Wird Die Essentielle Hypertonie Heilbar? †
Die Anfänge
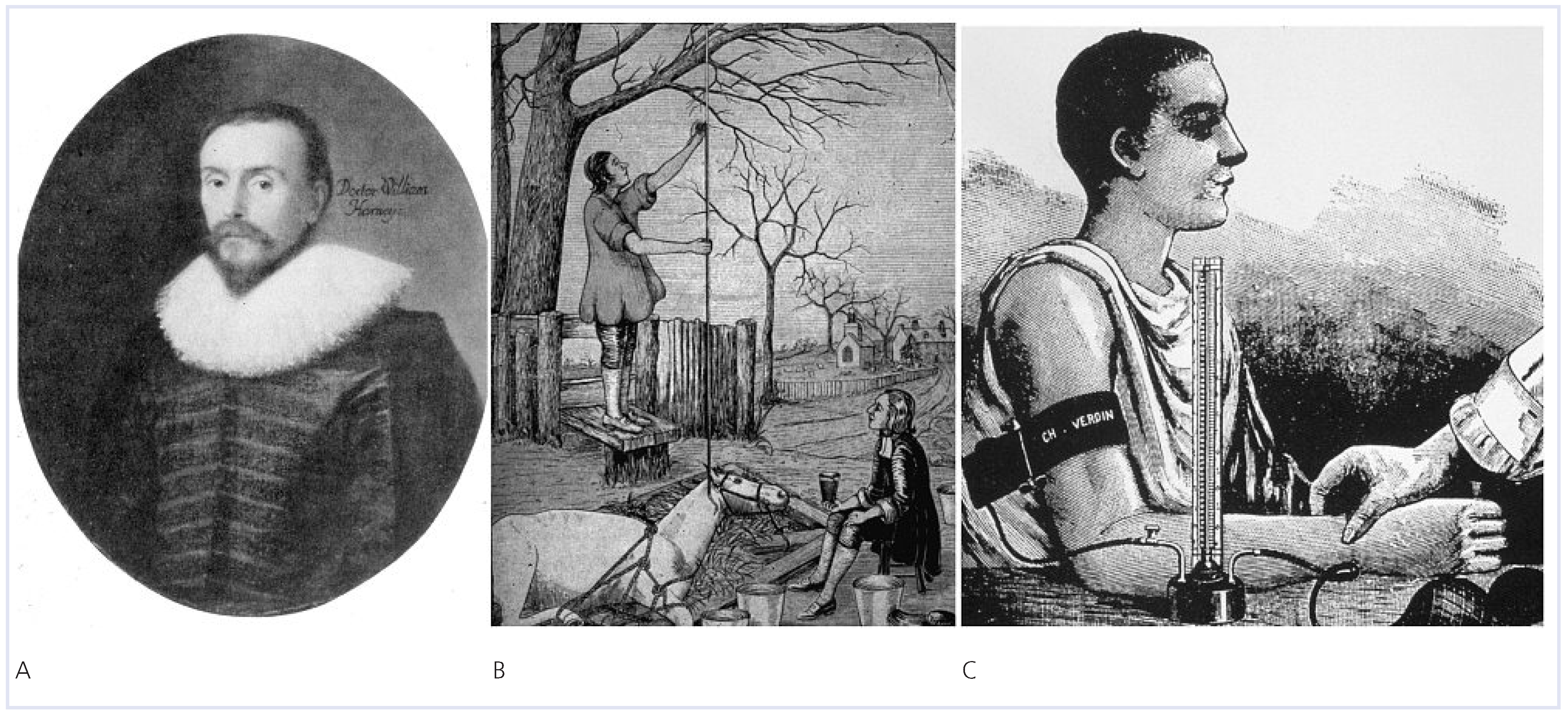
Der verkannte Risikofaktor
Erste Antihypertensiva

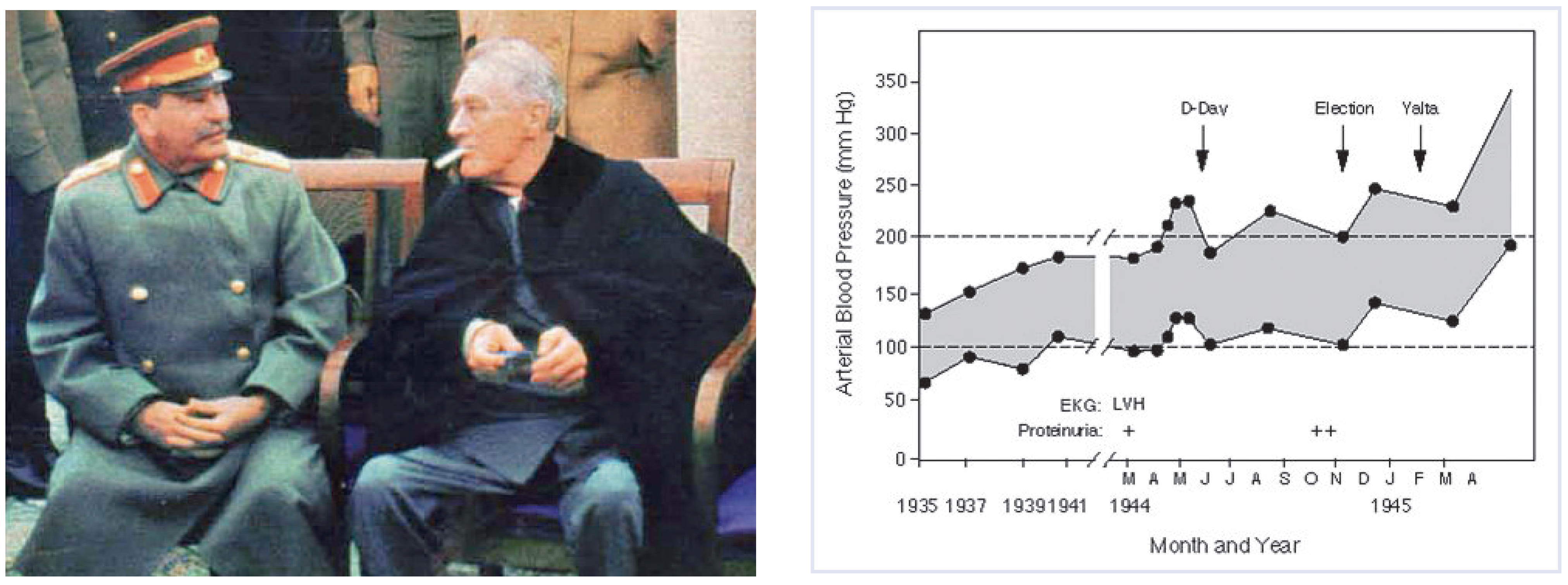
Das Ungelöste
- Viele Patienten nehmen die Medikamente nicht, nicht anhaltend oder nicht in der verordneten Dosierung ein, da sie die tägliche Einnahme der Medikamente als unangenehm oder langfristig gefährlich erachten.
- Trotz wirksamer Blutdrucksenkung gelang es nicht, die Prognose von Patienten mit arterieller Hypertonie derjenigen von Normotonikern anzugleichen.
- Es gibt einen geringen, aber doch klinisch bedeutsamen Teil von Patienten, welche trotz der verfügbaren Antihypertensiva keine befriedigende Blutdrucksenkung erreichen oder aufgrund verschiedener Unverträglichkeiten nicht angemessen medikamentös behandelt werden können.
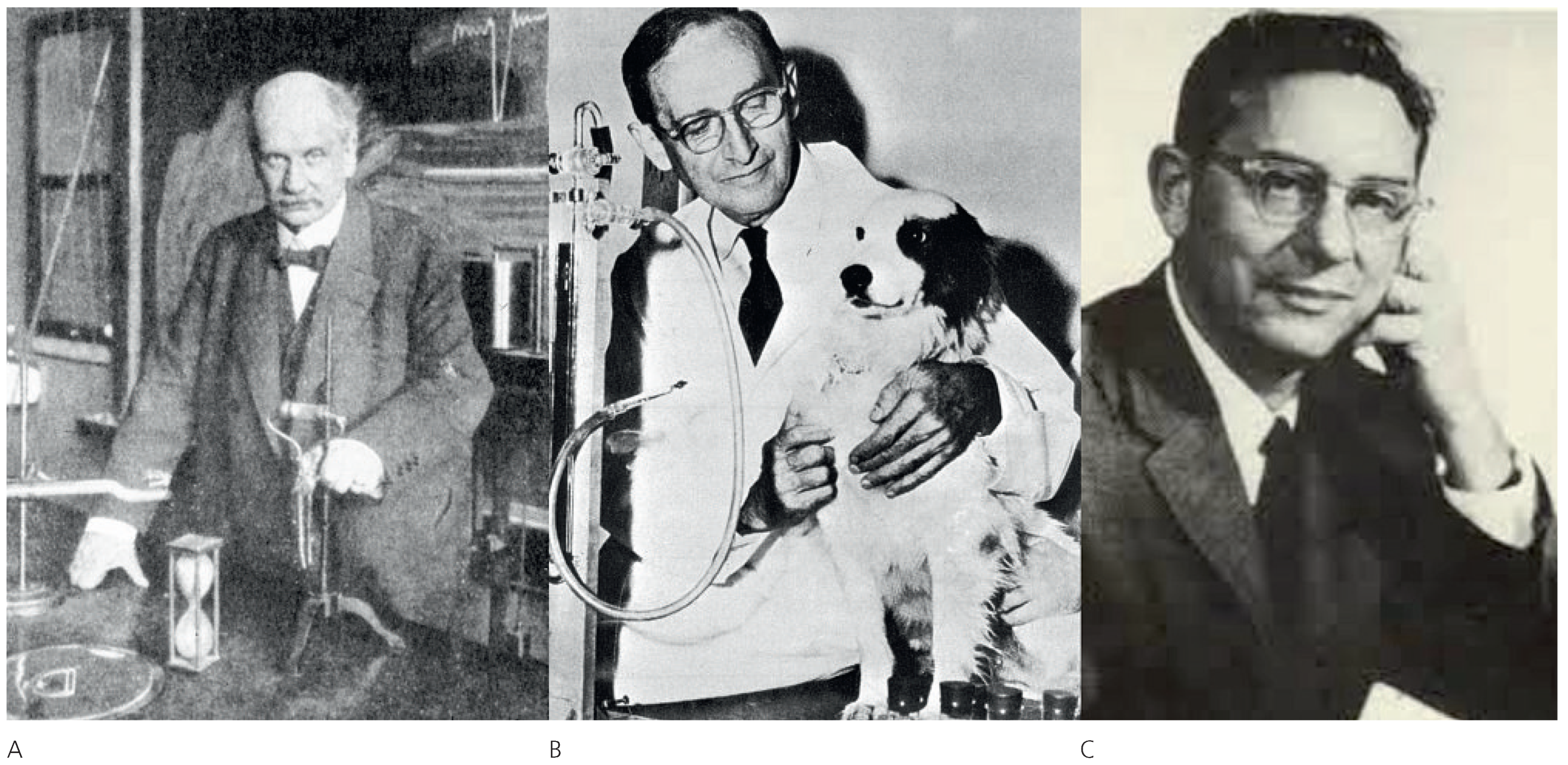
Der Gral des Hochdrucks
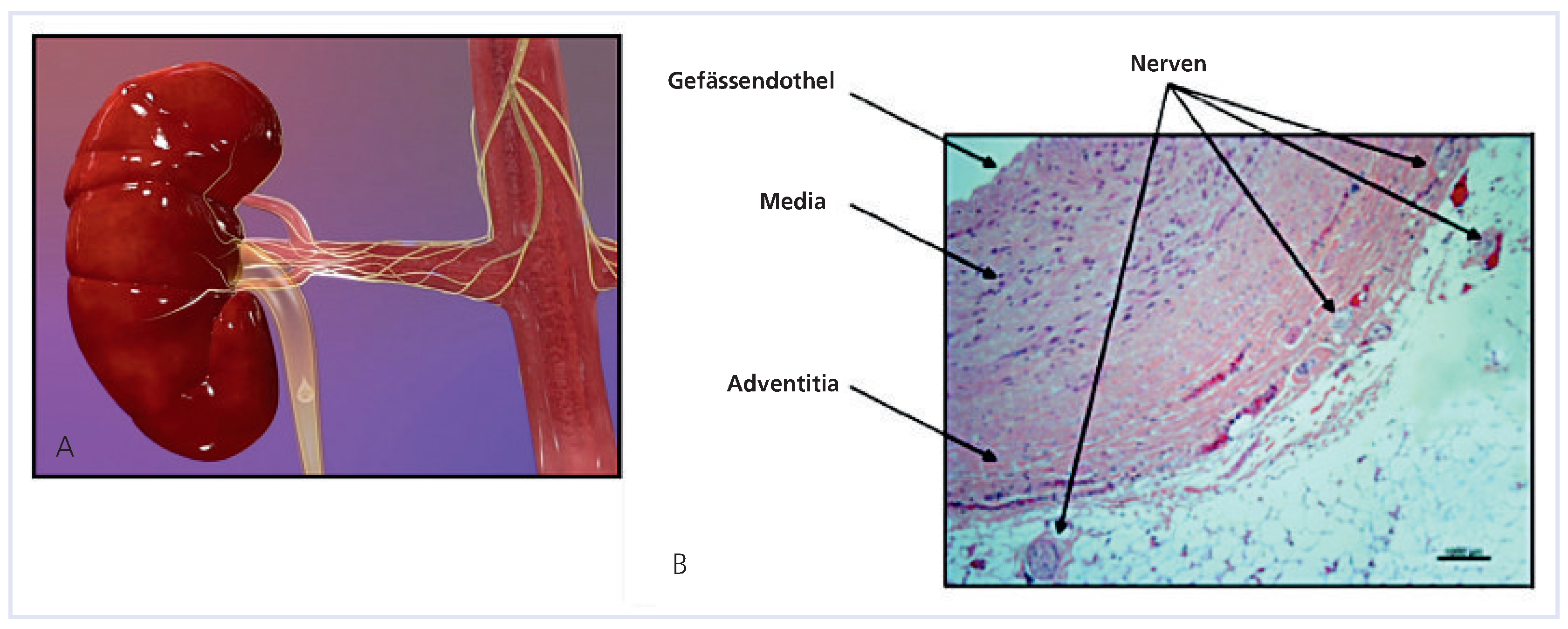
Neue Methoden

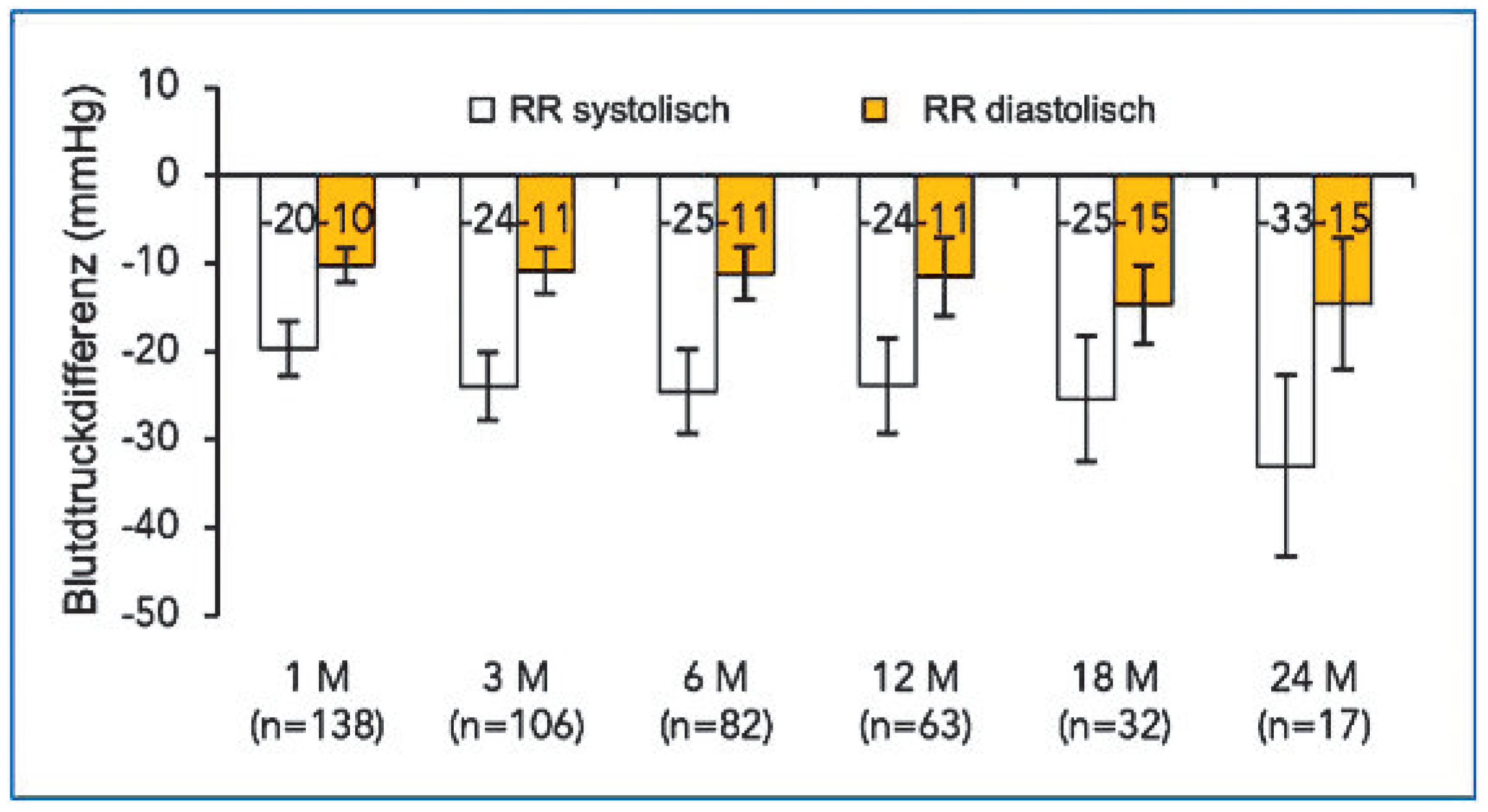
Blick in die Zukunft
Conflicts of Interest
Literatur
- Harvey, W.H. De Motu Cordis. Zitiert nach: Harvey William H. An Anatomical Disputation Concerning the Movement of the Heart and Blood in Living Creatures; G. Whitteridge Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen Hales measuring the blood pressure of a mare by means of a tube placed in the carotid artery. New York: The Granger Collection.
- Riva-Rocci, S. Un nuovo sfigmomanometro. Gazzetta Med Torino. 1896, 47, 881–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkoff, N.S. Concerning the methods of blood pressure measurement. Proc. Emperor’s Milit Med Acad St. Petersburg. 1905, 11, 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Volhard, F. Diskussionbemerkungen zum Morbus Brightii. Verh Deutsch Pathol Gesell. 1905, 9, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Messerli, F.H. This day 50 years ago. N Engl J Med. 1995, 332, 1038–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veterans Administration Study, I.I. JAMA 1970, 213, 1143–1152.
- Kannel, W.B. Epidemiologic assessment of the role of blood pressure: The Framingham Study 1970. JAMA 1996, 276, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigerstedt, R.; Bergamn, P.G. Niere und Kreislauf. Scand Arch Physiol. 1898, 8, 223–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, H.; et al. Studies on experimental hypertension I. The production of persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure by means of renal ischemia. J Exp Med. 1934, 59, 347–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, T.F.; Kaplan, N. Renovascular and Renal Parenchymatous Hypertension; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, J.W. Primary aldosteronism, a new clinical syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1955, 45, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher, T.F.; Vetter, H.; Vetter, W. Morbus Conn: Pathophysiologie und Klinik. In Die Chirurgie der Nebennieren; Mayor, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tordol, J.H. An implantable carotid sinus baroreflex activating system: Surgical technique and short-term outcome from a multi-center feasibility trial for the treatment of resistant hypertension. Eur J Endovasc Surg. 2007, 33, 414–421. [Google Scholar]
- Esler, M. Increased regional sympathetic nervous activity in human hypertension: Causes and consequences. J Hypertens. 1990, 8 (suppl. 7), S53–S57. [Google Scholar]
- Krum, H.; Schlaich, M.; Whitbaum, R.; Sadowski, P.A.; Bartus, K.; Kapelak, B.; et al. Catheter-based renal sympathetic demervation for resistant hypertension: A multicenter safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet. 2009. 373, 1275–1281. [PubMed]
- Wolfrum, M.; Landmesser, U.; Lüscher, T.F. Eine Patientin mit therapieresistenter Hypertonie. Cardiovasc Med. 2010, 13, 346–349. [Google Scholar]
- Farré, J.; Wellens, H.J.J.; Rubio, J.M.; Benezet, J. Supraventricular tachycardia. Chapter 28/29; In ESC Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine; Camm, J.A., Lüscher, T.F., Serruys, P.W., Eds.; Jerónimo Farré, Hein J.J. Wellens, José M. Rubio and Juan Benezet: Supraventricular Tachycardias; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 1013–1068. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Lüscher, T.F. Wird Die Essentielle Hypertonie Heilbar? Cardiovasc. Med. 2010, 13, 321. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2010.01538
Lüscher TF. Wird Die Essentielle Hypertonie Heilbar? Cardiovascular Medicine. 2010; 13(11):321. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2010.01538
Chicago/Turabian StyleLüscher, Thomas F. 2010. "Wird Die Essentielle Hypertonie Heilbar?" Cardiovascular Medicine 13, no. 11: 321. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2010.01538
APA StyleLüscher, T. F. (2010). Wird Die Essentielle Hypertonie Heilbar? Cardiovascular Medicine, 13(11), 321. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2010.01538



