Clinical Outcomes from Dose-Reduced Radiotherapy to the Prostate in Elderly Patients with Localized Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
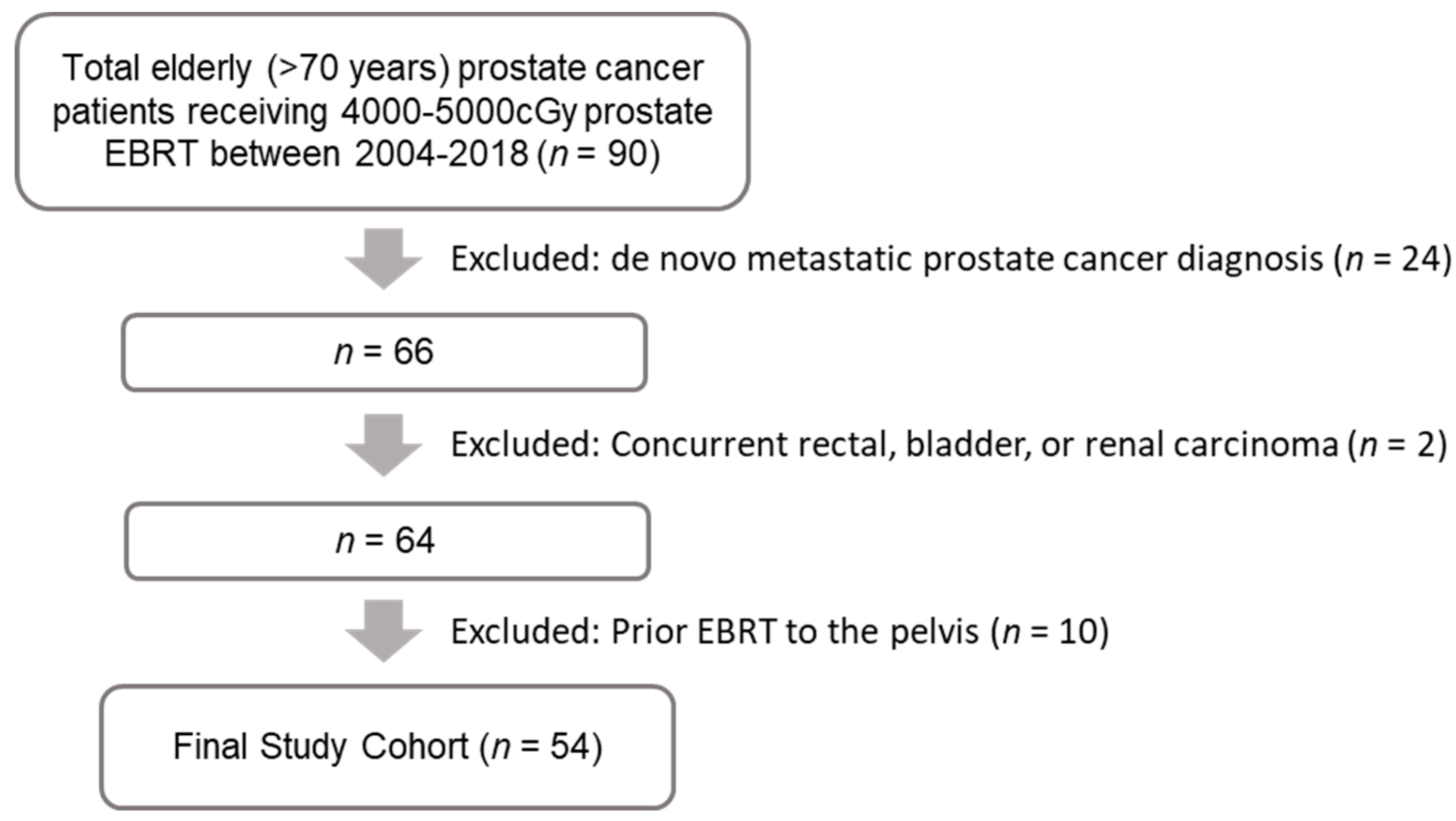
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Treatment Regimen(s) and Rationale(s)
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Study Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient and Tumor Characteristics
3.2. Radiotherapy Treatment Characteristics
3.3. Androgen Deprivation Therapy
3.4. Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Toxicity
3.5. PSA Response to Treatment
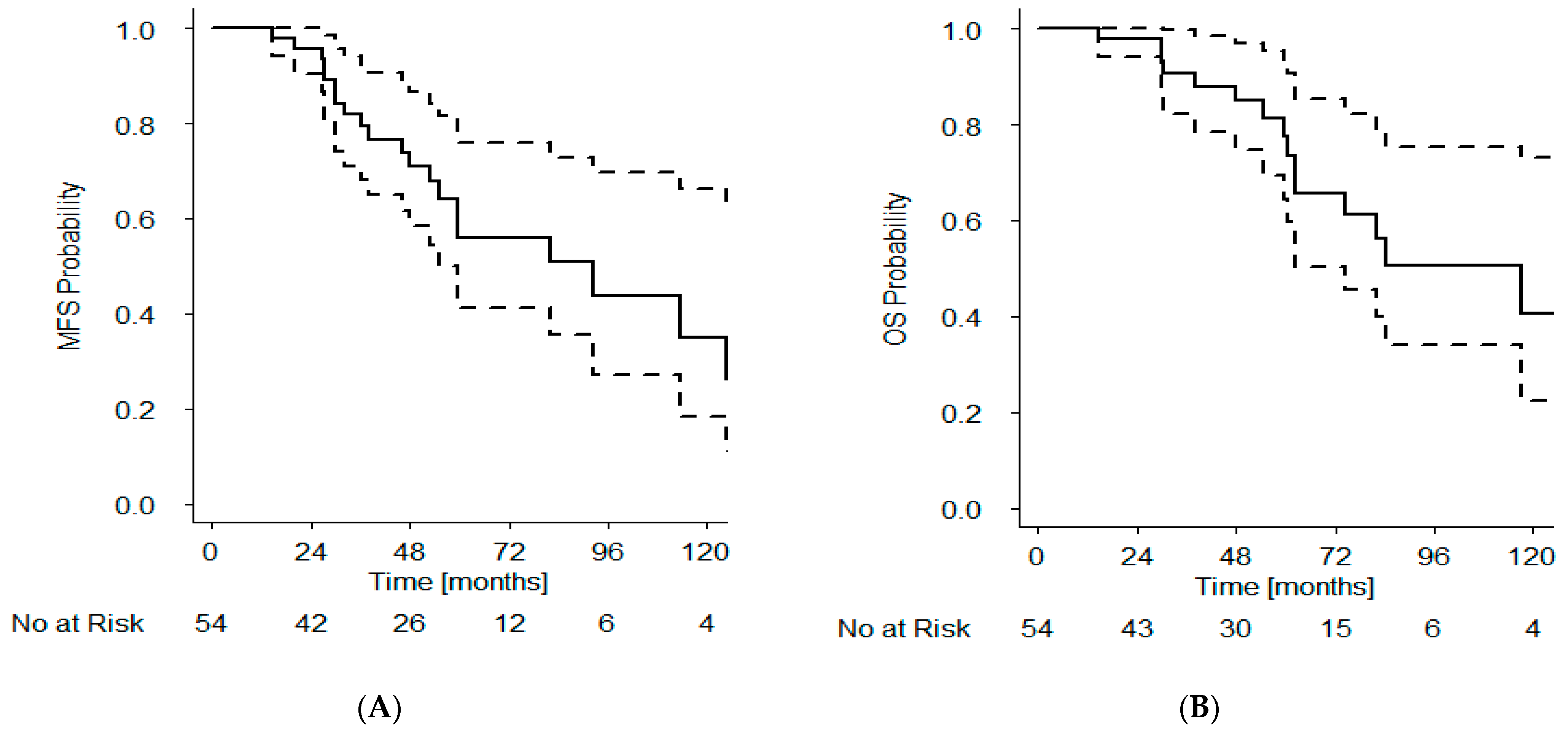
3.6. Metastasis-Free and Overall Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quon, H.; Loblaw, A.; Nam, R. Dramatic Increase in Prostate Cancer Cases by 2021. BJU Int. 2011, 108, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.R.; Weir, H.K.; Demers, A.A.; Ellison, L.F.; Louzado, C.; Shaw, A.; Turner, D.; Woods, R.R.; Smith, L.M. Projected Estimates of Cancer in Canada in 2020. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2020, 192, E199–E205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, M.S.; Tan, H.-J. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer. JAMA 2017, 317, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.V.; Whittington, R.; Malkowicz, S.B.; Schultz, D.; Blank, K.; Broderick, G.A.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Renshaw, A.A.; Kaplan, I.; Beard, C.J.; et al. Biochemical Outcome After Radical Prostatectomy, External Beam Radiation Therapy, or Interstitial Radiation Therapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. JAMA 1998, 280, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge from a Population-Based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Ouden, D.; Schröder, F.H. Management of Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer. World J. Urol. 2000, 18, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; Nielsen, M.E.; Han, M.; Partin, A.W. Contemporary Evaluation of the D’Amico Risk Classification of Prostate Cancer. Urology 2007, 70, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Imamoto, T. Management of Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer. Nihon rinsho. Jpn. J. Clin. Med. 2010, 68, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Yang, W.-C.; Hu, Y.-W.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Yang, K.-L.; Lai, I.-C.; Hsu, C.-X.; Wang, T.-H.; Lai, T.-Y.; Chen, K.-T.; et al. Definitive Radiotherapy for Older Patients with Prostate Cancer: Experience of a Medical Center in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, F.C.; Donovan, J.L.; Lane, J.A.; Mason, M.; Metcalfe, C.; Holding, P.; Davis, M.; Peters, T.J.; Turner, E.L.; Martin, R.M.; et al. 10-Year Outcomes after Monitoring, Surgery, or Radiotherapy for Localized Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quon, H.; Loblaw, D.A. Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer-Review of Indications in 2010. Curr. Oncol. 2010, 17 (Suppl. S2), 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.L.; Alibhai, S.M.H.; Basaria, S.; D’Amico, A.V.; Kantoff, P.W.; Keating, N.L.; Penson, D.F.; Rosario, D.J.; Tombal, B.; Smith, M.R. Adverse Effects of Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Strategies to Mitigate Them. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.V.; Chen, M.-H.; Renshaw, A.; Loffredo, M.; Kantoff, P.W. Long-Term Follow-up of a Randomized Trial of Radiation With or Without Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Localized Prostate Cancer. JAMA 2016, 314, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, C.A.; Bae, K.; Pilepich, M.; Hanks, G.; Shipley, W. Long-Term Treatment Sequelae After External Beam Irradiation With or Without Hormonal Manipulation for Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: Analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Studies 85-31, 86-10, and 92-02. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catton, C.N.; Lukka, H.; Gu, C.-S.; Martin, J.M.; Supiot, S.; Chung, P.W.M.; Bauman, G.S.; Bahary, J.-P.; Ahmed, S.; Cheung, P.; et al. Randomized Trial of a Hypofractionated Radiation Regimen for the Treatment of Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearnaley, D.; Syndikus, I.; Mossop, H.; Khoo, V.; Birtle, A.; Bloomfield, D.; Graham, J.; Kirkbride, P.; Logue, J.; Malik, Z.; et al. Conventional versus Hypofractionated High-Dose Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes of the Randomised, Non-Inferiority, Phase 3 CHHiP Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).v.5.0; Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017; Volume 183. [Google Scholar]
- Bill-Axelson, A.; Holmberg, L.; Filén, F.; Ruutu, M.; Garmo, H.; Busch, C.; Nordling, S.; Häggman, M.; Andersson, S.-O.; Bratell, S.; et al. Radical Prostatectomy versus Watchful Waiting in Localized Prostate Cancer: The Scandinavian Prostate Cancer Group-4 Randomized Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coen, J.J.; Feldman, A.S.; Smith, M.R.; Zietman, A.L. Watchful Waiting for Localized Prostate Cancer in the PSA Era: What Have Been the Triggers for Intervention? BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilt, T.J.; Jones, K.M.; Barry, M.J.; Andriole, G.L.; Culkin, D.; Wheeler, T.; Aronson, W.J.; Brawer, M.K. Follow-up of Prostatectomy versus Observation for Early Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill-Axelson, A.; Garmo, H.; Holmberg, L.; Johansson, J.E.; Adami, H.O.; Steineck, G.; Johansson, E.; Rider, J.R. Long-Term Distress after Radical Prostatectomy versus Watchful Waiting in Prostate Cancer: A Longitudinal Study from the Scandinavian Prostate Cancer Group-4 Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibhai, S.M.H.; Duong-Hua, M.; Sutradhar, R.; Fleshner, N.E.; Warde, P.; Cheung, A.M.; Paszat, L.F. Impact of Androgen Deprivation Therapy on Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsen, P.C.; Klotz, L.; Tombal, B.; Grady, J.; Olesen, T.K.; Nilsson, J. Cardiovascular Morbidity Associated with Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Agonists and an Antagonist. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.G.; Canfield, S.E.; Du, X.L. Review of Major Adverse Effects of Androgen-Deprivation Therapy in Men with Prostate Cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 2388–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.D.; Saad, F.; Cookson, M.S.; George, D.J.; Saltzstein, D.R.; Tutrone, R.; Akaza, H.; Bossi, A.; van Veenhuyzen, D.F.; Selby, B.; et al. Oral Relugolix for Androgen-Deprivation Therapy in Advanced Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.R.; Klotz, L.; Persson, B.E.; Olesen, T.K.; Wilde, A.A.M. Cardiovascular Safety of Degarelix: Results from a 12-Month, Comparative, Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Group Phase III Trial in Patients with Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 2313–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, T.W.; Miciek, R.; Travison, T.G. Muscle Function, Physical Performance and Body Composition Changes in Men with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basualto-Alarcón, C.; Varela, D.; Duran, J.; Maass, R.; Estrada, M. Sarcopenia and Androgens: A Link between Pathology and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Median (IQR) or Number (%) n = 54 | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 80 (76–83) |
| Pretreatment PSA (ng/mL) | 21 (8–45) |
| Clinical stage | |
| T1b | 4 (7%) |
| T1c | 16 (30%) |
| T2a | 7 (13%) |
| T2b | 3 (6%) |
| T2c | 5 (9%) |
| T3a | 11 (20%) |
| T3b | 1 (2%) |
| T4 | 7 (13%) |
| Method of pathologic diagnosis * | |
| TURP alone | 13 (25%) |
| TRUS biopsy | 40 (75%) |
| Grade group * | |
| 1 | 3 (6%) |
| 2 | 8 (15%) |
| 3 | 10 (19%) |
| 4 | 8 (15%) |
| 5 | 24 (45%) |
| Cores sampled | 12 (11–12) |
| Cores positive | 7 (5–10) |
| % core tissue positive (%) | 40 (17–54) |
| Pathologic peri-prostatic fat invasion | 14 (30%) |
| NCCN risk grouping | |
| Favorable intermediate risk | 2 (4%) |
| Unfavorable intermediate risk | 6 (11%) |
| High risk | 19 (35%) |
| Very high risk | 27 (50%) |
| Median (IQR) or Number (%) n = 54 | |
|---|---|
| Treatment technique | |
| 3D-CRT | 11 (20%) |
| IMRT | 2 (4%) |
| VMAT | 41 (76%) |
| Dose/Fractionation | |
| 4000 cGy in 15 fractions | 3 (6%) |
| 5000 cGy in 20 fractions | 51 (94%) |
| PTV dosimetry | |
| V95% [%] | 100 (100–100) |
| D1cc [%] | 105 (104–105) |
| D0.03cc [%] | 106 (104–106) |
| Body D0.03cc [EQD2Gy3] | 59 (58–60) |
| Bladder dosimetry | |
| V45Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 10 (7–15) |
| V50Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 8 (5–12) |
| V55Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 3 (2–6) |
| V60Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 0 (0–0) |
| Rectum dosimetry | |
| V45Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 18 (12–25) |
| V50Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 14 (9–19) |
| V55Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 0.9 (0.2–2.6) |
| V60Gy (EQD2Gy3) [%] | 0 (0–0) |
| Median (IQR) or Number (%) n = 54 | |
|---|---|
| PSA value at 3 months (ng/mL) | 0.2 (0.1–1.1) |
| Any PSA decline post-radiotherapy | 50 (93%) |
| PSA nadir post-radiotherapy (ng/mL) | 0.2 (0.1–1.2) |
| Time to PSA nadir (months) | 5 (1–7) |
| Post-radiotherapy PSA >0.5 | 29 (54%) |
| Time to PSA >0.5 (months) | 15 (2–24) |
| Post-radiotherapy PSA >10.0 | 13 (24%) |
| Time to PSA >10.0 (months) | 12 (1–17) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samson, N.; Khanolkar, R.A.; Quirk, S.; Quon, H.; Roumeliotis, M.; Balogh, A.; Sia, M.; Thind, K.; Husain, S.; Martell, K. Clinical Outcomes from Dose-Reduced Radiotherapy to the Prostate in Elderly Patients with Localized Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 3729-3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050318
Samson N, Khanolkar RA, Quirk S, Quon H, Roumeliotis M, Balogh A, Sia M, Thind K, Husain S, Martell K. Clinical Outcomes from Dose-Reduced Radiotherapy to the Prostate in Elderly Patients with Localized Prostate Cancer. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(5):3729-3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050318
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamson, Nina, Rutvij A. Khanolkar, Sarah Quirk, Harvey Quon, Michael Roumeliotis, Alex Balogh, Michael Sia, Kundan Thind, Siraj Husain, and Kevin Martell. 2021. "Clinical Outcomes from Dose-Reduced Radiotherapy to the Prostate in Elderly Patients with Localized Prostate Cancer" Current Oncology 28, no. 5: 3729-3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050318
APA StyleSamson, N., Khanolkar, R. A., Quirk, S., Quon, H., Roumeliotis, M., Balogh, A., Sia, M., Thind, K., Husain, S., & Martell, K. (2021). Clinical Outcomes from Dose-Reduced Radiotherapy to the Prostate in Elderly Patients with Localized Prostate Cancer. Current Oncology, 28(5), 3729-3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28050318





