Patent Foramen Ovale, Is It More Dangerous to Close It Than to Leave it Open?
CLOSURE I trial [1]
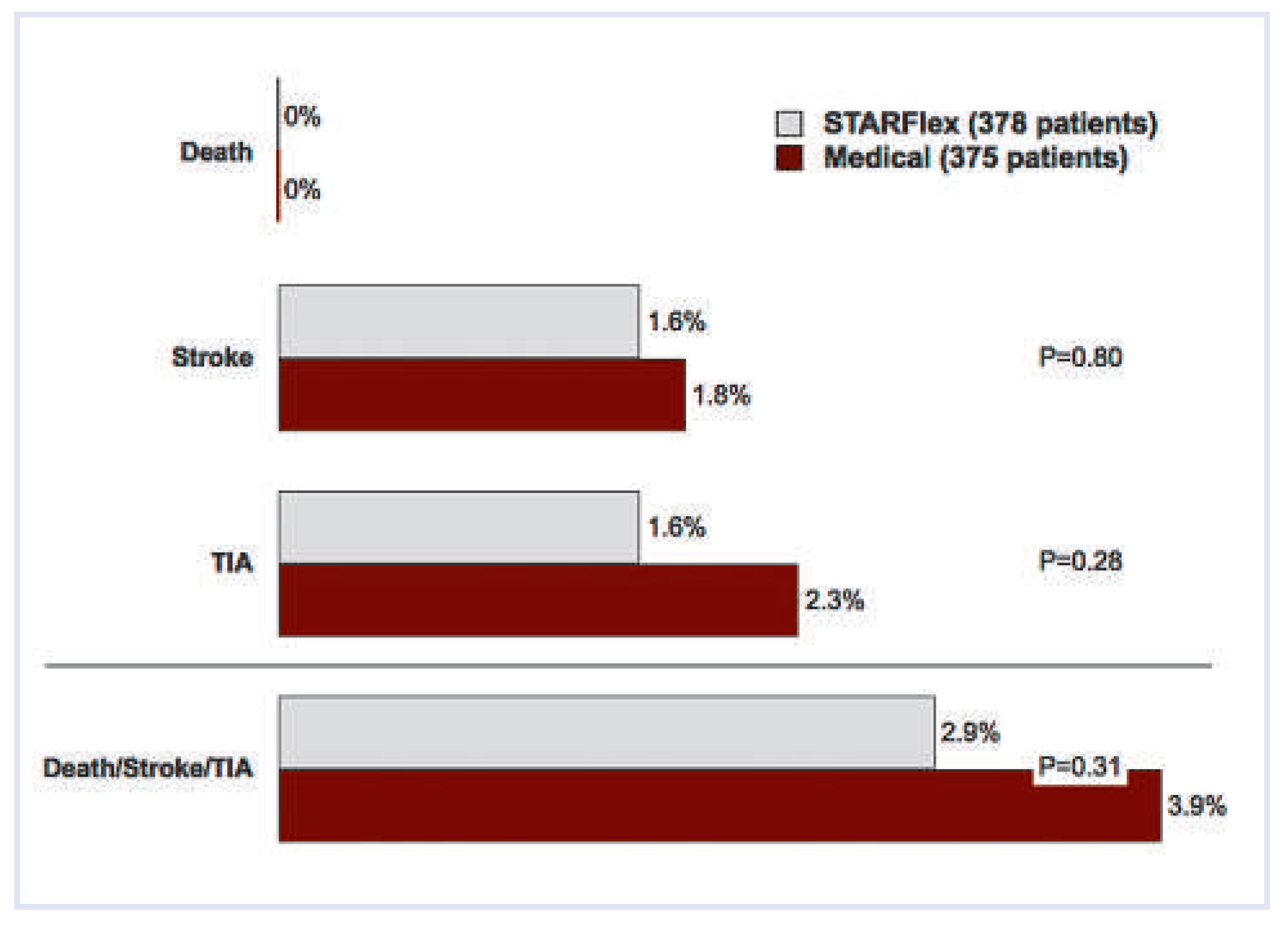
Other compelling data
Funding/potential conflict of interest
References
- Furlan, A.J.; Reisman, M.; Massaro, J.; Mauri, L.; Adams, H.; Albers, G.W.; et al. Closure or medical therapy for cryptogenic stroke with patent foramen ovale. N Engl J Med. 2012, 366, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.; Jüni, P.; Mono, M.L.; Kalesan, B.; Praz, F.; Geister, L.; et al. Long-term propensity score-matched comparison of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale with medical treatment after paradoxical embolism. Circulation 2012, 125, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, A.J.; Reisman, M.; Massaro, J.; Mauri, L.; Adams, H.; Albers, G.W.; et al. Study design of the CLOSURE I Trial: a prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the STARFlex septal closure system versus best medical therapy in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack due to presumed paradoxical embolism through a patent foramen ovale. Stroke 2010, 41, 2872–2883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.; Praz, F.; Stirnimann, J.; Windecker, S.; Seiler, C.; Nedeltchev, K.; et al. Safety and feasibility of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale without intra-procedural echocardiography in 825 patients. Swiss Med Wkly. 2008, 138, 567–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumsdorf, U.; Ostermayer, S.; Billinger, K.; Trepels, T.; Zadan, E.; Horvath, K.; et al. Incidence and clinical course of thrombus formation on atrial septal defect and patient foramen ovale closure devices in 1000 consecutive patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 43, 302–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuchlenz, H.W.; Weihs, W.; Berghold, A.; Lechner, A.; Schmidt, R. Secondary prevention after cryptogenic cerebrovascular events in patients with patent foramen ovale. Int J Cardiol. 2005, 101, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luermans, J.G.; Budts, W.; Ten Berg, J.M.; Plokker, H.W.; Suttorp, M.J.; Post, M.C. Comparison of outcome after patent foramen ovale closure in older versus younger patients. EuroIntervention 2011, 7, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.K.; Song, J.M.; Kang, D.H.; Yun, S.C.; Kang, D.W.; et al. Associ- ation between anatomic features of atrial septal abnormalities obtained by omni-plane transesophageal echocardiography and stroke recurrence in cryptogenic stroke patients with patent foramen ovale. Am J Cardiol. 2010, 106, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.; Geibel, A.; Kasper, W.; Olschewski, M.; Blumel, L.; Just, H. Patent foramen ovale is an important predictor of adverse outcome in patients with major pulmonary embolism. Circulation 1998, 97, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clergeau, M.R.; Hamon, M.; Morello, R.; Saloux, E.; Viader, F. Silent cerebral infarcts in patients with pulmonary embolism and a patent foramen ovale: a prospective diffusion-weighted MRI study. Stroke 2009, 40, 3758–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, H.T.; Horvath-Puho, E.; Pedersen, L.; Baron, J.A.; Prandoni, P. Venous thromboembolism and subsequent hospitalisation due to acute arterial cardiovascular events: a 20-year cohort study. Lancet 2007, 370, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattle, H.; Meier, B.; Nedeltchev, K. Prevention of stroke with patent foramen ovale. Int J Stroke. 2010, 5, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almekhlafi, M.A.; Wilton, S.B.; Rabi, D.M.; Ghali, W.A.; Lorenzetti, D.L.; Hill, M.D. Recurrent cerebral ischemia in medically treated patent foramen ovale: a meta-analysis. Neurology 2009, 73, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigatelli, G.; Dell’Avvocata, F.; Cardaioli, P.; Giordan, M.; Braggion, G.; Aggio, S.; et al. Permanent right-to-left shunt is the key factor in managing patent foramen ovale. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, D.; Kitsios, G.; Hill, M.D.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Wilton, S.B.; Ghali, W.A. Recurrent cerebral ischemia in medically treated patent foramen ovale: a meta-analysis. Neurology 2011, 77, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, A.A.; Windecker, S.; Juni, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Dudek, D.; Andersen, H.R.; et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale (PFO) using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder with medical treatment in patients with cryptogenic embolism (PC-Trial): rationale and design. Trials 2011, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.; Praz, F.; Tai, T.; Findling, O.; Walpoth, N.; Nedeltchev, K.; et al. Improvement of migraine headaches after percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale for secondary prevention of paradoxical embolism. Heart 2010, 96, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2012 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meier, B. Patent Foramen Ovale, Is It More Dangerous to Close It Than to Leave it Open? Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 15, 183. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01675
Meier B. Patent Foramen Ovale, Is It More Dangerous to Close It Than to Leave it Open? Cardiovascular Medicine. 2012; 15(6):183. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01675
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeier, Bernhard. 2012. "Patent Foramen Ovale, Is It More Dangerous to Close It Than to Leave it Open?" Cardiovascular Medicine 15, no. 6: 183. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01675
APA StyleMeier, B. (2012). Patent Foramen Ovale, Is It More Dangerous to Close It Than to Leave it Open? Cardiovascular Medicine, 15(6), 183. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01675



