A Less Invasive Approach to Repair the Aortic Arch Using a “Partial or Complete Debranching” of the Supraaortic Vessels
Summary
Introduction
Clinical experience
Illustrative cases
- Case1
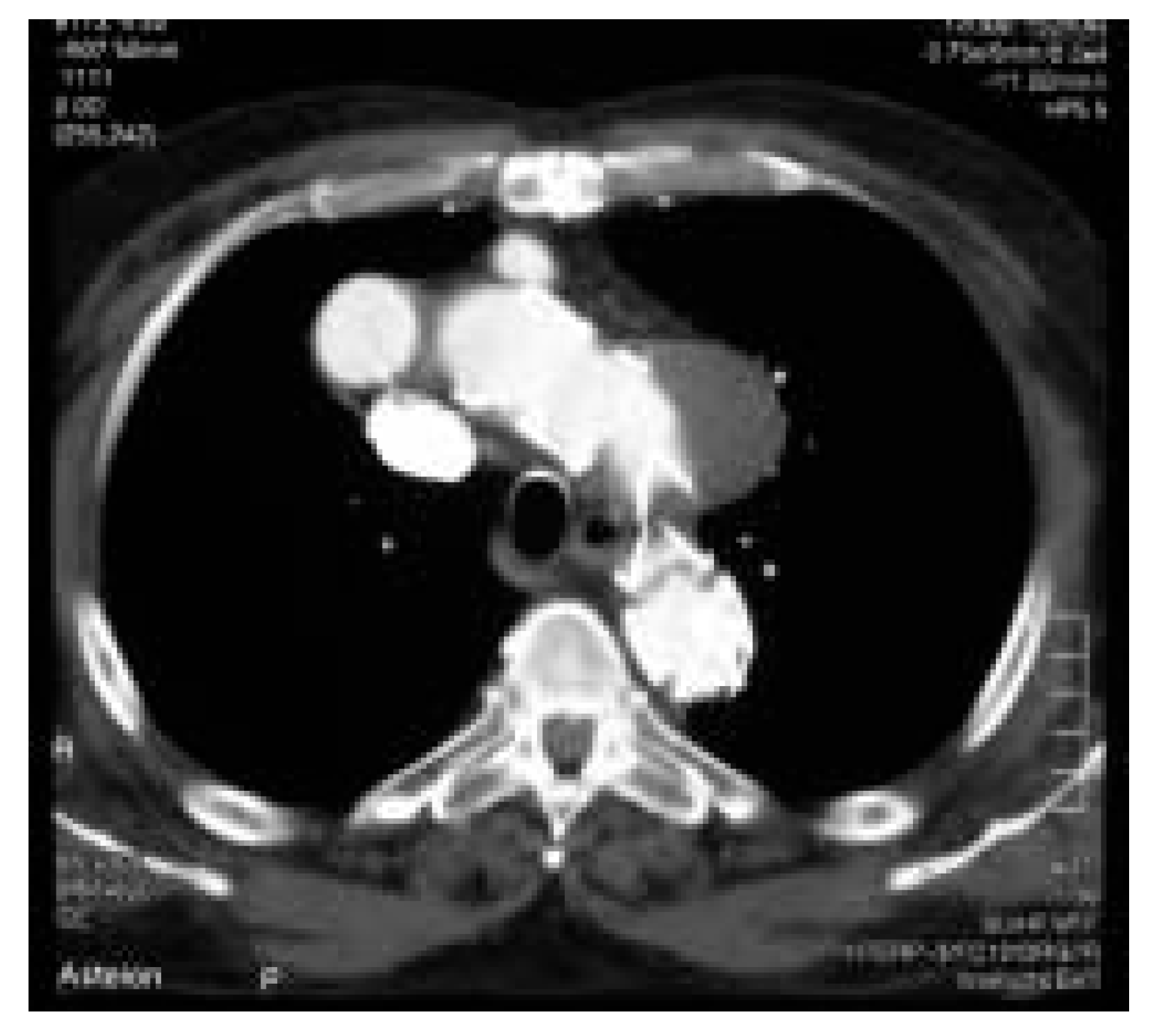
- 78-year-old man had a false atherosclerotic aneurysm (5.5 cm in size) located in the concavity of the aortic arch, with the entry being just opposite to the origin of the left common carotid artery. The patient and his relatives refused a conventional surgical approach. He has several cardiovascular risk factors, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, arterial hypertension and obstructive lung disease.
- Case2
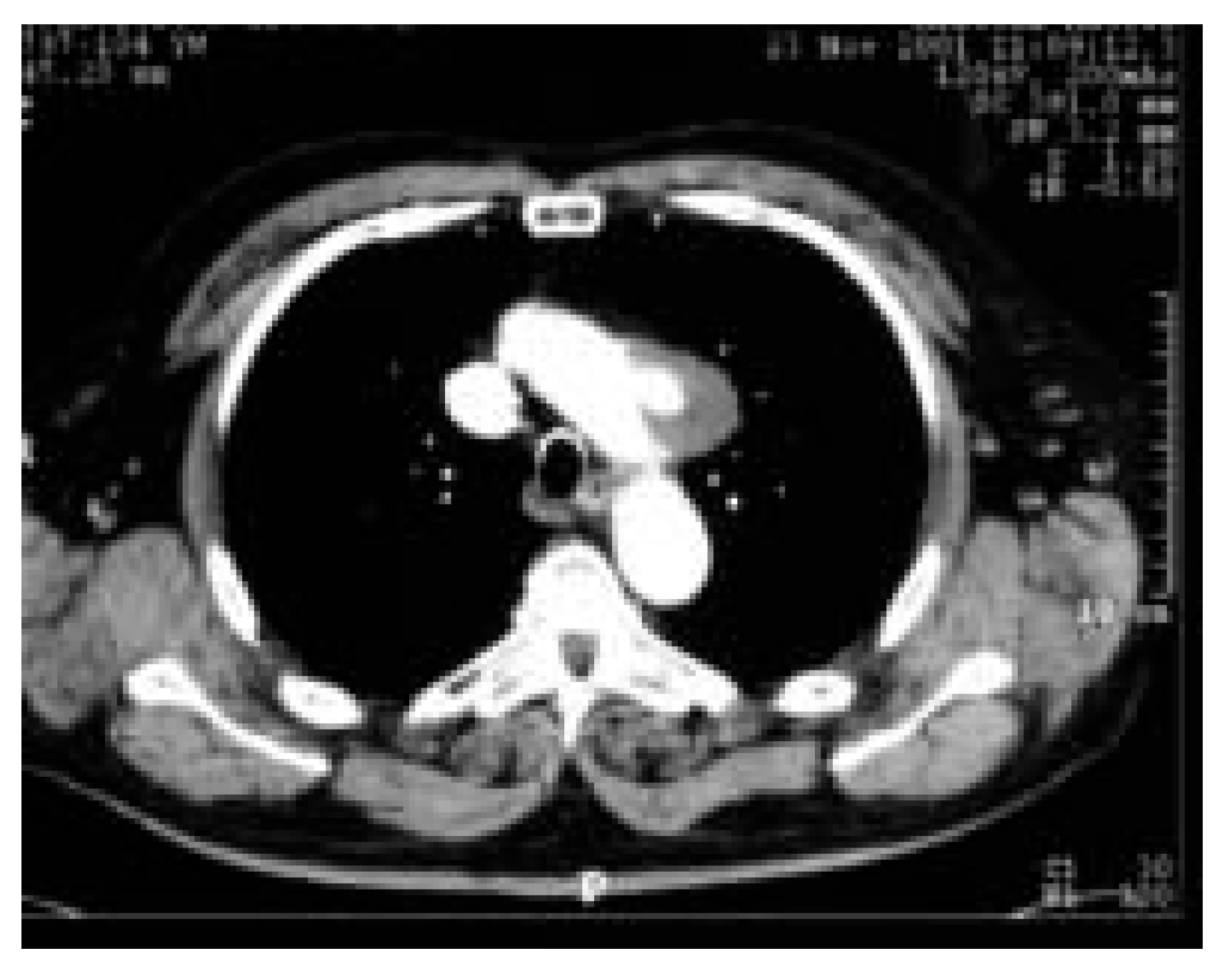
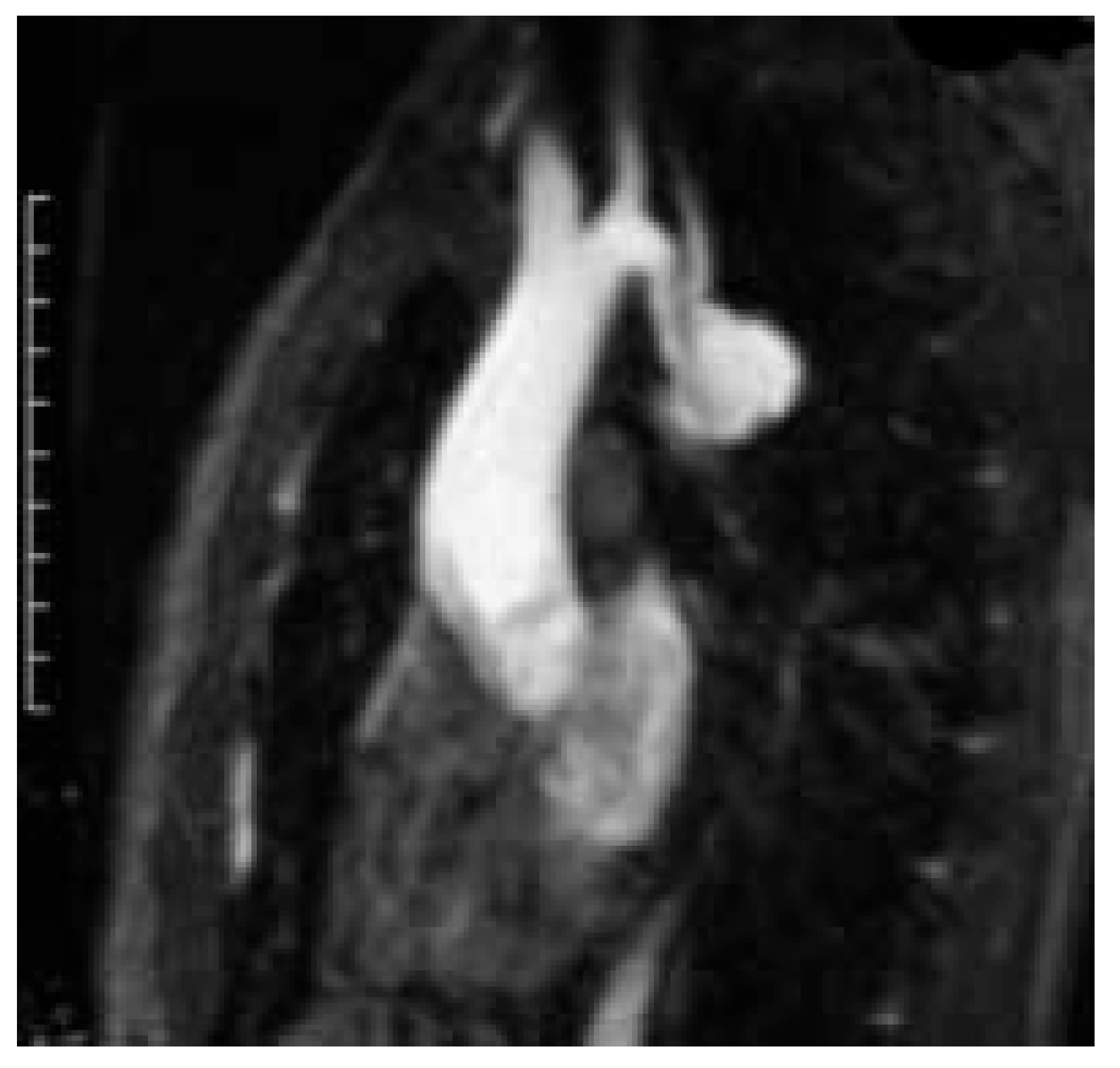
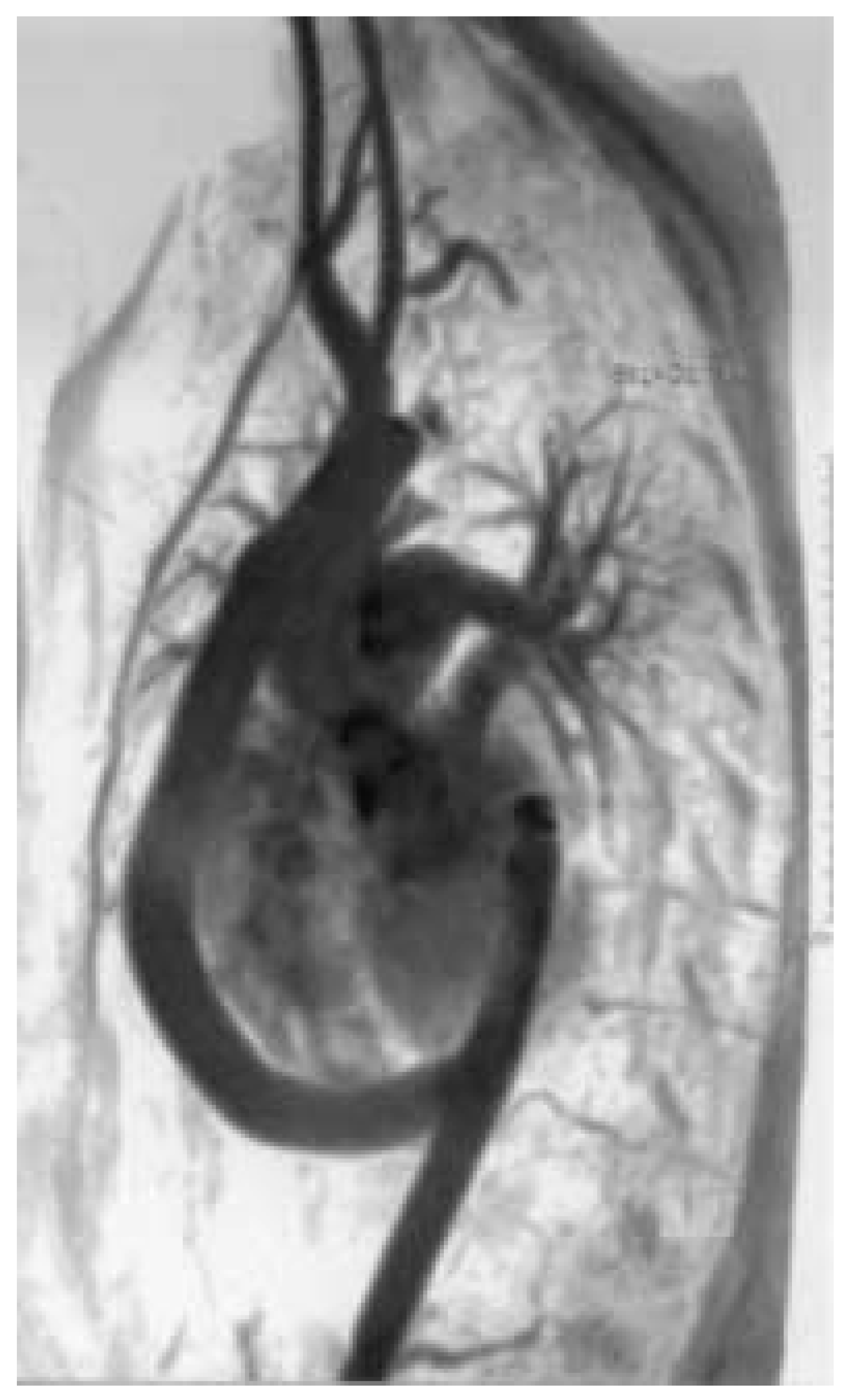
- The second patient was a 71-year-old woman with recurrent transient cerebral ischaemic episodes most probably caused by an atherosclerosis grade IV of the aortic arch with thick (1.5 cm) and mobile plaques and who had a small atherosclerotic aneurysm in the aortic arch as well (Figure 1)
- Case3
- The 21-year-old female presented with severe exercise arterial hypertension of the upper extremities (systolic blood pressure 220 mm Hg). She suffered from headache since 2 years. At the age of 3 weeks, she underwent surgery because of aortic coarctation. End-to-end anastomosis was performed. Two years later, percutaneous balloon dilatation was per-formed because of re-coarctation. At the age of 6 years, she suffered from arterial hyper-tension. A pericardial patch was used to enlarge the distal aortic arch and the proximal de-scending aorta. In the following, she required treatment with a beta-blocker and a con-verting-enzyme inhibitor.
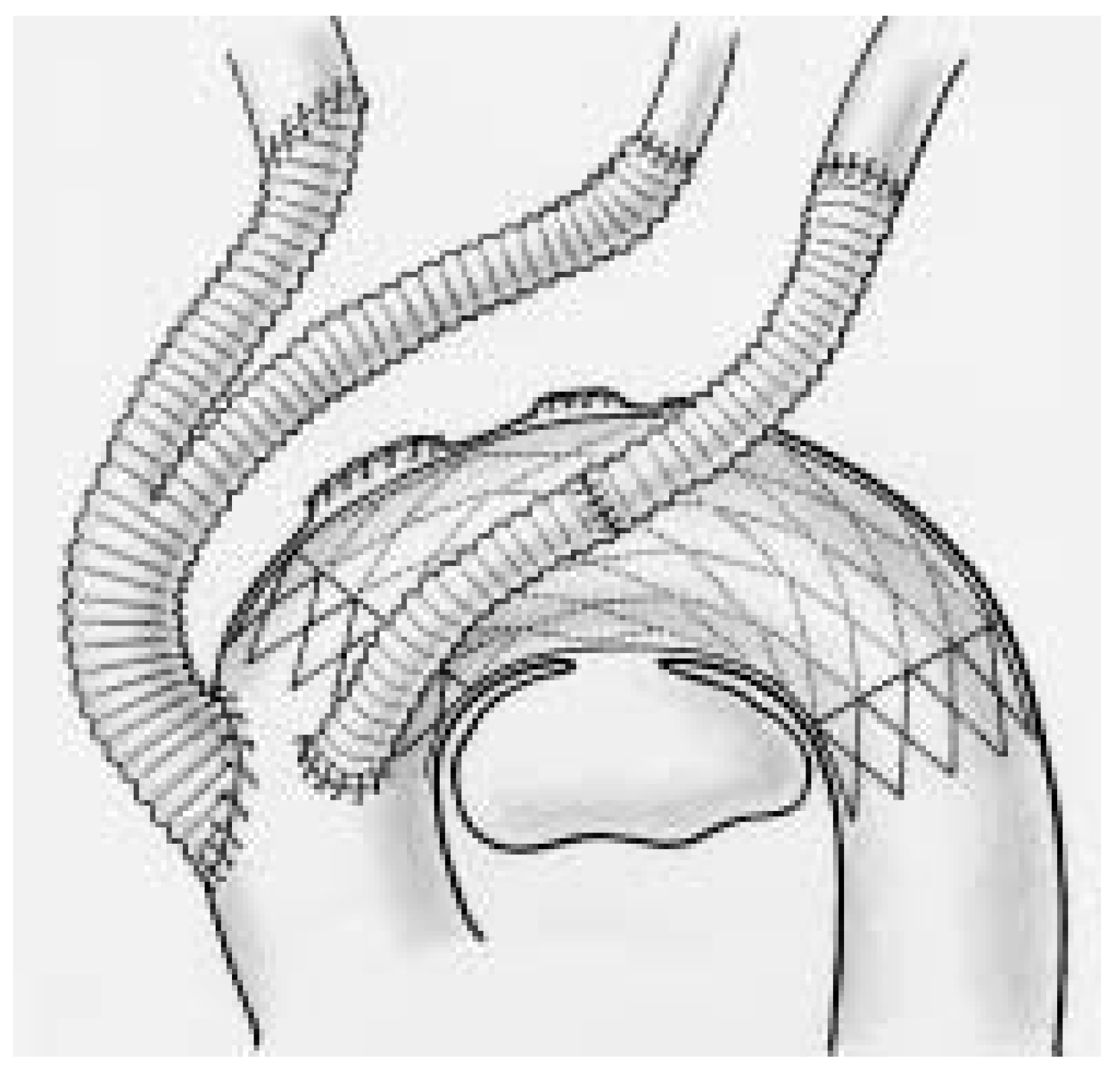
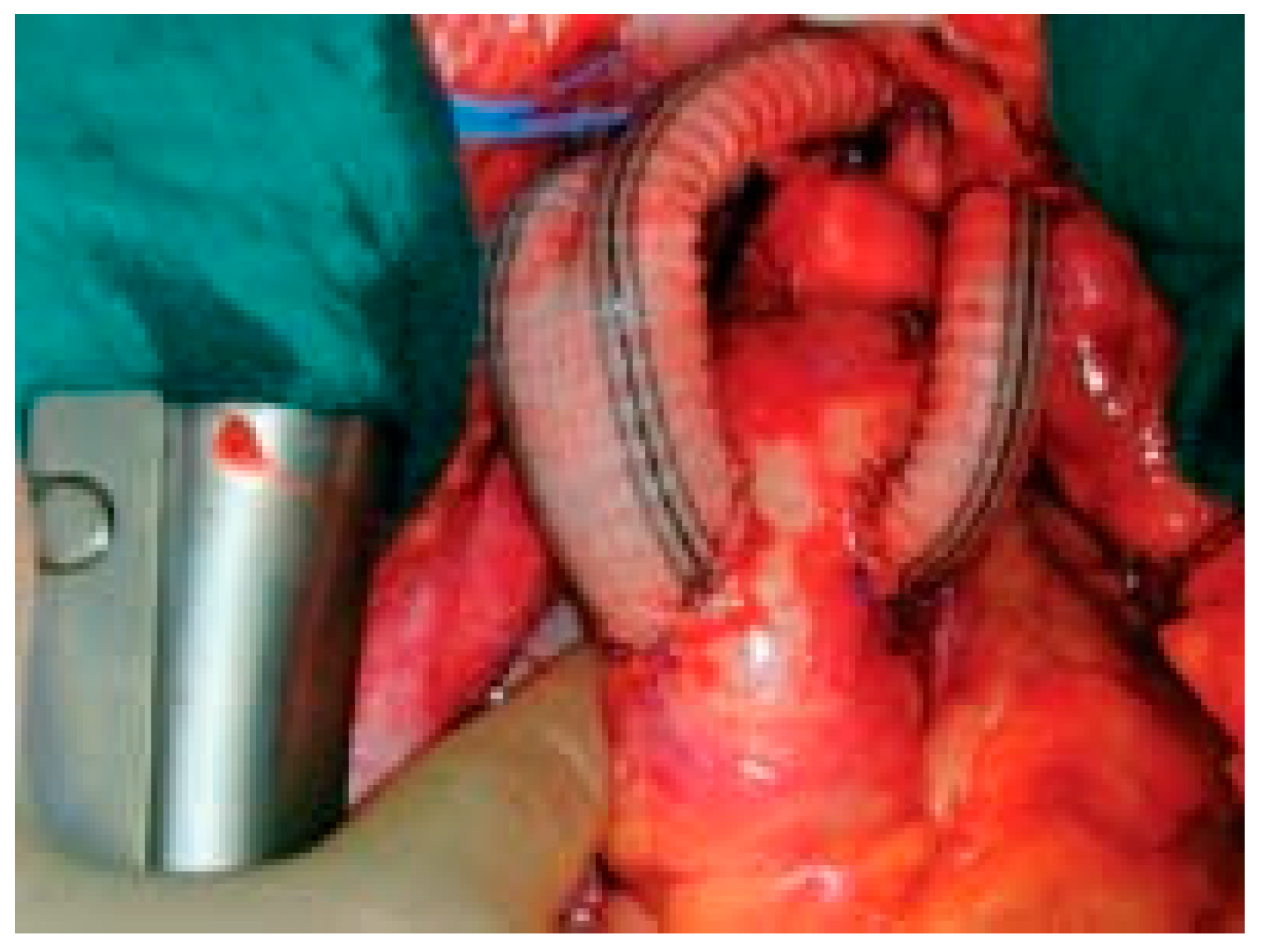
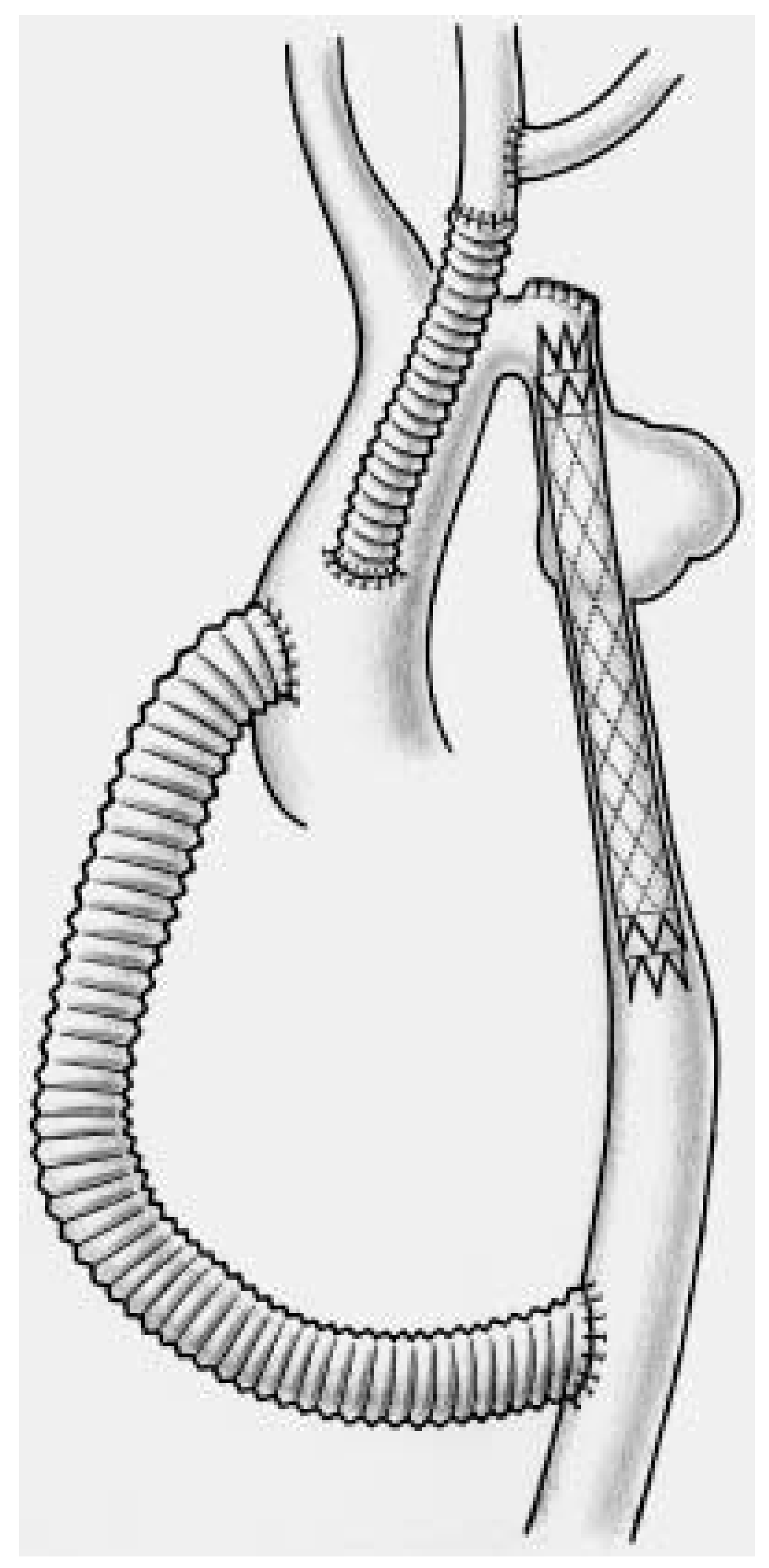
Endovascular and operative technique
- Complete aortic arch repair
Additional procedure
- Partial debranching and extra-anatomic bypass in complex aortic coarctation
Results
Comment
References
- Crawford, E.S.; Svensson, L.G.; Coselli, J.S.; et al. Surgical treatment of aneurysm and/or dissection of the ascending aorta, transverse aortic arch and ascending aorta and transverse aortic arch. Factors influencing survival in 717 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1989, 98, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagl, C.; Ergin, M.A.; Galla, S.D.; et al. Neurologic outcome after ascending aorta/aortic arch operations: effects of brain protection technique in high risk patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2001, 121, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westaby, S.; Katsumata, T.; Vaccari, G. Arch and descending aortic aneurysms: influence of perfusion technique on neurological outcome. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1999, 15, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazui, T.; Washiyama, N.; Muhammad, B.A.; Terada, H.; Yamashita, K.; Takinami, M. Improved results of atherosclerotic arch aneurysm operations with a refined technique. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2001, 121, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Iwase, T.; Sato, M.; et al. Clinical application of transluminal endovascular graft placement for aortic aneurysms. Ann Thorac Surg 1997, 63, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dake, M.D.; Miller, D.C.; Seimba, C.P.; et al. Transluminal placement of endovascular stent-grafts for the treatment of descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med 1994, 331, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.C. Stent grafts for the thoracic aorta: a new paradigm? Ann Thorac Surg 2002, 74, S1818–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienaber, C.A.; Fattori, R.; Lund, G.; et al. Nonsurgical reconstruction of thoracic aortic dissection by stent-graft placement. N Engl J Med 1999, 340, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Hosokawa, H.; Iwase, T.; et al. Aortic arch reconstruction by transluminally placed endovascular branched stent graft. Circulation 1999, 100 (Suppl. SII), II316–II321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Criado, F.J.; Clark, N.S.; Barnatan, M.F.; et al. Stent-graft repair in the aortic arch and descending thoracic aorta: a 4-year experience. J Vasc Surg 2002, 36, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, J.J.; Douglas, W.I.; James, T.; Desai, U. Coarctation of the aorta. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000, 3, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, A.G.; Brzezinska, G.; Qureshi, S.A.; Rosenthal, E.; Zubrzycka, M.; Ksiazyk, J.; et al. Stent implantation for aortic coarctation and recoarctation. Heart 1999, 82, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanter, K.R.; Erez, E.; Williams, W.H.; Tam, V.K. Extra-anatomic bypass via sternotomy for complex aortic arch stenosis in children. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000, 120, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, H.M.; Schaff, H.V.; Izhar, U.; Dereani, J.A.; Warnes, C.A.; Orszulak, T.A. Posteriorpericardial ascending-to-descending aortic bypass: an alternative surgical approach for complex coarctation of the aorta. Circulation 2001, 104, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, T.; Dai-Do, D.; Müller, M.; et al. Combined endovascular and surgical treatment of complex traumatic lesions of the thoracic aorta. Lancet 1997, 350, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidli, J.; Do, D.; Triller, J.; Carrel, T. A less invasive approach to completely repair the aortic arch. Ann Thorac Surg 2005, in press.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2005 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Schmidli, J.; Do, D.-D.; Triller, J.; Baumgartner, I.; Berdat, P.; Widmer, F.; Mahler, F.; Carrel, T. A Less Invasive Approach to Repair the Aortic Arch Using a “Partial or Complete Debranching” of the Supraaortic Vessels. Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01083
Schmidli J, Do D-D, Triller J, Baumgartner I, Berdat P, Widmer F, Mahler F, Carrel T. A Less Invasive Approach to Repair the Aortic Arch Using a “Partial or Complete Debranching” of the Supraaortic Vessels. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2005; 8(3):82. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidli, Jürg, Dai-Do Do, Jürgen Triller, Iris Baumgartner, Pascal Berdat, Fritz Widmer, Felix Mahler, and Thierry Carrel. 2005. "A Less Invasive Approach to Repair the Aortic Arch Using a “Partial or Complete Debranching” of the Supraaortic Vessels" Cardiovascular Medicine 8, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01083
APA StyleSchmidli, J., Do, D.-D., Triller, J., Baumgartner, I., Berdat, P., Widmer, F., Mahler, F., & Carrel, T. (2005). A Less Invasive Approach to Repair the Aortic Arch Using a “Partial or Complete Debranching” of the Supraaortic Vessels. Cardiovascular Medicine, 8(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01083



