The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Proliferation Assays (MTT Assay)
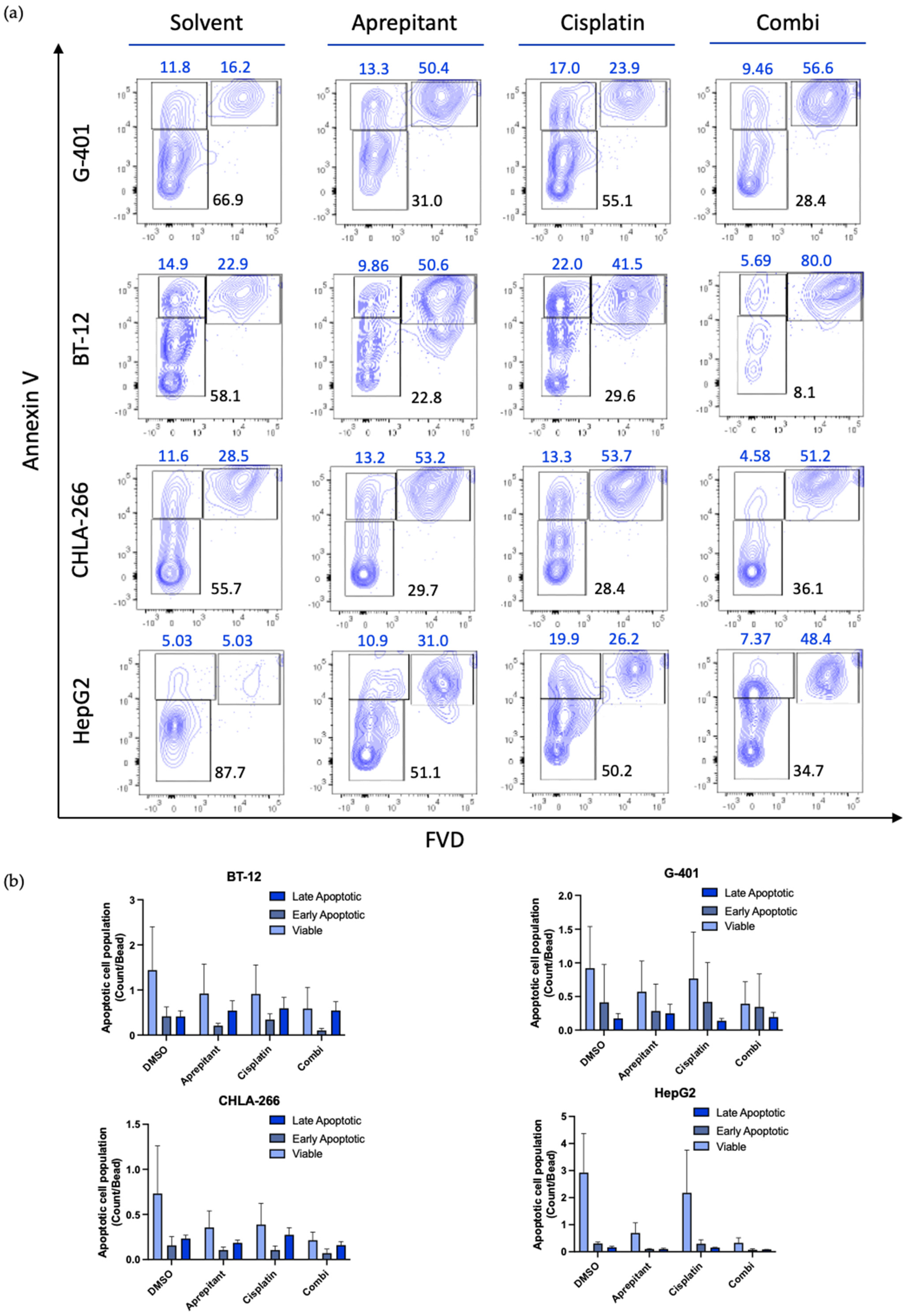
2.4. In Vitro Analysis of Apoptosis
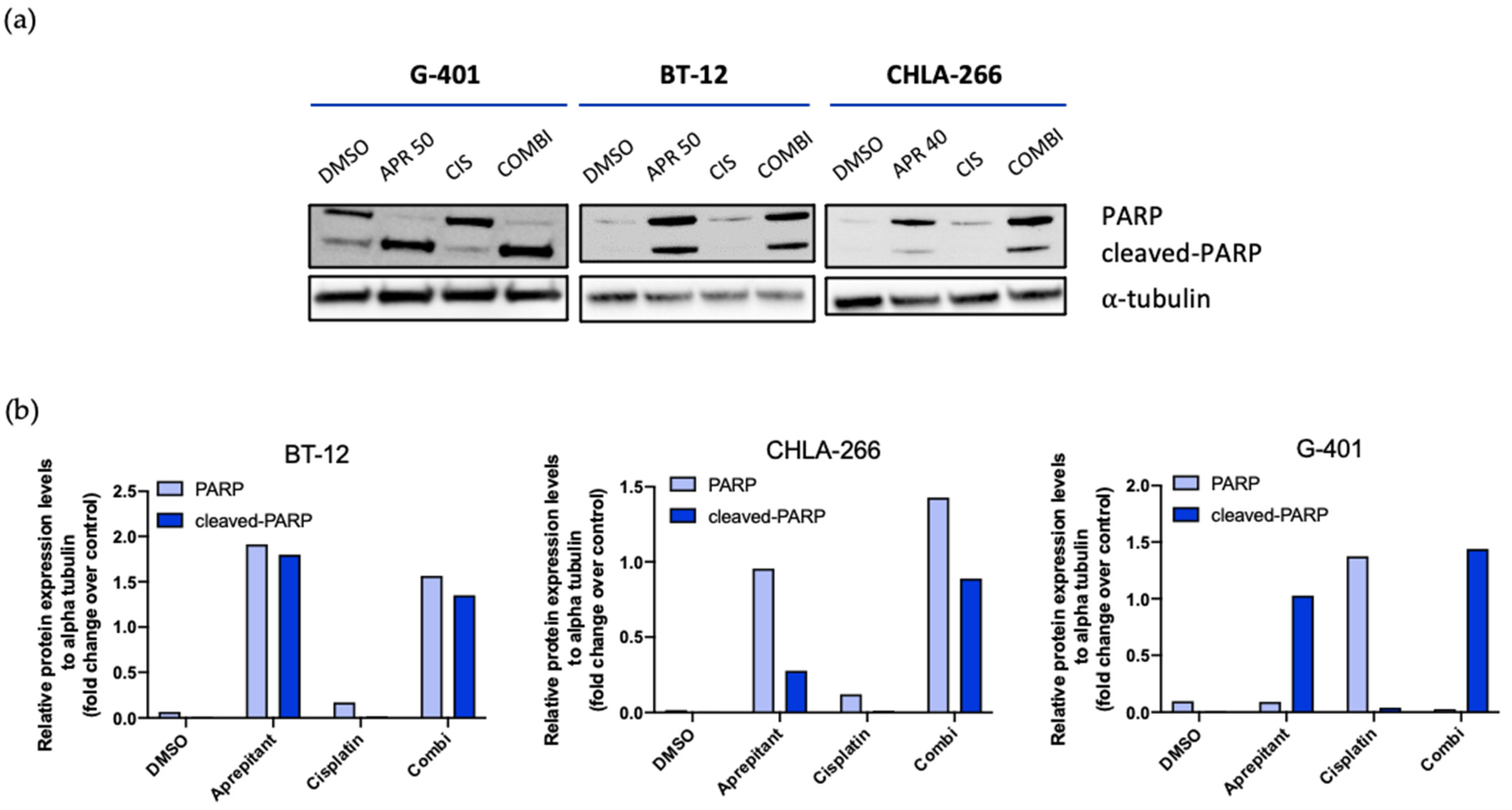
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction)
2.7. Patients and Tumor Samples
2.8. Data Base Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression of TACR1 and TAC1 in Pediatric Cancer
3.2. Clinical Outcome and Biological Characteristics of Patients with Rhabdoid Tumors
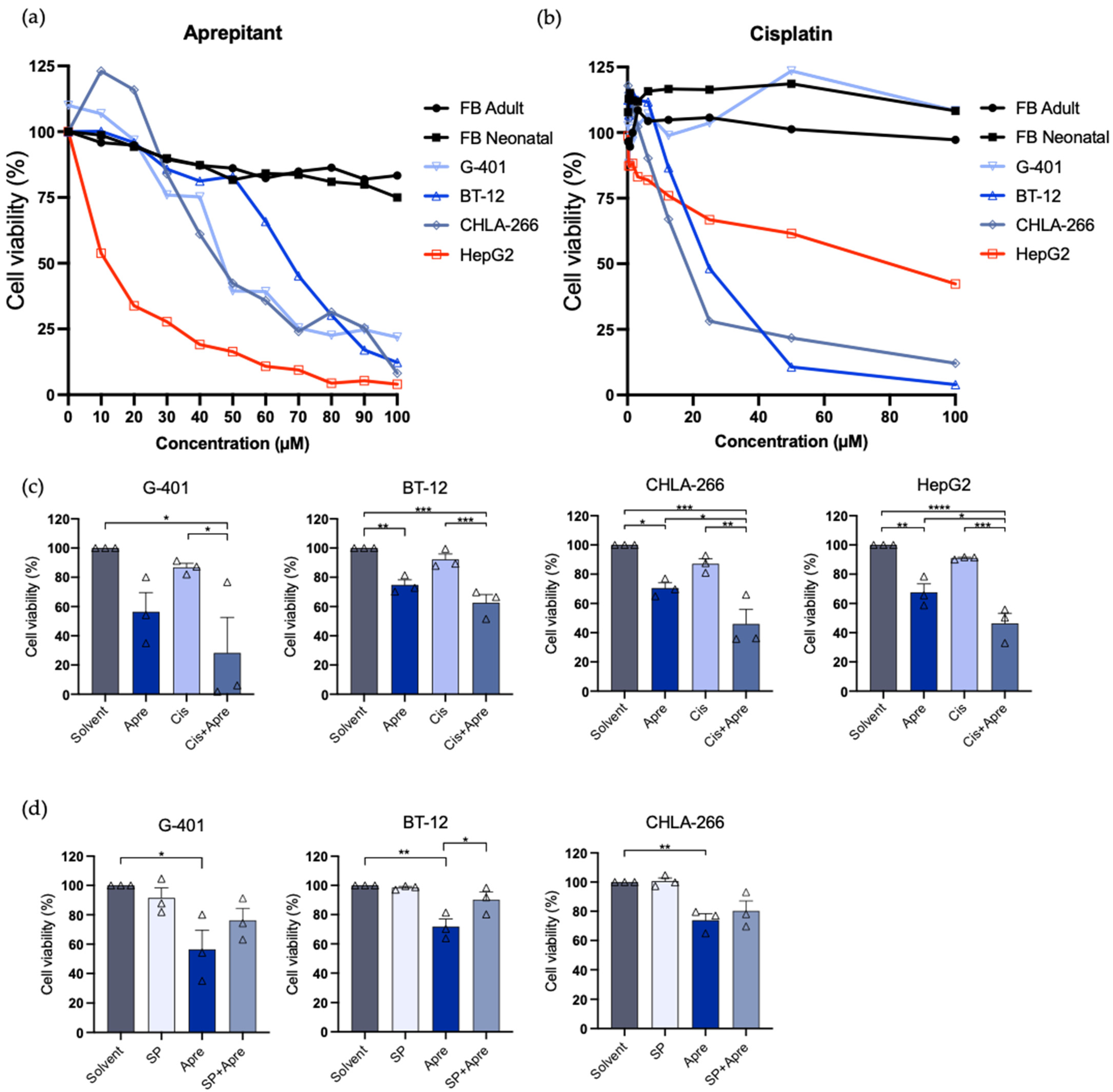
3.3. Aprepitant Inhibits Tumor Growth in Rhabdoid Tumor Cell Lines and Shows Increased Activity with Cisplatin
3.4. Substance P Reverses Anti-Proliferative Effect of Aprepitant
3.5. Aprepitant Triggers Apoptosis Signaling in Rhabdoid Tumor Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geller, J.I.; Roth, J.J.; Biegel, J.A. Biology and Treatment of Rhabdoid Tumor. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2015, 20, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.N.; Zimmerman, M.A.; Yao, X.; Cohen, K.J.; Burger, P.; Biegel, J.A.; Rorke-Adams, L.B.; Fisher, M.J.; Janss, A.; Mazewski, C.; et al. Intensive multimodality treatment for children with newly diagnosed CNS atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazlollahi, L.; Hsiao, S.J.; Kochhar, M.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Yamashiro, D.J.; Remotti, H.E. Malignant Rhabdoid Tumor, an Aggressive Tumor Often Misclassified as Small Cell Variant of Hepatoblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.F.; Su, Y.F.; Jaw, T.S.; Chiou, S.S.; Lin, C.H. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor of lumbar spine in a toddler child. Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2017, 3, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdeaut, F.; Freneaux, P.; Thuille, B.; Bergeron, C.; Laurence, V.; Brugieres, L.; Verite, C.; Michon, J.; Delattre, O.; Orbach, D. Extra-renal non-cerebral rhabdoid tumours. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 51, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, P.J.; Garen, P.D.; Powers, J.M.; Garvin, A.J. Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the central nervous system. Hum. Pathol. 1987, 18, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorke, L.B.; Packer, R.J.; Biegel, J.A. Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors of infancy and childhood: Definition of an entity. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 85, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y. Oncogenic roles of SMARCB1/INI1 and its deficient tumors. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.A.; Ho, B.; Huang, A. Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumour: From Tumours to Therapies. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2018, 61, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhwald, M.C.; Biegel, J.A.; Bourdeaut, F.; Roberts, C.W.; Chi, S.N. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors-current concepts, advances in biology, and potential future therapies. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, B.; De Salvo, G.L.; Orbach, D.; De Paoli, A.; Kelsey, A.; Mudry, P.; Francotte, N.; Van Noesel, M.; Bisogno, G.; Casanova, M.; et al. Outcome of extracranial malignant rhabdoid tumours in children registered in the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group Non-Rhabdomyosarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcoma 2005 Study-EpSSG NRSTS 2005. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 60, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.T.; Strother, D.R.; Judkins, A.R.; Burger, P.C.; Pollack, I.F.; Krailo, M.D.; Buxton, A.B.; Williams-Hughes, C.; Fouladi, M.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Efficacy of High-Dose Chemotherapy and Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation for Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group Trial ACNS0333. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, G.E.; Breslow, N.E.; Dome, J.; Guthrie, K.A.; Norkool, P.; Li, S.; Thomas, P.R.; Perlman, E.; Beckwith, J.B.; D’Angio, G.J.; et al. Rhabdoid tumor of the kidney in the National Wilms’ Tumor Study: Age at diagnosis as a prognostic factor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7641–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Arya, M.; Levitt, G.; Duffy, P.G.; Sebire, N.J.; Mushtaq, I. Part II: Treatment of primary malignant non-Wilms’ renal tumours in children. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R.; Esteban, F.; Redondo, M. The substance P/NK-1 receptor system: NK-1 receptor antagonists as anti-cancer drugs. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in cancer progression. Peptides 2013, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R. Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in human pathology. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1727–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Covenas, R. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists against Hepatoblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Neth, O.; Ilmer, M.; Garnier, A.; Salinas-Martin, M.V.; de Agustin Asencio, J.C.; von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R.; Munoz, M. Hepatoblastoma cells express truncated neurokinin-1 receptor and can be growth inhibited by aprepitant in vitro and in vivo. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: An Intelligent Bullet against Cancer? Cancers 2020, 12, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kage, R.; Leeman, S.E.; Boyd, N.D. Biochemical characterization of two different forms of the substance P receptor in rat submaxillary gland. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Yang, J.; Yao, Z. Roles of full-length and truncated neurokinin-1 receptors on tumor progression and distant metastasis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 140, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, E.; Leeman, S.E.; Watts, L.A.; Coukos, J.A.; O’Brien, M.J.; Cerda, S.R.; Farraye, F.A.; Stucchi, A.F.; Becker, J.M. Truncated neurokinin-1 receptor is increased in colonic epithelial cells from patients with colitis-associated cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17420–17425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R. Safety of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2013, 12, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant, a New Drug for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies: Focus on Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinos-Quintana, A.; Trujillo-Hacha, P.; Piruat, J.I.; Bejarano-Garcia, J.A.; Garcia-Guerrero, E.; Perez-Simon, J.A.; Munoz, M. Human acute myeloid leukemia cells express Neurokinin-1 receptor, which is involved in the antileukemic effect of Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenmüller, M.; Gruner, I.; Hagl, B.; Häberle, B.; Müller-Höcker, J.; von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R. Blocking the hedgehog pathway inhibits hepatoblastoma growth. Hepatology 2009, 49, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal. Available online: http://cbioportal.org (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Pohl, A.; Kappler, R.; Muhling, J.; Von Schweinitz, D.; Berger, M. Expression of Truncated Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Childhood Neuroblastoma is Independent of Tumor Biology and Stage. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6079–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Von Schweinitz, D. Therapeutic Innovations for Targeting Childhood Neuroblastoma: Implications of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor System. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5911–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Henssen, A.G.; Odersky, A.; Szymansky, A.; Seiler, M.; Althoff, K.; Beckers, A.; Speleman, F.; Schäfers, S.; De Preter, K.; Astrahanseff, K.; et al. Targeting tachykinin receptors in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenca, M.; Rossi, S.; Lorenzetto, E.; Piccinin, E.; Piccinin, S.; Rossi, F.M.; Giuliano, A.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Maestro, R.; Modena, P. SMARCB1/INI1 genetic inactivation is responsible for tumorigenic properties of epithelioid sarcoma cell line VAESBJ. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhu, X.; Meehan, B.; Venneti, S.; Martinez, D.; Morin, G.; Maiga, R.I.; Chen, H.; Papadakis, A.I.; Johnson, R.M.; et al. SMARCB1 loss induces druggable cyclin D1 deficiency via upregulation of MIR17HG in atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors. J. Pathol. 2020, 252, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvick, C.L.; Nageswara Rao, A.A.; Raghunathan, A.; Biegel, J.A.; Daniels, D.J. Case-based review: Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. Neurooncol. Pract. 2019, 6, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Clark, L.D.; Shao, Z.; Borek, D.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Crystal structure of the human NK1 tachykinin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13264–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, A.; Ilmer, M.; Becker, K.; Haberle, B.; Schweinitz, D.V.; Kappler, R.; Berger, M. Truncated neurokinin-1 receptor is an ubiquitous antitumor target in hepatoblastoma, and its expression is independent of tumor biology and stage. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hesketh, P.J. Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Crespo, J.C.; Crespo, J.P.; Covenas, R. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant and radiotherapy, a successful combination therapy in a patient with lung cancer: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Berger, M.; Rosso, M.; Gonzalez-Ortega, A.; Carranza, A.; Covenas, R. Antitumor activity of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists in MG-63 human osteosarcoma xenografts. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Gonzalez-Ortega, A.; Salinas-Martin, M.V.; Carranza, A.; Garcia-Recio, S.; Almendro, V.; Covenas, R. The neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant is a promising candidate for the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1658–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theruvath, J.; Sotillo, E.; Mount, C.W.; Graef, C.M.; Delaidelli, A.; Heitzeneder, S.; Labanieh, L.; Dhingra, S.; Leruste, A.; Majzner, R.G.; et al. Locoregionally administered B7-H3-targeted CAR T cells for treatment of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S.; Cutler, N.; Feighner, J.; Shrivastava, R.; Carman, J.; Sramek, J.J.; Reines, S.A.; Liu, G.; Snavely, D.; Wyatt-Knowles, E.; et al. Distinct mechanism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central substance P receptors. Science 1998, 281, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varty, G.B.; Cohen-Williams, M.E.; Hunter, J.C. The antidepressant-like effects of neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists in a gerbil tail suspension test. Behav. Pharmacol. 2003, 14, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Chen, Y.; de Blank, P.M.; Ondracek, A.; Farah, P.; Gittleman, H.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Cohen, M.L.; Brat, D.J.; et al. The descriptive epidemiology of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors in the United States, 2001–2010. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.; Stiller, C.; Bourdeaut, F. Extracranial rhabdoid tumours: What we have learned so far and future directions. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e329–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Line | Disease | Origin | INI1-Mutation |
|---|---|---|---|
| BT-12 | AT/RT | Female, 2 months, Caucasian | Loss-of-function |
| CHLA-266 | AT/RT | Female, 30 months, Caucasian | Loss-of-function |
| G-401 | RTK | Male, 3 months, Caucasian | Loss-of-function |
| HepG2 | HB | Male, 15 years, Caucasian | -- |
| Case | Name | Subtype of RT (Organ Compartment) | Gender (M/F) | Age at Diagnosis (Months) | INI1-Mutation | Treatment | Relapse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T190 | AT/RT → RTK * | M | <23 * | Germline mutation | Chemotherapy, Resection, Stem-cell therapy | Yes |
| 2 | T125II | MRT (liver) | M | 10 | Loss-of-function | Chemotherapy, Resection | Yes |
| 3 | T96 | MRT (liver) | F | 13 | Loss-of-function | Chemotherapy, Resection, Stem-cell therapy | No |
| 4 | T82 | MRT (liver) | M | 33 | Loss-of-function | Chemotherapy, Resection | No |
| 5 | T16A | AT/RT | M | 5 | Loss-of-function | - | - |
| 6 | T12IC | AT/RT | M | 127 | Loss-of-function | Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy | Yes |
| Characteristics | TACR1 * | TAC1 * |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Stage | ||
| I–II | 9 (22.5) | 9 (22.0) |
| II/IV–III | 17 (42.5) | 18 (43.9) |
| III/IV | 11 (27.5) | 11 (26.8) |
| IIIB–IIIB/IV | 3 (7.5) | 3 (7.3) |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 18 (45.0) | 18 (45.0) |
| Female | 22 (55.0) | 22 (55.0) |
| Age at Diagnosis (months) | ||
| <6 | 9 (22.5) | 9 (22.5) |
| 6–12 | 15 (37.5) | 15 (37.5) |
| 12–18 | 5 (12.5) | 5 (12.5) |
| 18–24 | 3 (7.5) | 3 (7.5) |
| 24–30 | 2 (5.0) | 2 (5.0) |
| >30 | 6 (15.0) | 6 (15.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolorz, J.; Demir, S.; Gottschlich, A.; Beirith, I.; Ilmer, M.; Lüthy, D.; Walz, C.; Dorostkar, M.M.; Magg, T.; Hauck, F.; et al. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 94-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29010008
Kolorz J, Demir S, Gottschlich A, Beirith I, Ilmer M, Lüthy D, Walz C, Dorostkar MM, Magg T, Hauck F, et al. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(1):94-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolorz, Julian, Salih Demir, Adrian Gottschlich, Iris Beirith, Matthias Ilmer, Daniel Lüthy, Christoph Walz, Mario M. Dorostkar, Thomas Magg, Fabian Hauck, and et al. 2022. "The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors" Current Oncology 29, no. 1: 94-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29010008
APA StyleKolorz, J., Demir, S., Gottschlich, A., Beirith, I., Ilmer, M., Lüthy, D., Walz, C., Dorostkar, M. M., Magg, T., Hauck, F., von Schweinitz, D., Kobold, S., Kappler, R., & Berger, M. (2022). The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors. Current Oncology, 29(1), 94-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29010008






