 |
| Serum LDH (normal/abnormal increase) | 27/12 | 21/18 | 27/9 |
| Serum β2-MG (normal/abnormal increase) | 33/6 | 24/15 | 33/3 |
| Urine β2-MG (normal/abnormal increase) | 27/12 | 27/12 | 24/12 |
| eGFR (normal/abnormal) | 27/12 | 33/6 | 27/9 |
| CSF Pandy test (positive/negative) | 24/15 | 18/21 | 15/21 |
| CSF Protein quantification (normal/abnormal increase) | 21/18 | 9/30 | 15/21 |
| CSF Glucose (normal/abnormal) | 21/18 | 27/12 | 24/12 |
| CSF Chloride (normal/abnormal) | 30/9 | 21/18 | 18/18 |
| CSF White blood cell count (normal/abnormal increase) | 27/12 | 24/15 | 24/12 |
| Lesion removed at the initial treatment (yes/no) | 12/27 | 15/24 | 12/24 |
| WBRT after initial treatment (yes/no) | 30/9 | 30/9 | 33/3 |
| Histopathological characteristics (DLBCL-non-GCB/ DLBCL-GCB/ DLBCL-unknown) | 24/15/0 | 24/12/3 | 21/15/0 |
| Variable | χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.348 | 0.555 |
| KPS | 0.022 | 0.882 |
| ECOG | 0.172 | 0.918 |
| PFS1 | - | 2.504 × 10−8 |
| Clinical symptoms | 0.143 | 0.706 |
| Location of recurrence | 0.579 | 0.447 |
| Deep brain involved | 0.210 | 0.647 |
| Number | 1.145 | 0.285 |
| Serum LDH | 0.151 | 0.697 |
| Serum β2-MG | 2.499 | 0.144 |
| Urine β2-MG | 1.122 | 0.290 |
| eGFR | 0.043 | 0.836 |
| CSF Pandy test | 0.022 | 0.883 |
| CSF Protein quantification | 0.011 | 0.918 |
| CSF Glucose | 0.085 | 0.771 |
| CSF Chloride | 0.011 | 0.918 |
| CSF White blood cell count | 0.005 | 0.941 |
| Lesion removed at the initial treatment | 0.151 | 0.697 |
| WBRT after initial treatment | 22.680 | 2.000 × 10−6 |
| Histopathological characteristics | 0.129 | 0.937 |
| Variable | B | SE | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFS1 | 0.089 | 0.014 | 5.261 × 10−8 |
| WBRT after initial treatment | 0.317 | 0.091 | 0.001 |
| Variable | χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 2.152 | 0.341 |
| KPS | 26.099 | 2.000 × 10−6 |
| ECOG | 1.736 | 0.784 |
| PFS1 | - | 0.605 |
| Clinical symptoms | 0.881 | 0.644 |
| Location of recurrence | 2.517 | 0.284 |
| Deep brain involved | 0.737 | 0.692 |
| Number | 2.263 | 0.323 |
| Serum LDH | 1.345 | 0.511 |
| Serum β2-MG | 3.790 | 0.150 |
| Urine β2-MG | 0.025 | 0.988 |
| eGFR | 0.868 | 0.648 |
| CSF Pandy test | 1.103 | 0.576 |
| CSF Protein quantification | 2.611 | 0.271 |
| CSF Glucose | 0.754 | 0.686 |
| CSF Chloride | 2.262 | 0.323 |
| CSF White blood cell count | 0.177 | 0.915 |
| Lesion removed at the initial treatment | 0.177 | 0.915 |
| WBRT after initial treatment | 1.188 | 0.552 |
| Histopathological characteristics | 2.152 | 0.708 |
| Variable | B | SE | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| KPS | 1.321 | 0.214 | 3.932 × 10−7 |
| Variable | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| T1WI | |
| hypo | 96 (49.2) |
| iso | 90 (46.2) |
| hyper | 9 (4.6) |
| T2WI | |
| hypo | 6 (3.1) |
| iso | 84 (43.1) |
| hyper | 105 (53.8) |
| DWI | |
| hypo | 6 (3.1) |
| hyper | 189 (96.9) |
| Enhanced pattern | |
| homogeneous | 171 (87.7) |
| heterogeneous | 24 (12.3) |
| Variable | χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | - | 0.836 |
| Maximum diameter | - | 0.905 |
| EI | - | 0.714 |
| T1WI | 0.185 | 0.883 |
| T2WI | 0.480 | 0.883 |
| DWI | 0.667 | 0.805 |
| Enhanced pattern | 0.146 | 0.604 |
| Variable | χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | - | 0.200 |
| Maximum diameter | - | 0.093 |
| EI | - | 0.581 |
| T1WI | 0.154 | 0.926 |
| T2WI | 0.154 | 0.926 |
| DWI | 2.225 | 0.329 |
| Enhanced pattern | 3.765 | 0.152 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, P.; Chen, H.; Shen, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, A.; Geng, D. Analysis of Key Factors Associated with Response to Salvage High-Dose Methotrexate Rechallenge in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with First Relapse. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6642-6656. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29090522
Du P, Chen H, Shen L, Liu X, Wu X, Chen L, Cao A, Geng D. Analysis of Key Factors Associated with Response to Salvage High-Dose Methotrexate Rechallenge in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with First Relapse. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(9):6642-6656. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29090522
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Peng, Hongyi Chen, Li Shen, Xiao Liu, Xuefan Wu, Lang Chen, Aihong Cao, and Daoying Geng. 2022. "Analysis of Key Factors Associated with Response to Salvage High-Dose Methotrexate Rechallenge in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with First Relapse" Current Oncology 29, no. 9: 6642-6656. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29090522
APA StyleDu, P., Chen, H., Shen, L., Liu, X., Wu, X., Chen, L., Cao, A., & Geng, D. (2022). Analysis of Key Factors Associated with Response to Salvage High-Dose Methotrexate Rechallenge in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with First Relapse. Current Oncology, 29(9), 6642-6656. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29090522





