Sleep Disturbance Affects Immune Factors in Clinical Liver Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements
Demographic, Disease Associated Variables and Immune Factors
2.3. Sleep Disturbance
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
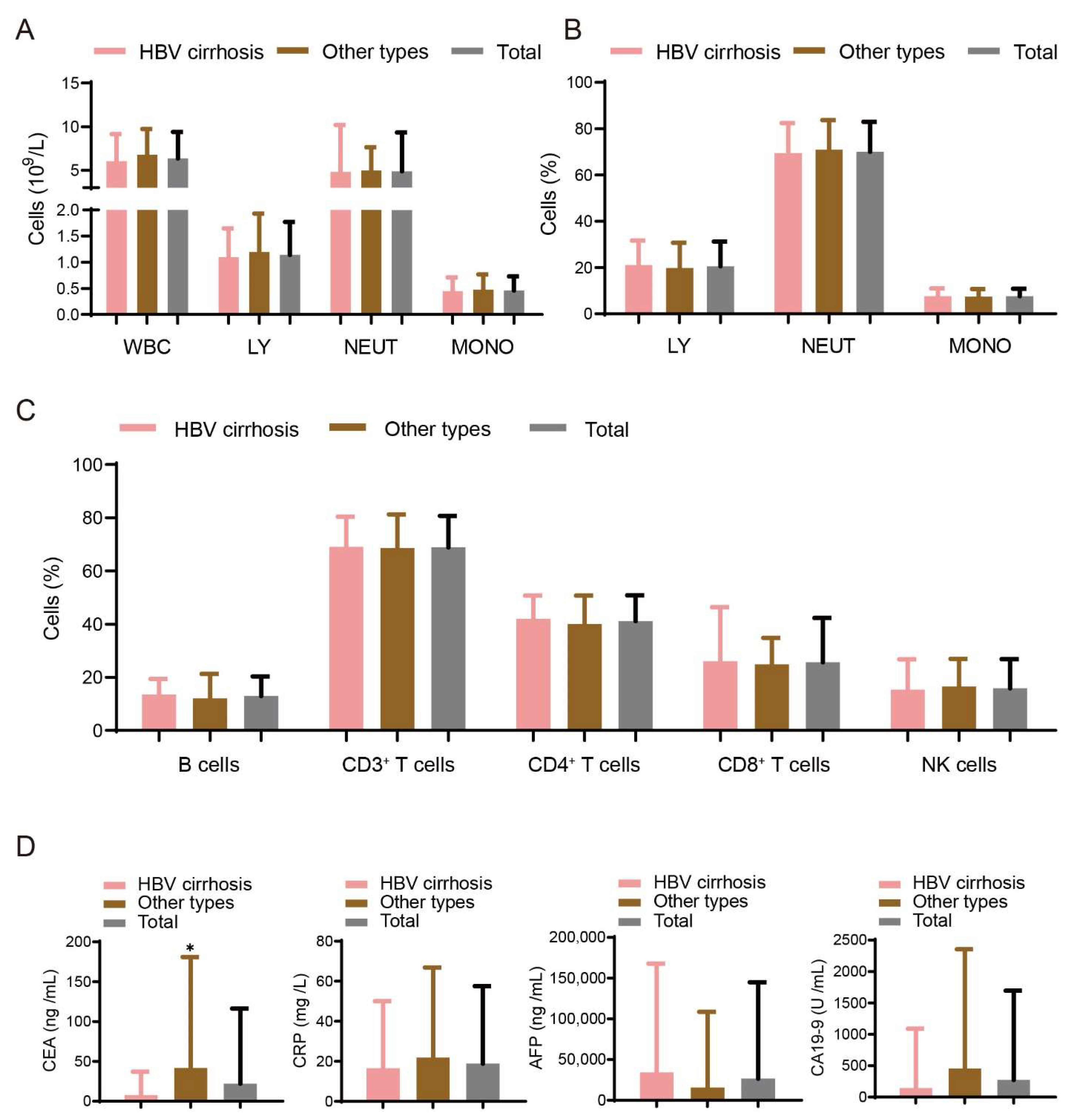
3.1. Demographic and Immune Factors for Study Populations
3.2. Prevalence of Sleep Disturbances in Patients with Liver Cancer of Different Etiologies
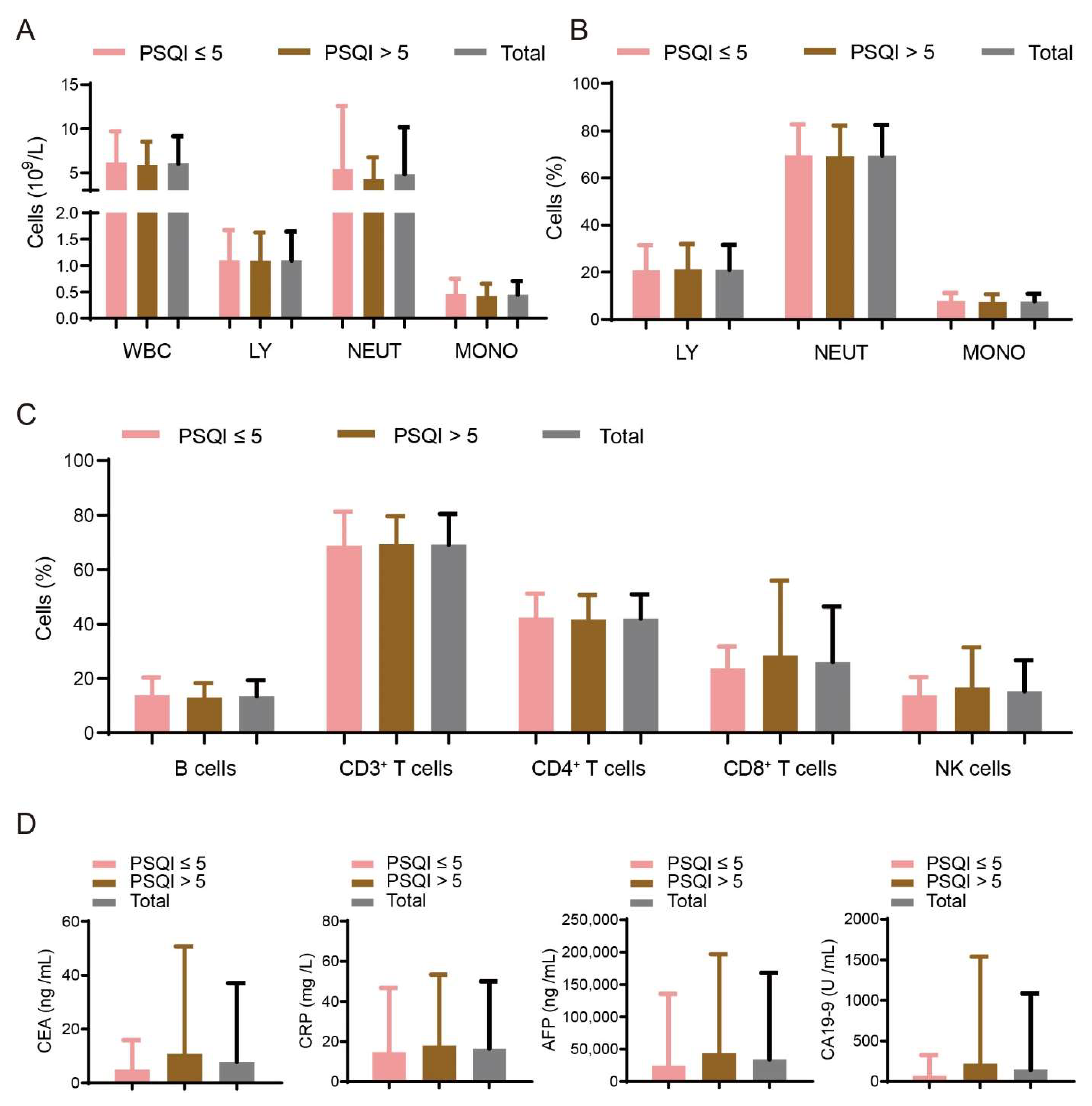
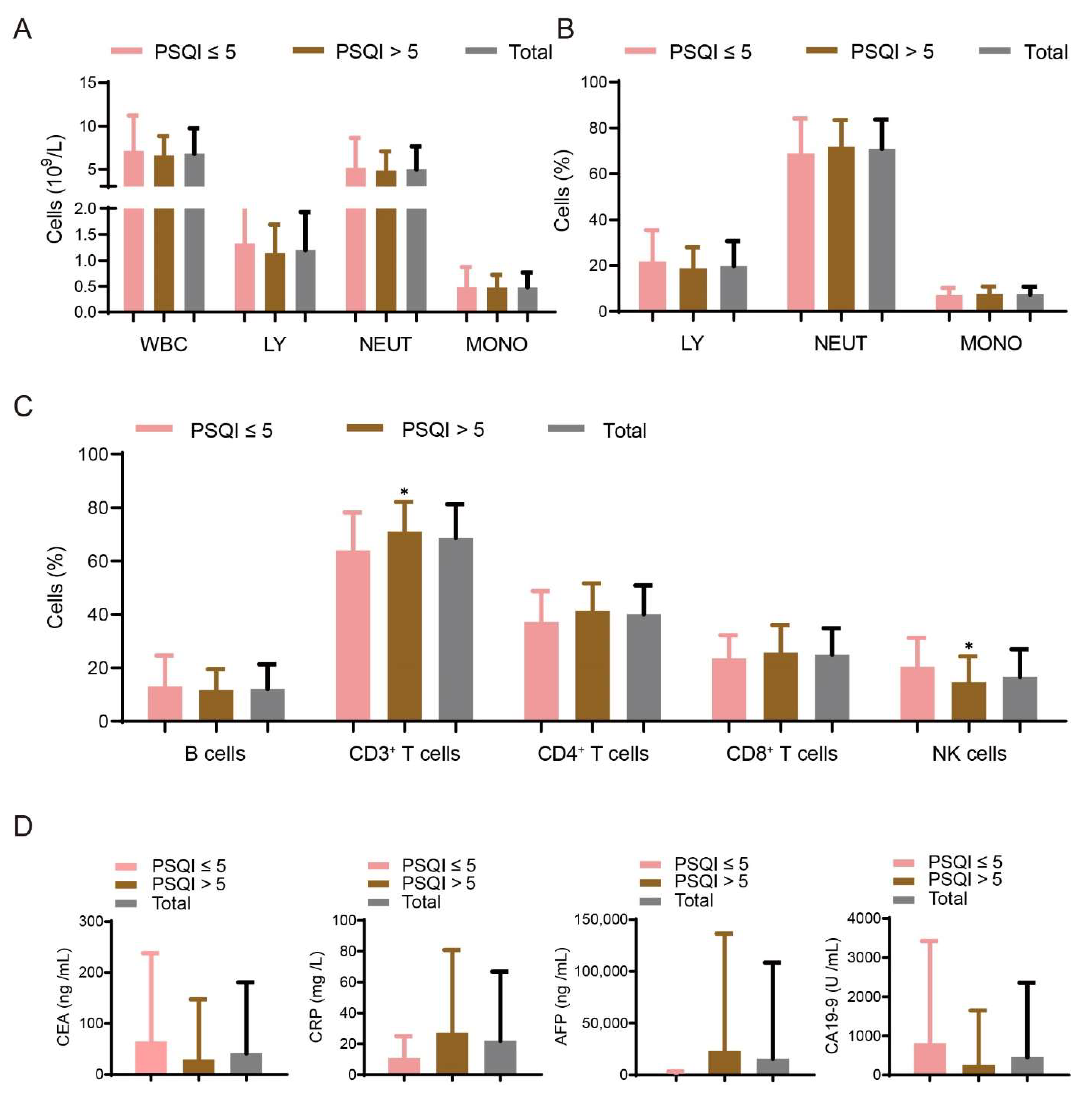
3.3. Association between Sleep Disturbances and Immune Factors
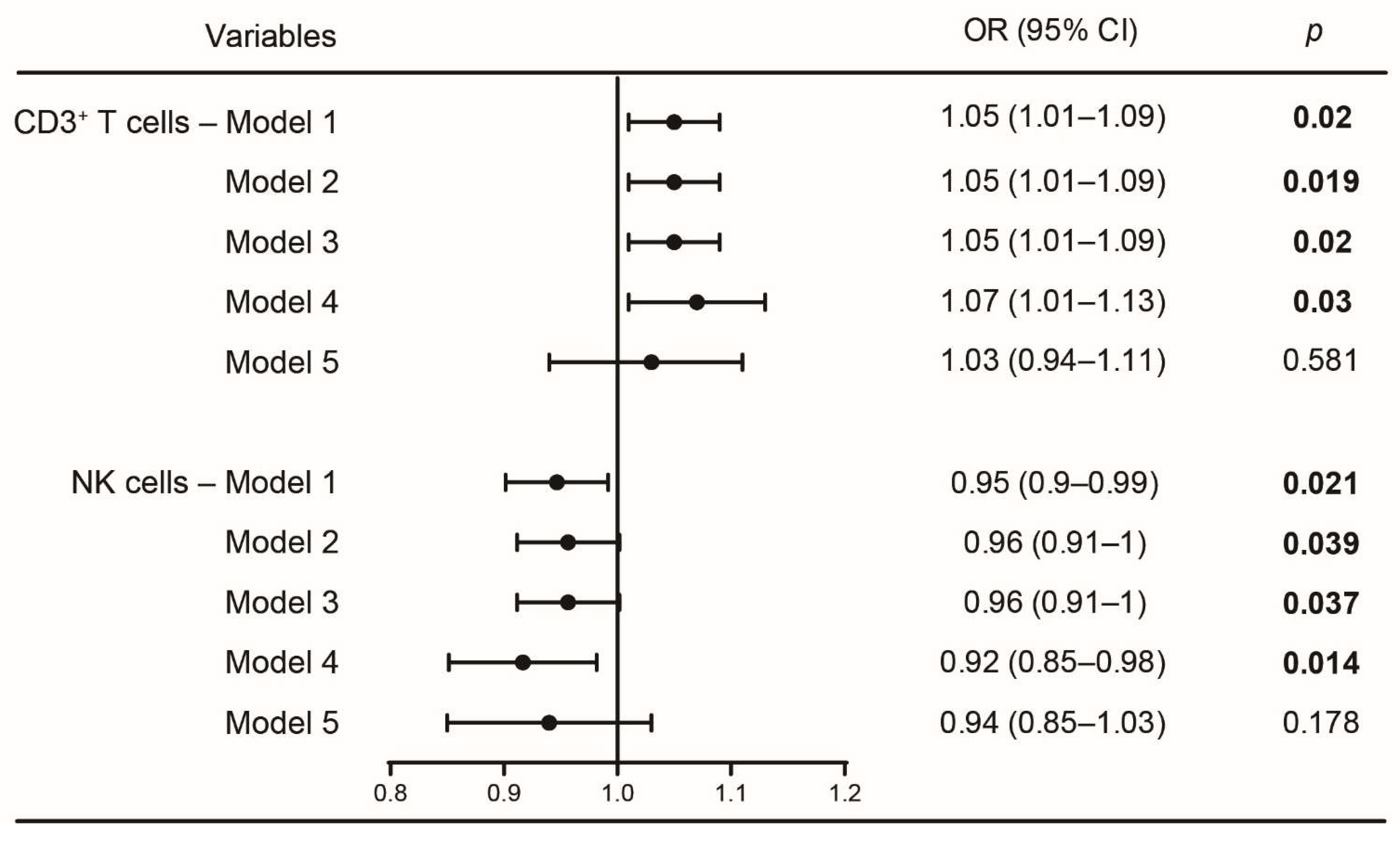
3.4. Logistic Regression Analyses between CD3+ T and NK Cells with Sleep Disturbances
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billings, M.E.; Hale, L.; Johnson, D.A. Physical and Social Environment Relationship with Sleep Health and Disorders. Chest 2020, 157, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besedovsky, L.; Lange, T.; Haack, M. The Sleep-Immune Crosstalk in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1325–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomers, M.L.; Hulsegge, G.; van Oostrom, S.H.; Proper, K.I.; Verschuren, W.M.M.; Picavet, H.S.J. Characterizing Adult Sleep Behavior Over 20 Years-The Population-Based Doetinchem Cohort Study. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricciani, L.; Bin, Y.S.; Lallukka, T.; Kronholm, E.; Dumuid, D.; Paquet, C.; Olds, T. Past, present, and future: Trends in sleep duration and implications for public health. Sleep Health 2017, 3, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Strong, C.; Li, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-S.; Ko, W.-C.; Ko, N.-Y. Sleep disturbances at the time of a new diagnosis: A comparative study of human immunodeficiency virus patients, cancer patients, and general population controls. Sleep Med. 2017, 36, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palesh, O.G.; Roscoe, J.A.; Mustian, K.M.; Roth, T.; Savard, J.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Heckler, C.; Purnell, J.Q.; Janelsins, M.C.; Morrow, G.R. Prevalence, demographics, and psychological associations of sleep disruption in patients with cancer: University of Rochester Cancer Center-Community Clinical Oncology Program. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, J.; Ivers, H.; Villa, J.; Caplette-Gingras, A.; Morin, C.M. Natural Course of Insomnia Comorbid with Cancer: An 18-Month Longitudinal Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, J.; Villa, J.; Ivers, H.; Simard, S.; Morin, C.M. Prevalence, Natural Course, and Risk Factors of Insomnia Comorbid with Cancer Over a 2-Month Period. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5233–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, S.; Sereika, S.; Harpel, C.; Diego, E.; Steiman, J.G.; McAuliffe, P.F.; Wesmiller, S. Factors associated with sleep disturbances in women undergoing treatment for early-stage breast cancer. Support. Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariniello, L.D.; Vicari, P.; Lee, K.S.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Tufik, S. Bone marrow and peripheral white blood cells number is affected by sleep deprivation in a murine experimental model. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R. Sleep and inflammation: Partners in sickness and in health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.X.L.; Zheng, J.; Yolcu, E.S.; Carreras, A.; Khalyfa, A.; Shirwan, H.; Almendros, I.; Gozal, D. Fragmented Sleep Accelerates Tumor Growth and Progression through Recruitment of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and TLR4 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, M.R.; Mark Davis, J.; Fadel, J.R.; Youngstedt, S.D. Influence of chronic moderate sleep restriction and exercise on inflammation and carcinogenesis in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mogavero, M.P.; DelRosso, L.M.; Fanfulla, F.; Bruni, O.; Ferri, R. Sleep disorders and cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 56, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.F.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Bai, F.Z.; Lei, L.; Peng, J.; Feletto, E.; Canfell, K.; Qu, C.; Chen, W. Is it possible to halve the incidence of liver cancer in China by 2050? Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Wong, G.; Gane, E.; Kao, J.H.; Dusheiko, G. Hepatitis B Virus: Advances in Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00046-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettner, N.M.; Voicu, H.; Finegold, M.J.; Coarfa, C.; Sreekumar, A.; Putluri, N.; Katchy, C.A.; Lee, C.; Moore, D.D.; Fu, L. Circadian Homeostasis of Liver Metabolism Suppresses Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Song, P.; Hang, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Qin, J.; Wang, B.; Qu, W.; et al. Sleep Deprivation Disturbs Immune Surveillance and Promotes the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 727959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjot, T.; Ray, D.W.; Williams, F.R.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Armstrong, M.J. Sleep and liver disease: A bidirectional relationship. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royse, K.E.; El-Serag, H.B.; Chen, L.; White, D.L.; Hale, L.; Sangi-Haghpeykar, H.; Jiao, L. Sleep Duration and Risk of Liver Cancer in Postmenopausal Women: The Women’s Health Initiative Study. J. Women’s Health 2017, 26, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.P.; Geller, D.A.; Antoni, M.; Donnell, D.M.; Tsung, A.; Marsh, J.W.; Burke, L.; Penedo, F.; Terhorst, L.; Kamarck, T.W.; et al. Sleep duration is associated with survival in advanced cancer patients. Sleep Med. 2017, 32, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, S.; Tovoli, F.; Barbera, M.A.; Garuti, F.; Palloni, A.; Frega, G.; Garajova, I.; Rizzo, A.; Trevisani, F.; Brandi, G. Metronomic capecitabine vs. best supportive care in Child-Pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma: A proof of concept. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Nannini, M.; Novelli, M.; Dalia Ricci, A.; Scioscio, V.D.; Pantaleo, M.A. Dose reduction and discontinuation of standard-dose regorafenib associated with adverse drug events in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920936932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdardottir, L.G.; Markt, S.C.; Rider, J.R.; Haneuse, S.; Fall, K.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Tamimi, R.M.; Flynn-Evans, E.; Batista, J.L.; Launer, L.; et al. Urinary Melatonin Levels, Sleep Disruption, and Risk of Prostate Cancer in Elderly Men. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | HBV Cirrhosis | Other Types | Total | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Age, years | 0.228 | ||||||
| Mean | 58.5 | 60 | 59.1 | ||||
| SD | 8.3 | 9.6 | 8.9 | ||||
| Sex | 0.258 | ||||||
| Male | 100 | 84.7 | 66 | 78.6 | 166 | 82.2 | |
| Female | 18 | 15.3 | 18 | 21.4 | 36 | 17.8 | |
| Diabetes | 0.200 | ||||||
| Yes | 9 | 7.6 | 11 | 13.1 | 20 | 9.9 | |
| No | 109 | 92.4 | 73 | 86.9 | 182 | 90.1 | |
| Hypertension | 0.188 | ||||||
| Yes | 23 | 19.5 | 23 | 27.4 | 46 | 22.8 | |
| No | 95 | 80.5 | 61 | 72.6 | 156 | 77.2 | |
| HBV Cirrhosis | Others | Total | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 118 | n = 84 | n = 202 | ||
| PSQI score | ||||
| Mean | 6.46 | 7.54 | 6.91 | 0.043 a |
| SD | 3.79 | 3.58 | 3.73 | |
| PSQI ≤ 5 | ||||
| N (%) | 59 (50) | 28 (33.3) | 87 (43.1) | 0.018 a |
| PSQI > 5 | ||||
| N (%) | 59 (50) | 56 (66.7) | 115 (56.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, L.; Qin, J.; Liu, B.; Liang, C. Sleep Disturbance Affects Immune Factors in Clinical Liver Cancer Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7943-7952. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100628
Wang Z, Wang Y, Huang J, Xu J, Chen F, Zhu Z, Gao L, Qin J, Liu B, Liang C. Sleep Disturbance Affects Immune Factors in Clinical Liver Cancer Patients. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7943-7952. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100628
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zuoyun, Yan Wang, Jing Huang, Jietian Xu, Fangzhen Chen, Zidan Zhu, Lingling Gao, Jie Qin, Binbin Liu, and Chunmin Liang. 2022. "Sleep Disturbance Affects Immune Factors in Clinical Liver Cancer Patients" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7943-7952. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100628
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, J., Xu, J., Chen, F., Zhu, Z., Gao, L., Qin, J., Liu, B., & Liang, C. (2022). Sleep Disturbance Affects Immune Factors in Clinical Liver Cancer Patients. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7943-7952. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100628





