Das Herz Beim Metabolischen Syndrom
Summary
Zusammenfassung
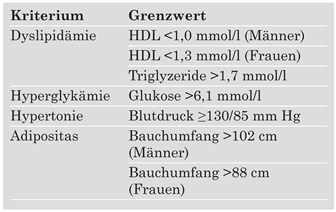
Definition und Risikostratifikation
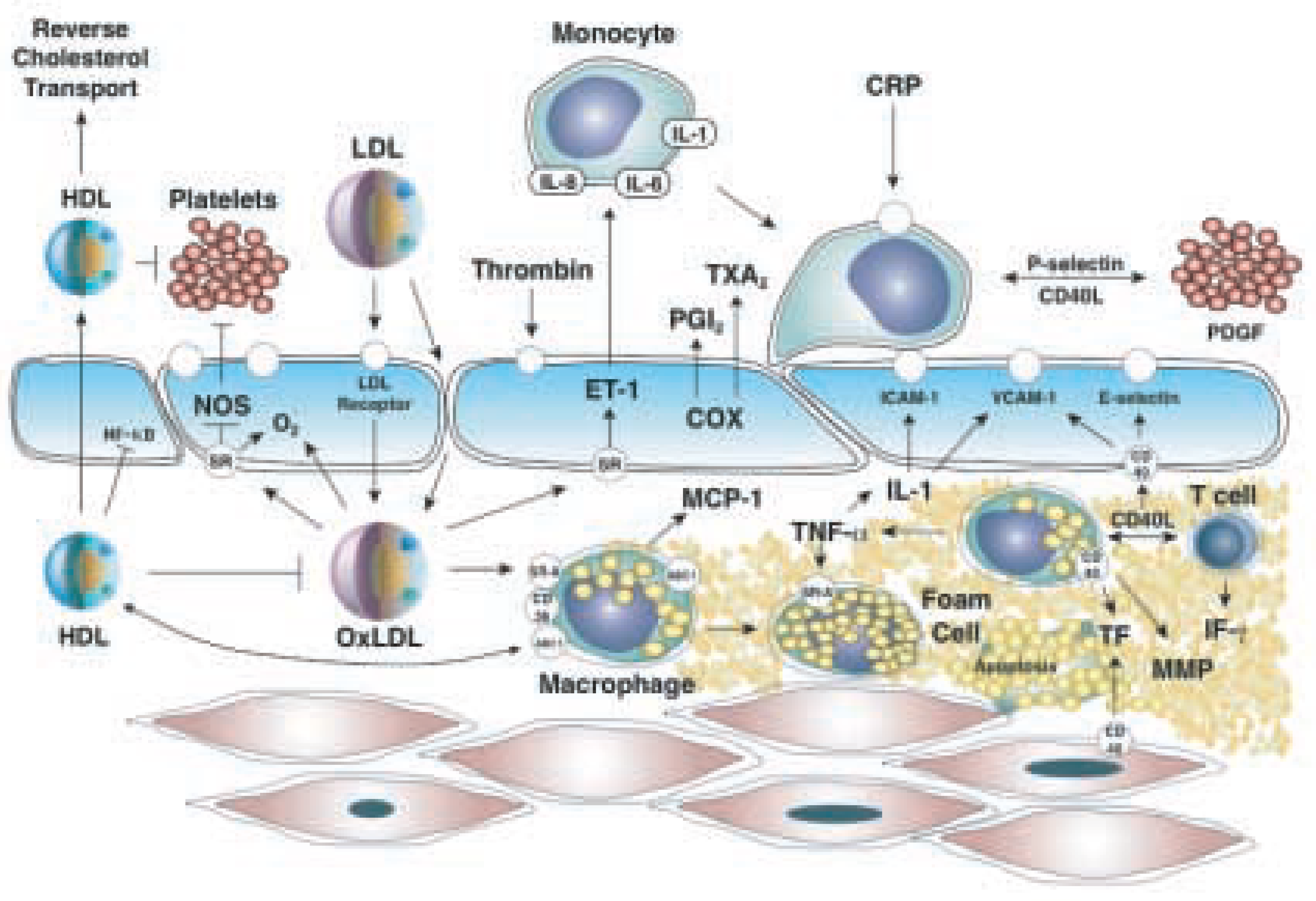
Pathophysiologie
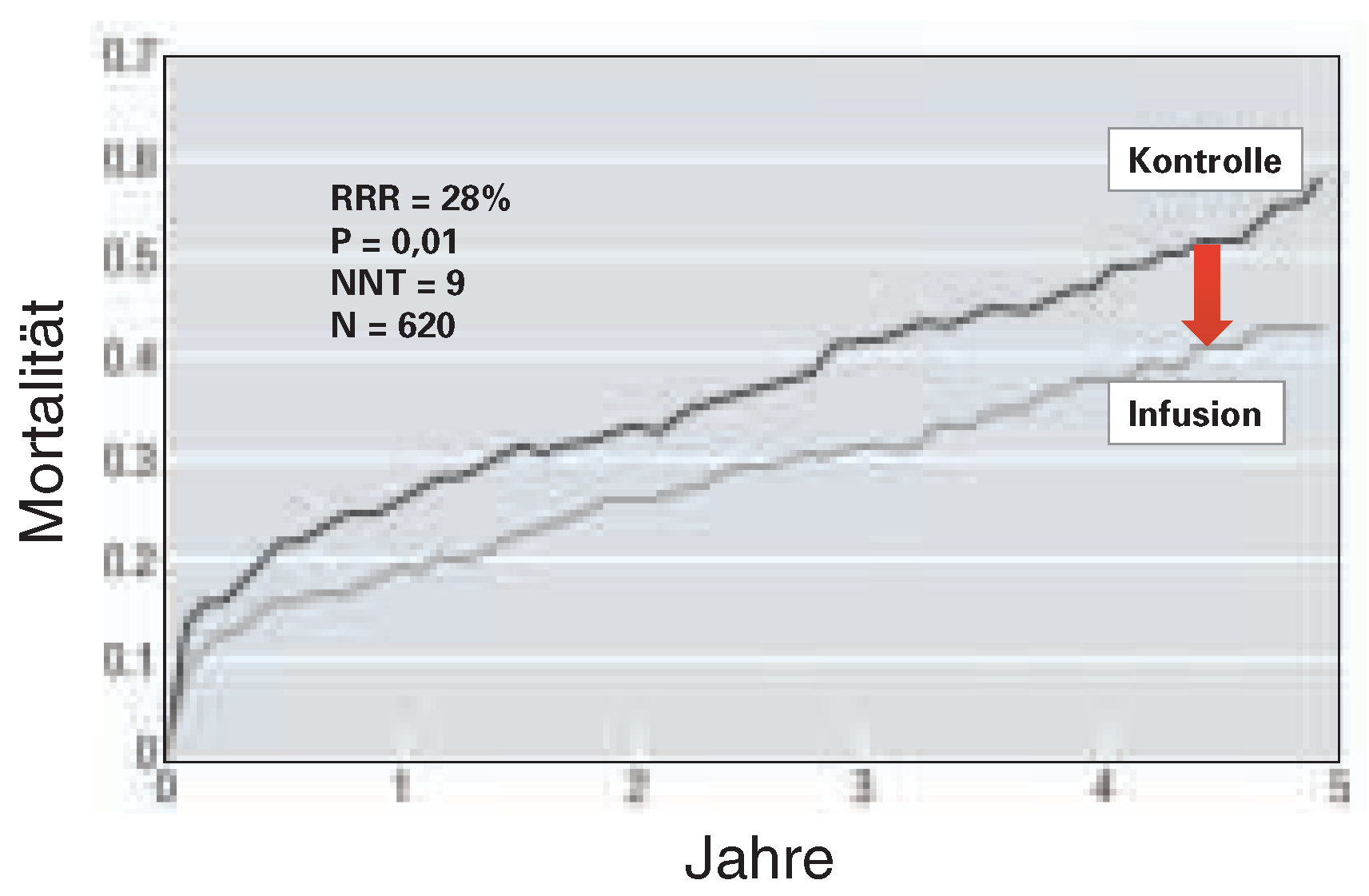
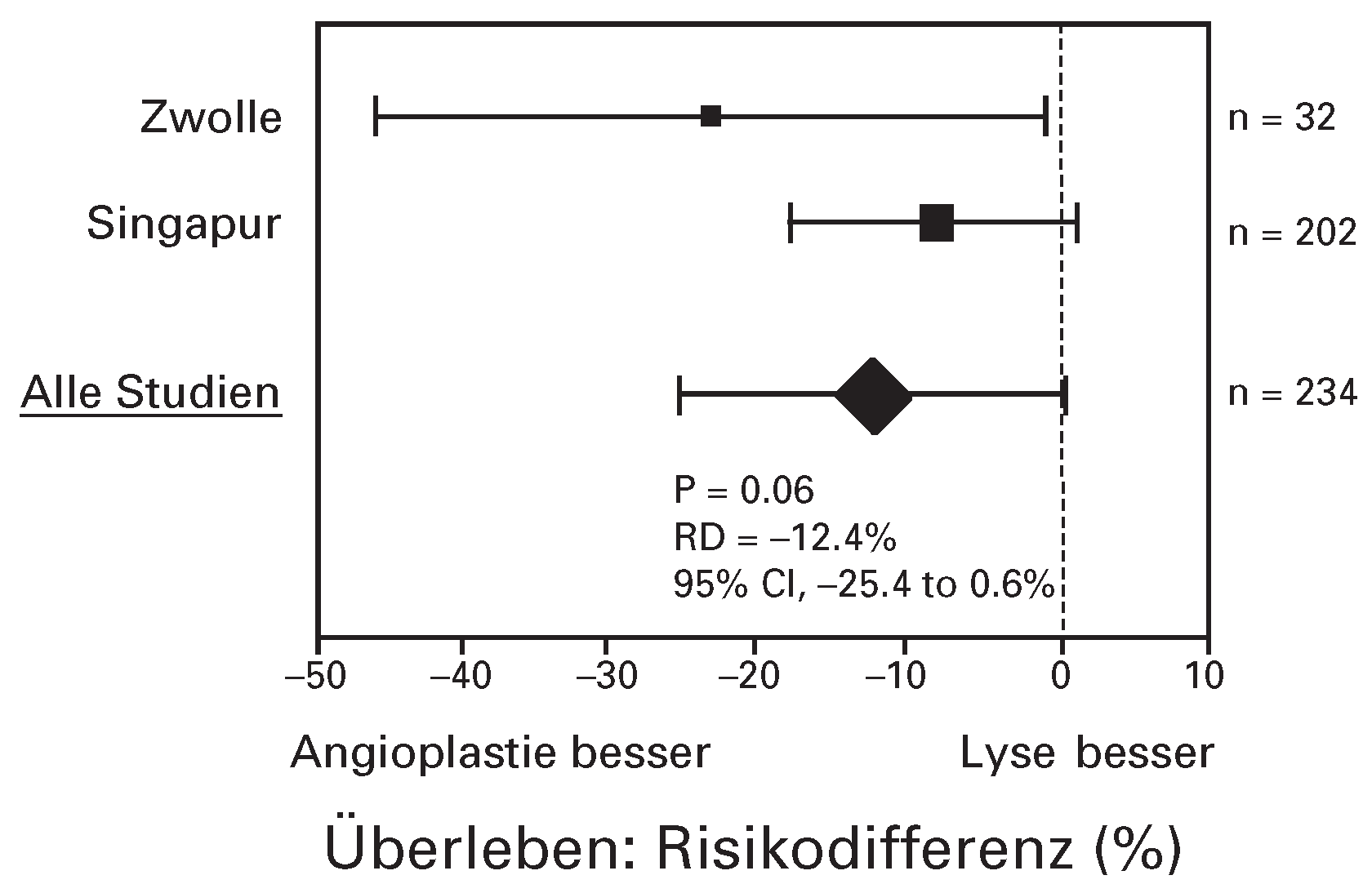
Akuter Myokardinfarkt bei Patienten mit metabolischem Syndrom
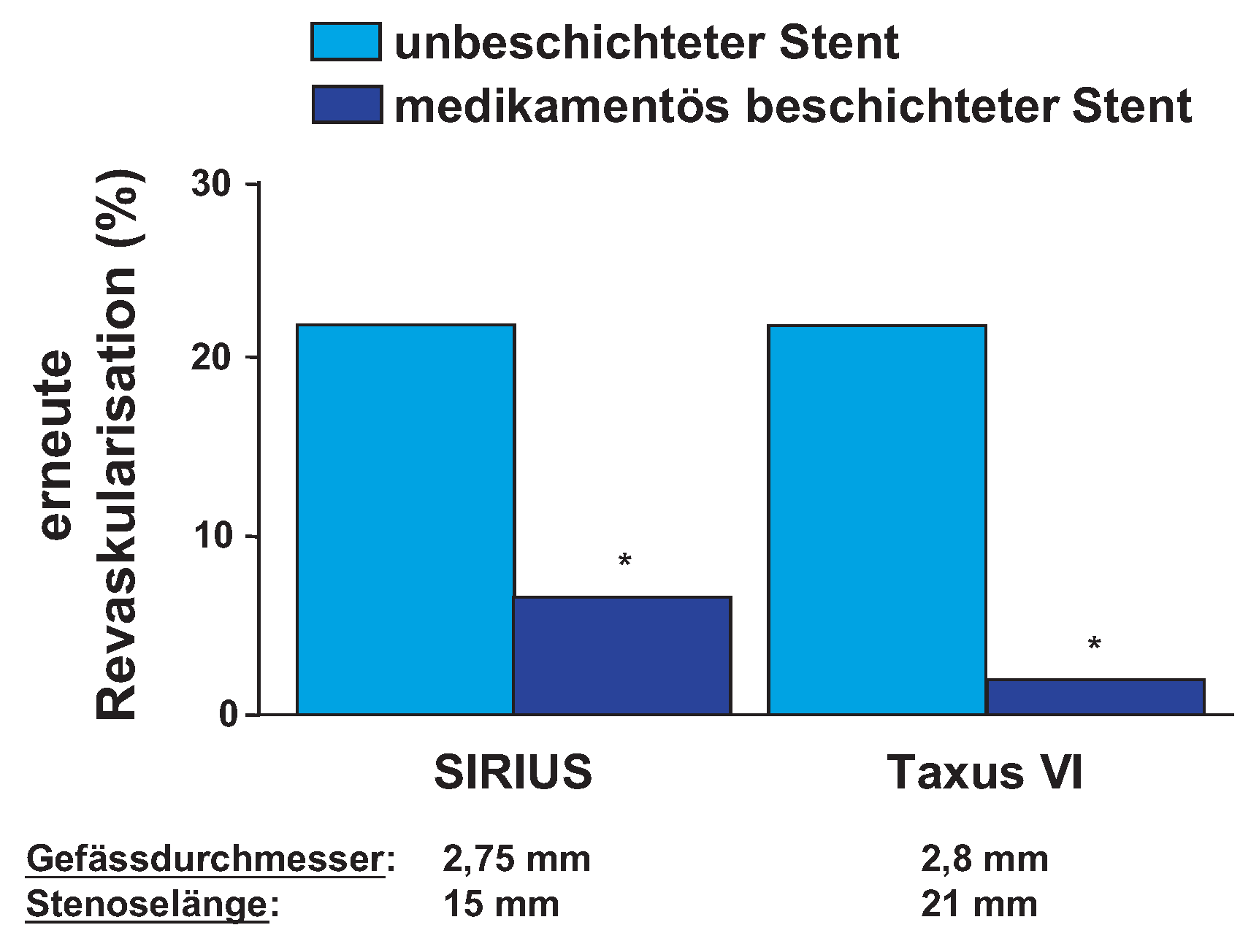
Revaskularisation bei stabiler koronarer Herzkrankheit
Medikamentöse Therapie
Literatur
- Dandona, P.; Aljada, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 2004, 25, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.R.; Murcia, A.M.; Palacios, I.F.; Leon, M.N.; Bernardi, V.H.; Fuster, V.; et al. Coronary composition and macrophage infiltration in atherectomy specimens from patients with diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2000, 102, 2180–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieker, L.E.; Ruschitzka, F.; Luscher, T.F.; Noll, G. HDL and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord 2004, 4, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genest, J., Jr.; McNamara, J.R.; Ordovas, J.M.; Jenner, J.L.; Silberman, S.R.; Anderson, K.M.; et al. Lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein A-I and B and lipoprotein (a) abnormalities in men with premature coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992, 19, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscher, T.F.; Creager, M.A.; Beckman, J.A.; Cosentino, F. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part II. Circulation 2003, 108, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creager, M.A.; Luscher, T.F.; Cosentino, F.; Beckman, J.A. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part I. Circulation 2003, 108, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranders, I.; Diamant, M.; van Gelder, R.E.; Spruijt, H.J.; Twisk, J.W.; Heine, R.J.; et al. Admission blood glucose level as risk indicator of death after myocardial infarction in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 2004, 164, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath-Ordoubadi, F.; Beatt, K.J. Glucose-insulin-potassium therapy for treatment of acute myocardial infarction: an overview of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Circulation 1997, 96, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, K. Prospective randomised study of intensive insulin treatment on long term survival after acute myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus. DIGAMI (Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin Glucose Infusion in Acute Myo-cardial Infarction) Study Group. BMJ 1997, 314, 1512–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fath-Ordoubadi, F.; Beatt, K.J. A comparison of thrombolytic therapy with primary coronary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1997, 336, 1103–1104; author reply 1104. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, L.F.; Mak, K.H.; Lau, K.W.; Sim, L.L.; Chan, C.; Koh, T.H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of patients with diabetes mellitus and acute myocardial infarction treated with primary angio-plasty or fibrinolysis. Heart 2002, 88, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, W.; Kleybrink, S.; Doering, W.; Standl, E.; Schnell, O. Hospital outcome of acute myocardial infarction in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 2004, 21, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Marso, S.P.; Lincoff, A.M.; Wolski, K.E.; Ellis, S.G.; Topol, E.J. Abciximab reduces mortality in diabetics following percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 35, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, M.K.; Wahid, S.T.; McComb, J.M.; Marshall, S.M. Significance of silent ischemia and microalbuminuria in predicting coronary events in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.F.; Goldberg, A.D.; Forman, S.; Pepine, C.J.; Knatterud, G.L.; Geller, N.; et al. Asymptomatic Cardiac Ischemia Pilot (ACIP) study two-year follow-up: outcomes of patients randomized to initial strategies of medical therapy versus revascularization. Circulation 1997, 95, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, V.; Gersh, B.J.; Williams, B.A.; Laskey, W.K.; Willerson, J.T.; Tilbury, R.T.; et al. Outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in the current era: a report from the Prevention of REStenosis with Tranilast and its Outcomes (PRESTO) trial. Circulation 2004, 109, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detre, K.M.; Guo, P.; Holubkov, R.; Califf, R.M.; Sopko, G.; Bach, R.; et al. Coronary revascularization in diabetic patients: a comparison of the randomized and observational components of the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI). Circulation 1999, 99, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, S.N.; TenBrook, J.A.; Wolf, M.P.; Pauker, S.G.; Salem, D.N.; Wong, J.B. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing coronary artery bypass graft with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: oneto eight-year outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 41, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlis, S.P.; Morrison, D.A.; Lorin, J.D.; Esposito, R.; Sethi, G.; Sacks, J.; et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary bypass graft surgery for diabetic patients with unstable angina and risk factors for adverse outcomes with bypass: outcome of diabetic patients in the AWESOME randomized trial and registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, V.M.; Serruys, P.W.; Unger, F.; van Hout, B.A.; Vrolix, M.C.; Fransen, G.M.; et al. Three-year outcome after coronary stenting versus bypass surgery for the treatment of multivessel disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gum, P.A.; O’Keefe, J.H., Jr.; Borkon, A.M.; Spertus, J.A.; Bateman, T.M.; McGraw, J.P.; et al. Bypass surgery versus coronary angioplasty for revascularization of treated diabetic patients. Circulation 1997, 96, II7–II10. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, I.; Leon, M.B.; Baim, D.S.; O’Neill, W.W.; Popma, J.J.; Buchbinder, M.; et al. Impact of sirolimus-eluting stents on outcome in diabetic patients: a SIRIUS (SIRolImUS-coated Bx Velocity balloon-expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo coronary artery lesions) substudy. Circulation 2004, 109, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belle, E.; Perie, M.; Braune, D.; Chmait, A.; Meurice, T.; Abolmaali, K.; et al. Effects of coronary stenting on vessel patency and long-term clinical outcome after percutaneous coronary revascularization in diabetic patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M.; Lehto, S.; Ronnemaa, T.; Pyorala, K.; Laakso, M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1998, 339, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Sleight, P.; Pogue, J.; Bosch, J.; Davies, R.; Dagenais, G. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 2000, 342, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, K.M. Efficacy of perindopril in reduction of cardiovascular events among patients with stable coronary artery disease: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial (the EUROPA study). Lancet 2003, 362, 782–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm, L.H.; Ibsen, H.; Dahlof, B.; Devereux, R.B.; Beevers, G.; de Faire, U.; et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): A randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002, 359, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parving, H.H.; Lehnert, H.; Brochner-Mortensen, J.; Gomis, R.; Andersen, S.; Arner, P. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viberti, G.; Wheeldon, N.M. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation 2002, 106, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensinreceptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2004 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Spieker, L. Das Herz Beim Metabolischen Syndrom. Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 7, 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2004.01048
Spieker L. Das Herz Beim Metabolischen Syndrom. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2004; 7(9):317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2004.01048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpieker, Lukas. 2004. "Das Herz Beim Metabolischen Syndrom" Cardiovascular Medicine 7, no. 9: 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2004.01048
APA StyleSpieker, L. (2004). Das Herz Beim Metabolischen Syndrom. Cardiovascular Medicine, 7(9), 317. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2004.01048




