Better Prognosis of Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Than Gastric Adenocarcinoma among Whites in the United States: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis Based on SEER
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SEER Database and Patients Selection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
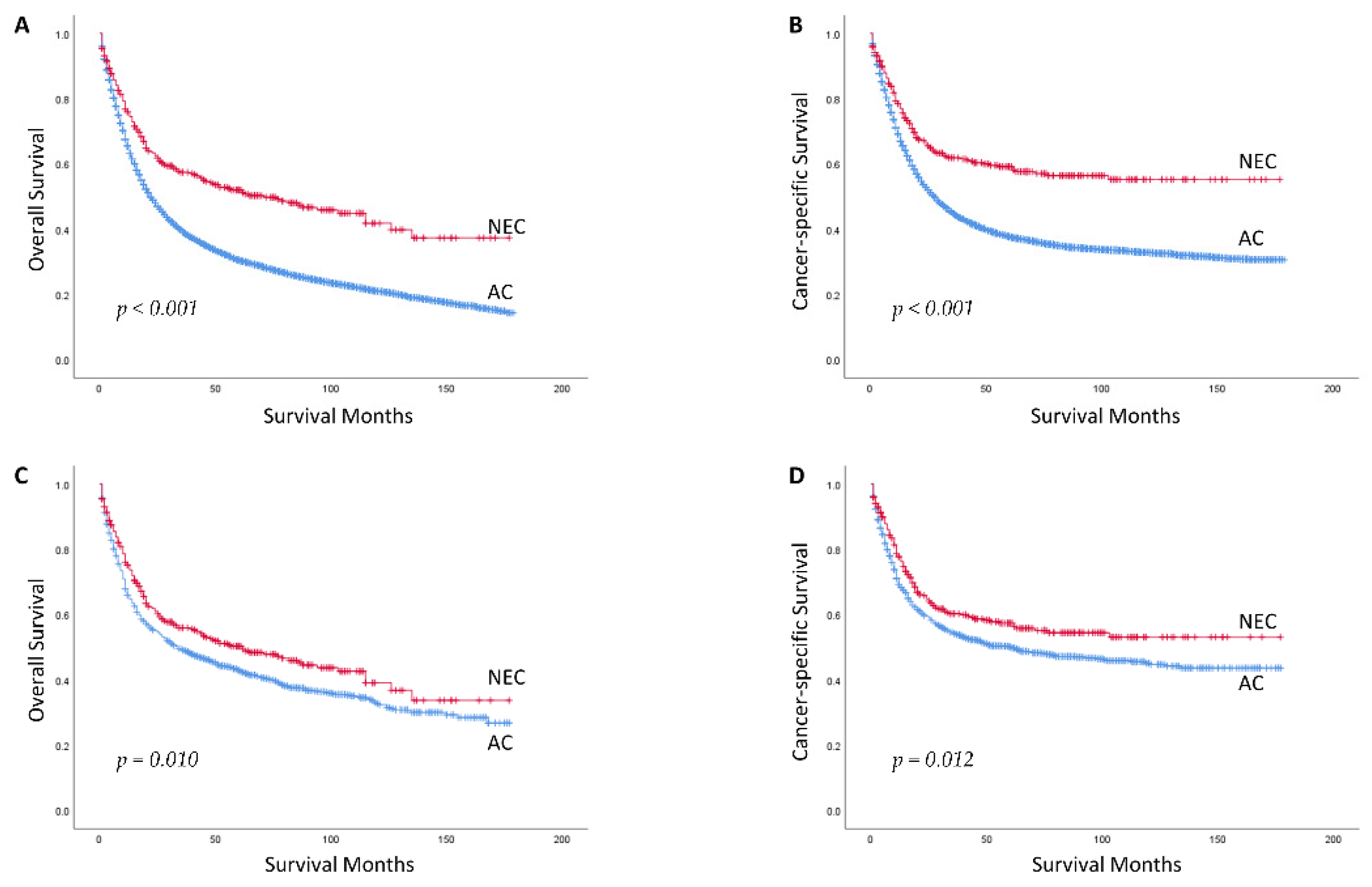
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Survival Outcomes between GNEC and GAC in Whites before PSM
3.2. Baseline Characteristics and Survival Outcomes between GNEC and GAC in Whites after PSM
3.3. Subgroup Analysis According to Stage in Whites
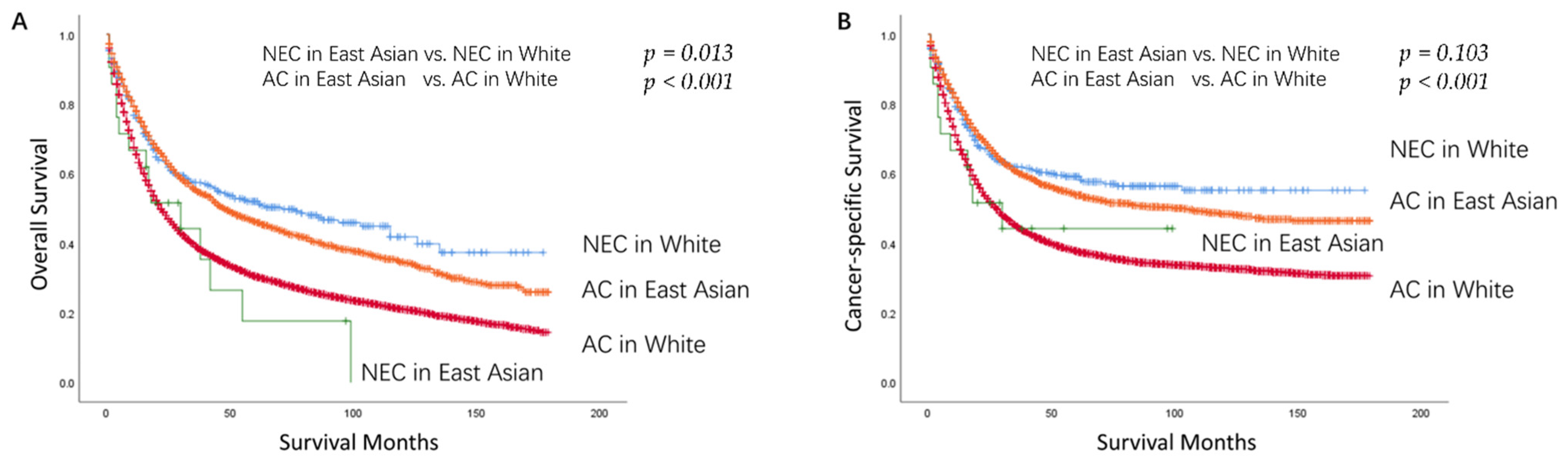
3.4. Baseline Characteristics and Survival Outcomes between GNEC and GAC in East Asians
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarajah, U.; Fernando, A.; Samarasekera, D.N.; Seneviratne, S. The incidence and patterns of gastric cancers in Sri Lanka from 2001 to 2012: Analysis of National Cancer Registry Data. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Bai, J.; Liu, M.; Xue, J.; Chen, T.; Li, R.; Kuai, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. Trends of incidence and prognosis of gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms: A study based on seer and our multicenter research. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felder, S.; Jann, H.; Arsenic, R.; Denecke, T.; Prasad, V.; Knappe-Drzikova, B.; Maasberg, S.; Wiedenmann, B.; Pavel, M.; Pascher, A.; et al. Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasias: Manifestations and comparative outcomes. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.; He, Q.; Tian, Y.; Hao, H.; Qiu, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, G.; Huang, C.M.; et al. Modified staging system for gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma based on american joint committee on cancer and european neuroendocrine tumor society systems. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Goldner, W.S.; Benson, A.B.; Bergsland, E.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Brock, P.; Chan, J.; Das, S.; Dickson, P.V.; Fanta, P.; et al. Neuroendocrine and Adrenal Tumors, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 839–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Ji, K.; Bu, Z.; Ji, J. Comparison of overall survival of gastric neoplasms containing neuroendocrine carcinoma components with gastric adenocarcinoma: A propensity score matching study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.W.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.B.; Lin, J.X.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, M.; Tu, R.H.; Huang, Z.N.; Lin, J.L.; et al. Prognostic factors for survival after curative resection of gastric mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma: A series of 80 patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; Zeng, S.; Wang, P.; Li, G.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Prognostic threshold of neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric carcinoma: A clinicopathological study of 945 cases. J. Gastric Cancer 2019, 19, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Kuo, Y.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Tzeng, C.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, P.M.; Chen, M.H.; Jeng, Y.M.; Chao, Y. High neuroendocrine component is a factor for poor prognosis in gastrointestinal high-grade malignant mixed adenoneuroendocrine neoplasms. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.S.; Park, Y.S.; Yook, J.H.; Kim, B.S. Comparison of relapse-free survival in gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma (WHO grade 3) and gastric carcinoma. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, T.; Ohyama, S.; Hiki, N.; Nunobe, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamaguchi, T. Endocrine carcinoma of the stomach: Clinicopathological analysis of 27 surgically treated cases in a single institute. Gastric Cancer 2012, 15, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Ryu, M.H.; Park, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Kim, M.G.; Yook, J.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, Y.K. Prognostic significance of neuroendocrine components in gastric carcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Sekine, S.; Fukagawa, T.; Ohashi, M.; Morita, S.; Taniguchi, H.; Katai, H.; Tsuda, H.; Kushima, R. Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the stomach: Morphologic and immunohistochemical characteristics and prognosis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.X.; Mikami, T.; Umezawa, A.; Saegusa, M.; Kameya, T.; Okayasu, I. Gastric large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: A distinct clinicopathologic entity. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, Q.; Lin, J.; Hao, H.; Zou, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, G.; et al. Comparison of survival and patterns of recurrence in gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma, mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2114180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Shi, S.S.; Wang, N.C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.T.; Zhao, D.B. The significant influence of the neuroendocrine component on the survival of patients with gastric carcinoma characterized by coexisting exocrine and neuroendocrine components. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 3671268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ishizu, K.; Kamiya, A.; Wada, T.; Hayashi, T.; Otsuki, S.; Katai, H. Is lymph node dissection for neuroendocrine carcinoma of the stomach effective as it is for adenocarcinoma? Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhome, R.M.; Ru, M.; Moshier, E.; Mazumdar, M.; Buckstein, M.H. Stage-matched survival differences by ethnicity among gastric cancer patients of Asian ancestry treated in the United States. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 119, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival Outcomes in Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, F.H.; Tuan, B.; Swenson, S.L.; Wong, R.J. Ethnic disparities in gastric cancer incidence and survival in the USA: An updated analysis of 1992-2009 SEER data. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 3027–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Song, Q. The clinicopathological features and overall survival of patients with gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211055340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Sun, C.L.; Mailey, B.; Prendergast, C.; Artinyan, A.; Bhatia, S.; Pigazzi, A.; Ellenhorn, J.D. Race and ethnicity correlate with survival in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapheke, A.K.; Carvajal-Carmona, L.G.; Cress, R.D. Racial/ethnic differences in survival among gastric cancer patients in california. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Pinheiro, P.S.; Callahan, K.E.; Altekruse, S.F. Examining the gastric cancer survival gap between Asians and whites in the United States. Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| No. (%) | No. (%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEC (392) | AC (12,835) | ||
| Characteristic | |||
| Age, median (IQR) | 63.50 (51–71.75) | 68 (59–77) | <0.001 |
| Sex | <0.001 | ||
| Men | 203 (51.8) | 9052 (70.5) | |
| Women | 189 (48.2) | 3783 (29.5) | |
| Tumor location | <0.001 | ||
| Proximal | 123 (31.4) | 6802 (53.0) | |
| Middle | 138 (35.2) | 2459 (19.2) | |
| Distal | 52 (13.3) | 2141 (16.7) | |
| Mix | 18 (4.6) | 722 (5.6) | |
| Unknown | 61 (15.5) | 711 (5.5) | |
| Tumor size, median (IQR), cm | 2.5 (1–5.5) | 4.0 (2.5–6.0) | <0.001 |
| T stage | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 147 (37.5) | 3392 (26.4) | |
| 2 | 96 (24.5) | 1626 (12.7) | |
| 3 | 82 (20.9) | 4858 (37.8) | |
| 4a | 32 (8.2) | 1823 (14.2) | |
| 4b | 35 (8.9) | 1136 (8.9) | |
| N stage | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 239 (61.0) | 5281 (41.1) | |
| 1 | 105 (26.8) | 4028 (31.4) | |
| 2 | 28 (7.1) | 1908 (14.9) | |
| 3a | 16 (4.1) | 1250 (9.7) | |
| 3b | 4 (1.0) | 368 (2.9) | |
| M stage | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 291 (74.2) | 10,377 (80.8) | |
| 1 | 101 (25.8) | 2458 (19.2) | |
| TNM stage | <0.001 | ||
| I | 183 (46.7) | 3398 (26.5) | |
| II | 68 (17.3) | 3540 (27.6) | |
| III | 40 (10.2) | 3439 (26.8) | |
| IV | 101 (25.8) | 2458 (19.1) | |
| Surgery | 0.364 | ||
| No | 118 (30.1) | 3595 (28.0) | |
| Yes | 274 (69.9) | 9240 (72.0) | |
| Receiving chemotherapy or/and radiotherapy | <0.001 | ||
| No | 268 (68.4) | 5097 (39.7) | |
| Yes | 124 (31.6) | 7738 (60.3) | |
| No. (%) | No. (%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEC (371) | AC (1059) | ||
| Characteristic | |||
| Age, median (IQR) | 65 (54–72) | 66 (55–73) | 0.182 |
| Sex | 0.429 | ||
| Men | 200 (53.9) | 596 (56.3) | |
| Women | 171 (46.1) | 463 (43.7) | |
| Tumor location | <0.001 | ||
| Proximal | 116 (31.3) | 574 (54.2) | |
| Middle | 129 (34.8) | 206 (19.5) | |
| Distal | 50 (13.5) | 175 (16.5) | |
| Mix | 18 (4.9) | 45 (4.2) | |
| Unknown | 58 (15.6) | 59 (5.6) | |
| Tumor size, median (IQR), cm | 2.5 (1–6.0) | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) | 0.012 |
| T stage | <0.001 | ||
| 1 | 133 (35.8) | 517 (48.8) | |
| 2 | 92 (24.8) | 109 (10.3) | |
| 3 | 80 (21.6) | 255 (24.1) | |
| 4a | 31 (8.4) | 104 (9.8) | |
| 4b | 35 (9.4) | 74 (7.0) | |
| N stage | 0.207 | ||
| 0 | 220 (59.3) | 626 (59.1) | |
| 1 | 103 (27.8) | 248 (23.4) | |
| 2 | 28 (7.5) | 112 (10.6) | |
| 3a | 16 (4.3) | 62 (5.9) | |
| 3b | 4 (1.1) | 11 (1.0) | |
| M stage | 0.405 | ||
| 0 | 271 (73.0) | 798 (75.4) | |
| 1 | 100 (27.0) | 261 (24.6) | |
| TNM stage | 0.422 | ||
| I | 165 (44.5) | 470 (44.4) | |
| II | 66 (17.8) | 180 (17.0) | |
| III | 40 (10.8) | 148 (14.0) | |
| IV | 100 (27.0) | 261 (24.6) | |
| Surgery | 0.896 | ||
| No | 111 (29.9) | 322 (30.4) | |
| Yes | 260 (70.1) | 737 (69.6) | |
| Receiving chemotherapy or/and radiotherapy | 0.643 | ||
| No | 247 (66.6) | 691 (65.3) | |
| Yes | 124 (33.4) | 368 (34.7) | |
| OS | |||
| 1 | 75.1 (70.6, 79.6) | 65.9 (63.0, 68.8) | |
| 3 | 56.0 (50.7, 61.3) | 49.1 (46.0, 52.2) | |
| 5 | 50.3 (44.8, 55.8) | 43.0 (39.9, 46.1) | |
| Median overall survival time | 62.0 (37.6, 86.4) | 34.0 (26.1, 41.9) | |
| CSS | |||
| 1 | 77.7 (73.4, 82.0) | 69.2 (66.5, 71.9) | |
| 3 | 60.3 (55.0, 65.6) | 54.2 (51.0, 57.3) | |
| 5 | 57.4 (51.9, 62.9) | 50.1 (47.0, 53.2) | |
| Median cancer-specific survival | NA | 61.0 (34.3, 87.7) | |
| Clinicopathological Features | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.026 (1.020, 1.032) | <0.001 | 1.024 (1.018, 1.030) | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Women | 0.790 (0.688, 0.906) | 0.001 | 0.937 (0.812, 1.080) | 0.369 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Proximal | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Middle | 0.818 (0.686, 0.976) | 0.025 | 0.864 (0.719, 1.037) | 0.116 |
| Distal | 0.844 (0.692, 1.030) | 0.095 | 1.098 (0.891, 1.352) | 0.381 |
| Mix | 1.497 (1.104, 2.209) | 0.009 | 1.252 (0.916, 1.712) | 0.158 |
| Unknown | 0.849 (0.648, 1.113) | 0.235 | 0.979 (0.741, 1.293) | 0.882 |
| Tumor size | 1.004 (1.003, 1.004) | <0.001 | 1.002 (1.001, 1.004) | <0.001 |
| T stage | NA | NA | ||
| 1 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 2 | 1.583 (1.270, 1.973) | <0.001 | ||
| 3 | 2.548 (2.138, 3.036) | <0.001 | ||
| 4a | 3.710 (2.973, 4.629) | <0.001 | ||
| 4b | 5.417 (4.280, 6.857) | <0.001 | ||
| N stage | NA | NA | ||
| 0 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 1 | 3.205 (2.737, 3.753) | <0.001 | ||
| 2 | 2.740 (2.221, 3.381) | <0.001 | ||
| 3a | 3.591 (2.760, 4.673) | <0.001 | ||
| 3b | 6.650 (3.881, 11.394) | <0.001 | ||
| M stage | NA | NA | ||
| 0 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 1 | 4.673 (4.037, 5.408) | <0.001 | ||
| TNM stage | ||||
| I | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| II | 2.711 (2.196, 3.346) | <0.001 | 2.645 (2.128, 3.287) | <0.001 |
| III | 4.603 (3.721, 5.694) | <0.001 | 4.669 (3.667, 5.946) | <0.001 |
| IV | 8.620 (7.164, 10.371) | <0.001 | 5.907 (4.721, 7.391) | <0.001 |
| Surgery | ||||
| No | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Yes | 0.239 (0.207, 0.275) | <0.001 | 0.387 (0.323, 0.464) | <0.001 |
| Receiving chemotherapy or/and radiotherapy | ||||
| No | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Yes | 2.718 (2.365, 3.123) | <0.001 | 0.772 (0.649, 0.920) | 0.004 |
| Type | ||||
| AC | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| NEC | 0.808 (0.685, 0.952) | 0.011 | 0.719 (0.607, 0.853) | <0.001 |
| Clinicopathological Features | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.017 (1.010, 1.024) | <0.001 | 1.016 (1.010, 1.023) | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Women | 0.756 (0.647, 0.883) | <0.001 | 0.951 (0.811, 1.116) | 0.541 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Proximal | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Middle | 0.771 (0.632, 0.941) | 0.010 | 0.824 (0.670, 1.014) | 0.067 |
| Distal | 0.766 (0.609, 0.962) | 0.022 | 1.029 (0.810, 1.307) | 0.814 |
| Mix | 1.539 (1.110, 2.135) | 0.010 | 1.192 (0.851, 1.668) | 0.307 |
| Unknown | 0.841 (0.624, 1.134) | 0.256 | 0.933 (0.686, 1.268) | 0.657 |
| Tumor size | 1.004 (1.003, 1.004) | <0.001 | 1.002 (1.001, 1.004) | <0.001 |
| T stage | NA | NA | ||
| 1 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 2 | 1.629 (1.254, 2.115) | <0.001 | ||
| 3 | 3.060 (2.501, 3.743) | <0.001 | ||
| 4a | 4.562 (3.565, 5.837) | <0.001 | ||
| 4b | 7.046 (5.473, 9.071) | <0.001 | ||
| N stage | NA | NA | ||
| 0 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 1 | 4.059 (3.398, 4.850) | <0.001 | ||
| 2 | 3.161 (2.493, 4.008) | <0.001 | ||
| 3a | 4.471 (3.362, 5.944) | <0.001 | ||
| 3b | 8.739 (5.076, 15.046) | <0.001 | ||
| M stage | NA | NA | ||
| 0 | 1[Reference] | |||
| 1 | 6.032 (5.144, 7.074) | <0.001 | ||
| TNM stage | ||||
| I | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| II | 4.177 (3.200, 5.453) | <0.001 | 4.091 (3.111, 5.380) | <0.001 |
| III | 7.424 (5.699, 9.673) | <0.001 | 7.624 (5.682, 10.231) | <0.001 |
| IV | 15.343 (12.136, 19.396) | <0.001 | 10.533 (8.004, 13.915) | <0.001 |
| Surgery | ||||
| No | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Yes | 0.201 (0.171, 0.235) | <0.001 | 0.377 (0.309, 0.461) | <0.001 |
| Receiving chemotherapy or/and radiotherapy | ||||
| No | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| Yes | 3.338 (2.855, 3.901) | <0.001 | 0.752 (0.621, 0.911) | 0.004 |
| Type | ||||
| AC | 1[Reference] | 1[Reference] | ||
| NEC | 0.792 (0.659, 0.952) | 0.013 | 0.691 (0.571, 0.835) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Ren, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, C.; Niu, P.; Wang, W.; Fei, H.; Guo, C.; et al. Better Prognosis of Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Than Gastric Adenocarcinoma among Whites in the United States: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis Based on SEER. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4879-4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070387
Li Z, Ren H, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang T, Sun C, Niu P, Wang W, Fei H, Guo C, et al. Better Prognosis of Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Than Gastric Adenocarcinoma among Whites in the United States: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis Based on SEER. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(7):4879-4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zefeng, Hu Ren, Lulu Zhao, Xiaojie Zhang, Tongbo Wang, Chongyuan Sun, Penghui Niu, Wanqing Wang, He Fei, Chunguang Guo, and et al. 2022. "Better Prognosis of Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Than Gastric Adenocarcinoma among Whites in the United States: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis Based on SEER" Current Oncology 29, no. 7: 4879-4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070387
APA StyleLi, Z., Ren, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, X., Wang, T., Sun, C., Niu, P., Wang, W., Fei, H., Guo, C., Chen, Y., & Zhao, D. (2022). Better Prognosis of Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Than Gastric Adenocarcinoma among Whites in the United States: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis Based on SEER. Current Oncology, 29(7), 4879-4892. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070387




