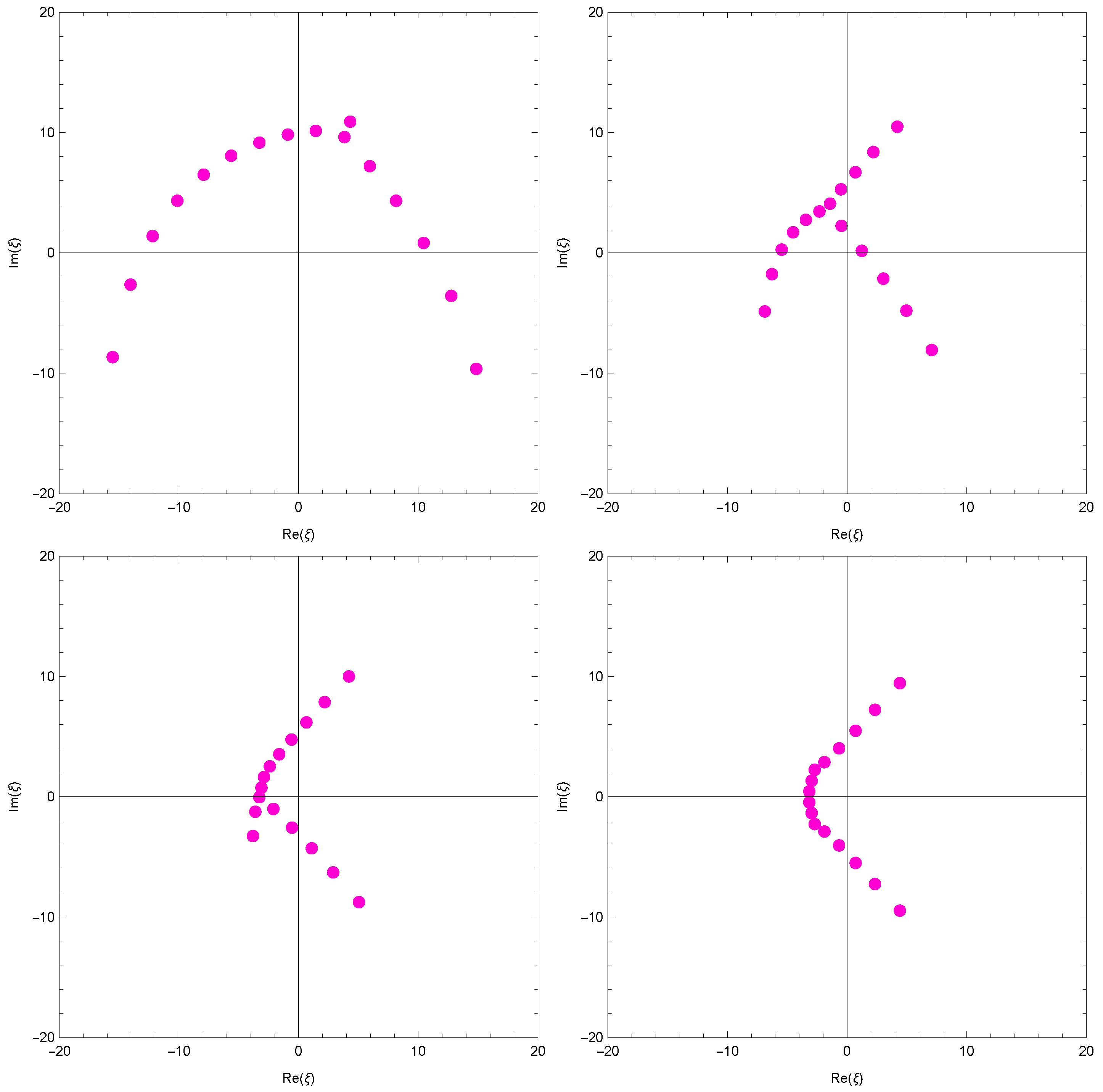Abstract
In this paper, we introduce new class of Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius–Euler polynomials and investigate some properties of these polynomials. We derive some explicit and implicit summation formulas and their symmetric identities by using different analytical means and applying generating functions of generalized Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials. In particular, parametric kinds of the Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials are introduced and some of their algebraic and analytical properties are established. In addition, illustrative examples of these families of polynomials are shown, focusing on their numerical values and piloting some beautiful computer-aided graphs of them.
Keywords:
Bell polynomials; Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials; Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials; Stirling numbers MSC:
05A15; 11B68; 11B73; 26C05; 33B10
1. Introduction
Nowadays, an increasing number of authors [1,2,3,4] have considered the use of generating functions method in order to introduce new families of special polynomials, including two parametric kinds of polynomials, such as Bernoulli, Euler, Genocchi, etc.
With a such work methodology, it is possible to establish novel properties for these families of polynomials, which include relations between trigonometric functions, as well as parametric kinds of special polynomials. By applying the partial derivative operator to the generating functions involved, it is possible to deduce some derivative formulae, and finite combinatorial sums related with aforementioned polynomials and their associated numbers. Moreover, these special polynomials allow for the derivation of different useful identities in a fairly straightforward way. The so-called Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials appear in combinatorial mathematics and play an important role in the theory and applications of mathematics, leading to a great number of theories; combinatorics experts have extensively studied their properties, obtaining a series of interesting results (cf., e.g., [5,6,7,8,9,10] and the references therein).
The Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order are defined by (see [7,8]):
and is an entire function of z for any .
At the point , are called the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler numbers of order . From (1), we find
and
where are the jth Apostol–Euler polynomials of order .
For , the Stirling numbers of the first kind are defined by
where , and . From (4), we obtain
For , the Stirling numbers of the second kind are defined by
From (6), we see that
For any nonnegative integer r, the r-Stirling numbers of the second kind are defined by (see [11])
For any positive integer m, the r-Whitney numbers of the second kind are defined by (see [12,13])
The Apostol-type Bernoulli polynomials of order , the Apostol-type Euler polynomials of order and the Apostol-type Genocchi polynomials of order are defined by (see [1,2,12]):
where when ; when .
where when ; when .
and
where when ; when , respectively.
Clearly, we have
The Bell polynomials are defined by the generating function (see [14,15])
When , are called the Bell numbers. From (7) and (13), we note that
Recently, Duran et al. [12], introduced the Bell polynomials of two variable defined by the generating function
Furthermore, they introduced the generalized Bell-based Bernoulli polynomials defined by
so that
Kim and Ryoo [16] and Jamei et al. [1] introduced the Bernoulli and Euler polynomials of complex variable defined by
and
respectively.
Furthermore, they have proven that (see [13,17,18,19]):
and
where
and
The manuscript of this paper is arranged as follows: In Section 2, we introduce Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler numbers and polynomials and investigate some properties of these numbers and polynomials. In Section 3, we derive summation formulas of Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler numbers and polynomials, connected with Apostol-type Bernoulli, Euler, and Genocchi polynomials. In Section 4, we prove several identities of Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials by using different analytical means and applying generating functions. In the last Section 5, we establish parametric kinds of Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and investigate some identities of these polynomials.
2. Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials
In this section, we define Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and explicit formula for the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and investigate its properties. First, we start with the following definition:
Definition 1.
The Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order α are defined by means of the following generating function:
where
A few of them are
Remark 1.
On taking in (26), we obtain new type Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order α as follows:
Remark 2.
Upon setting in (26), the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order α reduces to familiar Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order α in (1).
Remark 3.
When and , the polynomials reduce to the usual Frobenius-Euler polynomials .
We note that
Theorem 1.
For , we have
Proof.
Using (1), (13), (15) and (26), we obtain representation (29)–(31). □
Theorem 2.
. Then,
Proof.
In view of (15) and (26), we have
Now equating the coefficients of the like powers of t in the above equation, we obtain the result (32). Again by using (15) and (26), we have
yields the formula (33). □
Theorem 3.
The following differentiation formulas for the Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order α hold true:
Proof.
The proof follows from (26), we have
the proof is completed. Again, using (26), we note that
Equating the coefficients of z, we obtain (37). □
Theorem 4.
Let . Then,
Proof.
We set
We see that
In view of the above equation, we obtain (40). □
Theorem 5.
For , we have
Proof.
Consider
We find
Therefore, by (42), we obtain (41). □
Theorem 6.
Let . Then,
Proof.
In (26), we have
By (26) and (44), we obtain (43). □
Theorem 7.
Let . Then,
Proof.
By (26), we note that
In view of (26) and (46), we obtain (45). □
3. Summation Formulas for Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials
In this section, we derive some implicit formulas for Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of order related to Apostol-type Bernoulli polynomials, Apostol-type Euler polynomials, Apostol-type Genocchi polynomials and Stirling numbers of the second kind. Now, we begin with the following theorem.
Theorem 8.
The following formula holds true:
Proof.
By changing z with in (26), we have
Again changing with in the above equation, we obtain
By the last equations, we obtain
On expanding exponential function (50) provides
which on using formula [4]
In view of above equation, we obtain the required result. □
Remark 4.
Letting in Theorem 8, we obtain.
Remark 5.
On changing ξ with and setting in Theorem 8, we obtain
whereas by setting in Theorem 8, we obtain another result involving Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of one and two variables
Theorem 9.
Let . Then,
Proof.
By (26), we have
Therefore, by above equation, we obtain (57). □
Theorem 10.
Let . Then,
Proof.
Using Definition 1, we have
In view of above equation, we obtain (58). □
Theorem 11.
Let . Then,
Proof.
In (26), we have
yields the result (59). □
Theorem 12.
Let . Then,
Proof.
By (26), we have
yield the required result (60). □
Remark 6.
For , Theorem 12 reduces to
Remark 7.
For and in Theorem 12, we obtain
In particular, for in the above equation, we obtain
Theorem 13.
Let . Then,
Proof.
In view of (10) and (26), we have
On equating the coefficients of same powers of z after using Cauchy product rule in (62), assertion (61) follows. □
Theorem 14.
Let . Then,
Proof.
From (11) and (26), we have
On equating the coefficients of same powers of z after using Cauchy product rule in (64), assertion (63) follows. □
Theorem 15.
Let . Then,
Proof.
By (12) and (26), we have
On equating the coefficients of same powers of z after using Cauchy product rule in above equation, we obtain (65). □
4. Identities for Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials
In this section, we provide general symmetry identities for the Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and generalized Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials by applying the generating functions (5) and (26).
Theorem 16.
Let with and . Then,
Proof.
Let
Then, the expression for is symmetric in a and b; we obtain
Similarly, we can show that
On comparing the coefficients of on the right-hand sides of the last two equations, we arrive at the desired result (66). □
Remark 8.
For in Theorem 16, the result reduces to
Theorem 17.
Let with and . Then,
Proof.
Consider the identity
On the other hand, we have
By (70) and (71), we arrive at the desired result (69). □
5. Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials of Complex Variable
In this section, we consider the Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of complex variable and deduce some identities of these polynomials. First, we begin with the following definition.
On the other hand, we suppose that
Thus, by (72) and (73), we have
and
From (74) and (75), we obtain
and
Definition 2.
Let . We define two parametric kinds of cosine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and sine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials , for non negative integer j are defined by
and
respectively.
Note that .
From (76)–(79), we have
Remark 9.
For in (78) and (79), we obtain new types of cosine Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and sine Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials as
and
respectively.
It is clear that
Remark 10.
Letting in (78) and (79), we obtain two parametric kinds of cosine Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and sine Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials as
and
respectively.
Remark 11.
On setting in (78) and (79), we obtain new type of cosine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and sine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials as
and
respectively.
Theorem 18.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
By (82) and (83), we have
and
Therefore, by (90) and (91), we obtain (88). Similarly, we can easily obtain (89). □
Theorem 19.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
By using (74) and (75), we obtain (92) and (93). So we omit the proof. □
Theorem 20.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
Consider
Now,
which proves (94). The proof of (95) is similar. □
Theorem 21.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
Using (78) and (79), we obtain (96)–(99). Here, we omit the proof of the theorem. □
Theorem 22.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
By changing with in (78), we have
which complete the proof (100). The result (101) can be similarly proved. □
Theorem 23.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
Theorem 24.
Let . Then,
and
Proof.
Using (7) and (78), we find
In view of (78) and (108), we obtain (106). Similarly, we can easily obtain (107). □
6. Numerical Values and Graphical Representations of Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials
In this section, we find some numerical values of the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and, beautifully, graphical representations are shown.
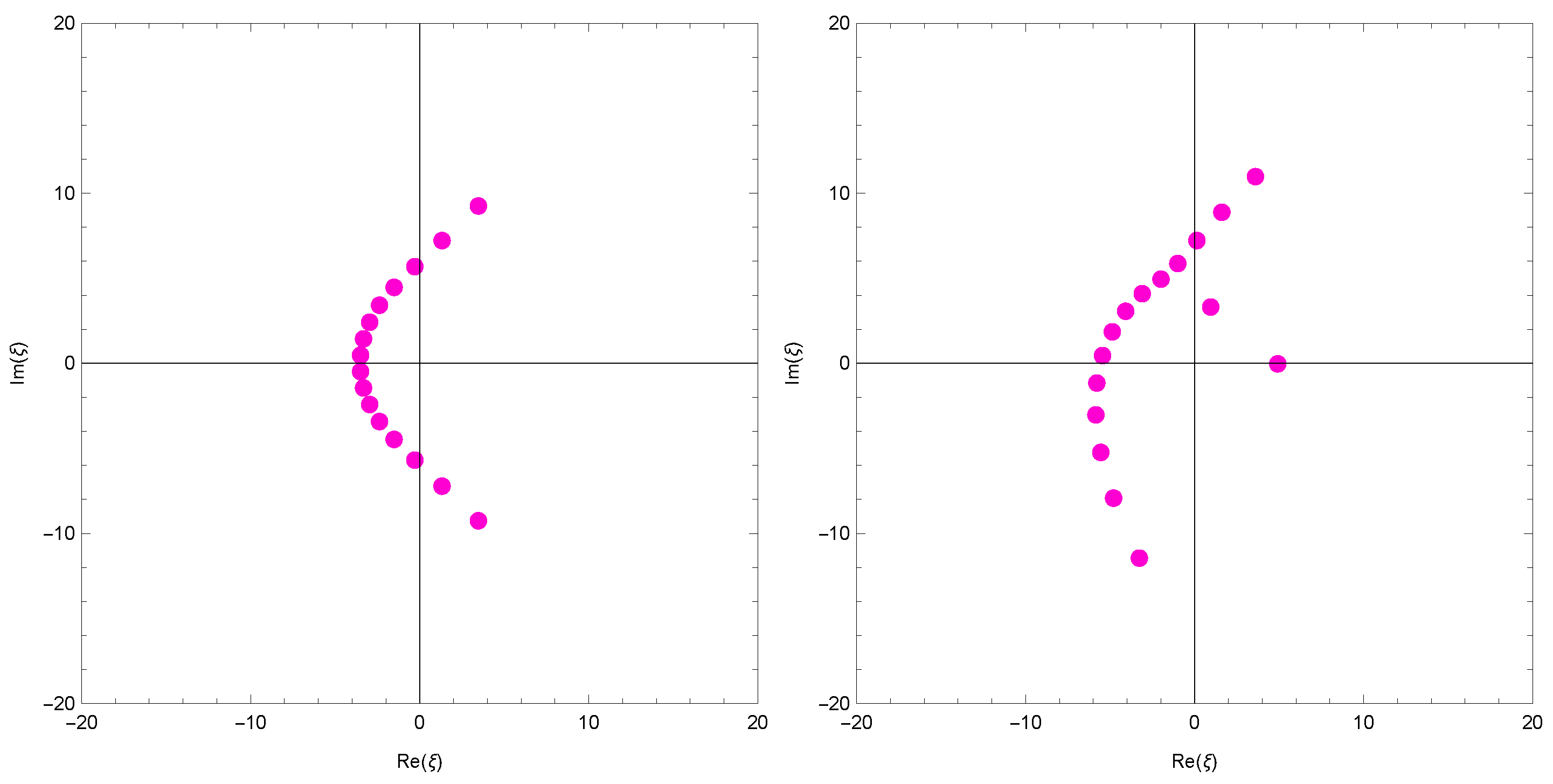
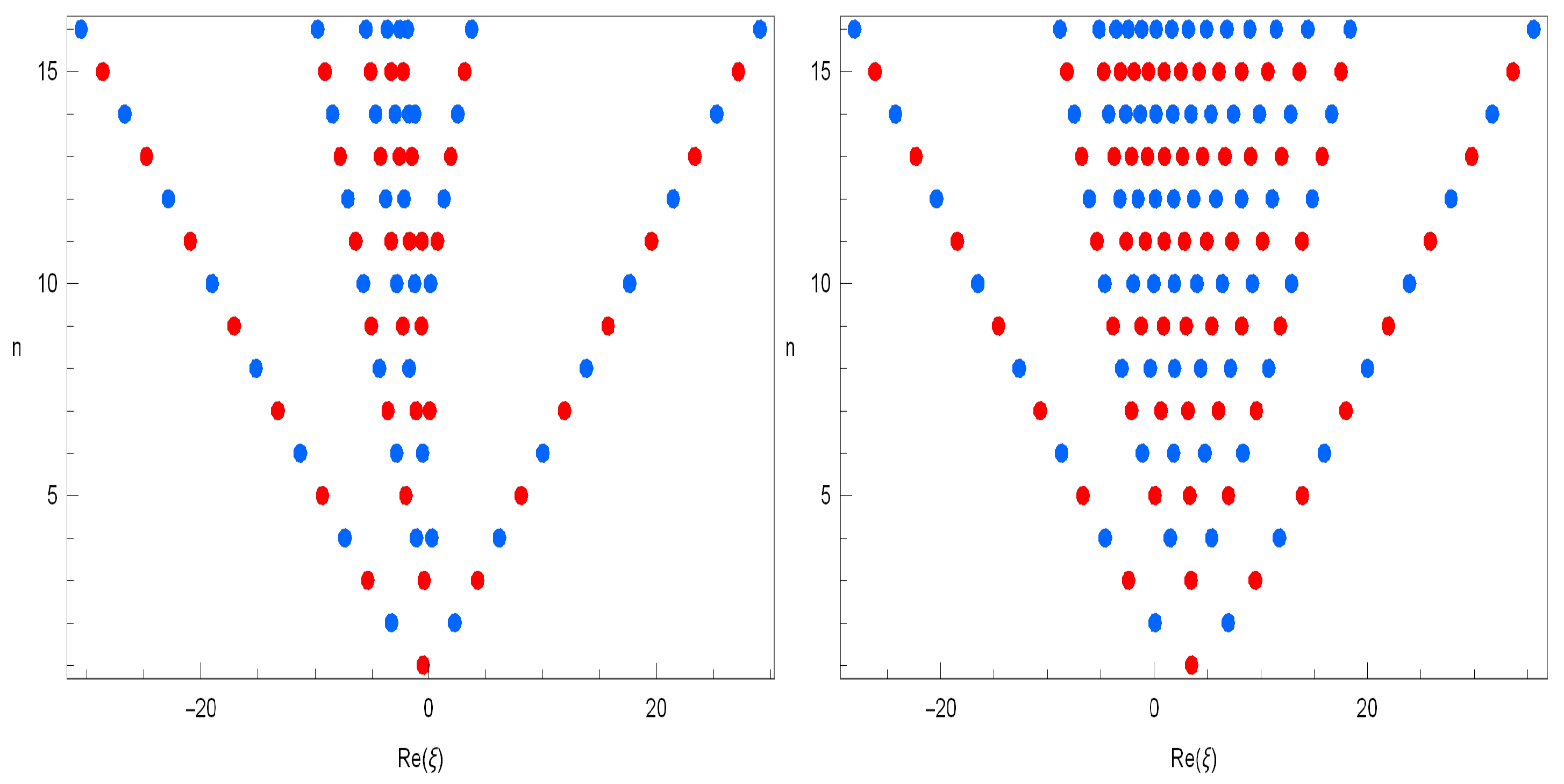
We investigated the beautiful zeros of the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials using a computer. We plotted the zeros of Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials for (Figure 1).
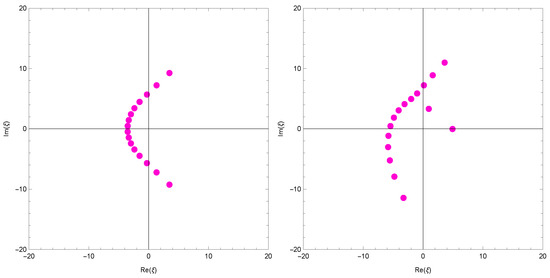
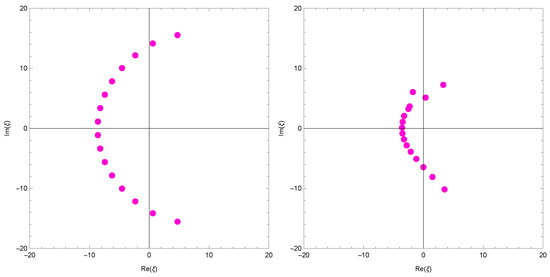
Figure 1.
Zeros of .
In Figure 1 (top left), we choose and . In Figure 1 (top right), we choose and . In Figure 1 (bottom left), we choose and . In Figure 1 (bottom right), we choose and .
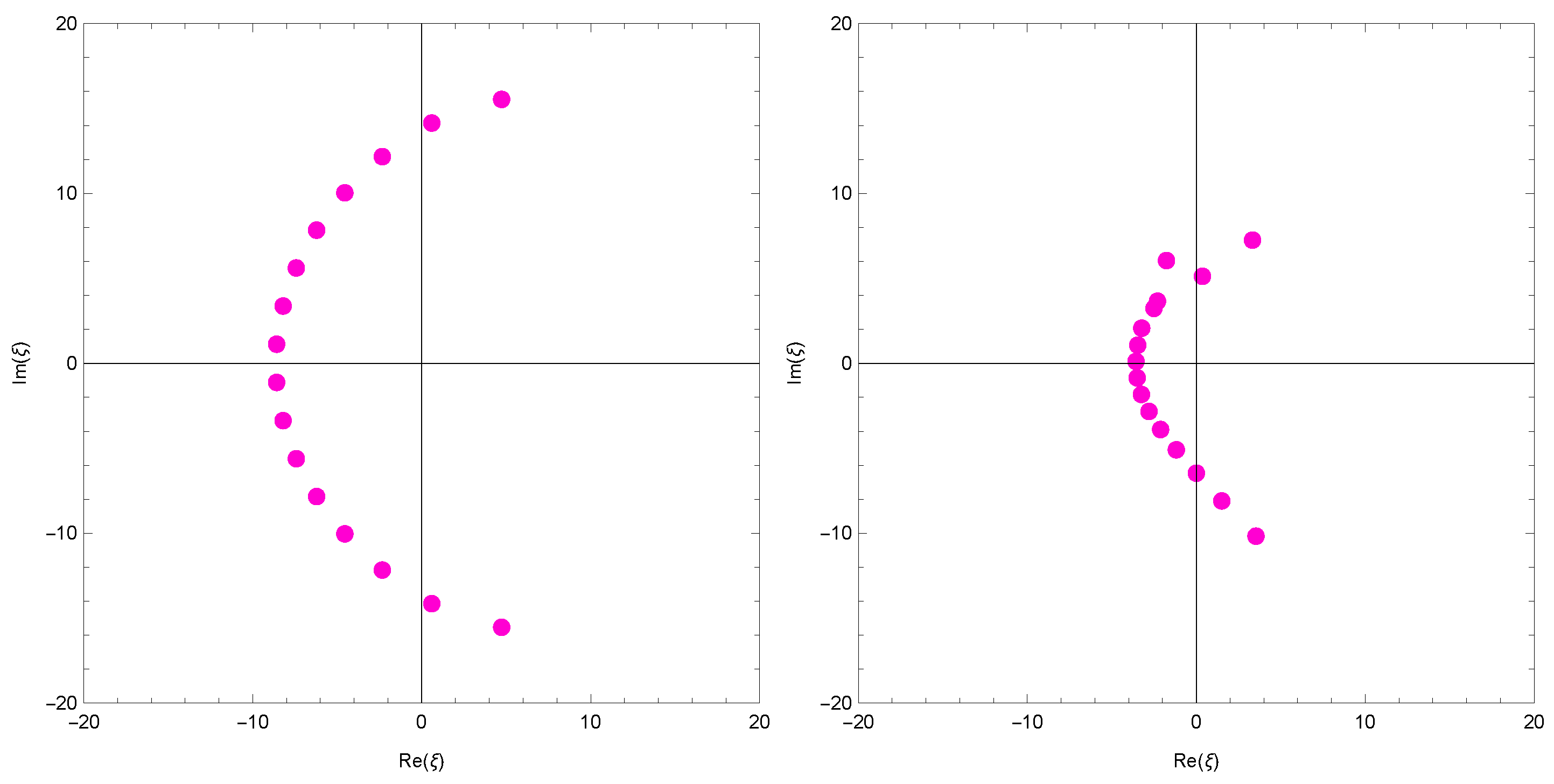
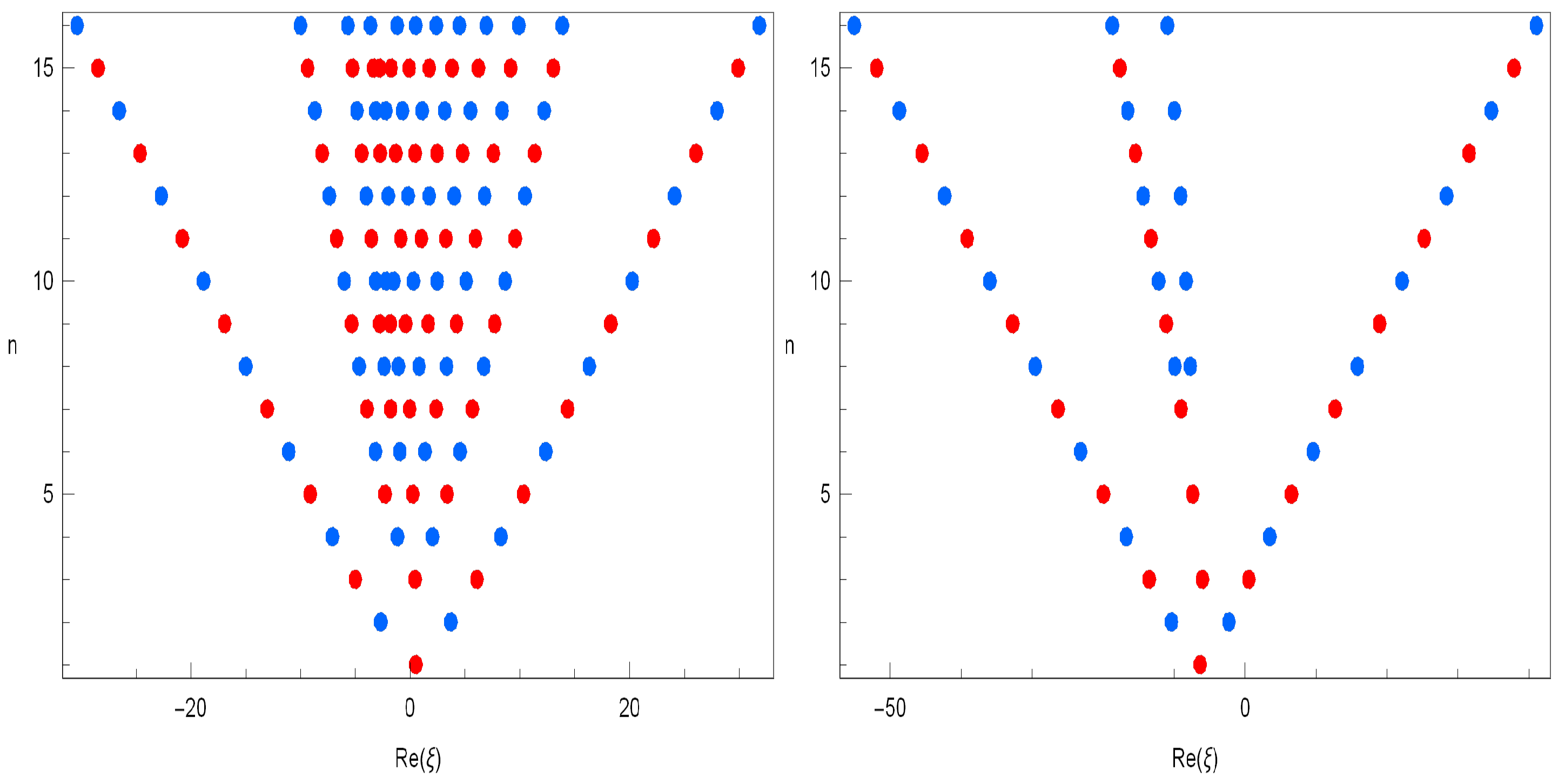
In Figure 2 (top left), we choose and . In Figure 2 (top right), we choose and . In Figure 2 (bottom left), we choose and . In Figure 2 (bottom right), we choose and .
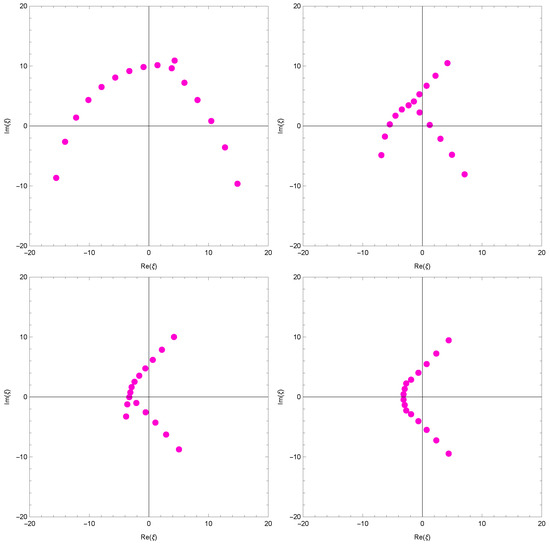
Figure 2.
Zeros of .
Next, we calculated an approximate solution satisfying the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials . The results are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Approximate solutions of .
7. Computational Values and Graphical Representations of Cosine Bell-Based Apostol-Type Frobenius-Euler Polynomials of Complex Variable
In this section, certain zeros of the cosine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of complex variable and, beautifully, graphical representations are shown.
A few of them are
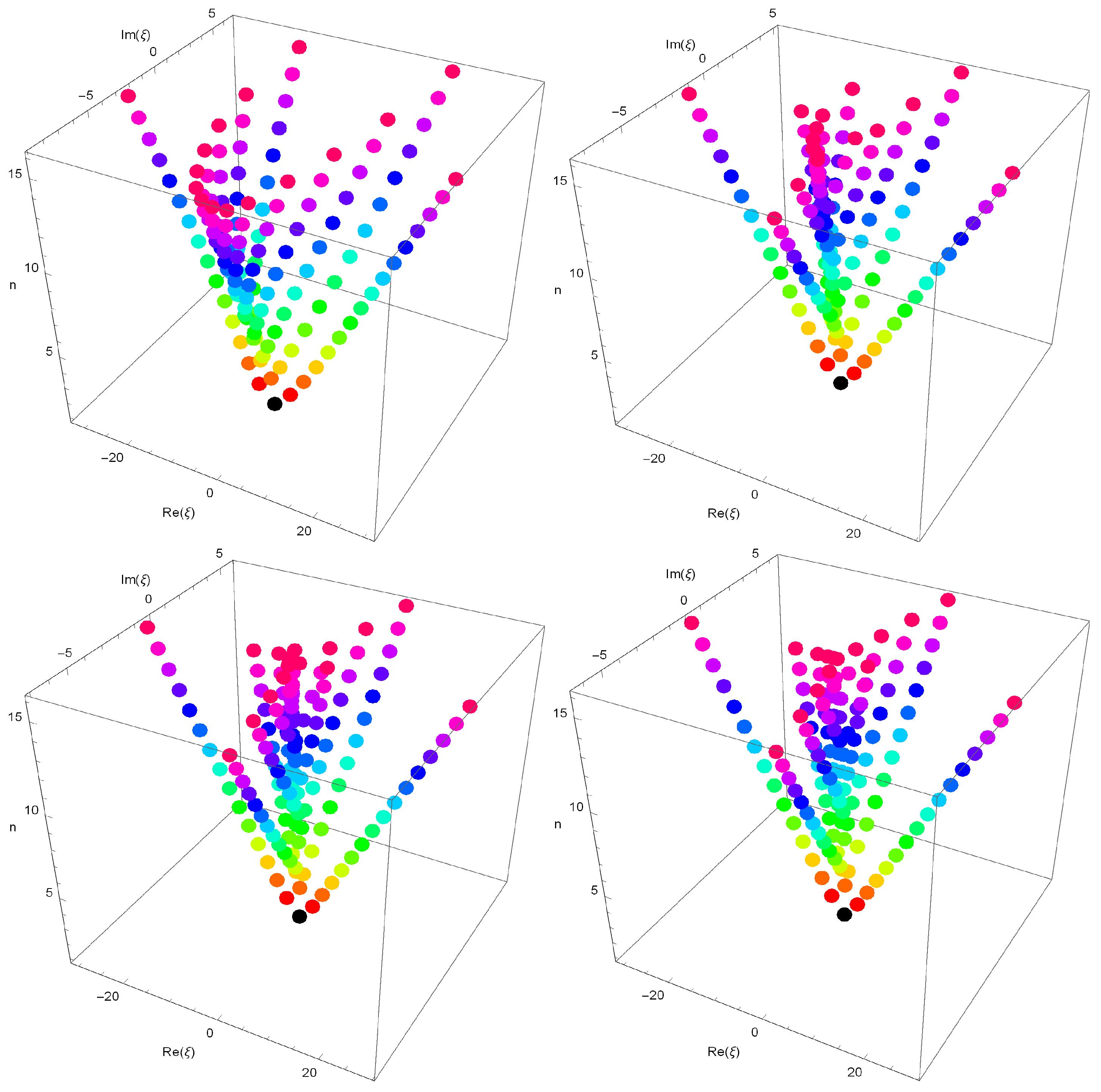
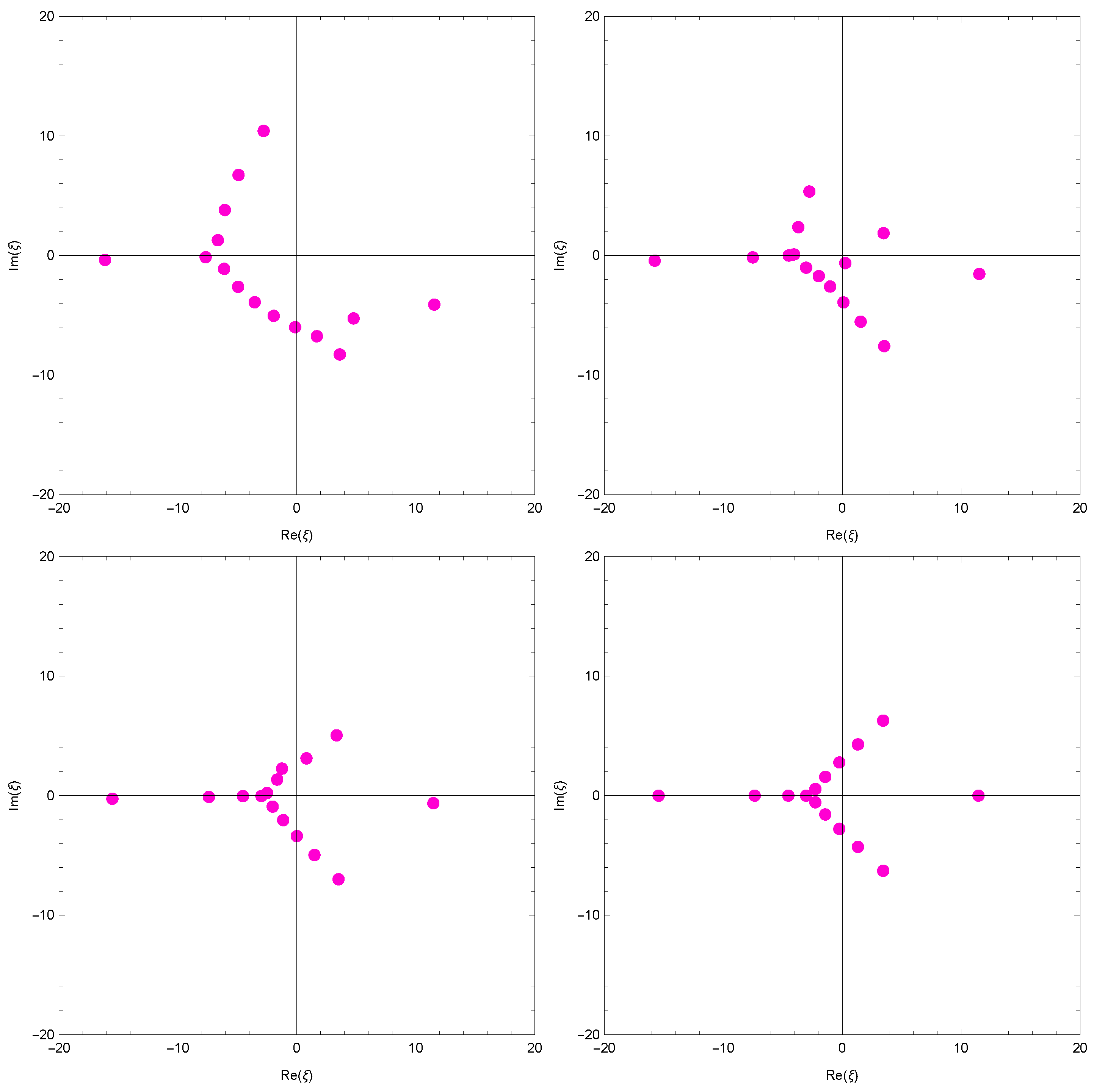
Stacks of zeros of for from a 3D structure are presented (Figure 3).
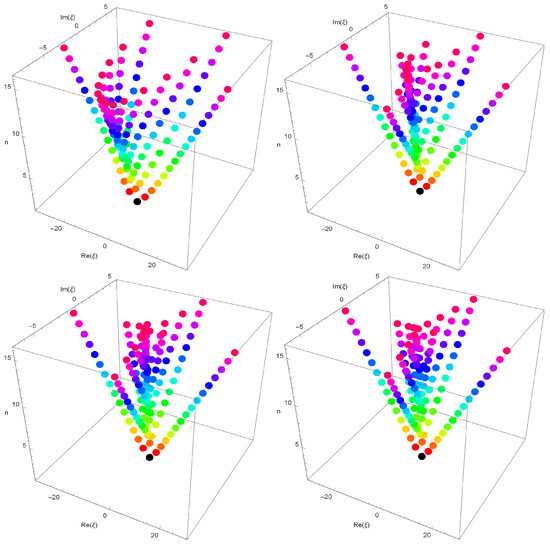
Figure 3.
Stacks of zeros of for
.
In Figure 3 (top left), we choose and . In Figure 3 (top right), we choose and . In Figure 3 (bottom left), we choose and . In Figure 3 (bottom right), we choose and .
The plots of real zeros of for structure are presented (Figure 4).
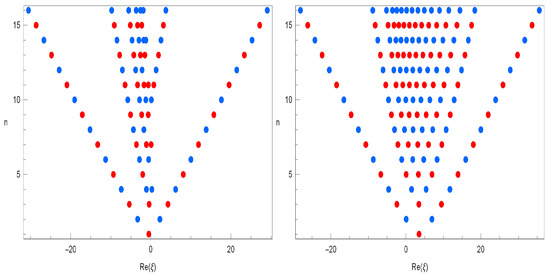
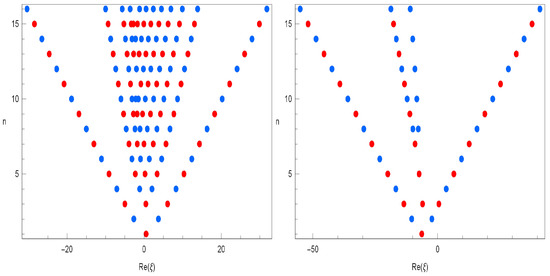
Figure 4.
Stacks of zeros of for
.
In Figure 4 (top left), we choose and . In Figure 4 (top right), we choose and . In Figure 4 (bottom left), we choose and . In Figure 4 (bottom right), we choose and .
Next, we calculated an approximate solution satisfying the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials for . The results are displayed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Approximate solutions of .
Finally, certain zeros of the sine Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials of complex variable and, beautifully, graphical representations are shown.
A few of them are as follows:
We investigated the beautiful zeros of the Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials using a computer. We plotted the zeros of Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials for (Figure 5).
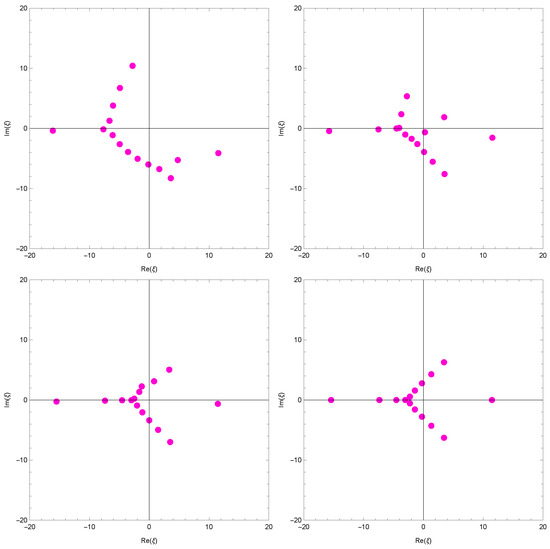
Figure 5.
Zeros of .
8. Conclusions
In this paper, we introduced the Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler numbers and polynomials and the properties of these numbers and polynomials. We derived summation formulas of Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler numbers and polynomials, connected with Apostol-type Bernoulli, Euler, Genocchi polynomials and Stirling numbers. Furthermore, we proved several identities of Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials by using different analytical means and applying generating functions. Furthermore, we established parametric kinds of Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and investigate some identities of these polynomials. We derived some numerical values of Bell-based Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials and drew some graphs of these polynomials using Mathematica. Consequently, the results of this article have potential applications in mathematics, mathematical physics, and engineering.
Author Contributions
Supervision, N.A.; writing—original draft, W.A.K.; writing—review & editing, C.S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data were used to support the study.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript. Also, the second author Waseem A. Khan thanks to Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Saudi Arabia for providing facilities and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jamei, M.M.; Beyki, M.R.; Koepf, W. A new type of Euler polynomials and numbers. Mediterr. J. Math. 2018, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.A.; Haroon, H. Some symmetric identities for the generalized Bernoulli, Euler and Genocchi polynomials associated with Hermite polynomials. Springer Plus 2016, 5, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özkan, E.Y.; Aksoy, G. Approximation by tensor- product kind bivariate operator of a new generalization of Bernstein-type rational functions and its GBS operator. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.A.; Khan, W.A. Some implicit summation formulas and symmetric identities for the generalized Hermite-Bernoulli polynomials. Mediterr. J. Math. 2015, 12, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A. Approximation of GBS type q-Jakimovski-Leviatam-Beta integral operators in Bögel space. Mathematics 2022, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlitz, L. Eulerian numbers and polynomials of higher order. Duke Math. J. 1960, 27, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, T. Some new identities of Frobenius-Euler numbers and polynomials. J. Inequal. Appl. 2012, 2012, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurt, B.; Simsek, Y. On the generalized Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler polynomials. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2013, 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilar, N.; Simsek, S. Two parametric kinds of Eulerian-type polynomials associated with Euler’s formula. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; Khan, W.A.; Ryoo, C.S. A parametric kind of Fubini polynomials of a complex variable. Mathematics 2020, 8, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Border, A.Z. The r-Stirling numbers. Discr. Math. 1984, 49, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duran, U.; Mehmet, A.; Araci, S. Bell-based Bernoulli polynomials. Axioms 2021, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhiuddin, G.; Khan, W.A.; Duran, U.; Al-Kadi, D. Some identities of the multi poly-Bernoulli polynomials of complex variable. J. Funct. Spaces 2021, 2021, 7172054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, T. Some identities of Bell polynomials. Sci. China Math. 2015, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.T. Exponential polynomials. Ann. Math. 1934, 35, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Ryoo, C.S. Some identities for Euler and Bernoulli polynomials and their zeros. Axioms 2018, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, T.; Lee, H. A note on degenerate Euler and Bernoulli polynomials of complex variables. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhiuddin, G.; Khan, W.A.; Al-Kadi, D. Construction on the degenerate poly-Frobenius-Euler polynomials of complex variable. J. Funct. Spaces 2021, 2021, 3115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.A.; Khan, W.A. A new class of generalized Apostol-type Frobenius-Euler–Hermite polynomials. Honam Math. J. 2020, 42, 477–499. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).