Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patient and Donor
2.2. Detection of LAA-Specific T Cells
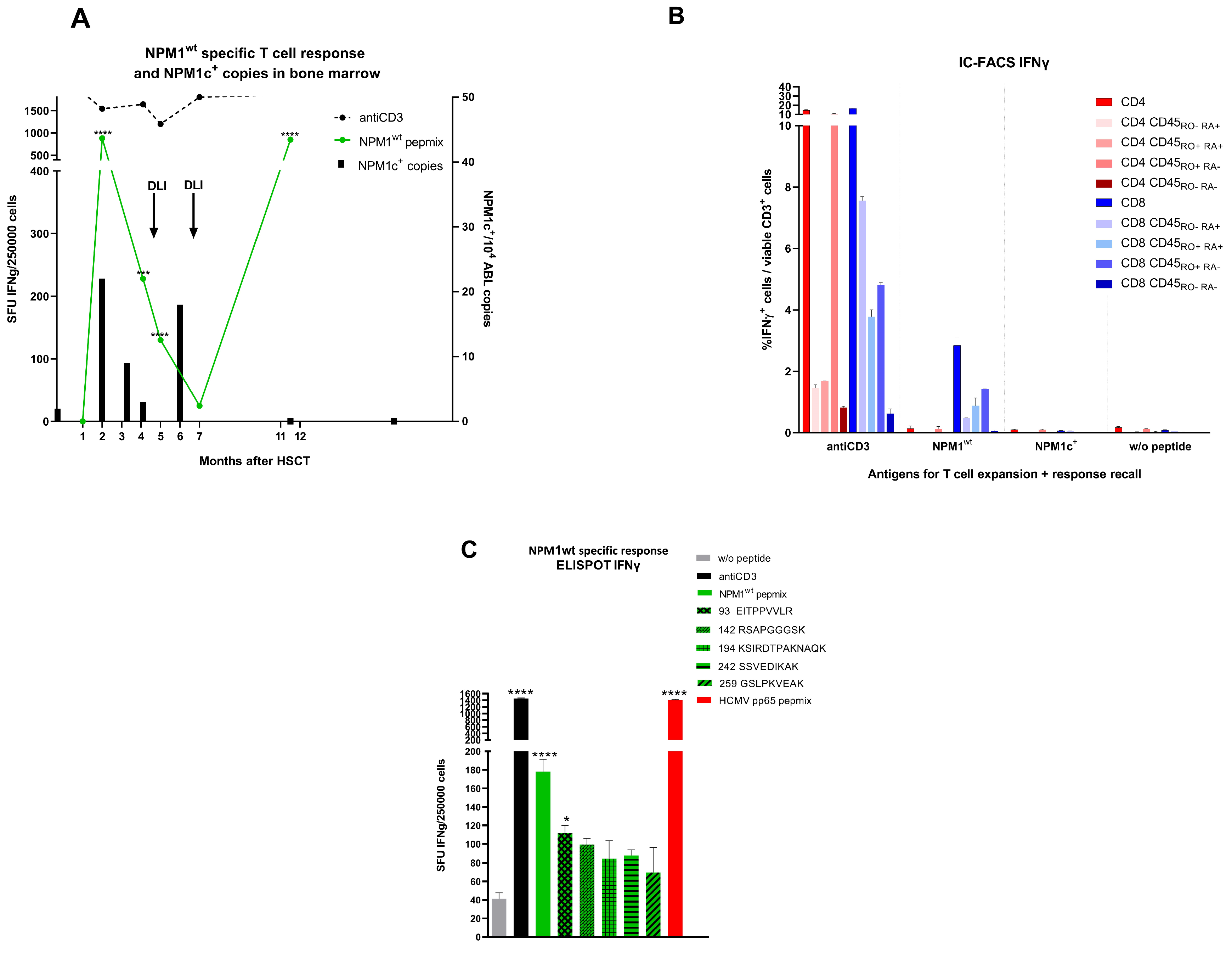
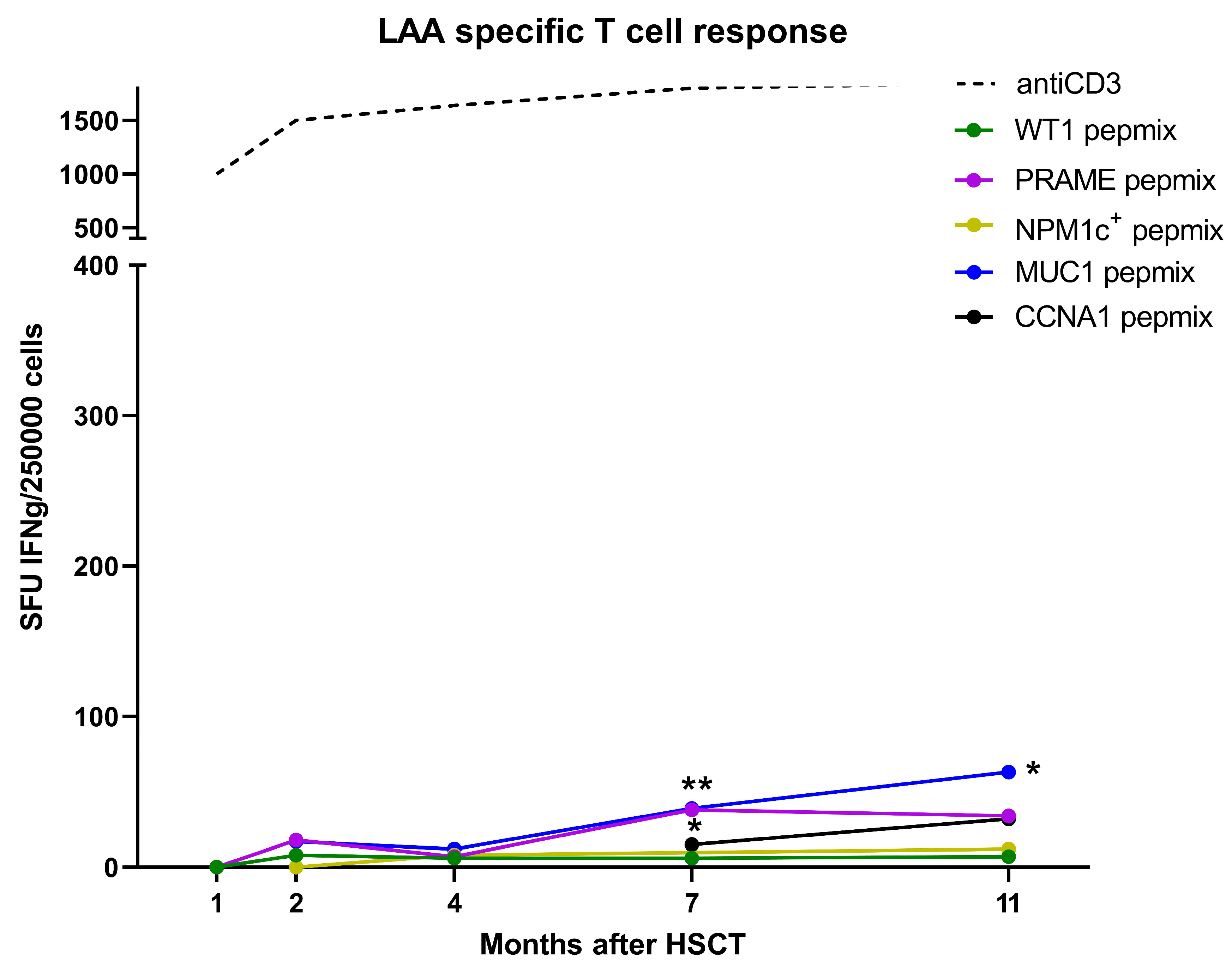
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Sportoletti, P.; Martelli, M.P. NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: From bench to bedside. Blood 2020, 136, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; You, H.; Dong, Y.; Lyu, J. Poor prognosis of nucleophosmin overexpression in solid tumors: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Mecucci, C.; Falini, B.; Pandolfi, P.P. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat. Cancer 2006, 6, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic Nucleophosmin in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a Normal Karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghieri, F.; Riva, G.; Lagreca, I.; Barozzi, P.; Vallerini, D.; Morselli, M.; Paolini, A.; Bresciani, P.; Colaci, E.; Maccaferri, M.; et al. Characterization and dynamics of specific T cells against nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1)-mutated peptides in patients with NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, J.; Ono, Y.; Hofmann, S.; Schmitt, A.; Mehring, E.; Götz, M.; Guillaume, P.; Döhner, K.; Mytilineos, J.; Döhner, H.; et al. Mutated regions of nucleophosmin 1 elicit both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesierska-Gadek, J.; Penner, E.; Hitchman, E.; Kier, P.; Sauermann, G. Nucleolar proteins B23 and C23 as target antigens in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1992, 79, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swoboda, R.K.; Somasundaram, R.; Caputo, L.; Berencsi, K.; Von Franzke, P.; Taylor, D.D.; Marincola, F.M.; Meropol, N.J.; Sigurdson, E.; Miller, E.; et al. Nucleophosmin is recognized by a cytotoxic T cell line derived from a rectal carcinoma patient. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 127, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, H.; Daouda, T.; Granados, D.P.; Durette, C.; Bonneil, E.; Courcelles, M.; Rodenbrock, A.; Laverdure, J.-P.; Côté, C.; Mader, S.; et al. MHC class I–associated peptides derive from selective regions of the human genome. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4690–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraibman, B.; Barnea, E.; Kadosh, D.M.; Haimovich, Y.; Slobodin, G.; Rosner, I.; López-Larrea, C.; Hilf, N.; Kuttruff, S.; Song, C.; et al. Identification of Tumor Antigens Among the HLA Peptidomes of Glioblastoma Tumors and Plasma. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayan, R.; Olsson, N.; Wagar, L.E.; Medeiros, B.C.; Meyer, E.; Czerwinski, D.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Schultz, L.; Davis, M.M.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia immunopeptidome reveals HLA presentation of mutated nucleophosmin. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amir, A.L.; Van Der Steen, D.M.; Van Loenen, M.M.; Hagedoorn, R.S.; De Boer, R.; Kester, M.D.; De Ru, A.H.; Lugthart, G.; van Kooten, C.; Hiemstra, P.; et al. PRAME-Specific Allo-HLA–Restricted T Cells with Potent Antitumor Reactivity Useful for Therapeutic T-Cell Receptor Gene Transfer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilde, S.; Sommermeyer, D.; Frankenberger, B.; Schiemann, M.; Milosevic, S.; Spranger, S.; Pohla, H.; Uckert, W.; Busch, D.H.; Schendel, D.J. Dendritic cells pulsed with RNA encoding allogeneic MHC and antigen induce T cells with superior antitumor activity and higher TCR functional avidity. Blood 2009, 114, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, C.; Obst, R.; Osen, W.; Stevanović, S.; Rammensee, H.G. Alloreactivity as a source of high avidity peptide-specific human CTL. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sadovnikova, E.; Stauss, H.J. Peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes restricted by nonself major histocompatibility complex class I molecules: Reagents for tumor immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13114–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šťastná-Marková, M.; Hamšíková, E.; Hainz, P.; Hubáček, P.; Kroutilová, M.; Kryštofová, J.; Ludvíková, V.; Musil, J.; Pecherková, P.; Saláková, M.; et al. Pretransplant BK Virus-Specific T-Cell-Mediated Immunity and Serotype Specific Antibodies May Have Utility in Identifying Patients at Risk of BK Virus-Associated Haemorrhagic Cystitis after Allogeneic HSCT. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammensee, H.-G.; Bachmann, J.; Emmerich, N.P.N.; Bachor, O.A.; Stevanović, S. SYFPEITHI: Database for MHC ligands and peptide motifs. Immunogenetics 1999, 50, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranzl, T.; Larsen, M.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Nielsen, M. NetCTLpan: Pan-specific MHC class I pathway epitope predictions. Immunogenetics 2010, 62, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, M.L. Virally-induced heterologous immunity in renal transplant recipients: Important or inconsequential? Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1348–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heutinck, K.M.; La Yong, S.; Tonneijck, L.; Heuvel, H.V.D.; Van Der Weerd, N.C.; Van Der Pant, K.A.; Bemelman, F.J.; Claas, F.H.; Berge, I.J.T. Virus-Specific CD8+T Cells Cross-Reactive to Donor-Alloantigen Are Transiently Present in the Circulation of Kidney Transplant Recipients Infected with CMV and/or EBV. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stranavova, L.; Pelak, O.; Svaton, M.; Hruba, P.; Fronkova, E.; Slavcev, A.; Osickova, K.; Maluskova, J.; Hubacek, P.; Fronek, J.; et al. Heterologous Cytomegalovirus and Allo-Reactivity by Shared T Cell Receptor Repertoire in Kidney Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuželová, K.; Brodská, B.; Fuchs, O.; Dobrovolná, M.; Soukup, P.; Cetkovský, P. Altered HLA Class I Profile Associated with Type A/D Nucleophosmin Mutation Points to Possible Anti-Nucleophosmin Immune Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.P.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Pierangeli, S.; Mulas, F.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Pettirossi, V.; Rossi, R.; et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Xu, A.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, B.; Shao, X.; He, Q.; Ying, M. The role of autophagy in targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Autophagy 2020, 17, 2665–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.; Edwards, D.K.; Eide, C.A.; Newell, L.; Traer, E.; Medeiros, B.C.; Pollyea, D.A.; Deininger, M.W.; Collins, R.H.; Tyner, J.W.; et al. Identification of interleukin-1 by functional screening as a key mediator of cellular expansion and disease progression in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nemeckova, S.; Alexova-Zurkova, K.; Hainz, P.; Krystofova, J.; Mackova, J.; Roubalova, K.; Stastna-Markova, M.; Vrana, M.; Vydra, J. Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2928-2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050239
Nemeckova S, Alexova-Zurkova K, Hainz P, Krystofova J, Mackova J, Roubalova K, Stastna-Markova M, Vrana M, Vydra J. Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(5):2928-2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050239
Chicago/Turabian StyleNemeckova, Sarka, Kamila Alexova-Zurkova, Petr Hainz, Jitka Krystofova, Jana Mackova, Katerina Roubalova, Marketa Stastna-Markova, Milena Vrana, and Jan Vydra. 2022. "Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor" Current Oncology 29, no. 5: 2928-2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050239
APA StyleNemeckova, S., Alexova-Zurkova, K., Hainz, P., Krystofova, J., Mackova, J., Roubalova, K., Stastna-Markova, M., Vrana, M., & Vydra, J. (2022). Non-Mutated Nucleophosmin 1 Is Recognized by the CD8+ T Lymphocytes of an AML Patient after the Transplantation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells from an HLA-Haploidentical Donor. Current Oncology, 29(5), 2928-2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050239




