Introduction
There is growing concern that patients are increasingly harmed by medical errors, e.g., by medication errors which are one of the most common types of medical error [
1,
2]. The American Institute of Medicine estimates that preventable medication errors result in more than 7000 deaths each year in US hospitals, and tens of thousands of additional deaths in the outpatient setting [
3]. Studies from US hospitals indicate that prescribing errors occur in 0.4–1.9% of all inpatient medication orders [
4,
5,
6] and cause harm in about 1% of all inpatients [
7]. The majority of medication errors are due to incorrect prescribing [
7,
8].
Previous studies on prescribing errors have focused on inpatients, but there is increasing evidence that a substantial number of errors already occur in the emergency department (ED) [
9,
10]. For the purpose of this study we therefore focused on prescribing errors in patients who are ready to be transferred from the ED to a medical ward. These orders are written just before a patient is transferred and represent the initial prescriptions for inpatients written by a junior physician, supervised by a senior physician and copied into the charts by a member of the nursing staff when the patient enters the ward. This process of copying and transcription is increasingly recognised as an additional source of errors [
11,
12]. The aim of our study was to describe the character of prescribing and transcription errors in patients transferred from the emergency department (ED) to the inpatient ward.
Methods
The study was conducted in the ED of a primary care hospital and tertiary referral centre in Zurich, Switzerland, with 555 beds. The interdisciplinary ED serves a population of 360 000 and is attended by more than 27 000 patients per year. 30% of them are admitted to inpatient wards and half are medical patients.
We included all consecutive adult patients aged over 18 who were admitted to a medical ward from the ED in September and October 2005. Surgical patients and patients admitted directly to the medical ward were excluded. Structured data were collected prospectively on a daily basis for each patient and entered into a database (SPSS). The data collection included patient characteristics, reason for admission, surveillance data from the ED, available laboratory results by the time the prescriptions were made and results from physical examination in the ED. Each single prescription on the handwritten prescription schedule was collected, including name of the drug, dosage, route of administration and whether it was ordered as scheduled medication or reserve medication. If a preparation contained more than one active substance, each active component was listed individually.
Prescribing errors
Prescribing errors were analysed by the investigators and independently reviewed by an independent expert panel composed of three board-certified physicians in internal medicine. Appropriateness of drug prescription was investigated according to the following categories: indication, consideration of known allergies, dosage (including adjustment to renal or hepatic function), and consideration of all contraindications. The Swiss Drug Compendium, which includes all drugs registered in Switzerland, was used as the gold standard to assess the appropriate dosage and indication. In questionable cases expert advice was sought from a clinical pharmacologist.
Prescribing errors were identified according to the definition of Dean et al. [
11]. A clinically significant prescribing error was defined as a “prescribing decision or prescription writing process that results in an unintentional, significant reduction in the probability of treatment being timely and effective, or increase in the risk of harm, when compared with generally accepted practice”.
We classified the prescribing errors into four groups:
- −
Selection errors: Disregarding contraindications, disregarding drug interactions, inappropriate or missing indications and inadequate drug selection (e.g., paracetamol as the only analgesic for severe pancreatitis).
- −
Dosage errors: Absolute overdoses or underdoses (in relation to the recommended dosages), relative overdoses (e.g., standard therapeutic amoxicillin dosage in cases of impaired renal function) and errors in drug administration route.
- −
Incorrect orders: Illegible and ambiguous prescription (e.g., “clarithromycin 1–0–0” since both 250 mg and 500 mg tablets are available).
- −
Drug classes withheld despite a compelling indication (e.g., no prescription of aspirin in a patient with acute coronary heart disease without a contraindication for platelet aggregation inhibiting drugs).
Prescribing errors were differentiated with regard to their clinical impact and potential severity, as suggested by Dean et al. [
13] as serious and nonserious errors: an error was considered clinically significant if it potentially results in an ADE. It was considered serious if it was likely to result in the need for additional therapeutic activities, a prolonged hospital stay, the need for an intensive care unit or surgery, or if it could be fatal. Remaining errors were classified as nonserious. Patients aged over 80 were screened for potential paradoxical reactions to benzodiazepines [
14]. If a patient had not previously been given benzodiazepines as his standard medication and was started on benzodia-zepines without a compelling indication, a nonserious selection error was recorded.
The correlation between prescribing errors and potential risk factors such as age, creatinine clearance and number of drugs prescribed per patient was calculated on the basis of the Pearson correlation coefficient.
Transcription errors
Loss of or a change in the initial transfer order during the process of copying by the nursing staff was considered a transfer error. The importance and severity of these errors were classified on the same basis as above.
We stratified our analysis on both prescribing and transcription errors according to working shifts with more or less manpower to investigate whether more errors occur during understaffed periods (day shifts at weekends or night shifts) with a fourfold contingency table and the resultant phi coefficient.
Results
Among 305 patients assessed, 152 (49.8%) were female and 153 (50.2%) male. The median (Q1, Q3) age was 79 (67, 84) for females and 73 (60, 81) for male patients.
The corresponding numbers for weight were 60 (53, 70) kg and 76 (68, 84) kg. Creatinine clearance was 49.9 (35.2, 79.9) ml/min for females and 62.5 (45.9, 87.0) ml/ min for males. In total we collected 2592 written drug orders with 2728 active substances. The median number of different drugs prescribed per patient was 8 (6, 10), and the mean number of drugs prescribed in reserve was 2.5.
We found a significant correlation between the mean number of prescribed drugs and the age of the patients (Pearson r = 0.75, p = 0.01). Paracetamol, ox- azepam and metoclopramide were the most frequently prescribed agents. They are the agents of the standard drugs prescribed in reserve for symptomatic therapy of pain, agitation and nausea in our hospital. They were prescribed in more than half of the patients (78, 63, and 58%, respectively).
Prescribing errors
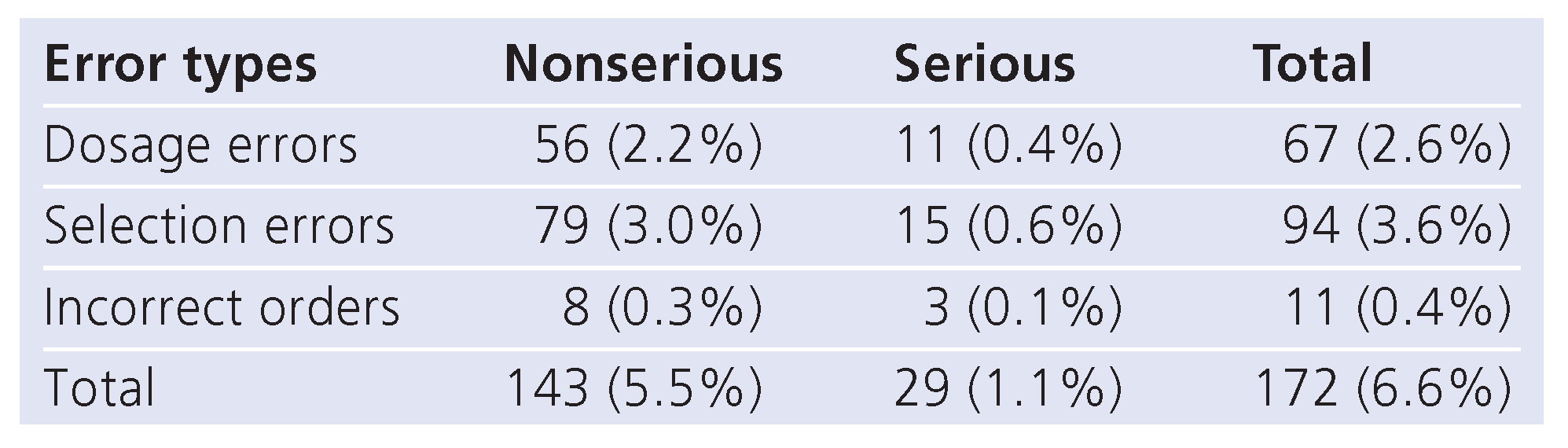
Over a period of six weeks, 233 prescribing errors were identified in 2728 prescriptions for 305 patients. Fifty errors (21.5%) were clinically irrelevant and 183 (78.5%) relevant, resulting in an extrapolated error rate of 6.7 (95% CI, 5.76–7.64%) prescribing errors per 100 prescriptions. Including “drug classes withheld despite compelling indication”, 60 prescribing errors occurred per 100 admissions.
35 (19.1%; 95% CI, 13.3–24.7%) of the clinically meaningful prescribing errors were serious with potential to harm patients (
table 1).
The majority of the 183 relevant prescribing errors were selection errors (51.4%), 36.6% dosage errors, 6.0% incorrect orders, and 6.0% drug classes withheld despite a compelling indication. Of the selection errors 89.4% were due to contraindications that were overlooked, 6.4% were due to missing indications and 4.3% were inappropriate drug selections. Of the dosage errors, 9.0% were absolute overdoses, 83.6% were relative overdoses and 7.5% were due to administration route errors.
Table 1.
Clinically meaningful prescribing errors subdivided by error types and severity, expressed as percentages of the total number of medication orders.
Table 1.
Clinically meaningful prescribing errors subdivided by error types and severity, expressed as percentages of the total number of medication orders.
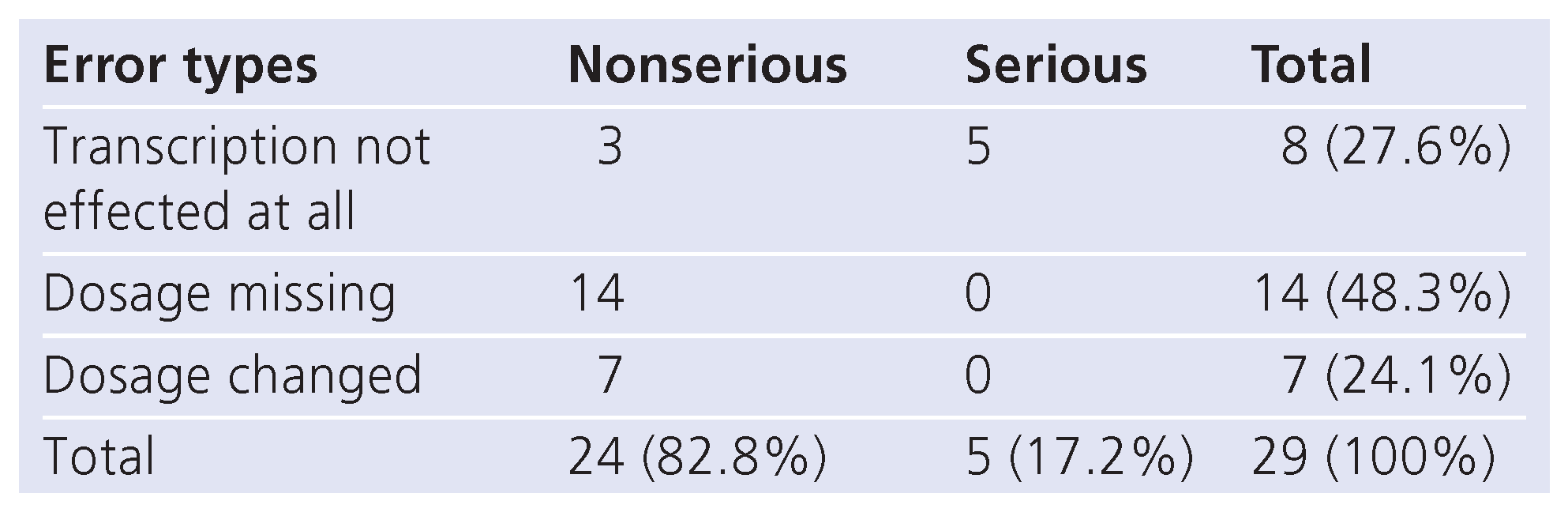
Table 2.
Types and severity of clinically meaningful transcription errors.
Table 2.
Types and severity of clinically meaningful transcription errors.
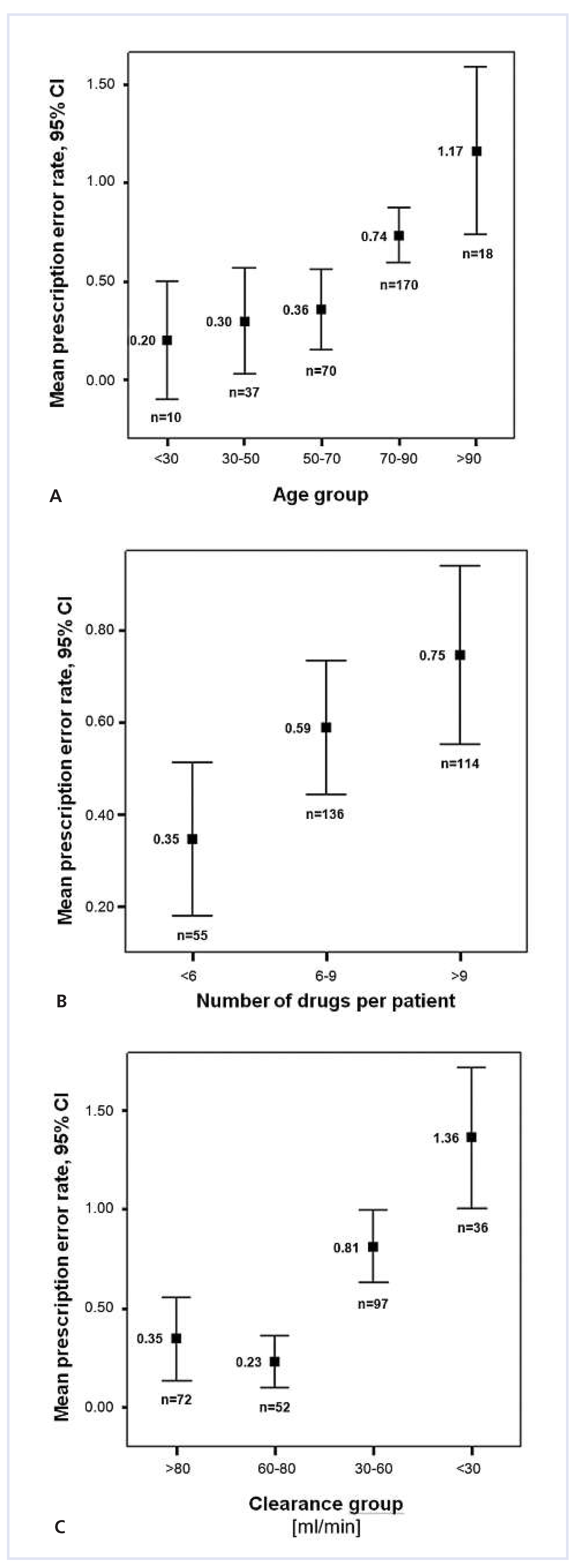
The mean prescribing error rate per patient depended on the patient’s age (r = 0.89, p = 0.01), the number of drugs per patient (r = 0.97, p = 0.01) and creatinine clearance (r = –0.80, p = 0.01) (
fig. 1).
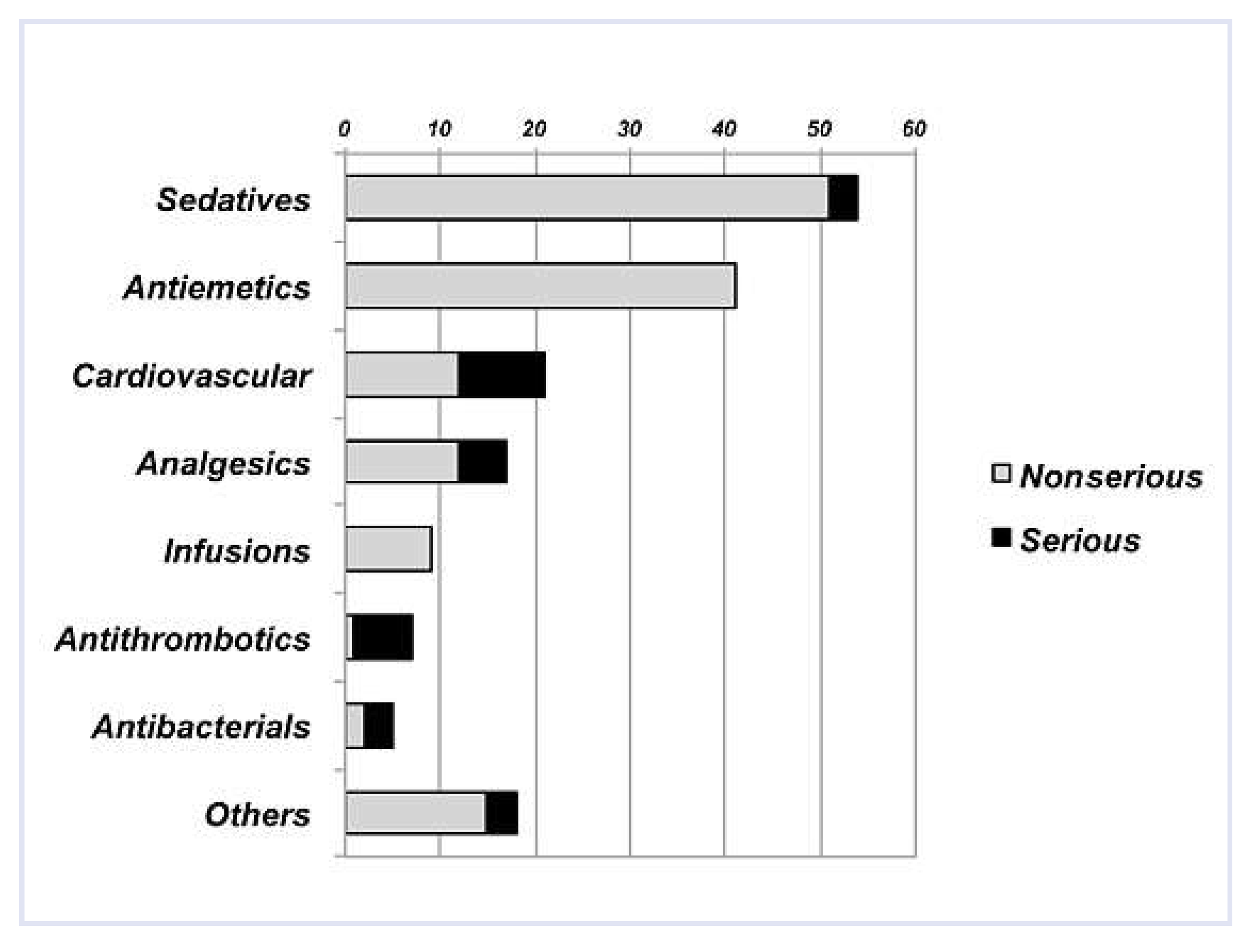
Figure 2 shows the drugs most frequently involved in prescribing errors. In the majority of cases (n = 51), a benzodiazepine was prescribed without a compelling indication (mostly in reserve) to patients aged over 80 who had not previously been given benzodiazepines as standard medication. In 41 patients the dosage of metoclopramide was not adapted to the creatinine clearance. This corresponds to 95.3% (95% CI, 88.5–100%) of all patients with a clearance below 40 ml/min who had been prescribed metoclopramide in reserve.
Transcription errors
Overall, 68 transcription errors were detected (2.6% of prescriptions; 95% CI, 1.99–3.21%). 29 were clinically meaningful (1.1% of transcribed orders; 95% CI, 0.7– 1.5%).
Table 2 shows their distribution by type and severity. An example of a serious transcription error was failure to transcribe enoxaparin (LMWH) for a patient with pulmonary embolism.
Neither prescribing errors (phi: –0.008) nor transcription errors (phi: 0.053) correlated with periods of understaffed shifts on the ED or the wards.
Discussion
This prospective study demonstrates a high rate of relevant prescribing errors (6.7 per 100 prescriptions) in a cohort of 305 consecutive patients admitted from the ED to the medical ward. The majority (78.5%) were clinically relevant errors and 19% of these were classified as serious with the potential to harm the patient. Potentially serious errors occurred chiefly in the selection of drugs, confirming the results of previous studies [
4,
5,
7,
13,
15]. Risk factors for prescribing errors were increasing age, creatinine clearance, and the number of drugs prescribed per patient. Since these factors are easily identified on the basis of clinical data, this knowledge could be effectively integrated into teaching and training, resulting in heightened awareness of risky prescribing situations.
The prescribing error rate in our study is higher than those quoted in studies on medical inpatients in the US [
4,
5,
6,
15] and the UK [
13]. We hypothesise that the main reason for this difference is that our study was conducted exclusively in the ED. There is evidence for a higher incidence of ADEs in EDs compared to medical wards [
9,
10]: EDs operate under greater time pressure and introduce more new drugs to a preexisting regimen. Moreover, during the evaluation of prescribing errors we adhered strictly to guidelines and clinical recommendations, thus considering more prescriptions as (nonserious) selection errors (e.g., prescribing a benzodiazepine as first choice reserve medication for insomnia in a benzodiazepine-naive patient).
Clinical pharmacists are not integrated into the daily prescribing process in our hospital, nor do they routinely screen prescriptions for errors. Additionally, there is no electronic support for error checking. Both involvement of pharmacists in reviewing drug orders and a well structured clinical information system, including an electronic expert system for drug prescription, significantly reduce the potential harm resulting from incorrect medication orders [
5,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Moreover, closer and more systematic supervision by an experienced physician could result in timely detection and correction of prescribing errors.
Our study confirms that the transcription of orders from the ED to the ward constitutes an important additional source of prescribing errors. All the serious errors (n = 5) were drug prescriptions that were not transcribed at all. These errors could have been avoided if an electronic prescribing system had been used.
The strengths of our study include a well defined study group of patients admitted from the ED to the medical ward (standardised patient flow) and rigorous predefined criteria of prescribing errors according to guidelines and clinical recommendations. Major limitations include its design as a monocentre study, the observational bias and the relatively short time period of data collection. The strict application of guidelines on appropriate dosages can be critical in this patient population with its acute and therefore not steady-state medical conditions. The level of medical education of physicians and nurses can be an additional bias. Moreover, we were not able to investigate how many prescribing errors would have been recognised and corrected by the team on the ward the following day. We were not able to correlate the rate of prescribing errors with the flow rate of patients through the ED, since alloutpatients were excluded for the purpose of our study and we did not record time and effort per patient for an individual physician. However, no correlation of errors with understaffed periods was found.
In conclusion, if strict criteria are applied, substantially more prescribing errors are detected than previously reported. The majority of these errors are clinically relevant. Since the impact of reducing prescribing errors on the prevention of ADEs is not known, studies with different interventional strategies are required to clarify this topic.