Abstract
Exosomes, extracellular vesicles with a diameter of 40 to 160 nm, are among the smallest extracellular vesicles released by cells. They deliver different cargoes, including proteins, DNAs, and RNAs, and facilitate communication between cells to coordinate a variety of physiological and pathological functions. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth common malignant tumor and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Its molecular mechanism remains largely unknown, and there is a lack of reliable and noninvasive biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis prediction. Mounting evidence has shown that exosomes carry a variety of ncRNAs, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), which play critical roles in the occurrence and progression of HCC. In this review, we summarize the recent findings of exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in HCC from their impact on the development of HCC to their potential applications in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
1. Introduction
Cells of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes can form and release cellular vesicles to carry out their physiological functions. In 2014, the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) adopted “extracellular vesicles” (EVs) as a generic term for naturally released particles from cells, including exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic bodies and other EV subsets [1]. Among them, exosomes are vesicles with a diameter of 40 to 160 nm (average ~100 nm) that originate from endosomes [2]. Owing to the similar size between exosomes and other EVs, theoretically and technically separating them is quite challenging. Yet, exosomes display distinct roles both in physical and pathological process.
Depending on the cells from which the exosomes are derived and the physiological or pathological processes involved, exosomal contents vary widely from DNAs or RNAs to proteins or lipids [3]. Upon formation, endosomes are secreted out of cells by exocytosis to play central roles in cell–cell communication [4]. With the increase in the number of studies on exosomes, it has been reported that cancer-derived exosomes are closely related to the occurrence and development of cancer. Exosomal communication between different types of cells can support the proliferation of tumor cells [4], and the pivotal role of tumor-derived exosomes in the tumor microenvironment (TME) has been confirmed [5]. A myriad of experimental studies has indicated the great potential for the application of exosomes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of tumors [6].
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common type of tumor that threatens human health. According to the latest statistics in 2022, among the leading types of cancers, deaths related to liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancers rank fifth in males and seventh in females [7]. Numerous studies have shown that chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and C (CHC), alcohol addiction, as well as metabolic liver disease (especially non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)) are risk factors for HCC [8]. Early diagnosis and HCC monitoring can increase the possibility of a cure and improve the overall survival (OS) rate, albeit to a certain degree [9]. For instance, liquid biopsy can be used as an important means of the early diagnosis of HCC [10]. According to previous studies, the most widely used biomarker is alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, threshold of 20 ng/mL), which shows a low sensitivity of 40–60% and a high specificity of 80–90% [9]. Despite the high specificity of AFP, the low sensitivity of AFP puts forward a higher demand for the early diagnosis of HCC. Thus, cancer-derived exosomes are a worthy research direction [11,12], as they may lead to the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for improving the clinical outcomes of HCC.
Currently, HCC-related exosomal ncRNAs have been reviewed in a few papers, yet we provided a updated insight into this issue by deep mining the latest literatures and quantitatively assessing the exomal diagnostic biomarkers. Furthermore, based on the functions and roles of exosomal ncRNAs in HCC, we summarize the current knowledge on the contribution of exosomal-related ncRNAs in HCC to TME (e.g., crosstalk between tumor and non-tumor cells, tumor angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis) and tumor resistance.
2. Exosome Biology
Exosomes were first noticed by Peter Wolf when he discovered that red blood cells can release vesicles and that these extracellular vesicles have anticoagulant activity [13]. In subsequent studies, Rose Johnstone officially named these vesicles “exosomes” [14]. Exosome biology plays a critical role in a variety of human diseases. Presently, there are some notable research findings on the mechanism of exosome formation, but there are still many unknown processes that remain unexplored.
The formation of exosomes occurs as follows (Figure 1). First, the plasma membrane internalizes extracellular components by endocytosis to form early endosomes [15]. Exosomal membrane cargoes are internalized by the plasma membrane or the Golgi apparatus into the endosome and are subsequently classified as intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) during endosomal maturation [16]. Early endosomal membranes are further enfolded to form multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) that contain ILVs [17], whose cargoes selectively or passively integrate a variety of intracellular materials, such as RNAs (including mRNAs, miRNAs, and other ncRNAs), DNAs, and lipids, into vesicles [18]. Cargoes aggregate and MVE transport in ILVs can occur by endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) dependent machinery or the ESCRT-independent machinery [19]. The ESCRT-dependent mechanism involves four complexes. ESCRT-0 is comprised of two subunits and recruits exosomal cargoes through ubiquitination. ESCRT-I is recruited by ESCRT-0 and then transported to the membrane. ESCRT-I interacts with ESCRT-II to form buds [20,21]. Lastly, ESCRT-III cleaves buds to form ILVs and promote the shedding of MVEs. The polymerized ESCRT-III complex can be dissociated from the MVE membrane by the energy provided by the sorting protein Vps4 [22]. However, several studies have revealed some ESCRT-independent mechanisms for exosomal cargo sorting, indicating that the mechanisms are more extensive and complex.
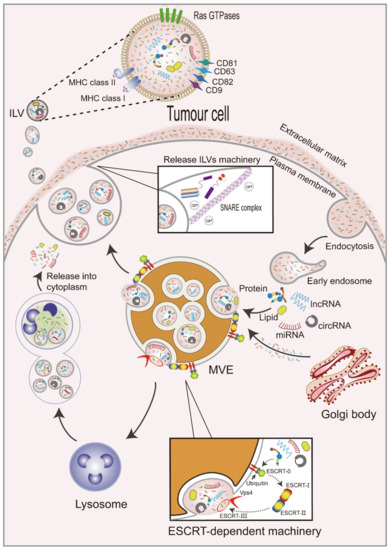
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of exosomes. Extracellular components are internalized along with the plasma membrane to form early endosomes. Exosomal cargoes enter early endosomes to form multivesicular bodies (MVBs) through an ESCRT-dependent mechanism, which is shown in this figure. MVBs bind with lysosomes and release cargoes from vesicles into the cytoplasm, or under the actions of Rab GTPases, SNARE, and calcium (Ca2+), they fuse with the plasma membrane and release ILVs into the extracellular matrix. Exosomal surface proteins include Rab GTPases, tetraspanins, and MHC class I and II molecules.
Subsequently, MVEs can be fused with lysosomes for degradation [23] or plasma membranes for the release of ILVs, which are called exosomes, into the extracellular space to carry out their physiological functions [24]. This process is regulated by Rabs and other Ras GTP enzymes, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins and their regulators [25], and intracellular Ca2+ [26]. Rab GTPases are the largest class of small GTPases involved in the regulation of MVE maturation and targeting to the plasma membrane [27]. For example, Rab27a and Rab27b have been demonstrated to participate in the docking of MVEs to plasma membranes [28], and Rab27a can be inhibited by KIBRA to control exosome release [29]. Rab GTPases are located in exosomal membranes, and tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81, and CD82) [30,31] and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II molecules [32] have also been reported to be enriched, playing important roles in the membranes of exosomes. SNARE proteins promote the membrane fusion of vesicles with plasma membranes or different organelles [33]. Furthermore, increased intracellular Ca2+ levels in human erythrocytic leukemia K562 cells treated with monensin (Na+/H+ exchanger that induces intracellular changes) resulted in increased exosome release [34].
3. Non-Coding RNAs
RNAs are divided into coding RNAs (mRNAs) and non-coding RNAs based on whether they can encode proteins. Studies have shown that mRNAs account for less than 2% of the total genome, and more than 98% are ncRNAs, such as lncRNAs, miRNAs, circRNAs, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) [35], tRNA-derived small RNAs [36], and piwi-interacting RNAs [37,38]. At a time when ncRNAs were poorly understood, they were considered nonfunctional “junk” [39]. However, with further research, ncRNAs have been found to not only regulate basic biological processes, such as growth, development, and organ function, but also appear to play key roles in a wide spectrum of human diseases, especially cancer [40]. Extensive alterations in ncRNA processing factors or ncRNAs themselves can affect multiple aspects of tumorigenesis [41]. Exosomes are intracellular vesicles secreted by most cells, and ncRNAs have been detected in exosomes isolated from the body fluids of cancer patients. For instance, Yu et al. extracted exosomes from serum samples of 79 HCC patients and confirmed that circulating exosomal ncRNAs (miRNA-21 and lncRNA-ATB) were associated with the TNM stage and other prognostic factors. These results suggest that exosomal miRNA-21 and lncRNA-ATB are new prognostic markers and therapeutic targets for HCC [42].
4. Functions of Exosomal miRNAs in HCC
MiRNAs are ncRNAs with a length of 21–22 nucleic acids that regulate gene expression by recognizing homologous sequences and interfering with transcription, translation, or epigenetic processes [43]. Multiple genes in the same cellular signaling pathway can be simultaneously targeted by a certain miRNA [44]. Complex interactions between miRNAs and other RNAs, including mRNA, lncRNA, circRNA and pseudogenes, have been found [45]. RNAs or pseudogenes that communicate with each other can regulate other RNAs’ transcripts through competing the shared miRNAs, known as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) [46]. MiRNA regulates mRNA expression by matching with the 3′-UTR of mRNA [47], and exosomal miRNA also has the conserved function of targeting cancer-related genes’ 3′-UTR [48,49].
The increasing research on exosomal miRNAs secreted by HCC cells suggests that a further understanding of exosomal miRNAs in HCC is of great significance for diagnosis and treatment.
4.1. Exosomal miRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for HCC
HCC shows poor prognosis and high risk of recurrence. Resection, liver transplantation, and chemotherapy are the primary treatment options for HCC, although there is still a lack of reliable biomarkers for the diagnosis of unresectable HCC [50]. Because exosomes can provide the specificity required of liver biopsy samples, as well as the non-invasive nature of peripheral blood samples, exosomal miRNAs have advantages in diagnosis, and they are potential biomarkers for liver disease. Further details are described in Table 1. Notably, the role of exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers cannot be substituted by serum-free miRNAs because exosomal miRNAs are more stable, owing to the encapsulation by lipid bilayers [15]. The expression of exosomal miRNAs is less vulnerable to the interferences from other blood components relative to that of serum-free miRNAs. Furthermore, miRNAs are selectively enriched in exosomes [51].
Despite the above advantages, there is still a long way to go before exosomal miRNAs can be used as biomarkers for clinical application. The isolation and purification of exosomes from blood will be a crucial step [52]. A variety of attempts have been made to separate exosomes with other EVs of a similar size, including supercentrifugation-based separation, density gradient centrifugation, polymer-based precipitation separation, microfiltration and sides-based exclusion separation, etc. The most commonly used method for separating exosomes is supercentrifugation [53]. After ultracentrifugation (100,000× g), relatively pure exosomes can be separated through additional sucrose gradient steps [54]. However, exosomes isolated by this method are still contaminated not only by non-vesicular macromolecules [55], but also the microvesicles and apoptotic bodies with a similar size [56].

Table 1.
Exosomal miRNAs are biomarkers for HCC.
Table 1.
Exosomal miRNAs are biomarkers for HCC.
| MiRNA | Source | Application | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-10b-5P | serum | differential diagnosis of HCC and normal tissues | 0.934 | 90.7 | 75 | [57] |
| miR-466-5p, miR-4746-5p | serum | early diagnosis | 0.947 | 81.8 | 91.7 | [58] |
| miR-638 | serum | predicts the survival rate of HCC patients | - | - | - | [59] |
| miR-320d | serum | differential diagnosis of HCC and normal tissues | 0.8694 | - | - | [60] |
| miR-146a | plasma | identifies patients with HCC and cirrhosis | 0.80 ± 0.4 | 81 ± 13 | 58 ± 22 | [61] |
| miR-122, miR-148a, AFP | serum | differential diagnosis of early HCC and cirrhosis | 0.931 | 86.0 | 87.5 | [62] |
| miR-125b | serum | predicts the recurrence rate of HCC patients | 0.739 | 83.0 | 67.9 | [63] |
| predicts the survival rate of HCC patients | 0.702 | 85.5 | 53.4 |
Several studies have shown that certain differentially expressed exosomal miRNAs secreted by HCC cells can be used as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of HCC. HCC is a highly malignant tumor, and early diagnosis can help patients with treatment and prolong survival. In a report by Hyo et al., exosomal miR-10b-5p (AUC: 0.934, sensitivity: 90.7%; specificity: 75.0%; cutoff value: 1.8-fold) was identified as a potential serum biomarker for the early diagnosis of HCC through the analysis of exosomes extracted from normal liver and HCC cells [57]. Another study identified the combined use of exosomal miR-466-5p and exosomal miR-4746-5p as more accurate serum biomarkers for the early diagnosis of HCC (AUC: 0.947, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.889–0.980, sensitivity: 81.8%, and specificity: 91.7%) [58].
Some exosomal miRNAs can be used as novel serum biomarkers in patients with HCC. Shi et al. reported a decreased level of exosomal miR-638 in serum samples from patients with HCC, and a negative correlation of exosomal miR-638 with tumor size, vascular invasion, and TNM stage. In addition, overexpression of miR-638 significantly inhibited the proliferation of Huh7 and SMCC7721 cells. HCC patients with higher serum exosomal miR-638 levels had longer OS, and low serum exosomal miR-638 levels were identified as an independent adverse prognostic factor for HCC [59]. Similarly, the significantly reduced level of exosomal miR-320d in the sera of HCC patients, as well as the culture media of HCC cell lines, could accurately distinguish HCC patients from healthy controls, and the low expression of exosomal miR-320d indicated the poor prognosis of HCC patients [60]. Furthermore, patients with cirrhosis were at high risk of developing HCC. Thorben et al. determined that exosomal miR-146a expression could separate HCC patients from cirrhosis patients, with an AUC of 0.80 ± 0.14 (sensitivity: 81 ± 13%; specificity: 58 ± 22%). Low expression of exosomal miR-16 was also associated with poor OS in patients with cirrhosis (p = 0.034) [61]. Wang et al. found that the combined use of serum exosomal miR-122, exosomal miR-148a, and AFP, with an AUC of 0.931 (95% CI: 0.857–0.973), could be used to distinguish early-stage HCC from cirrhosis [62].
Some miRNAs can be used as predictors of clinical disease recurrence and survival. Liu et al. found that miR-125b levels in exosomal samples were significantly higher in patients with CHB, cirrhosis, and HCC than in serum samples (p < 0.01, respectively). Moreover, compared with CHB patients (p < 0.01 and p = 0.06) and cirrhosis patients (p < 0.01), miR-125b levels in exosomal and serum samples of HCC patients were decreased. HCC patients with lower levels of exosomal miR-125b had shorter recurrence time (TTR) (p < 0.01) and OS (p < 0.01). Therefore, the levels of exosomal miR-125b can predict the postoperative recurrence and survival of HCC patients [63].
4.2. Effects of Exosomal miRNAs on Tumor Microenvironment, Angiogenesis, Invasion, Proliferation, and Metastasis
HCC cells and tumor growth-related cells release exosomes that not only enhance signaling between the TME and the tumor but also promote angiogenesis, invasion, proliferation, and metastasis (details in Table 2).
The tumor microenvironment consists of fibroblasts, endothelial cells, extracellular matrix (ECM), and other components. Several studies have indicated that abnormalities within the TME are the main cause of tumor progression and metastasis, and exosomal crosstalk between cells of the TME and tumor cells has been reported to be critical [64]. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are important components of the TME, and their interactions with cancer cells play a major role in mediating the formation and activation of CAFs. However, CAFs release a variety of regulatory factors to modulate the biological characteristics of tumor cells and other stromal cells, thereby affecting the occurrence and progression of tumors [65,66]. A recent study indicated that normal HSCs are transformed into CAFs after the action of HCC cell-derived exosomes. For example, HCC cell-derived exosomal miRNA-21 activates the PDK1/AKT signaling pathway in HSCs by downregulating the target PTEN and transforming HSCs into CAFs [67]. In turn, HSC-derived exosomal miRNA-335-5P can be delivered to HCC cells to inhibit tumor growth and invasion, thereby playing an antitumor role [68]. Another study showed that exosomal miR-320a derived from CAFs of HCC patients, combined with its downstream target PBX3, could inhibit the growth and migration of HCC cells [69]. Li et al. confirmed that mast cells (MCs) and tumor cells could interact through exosomal miRNAs. MCs were stimulated by the hepatitis C virus E2 envelope glycoprotein (HCV-E2), which increased exosomal miRNA-490 levels that affected HCC cells, thereby inhibiting the EGFR/AKT/ERK1/2 pathway, and ultimately suppressing tumor metastasis [70]. Wang et al. showed that the treatment or transfection of HCC cells with exosomal miR-125a and exosomal miR-125b from tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) inhibited tumor cell proliferation and stem cell characteristics, which was associated with exosomal miR-125a/b targeting CD90 [71]. Another study reported that miR-146a-5p was regulated by the transcription factor SALL4 during the M2 polarization of macrophages [72]. Immune cells in the TME are also affected by HCC cell-derived exosomes. Researchers have demonstrated that HCC cell-derived exosomal miR-92b could suppress the expression of CD69 and the cytotoxicity of natural killer (NK) cells mediated by CD69, and ultimately lead to immune escape [73]. Similarly, Liu et al. showed that the effects of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress on HCC cells promoted the release of exosomal miR-23a-3p. Exosomal miR-23a-3p could up-regulate the expression of PD-L1 in macrophages by inhibiting PTEN to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, while the elevated level of PD-L1 in macrophages inhibited T-cell function and induced immunosuppression [74].
It is well known that solid tumors require an adequate blood supply to grow [75]. Tumor-induced angiogenesis, vascular invasion, and metastasis in cancer patients are contributing factors to the poor prognosis of patients with malignant tumors [76,77]. Many types of exosomes can affect angiogenesis. For example, Fang et al. reported that the stable expression of exosomal miR-103 in HCC cells weakened the integrity of endothelial junctions by targeting multiple endothelial junction proteins, thereby increasing vascular permeability and promoting tumor metastasis [78]. Recently, a novel biomarker miRNA was identified from a highly metastatic hepatic cell line (HuH-7M), where exosomal miR-638 secreted by HuH-7M cells could promote vascular permeability by inhibiting the endothelial expression of VE-cadherin and ZO-1 [79]. Wang et al. reported that elevated exosomal miR-1290 levels were found in the sera of patients with HCC, and miR-1290 promoted tumor angiogenesis by targeting SMEK1 [80]. In another study, miRNA-210 was delivered to endothelial cells, where it directly inhibited SMAD4 and STAT6 expression to enhance angiogenesis [81], while miRNA-378b promoted angiogenesis and HCC progression by targeting transforming growth factor β receptor III (TGFBR3) [82]. In addition to autonomously secreting miRNAs, HCC cells can also derive related exosomal miRNAs to affect angiogenesis, if they are affected by TAMs. Human liver stem-like cells (HLSCs) can derive a set of specific miRNAs, namely, miR-15a, miR-181b, miR-320c, and miR-874, which can inhibit the angiogenic properties of tumor-derived endothelial cells (TECs) [83]. Under hypoxia, exosomal miR-155 derived from HCC cells can affect angiogenesis [84]. Taken together, exosomal miRNAs can orchestrate various angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors.
Cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis are often the leading causes of cancer-related death. Many studies have reported that the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of HCC cells are closely related to the aberrant expression of miRNAs, such as miR-224, which can reduce the expression of glycine N-methyltransferase and promote tumor cell proliferation and invasion [85]. For example, miR-21 and miR-10b expression can be induced by the acidic environment of HCC to promote the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells [86]. The mechanism by which miR-21 promotes HCC cell growth is that it affects the expression of the tumor suppressor gene phosphatase and tensin homolog pseudogene 1 (PTENp1) and PTEN by regulating the expression of Tet methylcytosine dioxygenases (TETs) [87]. Yu and colleagues reported that patient-derived cell (PDC) cultures of HCC showed both rapid and slow cell migration, and differentially expressed miRNAs were identified in both rapid and slow cell migration groups. Interestingly, the target genes of these miRNAs were significantly enriched in the “focus adhesion” pathway. Further evidence shows that these miRNAs influence tumor metastasis [88].
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process of transformation from epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells. The EMT is closely related to tumor cell migration and invasion [89]. In one study, Lin et al. highlighted that differentially expressed miRNAs appeared in HCC cells after the EMT, compared with HCC cells in which low exosomal miR-374a-5p expression inhibited the proliferation and migration of HCC cells [90]. Another study demonstrated that an elevated exosomal miR-92a-3p level in highly metastatic HCC cells promoted the EMT in receptor cancer cells by targeting PTEN and activating AKT/Snail signaling [91]. In a study by You and colleagues, local hypoxia induced the production of exosomal miR-123f by HCC cells, and miR-123f, in turn, enhanced the proliferation, migration, invasion, and the EMT of HCC cells under low oxygen conditions by targeting LHX6 to inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [92].
The formation of pre-metastatic niches in the TME supports tumor cell growth. Studies have shown that normal fibroblasts are more easily transformed into CAFs by highly metastatic HCC cells. During this process, exosomal miR-1247-3p was secreted by highly metastatic HCC cells to directly target β-1,4-galactosyltransferases III (B4GALT3) and activate β1-integrin-NF-κB signaling in fibroblasts [93].
Autophagy plays a protective role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. The mechanism of autophagy deficiency in HCC was studied through numerous mouse experiments. It was found that defects in autophagy affected the level of associated protein 9b (Atg9b) and caused ubiquitin-mediated protein accumulation, which rendered Atg9b-deficient hepatocytes susceptible to ER stress-induced cell death. Meanwhile, Atg9b-driven phagocytes may promote the docking of LC3 and p62 proteins to initiate autophagy-mediated degradation, while the absence of Atg9b prevents the recruitment of p62-related ubiquitin proteins for autophagosome–lysosomal degradation. Furthermore, tumor-derived exosomal miR-3091-3p was internalized by hepatocytes to inhibit the expression of Atg9b [94]. Thus, exosomal miRNAs are involved in biological events, leading to tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.
4.3. Effects of Exosomal miRNAs on Drug Resistance of HCC
Multiple miRNAs not only serve as biomarkers for the early diagnosis of HCC, but are also involved in drug resistance. Acquired drug resistance to targeted cancer therapy is challenging in that tumor cells initially respond to treatment but subsequently develop acquired drug resistance after long-term treatment [95,96]. Studying the mechanism of drug resistance during the treatment of HCC is helpful to the treatment and prognosis of patients. Currently, the drug therapies for HCC include 5-FU, sorafenib, and cisplatin (DDP). Fu et al. reported that multidrug-resistant cells (Bel/5-FU) activated the PI3K/AKT pathway to regulate angiogenesis and EMT by transferring exosomal miR-32-5p to HCC sensitive cells (Bel7402), thereby inducing the transformation of sensitive cells into drug-resistant cells [97]. In another study, the expression of exosomal miR-744 in the sera of HCC patients was lower than that in the sera of healthy individuals, demonstrating that low levels of miR-744 promoted the resistance of HCC cells to sorafenib and that PAX2 was a direct target of miR-744 [98]. In addition, resistance to DDP was not conducive to the prognosis of patients with HCC, and researchers have demonstrated that DDP resistance can be reversed by exosomal miR-199a-3p, thereby slowing the progression of HCC [99].

Table 2.
Roles of exosomal miRNAs in HCC.
Table 2.
Roles of exosomal miRNAs in HCC.
| MiRNA | Expression | Source | Biological Function | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | - | HCC cell | converts normal HSCs to CAFs | activates PDK1/AKT pathway in HSCs by targeting PTEN | [67] |
| miR-335-5p | - | HSC | inhibits tumor growth and invasion | downregulates the target of miRNA-335 | [68] |
| miR-320a | - | CAF | inhibits growth and migration of HCC cells | targets PBX3 | [69] |
| miR-490 | - | MC | inhibits metastasis of HCC | inhibits EGFR/AKT/ERK1/2 pathway | [70] |
| miR-125a/b | - | TAM | inhibits HCC cell proliferation and stem cell characteristics | targets CD90 | [71] |
| miR-146a-5p | - | M2 polarization of macrophage | promotes M2 polarization of macrophages | is regulated by SRLL4 | [72] |
| miR-92b | ↑ | HCC cell | causes immune escape | inhibits CD69 and NK cytotoxicity | [73] |
| miR-23a-3p | ↑ | HCC cell | induces immunosuppression | inhibits PTEN activation of PI3K-AKT pathway | [74] |
| miR-103 | - | HCC cell | increases permeability of proliferating vessels promotes metastasis | inhibits VE-cadherin expression in endothelial cells | [78] |
| miR-638 | - | HCC cell | promotes vascular permeability | downregulates VE-cadherin and ZO-1 | [79] |
| miR-1290 | ↑ | serum | promotes angiogenesis | acts on the target SMEK1 | [80] |
| miR-210 | ↑ | HCC cell | promotes angiogenesis and progression of HCC | inhibits SNIAD4 and STAT6 expression in endothelial cells | [81] |
| miR-378b | ↑ | HCC cell | promote angiogenesis and progression of HCC | targets TGFBR3 | [82] |
| miR-15a, miR-181b, miR-370c, miR-874 | - | HLSC | inhibits growth of tumor cells | down-regulates FGF1 and PLAU | [83] |
| miR-155 | ↑ a | HCC cell | promotes angiogenesis | - | [84] |
| miR-224 | ↑ | HCC cell | promotes tumor cell invasion and proliferation | decreases glycine N-methyltransferase expression | [85] |
| miR-21, miR-10b | ↑ b | HCC cell | promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of HCC cells | acts on the TETs/PTENp1/PTEN pathway | [86,87] |
| miR-374a-5p | ↑ c | HCC cell | promotes proliferation and migration of HCC cells | regulates GADD45A expression | [90] |
| miR-92a-3p | ↑ d | HCC cell | promotes EMT | targets PTEN; activates the AKT/Snail pathway | [91] |
| miR-1273f | ↑a | HCC cell | enhances proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells, as well as EMT | targets LHX6; inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [92] |
| miR-1247-3p | ↑ d | HCC cell | promotes transfer niche formation | targets B4GALT3 activates β1-integrin-NF-κB pathway in fibroblasts | [93] |
| miR-3091-3p | - | HCC cell | promotes tumor autophagy deficiency | inhibits Atg9b | [94] |
| miR-32-5p | ↑ e | HCC multidrug resistant cell | induces multidrug resistance of HCC cells | activates the PI3K/AKT pathway | [97] |
| miR-744 | ↓ | serum | increases sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib | targets PAX2 | [98] |
| miR-199a-3p | - | HCC cell | reverses the resistance of HCC cells to DPP | - | [99] |
HSC, hepatic stellate cell; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; MC, mast cell; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; SALL4, Sal-like protein-4; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial-cadherin; ZO-1, Zonula occludens-1; TGFBR3, transforming growth factor β receptor III; DPP, cisplatin; HLSC, human liver stem-like cell; a oxygen-deficient environment; b acidic environment; c epithelial–mesenchymal transformation of HCC cells; d highly metastatic HCC cells; e multidrug-resistant HCC cells; ↑, miRNA expression is increased; ↓, miRNA expression is decreased; -, miRNA expression is not described in the original study.
5. Functions of Exosomal LncRNAs in HCC
Currently, lncRNAs are a new class of ncRNAs comprised of more than 200 nucleic acids, which distinguishes them from other functional ncRNAs [100]. However, similar to other ncRNAs, lncRNAs regulate a variety of DNA sequence-specific transcriptional and epigenetic processes, including transcription initiation, splicing, processing, DNA and nucleosome modifications, isolation, and imprinting [101]. Studies indicate that they are regulatory RNAs that can be selectively packaged into exosomes to act as messengers for intercellular communication, thereby modulating tumor growth, metastasis, angiogenesis, and TME remodeling [102].
5.1. Exosomal LncRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for HCC
Numerous studies have shown that exosomal lncRNAs have many advantages as diagnostic biomarkers for HCC (see Table 3 for details), which will be discussed in detail in the following sections.

Table 3.
Exosomal lncRNAs serving as biomarkers for HCC.
Exosomal lncRNAs can be used as serum biomarkers for the early diagnosis of HCC. Researchers have confirmed that lncRNAs derived from small extracellular vesicles (EV-lncRNAs) in serum, such as EV-DLEU2, EV-HOTTIP, EV-MALAT1, and EV-SNHG1, can distinguish HCC patients from non-HCC patients. In addition, they have numerous advantages over AFP in the diagnosis of very early-stage HCC. In very early-stage HCC, the combined use of EV-MALAT1 and EV-SNHG1 provides the optimal biomarker panel [12]. Certain lncRNAs can also distinguish early-stage HCC patients from healthy individuals, as well as those with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis. For example, Sun et al. evaluated exosomal biomarkers in the sera of 15 HCC patients and 15 healthy individuals by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The results showed that the expression level of exosomal LINC00161 in the sera of HCC patients was significantly higher than that in healthy individuals (p = 0.011, fold change: 4.27) and was significantly correlated with serum AFP concentration and TNM stage. Therefore, exosomal LINC00161 may be a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis of HCC [103]. In addition, HCC patients and healthy individuals were distinguished by exosomal lncRNA SENP3-EIF4A1 expression (AUC: 0.8028) [104]. In a study by Xu and colleagues, the expression levels of two exosomal lncRNAs, ENSG00000258332.1 and LINC00635, were significantly higher in the sera of HCC patients than those in healthy individuals and patients with CHB (both p < 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that ENSG00000258332.1 could distinguish HCC patients from CHB patients, and the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.719 (critical value: 1.345), while the AUC of LINC00635 was 0.750 (critical value: 1.690). When the two lncRNAs were combined with serum AFP (critical value: 20 μg/L), the AUC was 0.894, indicating that the combined use of ENSG00000258332.1, LINC00635, and AFP was optimal for the diagnostic and prognostic prediction of HCC patients [105]. Another study demonstrated that exosomal lncRNA-RP11-583F2.2 expression was higher in the sera of patients with HCC than in those with CHC and healthy individuals, and the optimal threshold for distinguishing serum parameters between HCC patients and non-HCC patients was ≥5.02, the sensitivity was 96.7%, and the specificity was 91.7% [106]. Similarly, exosomal lncRNA-HEIH was differentially expressed in CHC patients and hepatitis C virus (HCV)-associated HCC patients [107], and plasma exosomal lncRNA and RP11-85G21.1 (lnc85) were differentially expressed between HCC patients and healthy individuals [108]. Exosomal lncRNAs, as biomarkers, were also associated with the progression of HCC. For example, three differentially expressed lncRNAs, namely, ENSG00000248932.1, ENST00000440688.1, and ENST00000457302.2, were up-regulated in patients with metastatic HCC compared to those with non-metastatic HCC, suggesting that these lncRNAs can be used to monitor HCC metastasis [109]. In addition, Lee et al. reported that the high expression of exosomal lncRNA-ATB was an independent adverse factor for OS and progression-free survival [42].
5.2. Effects of Exosomal LncRNAs on the Tumor Microenvironment, Proliferation, Invasion, Metastasis, and Angiogenesis
Exosomal lncRNAs can not only serve as biomarkers for HCC, but can also remodel the TME, promote angiogenesis, and regulate the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of HCC cells (see Table 4 for details).
Intercellular crosstalk is one of the most important processes affecting tumor progression. It has been reported that cancer stem cell (CSC)-derived exosomes act on liver cancer cells to promote the expression of exosomal lncRNA TUC339, lncHEIH, and lncHOTAIR [110]. CD90+ HCC cells are characterized as invasive and metastatic CSCs. CD90+ HCC cells can release exosomal lncRNA H19, which is transported to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to induce angiogenesis and influence intercellular adhesion, thereby affecting the TME. The mechanism of angiogenesis may be related to the increased mRNA expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGF-R1) by CD90+ HCC cell exosomes [111]. In a study by Li and colleagues, the depletion of YAP1 in endothelial cells resulted in an increase in exosomal MALAT1 released by these cells, which was transferred by exosomes into HCC cells to promote tumor cell invasion and metastasis by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling [112]. Normal cells also secrete exosomes that affect HCC cells. Exosomal SENP3-EIF4A1-derived from normal cells can be transferred to HCC cells and inhibit tumor growth by competitively binding to miR-9-5p [104]. It has been reported that the ultra-conserved lncRNA TUC339 secreted by HCC cells can regulate cell proliferation and adhesion to the ECM [113]. Another study showed that exosomal TUC339 targets adjacent macrophages, modulating their activation and promoting their polarization to the macrophage (IL-4) phenotype, indicating that there is crosstalk between exosomal lncRNAs and tumor and immune cells [114]. Similarly, a study by Fan et al. revealed that exosomal PCED1B-AS1 sponges hsa-miR194-5p to increase the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in recipient tumor cells, thereby inhibiting the expression of related genes in recipient T cells and macrophages and inducing immunosuppression [115]. Low oxygen environments also affect the progression of tumors. For example, researchers confirmed that exosomal linc-RoR is highly expressed, promoting tumor cell survival in hypoxic environments [116].
Presently, several researchers are focusing on the effects of tumor-derived exosomes on tumors. For example, Li et al. showed that exosomal lncRNA FAL1 expression was up-regulated in the sera of HCC patients and that the transfer of lncRNA FAL1 into HCC cells increased cell proliferation and migration [117]. Exosomal lncRNA-FAM138B derived from HCC cells inhibited the development of HCC cells by targeting miR-765 [118]. Secreted by tumor cells, exosomal lnc85 can bind and regulate miR-324-5p to promote the proliferation and migration of HCC cells [108], while exosomal LINC00161 can activate growth and metastasis-related signaling in HCC cells by targeting miR-590-3p and suppressing its downstream target ROCK2 [119]. The expression of lnc-FAM72D-3, as an oncogene, was up-regulated in HCC tissues, which enhanced cell survival and inhibited cell death. As a tumor suppressor gene, lnc-EPC1-4 was downregulated in HCC, which could enhance cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis [11]. Ma and colleagues reported on the mechanism by which insufficient radiofrequency ablation (RFA) causes HCC tumor recurrence and metastasis. The study showed that the expression of exosomal lncRNA ASMTL-AS1 was highly expressed in HCC tissues, and the miR-342-3p/NLK/YAP signaling pathway could promote the malignancy of residual HCC after RFA deficiency [120]. Another study showed that HCC cells treated with propofol, a common intravenous anesthetic, reduced the expression of exosomal H19, which enhanced LIMK1 expression in HCC cells by sponging miR-520a-3p, thereby increasing the malignant potential of propofol-treated HCC cells [121].
5.3. Effects of Exosomal LncRNAs on Drug Resistance of HCC
Several lncRNAs have been found to be involved in the drug resistance of HCC. Linc-VLDLR is an exosomal lncRNA that contributes to chemotherapeutic stress in HCC. HCC cells treated with multiple anti-tumor drugs can release more exosomal linc-VLDLR, and a study has shown that exosomal linc-VLDLR is a new medium for the development of resistance in HCC cells [122]. Researchers found that the highly expressed lncRNA ribonucleic acid-ROR (linc-ROR) in HCC cells was a stress-induced lncRNA that was enriched in exosomes. After HCC cells were incubated with sorafenib, the expression of linc-ROR was increased in HCC cells and released via exosomes, suggesting that EV-linc-ROR regulates the chemical sensitivity of HCC cells [123].

Table 4.
Roles of exosomal lncRNAs in HCC.
Table 4.
Roles of exosomal lncRNAs in HCC.
| LncRNA | Expression | Source | Biological Function | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H19 | - | CD90+ HCC cell | promotes angiogenesis | increases the expression of VEGF and VEGF-R1 | [111] |
| MALAT1 | - | - | promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis | activates the ERK1/2 pathway | [112] |
| SENP3-EIF4A1 | - | normal cell | inhibits tumor growth | competitively binds to miR-9-5p | [104] |
| TUC339 | ↑ | HCC cell | promotes tumor cell proliferation and adhesion to extracellular matrix | siRNA inhibits TUC339 | [113] |
| TUC339 | ↑ | HCC cell | promotes macrophage polarization promotes the expression of M (IL-4) in macrophages | siRNA inhibits TUC339 | [114] |
| PCED1B-AS1 | ↑ | HCC cell | induces immunosuppression | sponges has-miR194-5P; enhances the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 | [115] |
| linc-ROR | ↑ a | HCC cell | promotes the survival of HCC cells | P7OS6K1 phosphorylation (RPS6KB1), PDK1, and HIF-1α expression are decreased, and miR-145 expression is increased | [116] |
| FAL1 | ↑ | serum | increases cell proliferation and migration | competitively binds to miR-1236 | [117] |
| FAM138B | ↓ | HCC cell | inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells | regulates miR-765 | [118] |
| lnc85 | ↑ | plasma | promotes proliferation and migration of HCC cells | binds and regulates miR-324-5p | [108] |
| LINC00161 | ↑ | HCC cell | promotes the occurrence and metastasis of tumors | represses the activation of the ROCK2 pathway initiated by miR-590-3P | [119] |
| Inc-FAM72D-3 | ↑ | HCC tissue | inhibits apoptosis | - | [11] |
| lnc-EPC1-4 | ↓ | HCC tissue | inhibits apoptosis | - | |
| ASMTL-AS1 | ↑ | HCC tissue | exacerbates the malignant behavior of HCC | acts on the miR-342-3P/NLK/YAP signaling pathway | [120] |
| H19 | ↓ b | HCC cell | increases the malignant behavior of HCC cells | acts on the miR-520a-3P/LIMKT signaling pathway | [121] |
| linc-VLDLR | ↑ c | HCC cell | mediates drug resistance of HCC cells | - | [122] |
| linc-ROR | ↑ d | HCC cell | enhances the chemical sensitivity of HCC cells | - | [123] |
a Oxygen-deficient environment; b HCC cells treated with propofol (intravenous anesthetic); c HCC cells treated with a variety of antitumor drugs; d HCC cells treated with sorafenib; ↑, lncRNA expression is increased; ↓, lncRNA expression is decreased; -, lncRNA expression is not described in the original study.
6. Function of Exosomal CircRNAs in HCC
CircRNAs were first identified as viroids in RNA viruses in 1976 and are believed to be caused by endogenous RNA splicing errors [124]. They are a unique class of ncRNAs without 5′-3′ polarity and a circular structure with a polymeric acid tail [125]. It has been reported that circRNAs are enriched in exosomes, where they perform important biological functions by acting as competitive inhibitors of miRNAs to regulate protein translation and/or function [126]. It is worth noting that the high abundance, relative stability, and evolutionary conservation of circRNAs render them as likely candidates to exert biological effects in cancer progression [127,128]. Furthermore, exosomal circRNAs may participate in the pathophysiology of HCC.
6.1. Exosomal CircRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for HCC
A study reported that exosomal circ_0070396 was differentially expressed in HCC patients compared with healthy individuals, suggesting that it can distinguish HCC patients from healthy individuals, as well as those with CHB and cirrhosis [129]. In another study, exosomal circRNAs served as biomarkers for predicting HCC recurrence and prognosis. qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression level of circAKT3 in exosomes in 124 HCC patients and 100 healthy subjects, and the results showed that the expression level of exosomal circAKT3 in HCC patients was significantly higher than that in healthy individuals. In addition, circAKT3 was found to be associated with a higher rate of tumor recurrence in HCC patients (hazard risk (HR): 3.14; 95% CI: 1.29–6.21; p = 0.012) and higher mortality (HR: 1.89; 95% CI: 1.04–3.01; p = 0.048) [130].
6.2. Effects of Exosomal CircRNAs on the Tumor Microenvironment, Proliferation, Invasion, Metastasis, and Angiogenesis
Several exosomal circRNAs have been reported to affect the TME, proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis (see Table 5 for more details).

Table 5.
Roles of exosomal circRNAs in HCC.
A study by Huang et al. found that exosomal circRNA-100,338 was a mediator of signal transduction between HCC cells and endothelial cells. CircRNA-100,338 was overexpressed in the exosomes of highly metastatic HCC cells and could affect HUVEC proliferation, angiogenesis, and tight junctions between HUVECs to promote endothelial cell permeability [131]. Similarly, exosomal circCMTM3 expression was elevated in the sera of HCC patients and HCC cell lines, affecting the activity, migration, and invasion of HUVECs. Overexpression of circCMTM3 promotes angiogenesis by regulating SOX9 through sponging miR-3619-5p [132]. Exosomal circular de-ubiquitination (circ-DB) secreted by adipocytes also acts on HCC cells to promote tumor growth and reduce DNA damage. The mechanism was that the overexpression of exosomal circ-DB downregulates miR-34a, which in turn activates the expression of USP7 and cyclin A2, promotes tumor growth, and facilitates metastasis [133]. Circ-0051443 derived from normal cells was transported to HCC cells by exosomes, where BAK1 expression was upregulated by competitive binding with miR-331-3p, and this mechanism was utilized to promote apoptosis and halt the cell cycle [134]. Hsa_circ_0074854, which was upregulated in several HCC cell lines, was transferred to macrophages via exosomes, where it interacted with human antigen R (HuR) and promoted macrophage M2 polarization to enhance HCC invasion and migration [135]. In turn, normal liver cells were affected by exosomal circ_MMP2 of metastatic HCC cells, which formed a malignant phenotype and promoted HCC metastasis [136]. In addition, NK cells in the TME were also affected by exosomal circUHRF1. The secretion of circUHRF1 from HCC cells was transmitted to NK cells through exosomes, which reduced the secretion of IFN-γ and TNF-α by NK cells to promote immunosuppression [137].
Su et al. revealed that circRNA Cdr1as derived from HCC cells was mainly located in exosomes and directly bound to miR-1270, which upregulated AFP expression and stimulated the proliferation and migration of HCC cells. At the same time, circRNA Cdr1as stimulated the malignant behavior of surrounding normal cells through exosomes, contributing to the progression of HCC [138]. Similar studies have shown that in HCC, exosomal circPTGR1 secreted by cells with high metastatic potential could enhance the migration and invasion of these cells by interacting with miR449A-MET in weakly metastatic and non-metastatic cells [139]. Exosomal circTMEM45A was enriched in the sera of HCC patients, where it promoted tumor progression. CircTMEM45A acts as a sponge for miR-665 and modulates the direct interaction of miR-665 with insulin growth factor 2 (IGF2) [140]. In addition, circ_0061395 promotes the malignant behavior in HCC cells by regulating the miR-877-5p/PIK3R3 axis [141]. Lai et al. demonstrated that miR-338 inhibited HCC progression and glycolysis by targeting LRP6, and exosomal circFBLIM1 acted as a sponge for miR-338 to promote HCC progression [142]. Exosomal circ-ZNF652 was transferred to HCC cells, where it promoted cell proliferation, migration, and glycolysis. The binding of miR-29a-3p by circ-ZNF652 reduces the effect of GUCD1 on tumors [143].
6.3. Effects of Exosomal CircRNAs on Drug Resistance of HCC
Recent studies have shown that several circRNAs participate in the drug resistance of HCC patients. Xu et al. reported that the overexpression of circRNA-SORE was detected in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells and demonstrated the use of exosomes in the transmission of sorafenib resistance between HCC cells. Exosomal circRNA-SORE, upon transfer to HCC cells, can bind to YBX1 in the cytoplasm, block pre-mRNA processing factor 19 (PRP19)-mediated degradation to stabilize YBX1, and affect the expression of the downstream gene targets of YBX1 to transmit sorafenib resistance [144]. In addition, exosomal circ-G004213 promotes cisplatin sensitivity and improves cell survival. Circ-G004213 is a sponge of miR-513b-5p and regulates DDP sensitivity by modulating the interaction between miR-513b-5p and its downstream target gene PRPF39 [145].
Except for the exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs, some other ncRNAs, including tRNA-derived small RNAs [36] and piwi-interacting RNAs [37,38], also participate in tumorigenesis. Due to the lack of adequate literature, we do not make too much of an elaboration here.
Generally, this review not only lists the roles of exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs as biomarkers for HCC, but also illustrates the crosstalk between exosomal ncRNAs and TME as well as other cells in the process of tumor occurrence and development (Figure 2).
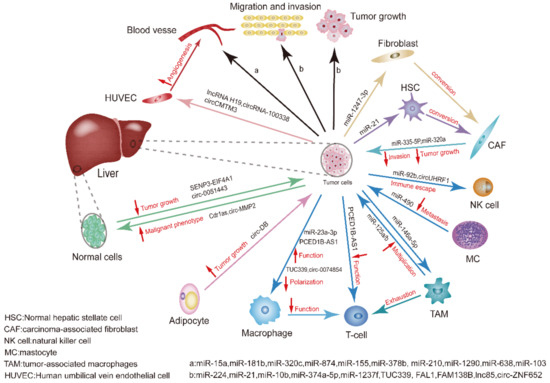
Figure 2.
Summary of non-coding RNAs affecting HCC development. Exosomal ncRNAs mediate crosstalk between tumor cells and cells in the TME, where different types of cells interact with cancer cells, including infiltrating immune cells, CAFs, normal hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), adipocytes, and thin blood vessels that make up tumors. The complex multidirectional communication between these cells and tumor cells through exosomal ncRNAs promotes tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. The blue arrows indicate that the exosomal ncRNAs are originated from immune cells or acting on immune cells. The red up arrows show the function of promoting the corresponding exosomal ncRNAs, and red down arrows represent the function of inhibiting the corresponding exosomal ncRNAs. For example, adipocyte-stemmed circ-DB can facilitate tumor growth.
Since there is no standardized evaluation system, we may obtain more reliable biomarkers to distinguish HCC from normal individuals by comparing the AUC of diagnostic models constructed from exosomal ncRNAs (Table 6). As shown, using combination of miR-466-5p and miR-4746-5p reached the highest AUC value of 0.947, which suggested the great possibility and reliability of these two exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers. However, it is crucial to note that such a comparison might be invalid when testing is not conducted on the same cohort. In addition, the standardized extraction of exosomal ncRNAs is the cornerstone of comparing the results of different studies.

Table 6.
The AUC of exosomal ncRNAs for the diagnosis of HCC.
7. Conclusions
Exosomes are important tools for intercellular communication, and ncRNAs are transported between different tumor cells through exosomes. In recent years, scientific evidence has shown that miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in HCC cell-derived exosomes have become novel biomarkers due to their high sensitivity, specificity and non-invasive detection, but there are still several factors to be considered. For example, how do researchers identify the best biomarkers, compare the results from different laboratories, and decide whether these biomarkers can be used to guide clinical treatment? Oncogenesis is a highly complicated process, and HCC progression depends not only on tumor cell-derived exosomes, but also on the influence of various cell-derived exosomes in the TME. Similarly, the drug resistance of tumor cells is also affected by exosomal ncRNAs, and studies on drug resistance mechanisms in HCC may improve the therapeutic benefits.
Although there is a myriad of research on exosomes, this field is still in its infancy, thus some further steps are needed to translate the existing findings into clinics: first, to break through the bottleneck of the extraction and purification method for exosome ncRNAs, namely, to ensure the corresponding biomarkers are from exosomes but not other EVs; second, to standardize the evaluation system of exosomal ncRNA biomarkers; third, more extensive clinical samples are required to validate the effectiveness of exosomal biomarkers; and the fourth, targeting the delivering of exosomes may be promising for drug delivery. In a word, the comprehensive understanding of exosomal ncRNAs will foster the early diagnosis, surveillance of recurrence, and prognosis prediction of HCC, as well as the improvement and optimization of clinical treatment.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft and visualization: Q.Z.; Data curation and investigation: H.L., Y.L. and J.L.; Writing—review and editing: C.W.; Conceptualization, funding acquisition and writing—review and editing: H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62172343).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lötvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Sanwlani, R.; Van Deun, J.; Hendrix, A.; Mathivanan, S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, C.; Bi, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Comprehensive landscape of extracellular vesicle-derived RNAs in cancer initiation, progression, metastasis and cancer immunology. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicles in cancer—Implications for future improvements in cancer care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.J.; von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Sarcognato, S.; Villanueva, A. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Jia, C.; Tai, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Deng, M.; Zhang, Q. Serum exosomal long noncoding RNAs lnc-FAM72D-3 and lnc-EPC1-4 as diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 11843–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Baek, G.O.; Son, J.A.; Ahn, H.R.; Yoon, M.K.; Cho, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Nam, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y.; Eun, J.W. Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma via liquid biopsy: Panel of small extracellular vesicle-derived long noncoding RNAs identified as markers. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2715–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumperman, J.; Raposo, G. The complex ultrastructure of the endolysosomal system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catoni, C.; Di Paolo, V.; Rossi, E.; Quintieri, L.; Zamarchi, R. Cell-Secreted Vesicles: Novel Opportunities in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring and Treatment. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H. ESCRT complexes and the biogenesis of multivesicular bodies. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larios, J.; Mercier, V.; Roux, A.; Gruenberg, J. ALIX- and ESCRT-III-dependent sorting of tetraspanins to exosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201904113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fader, C.M.; Colombo, M.I. Autophagy and multivesicular bodies: Two closely related partners. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bebelman, M.P.; Smit, M.J.; Pegtel, D.M.; Baglio, S.R. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.R. Unsolved mysteries in membrane traffic. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, W.C.; Chapman, E.R. Role of synaptotagmin in Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, M.; Carmo, N.B.; Krumeich, S.; Fanget, I.; Raposo, G.; Savina, A.; Moita, C.F.; Schauer, K.; Hume, A.N.; Freitas, R.P.; et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, L.; Tang, S.; Han, X.; Jiang, Z.; Dong, L.; Liu, C.; Liang, X.; Dong, J.; Qiu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. KIBRA controls exosome secretion via inhibiting the proteasomal degradation of Rab27a. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escola, J.M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Stoorvogel, W.; Griffith, J.M.; Yoshie, O.; Geuze, H.J. Selective enrichment of tetraspan proteins on the internal vesicles of multivesicular endosomes and on exosomes secreted by human B-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20121–20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.L.; Liu, D.; Masuya, D.; Kameyama, K.; Nakashima, T.; Yokomise, H.; Ueno, M.; Miyake, M. MRP-1/CD9 gene transduction downregulates Wnt signal pathways. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7475–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifacino, J.S.; Glick, B.S. The mechanisms of vesicle budding and fusion. Cell 2004, 116, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savina, A.; Furlán, M.; Vidal, M.; Colombo, M.I. Exosome release is regulated by a calcium-dependent mechanism in K562 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20083–20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tan, S.; Sun, D.; Xu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; et al. Exosomal tRNA-derived small RNA as a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Qi, Q.; Wu, Y.; Dong, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, F. PIWI-Interacting RNAs (piRNAs): Promising Applications as Emerging Biomarkers for Digestive System Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 848105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, I.; Pérez-Moreno, P.; Letelier, P.; Brebi, P.; Roa, J.C. The Emerging Role of PIWI-Interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in Gastrointestinal Cancers: An Updated Perspective. Cancers 2021, 14, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, P.E.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Song, E.W. Non-coding RNAs: The new central dogma of cancer biology. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 22–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, G.J.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Kim, G.; Tak, W.Y.; Jang, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Park, J.G.; Lee, H.W.; Han, Y.S.; Chun, J.M.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Circulating exosomal noncoding RNAs as prognostic biomarkers in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Heikkinen, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wong, G. Trends in the development of miRNA bioinformatics tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.T.; Busacca, S.; Almeida, G.M.; Gaudino, G.; Fennell, D.A.; Vasconcelos, M.H. MicroRNA regulation of core apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Guan, B.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lin, F.; Sun, W.; Zhu, W.; Fang, D.; Luo, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L. Exosome-transmitted miRNA-335-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by facilitating EMT via targeting RASA1. Mol. Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, N.; Zeng, X.; Han, Q.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. Hepatocellular carcinoma in a large medical center of China over a 10-year period: Evolving therapeutic option and improving survival. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4440–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.X.; Fan, X.; Drummond, C.A.; Majumder, R.; Xie, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, L.; Haller, S.T.; Brewster, P.S.; Dworkin, L.D.; et al. MicroRNA profiling in kidney disease: Plasma versus plasma-derived exosomes. Gene 2017, 627, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Larcher, L.M.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation—Efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrie, A.; Colombo, M.; Krumeich, S.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Diverse subpopulations of vesicles secreted by different intracellular mechanisms are present in exosome preparations obtained by differential ultracentrifugation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, J.; Clayton, A. How pure are your vesicles? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 19861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.E.; Korbie, D.; Trau, M.; Hill, M.M. Purification Protocols for Extracellular Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Eun, J.W.; Baek, G.O.; Seo, C.W.; Ahn, H.R.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.W.; Cheong, J.Y. Serum Exosomal MicroRNA, miR-10b-5p, as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Baek, G.O.; Seo, C.W.; Ahn, H.R.; Sung, S.; Son, J.A.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.W.; Jang, J.W.; Nam, S.W.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-4661-5p-based serum panel as a potential diagnostic biomarker for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5459–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.G.; Lu, X.J. Decreased levels of serum exosomal miR-638 predict poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4711–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ding, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Yin, T.; Han, S.; Geng, J.; Sun, W. Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-320d predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fründt, T.; Krause, L.; Hussey, E.; Steinbach, B.; Köhler, D.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Lohse, A.W.; Wege, H.; Schwarzenbach, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of miR-16, miR-146a, miR-192 and miR-221 in Exosomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Cirrhosis Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P.; Guo, G.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Huang, X.; Tong, H.; Tian, Y. Serum exosomal microRNAs combined with alpha-fetoprotein as diagnostic markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Liao, B.; Dai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3843–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Song, E. Turning foes to friends: Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Piontek, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Selaru, F.M. Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Yue, S.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Pu, M.; et al. Loss of exosomal miR-320a from cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to HCC proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhen, S.; Yu, Q.; Gong, Z. HCV-E2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by stimulating mast cells to secrete exosomal shuttle microRNAs. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q. miR-125a/b inhibits tumor-associated macrophages mediated in cancer stem cells of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CD90. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Han, Q.; Xu, D.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. SALL4-mediated upregulation of exosomal miR-146a-5p drives T-cell exhaustion by M2 tumor-associated macrophages in HCC. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1601479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Chen, I.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, P.J.; Tseng, H.P.; Huang, K.T.; Hu, T.H.; Li, L.C.; Goto, S.; Cheng, Y.F.; et al. Circulating exosomal miR-92b: Its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2019, 19, 3250–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Causes Liver Cancer Cells to Release Exosomal miR-23a-3p and Up-regulate Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Macrophages. Hepatology 2019, 70, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.A.; Singal, A.G.; Marrero, J.A.; Zhu, H.; Yopp, A.C. Vascular Invasion and Metastasis is Predictive of Outcome in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2017, 15, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Shan, B.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C. Vasculogenic mimicry in carcinogenesis and clinical applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, L.R.; Luo, Y.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, Y.; Noda, T.; Okumura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwagami, Y.; Yamada, D.; Tomimaru, Y.; Akita, H.; Gotoh, K.; Takeda, Y.; et al. Serum exosomal miR-638 is a prognostic marker of HCC via downregulation of VE-cadherin and ZO-1 of endothelial cells. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Niu, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; et al. Exosomal MiR-1290 Promotes Angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Targeting SMEK1. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 6617700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.J.; Fang, J.H.; Yang, X.J.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, S.M. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell-Secreted Exosomal MicroRNA-210 Promotes Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Huang, L.; Liang, J.; Ye, Y.; He, S.; Niu, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma cells-derived exosomal microRNA-378b enhances hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, T.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tapparo, M.; Brossa, A.; Fallo, S.; Pitino, A.; Herrera-Sanchez, M.B.; Kholia, S.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, Y.; Wada, H.; Eguchi, H.; Gotoh, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Kubo, M.; Hayashi, K.; Iwagami, Y.; Yamada, D.; et al. Exosomal miR-155 Derived from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Under Hypoxia Promotes Angiogenesis in Endothelial Cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, H.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; He, J.C.; Zhou, Y.; Cang, S.D. Mechanism of exosomal microRNA-224 in development of hepatocellular carcinoma and its diagnostic and prognostic value. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Jin, X.H.; Li, M.; Wang, F.W.; Huang, W.J.; Yun, J.P.; Xu, R.H.; Cai, Q.Q.; Xie, D. Acidic Microenvironment Up-Regulates Exosomal miR-21 and miR-10b in Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Promote Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Q.; Yang, X.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, D.W.; Jiang, X.F.; Xue, P. Exosomal miR-21 regulates the TETs/PTENp1/PTEN pathway to promote hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.X.; Zhang, B.L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.C.; Lei, G.L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, C.H.; Xu, J.J.; Qin, H.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer cell migration and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patient-derived cell models. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Zhou, C.R.; Bai, M.J.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, H.F.; Li, M.A.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.R.; Huang, M.S. Exosome-mediated miRNA delivery promotes liver cancer EMT and metastasis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Tong, R.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. High-metastatic cancer cells derived exosomal miR92a-3p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of low-metastatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6529–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Min, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Linhong, M.; Tao, R.; Yan, L.; Song, H. Hypoxia-induced exosomes promote hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis via miR-1273f transfer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 385, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Atg9b Deficiency Suppresses Autophagy and Potentiates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Hepatocyte Apoptosis in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2325–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, N.; Bivona, T.G. Polytherapy and Targeted Cancer Drug Resistance. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanos, H.F.; Hata, A.N. Emerging Insights into Targeted Therapy-Tolerant Persister Cells in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Qiu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, G.; Li, X. Exosomal MiR-744 Inhibits Proliferation and Sorafenib Chemoresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PAX2. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 7209–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shao, C.X.; Zhu, J.D.; Lv, X.L.; Tu, C.Y.; Jiang, C.; Shang, M.J. Exosomes function as nanoparticles to transfer miR-199a-3p to reverse chemoresistance to cisplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20194026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jandura, A.; Krause, H.M. The New RNA World: Growing Evidence for Long Noncoding RNA Functionality. Trends Genet. TIG 2017, 33, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, K.; Chang, Y.; et al. Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Bai, T.; Dong, L.; Wei, C.; et al. Serum and exosome long non coding RNAs as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, T.; Luo, Z.; Li, W.; Xu, G.; Liu, J.; Wei, W.; Deng, Y. Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA SENP3-EIF4A1 suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 11550–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, X. Serum Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs ENSG00000258332.1 and LINC00635 for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. A Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2018, 27, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matboli, M.; Labib, M.E.; Nasser, H.E.; El-Tawdi, A.H.F.; Habib, E.K.; Ali-Labib, R. Exosomal miR-1298 and lncRNA-RP11-583F2.2 Expression in Hepato-cellular Carcinoma. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Qi, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wei, Q.; Han, S. lncRNA-HEIH in serum and exosomes as a potential biomarker in the HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2018, 21, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sun, L.; Wen, S.; Deng, D.; Wan, F.; He, X.; Tian, L.; Liang, L.; Wei, C.; Gao, K.; et al. RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3338–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Qu, Z.; Wu, B.; Liu, W.; Shi, L.; Wu, D.; et al. Circulating exosome-derived bona fide long non-coding RNAs predicting the occurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.A.; El-Magd, M.A.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Saleh, A.A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; El-Shetry, E.S.; Badawy, A.A.; Alkarim, S. Potential Effect of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells and MSCs on Progression of DEN-Induced HCC in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 8058979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; et al. YAP1 Inhibition in HUVECs Is Associated with Released Exosomes and Increased Hepatocarcinoma Invasion and Metastasis. Mol. Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Yan, I.K.; Lin, W.L.; Patel, T. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUC339: A Mechanism of Intercellular Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, N. Regulation of Macrophage Activation and Polarization by HCC-Derived Exosomal lncRNA TUC339. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, F.; Chen, K.; Lu, X.; Li, A.; Liu, C.; Wu, B. Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1 via sponging hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Modulation of hypoxia-signaling pathways by extracellular linc-RoR. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Mao, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z. LncRNA FAL1 promotes cell proliferation and migration by acting as a CeRNA of miR-1236 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 2018, 197, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Yi, T.; Pu, J.; Cen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, S.; Wei, C.; Chen, P.; Wang, W.; Bao, C.; et al. Exosomal linc-FAM138B from cancer cells alleviates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulating miR-765. Aging 2020, 12, 26236–26247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.N.; Tai, Q.W.; Xu, L.; Hao, Y.; Guo, W.J.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.K. Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis via regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Ju, H.; Zhang, N. Exosome-transferred long non-coding RNA ASMTL-AS1 contributes to malignant phenotypes in residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xing, N.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; He, J.; Ai, Y.; Yang, J. Exosomal lncRNA H19 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with Propofol via miR-520a-3p/LIMK1 axis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7218–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Kogure, T.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of long non-coding RNA ROR modulates chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Wood, J.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Involvement of extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) in tumor cell responses to chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2014, 12, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, N.; Wang, T.; Xu, T.; Shu, Y. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: A review. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, L.; Yang, W.; Yao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Jin, A.; Liu, T.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; et al. The diagnostic value of plasma exosomal hsa_circ_0070396 for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark. Med. 2021, 15, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Gui, R. High expression of circulating exosomal circAKT3 is associated with higher recurrence in HCC patients undergoing surgical treatment. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 33, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Huang, Z.L.; Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Huang, X.Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Z.Y. Exosomal circRNA-100338 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via enhancing invasiveness and angiogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2020, 39, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Li, N.F.; Li, J.R.; Chen, Z.G.; Wang, J.H.; Sheng, L.Q. Exosome circCMTM3 promotes angiogenesis and tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-3619-5p/SOX9. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2021, 51, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Ge, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhu, K.; Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Ning, T.; Tian, F.; et al. Exosome circRNA secreted from adipocytes promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting deubiquitination-related USP7. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2844–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Quan, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Ye, Y. Exosome-transmitted circular RNA hsa_circ_0051443 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2020, 475, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Li, S.; Tong, Q.; Li, S. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0074854 Suppresses the Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Interacting with HuR and via Suppressing Exosomes-Mediated Macrophage M2 Polarization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kang, H.; Gao, M.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Xiao, L. Exosome-transmitted circ_MMP2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by upregulating MMP2. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.F.; Gao, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Lu, J.C.; Guo, X.J.; Shi, G.M.; Cai, J.B.; Ke, A.W. Cancer cell-derived exosomal circUHRF1 induces natural killer cell exhaustion and may cause resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Lv, X.; Yin, W.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Qi, F. CircRNA Cdr1as functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Aging 2019, 11, 8183–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Zou, Y.; Wang, G.; Deng, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Three isoforms of exosomal circPTGR1 promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via the miR449a-MET pathway. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Jing, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Circular RNA circTMEM45A Acts as the Sponge of MicroRNA-665 to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Mol. Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Bian, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0061395 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of the miR-877-5p/PIK3R3 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Wei, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Exosomal circFBLIM1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Glycolysis by Regulating the miR-338/LRP6 Axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zang, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G. Exosomal Circ-ZNF652 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via miR-29a-3p/GUCD1 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7739–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ji, L.; Liang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Song, X.; Gorshkov, K.; Sun, Q.; Lin, H.; Zheng, X.; et al. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Zhan, Z.; Wei, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. Hsa-circRNA-G004213 promotes cisplatin sensitivity by regulating miR-513b-5p/PRPF39 in liver cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).