A Qualitative Study of Patient and Healthcare Provider Perspectives on Building Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation into the Surgical Care Pathway for Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Interview Procedures
2.3. Interviews with Patients
2.4. Interviews with Healthcare Providers
2.5. Qualitative Methodology, Interpretive Description
2.6. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
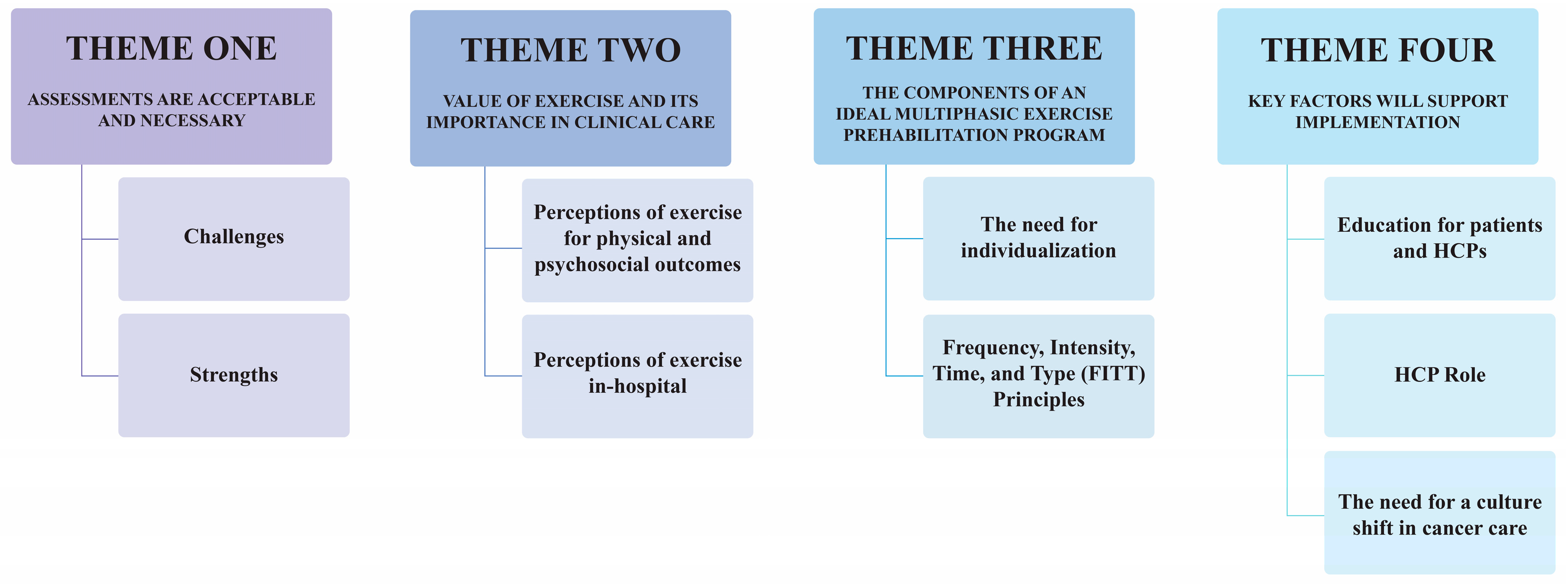
3.2. Themes
3.2.1. Theme One: Assessments Are Acceptable and Necessary
Patient Perspectives
The questionnaires, the only difficulty I had was the very first time and the one in the hospital, some things hadn’t happened yet so it was unclear how to answer those because there was no ‘not applicable’, or something like that or a way I could say ‘I haven’t experienced that problem yet so it doesn’t count’ that was my only real problem with those.P 6.
Oh, no problem with that. Yeah, that makes sense to find out how fast one recovers from the surgery. I think is really quite critical and I sort of almost wondered if there would be another one like a week or ten days later, to see how the improvement is.P 6.
Hindsight you probably could’ve put a bit more emphasis put on the watch and ‘hey we’re gonna track what you’re doing and really want you to push yourself each day’.P 8.
HCP Perspectives
I think we know it’s a very challenging patient population, not because of the people, particularly but because of what they’re being subjected to […] it’s a time-sensitive cancer…when surgery’s involved is complex and so there’s a lot of moving parts.HCP 6—Surgeon.
As you may know, we’re not very good at documenting mobility, and hence, why I think that these uhm, [activity trackers], might be very useful for nurses in helping reduce some of their workload.HCP 1—Clinical Nurse Educator.
I think we’re all really interested and excited and really proud that this is happening for our patients.HCP 8—Surgeon.
[patient-reported outcomes] get patients to intellectualize what’s going on with their body, and I think that can be a really helpful process, especially when they start realizing what they can do. These questions are pretty, straightforward right, they’re about your body […] there’s no right or wrong, they just have to say how they’re feeling, and I think that kinda introspection’s really important at that stressful time.HCP 7—Surgeon.
The fact I’m talking to them about the idea of optimizing their journey through this treatment, it, I guess maybe sends a signal that we’re already thinking about that far, so it’s not all doom and gloom, it’s not like ‘I don’t even know if you’re gonna make it through this surgery.’ If I’m already talking about what comes after, then I think kind of puts a bit of a positive spin on things.HCP 10—Surgeon.
3.2.2. Theme Two: Value of Exercise and Its Importance in Clinical Care
Patient Perspectives
It brings a normality back rather than the sick room and the hospital and sitting in a chair and trying to reach over, it brings movement back to this arm and exercise the muscles on my right shoulder and uhm, doing all those small exercises get the body moving, so I think the whole-body exercise is so important.P 6.
I think the only reason why I survived the first time with stage four was because I was fit to be able to do it. How many people survive stage four? Usually that’s a death sentence.P 2.
HCP Perspectives
It’s priceless, I mean it can’t be overstated how valuable it is […] having seen so many patients over so many years, the ones that move feel better, recover better and just feel more alive, they just do better, so I think this is very, very important.HCP 6—Surgeon.
Exercise is a hugely important part of going through a big surgery and hugely important to the recovery process. I’m kind of already sold on that idea, it plays a huge role and I think it’s huge psychologically and emotionally for that part of things, for people – their resilience, being able to get through the recovery and feeling stronger, and better after the fact.HCP 8—Surgeon.
3.2.3. Theme Three: The Components of an Ideal Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation Program
Patient Perspectives
I’d never thought about going to the gym but I’ve uhm yeah, just walking and in you know, spring summer and fall, working in the garden and other things like that, that sort of physical activity.P 6.
I would exercise a bit every day if I could.P 3.
Oh, well, pre-surgery, probably pretty intensive.P 3.
In-hospital was good, I mean, if you do it for an hour in the hospital, you’re getting quite a bit of exercise in.P 1.
Is this in-hospital? I’d suggest it for fifteen minutes to begin with somebody.P 2.
Would be good for me in the hospital, there like, five minutes is enough.P 3.
Well, I think you should start out slower and increase by the time you get to the six weeks.P 1.
Individualize it and make them feel more special.P 2.
Yeah, I think movement’s a gentle way to say ‘you know, get up and move’ you know what I mean? Get up and walk, your heart doesn’t have to race at 170 beats a minute.P 8.
I wouldn’t have bought-into jumping into a high intensity short-term program.P 10.
HCP Perspectives
I wish we could start this tomorrow. I wish we could have an exercise physiologist in our clinic.HCP 2—Oncology Nurse.
I definitely think that the patients would be pleased to hear that there’s a program in place that they have access to, and again this whole idea that to some degree, dove tails into survivorship. I definitely see this as a huge bonus, this would really upgrade what we have to offer these patients.HCP 10—Surgeon.
The ideal time do present all this to the patient would be on a second visit, that comes after the initial sorta, discussion about the primary treatment […] I think that they need a bit of time to just sort of digest that, even if like, for 24hours, just to kind of get their head around what’s going on […] if there was a way to make this part of the package, to present this information like even a day later or something, the patient would absorb a lot more of this.HCP 10—Surgeon.
3.2.4. Theme Four: Key Factors Will Support Implementation
Patient Perspectives
I think a quick consult before they release you from the hospital […] to sit down and say ‘okay, these are resources available and these are the things you can and can’t do,’ cause I have this new flap, am I not supposed to have a beer? What can’t I do with this flap, they never ever told me, right?P 8.
You really wanna listen to him I would think, he’s the big guy.P 4.
If the doctor woulda told me ‘we need you to get your heart movin’ so get workin’ out hard here in the next month’ I would’ve worked out super hard every day before surgery, right? Uhm, but there was really nothing, just ‘go about your life’ right, ‘enjoy your life’.P 8.
HCP Perspectives
I think what you’re really trying to achieve is a cultural shift, a change in brain functioning for everybody. I think what I would be looking at is what is the brand of exercise in cancer care and how do we change that on a much larger scale than largely advertising what we see in the hospital that is going out to people who already believe it.HCP 7—Surgeon.
I do think that it’s important that the patient’s surgeon at some point has a direct conversation with the patient to uh indicate how really important it is.HCP 8—Surgeon.
Right now, it’s working because it’s within the context of a study, and even more so when it becomes a [prehabilitation trial]. I would imagine there needs to be some funding to provide support, staff, and so forth to actually take the patients through all this. Like, if it becomes standard of care, who’s actually gonna administer all this stuff?HCP 10—Surgeon.
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Implications for a Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation Intervention
4.2. Utilizing a Patient-Oriented Research Approach
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parke, S.C.; Oza, S.; Shahpar, S.; Ngo-Huang, A.; Herbert, A.; Barksdale, T.; Gerber, L. Identifying gaps in research on rehabilitation for patients with head and neck cancer: A scoping review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abendstein, H.; Nordgren, M.; Boysen, M.; Jannert, M.; Silander, E.; Ahlner-Elmqvist, M.; Hammerlid, E.; Bjordal, K. Quality of life and head and neck cancer: A 5 year prospective study. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, L.; Conlee, J.; Hunt, J.; Agarwal, J.; White, S. Psychosocial distress is prevalent in head and neck cancer patients. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, S.A.; Khan, M.J.; Ronis, D.L.; Fowler, K.E.; Gruber, S.B.; Wolf, G.T.; Terrell, J.E. Health behaviors of head and neck cancer patients the first year after diagnosis. Head Neck 2008, 30, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howren, M.B.; Christensen, A.J.; Karnell, L.H.; Funk, G.F. Psychological factors associated with head and neck cancer treatment and survivorship: Evidence and opportunities for behavioral medicine. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 81, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiris, A.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Raben, D.; Ferris, R.L. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2008, 371, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.E.; LaMonte, S.J.; Erb, N.L.; Beckman, K.L.; Sadeghi, N.; Hutcheson, K.A.; Stubblefield, M.D.; Abbott, D.M.; Fisher, P.S.; Stein, K.D. American Cancer Society head and neck cancer survivorship care guideline. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 203–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, F.; Scheede-Bergdahl, C. Prehabilitation to enhance perioperative care. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2015, 33, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, F.; Silver, J.K.; Feldman, L.S.; McKee, A.; Gilman, S.; Gillis, C.; Scheede-Bergdahl, C.; Gamsa, A.; Stout, N.; Hirsch, B. Surgical prehabilitation in patients with cancer: State-of-the-science and recommendations for future research from a panel of subject matter experts. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2017, 28, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, B.; Selvy, M.; Slim, K. The concept of prehabilitation: What the surgeon needs to know? J. Visc. Surg. 2016, 153, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewen, I.; Jeffery, C.C.; Rieger, J.; Constantinescu, G. Prehabilitation in head and neck cancer patients: A literature review. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, J.K.; Baima, J. Cancer prehabilitation: An opportunity to decrease treatment-related morbidity, increase cancer treatment options, and improve physical and psychological health outcomes. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautremont, J.F.; Rudmik, L.R.; Nakoneshny, S.C.; Chandarana, S.P.; Matthews, T.W.; Schrag, C.; Fick, G.H.; Dort, J.C. Understanding the impact of a clinical care pathway for major head and neck cancer resection on postdischarge healthcare utilization. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1216–E1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautremont, J.F.; Rudmik, L.R.; Yeung, J.; Asante, T.; Nakoneshny, S.C.; Hoy, M.; Lui, A.; Chandarana, S.P.; Matthews, T.W.; Schrag, C. Cost-effectiveness analysis of a postoperative clinical care pathway in head and neck surgery with microvascular reconstruction. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 42, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.; Wiskemann, J.; May, A.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Courneya, K.S.; Zucker, D.; Matthews, C.; Ligibel, J.; Gerber, L. Exercise guidelines for cancer survivors: Consensus statement from international multidisciplinary roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports. Exerc. 2019, 51, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cormie, P.; Atkinson, M.; Bucci, L.; Cust, A.; Eakin, E.; Hayes, S.; McCarthy, A.L.; Murnane, A.; Patchell, S.; Adams, D. Clinical Oncology Society of Australia position statement on exercise in cancer care. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 209, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twomey, R.; Culos-Reed, S.N.; Dort, J.C. Exercise Prehabilitation—Supporting Recovery From Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa Mina, D.; Sabiston, C.; Au, D.; Fong, A.; Capozzi, L.; Langelier, D.; Chasen, M.; Chiarotto, J.; Tomasone, J.; Jones, J. Connecting people with cancer to physical activity and exercise programs: A pathway to create accessibility and engagement. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dort, J.C.; Farwell, D.G.; Findlay, M.; Huber, G.F.; Kerr, P.; Shea-Budgell, M.A.; Simon, C.; Uppington, J.; Zygun, D.; Ljungqvist, O. Optimal perioperative care in major head and neck cancer surgery with free flap reconstruction: A consensus review and recommendations from the enhanced recovery after surgery society. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Canada’s Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research (SPOR); Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2011. Available online: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/44000.html (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Sacristán, J.A. Patient-centered medicine and patient-oriented research: Improving health outcomes for individual patients. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2013, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daun, J.T.; Twomey, R.; Capozzi, L.C.; Crump, T.; Francis, G.J.; Matthews, T.W.; Chandarana, S.; Hart, R.D.; Schrag, C.; Mathews, J.; et al. The feasibility of patient-reported outcomes, physical function, and mobilization in the care pathway for head and neck cancer surgical patients. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2022, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales; Human kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, S. Interpretive Description: Qualitative Research for Applied Practice; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, E. Constructivism: From Philosophy to Practice,1997. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED444966 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- NCH. Express Scribe Transcription Software 2021. Available online: https://www.nch.com.au/scribe/index.html (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- QSR International. NVivo Qualitative Data Analysis Software. Available online: https://www.qsrinternational.com/nvivo-qualitative-data-analysis-software/home (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Banerjee, S.; Semper, K.; Skarparis, K.; Naisby, J.; Lewis, L.; Cucato, G.; Mills, R.; Rochester, M.; Saxton, J. Patient perspectives of vigorous intensity aerobic interval exercise prehabilitation prior to radical cystectomy: A qualitative focus group study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 43, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Thaysen, H.V.; Soegaard, C.H.; Blaakaer, J.; Seibaek, L. From waiting to preparing: A qualitative feasibility study of cancer patients’ perspectives on prehabilitation. Eur. J. Pers. Cent. Healthc. 2019, 7, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, C.; McIlfatrick, S.; Larkin, P.; Dunwoody, L.; Gracey, J. A qualitative exploration of patient and healthcare professionals’ views and experiences of palliative rehabilitation during advanced lung cancer treatment. Palliat. Med. 2018, 32, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Campbell, A.M.; Stuiver, M.M.; Pinto, B.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Morris, G.S.; Ligibel, J.A.; Cheville, A.; Galvão, D.A.; Alfano, C.M. Exercise is medicine in oncology: Engaging clinicians to help patients move through cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrick, K.; Kebbe, M.; Aubin, D. A home for patient-oriented research. CMAJ 2018, 190, E607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manafo, E.; Petermann, L.; Mason-Lai, P.; Vandall-Walker, V. Patient engagement in Canada: A scoping review of the ‘how’and ‘what’of patient engagement in health research. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffett, L. Patient engagement: What partnering with patient in research is all about. Thromb. Res. 2017, 150, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilling, J.A.; Swensen, S.J.; Hoover, M.R.; Dankbar, G.C.; Donahoe-Anshus, A.L.; Murad, M.H.; Mueller, J.T. Accelerating the use of best practices: The Mayo Clinic model of diffusion. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2013, 39, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.C.; Elliott, M.J.; Cassidy, C. Moving patient-oriented research forward: Thoughts from the next generation of knowledge translation researchers. Res. Involv. Engagem. 2018, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M. Barriers, Facilitators, and Experiences with Exercise Among Individuals of South Asian Heritage Living with and Beyond Cancer. Kinesiology 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa-Singer, M.; Valdez Dadia, A.; Yu, M.C.; Surbone, A. Cancer, culture, and health disparities: Time to chart a new course? CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 12–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowich, M. When women study men: Gendered implications for qualitative research. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2019, 18, 1609406919872388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagoner, C.W.; Capozzi, L.C.; Culos-Reed, S.N. Tailoring the Evidence for Exercise Oncology within Breast Cancer Care. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4827–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, N.L.; Brown, J.C.; Schwartz, A.L.; Marshall, T.F.; Campbell, A.M.; Nekhlyudov, L.; Zucker, D.S.; Basen-Engquist, K.; Campbell, G.; Meyerhardt, J. An exercise oncology clinical pathway: Screening and referral for personalized interventions. Cancer 2020, 126, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covington, K.R.; Marshall, T.; Campbell, G.; Williams, G.R.; Fu, J.B.; Kendig, T.D.; Howe, N.; Alfano, C.M.; Pergolotti, M. Development of the Exercise in Cancer Evaluation and Decision Support (EXCEEDS) algorithm. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 6469–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Owen, N.; Fisher, E. Ecological models of health behavior. In Health behavior: Theory, Research, and Practice; Glanz, K., Rimer, B.K., Viswanath, K., Eds.; Wiley: Newe York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 43–64. [Google Scholar]
| Patient Characteristics | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender (Self-Identified) Male Female | 9 (90%) 1 (10%) |
| Age: Mean ± SD, y | 60.8 ± 8.5 |
| Time Until Surgery: Mean ± SD, days | 10.5 ± 8.6 |
| Primary Tumor Site Oral Cavity Oropharynx Paranasal Sinuses | 8 (10%) 1 (80%) 1 (10%) |
| Cancer Stage I II III IV Unknown | 1 (10%) 2 (20%) 2 (20%) 4 (40%) 1 (10%) |
| Histology Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 10 (100%) |
| Ultimate Treatment Surgery Alone Surgery + Radiation Therapy Surgery + Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy | 4 (40%) 3 (30%) 3 (30%) |
| Patient Demographic Variable | No. of Patients (%) |
| Race (Self-Identified) White Not Specified | 9 (90%) 1 (10%) |
| Employment Status Disability Part Time Full Time Unemployed | 1 (10%) 3 (30%) 4 (40%) 2 (20%) |
| Annual Family Income, CDN$ $60,000–79,999 $80,000–99,000 >100,000 Prefer Not to Answer | 1 (10%) 1 (10%) 3 (30%) 5 (50%) |
| Smoking Status Never Smoked Ex-Smoker Current Smoker | 2 (20%) 6 (60%) 2 (20%) |
| Alcohol Consumption Never Drinker Light Drinker Moderate Drinker Heavy Drinker Previous Drinker | 3 (30%) 2 (20%) 1 (10%) 2 (20%) 2 (20%) |
| Healthcare Providers (n = 10) | No. of Healthcare Providers (%) |
| Gender (Self-Identified) Male Female | 4 (40%) 6 (60%) |
| Discipline Surgeon Oncology Nurse Physiotherapist Unit Manager Clinical Nurse Educator Unit nurse/research assistant | 4 (40%) 2 (20%) 1 (10%) 1 (10%) 1 (10%) 1 (10%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daun, J.T.; Twomey, R.; Dort, J.C.; Capozzi, L.C.; Crump, T.; Francis, G.J.; Matthews, T.W.; Chandarana, S.P.; Hart, R.D.; Schrag, C.; et al. A Qualitative Study of Patient and Healthcare Provider Perspectives on Building Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation into the Surgical Care Pathway for Head and Neck Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5942-5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080469
Daun JT, Twomey R, Dort JC, Capozzi LC, Crump T, Francis GJ, Matthews TW, Chandarana SP, Hart RD, Schrag C, et al. A Qualitative Study of Patient and Healthcare Provider Perspectives on Building Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation into the Surgical Care Pathway for Head and Neck Cancer. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(8):5942-5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080469
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaun, Julia T., Rosie Twomey, Joseph C. Dort, Lauren C. Capozzi, Trafford Crump, George J. Francis, T. Wayne Matthews, Shamir P. Chandarana, Robert D. Hart, Christiaan Schrag, and et al. 2022. "A Qualitative Study of Patient and Healthcare Provider Perspectives on Building Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation into the Surgical Care Pathway for Head and Neck Cancer" Current Oncology 29, no. 8: 5942-5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080469
APA StyleDaun, J. T., Twomey, R., Dort, J. C., Capozzi, L. C., Crump, T., Francis, G. J., Matthews, T. W., Chandarana, S. P., Hart, R. D., Schrag, C., Matthews, J., McKenzie, C. D., Lau, H., & Culos-Reed, S. N. (2022). A Qualitative Study of Patient and Healthcare Provider Perspectives on Building Multiphasic Exercise Prehabilitation into the Surgical Care Pathway for Head and Neck Cancer. Current Oncology, 29(8), 5942-5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080469







