Abklärung von Karotisstenose und -Verschluss
Summary
Zusammenfassung
Einleitung
Die symptomatische Karotisstenose
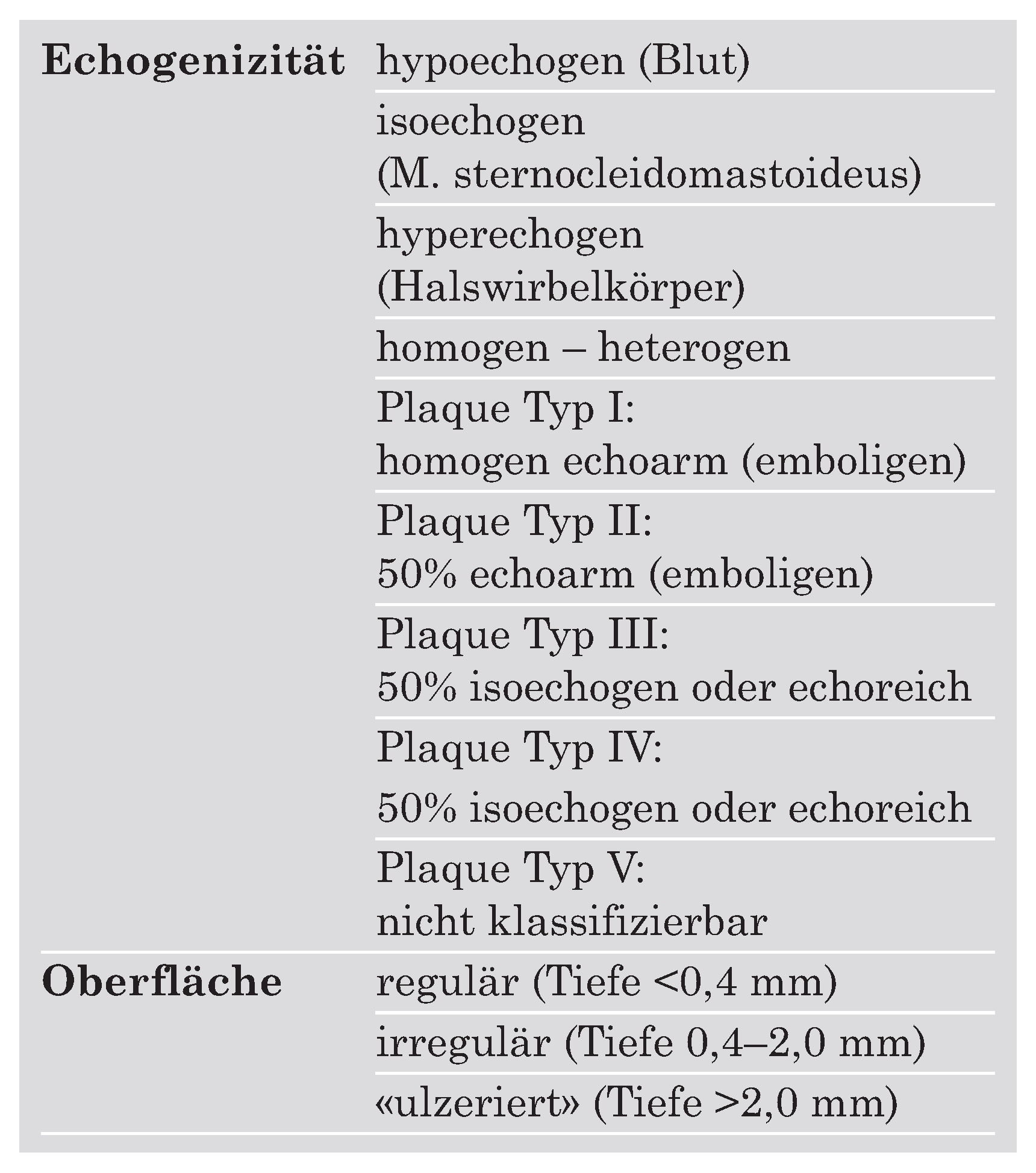 |
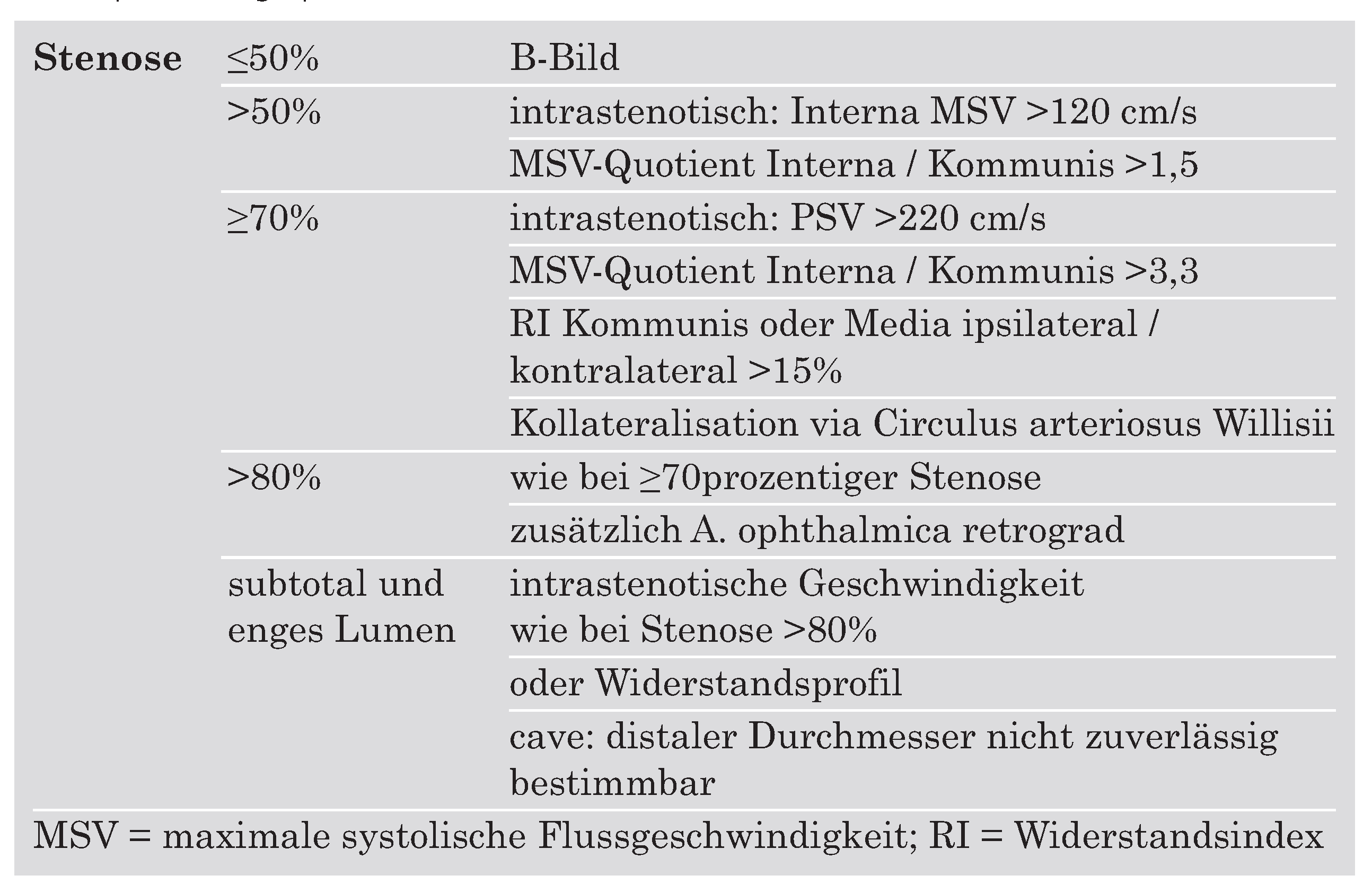 |
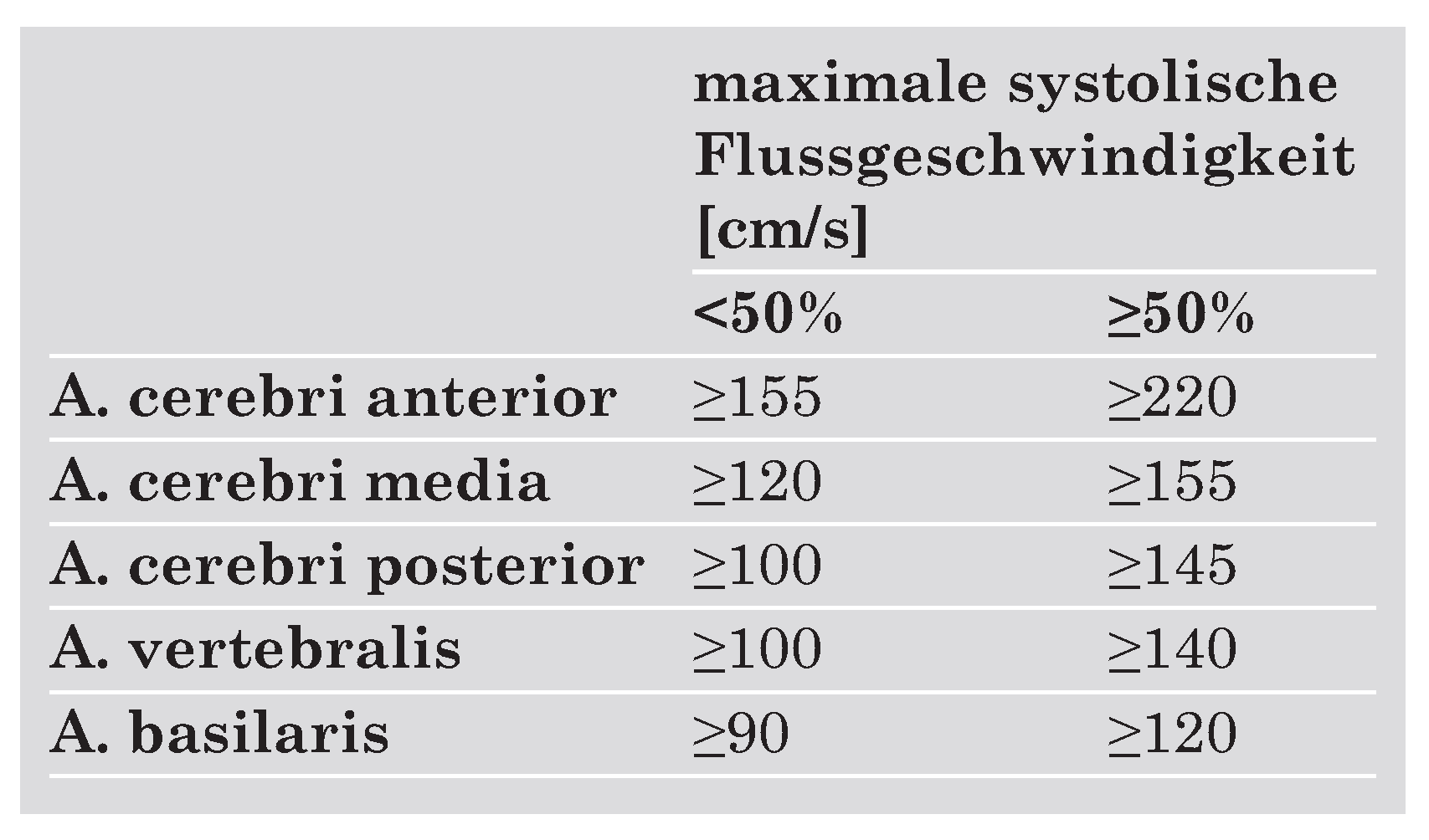 |
 |
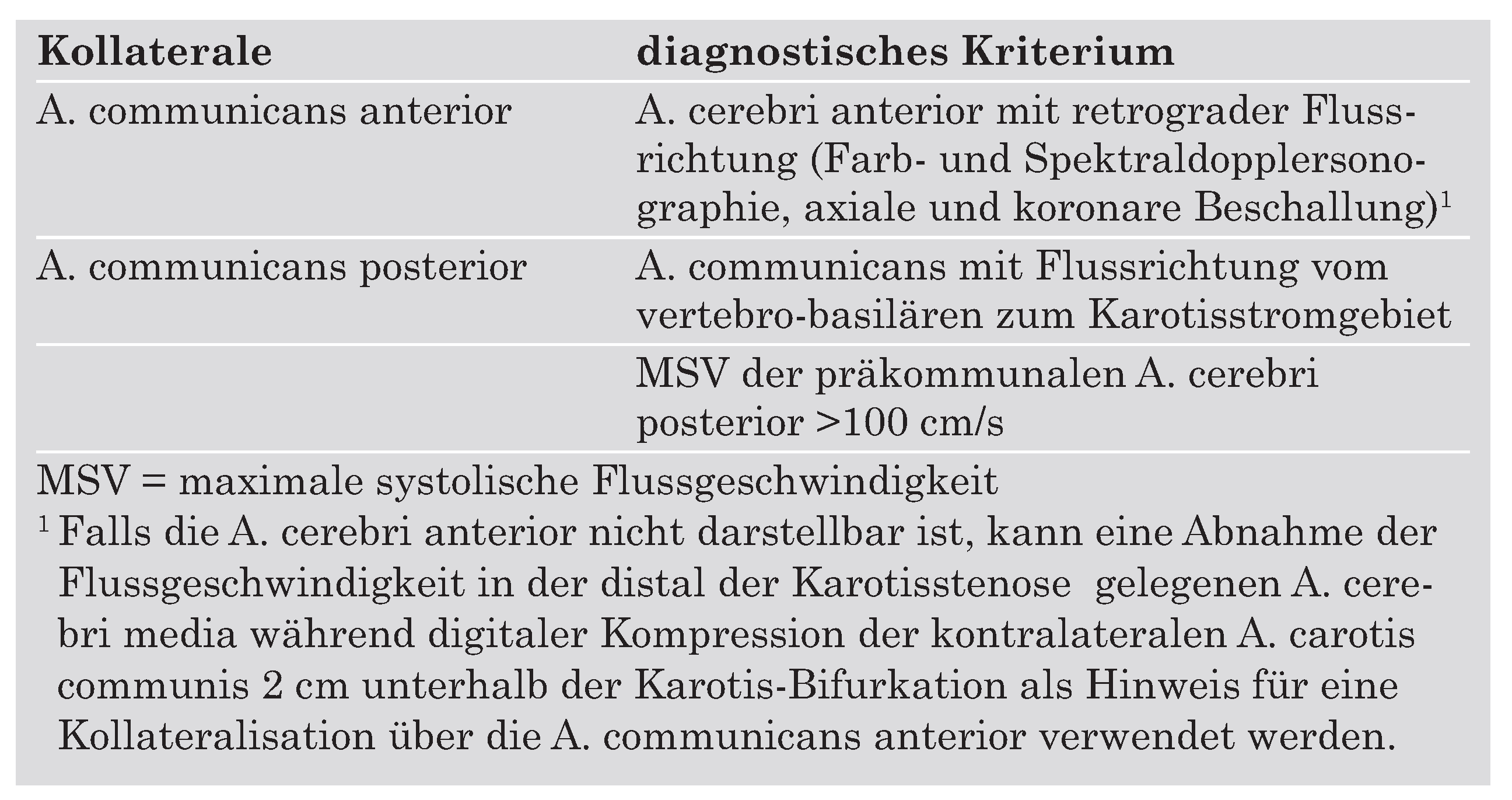 |
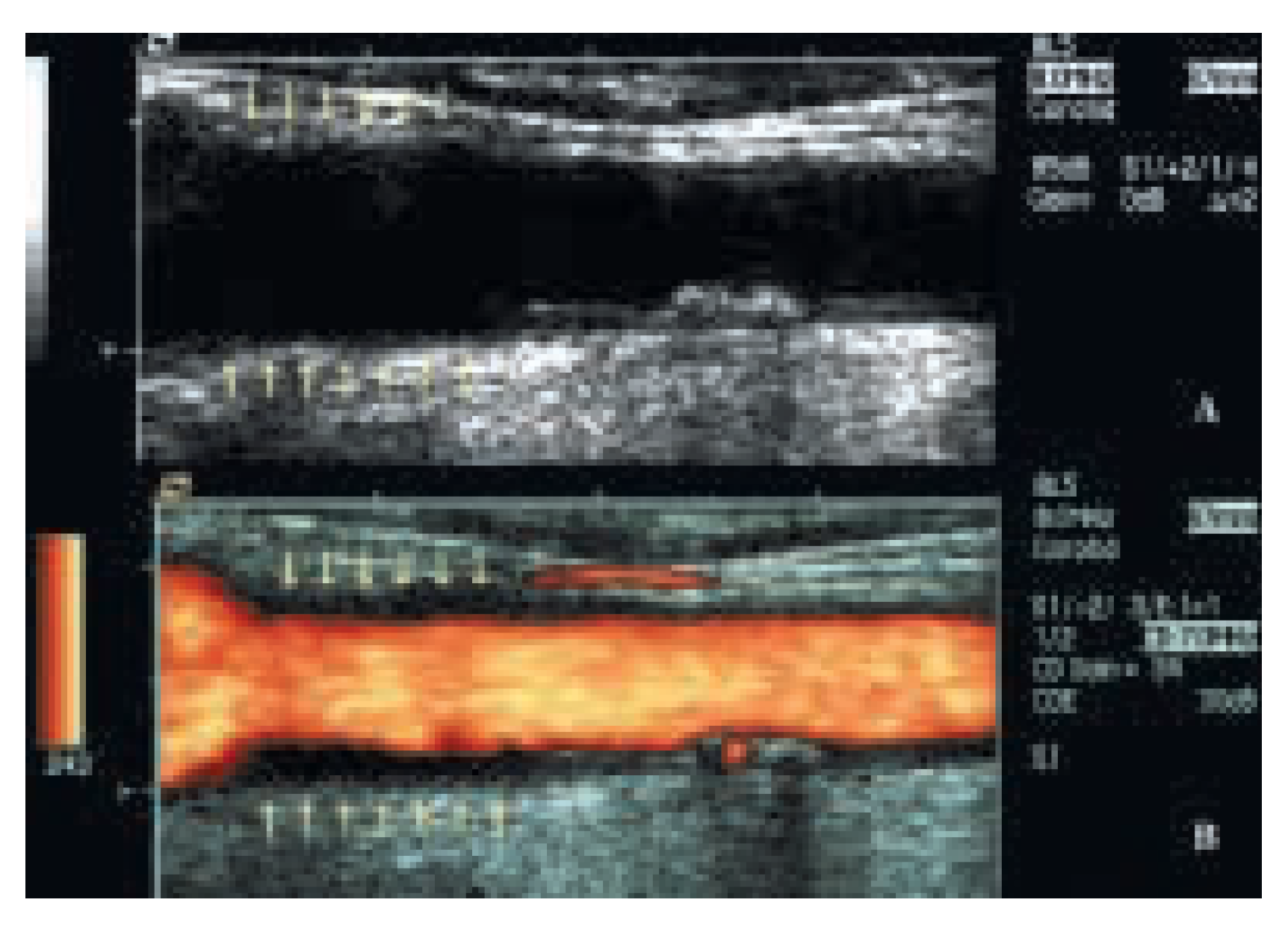
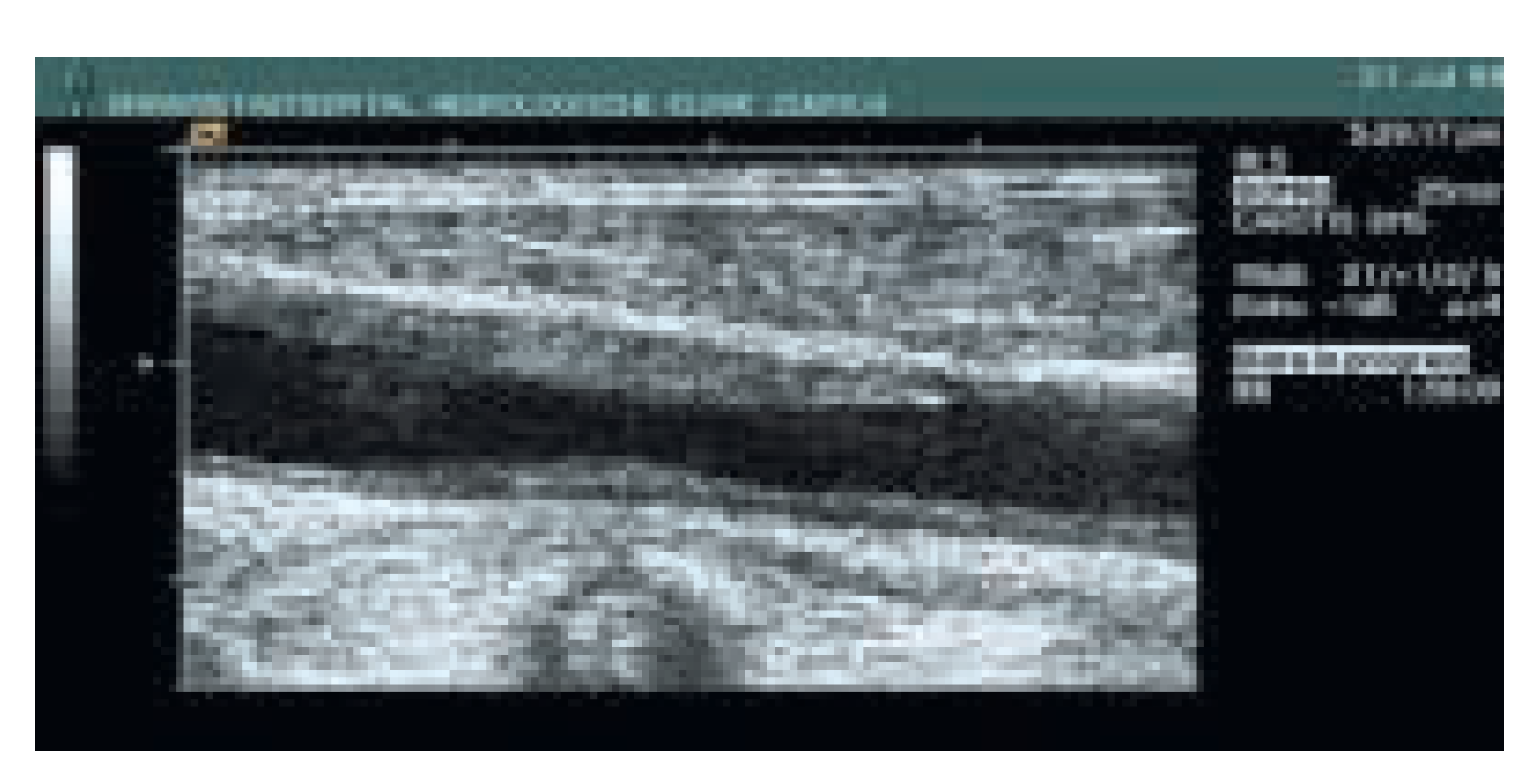
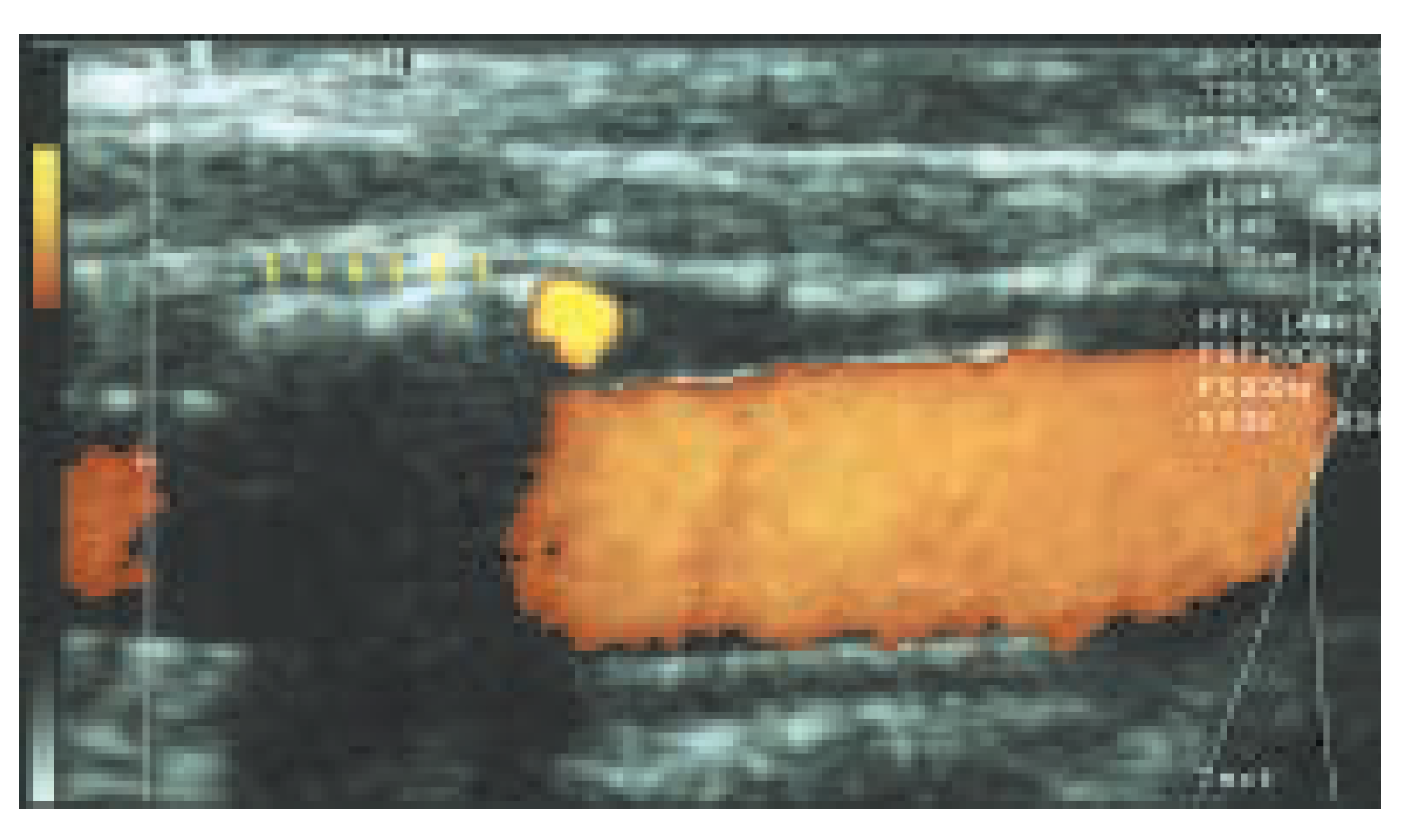
Die asymptomatische Karotisstenose
Die symptomatische Karotisverschluss
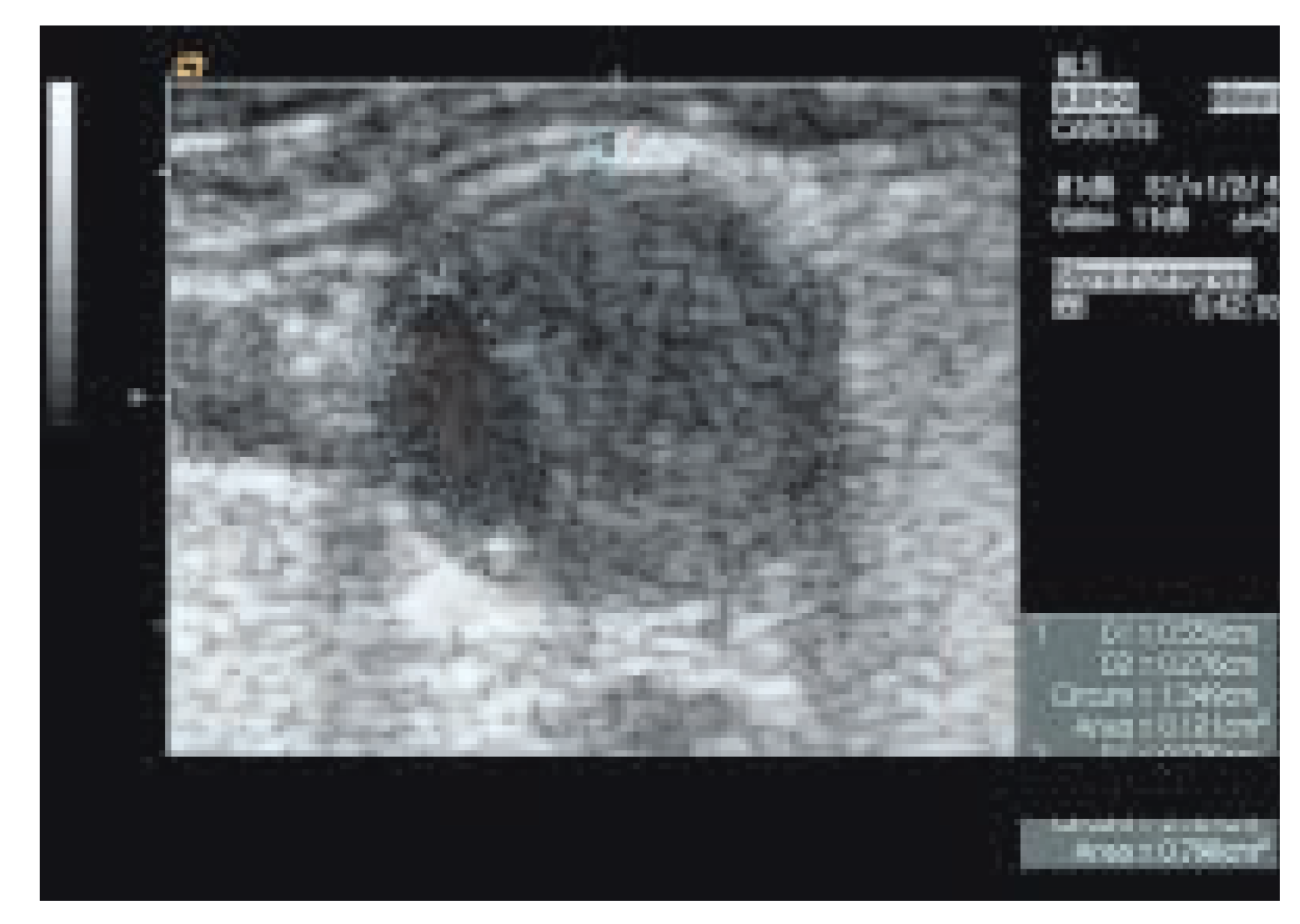
Ultrasonographische Verfahren

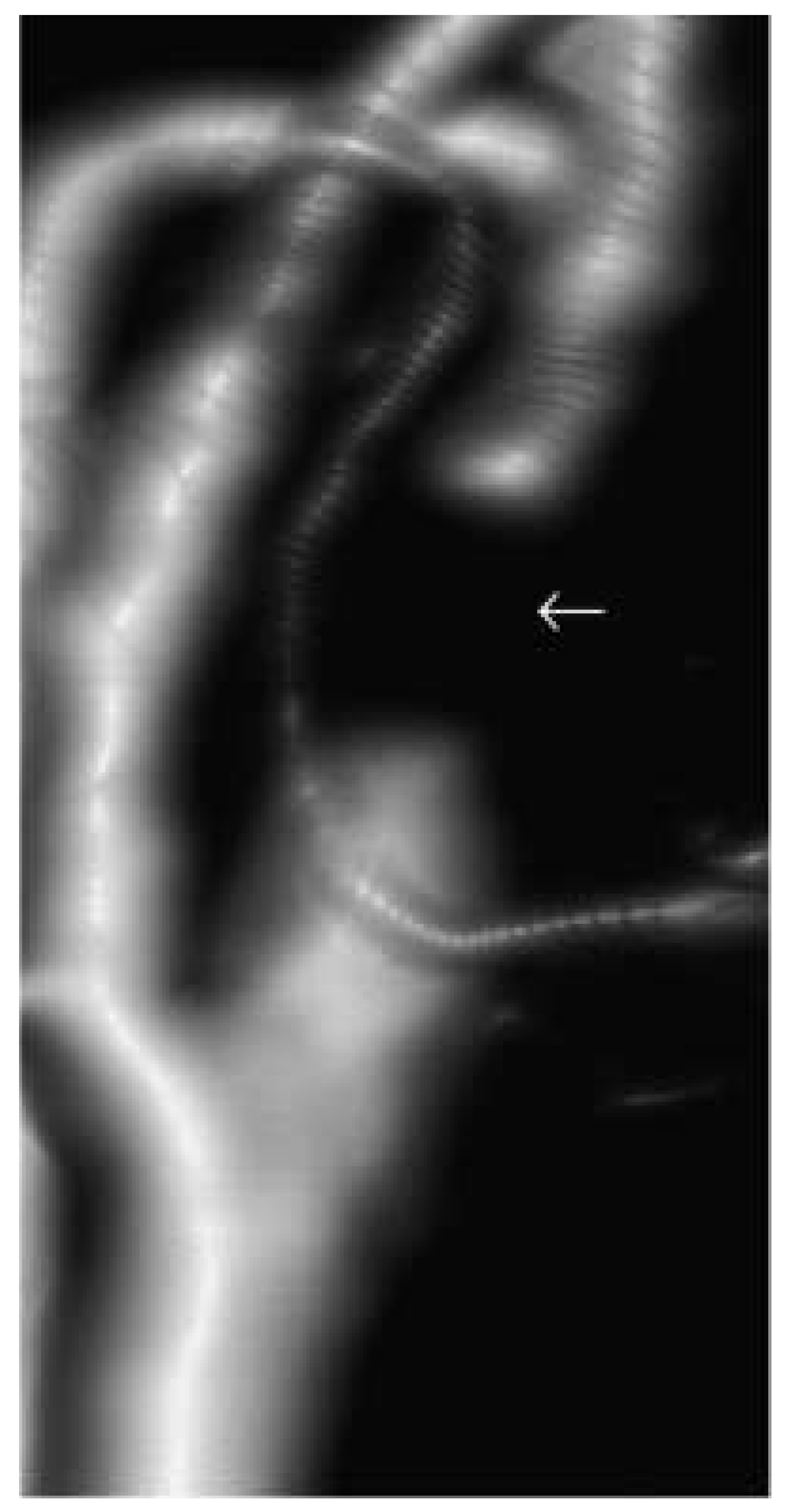
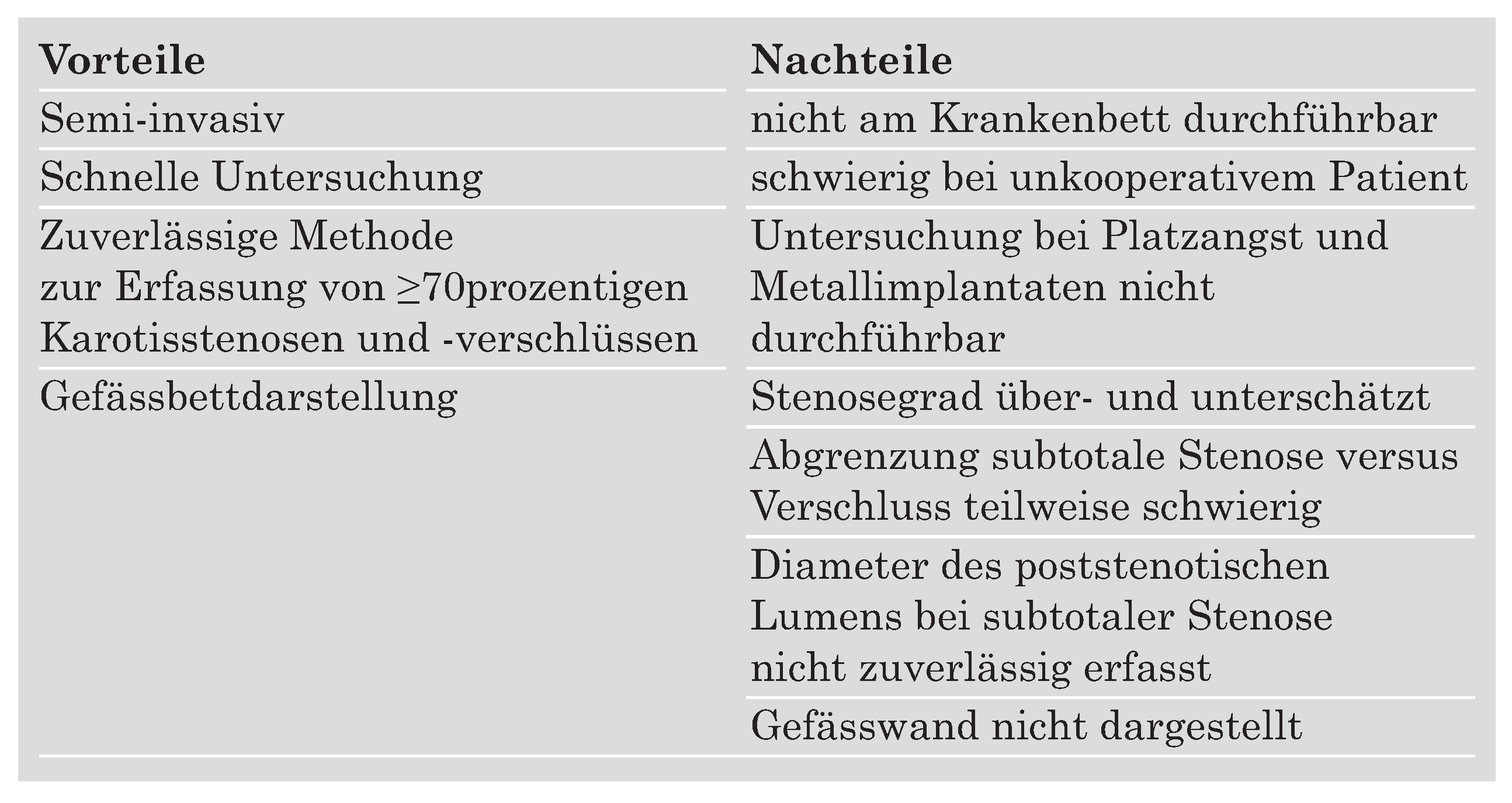
Die MR-Angiographie
 |
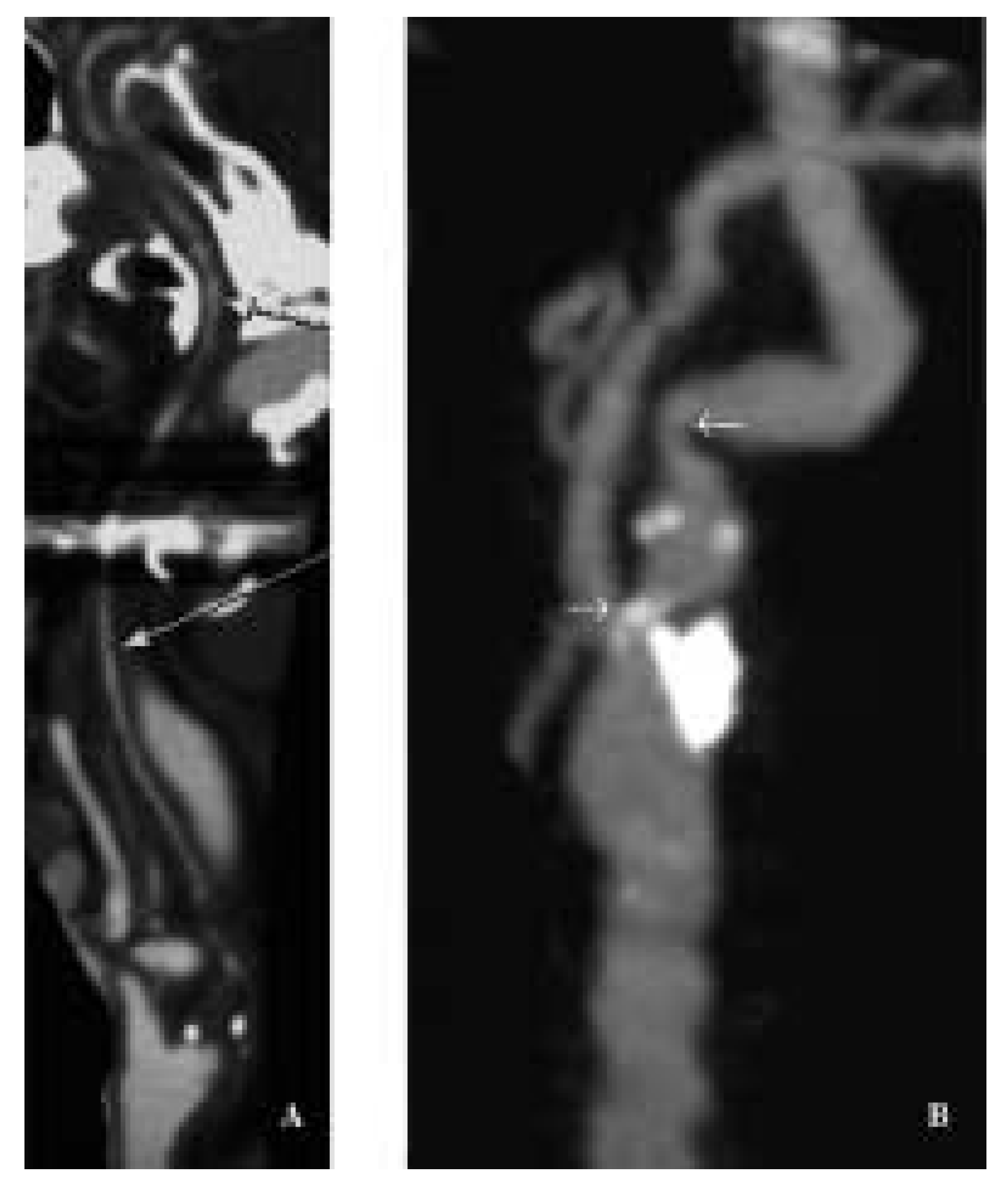
Die CT-Angiographie
Die Katheter-Angiographie
References
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Arnold, M.; Baumgartner, I.; Mosso, M.; Gönner, F.; Studer, A.; et al. Carotid dissection with and without ischemic events: local symptoms and cerebral artery findings. Neurology 2001, 57, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, H.J.M.; Taylor, D.W.; Eliasziw, M.; Fox, A.J.; Ferguson, G.G.; Haynes, B.R.; et al. for the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaboraters. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. N Engl J Med 1998, 339, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 1991, 325, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group. MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial: interim results for symptomatic patients with severe (70–99%) or with mild (0–29%) carotid stenosis. Lancet 1991, 337, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of endarterectomy for recently symptomatic carotid stenosis: final results of the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST). Lancet 1998, 351, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayberg, M.R.; Wilson, S.E.; Yatsu, F.; Weiss, D.G.; Messina, L.; Hershey, L.A.; et al. for the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Program 309 Trialist Group. Carotid endarterectomy and prevention of cerebral ischemia in symptomatic carotid stenosis. JAMA 1991, 266, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Eliasziw, M.; Gutnikov, S.A.; Fox, A.J.; Taylor, D.W.; Mayberg, M.R.; et al. for the Carotid Endarterectomy Trialists’ Collaboration. Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet 2003, 361, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, Warlow CP, Barnett HJM for the Carotid Endarterectomy Trialists Collaboration. Endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis in relation to clinical subgroups and timing of surgery. Lancet 2004, 363, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosick, S.M.; Whalen, R.C.; Gale, S.S.; Brown, O.W. Carotid endarterectomy in the stroke patient: computerized axial tomography to determine timing. J Vasc Surg 1985, 2, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johnston, S.C.; Gress, D.R.; Browner, W.S.; Sidney, S. Short-term prognosis after emergency department diagnosis of TIA. JAMA 2000, 284, 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, J.K.; Dennis, M.S.; Sandercock, P.A.; Bamford, J.; Warlow, C.P.; Rothwell, P.M. Very early risk of stroke after a first transient ischemic attack. Stroke 2003, 34, e138–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasecki, A.P.; Ferguson, G.G.; Eliasziw, W.M.; Clagett, G.P.; Fox, A.J.; Hachinski, V.; et al. Early endarterectomy for severe carotid stenosis after a nondisabling stroke: results from the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial. J Vasc Surg 1994, 20, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paty, P.S.K.; Darling, R.C.; Woratyla, S.; Chang, B.B.; Kreienberg, P.B.; Shah, D.M. Timing of carotid endarterectomy in patients with recent stroke. Surgery 1997, 122, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, J.J.; Bernhard, V.M.; Rubin, J.R.; McIntyre, K.E.; Malone, J.M.; Parrent, F.N.; et al. Timing of carotid endarterectomy after acute stroke. J Vasc Surg 1990, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricco, J.B.; Illuminati, G.; Bouin-Pineau, M.H.; Demarque, C.; Camiade, C.; Blecha, L.; et al. Early carotid endarterectomy after a nondisabling stroke: a prospective study. Ann Vasc Surg 2000, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittemore, A.D.; Ruby, S.T.; Couch, N.P.; Mannick, J.A. Early carotid endarterectomy in patients with small, fixed neurologic deficits. J Vasc Surg 1984, 1, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappelle LJ, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Sharpe BL, Barnett HJM for the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) Group. Importance of intracranial atherosclerotic disease in patients with symptomatic stenosis of the internal carotid artery. Stroke 1999, 30, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.; Warlow, C.; Group, f.t.E.T.C. Low risk of ischemic stroke in patients with symptomatic carotid nearocclusion: implications for imaging and treatment. Cerebrovasc Dis 1999, 9 (Suppl. 1), 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell PM, Warlow CP, on behalf of the European Carotid Surgery Trialists’Collaborative Group. Low risk of ischemic stroke in patients with reduced internal carotid artery lumen diameter distal to severe symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cerebral protection due to low poststenotic flow? Stroke 2000, 31, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CASANOVA Study Group. Carotid surgery versus medical therapy in asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Stroke 1991, 22, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, R.W.I.; Weiss, D.G.; Fields, W.S.; Goldstone, J.; Moore, W.S.; Towne, J.B.; et al. for the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. Efficacy of carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 1993, 328, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Asymptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Study Group. Results of a randomized controlled trial of carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Mayo Clin Proc 1992, 67, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Executive committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study. Endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. JAMA 1995, 273, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRC Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial (ACST) Collaborative Group. Prevention of disabling and fatal strokes by successful carotid endarterectomy in patients without recent neurological symptoms: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widder, B.; Kleiser, B.; Krapf, H. Course of cerebrovascular reactivity in patients with carotid artery occlusions. Stroke 1994, 25, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Extracranial Intracranial Bypass Study Group. Failure of extracranial-intracranial bypass to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 1985, 313, 1191–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.S.; Devine, J.J.; Erdoes, L.L.; Hunter, G.C. Distinguishing carotid artery pseudoocclusion with color-flow Doppler. Stroke 1995, 26, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.F.; Dobkin, G.R.; O’Leary, D.H.; et al. Internal carotid artery stenosis: accuracy and reproducibility of color-Doppler assisted duplex imaging. Radiology 1989, 173, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzer, M.; Fürst, G.; Fischer, H.; Siebler, M.; Fehlings, T.; Kleinschmidt, A.; et al. Between method correlation in quantifying internal carotid stenosis. Stroke 1993, 24, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeley, D.D.; Oddone, E.Z.; Hasselblad, V.; Simel, D.L.; Matchar, D.B. Noninvasive carotid artery testing. A meta-analytic review. Ann Intern Med 1995, 122, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bray JM, Baud JM, Dauziat M, on behalf of the Consensus Conference. Consensus concerning the morpholgy and the risk of carotid plaques. Cerebrovasc Dis 1997, 7, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.W.; Gray-Weale, A.C.; Mock, P.A.; App Stats, M.; Robinson, D.A.; Irwig, L.; et al. The natural history of asymptomatic carotid artery disease. J Vasc Surg 1993, 17, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiesen, E.B.; Bonaa, K.H.; Joakimsen, O. Echolucent plaques are associated with high risk of ischemic cerebrovascular events in carotid stenosis: the tromso study. Circulation 2001, 103, 2171–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasi, G.M.; Froio, A.; Diethrich, E.B.; Deleo, G.; Galimberti, S.; Mingazzini, P.; et al. Carotid plaque echolucency increases the risk of stroke in carotid stenting: the Imaging in Carotid Angioplasty and Risk of Stroke (ICAROS) study. Circulation 2004, 110, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bray, J.M.; Glatt, B. Quantification of atheromatous stenosis in the extracranial internal carotid artery. Cerebrovasc Dis 1995, 5, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.C.; Goldstein, L.B. Clinical carotid endarterectomy decision making: noninvasive vascular imaging versus angiography. Neurology 2001, 56, 1009–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzer, M.; Siebler, M.; Steinmetz, H. Non-invasive evaluation of internal carotid stenosis with colour Doppler-assisted duplex imaging. Clin Radiol 1996, 51 (Suppl. 1), 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Steinke, W.; Hennerici, M.; Rautenberg, W.; Mohr, J.P. Symptomatic and asymptomatic high-grade carotid stenoses in Doppler color-flow imaging. Neurology 1992, 42, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Mattle, H.P.; Schroth, G. Assessment of ≥50 and <50% intracranial stenoses by transcranial color-coded duplex sonography. Stroke 1999, 30, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenton, A.; Martin, P.; Tabott, R.; Moody, A. Comparison of transcranial color-coded duplex sonography and magnetic resonance angiography in acute stroke. Stroke 1997, 28, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerriets, T.; Seidel, G.; Fiss, I.; Modrau, B.; Kaps, M. Contrastenhanced transcranial color-coded duplex sonography. Neurology 1999, 52, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Baumgartner, I.; Schroth, G. Diagnostic criteria for transcranial colour-coded duplex sonography evaluation of cross-flow through the circle of Willis in unilateral obstructive carotid artery disease. J Neurol 1996, 243, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Baumgartner, I.; Mattle, H.P.; Schroth, G. Transcranial color-coded duplex sonography in unilateral flow-restrictive extracranial carotid artery disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1996, 17, 777–783. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Baumgartner, I.; Mattle, H.P.; Schroth, G. Transcranial color-coded duplex sonography in the evaluation of collateral flow through the circle of Willis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997, 18, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiadis, D.; Grosset, D.G.; Quin, R.; Bone, I.; Nicoll, I.; Lees, K.R. Detection of intracranial emboli in patients with carotid disease. Eur J Vasc Surg 1994, 8, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebler, M.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Sitzer, M.; Steinmetz, H.; Freund, H.J. Cerebral microembolism in symptomatic and asymptomatic high-grade internal carotid artery stenosis. Neurology 1994, 44, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forteza, A.M.; Babikian, V.L.; Hyde, C.; Winter, M.; Pochay, V. Effect of time and cerebrovascular symptoms of the prevalence of microembolic signals in patients with cervical carotid stenosis. Stroke 1996, 27, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebler, M.; Sitzer, M.; Rose, G.; Bendfeldt, D.; Steinmetz, H. Silent cerebral embolism caused by neurologically symptomatic high-grade carotid stenosis. Brain 1993, 116, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zuilen, E.V.; Moll, F.L.; Vermeulen, F.E.; Mauser, H.W.; van Gijn, J.; Ackerstaff, RG. Detection of cerebral microemboli by means of transcranial Doppler monitoring before and after carotid endarterectomy. Stroke 1995, 26, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzer, M.; Möller, W.; Siebler, M.; Hort, W.; Kniemeyer, H.W.; Jäncke, L.; et al. Plaque ulceration and lumen thrombus are the main sources of cerebral microemboli in high-grade internal carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 1995, 26, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valton, L.; Larrue, V.; Arrue, P.; Geraud, G.; Bes, A. Asymptomatic cerebral embolic signals in patients with carotid stenosis. Correlation with appearance of plaque ulceration on angiography. Stroke 1995, 26, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebler, M.; Nachtmann, A.; Sitzer, M.; Rose, G.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Rademacher, J.; et al. Cerebral microembolism and the risk of ischemia in asymptomatic high-grade internal carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 1995, 26, 2184–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, J.; Markus, H.S. Asymptomatic embolization predicts stroke and TIArisk in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 1999, 30, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randoux, B.; Marro, B.; Koskas, F.; Duyme, M.; Sahel, M.; Zouaoui, A.; et al. Carotid artery stenosis: prospective comparison of CT, three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR, and conventional angiography. Radiology 2001, 220, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Linera, J.; Benito-Leon, J.; Escribano, J.; Campollo, J.; Gesto, R. Prospective evaluation of carotid artery stenosis: elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR angiography and spiral CT angiography compared with digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Borisch, I.; Horn, M.; Butz, B.; Zorger, N.; Draganski, B.; Hoelscher, T.; et al. Preoperative evaluation of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of contrast-enhanced MR angiography and duplex sonography with digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar]
- DeMarco, J.K.; Huston Jr Bernstein, M.A. Evaluation of classic 2D time-of-flight MR angiography in the depiction of severe carotid stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004, 183, 787–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonent M, Serfaty JM, Nighoghossian N, Rouhart F, Derex L, Rotaru C, et al for CARMEDAS Study Group. Concordance rate differences of 3 noninvasive imaging techniques to measure carotid stenosis in clinical routine practice: results of the CARMEDAS multicenter study. Stroke 2004, 35, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederkoorn, P.J.; Elgersma, O.E.; van der Graaf, Y.; Eikelboom, B.C.; Kappelle, L.J.; Mali, W.P. Carotid artery stenosis: accuracy of contrast-enhanced MR angiography for diagnosis. Radiology 2003, 228, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutke, R.; Lang, W.; Fellner, C.; Janka, R.; Denzel, C.; Lell, M.; et al. High-resolution, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography with elliptical centric k-space ordering of supra-aortic arteries compared with selective X-ray angiography. Stroke 2002, 33, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Lewis, S.C.; Humphrey, P.; Young, G.; Collie, D.; Warlow, C.P. How does the degree of carotid stenosis affect the accuracy and interobserver variability of magnetic resonance angiography? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001, 71, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turski, P. Sources of variability in measuring carotid stenosis on time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiograms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23, 178–179. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Nederkoorn, P.J.; van der Graaf, Y.; Eikelboom, B.C.; van der Lugt, A.; Bartels, L.W.; Mali, W.P. Time-of-flight MR angiography of carotid artery stenosis: does a flow void represent severe stenosis? Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Remonda, L.; Senn, P.; Barth, A.; Arnold, M.; Lovblad, K.O. Contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography of the carotid artery: comparison with conventional digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23, 213–219. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Anderson, G.B.; Ashforth, R.; Steinke, D.E.; Ferdinandy, R.; Findlay, J.M. CT angiography for the detection and characterization of carotid artery bifurcation disease. Stroke 2000, 31, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, R.; Ferrari, C.; Roberti, M.; Alerci, M.; Pedrazzi, P.L.; Gallino, A. Spiral computed tomography: a novel diagnostic approach for investigation of the extracranial cerebral arteries and its complementary role in duplex ultrasonography. Circulation 1998, 98, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, S.A.; Bryant, S.O.; Mak, H.K.; Johnston, S.C.; Dillon, W.P.; Smith, W.S. Evaluation of carotid stenosis using CT angiography in the initial evaluation of stroke and TIA. Neurology 2004, 63, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev, M.H.; Romero, J.M.; Goodman, D.N.; Bagga, R.; Kim, H.Y.; Clerk, N.A.; et al. Total occlusion versus hairline residual lumen of the internal carotid arteries: accuracy of single section helical CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.N.; Humphrey, P.R. Complications of cerebral angiography in patients with symptomatic carotid territory ischaemia screened by carotid ultrasound. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 1993, 56, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grood, P.A. Dissecting aneurysm of the carotid as a complication of carotid angiography. Rev Neurol 1954, 90, 661. [Google Scholar]
- Taniura, S.; Watanebe, T. A ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the anterior radiculomedullary artery caused by vertebral angiography. Neuroradiology 2000, 42, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
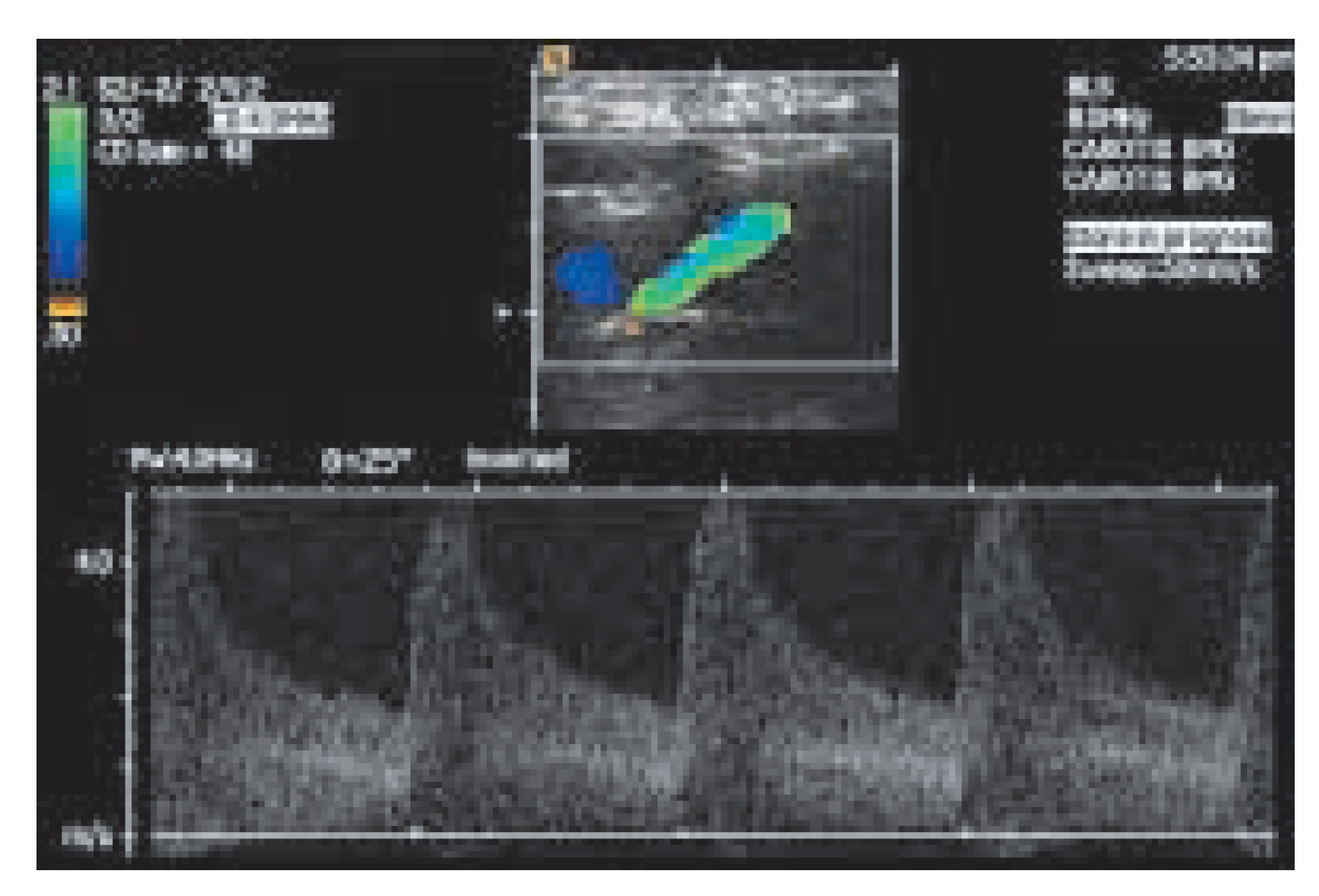

 |
 |
 |
© 2005 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Baumgartner, R.W. Abklärung von Karotisstenose und -Verschluss. Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 8, 270. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01117
Baumgartner RW. Abklärung von Karotisstenose und -Verschluss. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2005; 8(7):270. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01117
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumgartner, Ralf W. 2005. "Abklärung von Karotisstenose und -Verschluss" Cardiovascular Medicine 8, no. 7: 270. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01117
APA StyleBaumgartner, R. W. (2005). Abklärung von Karotisstenose und -Verschluss. Cardiovascular Medicine, 8(7), 270. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01117




