A Canadian Perspective on the Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Initiation of Treatment
3. Treatment Options for Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
3.1. Chemoimmunotherapy (CIT)
3.2. Proteasome Inhibitor-Based Therapy
3.3. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitors
3.4. Stem Cell Transplantation
3.5. Other Novel Therapies under Investigation
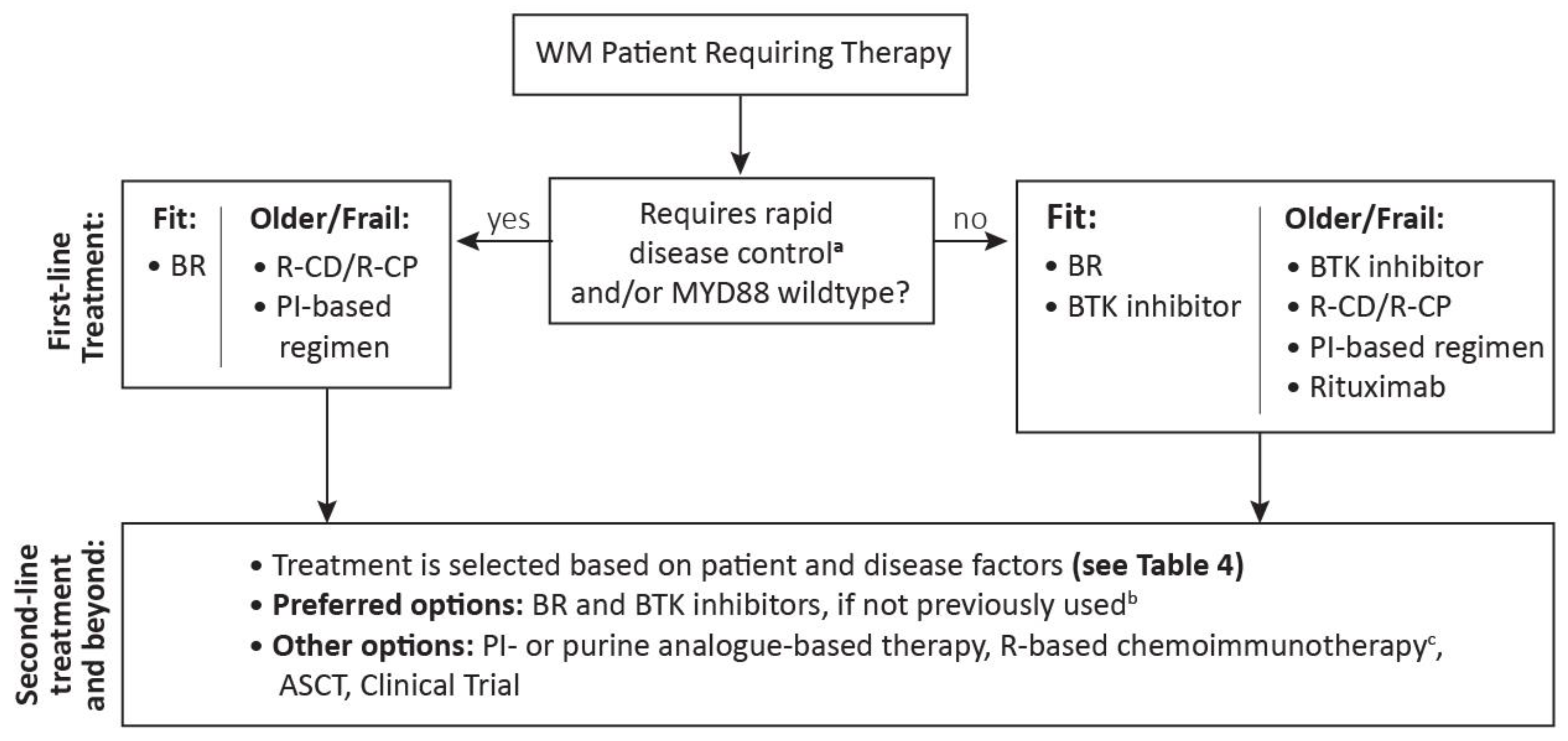
4. Canadian Perspective on Treatment Selection
4.1. Treatment Selection in First Line
4.2. Treatment Selection by MYD88 and CXCR4 Mutation Status
4.3. Management of Patients with Elevated IgM Levels
4.4. Treatment Selection for Disease-Related Complications
4.5. Treatment Selection for Relapsed Disease
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Facts. Available online: https://www.lls.org/sites/default/files/file_assets/waldenstrommacroglobulinemia.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulienmia Foundation of Canada. Newly Diagnosed. Available online: https://www.wmfc.ca/about-wm/newly-diagnosed/#:~:text=WM%20is%20a%20very%20rare%20cancer.,approximately%201500%20patients%20in%20total (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Morel, P.; Duhamel, A.; Gobbi, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; McCoy, J.; Crowley, J.; Ocio, E.M.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Treon, S.P.; et al. International prognostic scoring system for Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2009, 113, 4163–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastritis, E.; Morel, P.; Duhamel, A.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Kyrtsonis, M.C.; Durot, E.; Symeonidis, A.; Laribi, K.; Hatjiharissi, E.; Ysebaert, L.; et al. A revised international prognostic score system for Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Olszewski, A.J.; Cronin, A.M.; Hunter, Z.R.; Treon, S.P. Survival trends in Waldenström macroglobulinemia: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Blood 2014, 123, 3999–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Olszewski, A.J.; Kanan, S.; Meid, K.; Hunter, Z.R.; Treon, S.P. Overall survival and competing risks of death in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinaemia: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Waldenström Macroglobulinemia/Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma, Version 2.2022. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/waldenstroms.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Cingam, S.; Sidana, S. Differential Diagnosis of Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia and Early Management: Perspectives from Clinical Practice. Blood Lymphat. Cancer Targets Ther. 2022, 12, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Leblond, V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kimby, E.; Staber, P.; Kersten, M.J.; Tedeschi, A.; Buske, C. Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv41–iv50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, N.; Ocio, E.M.; Jiménez, C.; Paiva, B.; Miguel, J.F.S.; García-Sanz, R. Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia Immunophenotype. In Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia; Leblond, V., Treon, S., Dimoploulos, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Poulain, S.; Roumier, C.; Decambron, A.; Renneville, A.; Herbaux, C.; Bertrand, E.; Tricot, S.; Daudignon, A.; Galiègue-Zouitina, S.; Soenen, V.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4504–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varettoni, M.; Arcaini, L.; Zibellini, S.; Boveri, E.; Rattotti, S.; Riboni, R.; Corso, A.; Orlandi, E.; Bonfichi, M.; Gotti, M.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of the MYD88 (L265P) somatic mutation in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia and related lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2013, 121, 2522–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hunter, Z.R.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Morra, E.; Trojani, A.; Greco, A.; Arcaini, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P in Waldenström macroglobulinemia, immunoglobulin M monoclonal gammopathy, and other B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders using conventional and quantitative allele-specific polymerase chain reaction. Blood 2013, 121, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Gustine, J.; Xu, L.; Manning, R.J.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.; Meid, K.; Guerrera, M.L.; Munshi, M.; Chan, G.; et al. MYD88 wild-type Waldenstrom Macroglobulinaemia: Differential diagnosis, risk of histological transformation, and overall survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Hunter, Z.R.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Cao, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Kanan, S.; Castillo, J.J.; Tai, Y.-T.; et al. Clonal architecture of CXCR4WHIM-like mutations in Waldenström Macroglobulinaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treon, S.P.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Hunter, Z.R. Somatic mutations in MYD88 and CXCR4 are determinants of clinical presentation and overall survival in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pophali, P.A.; Bartley, A.; Kapoor, P.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Ashrani, A.A.; Marshall, A.L.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Go, R.S. Prevalence and survival of smouldering Waldenström macroglobulinaemia in the United States. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, P.G.; Baldini, L.; Broglia, C.; Goldaniga, M.; Comelli, M.; Morel, P.; Morra, E.; Cortelazzo, S.; Bettini, R.; Merlini, G. Prognostic Validation of the International Classification of Immunoglobulin M Gammopathies: A Survival Advantage for Patients with Immunoglobulin M Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance? Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Benson, J.T.; Larson, D.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kumar, S.; Melton, L.J.; Rajkumar, S.V. Progression in smoldering Waldenström macroglobulinemia: Long-term results. Blood 2012, 119, 4462–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustoros, M.; Sklavenitis-Pistofidis, R.; Kapoor, P.; Liu, C.-J.; Kastritis, E.; Zanwar, S.; Fell, G.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Hornburg, K.; Neuse, C.J.; et al. Progression Risk Stratification of Asymptomatic Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paba-Prada, C.E.; Banwait, R.; Treon, S.; Ghobrial, I.M. Incidence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Patients At Diagnosis. Blood 2011, 118, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.J.; Pascual, V. Pathophysiology of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Haematologica 2010, 95, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, M.J.; Niederle, N.; Maschmeyer, G.; Banat, G.A.; von Grünhagen, U.; Losem, C.; Kofahl-Krause, D.; Heil, G.; Welslau, M.; Balser, C.; et al. Bendamustine plus rituximab versus CHOP plus rituximab as first-line treatment for patients with indolent and mantle-cell lymphomas: An open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, M.J.; Lerchenmüller, C.; Hensel, M.; Goerner, M.; Buske, C.; Schulz, H.; Schmidt, B.; Kojouharoff, G.; Lange, E.; Willenbacher, W.; et al. Two Years Rituximab Maintenance Vs. Observation after First Line Treatment with Bendamustine Plus Rituximab (B-R) in Patients with Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia (MW): Results of a Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Phase 3 Study (the StiL NHL7-2008 MAINTAIN trial). Blood 2019, 134, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi, A.; Picardi, P.; Ferrero, S.; Benevolo, G.; Margiotta Casaluci, G.; Varettoni, M.; Baratè, C.; Motta, M.; Gini, G.; Goldaniga, M.C.; et al. Bendamustine and rituximab combination is safe and effective as salvage regimen in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Hanzis, C.; Tripsas, C.; Ioakimidis, L.; Patterson, C.J.; Manning, R.J.; Sheehy, P. Bendamustine therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011, 11, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Roussou, M.; Hadjiharissi, E.; Symeonidis, A.; Repoussis, P.; Michalis, E.; Delimpasi, S.; Tsatalas, K.; et al. Dexamethasone, rituximab, and cyclophosphamide as primary treatment of Waldenström macroglobulinemia: Final analysis of a phase 2 study. Blood 2015, 126, 1392–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Zervas, K.; Tsatalas, C.; Kokkinis, G.; Repoussis, P.; Symeonidis, A.; Delimpasi, S.; Katodritou, E.; et al. Primary Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia With Dexamethasone, Rituximab, and Cyclophosphamide. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Gustine, J.N.; Meid, K.; Dubeau, T.E.; Severns, P.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Hunter, Z.R.; Treon, S.P. Response and survival for primary therapy combination regimens and maintenance rituximab in Waldenström macroglobulinaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludo, J.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Shreders, A.; Ansell, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Ailawadhi, S.; King, R.L.; Koehler, A.B.; Reeder, C.B.; Buadi, F.K.; et al. Bendamustine and rituximab (BR) versus dexamethasone, rituximab, and cyclophosphamide (DRC) in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, V.; Johnson, S.; Chevret, S.; Copplestone, A.; Rule, S.; Tournilhac, O.; Seymour, J.F.; Patmore, R.D.; Wright, D.; Morel, P.; et al. Results of a randomized trial of chlorambucil versus fludarabine for patients with untreated Waldenström macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma, or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, D.; Andreola, G.; Rigacci, L.; Fabbri, A.; Rabascio, C.; Mancuso, P.; Pruneri, G.; Radice, D.; Pinto, A.; Frigeri, F.; et al. Rituximab and subcutaneous 2-chloro-2’-deoxyadenosine combination treatment for patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: Clinical and biologic results of a phase II multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Branagan, A.R.; Ioakimidis, L.; Soumerai, J.D.; Patterson, C.J.; Turnbull, B.; Wasi, P.; Emmanouilides, C.; Frankel, S.R.; Lister, A.; et al. Long-term outcomes to fludarabine and rituximab in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2009, 113, 3673–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Souchet, L.; Levy, V.; Ouzegdouh, M.; Tamburini, J.; Delmer, A.; Dupuis, J.; Le Gouill, S.; Pégourié-Bandelier, B.; Tournilhac, O.; Boubaya, M.; et al. Efficacy and long-term toxicity of the rituximab-fludarabine-cyclophosphamide combination therapy in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, A.; Benevolo, G.; Varettoni, M.; Battista, M.L.; Zinzani, P.L.; Visco, C.; Meneghini, V.; Pioltelli, P.; Sacchi, S.; Ricci, F.; et al. Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide and rituximab in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: An effective but myelosuppressive regimen to be offered to patients with advanced disease. Cancer 2012, 118, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakimidis, L.; Patterson, C.J.; Hunter, Z.R.; Soumerai, J.D.; Manning, R.J.; Turnbull, B.; Sheehy, P.; Treon, S.P. Comparative outcomes following CP-R, CVP-R, and CHOP-R in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2009, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, M.A.; Rue, M.; Blood, E.; Kaminer, L.S.; Vesole, D.H.; Greipp, P.R. Multicenter Phase 2 Trial of Rituximab for Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM): An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study (E3A98). Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lozano, A.; Morales-Gonzalez, A.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Cristi-Montero, C.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Martínez-López, J.; Garatachea, N.; Lucia, A. Response rate to the treatment of Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A meta-analysis of the results of clinical trials. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 105, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Trotman, J.; García-Sanz, R.; Macdonald, D.; Leblond, V.; Mahe, B.; Herbaux, C.; Matous, J.V.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Rituximab Versus Placebo Plus Rituximab for Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: Final Analysis From the Randomized Phase III iNNOVATE Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Zervas, C.; Zomas, A.; Kiamouris, C.; Viniou, N.A.; Grigoraki, V.; Karkantaris, C.; Mitsouli, C.; Gika, D.; Christakis, J.; et al. Treatment of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia with rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2327–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Fonseca, R.; Greipp, P.R.; Blood, E.; Rue, M.; Vesole, D.H.; Gertz, M.A. Initial immunoglobulin M flare after rituximab therapy in patients diagnosed with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Cancer 2004, 101, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitzsch, E.; Passerini, V.; Khatamzas, E.; Strobl, C.D.; Muenchhoff, M.; Scherer, C.; Osterman, A.; Heide, M.; Reischer, A.; Subklewe, M.; et al. COVID-19 in Patients Receiving CD20-depleting Immunochemotherapy for B-cell Lymphoma. Hemasphere 2021, 5, e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.I.; Kouroukis, C.T.; White, D.; Voralia, M.; Stadtmauer, E.; Stewart, A.K.; Wright, J.J.; Powers, J.; Walsh, W.; Eisenhauer, E. Bortezomib Is Active in Patients With Untreated or Relapsed Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: A Phase II Study of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Hunter, Z.R.; Matous, J.; Joyce, R.M.; Mannion, B.; Advani, R.; Cook, D.; Songer, J.; Hill, J.; Kaden, B.R.; et al. Multicenter Clinical Trial of Bortezomib in Relapsed/Refractory Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia: Results of WMCTG Trial 03-248. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3320–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Hong, F.; Padmanabhan, S.; Badros, A.; Rourke, M.; Leduc, R.; Chuma, S.; Kunsman, J.; Warren, D.; Harris, B.; et al. Phase II Trial of Weekly Bortezomib in Combination With Rituximab in Relapsed or Relapsed and Refractory Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Pylypenko, H.; Grosicki, S.; Karamanesht, I.; Leleu, X.; Grishunina, M.; Rekhtman, G.; Masliak, Z.; Robak, T.; Shubina, A.; et al. Subcutaneous versus intravenous administration of bortezomib in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma: A randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Padmanabhan, S.; Badros, A.Z.; Leduc, R.; Rourke, M.; Chuma, S.; Kunsman, J.; Warren, D.; Harris, B.; Sam, A.; et al. Phase II Trial of Weekly Bortezomib in Combination with Rituximab in Untreated Patients with Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Blood 2009, 114, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Grunenberg, A.; Kastritis, E.; Tomowiak, C.; Mahé, B.; Troussard, X.; Hajek, R.; Viardot, A.; Tournilhac, O.; et al. Bortezomib in Combination with Dexamethasone, Rituximab and Cyclophosphamide (B-DRC) As First-Line Treatment of Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia: Results of a Prospectively Randomized Multicenter European Phase II Trial. Blood 2020, 136, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; García-Sanz, R.; Kastritis, E.; Morel, P.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Michalis, E.; Kartasis, Z.; Leleu, X.; Palladini, G.; Tedeschi, A.; et al. BDR in newly diagnosed patients with WM: Final analysis of a phase 2 study after a minimum follow-up of 6 years. Blood 2017, 129, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Ioakimidis, L.; Soumerai, J.D.; Patterson, C.J.; Sheehy, P.; Nelson, M.; Willen, M.; Matous, J.; Mattern, J.; Diener, J.G.; et al. Primary Therapy of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia With Bortezomib, Dexamethasone, and Rituximab: WMCTG Clinical Trial 05-180. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3830–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meid, K.; Dubeau, T.; Severns, P.; Gustine, J.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Castillo, J.J.; Treon, S.P. Long-Term Follow-up of a Prospective Clinical Trial of Carfilzomib, Rituximab and Dexamethasone (CaRD) in Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Blood 2017, 130, 2772. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, J.J.; Meid, K.; Flynn, C.A.; Chen, J.; Demos, M.G.; Guerrera, M.L.; Kofides, A.; Liu, X.; Munshi, M.; Tsakmaklis, N.; et al. Ixazomib, dexamethasone, and rituximab in treatment-naive patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: Long-term follow-up. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3952–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, M.J.; Minnema, M.C.; Vos, J.M.; Nasserinejad, K.; Kap, M.; Kastritis, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Deeren, D.; Tick, L.W.; et al. Ixazomib, Rituximab and Dexamethasone (IRD) in Patients with Relapsed or Progressive Waldenstrom’s Macroblobulinemia: Results of the Prospective Phase I/II HOVON 124/Ecwm-R2 Trial. Blood 2019, 134, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; García-Sanz, R.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Morel, P.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Michalis, E.; Kartasis, Z.; Leleu, X.; Palladini, G.; Tedeschi, A.; et al. Primary therapy of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) with weekly bortezomib, low-dose dexamethasone, and rituximab (BDR): Long-term results of a phase 2 study of the European Myeloma Network (EMN). Blood 2013, 122, 3276–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, R.L.; Owen, R.G.; D’Sa, S.; Pratt, G.; Popova, B.; Clifton Hadley, L.; Schofield, O.; Counsell, N.; Smith, P. R2W: Subcutaneous Bortezomib, Cyclophosphamide and Rituximab (BCR) Versus Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide and Rituximab (FCR) for Initial Therapy of WaldenstrőM’s Macroglobulinemia: A Randomised Phase II Study. Blood 2016, 128, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Gustine, J.; Meid, K.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Demos, M.; Kofides, A.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Chen, J.G.; et al. Ibrutinib Monotherapy in Symptomatic, Treatment-Naïve Patients With Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Meid, K.; Gustine, J.N.; Leventoff, C.; White, T.; Flynn, C.A.; Sarosiek, S.; Demos, M.G.; Guerrera, M.L.; Kofides, A.; et al. Long-term follow-up of ibrutinib monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Trotman, J.; García-Sanz, R.; Macdonald, D.; Leblond, V.; Mahe, B.; Herbaux, C.; Tam, C.; Orsucci, L.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Ibrutinib plus Rituximab in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Sivina, M.; Jain, N.; Kim, E.; Kadia, T.; Estrov, Z.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.M.; Huang, X.; Jorgensen, J.; Li, J.; et al. Randomized trial of ibrutinib vs ibrutinib plus rituximab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Meid, K.; Gustine, J.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Patterson, C.J.; Hunter, Z.R.; Branagan, A.R.; Laubach, J.P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Ibrutinib Monotherapy in Symptomatic, Previously Treated Patients with Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treon, S.P.; Tripsas, C.K.; Meid, K.; Warren, D.; Varma, G.; Green, R.; Argyropoulos, K.V.; Yang, G.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, J.; Buske, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Matous, J.V.; Macdonald, D.; Tam, C.S.; Tournilhac, O.; Ma, S.; Treon, S.P.; Oriol, A.; et al. Single-Agent Ibrutinib for Rituximab-Refractory Waldenström Macroglobulinemia: Final Analysis of the Substudy of the Phase III InnovateTM Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5793–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Gottlieb, D.; Simpson, D.; Marlton, P.; Cull, G.; Munoz, J.; Tedeschi, A.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: 3 years of follow-up. Blood 2020, 136, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.L.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Jurczak, W.; Lee, H.-P.; Cull, G.; Owen, R.G.; Marlton, P.; Wahlin, B.E.; et al. ASPEN: Long-term follow-up results of a phase 3 randomized trial of zanubrutinib (ZANU) versus ibrutinib (IBR) in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Jurczak, W.; Lee, H.-P.; Cull, G.; Owen, R.G.; Marlton, P.; Wahlin, B.E.; Sanz, R.G.; et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: The ASPEN study. Blood 2020, 136, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.G.; McCarthy, H.; Rule, S.; D’Sa, S.; Thomas, S.K.; Tournilhac, O.; Forconi, F.; Kersten, M.J.; Zinzani, P.L.; Iyengar, S.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e112–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, N.; Rai, S.; Munakata, W.; Suzuki, K.; Handa, H.; Shibayama, H.; Endo, T.; Terui, Y.; Iwaki, N.; Fukuhara, N.; et al. A multicenter, open-label, phase II study of tirabrutinib (ONO/GS-4059) in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3327–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Burger, J.A.; Cull, G.; Gottlieb, D.; Harrup, R.; Johnston, P.B.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood 2019, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravita, T.; Siniscalchi, A.; Tendas, A.; Cupelli, L.; Dentamaro, T.; Natale, G.; Spagnoli, A.; De Fabritiis, P. High-dose therapy with autologous PBSC transplantation in the front-line treatment of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2009, 43, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreger, P.; Schmitz, N. Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation as Part of First-Line Treatment of Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2007, 13, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, C.; Boumendil, A.; Finel, H.; Vernant, J.-P.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Thieblemont, C.; Chevallier, P.; Hamladji, R.-M.; Mufti, G.J.; Mazza, P.; et al. Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation (ASCT) for the Treatment of Patients with Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia/Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma (WM/LPL). A Risk Factor Analysis By the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Lymphoma Working Party. Blood 2014, 124, 678. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier, A.; Robin, M.; Larosa, F.; Golmard, J.L.; Le Gouill, S.; Coiteux, V.; Tabrizi, R.; Bulabois, C.E.; Cacheux, V.; Kuentz, M.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation allows long-term complete remission and curability in high-risk Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Results of a retrospective analysis of the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Haematologica 2010, 95, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stakiw, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kuruvilla, J.; Gupta, V.; Messner, H.; Lipton, J.H. Evidence of graft-versus-Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinaemia effect after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: A single centre experience. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2007, 40, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sermer, D.; Sarosiek, S.; Branagan, A.R.; Treon, S.P.; Castillo, J.J. SOHO State of the Art Updates and Next Questions: Targeted therapies and emerging novel treatment approaches for Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Advani, R.H.; Meid, K.; Leventoff, C.; White, T.P.; Flynn, C.A.; Sarosiek, S.; Branagan, A.R.; et al. Venetoclax in Previously Treated Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomba, M.L.; Qualls, D.; Monette, S.; Sethi, S.; Dogan, A.; Roshal, M.; Senechal, B.; Wang, X.; Rivière, I.; Sadelain, M.; et al. CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A preclinical model and initial clinical experience. J. Immunotherapy Cancer 2022, 10, e004128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadman, M.; Yeung, C.; Redman, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Ra, S.; Qian, D.; Ujjani, C.; Dezube, B.; Poh, C.; et al. S207: Efficacy and safety of a third generation CD20 CART (MB-106) for treatment of relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma (FL). HemaSphere 2022, 6, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.D.; Popplewell, L.L.; Subklewe, M.; Ghobadi, A.; Kuruvilla, J.; Kimball, A.; Tuglus, C.; Agarwal, S.; Stieglmaier, J. Phase I study of the CD19/CD3 half-life extended BiTE® molecule AMG 562 in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Michot, J.-M.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Ghesquieres, H.; Bouabdallah, K.; Byrd, J.C.; Cartron, G.; Portell, C.A.; Solh, M.; Tilly, H.; et al. Safety and Anti-Tumor Activity of Plamotamab (XmAb13676), an Anti-CD20 x Anti-CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Subjects with Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Blood 2021, 138, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.; Flinn, I.W.; Levy, M.Y.; Porter, R.; Burke, J.M.; Cultrera, J.L.; Misleh, J.; Zafar, S.F.; Freeman, B.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Zanubrutinib in BTK Inhibitor-Intolerant Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2021, 138, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanz, R.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Lee, H.-P.; Trneny, M.; Varettoni, M.; Owen, R.G.; Castillo, J.J.; Siddiqi, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Buske, C.; et al. Updated results of the ASPEN trial from a cohort of patients with MYD88 wild-type (MYD88WT) Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, e20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Sanz, R.G.; Lee, H.-P.; Trneny, M.; Varettoni, M.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Owen, R.G.; Cull, G.; Mulligan, S.; et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of MYD88 wild-type Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A substudy of the phase 3 ASPEN trial. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6009–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Tripsas, C.K.; Meid, K.; Kanan, S.; Sheehy, P.; Chuma, S.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Carfilzomib, rituximab, and dexamethasone (CaRD) treatment offers a neuropathy-sparing approach for treating Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Blood 2014, 124, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laribi, K.; Poulain, S.; Willems, L.; Merabet, F.; Le Calloch, R.; Eveillard, J.R.; Herbaux, C.; Roos-Weil, D.; Chaoui, D.; Roussel, X.; et al. Bendamustine plus rituximab in newly-diagnosed Waldenström macroglobulinaemia patients. A study on behalf of the French Innovative Leukaemia Organization (FILO). Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Itchaki, G.; Paludo, J.; Varettoni, M.; Buske, C.; Eyre, T.A.; Chavez, J.C.; Shain, K.H.; Issa, S.; Palomba, M.L.; et al. Ibrutinib for the treatment of Bing-Neel syndrome: A multicenter study. Blood 2019, 133, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guan, W.; Peng, X. Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase With Zanubrutinib for Treatment of Vitreoretinal Lymphoma: Report of 3 Cases. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 676792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. CADTH Reimbursement Review-Zanubrutinib (Brukinsa). Can. J. Health Technol. 2022, 2, 1–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, W. Preliminary Evaluation of Zanubrutinib-Containing Regimens in DLBCL and the Cerebrospinal Fluid Distribution of Zanubrutinib: A 13-Case Series. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Cher, L.; Griffiths, J.; Cohen, A.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Gregory, G.; Opat, S. Efficacy of Zanubrutinib in the Treatment of Bing-Neel Syndrome. Hemasphere 2018, 2, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, C.; Xu, J. Successful Management of a Patient with Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma by Zanubrutinib. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.T.; Chen, W.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Fu, H.R.; Huang, H.; Shi, J.M. Zanubrutinib Treatment of Central Nervous System Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Report. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 672052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Regimen | Phase | Population | ORR (%) | MRR (%) | PFS | Notable Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR vs. R-CHOP [24] | 3 | TN | Median: | More common with BR: rash More common with R-CHOP: Alopecia, cytopenia, peripheral neuropathy, stomatitis | ||
| N(BR) = 22 | 93 | NR | 70 months | |||
| N(R-CHOP) = 19 | 91 | NR | 28 months | |||
| R-CD [29] | 2 | TN, N = 72 | 83 | 74 | 2 y: 67% | Neutropenia, IRR, infections |
| Chlorambucil vs. Fludarabine [32] | 3 | TN | Median: | More common with CLB: second malignancy More common with F: Grade 3/4 neutropenia | ||
| N(CLB) = 169 | 36 | NR | 27 months | |||
| N(F) = 170 | 46 | NR | 36 months | |||
| Cladribine + rituximab [33] | 2 | N(TN) = 16 | 94 | 79 | NR | Neutropenia, cardiac toxicity |
| N(R/R) = 13 | 85 | |||||
| Fludarabine + rituximab [34] | 2 | N(TN) = 27 | 96 | 89 | 4 y: 67% | Cytopenia, infection, transformation to aggressive lymphomas |
| N(R/R) = 16 | 94 | 81 | 4 y: 38% | |||
| FCR [35] | 2 | N(TN) = 25 N(R/R) = 57 | 88 84 | 64 65 | 3 y: 96% 3 y: 73% | Cytopenia, infection, MDS |
| FCR [36] | 2 | N(TN) = 28 | 79 | 74 | NR | Neutropenia, MDS |
| N(R/R) = 15 |
| Regimen | Phase | Population | ORR (%) | MRR (%) | PFS | Notable Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bortezomib a [44] | 2 | N(TN) = 12 | 25 | 26 | Median: | Peripheral neuropathy, hematologic toxicity |
| N(R/R) = 15 | 27 | 16 months | ||||
| Bortezomib b [45] | 2 | N(TN) = 1 | 85 | 48 | Median: | Neuropathy, hematologic toxicity, dizziness |
| N(R/R) = 26 | 8 months | |||||
| Bortezomib c-rituximab [48] | 2 | TN | 92 | 62 | NR | Neuropathy j, Cytopenia, fatigue |
| N = 26 | ||||||
| Bortezomib c-rituximab [46] | 2 | R/R | 81 | 51 | Median: | Neuropathy j, Cytopenia |
| N = 37 | 16 months | |||||
| Bortezomib d-R-CD vs. R-CD [49] | 2 | TN | Neuropathy (bortezomib arm) j, Neutropenia (both arms) | |||
| N(B-R-CD) = 101 | 91 | 79 | 2 y: 81% | |||
| N(R-CD) = 101 | 87 | 69 | 2 y: 73% | |||
| Bortezomib e-rituximab-dexamethasone [50] | 2 | TN | 85 | 68 | Median: | Peripheral neuropathy |
| N = 59 | 43 months | |||||
| Bortezomib f-rituximab-dexamethasone [51] | 2 | TN | 96 | 83 | NR | Peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia |
| N = 23 | ||||||
| Carfilzomib g-rituximab-dexamethasone [52] | 2 | TN and R/R | 80 | 71 | Median: | Lipase elevation, neutropenia, cardiomyopathy |
| N = 31 | 46 months | |||||
| Ixazomib h-rituximab-dexamethasone [53] | 2 | TN | 96 | 77 | Median: | Infection, hyperglycemia, infusion reaction |
| N = 26 | 40 months | |||||
| Ixazomib i-rituximab-dexamethasone [54] | 1/2 | R/R | 88 | 74 | NR | Infection |
| N = 59 |
| Regimen | Phase | Population | ORR (%) | MRR (%) | PFS | Notable Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib [61,62] | 2 | R/R | 91 | 79 | 5 y: 54% | Afib |
| N = 63 | ||||||
| Ibrutinib [63] | 3 a | R/R | 87 | 77 | 5 y: 40% | Neutropenia, infection, hypertension |
| n = 31 | ||||||
| Ibrutinib [57,58] | 2 | TN | 100 | 87 | 4 y: 76% | Afib, hypertension |
| N = 30 | ||||||
| Ibrutinib-rituximab vs. Placebo-rituximab [40,59] | 3 | N(TN) = 68 | I-R: 92 P-R: 44 | I-R: 76 P-R: 31 | 54 m: I-R: 68% P-R: 25% | More common with I-R: Afib, hypertension More common with P-R: IRR, IgM flare |
| N(R/R) = 82 | ||||||
| Zanubrutinib [64] | 2 | N(TN) = 24 | 100 | 88 | 2 y: 92% | Neutropenia |
| N(R/R) = 53 | 94 | 80 | 2 y: 76% | |||
| Zanubrutinib vs. ibrutinib [65,66] | 3 | 42 m: | More common with Z: neutropenia More common with I: Diarrhea, muscle spasms, Afib, pneumonia | |||
| N(TN) = 37 | Z: 94 | Z: 77 | Z: 78% | |||
| N(R/R) = 164 | I: 93 | I: 78 | I: 70% | |||
| Acalabrutinib [67] | 2 | N(TN) = 14 | 93 | 79 | 2 y: 90% | Headache, infection, neutropenia |
| N(R/R) = 92 | 93 | 80 | 2 y: 82% | |||
| Tirabrutinib [68] | 2 | N(TN) = 18 | 94 | 89 | NR | Rash, Neutropenia |
| N(R/R) = 9 | 100 | 89 | ||||
| Pirtobrutinib [69] | 1/2 | R/R | 68 | 47 | NR | Neutropenia |
| N = 26 |
| Regimen | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred regimens | ||
| Bendamustine-rituximab |
|
|
| Zanubrutinib |
|
|
| Ibrutinib +/− rituximab b |
|
|
| Other regimens | ||
| Rituximab-cyclophosphamide-dexamethasone (or prednisone) |
|
|
| Bortezomib-dexamethasone-rituximab |
|
|
| Rituximab |
|
|
| Carfilzomib-dexamethasone-rituximab |
|
|
| Autologous stem cell transplant |
|
|
| Purine analogue-based therapy (fludarabine, cladribine) |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaedbey, R.; Forward, N.; Sehn, L.H.; Shafey, M.; Doucette, S.; Chen, C.I. A Canadian Perspective on the Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7122-7139. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100560
Kaedbey R, Forward N, Sehn LH, Shafey M, Doucette S, Chen CI. A Canadian Perspective on the Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7122-7139. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100560
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaedbey, Rayan, Nicholas Forward, Laurie H. Sehn, Mona Shafey, Sarah Doucette, and Christine I. Chen. 2022. "A Canadian Perspective on the Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7122-7139. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100560
APA StyleKaedbey, R., Forward, N., Sehn, L. H., Shafey, M., Doucette, S., & Chen, C. I. (2022). A Canadian Perspective on the Treatment of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. Current Oncology, 29(10), 7122-7139. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100560





