Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Switzerland: Range of Pathology in Screening-Positive Individuals
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Results
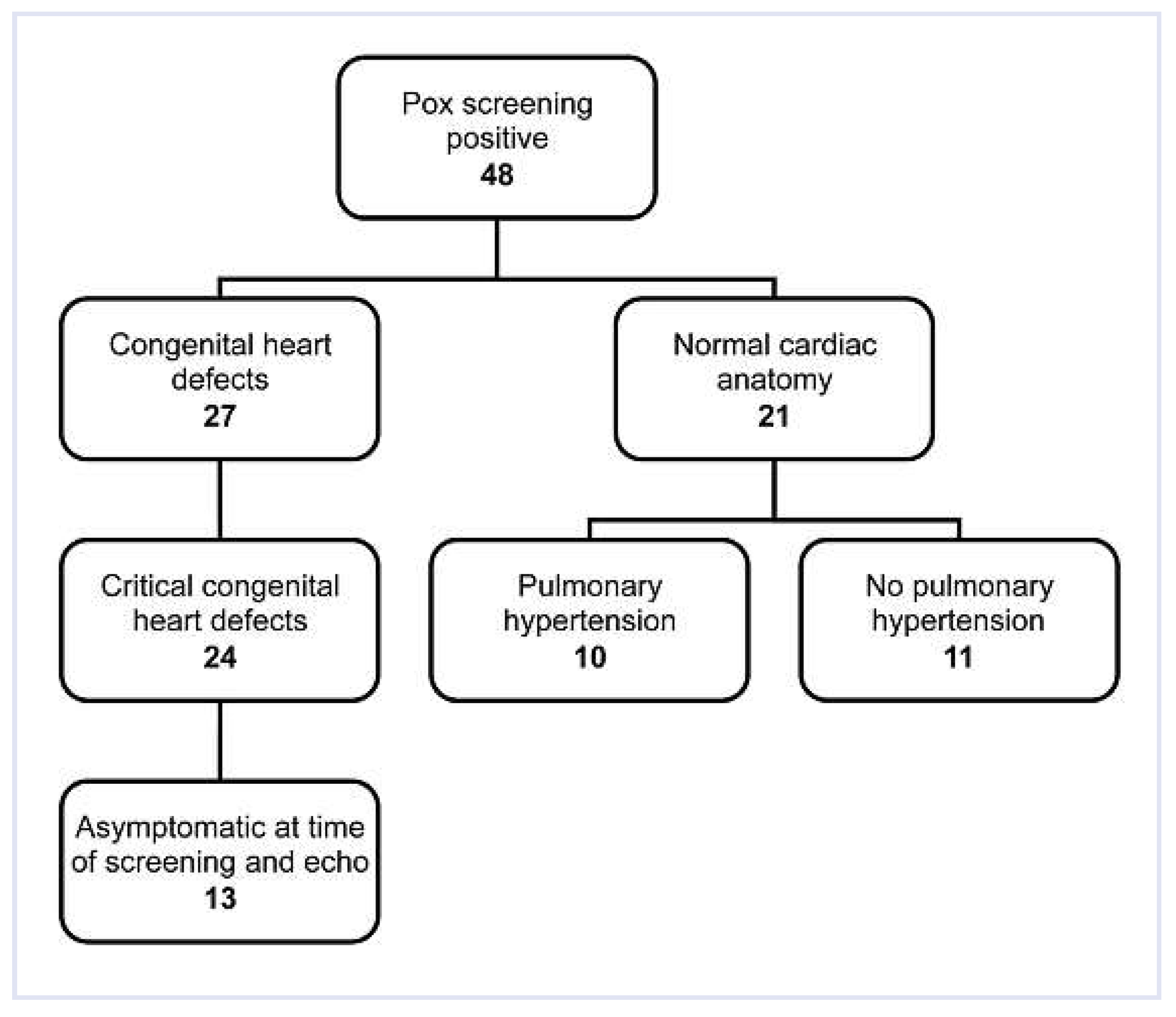
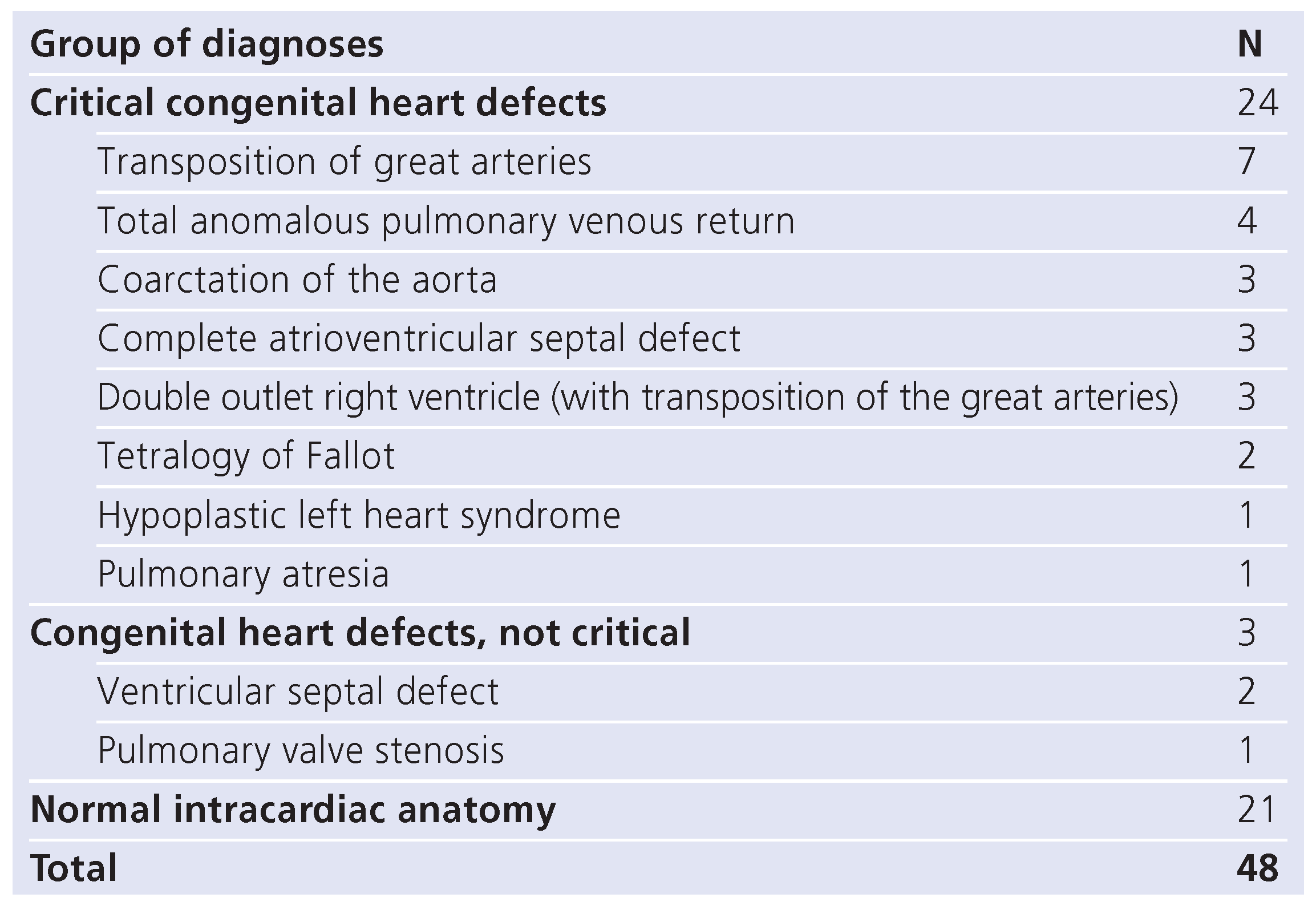
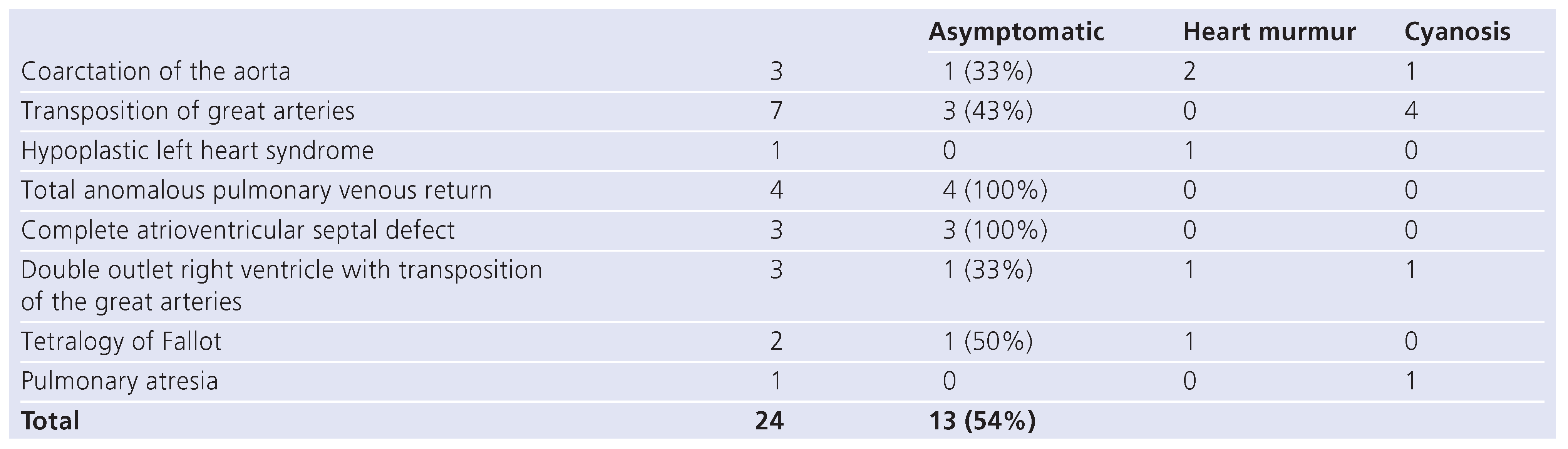
Discussion
Conclusion
Funding/potential competing interests
References
- Arlettaz, R.; Bauschatz, A.; Monkhoff, M.; Essers, B.; Bauersfeld, U. The contribution of pulse oximetry to the early detection of congenital heart disease in newborns. Eur J Pediatr. 2006, 165, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuelling, B.; Arlettaz Mieth, R.; Bauersfeld, U.; Balmer, C. Pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart defects in Switzerland: most but not all maternity units screen their neonates. Swiss Med Wkly. 2009, 139, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppel, R.I.; Druschel, C.M.; Carter, T.; Goldberg, B.E.; Mehta, P.N.; Talwar, R.; et al. Effectiveness of pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart disease in asymptomatic newborns. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahle, W.T.; Newburger, J.W.; Matherne, G.P.; Smith, F.C.; Hoke, T.R.; Koppel, R.; et al. Role of pulse oximetry in examining newborns for congenital heart disease: a scientific statement from the AHA and AAP. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaratinam, S.; Daniels, J.; Ewer, A.; Zamora, J.; Khan, K. Accuracy of pulse oximetry in screening for congenital heart disease in asymptomatic newborns: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007, 92, F176–F180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, E.; Chitano, G.; Dipaola, L.; De Felice, C.; Latini, G. Indications and limitations for a neonatal pulse oximetry screening of critical congenital heart disease. J Perinat Med. 2005, 33, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruangritnamchai, C.; Bunjapamai, W.; Pongpanich, B. Pulse oximetry screening for clinically unrecognized critical congenital heart disease in the newborns. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2007, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerholm, U.; Daxberg, E.; Fassoulas, A.; Hafström, O.; Liljegren, A.; Samuelsson, O.; et al. Pulse oximetry (POX) screening for congenital heart defects in newborns. Västra Götalandsregionen 2011, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Arlettaz, R.; Bauersfeld, U. Empfehlungen zum neonatalen Screening kongenitaler Herzfehler. Pediatrica 005, 16-5, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerholm, U.; Daxberg, E.; Fassoulas, A.; Hafström, O.; Liljegren, A.; Samuelsson, O.; et al. Pulse oximetry (POX) screening for congenital heart defects in newborns. [Pulsoximetri screening för upptäckt av hjärtmiss-bildningar hos nyfödda]; Västra Götalandsregionen, Sahlgrenska Universitetssjukhuset, HTA-centrum: Göteborg, Zweden, 2011; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Mahle, W.T.; Martin, G.R.; Beekman, R.H.; Morrow, W.R. Endorsement of Health and Human Services recommendation for pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart disease. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toth, B.; Becker, A.; Seelbach-Gobel, B. Oxygen saturation in healthy newborn infants immediately after birth measured by pulse oximetry. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2002, 266, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riede, F.; Dähnert, I.; Woerner, C.; Möckel, A.; Lorenz, N.; Kabus, M.; et al. Verkleinerung der diagnostischen Lücke bei kritischen angeborenen Herzfehlern durch Pulsoxymetriescreening. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 2009, 157, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmari, P. Should pulse oximetry be used to screen for congenital heart disease? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal. 2007, 92, 219–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fasnacht, M.; Pfammatter, J.P.; Ghisla, R.; Sekarski, N.; Steinmann, H.; Kuen, P.; et al. FETCH-study: prospective fetal cardiology study in Switzerland. Cardiology in the Young 2005, 15 (Suppl. 2), 35A. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kamlin, C.; O’Donnell, C.; Davis, P.; Morley, C. Oxygen saturation in healthy infants immediately after birth. J Pediatr. 2006, 148, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schelp, J.; Arlettaz, R.; Hug, M.I.; Balmer, C. Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Switzerland: Range of Pathology in Screening-Positive Individuals. Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 15, 198. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01676
Schelp J, Arlettaz R, Hug MI, Balmer C. Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Switzerland: Range of Pathology in Screening-Positive Individuals. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2012; 15(6):198. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01676
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchelp, Johanna, Romaine Arlettaz, Maja Isabel Hug, and Christian Balmer. 2012. "Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Switzerland: Range of Pathology in Screening-Positive Individuals" Cardiovascular Medicine 15, no. 6: 198. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01676
APA StyleSchelp, J., Arlettaz, R., Hug, M. I., & Balmer, C. (2012). Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Switzerland: Range of Pathology in Screening-Positive Individuals. Cardiovascular Medicine, 15(6), 198. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01676



