Laiendefibrillation Ausserhalb des Spitals–Häufig Propagiert, Aber zu Selten Eingesetzt
Summary
Zusammenfassung
Einleitung
Fragestellung und Methodik
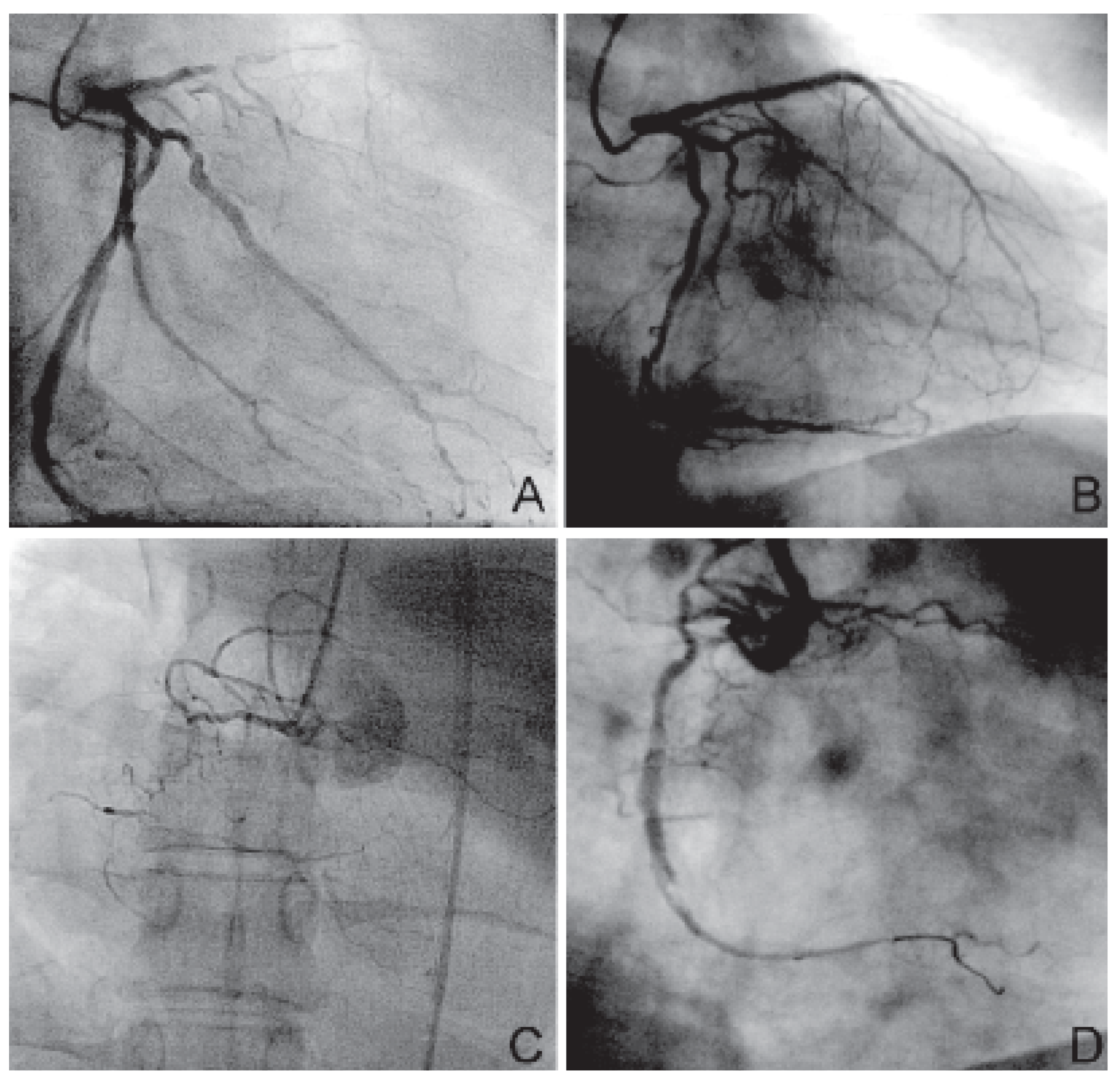
Kasuistik
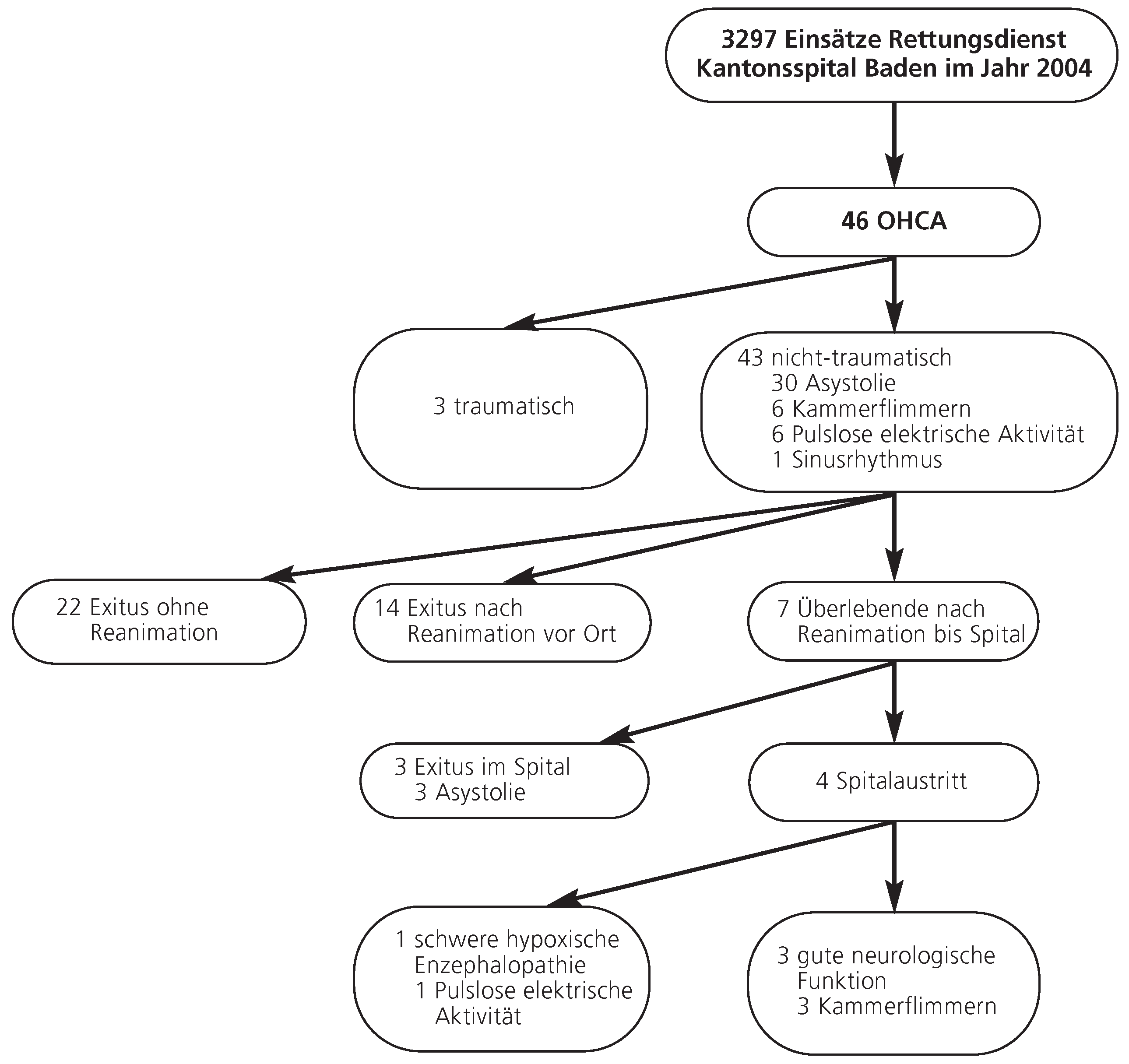
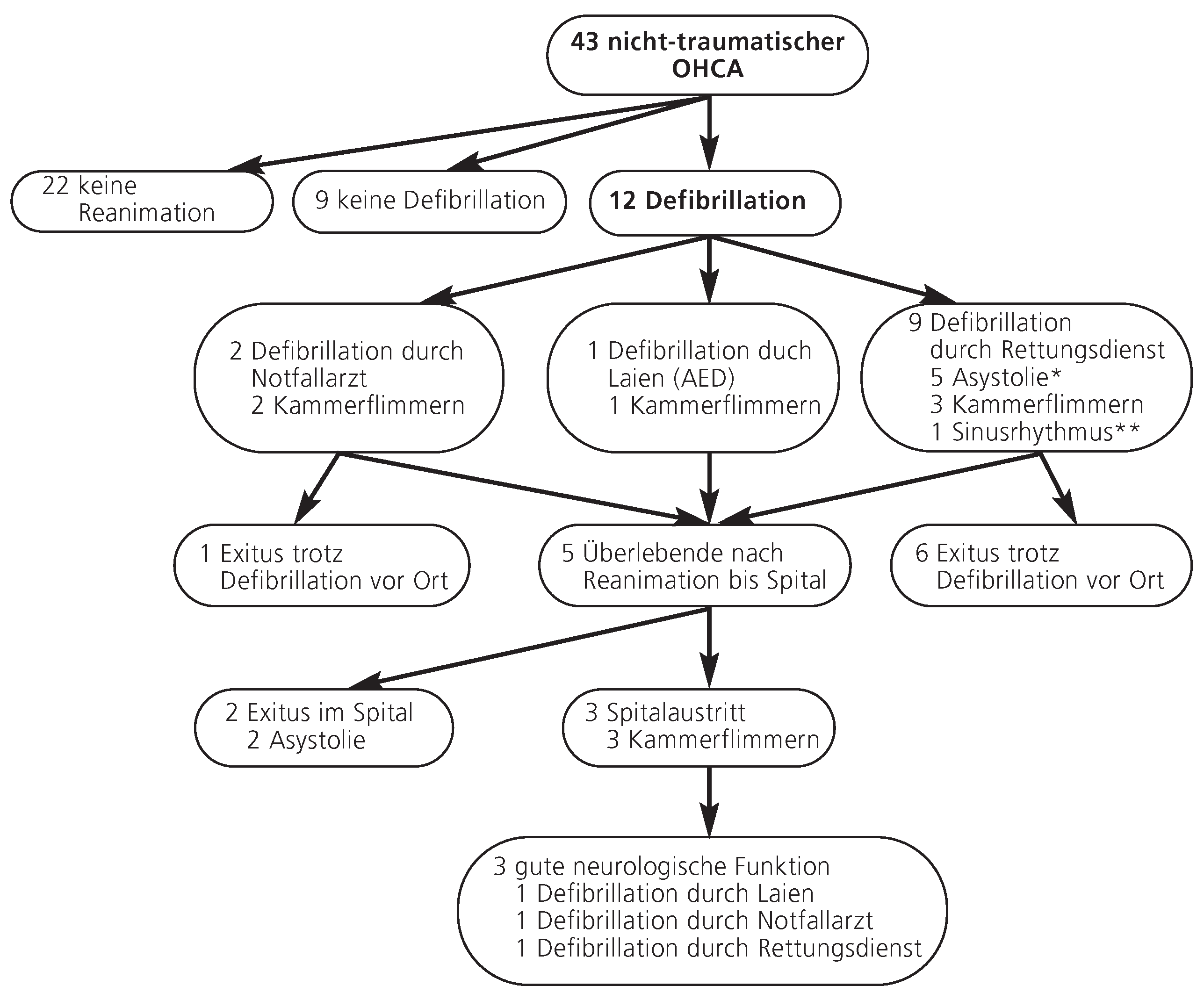
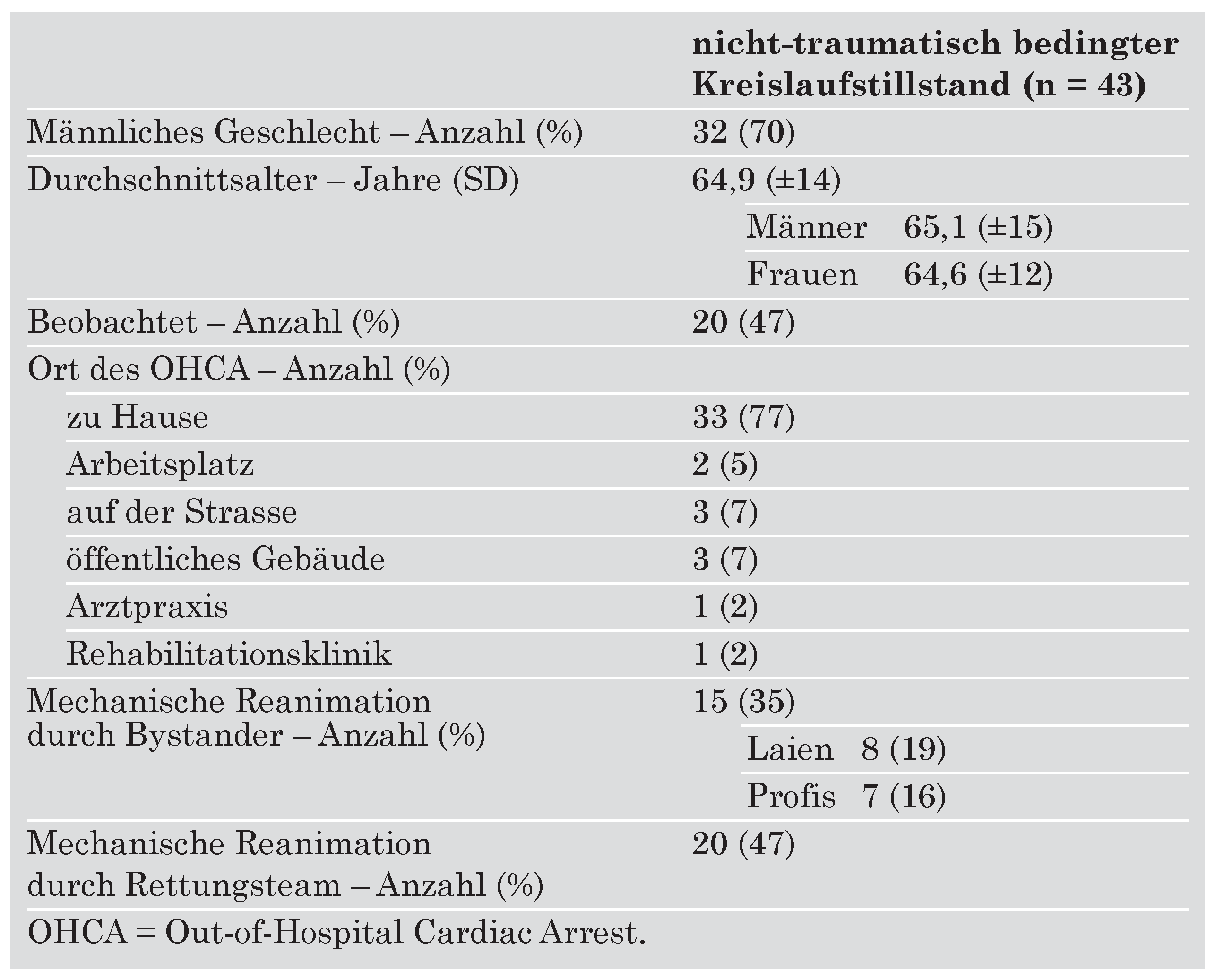
Resultate
Nicht-traumatisch bedingter Kreislaufstillstand ausserhalb des Spitals
Elektrische Reanimation bei nicht-traumatisch bedingtem Kreislaufstillstand ausserhalb des Spitals
Diskussion
«Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest»
Überlebenskette—«Chain of Survival»
Konzept der Defibrillation durch Rettungsdienste
Konzept der First-Responder-Defibrillation
Konzept der Laienfrühdefibrillation—Public-Access-Defibrillation
Kosteneffizienz der Public-Access-Defibrillation
Situation der Public-Access-Defibrillation in der Schweiz
Schlussfolgerung
Dank
Anhang
Glossar
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
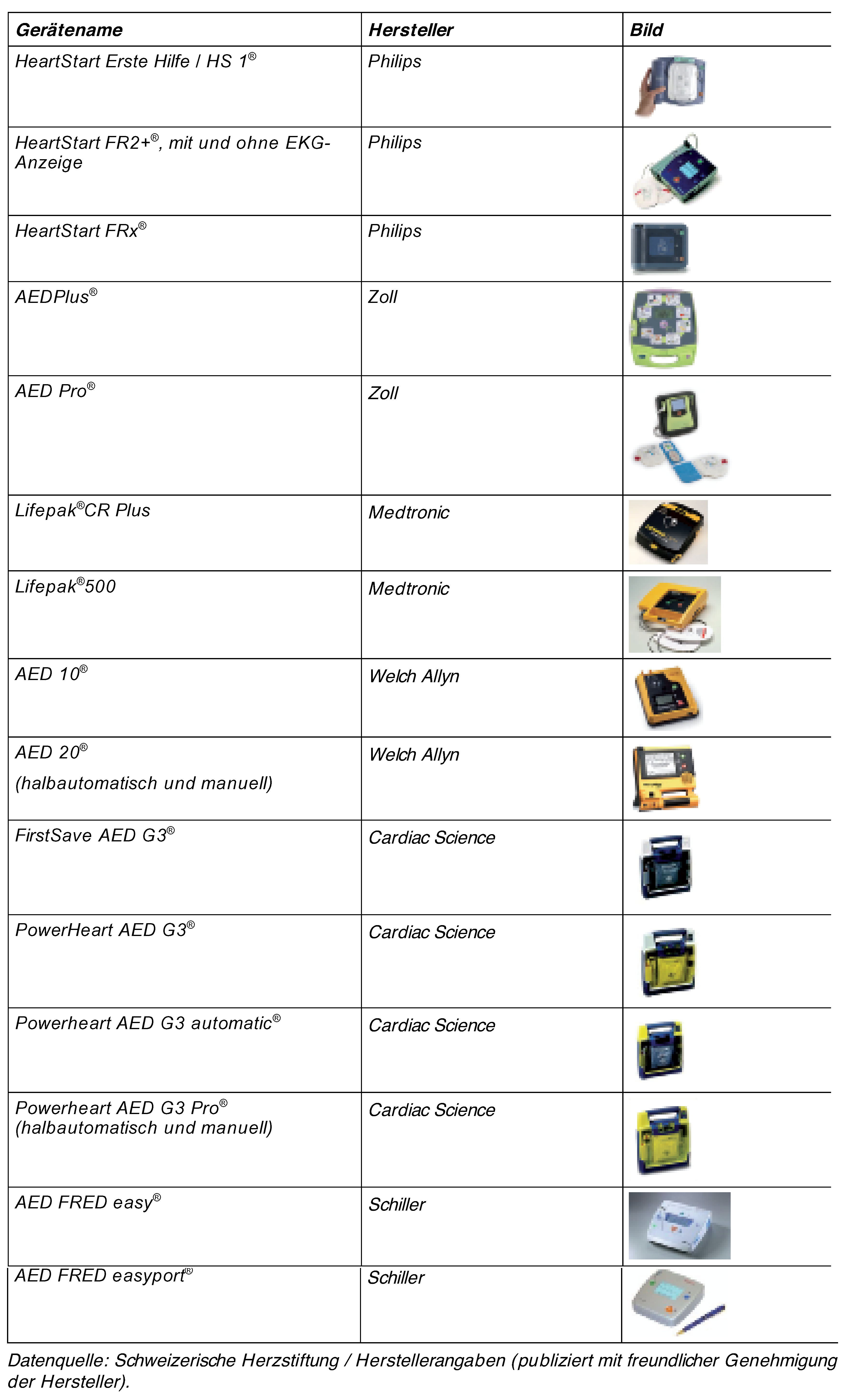
Automatischer externer Defibrillator (AED)
Basic Life Support (BLS)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR)
Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA)
Swiss Resuscitation Council (SRC)
Helfer bei OHCA
Bystander
Rettungssanität
First Responder
Public Access Defibrillation (PAD)—Laiendefibrillation
References
- Rudner, R.; Jalowiecki, P.; Karpel, E.; Dziurdzik, P.; Alberski, B.; Kawecki, P. Survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Katowice (Poland): Outcome report according to the “Utstein style”. Resuscitation 2004, 61, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.; Van Ottingham, L.; Schron, E. Public defibrillation: Increased survival from a structured response system. J Cardiovasc Nurs 2004, 19, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State-specific mortality from sudden cardiac death—United States, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002, 51, 123–126.
- Bottiger, B.W.; Grabner, C.; Bauer, H.; Bode, C.; Weber, T.; Motsch, J.; et al. Long term outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with physician staffed emergency medical services: The Utstein style applied to a midsized urban/suburban area. Heart 1999, 82, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Gaul, G.B.; Gruska, M.; Titscher, G.; Blazek, G.; Havelec, L.; Marktl, W.; et al. Prediction of survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Results of a community-based study in Vienna. Resuscitation 1996, 32, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, G.; Detsky, A.S.; Stiell, I.G.; O’Rourke, K.; Wells, G.; Laupacis, A. Effectiveness of emergency medical services for victims of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A metaanalysis. Ann Emerg Med 1996, 27, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Planta, M.; Osterwalder, J. Cardio-Pulmonale Reanimation und Früh-Defibrillation. SAeZ 2001, 82, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, M.S.; Mengert, T.J. Cardiac resuscitation. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, R.O.; Ornato, J.P.; Thies, W.H.; Pepe, P.E. Improving survival from sudden cardiac arrest: The “chain of survival” concept. A statement for health professionals from the Advanced Cardiac Life Support Subcommittee and the Emergency Cardiac Care Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation 1991, 83, 1832–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, E.; Bernoulli, L.; Klemmer, U.; Malacrida, R.; Osterwalder, J.; von Planta, M.; et al. Defibrillation mit automatischen und halbautomatischen externen Defibrillatoren (AED). SAeZ 2001, 82, 2088–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, I.; Nadkarni, V.; Bahr, J.; Berg, R.A.; Billi, J.E.; Bossaert, L.; et al. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: Update and simplification of the Utstein templates for resuscitation registries. A statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the international liaison committee on resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian Resuscitation Council, New Zealand Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa). Resuscitation 2004, 63, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cummins, R.O.; Chamberlain, D.A.; Abramson, N.S.; Allen, M.; Baskett, P.J.; Becker, L.; et al. Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting of data from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: The Utstein Style. A statement for health professionals from a task force of the American Heart Association, the European Resuscitation Council, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, and the Australian Resuscitation Council. Circulation 1991, 84, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiell, I.G.; Wells, G.A.; Field, B.; Spaite, D.W.; Nesbitt, L.P.; De Maio, V.J.; et al. Advanced cardiac life support in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med 2004, 351, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotz, M.; Albrecht, R.; Zwicker, G.; Drewe, J.; Ummenhofer, W. EMS defibrillation-first policy may not improve outcome in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2003, 58, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, L.; Hansen, T.B.; Fylling, F.; Steen, T.; Vaagenes, P.; Auestad, B.H.; et al. Delaying defibrillation to give basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to patients with out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation: A randomized trial. JAMA 2003, 289, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, L.A.; Fahrenbruch, C.E.; Walsh, T.R.; Copass, M.K.; Olsufka, M.; Breskin, M.; et al. Influence of cardiopulmonary resuscitation prior to defibrillation in patients with out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation. JAMA 1999, 281, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.F.; Dorian, P. Update on advanced life support and resuscitation techniques. Curr Opin Cardiol 2005, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, T.D.; Roe, D.J.; Nichol, G.; Clark, L.L.; Spaite, D.W.; Hardman, R.G. Outcomes of rapid defibrillation by security officers after cardiac arrest in casinos. N Engl J Med 2000, 343, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R.D.; Mottley, J.L.; Weinstein, C. Impact of prompt defibrillation on cardiac arrest at a major international airport. Prehosp Emerg Care 2002, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.L.; Joglar, J.A.; Kowal, R.C.; Zagrodzky, J.D.; Nelson, L.L.; Ramaswamy, K.; et al. Use of automated external defibrillators by a U.S. airline. N Engl J Med 2000, 343, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, C.; Rodriguez Redington, P.; Lecarpentier, E.; Bellaiche, G.; Michel, D.; Teiger, E.; et al. Preliminary report on AED deployment on the entire Air France commercial fleet: A joint venture with Paris XII University Training Programme. Resuscitation 2004, 63, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerburg, R.J.; Fenster, J.; Velez, M.; Rosenberg, D.; Lai, S.; Kurlansky, P.; et al. Impact of community-wide police car deployment of automated external defibrillators on survival from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Circulation 2002, 106, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.D.; Hankins, D.G.; Bugliosi, T.F. Seven years’ experience with early defibrillation by police and paramedics in an emergency medical services system. Resuscitation 1998, 39, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosesso VNJr Davis, E.A.; Auble, T.E.; Paris, P.M.; Yealy, D.M. Use of automated external defibrillators by police officers for treatment of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Ann Emerg Med 1998, 32, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Alem, A.P.; Vrenken, R.H.; de Vos, R.; Tijssen, J.G.; Koster, RW. Use of automated external defibrillator by first responders in out of hospital cardiac arrest: Prospective controlled trial. BMJ 2003, 327, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenco, J.P.; Wang, P.J.; Link, M.S.; Homoud, M.K.; Estes, N.A., 3rd. Improving survival from sudden cardiac arrest: The role of the automated external defibrillator. JAMA 2001, 285, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgenson, D.B.; Skarr, T.; Russell, J.K.; Snyder, D.E.; Uhrbrock, K. AED use in businesses, public facilities and homes by minimally trained first responders. Resuscitation 2003, 59, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffrey, S.L.; Willoughby, P.J.; Pepe, P.E.; Becker, L.B. Public use of automated external defibrillators. N Engl J Med 2002, 347, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, A.; Aschieri, D.; Piepoli, M.F.; Bardy, G.H.; Iconomu, E.; Arvedi, M. Tripling survival from sudden cardiac arrest via early defibrillation without traditional education in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Circulation 2002, 106, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pell, J.P.; Sirel, J.M.; Marsden, A.K.; Ford, I.; Walker, N.L.; Cobbe, S.M. Potential impact of public access defibrillators on survival after out of hospital cardiopulmonary arrest: Retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2002, 325, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornato, J.P.; McBurnie, M.A.; Nichol, G.; Salive, M.; Weisfeldt, M.; Riegel, B.; et al. The Public Access Defibrillation (PAD) trial: Study design and rationale. Resuscitation 2003, 56, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hallstrom, A.P.; Ornato, J.P.; Weisfeldt, M.; Travers, A.; Christenson, J.; McBurnie, M.A.; et al. Public-access defibrillation and survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med 2004, 351, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- Andre, A.D.; Jorgenson, D.B.; Froman, J.A.; Snyder, D.E.; Poole, J.E. Automated external defibrillator use by untrained bystanders: Can the public-use model work? Prehosp Emerg Care 2004, 8, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollard, M.; Whitfeild, R.; Smith, A.; Colquhoun, M.; Newcombe, R.G.; Vetteer, N.; et al. Skill acquisition and retention in automated external defibrillator (AED) use and CPR by lay responders: A prospective study. Resuscitation 2004, 60, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejas, S.; Barry, A.; Demertsidis, E.; Jorgenson, D.; Becker, L.B. Human factors impact successful lay person automated external defibrillator use during simulated cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med 2004, 32, S406–S413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, L.; Dorph, E.; Auestad, B.; Andreas Steen, P. Evaluation of a defibrillator-basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation programme for non medical personnel. Resuscitation 2003, 56, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichol, G.; Valenzuela, T.; Roe, D.; Clark, L.; Huszti, E.; Wells, G.A. Cost effectiveness of defibrillation by targeted responders in public settings. Circulation 2003, 108, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alem, A.P.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Tijssen, J.G.; Koster, R.W. Health system costs of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in relation to time to shock. Circulation 2004, 110, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.; Eisenberg, M.; Fahrenbruch, C.; Cobb, L. Public locations of cardiac arrest. Implications for public access defibrillation. Circulation 1998, 97, 2106–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, P.; Vijan, S.; Fendrick, A.M. Cost-effectiveness of automated external defibrillator deployment in selected public locations. J Gen Intern Med 2003, 18, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naess, A.C.; Steen, P.A. Long-term survival and costs per life year gained after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2004, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, M.; Lindholm, D.J.; Campbell, J.P. Public-access defibrillation: Where do we place the AEDs? Prehosp Emerg Care 1999, 3, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoruk, J.C.; Currie, W.L.; Gobet, M. Locations of cardiac arrest: Affirmation for community Public Access Defibrillation (PAD) Program. Prehospital Disaster Med 2002, 17, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.L.; Rausch, M.A.; Menegazzi, J.J.; Rickens, M. The locations of nonresidential out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in the City of Pittsburgh over a three-year period: Implications for automated external defibrillator placement. Prehosp Emerg Care 2001, 5, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, P.; Vijan, S.; Katz, D.; Fendrick, A.M. Cost-effectiveness of in-home automated external defibrillators for individuals at increased risk of sudden cardiac death. J Gen Intern Med 2005, 20, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, P.W.; Owens, D.K. Cost-effectiveness of training unselected laypersons in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and defibrillation. Am J Med 2005, 118, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.; Sirel, J.M.; Marsden, A.K.; Cobbe, S.M.; Pell, J.P. Cost effectiveness and cost utility model of public place defibrillators in improving survival after prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest. BMJ 2003, 327, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portner, M.E.; Pollack, M.L.; Schirk, S.K.; Schlenker, M.K. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest locations in a rural community: Where should we place AEDs? Prehospital Disaster Med 2004, 19, 352–355; discussion 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterwalder, J.; Gerecke, P.; Oechslin, E.; von Planta, M. Neuerungen der ACLS-Richtlinien 2000 im Überblick. SAeZ 2002, 83, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale, G.; Jennet, B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical approach. Lancet 1974, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
© 2006 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Friedli, B.C.; Erb, R.; Stoffel, P.; Gloor, H.O.; Beer, J.H. Laiendefibrillation Ausserhalb des Spitals–Häufig Propagiert, Aber zu Selten Eingesetzt. Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01151
Friedli BC, Erb R, Stoffel P, Gloor HO, Beer JH. Laiendefibrillation Ausserhalb des Spitals–Häufig Propagiert, Aber zu Selten Eingesetzt. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2006; 9(2):54. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01151
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriedli, Bernhard C., Regula Erb, Peter Stoffel, Hans O. Gloor, and Jürg H. Beer. 2006. "Laiendefibrillation Ausserhalb des Spitals–Häufig Propagiert, Aber zu Selten Eingesetzt" Cardiovascular Medicine 9, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01151
APA StyleFriedli, B. C., Erb, R., Stoffel, P., Gloor, H. O., & Beer, J. H. (2006). Laiendefibrillation Ausserhalb des Spitals–Häufig Propagiert, Aber zu Selten Eingesetzt. Cardiovascular Medicine, 9(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01151




