Wide Dissection Trans-Sulcal Approach for Resection of Deep Intra-Axial Lesions in Eloquent Brain Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Data
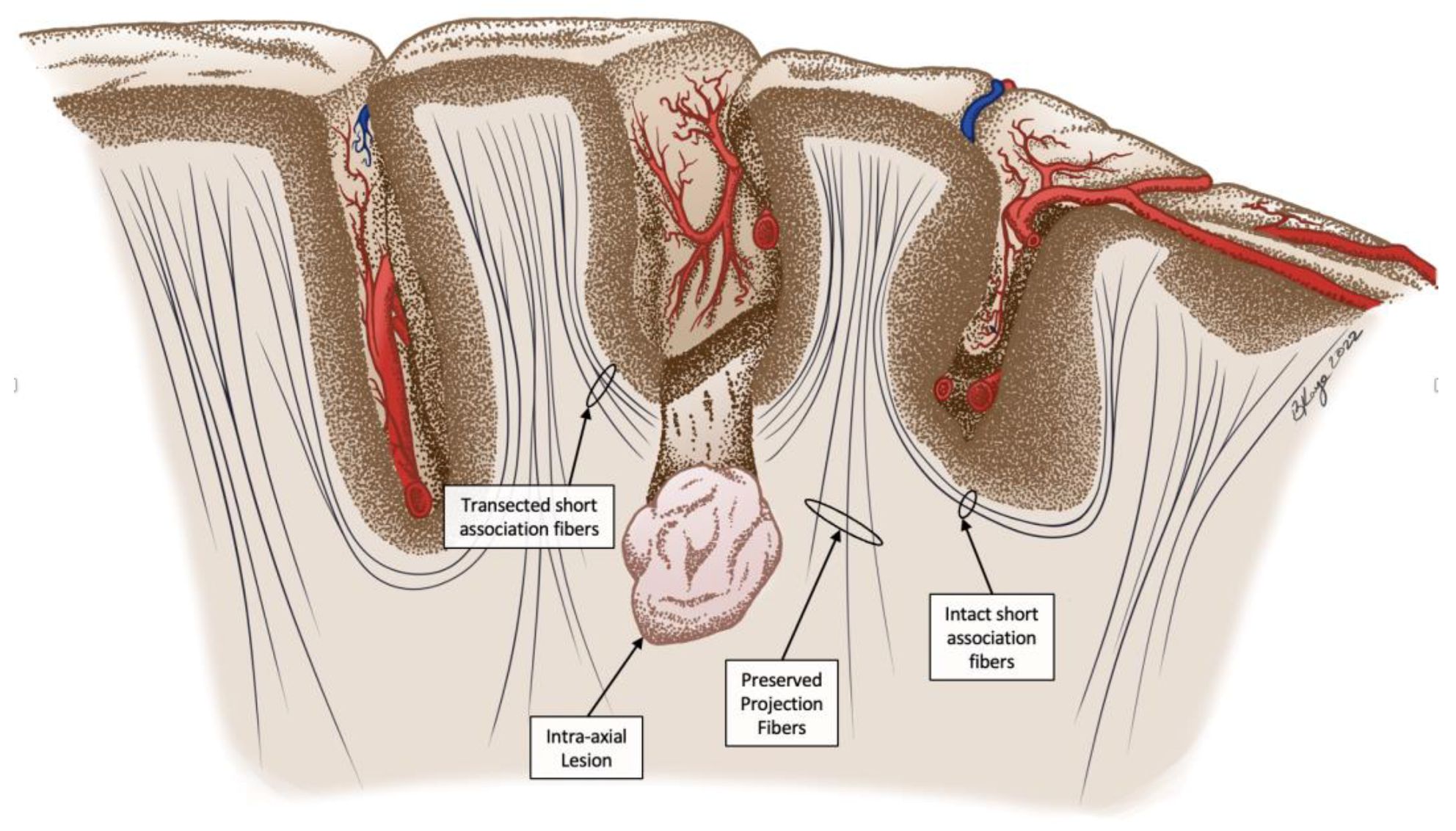
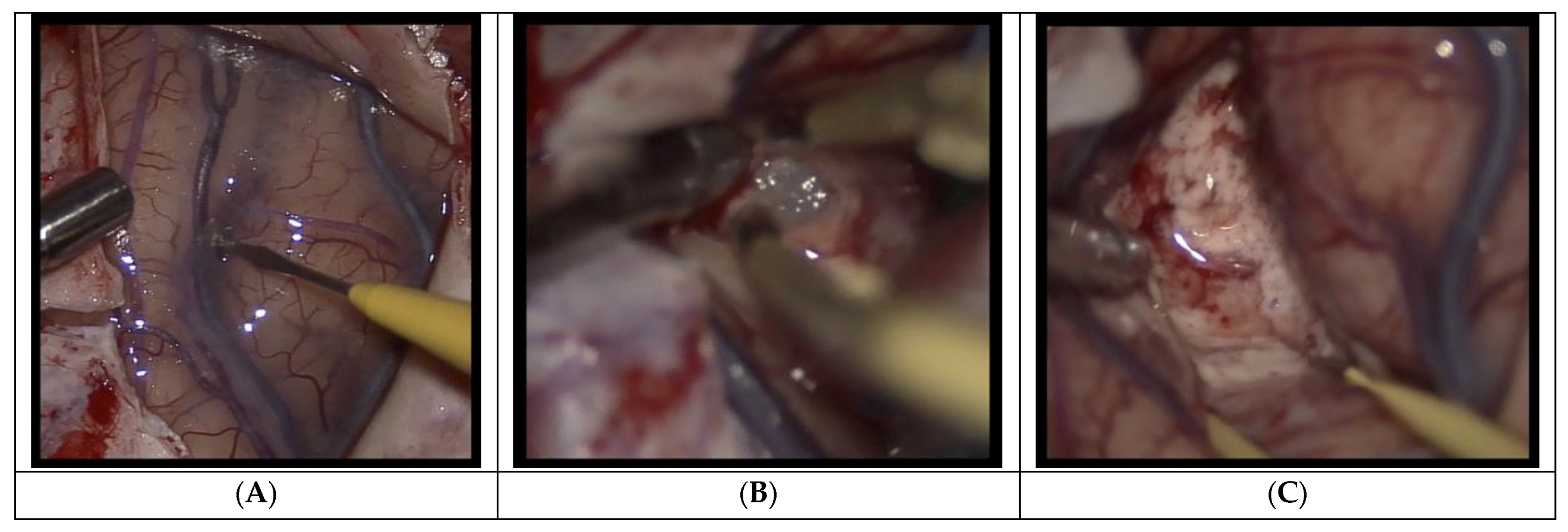
2.2. Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Operative Results
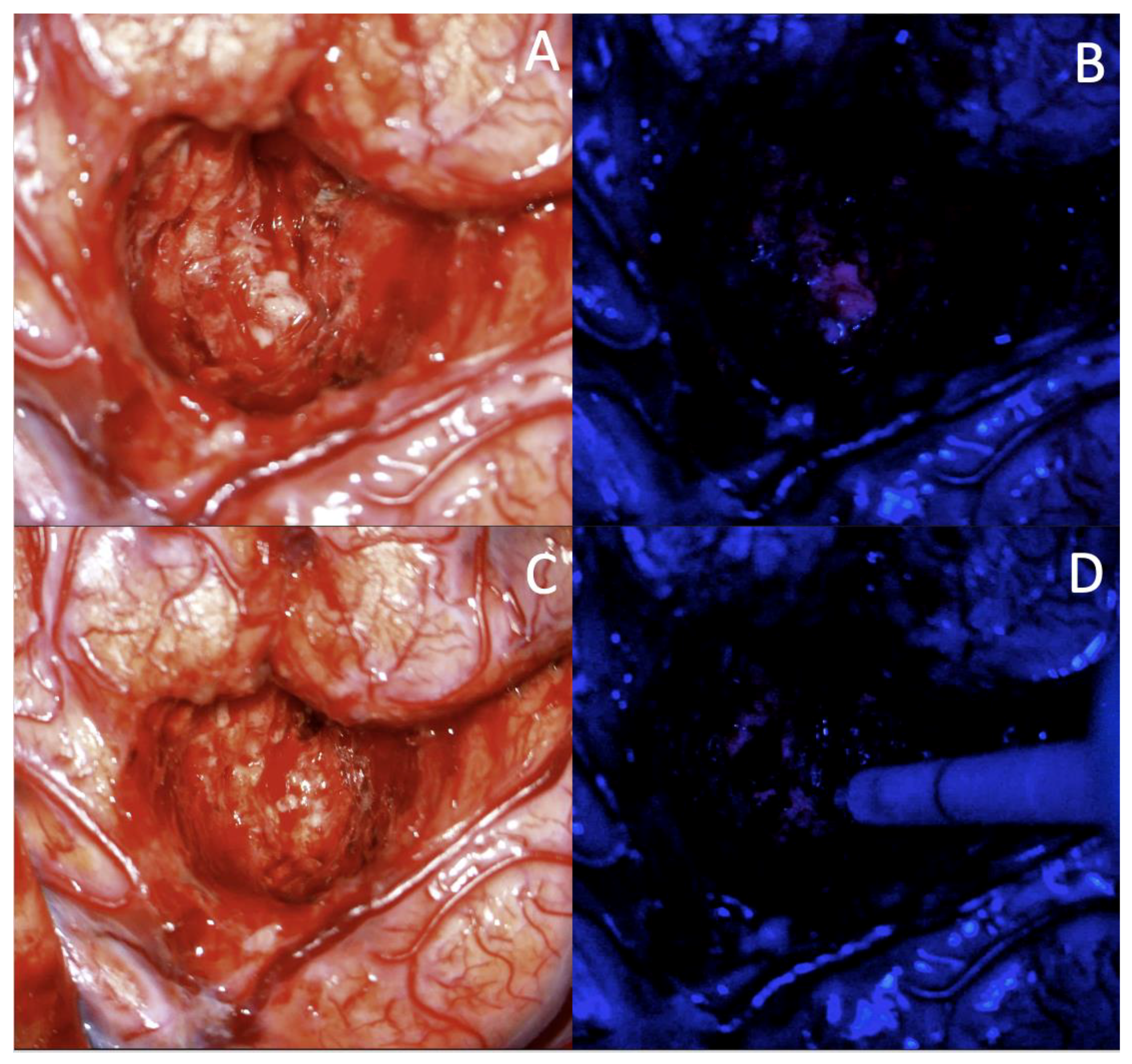
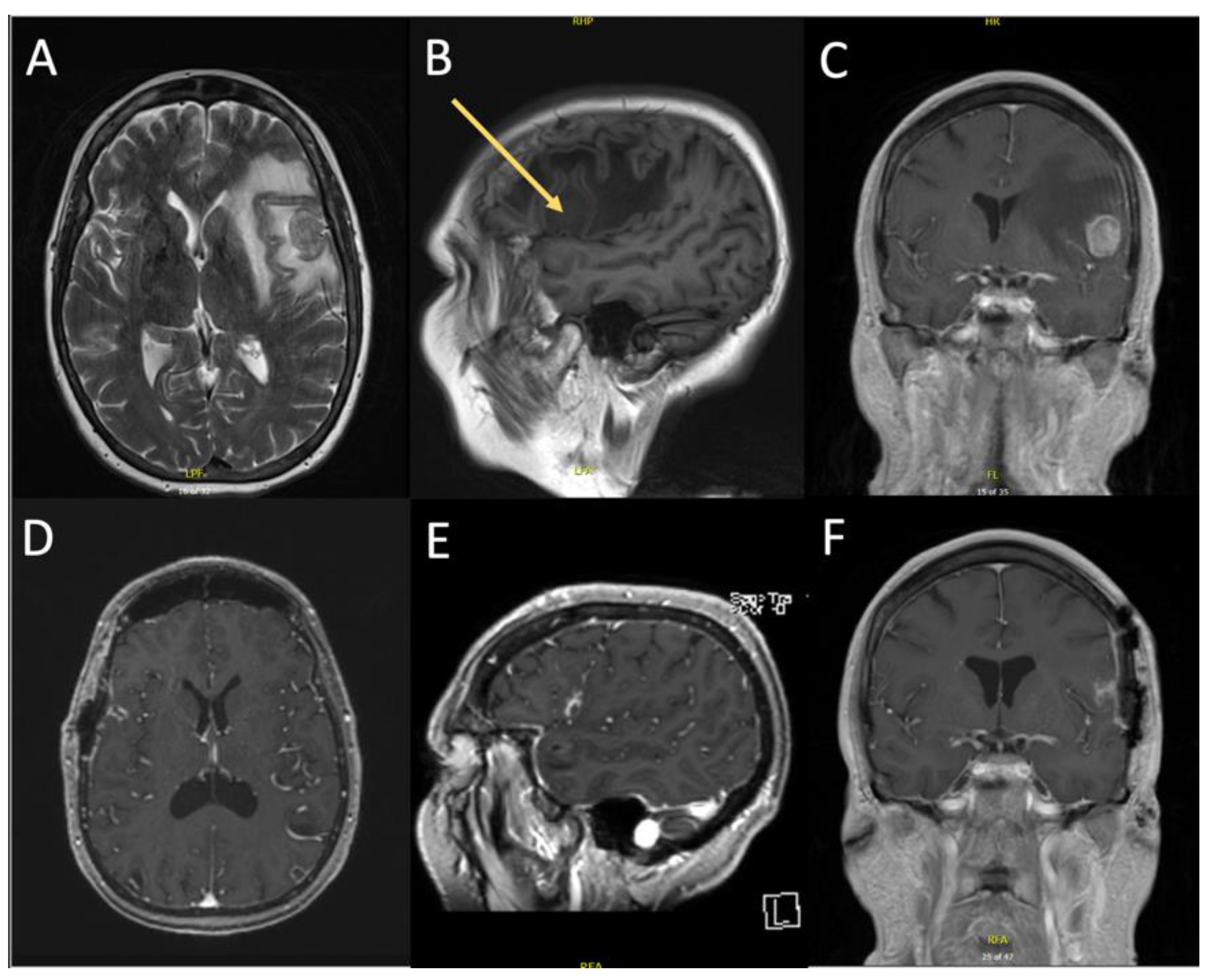
3.2.1. Case 1
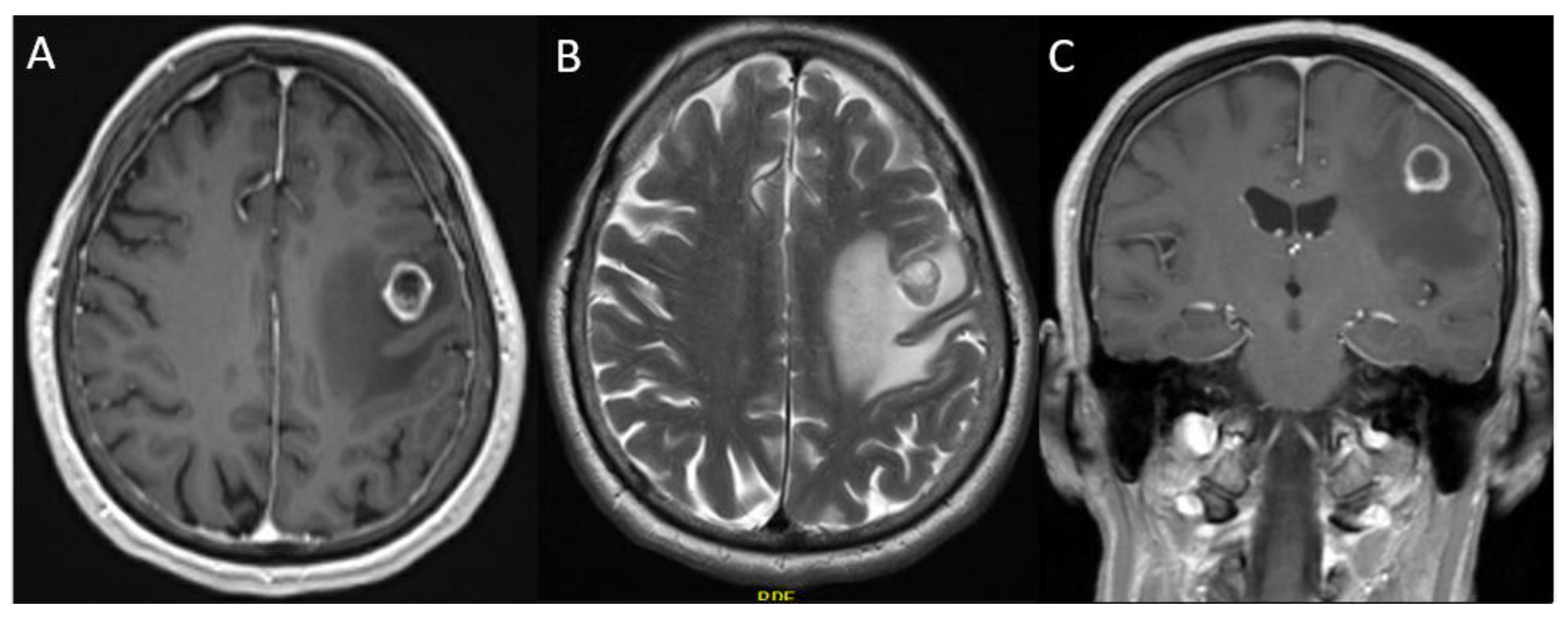
3.2.2. Case 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaşargil, M.G.; Kadri, P.A.; Yasargil, D.C. Microsurgery for malignant gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2004, 69, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadul, C.; Wood, J.; Thaler, H.; Galicich, J.; Patterson, R.H., Jr.; Posner, J.B. Morbidity and mortality of craniotomy for excision of supratentorial gliomas. Neurology 1988, 38, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, R.; Hammoud, M.; Schoppa, D.; Hess, K.R.; Wu, S.Z.; Shi, W.-M.; Wildrick, D.M. Neurosurgical Outcomes in a Modern Series of 400 Craniotomies for Treatment of Parenchymal Tumors. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Berger, M.S. Functional Outcome after Language Mapping for Glioma Resection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, O.R.; Joshi, S.H.; Piras, F.; Orfei, M.D.; Iorio, M.; Narr, K.L.; Shattuck, D.W.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G.; Di Paola, M. The superficial white matter in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.K.; Keehn, B.; Smylie, D.M.; Müller, R.A. Microstructural abnormalities of short-distance white matter tracts in autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Berger, M.S. Maximizing safe resection of low- and high-grade glioma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 130, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Berger, M.S. Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 753–764, discussion 264–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnt, D.; Becker, A.; Ganslandt, O.; Bauer, M.; Buchfelder, M.; Nimsky, C. Correlation of the extent of tumor volume resection and patient survival in surgery of glioblastoma multiforme with high-field intraoperative MRI guidance. Neuro-oncology 2011, 13, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.R.; Parney, I.F.; Huang, W.; Anderson, F.; Morris, A.M.; Asher, A.; Lillehei, K.O.; Bernstein, M.; Brem, H.; Sloan, A.; et al. Survival following surgery and prognostic factors for recently diagnosed malignant glioma: Data from the Glioma Outcomes Project. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, M.A.; Dibué, M.; Niemann, L.; Reichelt, D.C.; Felsberg, J.; Steiger, H.-J.; Szelényi, A.; Rapp, M.; Sabel, M. Proof of principle: Supramarginal resection of cerebral metastases in eloquent brain areas. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasanker, M.; Madhugiri, V.S.; Moiyadi, A.V.; Shetty, P.; Subi, T.S. Surgery for brain metastases: An analysis of outcomes and factors affecting survival. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 168, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendulkar, R.D.; Liu, S.W.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Toms, S.A.; Jin, T.; Suh, J.H. RPA classification has prognostic significance for surgically resected single brain metastasis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, S.M.; Schäffner, M.; Shiban, E.; Droese, D.; Obermüller, T.; Gempt, J.; Meyer, B.; Ringel, F. Reliability of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring using motor evoked potentials during resection of metastases in motor-eloquent brain regions: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2013, 118, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, G.; Scibilia, A.; Conti, A.; Ricciardo, G.; Rizzo, V.; Morelli, A.; Angileri, F.F.; Cardali, S.M.; Germanò, A. The role of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for surgery of motor-eloquent brain tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 180, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gelb, A.W. Awake craniotomy: Indications, benefits, and techniques. Colomb. J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 46, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, T.; Bernstein, M. Awake craniotomy for brain tumor: Indications, technique and benefits. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2014, 14, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Goerss, S.J.; Kall, B.A. The stereotaxic retractor in computer-assisted stereotaxic microsurgery. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 69, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinos, P.F.; Raza, S.M.; Jallo, G.I.; Recinos, V.R. Use of a minimally invasive tubular retraction system for deep-seated tumors in pediatric patients: Technical note. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. PED 2011, 7, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.M.; Recinos, P.F.; Avendano, J.; Adams, H.; Jallo, G.I.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. Minimally invasive trans-portal resection of deep intracranial lesions. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2011, 54, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.S.; Ojemann, G.A. Intraoperative brain mapping techniques in neuro-oncology. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1992, 58, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witt Hamer, P.C.; Robles, S.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Duffau, H.; Berger, M.S. Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, H.A.; Ojemann, G.A. Graded localisation of naming from electrical stimulation mapping of left cerebral cortex. Nature 1977, 270, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenco-Hillembrand, L.; Alvarado-Estrada, K.; Chaichana, K.L. Contemporary Surgical Management of Deep-Seated Metastatic Brain Tumors Using Minimally Invasive Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, A.G.; Thomas, S.G.; Babu, K.S.; Daniel, R.T.; Chacko, G.; Prabhu, K.; Cherian, V.; Korula, G. Awake craniotomy and electrophysiological mapping for eloquent area tumours. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Suki, D.; Weinberg, J.S.; Sawaya, R.; Lang, F.F.; Ferson, D.; Heimberger, A.B.; DeMonte, F.; Prabhu, S.S. Awake craniotomy for brain tumors near eloquent cortex: Correlation of intraoperative cortical mapping with neurological outcomes in 309 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 836–845, discussion 345–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhomme, V.; Franssen, C.; Hans, P. Awake craniotomy. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccioni, F.; Fanzio, M. Management of anesthesia in awake craniotomy. Minerva. Anestesiol. 2008, 74, 393–408. [Google Scholar]
- Balogun, J.A.; Khan, O.H.; Taylor, M.; Dirks, P.; Der, T.; Carter Snead Iii, O.; Weiss, S.; Ochi, A.; Drake, J.; Rutka, J.T. Pediatric awake craniotomy and intra-operative stimulation mapping. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossek, E.; Matot, I.; Shahar, T.; Barzilai, O.; Rapoport, Y.; Gonen, T.; Sela, G.; Korn, A.; Hayat, D.; Ram, Z. Failed awake craniotomy: A retrospective analysis in 424 patients undergoing craniotomy for brain tumor: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2013, 118, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milian, M.; Luerding, R.; Ploppa, A.; Decker, K.; Psaras, T.; Tatagiba, M.; Gharabaghi, A.; Feigl, G.C. “Imagine your neighbor mows the lawn”: A pilot study of psychological sequelae due to awake craniotomy: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2013, 118, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejrati, N.; Spieler, D.; Samuel, R.; Regli, L.; Weyerbrock, A.; Surbeck, W. Conscious Experience and Psychological Consequences of Awake Craniotomy. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, e381–e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, B.; Talacchi, A.; Casagrande, F.; Casartelli, M.; Savazzi, S.; Procaccio, F.; Gerosa, M. Eligibility Criteria and Psychological Profiles in Patient Candidates for Awake Craniotomy: A Pilot Study. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2012, 24, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşargil, M.G.; Cravens, G.F.; Roth, P. Surgical approaches to “inaccessible” brain tumors. Clin. Neurosurg. 1988, 34, 42–110. [Google Scholar]
- Schüz, A.; Braitenberg, V. The human cortical white matter: Quantitative aspects of cortico-cortical long-range connectivity. In Cortical Areas; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Catani, M.; Dell’acqua, F.; Vergani, F.; Malik, F.; Hodge, H.; Roy, P.; Valabregue, R.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M. Short frontal lobe connections of the human brain. Cortex 2012, 48, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuys, R.; Voogd, J.; van Huijzen, C. Long Association and Commissural Connections. In The Human Central Nervous System; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988; pp. 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, M.; Kang, H.; Detre, J.A.; Roberts, T.P.L.; Huang, H. Short-range connections in the developmental connectome during typical and atypical brain maturation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 83, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, M.; Robertsson, N.; Beyh, A.; Huynh, V.; de Santiago Requejo, F.; Howells, H.; Barrett, R.L.C.; Aiello, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Dyrby, T.B.; et al. Short parietal lobe connections of the human and monkey brain. Cortex 2017, 97, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedian Attar, F.; Kirilina, E.; Haenelt, D.; Pine, K.J.; Trampel, R.; Edwards, L.J.; Weiskopf, N. Mapping Short Association Fibers in the Early Cortical Visual Processing Stream Using In Vivo Diffusion Tractography. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 4496–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Yagmurlu, K.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; Karadag, A.; Ovalioglu, T.C.; Jagadeesan, B.; Sandhu, G.; Tanriover, N.; Grande, A.W. Microsurgical and Tractographic Anatomy of the Supplementary Motor Area Complex in Humans. World Neurosurg. 2016, 95, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; He, Y.; Concha, L.; Lebel, C.; Gross, D.W.; Evans, A.C.; Beaulieu, C. Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazeron, R.H.; Langdon, D.W.; Filippi, M.; van Waesberghe, J.H.; Stevenson, V.L.; Boringa, J.B.; Origgi, D.; Thompson, A.J.; Falautano, M.; Polman, C.H.; et al. Neuropsychological impairment in multiple sclerosis patients: The role of (juxta)cortical lesion on FLAIR. Mult. Scler. 2000, 6, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, A.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Felsky, D.; Lobaugh, N.J.; Rajji, T.K.; Mulsant, B.H.; Voineskos, A.N. Alterations of superficial white matter in schizophrenia and relationship to cognitive performance. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabre, A.; Patel, A. Transsulcal microsurgical approach for subcortical small brain lesions: Technical note. Surg. Neurol. 2006, 65, 312–313, discussion 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuni, N.; Hashimoto, N. A minimally invasive transsulcal approach to the paracentral inner lesion. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2006, 49, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Sola, R.; Pulido, P.; Kusak, E. Trans-fissural or trans-sulcal approach versus combined stereotactic-microsurgical approach. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 1991, 52, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, A.M.; Elkholy, A.R.; Shamhoot, E.A. Trans-sulcal or fissure approach for supratentorial brain lesions: Evaluation. Egypt. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 34, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. Hodotopy, neuroplasticity and diffuse gliomas. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.H.A.; Sylvester, P.T.; Kulwin, C.; Shah, M.V.; Somasundaram, A.; Kamath, A.A.; Beaumont, T.L.; Rich, K.M.; Chicoine, M.R. Initial Experience Using Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging During a Trans-Sulcal Tubular Retractor Approach for the Resection of Deep-Seated Brain Tumors: A Case Series. Oper. Neurosurg. (Hagerstown) 2019, 16, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Echeverry, N.; Shapiro, S.; Snelling, B. The Use of BrainPath Tubular Retractors in the Management of Deep Brain Lesions: A Review of Current Studies. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.D. Transsulcal Parafascicular Surgery Using Brain Path® for Subcortical Lesions. Neurosurgery 2017, 64, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schödel, P.; Schebesch, K.-M.; Brawanski, A.; Proescholdt, M.A. Surgical Resection of Brain Metastases—Impact on Neurological Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8708–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogne, S.G.; Rønning, P.; Helseth, E.; Johannesen, T.B.; Langberg, C.W.; Lote, K.; Scheie, D.; Meling, T.R. Craniotomy for brain metastases: A consecutive series of 316 patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, P.; Xia, L.; Sun, C. Risk factors of neurosurgical site infection after craniotomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2017, 45, e123–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hamdeh, S.; Lytsy, B.; Ronne-Engström, E. Surgical site infections in standard neurosurgery procedures- a study of incidence, impact and potential risk factors. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 28, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipmann, S.; Akalin, E.; Doods, J.; Ewelt, C.; Stummer, W.; Suero Molina, E. When the Infection Hits the Wound: Matched Case-Control Study in a Neurosurgical Patient Collective Including Systematic Literature Review and Risk Factors Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2016, 95, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshian, J.; Strickland, B.A.; Jackson, C.; Chaichana, K.L.; Young, R.; Pradilla, G.; Chen, J.W.; Bailes, J.; Zada, G. Multicenter Investigation of Channel-Based Subcortical Trans-Sulcal Exoscopic Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Retrospective Case Series. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 16, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.R.; Lall, R.R.; Graham, R.B.; McClendon, J., Jr.; Lall, R.R.; Nanney, A.D.; Adel, J.G.; Zakarija, A.; Chandler, J.P. Venous thromboembolism in high grade glioma among surgical patients: Results from a single center over a 10 year period. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Scelzi, E.; Salmistraro, G.; Ermani, M.; Carollo, C.; Berti, F.; Zampieri, P.; Baiocchi, C.; Fiorentino, M.V. Incidence and risk of thromboembolism during treatment of high-grade gliomas: A prospective study. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, L.C.; Geerts, W.H.; Perry, J.R. The risk of venous thromboembolism is increased throughout the course of malignant glioma. Cancer 2000, 89, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.G.; Hull, R.D.; Pineo, G.F. Venous Thromboembolism in Neurosurgery and Neurology Patients: A Review. Neurosurgery 1994, 34, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Bakhsheshian, J.; Strickland, B.; Rennert, R.C.; Chu, R.M.; Chaichana, K.L.; Zada, G. Exoscopic resection of atrial intraventricular meningiomas using a navigation-assisted channel-based trans-sulcal approach: Case series and literature review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 71, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy-Sosa, A.; Navarro-Fernández, J.O.; Chakravarthi, S.S.; Rodríguez-Orozco, J.; Rovin, R.; de la Garza, J.; Kassam, A. Minimally invasive trans-sulcal parafascicular surgical resection of cerebral tumors: Translating anatomy to early clinical experience. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Berger, M.S. Role of Surgical Resection in Low- and High-Grade Gliomas. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2014, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassie, K.; Wijesekera, O.; Chaichana, K.L. Minimally invasive tubular retractor-assisted biopsy and resection of subcortical intra-axial gliomas and other neoplasms. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 62, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, R.; Chaichana, K.L. Minimally Invasive Resection of Deep-seated High-grade Gliomas Using Tubular Retractors and Exoscopic Visualization. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2018, 79, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liang, T.; Zhang, C.; Cai, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Qiu, X.; Yao, K.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; et al. Clinicopathological factors predictive of postoperative seizures in patients with gliomas. Seizure 2016, 35, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skardelly, M.; Brendle, E.; Noell, S.; Behling, F.; Wuttke, T.V.; Schittenhelm, J.; Bisdas, S.; Meisner, C.; Rona, S.; Tatagiba, M.S.; et al. Predictors of preoperative and early postoperative seizures in patients with intra-axial primary and metastatic brain tumors: A retrospective observational single center study. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.H.; Morshed, R.A.; Chung, J.; Millares Chavez, M.A.; Sudhakar, V.; Saggi, S.; Avalos, L.N.; Gallagher, A.; Young, J.S.; Daras, M.; et al. Factors associated with preoperative and postoperative seizures in patients undergoing resection of brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dorzi, H.M.; Alruwaita, A.A.; Marae, B.O.; Alraddadi, B.S.; Tamim, H.M.; Ferayan, A.; Arabi, Y.M. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of seizures occurring after craniotomy for primary brain tumor resection. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2017, 22, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuchi, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; Sakaida, T. Epilepsy in patients with gliomas: Incidence and control of seizures. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijlen, J.M.; Teernstra, O.P.; Kessels, A.G.; Herpers, M.J.; Beuls, E.A. Effectiveness of antiepileptic prophylaxis used with supratentorial craniotomies: A meta-analysis. Seizure 1996, 5, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Dujovny, M.; Perlin, A.R.; Perez-Arjona, E.; Park, H.K.; Diaz, F.G. Brain retraction injury. Neurol. Res. 2003, 25, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.J.; Bringas, J.R. A review of brain retraction and recommendations for minimizing intraoperative brain injury. Neurosurgery 1993, 33, 1052–1063, discussion 1063–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.R.; Shin, J.H.; Chan, M.; Kouloumberis, P.; Goellner, E.; Slavin, K.V. Use of transparent plastic tubular retractor in surgery for deep brain lesions: A case series. Surg. Technol. Int. 2010, 19, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro Olvera, J. Management of Brain Tumors in Eloquent Areas with Awake Patient; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Weston, S.D.; Chang, E.F.; Gelb, A.W. Awake craniotomy in a patient with ejection fraction of 10%: Considerations of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular physiology. J. Clin. Anesth. 2015, 27, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, E.; Abdelghany, M.S.; Abdelkhalek, H.; Elatrozy, H.I.S. Awake surgery for lesions near eloquent brain under scalp block and clinical monitoring: Experience of single center with limited resources. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2021, 57, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spena, G.; Nava, A.; Cassini, F.; Pepoli, A.; Bruno, M.; D’Agata, F.; Cauda, F.; Sacco, K.; Duca, S.; Barletta, L.; et al. Preoperative and intraoperative brain mapping for the resection of eloquent-area tumors. A prospective analysis of methodology, correlation, and usefulness based on clinical outcomes. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; Pichlmeier, U.; Meinel, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Zanella, F.; Reulen, H.J. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Dong, X.; Shi, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Teng, L.; Han, D.; et al. Intraoperative fluorescence-guided resection of high-grade malignant gliomas using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrins: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Puppa, A.; De Pellegrin, S.; d’Avella, E.; Gioffrè, G.; Rossetto, M.; Gerardi, A.; Lombardi, G.; Manara, R.; Munari, M.; Saladini, M.; et al. 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) fluorescence guided surgery of high-grade gliomas in eloquent areas assisted by functional mapping. Our experience and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2013, 155, 965–972, discussion 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucholz, R.D.; Yeh, D.D.; Trobaugh, J.; McDurmont, L.L.; Sturm, C.D.; Baumann, C.; Henderson, J.M.; Levy, A.; Kessman, P. The Correction of Stereotactic Inaccuracy Caused by Brain Shift Using an Intraoperative Ultrasound Device; Spring: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Prada, F.; Del Bene, M.; Mattei, L.; Lodigiani, L.; DeBeni, S.; Kolev, V.; Vetrano, I.; Solbiati, L.; Sakas, G.; DiMeco, F. Preoperative magnetic resonance and intraoperative ultrasound fusion imaging for real-time neuronavigation in brain tumor surgery. Ultraschall Med. 2015, 36, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdoğan, N.; Tucer, B.; Mavili, E.; Menkü, A.; Kurtsoy, A. Ultrasound guidance in intracranial tumor resection: Correlation with postoperative magnetic resonance findings. Acta Radiol. 2005, 46, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorward, N.L.; Alberti, O.; Velani, B.; Gerritsen, F.A.; Harkness, W.F.; Kitchen, N.D.; Thomas, D.G. Postimaging brain distortion: Magnitude, correlates, and impact on neuronavigation. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnt, D.; Bauer, M.H.; Becker, A.; Merhof, D.; Zolal, A.; Richter, M.; Grummich, P.; Ganslandt, O.; Buchfelder, M.; Nimsky, C. Intraoperative visualization of fiber tracking based reconstruction of language pathways in glioma surgery. Neurosurgery 2012, 70, 911–919, discussion 919–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latini, F.; Ryttlefors, M. Rethinking the standard trans-cortical approaches in the light of superficial white matter anatomy. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Miranda, J.C.; Rhoton, A.L., Jr.; Alvarez-Linera, J.; Kakizawa, Y.; Choi, C.; de Oliveira, E.P. Three-dimensional microsurgical and tractographic anatomy of the white matter of the human brain. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 989–1026, discussion 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Number | Age | Diagnosis | Comprehensive Preoperative Neurological Examination | Comprehensive Postoperative Neurological Examination | Length of Stay | Postoperative Complications | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | M | S | Sp | C | M | S | Sp | |||||
| 1 | 68 | GBM | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | 4 days | No |
| 2 | 67 | GBM | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 8 days | No |
| 3 | 76 | GBM | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | 5 days | Subdural hematoma, DVT |
| 4 | 52 | Lung Adenocarcinoma | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 2 days | DVT |
| 5 | 75 | GBM | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | 5 days | Seizures, DVT |
| 6 | 46 | GBM | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | 2 days | No |
| 7 | 57 | GBM | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 4 days | Seizures |
| 8 | 56 | GBM | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | 5 days | Seizures, Subdural hematoma |
| 9 | 30 | Diffuse Astrocytoma (WHO 2) | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | 3 days | No |
| 10 | 70 | Anaplastic Astrocytoma (WHO 3) | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | 3 days | No |
| 11 | 64 | GBM | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | 3 days | No |
| 12 | 65 | GBM | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 3 days | No |
| 13 | 61 | GBM | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | 3 days | Seizures |
| 14 | 59 | Lung Adenocarcinoma | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 3 days | No |
| 15 | 61 | Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | 5 days | Seizures |
| 16 | 73 | Colon Adenocarcinoma | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | 4 days | Seizures |
| 17 | 61 | GBM | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y* | N | N | 2 days | No |
| Patient Demographics. | N (Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Total subjects Gender | 17 |
| Males | 10 (58.8%) |
| Females | 7 (41.2%) |
| Age | |
| Range | 21–76 |
| Average | 61.2 |
| Lesion Location | |
| Left Precentral gyrus | 3 (17.6%) |
| Right Precentral gyrus | 4 (23.5%) |
| Left Postcentral gyrus | 1 (5.9%) |
| Left Frontal Speech Area | 2 (11.8%) |
| Left Posterior Speech Area | 5 (29.4%) |
| Left Visual Cortex | 1 (5.9%) |
| Primary CNS Lesion | |
| Grade 4 Glioblastoma | 11 (64.7%) |
| Grade 3 Astrocytoma | 1 (5.9%) |
| Grade 2 Diffuse Astrocytoma | 1 (5.9%) |
| Total Primary CNS lesions | 13 (76.5 %) |
| Metastatic Lesion | |
| Small Cell Lung Cancer | 1 (5.9%) |
| Lung Adenocarcinoma | 2 (11.8%) |
| Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | 1 (5.9%) |
| Total Metastatic Lesions | 4 (23.5%) |
| Preoperative Deficits (N, Number; Percentage) | Postoperative Deficits (N, Number: Percentage) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive | 4 (23.5%) | 1 (5.8%) |
| Speech | 12 (70.6%) | 1 (5.8%) |
| Motor | 9 (52.9%) | 3 (17.6%) |
| Sensory | 5 (29.4%) | 1 (5.8%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaye, B.; Correa Bastianon Santiago, R.A.; MacKinnon, G.; Dabecco, R.; Ibrahim, B.; Ali, A.; Santos, R.; Johansen, P.; Ranjan, S.; Obrzut, M.; et al. Wide Dissection Trans-Sulcal Approach for Resection of Deep Intra-Axial Lesions in Eloquent Brain Areas. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7396-7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100581
Kaye B, Correa Bastianon Santiago RA, MacKinnon G, Dabecco R, Ibrahim B, Ali A, Santos R, Johansen P, Ranjan S, Obrzut M, et al. Wide Dissection Trans-Sulcal Approach for Resection of Deep Intra-Axial Lesions in Eloquent Brain Areas. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7396-7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100581
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaye, Brandon, Raphael Augusto Correa Bastianon Santiago, Gerard MacKinnon, Rocco Dabecco, Bilal Ibrahim, Assad Ali, Romel Santos, Phillip Johansen, Surabhi Ranjan, Michal Obrzut, and et al. 2022. "Wide Dissection Trans-Sulcal Approach for Resection of Deep Intra-Axial Lesions in Eloquent Brain Areas" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7396-7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100581
APA StyleKaye, B., Correa Bastianon Santiago, R. A., MacKinnon, G., Dabecco, R., Ibrahim, B., Ali, A., Santos, R., Johansen, P., Ranjan, S., Obrzut, M., Borghei-Razavi, H., & Adada, B. (2022). Wide Dissection Trans-Sulcal Approach for Resection of Deep Intra-Axial Lesions in Eloquent Brain Areas. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7396-7410. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100581





