Vena Cava Interruption and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Summary
Zusammenfassung
Vena cava interruption
Mechanical thrombectomy
Surgical embolectomy
Percutaneous catheter thrombectomy
- Pulmonary embolism and cardiogenic shock, defined as a systolic arterial pressure 90 mm Hg, a drop in systolic arterial pressure 40 mm Hg for 15 minutes, or ongoing administration of catecholamines for systemic arterial hypotension
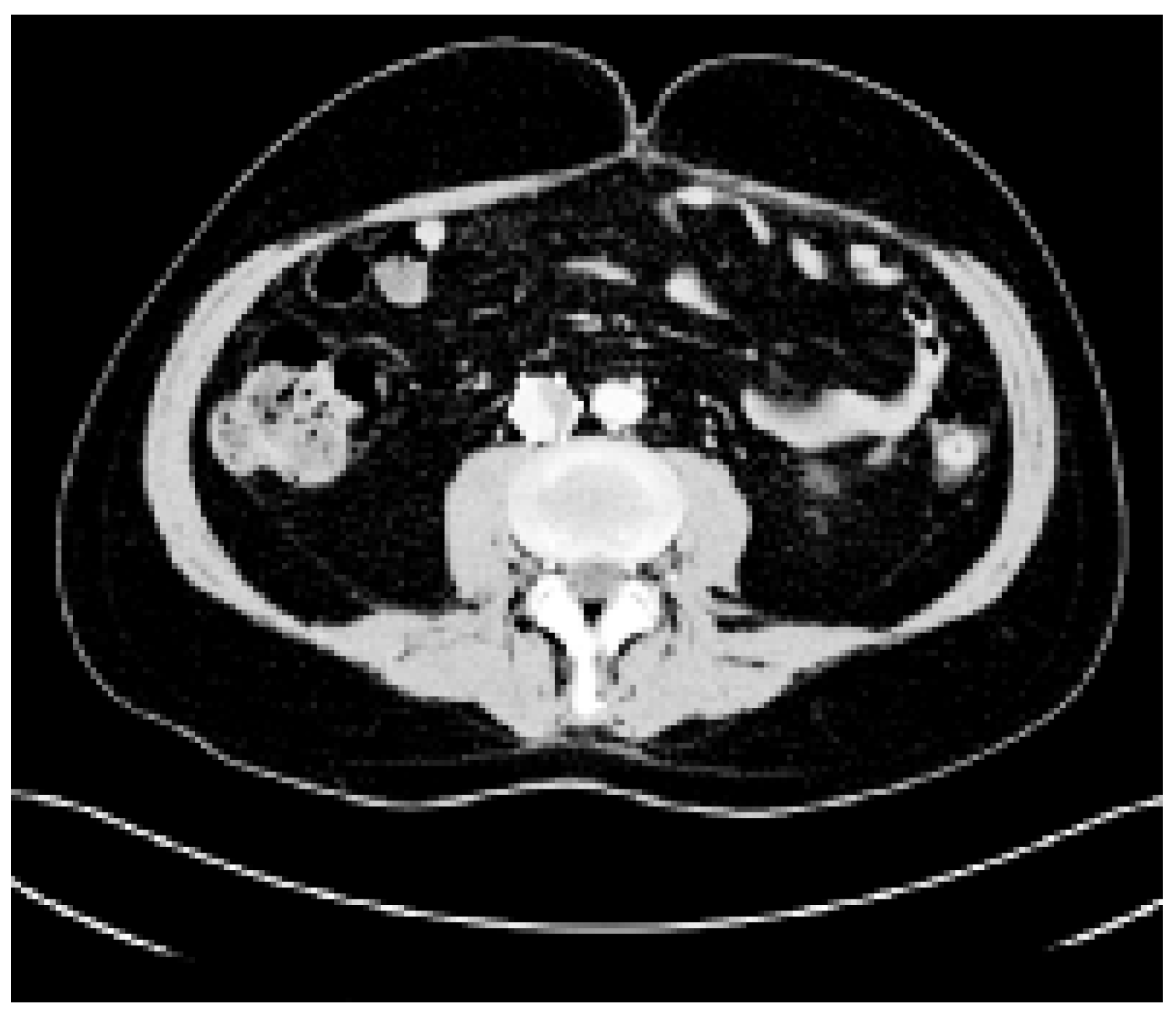
- Subtotal or total filling defect in the left and/or right main pulmonary artery by chest computed tomography or by conventional pulmonary angiography
- Presence of at least one of the following contraindiations to PE thrombolysis:
- –
- Active bleeding
- –
- History of intracranial bleeding, or head injury, or ischaemic stroke, or brain tumor, or neurosurgery
- –
- Surgery, delivery, organ biopsy, puncture of a non-compressible vessel within 10 days
- –
- Gastrointestinal bleeding within 15 days
- –
- Major trauma within 15 days
- –
- Active cancer with known haemorrhagic risk
- –
- Platelets <50 000 or INR >2.0
- –
- Pregnancy
Percutaneous pulmonary embolism catheter devices
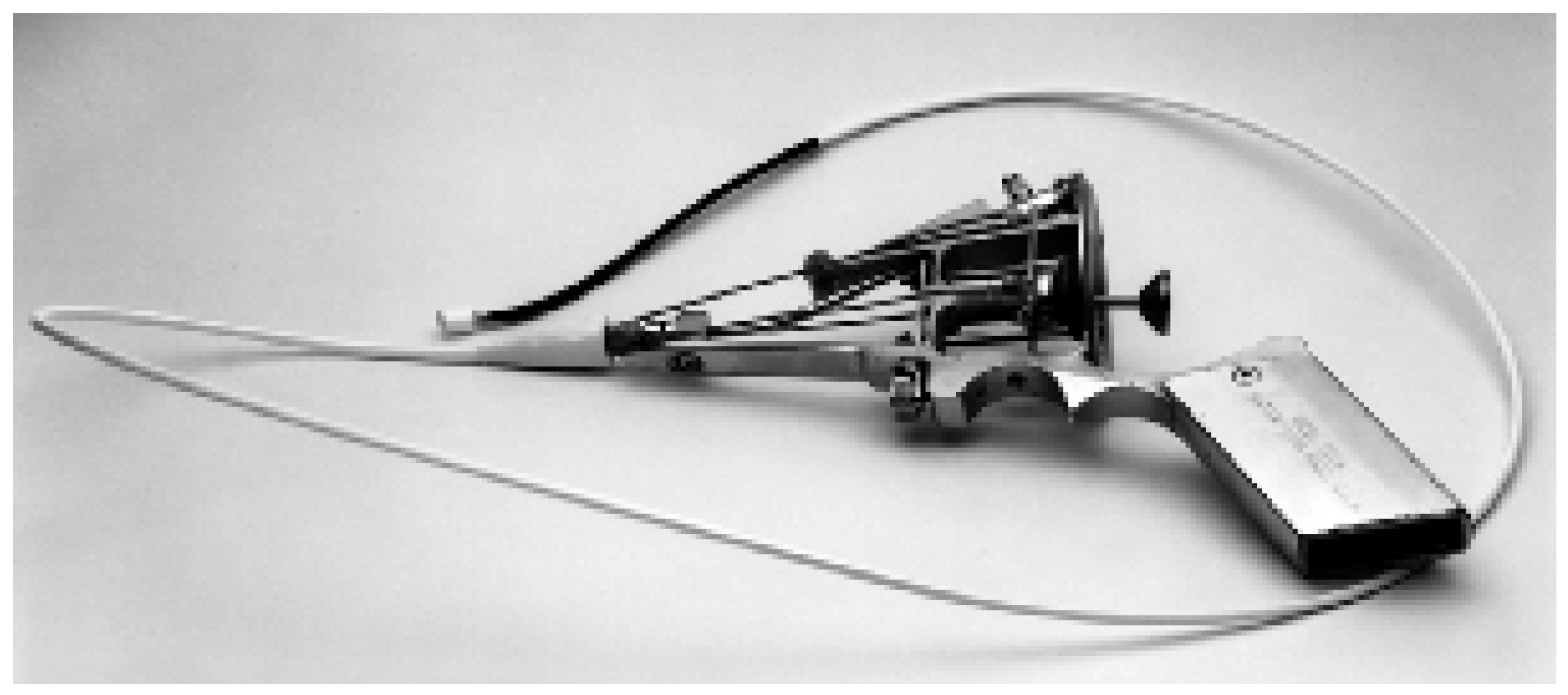
Greenfield embolectomy catheter
Balloon angioplasty
Pigtail rotational catheter
Hydrodynamic thrombectomy catheter devices
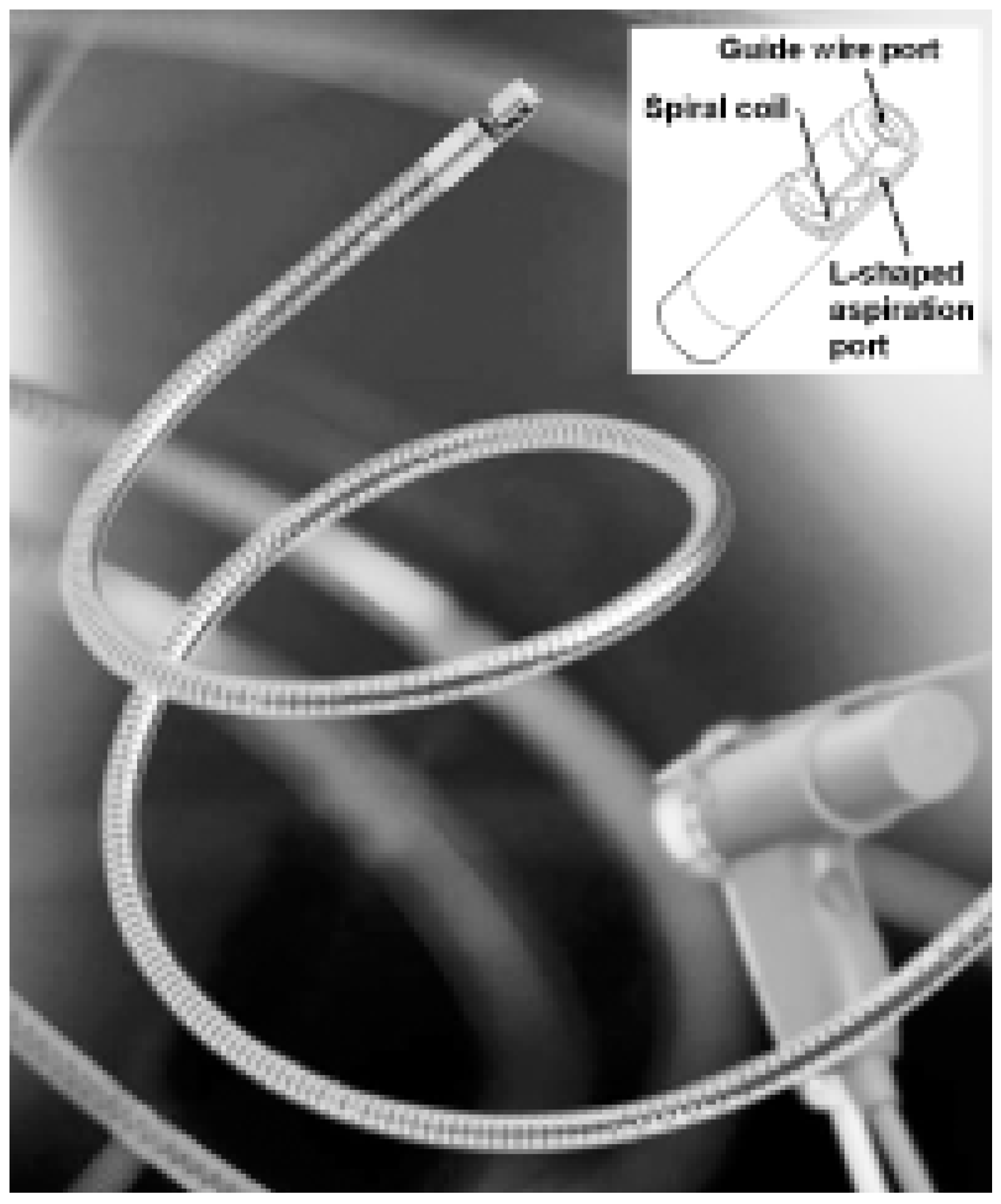
Aspirex pulmonary embolism catheter
Catheter-directed thrombolysis
Complications of catheter interventions
References
- Decousus, H.; Leizorovics, A.; Parent, F. et al. A clinical trial of vena caval filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med 1998, 338, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucher, N.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Management of massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation 2005, 112, e28–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Visani, L.; De Rosa, M. Acute pulmonary embolism: Clinical outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER). Lancet 1999, 353, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uflacker, R. Interventional therapy for pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001, 12, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aklog, L.; Williams, C.S.; Byrne, J.G. et al. Acute pulmonary embolectomy: A contemporary approach. Circulation 2002, 105, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, W.; Konstantinides, S.; Geibel, A. et al. Management strategies and determinants of outcome in acute major pulmonary embolism: Results of a multicenter registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997, 30, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, L.J.; Proctor, M.C.; Williams, D.M.; Wakefield, T.W. Long-term experience with transvenous catheter pulmonary embolectomy. J Vasc Surg 1993, 18, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Greenfield, L.J.; Kimmell, G.O.; McCurdy, W.C. , 3rd. Transvenous removal of pulmonary emboli by vacuum-cup catheter technique. J Surg Res 1969, 9, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskal, Z.J.; Soulen, M.C.; Huetti, E.A.; Palevsky, H.I.; Cope, C. Life-threatening pulmonary emboli and cor pulmonale: Treatment with percutaneous pulmonary artery stent placement. Radiology 1994, 191, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, J.; Kusano, S.; Akima, T. et al. Emergent Z stent placement for treatment of cor pulmonale due to pulmonary emboli after failed lytic treatment: Technical considerations. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1998, 21, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Rode, T.; Janssens, U.; Duda, S.H. et al. Massive pulmonary embolism: Percutaneous emergency treatment by pigtail rotation catheter. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 36, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Hulsbeck, S.; Grimm, J.; Leidt, J.; Heller, M. In vitro effectiveness of mechanical thrombectomy devices for large vessel diameter and low-pressure fluid dynamic applications. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002, 13, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koning, R.; Cribier, A.; Gerber, L. et al. A new treatment for severe pulmonary embolism. Circulation 1997, 96, 2498–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigtlander, T.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Nowak, B. et al. Clinical application of a new rheolytic thrombectomy catheter system for massive pulmonary embolism. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent 1999, 47, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kucher, N.; Windecker, S.; Banz, Y.; Mettler, D.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Meier, B. et al. Percutaneous catheter thrombectomy device for acute pulmonary embolism. Radiology 2005, 236, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Juanatey, J.R.; Valdes, L.; Amaro, A. et al. Treatment of massive pulmonary thromboembolism with low intrapulmonary dosages of urokinase: Short term angiographic and hemodynamic evolution. Chest 1992, 102, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujic, I.; Young, J.W.R.; Gobien, R.P. et al. Massive pulmonary embolism treatment with full heparinization and topical low-dose streptokinase. Radiology 1983, 148, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, M.; Miller, G.A.H.; Bounameaux, H. et al. Intravenous and intrapulmonary recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in the treatment of acute massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation 1988, 77, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2006 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Kucher, N. Vena Cava Interruption and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 9, 162. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01170
Kucher N. Vena Cava Interruption and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2006; 9(4):162. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01170
Chicago/Turabian StyleKucher, Nils. 2006. "Vena Cava Interruption and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Pulmonary Embolism" Cardiovascular Medicine 9, no. 4: 162. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01170
APA StyleKucher, N. (2006). Vena Cava Interruption and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Cardiovascular Medicine, 9(4), 162. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01170



