A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
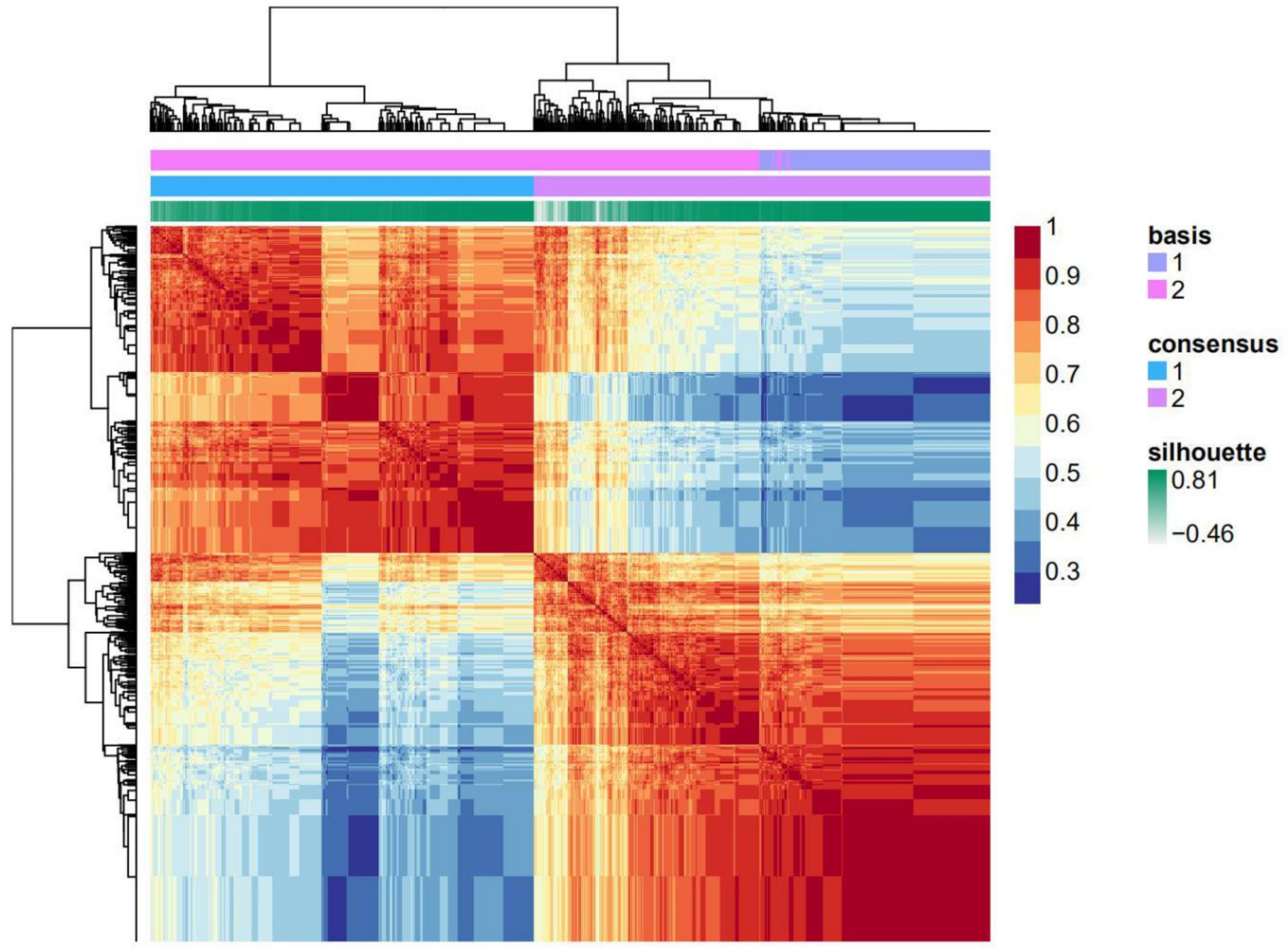
2.1. A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature Could Classify Breast Cancers into Two Groups
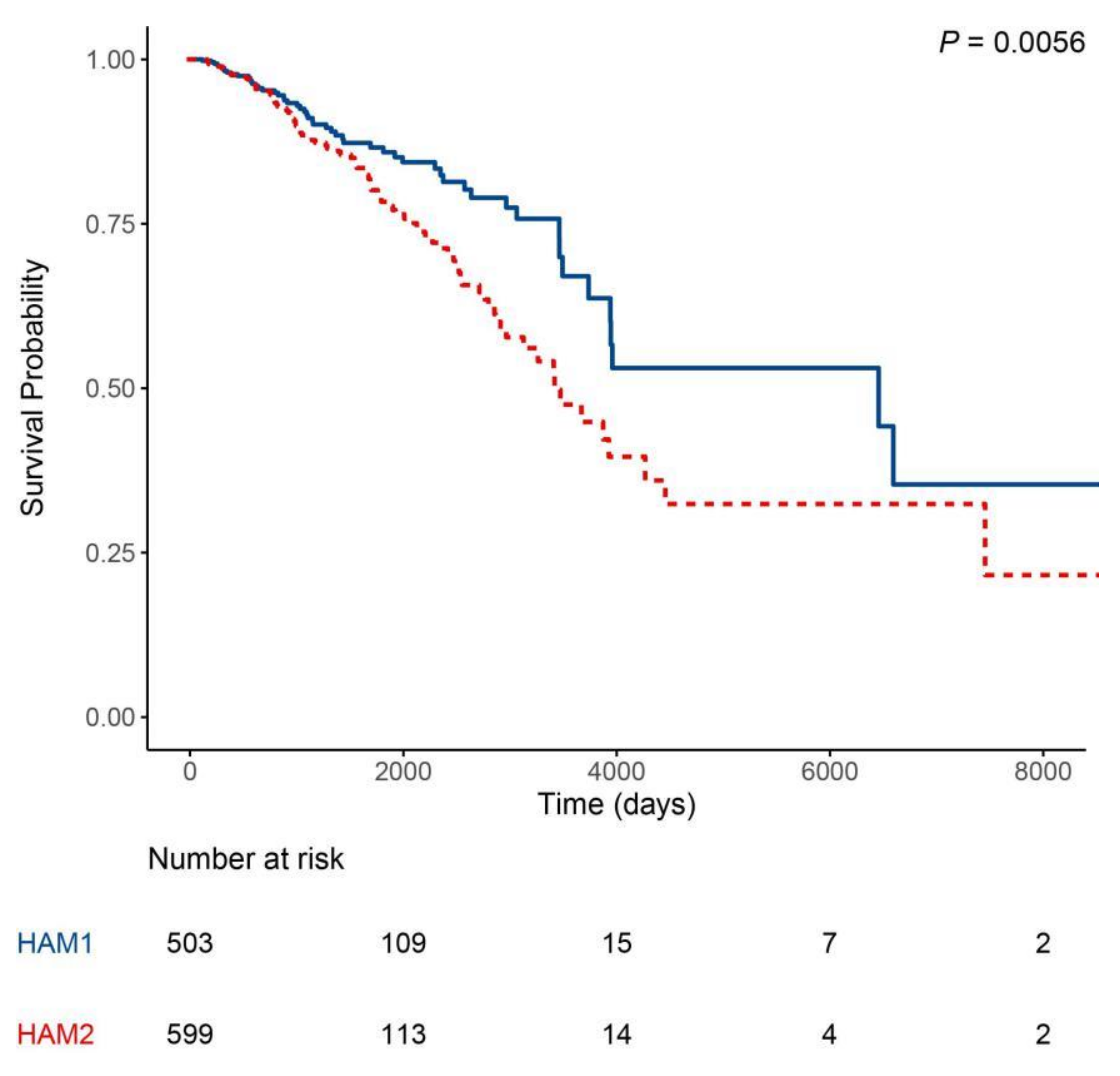
2.2. Classification Using Histone Acetylation Modulator Genes Distinguished Two Prognosis Groups in HER2-Enriched and Basal-Like Intrinsic Subtypes
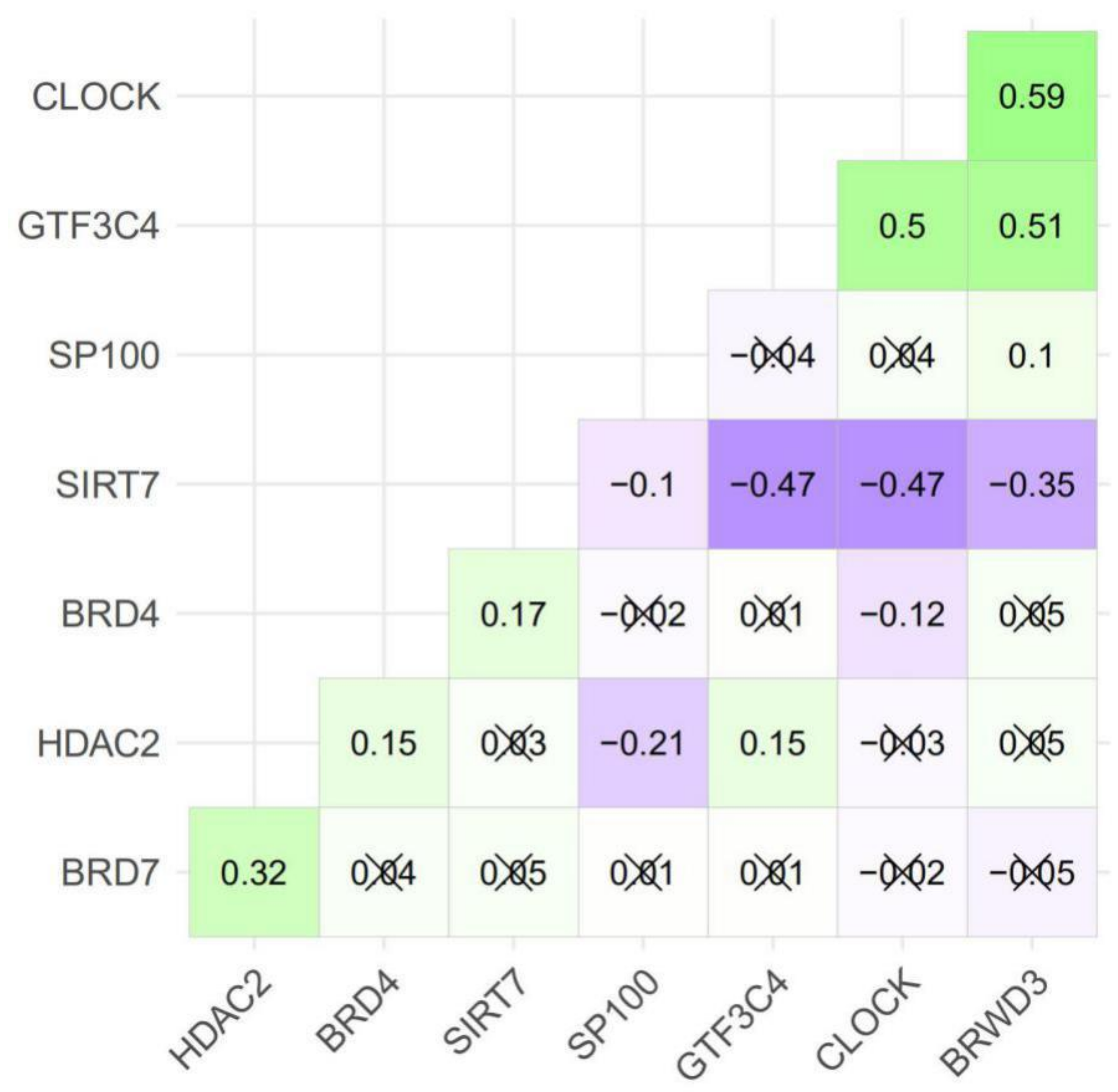
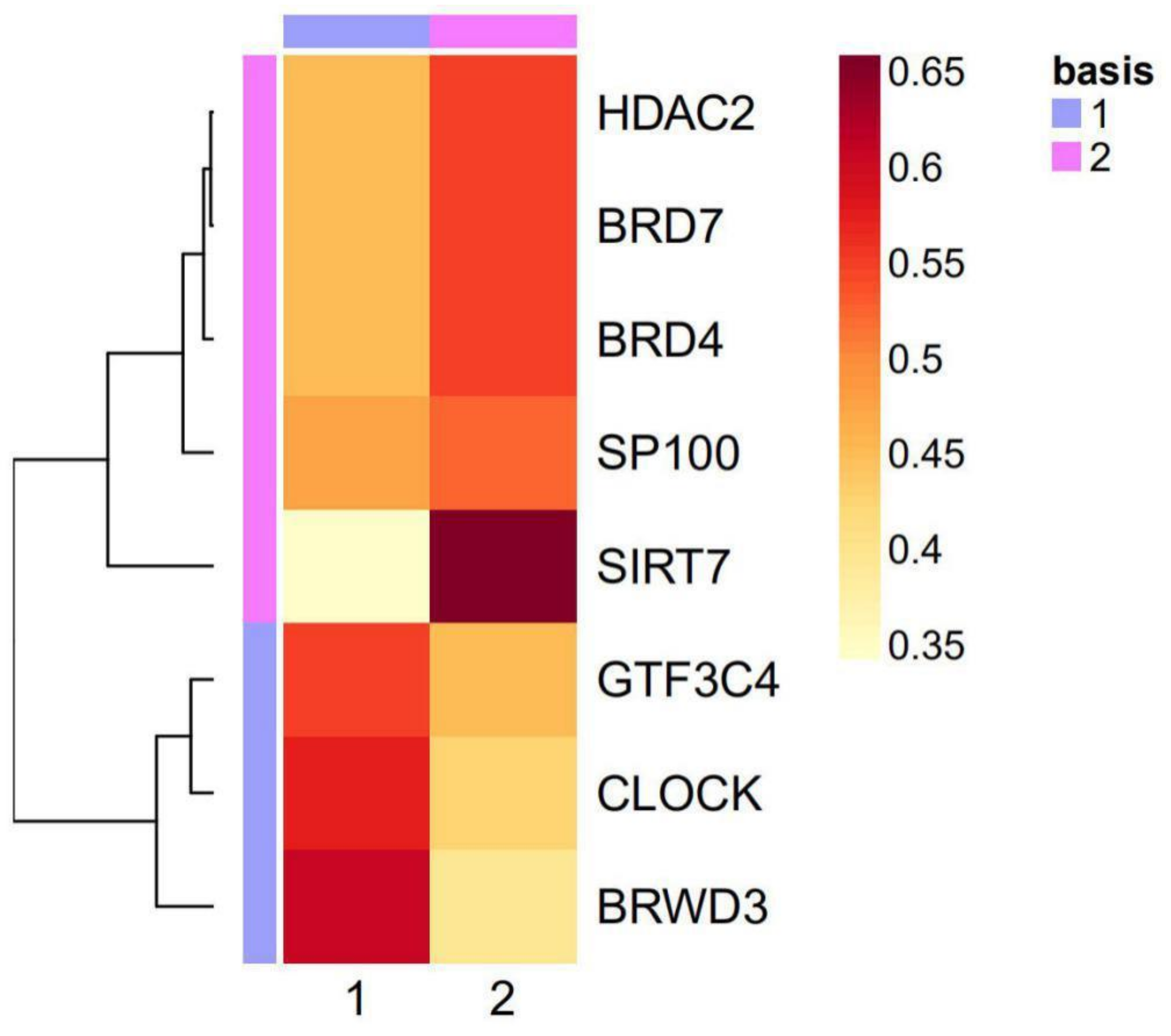
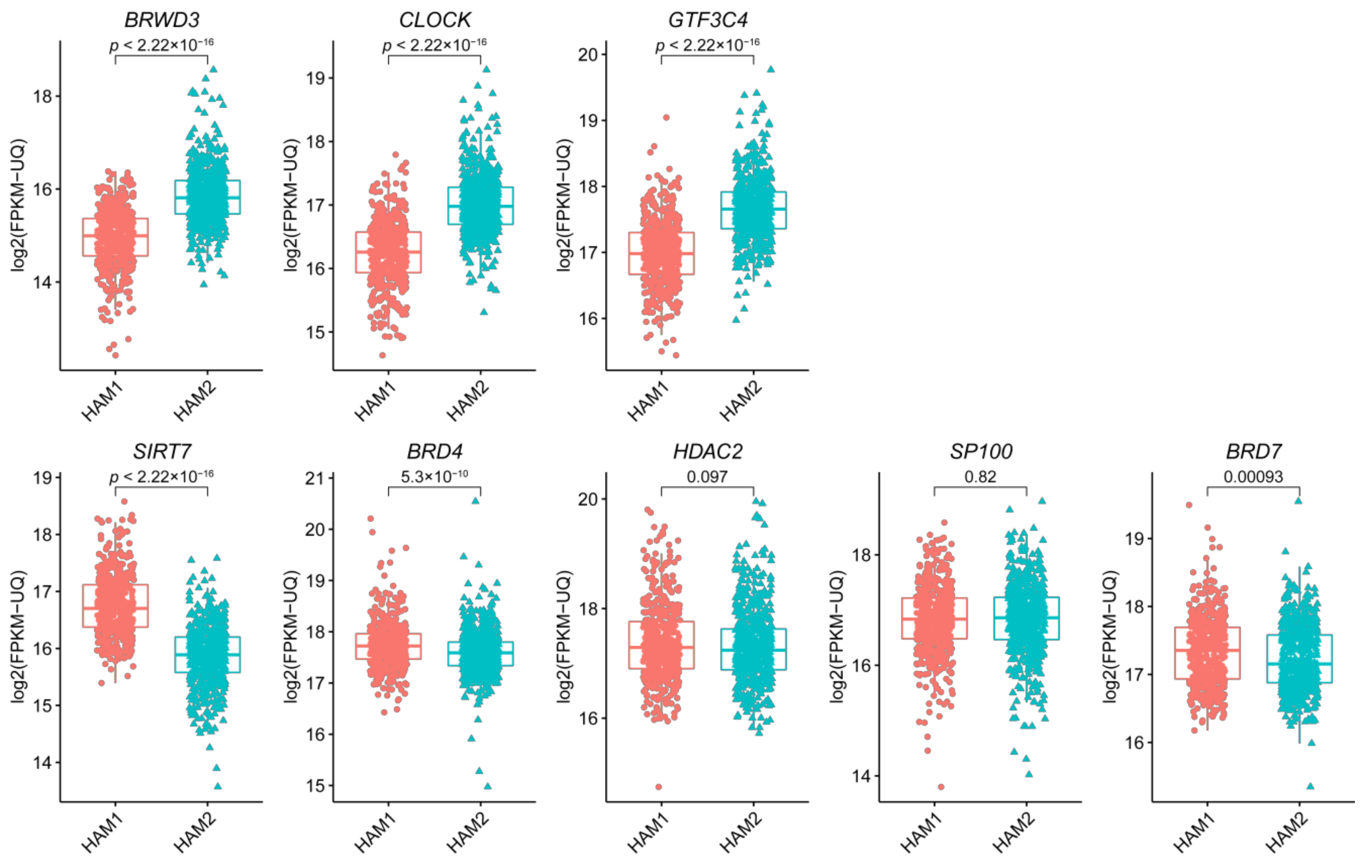
2.3. The Eight Featured Genes Belonged to Two Basis Components with a Different Expression Pattern
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Processing
4.2. Identification and Verification of Featured Genes
4.3. Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Clustering
4.4. Survival Analysis
4.5. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes between the HAM1 and HAM2 Groups
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymiczek, A.; Lone, A.; Akbari, M.R. Molecular Intrinsic versus Clinical Subtyping in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Genet. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; Van De Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascianelli, S.; Molineris, I.; Isella, C.; Masseroli, M.; Medico, E. Machine Learning for RNA Sequencing-Based Intrinsic Subtyping of Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.P.; Barbash, O.; Creasy, C.L. Targeting Epigenetic Modifications in Cancer Therapy: Erasing the Roadmap to Cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Han, J.-W. Targeting Epigenetics for Cancer Therapy. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2019, 42, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefansson, O.A.; Moran, S.; Gomez, A.; Sayols, S.; Arribas-Jorba, C.; Sandoval, J.; Hilmarsdottir, H.; Ólafsdóttir, E.; Tryggvadottir, L.; Jonasson, J.G.; et al. A DNA Methylation-Based Definition of Biologically Distinct Breast Cancer Subtypes. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 9, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.; Wu, J.; Workman, J.L.; Li, B. Readers of Histone Modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Barton, M.C. Bromodomain Histone Readers and Cancer. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmorstein, R.; Zhou, M.-M. Writers and Readers of Histone Acetylation: Structure, Mechanism, and Inhibition. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Scott, G.K.; Devries, S.; Chin, K.; Benz, C.C.; Waldman, F.M.; Hwang, E.S. Protein Acetylation and Histone Deacetylase Expression Associated with Malignant Breast Cancer Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, S.E.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Powe, D.G.; Ahmed, R.A.; Collins, H.M.; Soria, D.; Garibaldi, J.M.; Paish, C.E.; Ammar, A.A.; et al. Global Histone Modifications in Breast Cancer Correlate with Tumor Phenotypes, Prognostic Factors, and Patient Outcome. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3802–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzotti, G.; Ciarrocchi, A.; Sancisi, V. Inhibition of BET Proteins and Histone Deacetylase (HDACs): Crossing Roads in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D. HDAC Inhibitors Tested in Phase III Trial. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilting, R.H.; Dannenberg, J.-H. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Tumorigenesis, Tumor Cell Heterogeneity and Drug Resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2012, 15, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Loo, N.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, T. Genomic Characterization of Genes Encoding Histone Acetylation Modulator Proteins Identifies Therapeutic Targets for Cancer Treatment. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Le, T.D.; Liu, L.; Su, N.; Wang, R.; Sun, B.-Y.; Colaprico, A.; Bontempi, G.; Li, J. Cancer Subtypes: An R/Bioconductor Package for Molecular Cancer Subtype Identification, Validation and Visualization. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3131–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, J.C.; Nadeem, S.; Levine, A.J.; Pouryahya, M.; Deasy, J.O.; Tannenbaum, A. Robust and Interpretable PAM50 Reclassification Exhibits Survival Advantage for Myoepithelial and Immune Phenotypes. npj Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes and Preclinical Models for Selection of Targeted Therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, A.; Goodman, L.; Leitzel, K.; Cook, J.; Sperinde, J.; Haddad, M.; Köstler, W.J.; Huang, W.; Weidler, J.M.; Ali, S.; et al. HER3, p95HER2, and HER2 Protein Expression Levels Define Multiple Subtypes of HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 141, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.E.; Yi, C.-H.; Zheng, T.; Stevens, R.G.; Leaderer, D.; Zhang, Y.; Holford, T.R.; Hansen, J.; Paulson, J.; Zhu, Y. CLOCK in Breast Tumorigenesis: Genetic, Epigenetic, and Transcriptional Profiling Analyses. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, E.; Taylor, W.; Li, X.-M.; Aslan, Y.; Villote, M.; Rivière, J.; Duvallet, G.; Auriau, C.; Dulong, S.; Ray-Mond-Letron, I. Chronic Circadian Disruption Modulates Breast Cancer Stemness and Immune Microenvi-Ronment to Drive Metastasis in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, S.; Mansoori Derakhshan, S.; Mansoori Derakhshan, N.; Shekari Khaniani, M.; Alivand, M.R. Down-Regulation of HDAC2 and HDAC3 Via Oleuropein as a Potent Prevention and Therapeutic Agent in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9172–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z. HDAC2 Overexpression Correlates with Aggressive Clinicopathological Features and DNA-Damage Response Pathway of Breast Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1213. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, B.M.; Jana, L.; Kasajima, A.; Lehmann, A.; Prinzler, J.; Budczies, J.; Winzer, K.-J.; Dietel, M.; Weichert, W.; Denkert, C. Differential Expression of Histone Deacetylases HDAC1, 2 and 3 In Human Breast Cancer-Overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 is Associated with Clinicopathological Indicators of Disease Progression. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Li, Z.; Cheng, L.; Yang, F.; Xie, N. SIRT7 Is a Prognostic Biomarker Associated With Immune Infiltration in Luminal Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Shi, L.; Xie, N.; Liu, Z.; Qian, M.; Meng, F.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Cao, X.; Zhu, W.-G.; et al. SIRT7 Antagonizes TGF-β Signaling and Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Peng, H.; Chen, F.; Luo, R.; Li, R. High Expression of Sirt7 Served as a Predictor of Adverse Outcome in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Network, C.G.A. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor Package for Integrative Analysis of TCGA Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.A.; Ferretti, V.; Grossman, R.L.; Staudt, L.M. The NCI Genomic Data Commons as an Engine for Precision Medicine. Blood 2017, 130, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Church, G. Improving Molecular Cancer Class Discovery through Sparse Non-negative Matrix Factorization. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzal, A. Nonparametric Tikhonov Regularized NMF and Its Application in Cancer Clustering. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux, R.; Seoighe, C. A Flexible R Package for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. The Cox Model. In Statistics for Biology and Health; Springer Science and Business Media LLC.: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 39–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. The Logrank Test. BMJ 2004, 328, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| HAM Groups | Luminal A | Luminal B | Basal-Like | HER2-Enriched |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAM1 | 68 (35.1%) | 47 (24.2%) | 55 (28.3%) | 24 (12.4%) |
| HAM2 | 164 (50.9%) | 78 (24.2%) | 46 (14.3%) | 34 (10.6%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, M.; Hou, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, T. A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 928-939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010091
Long M, Hou W, Liu Y, Hu T. A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(1):928-939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010091
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Mengping, Wei Hou, Yiqiang Liu, and Taobo Hu. 2021. "A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer" Current Oncology 28, no. 1: 928-939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010091
APA StyleLong, M., Hou, W., Liu, Y., & Hu, T. (2021). A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Current Oncology, 28(1), 928-939. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010091





