TP53 Mutation Mapping in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Eligibility
2.2. Patient Variables
2.3. Tissue-Based Next-Generation Sequencing
2.4. TP53 Mutation Classification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Outcomes
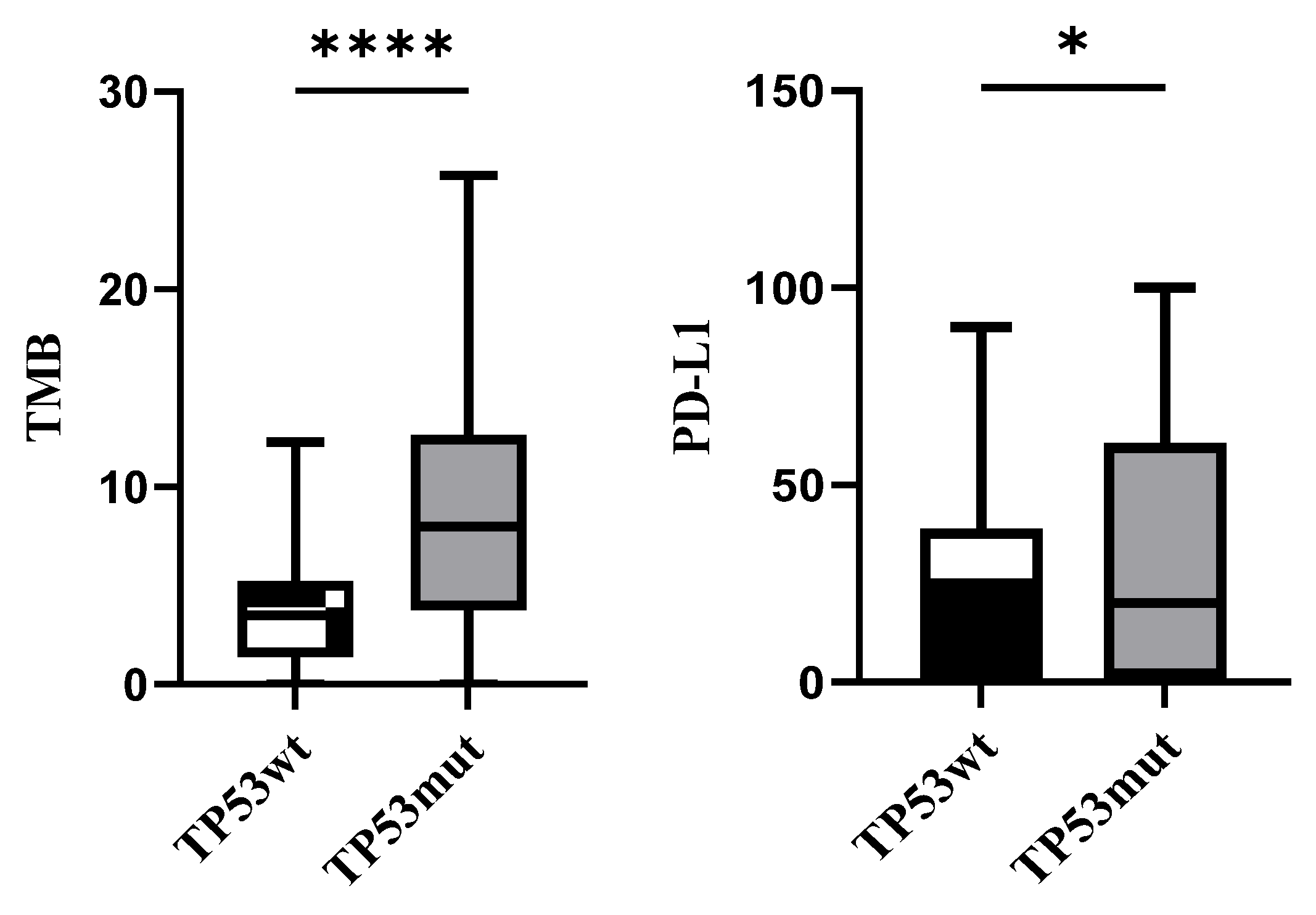
3.2. Association with PD-L1 and TMB Expression
3.3. Mutation Mapping for TP53
3.4. Co-Mutation Status in TP53wt and TP53mut Cohort
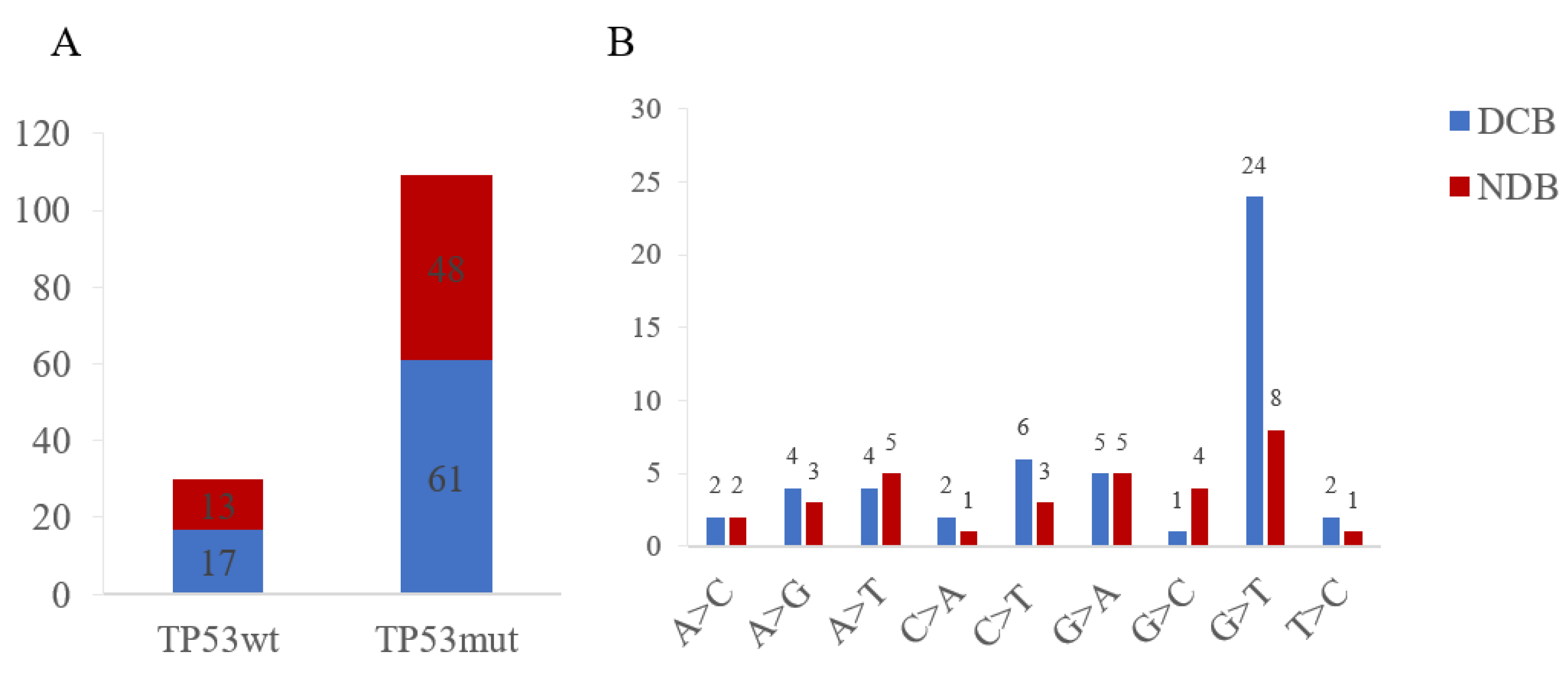
3.5. Therapy Response for Patients with TP53wt and TP53mut
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dey, R.; Chen, L. Crystal Structure of the p53 Core Domain Bound to a Full Consensus Site as a Self-Assembled Tetramer. Structure 2010, 18, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, S.S.; Attardi, L.D. Deciphering p53 signaling in tumor suppression. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 51, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hickman, J.H.; Wang, S.-J.; Gu, W. Dynamic roles of p53-mediated metabolic activities in ROS-induced stress responses. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2881–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed-Pastor, W.A.; Prives, C. Mutant p53: One name, many proteins. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, V.J.N.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeta, M.L.; Manola, J.; Goldwasser, M.A.; Forastiere, A.; Benoit, N.; Califano, J.A.; Ridge, J.A.; Goodwin, J.; Kenady, D.; Saunders, J.; et al. TP53Mutations and Survival in Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, E.H.; Ke, H.; Levine, A.J.; Bonneau, R.A.; Chan, C.S. Why are there hotspot mutations in the TP53 gene in human cancers? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotler, E.; Shani, O.; Goldfeld, G.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Tarcic, O.; Gershoni, A.; Hopf, T.A.; Marks, D.S.; Oren, M.; Segal, E. A systematic p53 mutation library links differential functional impact to cancer mutation pattern and evolutionary conservation. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The first 30 years of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, B.; Anderson, M.; Soussi, T. TP53 Mutations in Human Cancer: Database Reassessment and Prospects for the Next Decade. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 672–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussi, T.; Wiman, K. TP53: An oncogene in disguise. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yin, X.B.; Shi, G.Y.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q.; Liang, X.W. Emodin enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer cells through ROS elevation and MRP1 downregulation. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanden, A.R.; Yu, X.; Wolfe, A.J.; Gilleran, J.A.; Augeri, D.J.; O’Dell, R.S.; Olson, E.C.; Kimball, S.D.; Emge, T.J.; Movileanu, L.; et al. Synthetic Metallochaperone ZMC1 Rescues Mutant p53 Conformation by Transporting Zinc into Cells as an Ionophore. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variants | Total No.139 | Patients with TP53wt, No. (%) | Patients with TP53mut, No. (%) | p Value (Chi-Square) | Patients with TP53“Other Mutations,” No. (%) | Patients with TP53 Missense Mutations, No. (%) | p Value (Chi-Square) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at study entry (y) | 0.838 | 0.999 | |||||
| ≤65 | 58(41.7) | 13(43.3) | 45(41.3) | 17(41.5) | 28(41.2) | ||
| >65 | 81(58.3) | 17(56.7) | 64(58.7) | 24(58.5) | 40(58.8) | ||
| Sex | p < 0.001 | 0.803 | |||||
| Male | 102(73.4) | 14(46.7) | 88(80.7) | 34(82.9) | 54(79.4) | ||
| Female | 37(26.6) | 16(53.3) | 21(19.3) | 7(17.1) | 14(20.6) | ||
| Histological type | |||||||
| LUAD | 83(59.7) | 25(83.4) | 58(53.2) | 0.011 | 21(51.2) | 37(54.4) | 0.429 |
| LSCC | 43(30.9) | 4(13.3) | 39(35.8) | 13(31.7) | 26(38.2) | ||
| Sarcomatoid carcinoma | 13(9.4) | 1(3.3) | 12(11.0) | 7(17.1) | 5(7.4) | ||
| Smoking history | 0.003 | 0.629 | |||||
| No | 38(27.3) | 15(50) | 23(21.1) | 10(24.4) | 13(19.1) | ||
| Yes | 101(72.7) | 15(50) | 86(78.9) | 31(75.6) | 55(80.9) | ||
| PD-L1 | 0.015 | 0.603 | |||||
| <1% | 20(14.4) | 9(30) | 11(10.1) | 4(9.8) | 7(10.3) | ||
| 1–49% | 68(48.9) | 14(46.7) | 54(49.5) | 18(43.9) | 36(52.9) | ||
| ≥50% | 51(36.7) | 7(23.3) | 44(40.4) | 19(46.3) | 25(36.8) | ||
| TMB | p < 0.001 | 0.417 | |||||
| <10 | 95(68.3) | 28(93.3) | 67(61.5) | 23(56.1) | 44(64.7) | ||
| ≥10 | 44(31.7) | 2(6.7) | 42(38.5) | 18(43.9) | 24(35.3) |
| Variants | Total No. 139 | Patients with TP53wt, No. (%) | Patients with TP53mut, No. (%) | p Value (Chi-Square) | Patients with TP53 Missense Mutations, No. (%) | Patients with TP53 “Other Mutations,” No. (%) | p Value (Chi-Square) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beneficial genes | |||||||
| PBRM1 | |||||||
| Wild type | 130(93.5) | 26(86.7) | 104(95.4) | 0.085 | 66(97.1) | 38(92.7) | 0.004 |
| Mutant | 9(6.5) | 4(13.3) | 5(4.6) | 2(2.9) | 3(7.3) | ||
| KRAS | |||||||
| Wild type | 115(82.7) | 23(76.7) | 92(84.4) | 0.321 | 59(86.8) | 33(80.5) | 0.382 |
| Mutant | 24(17.3) | 7(23.3) | 17(15.6) | 9(13.2) | 8(19.5) | ||
| ARID1A | |||||||
| Wild type | 122(87.8) | 27(90.0) | 95(87.2) | 0.674 | 61(89.7) | 34(82.9) | 0.306 |
| Mutant | 17(12.2) | 3(10.0) | 14(12.8) | 7(10.3) | 7(17.1) | ||
| SMARCA4 | |||||||
| Wild type | 126(90.6) | 27(90.0) | 99(90.8) | 0.891 | 63(92.6) | 36(87.8) | 0.396 |
| Mutant | 13(9.4) | 3(10.0) | 10(9.2) | 5(7.4) | 5(12.2) | ||
| DDR pathway | |||||||
| Wild type | 54(38.8) | 12(40.0) | 42(38.5) | 0.884 | 18(26.5) | 24(58.5) | p < 0.001 |
| Mutant | 85(61.2) | 18(60.0) | 67(61.5) | 50(73.5) | 17(41.5) | ||
| Noxious genes | |||||||
| EGFR | 0.061 | 0.849 | |||||
| Wild type | 102(73.4) | 18(60.0) | 84(77.1) | 52(76.5) | 32(78.0) | ||
| Mutant | 37(26.6) | 12(40.0) | 25(22.9) | 16(23.5) | 9(22.0) | ||
| KEAP1 | |||||||
| Wild type | 124(89.2) | 29(96.7) | 95(87.2) | 0.137 | 59(86.8) | 36(87.8) | 0.875 |
| Mutant | 15(10.8) | 1(3.3) | 14(12.8) | 9(13.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| MDM2/MDM4 | |||||||
| Amplification | 7(5.0) | 3(10.0) | 4(3.7) | 0.161 | 2(2.9) | 2(4.9) | 0.602 |
| No amplification | 132(95.0) | 27(90.0) | 105(96.3) | 66(97.1) | 39(95.1) | ||
| 11q13 | |||||||
| Amplification | 8(5.8) | 1(3.3) | 7(6.4) | 0.521 | 4(58.8) | 3(7.3) | 0.767 |
| No amplification | 131(94.2) | 29(96.7) | 102(93.6) | 64(94.1) | 38(92.7) | ||
| JAK1/JAK2 | |||||||
| Wild type | 126(90.6) | 29(96.7) | 97(89.0) | 0.201 | 62(91.2) | 35(85.4) | 0.348 |
| Mutant | 13(9.4) | 1(3.3) | 12(11.0) | 6(8.8) | 6(14.6) | ||
| CTNNB1 | |||||||
| Wild type | 133(95.7) | 27(90.0) | 106(97.2) | 0.084 | 66(97.1) | 40(97.6) | 0.877 |
| Mutant | 6(4.3) | 3(10.0) | 3(2.8) | 2(2.9) | 1(2.4) | ||
| STK11 | |||||||
| Wild type | 127(91.4) | 28(93.3) | 99(90.8) | 0.665 | 61(89.7) | 38(92.7) | 0.602 |
| Mutant | 12(8.6) | 2(6.7) | 10(9.2) | 7(10.3) | 3(7.3) | ||
| KMT2D | |||||||
| Wild type | 120(86.3) | 28(93.3) | 92(84.4) | 0.207 | 58(85.3) | 34(82.9) | 0.741 |
| Mutant | 19(13.7) | 2(6.7) | 17(15.6) | 10(14.7) | 7(17.1) | ||
| DNMT3A | |||||||
| Wild type | 133(95.7) | 29(96.7) | 104(95.4) | 0.765 | 65(95.6) | 39(95.1) | 0.911 |
| Mutant | 6(4.3) | 1(3.3) | 5(4.6) | 3(4.4) | 2(4.9) | ||
| PTEN | |||||||
| Wild type | 127(91.4) | 28(93.3) | 99(90.8) | 0.665 | 63(92.6) | 36(87.8) | 0.396 |
| Mutant | 12(8.6) | 2(6.7) | 10(9.2) | 5(7.4) | 5(12.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, F.; Gu, L.; Zhong, D. TP53 Mutation Mapping in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7411-7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100582
Hao F, Gu L, Zhong D. TP53 Mutation Mapping in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7411-7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100582
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Fang, Liyan Gu, and Diansheng Zhong. 2022. "TP53 Mutation Mapping in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7411-7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100582
APA StyleHao, F., Gu, L., & Zhong, D. (2022). TP53 Mutation Mapping in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7411-7419. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100582




