The Role and Safety of Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals as Adjuvant Treatments for Pain Management: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Referent Scientific Databases
3. Pharmacological Effects of Nutraceuticals on Pain
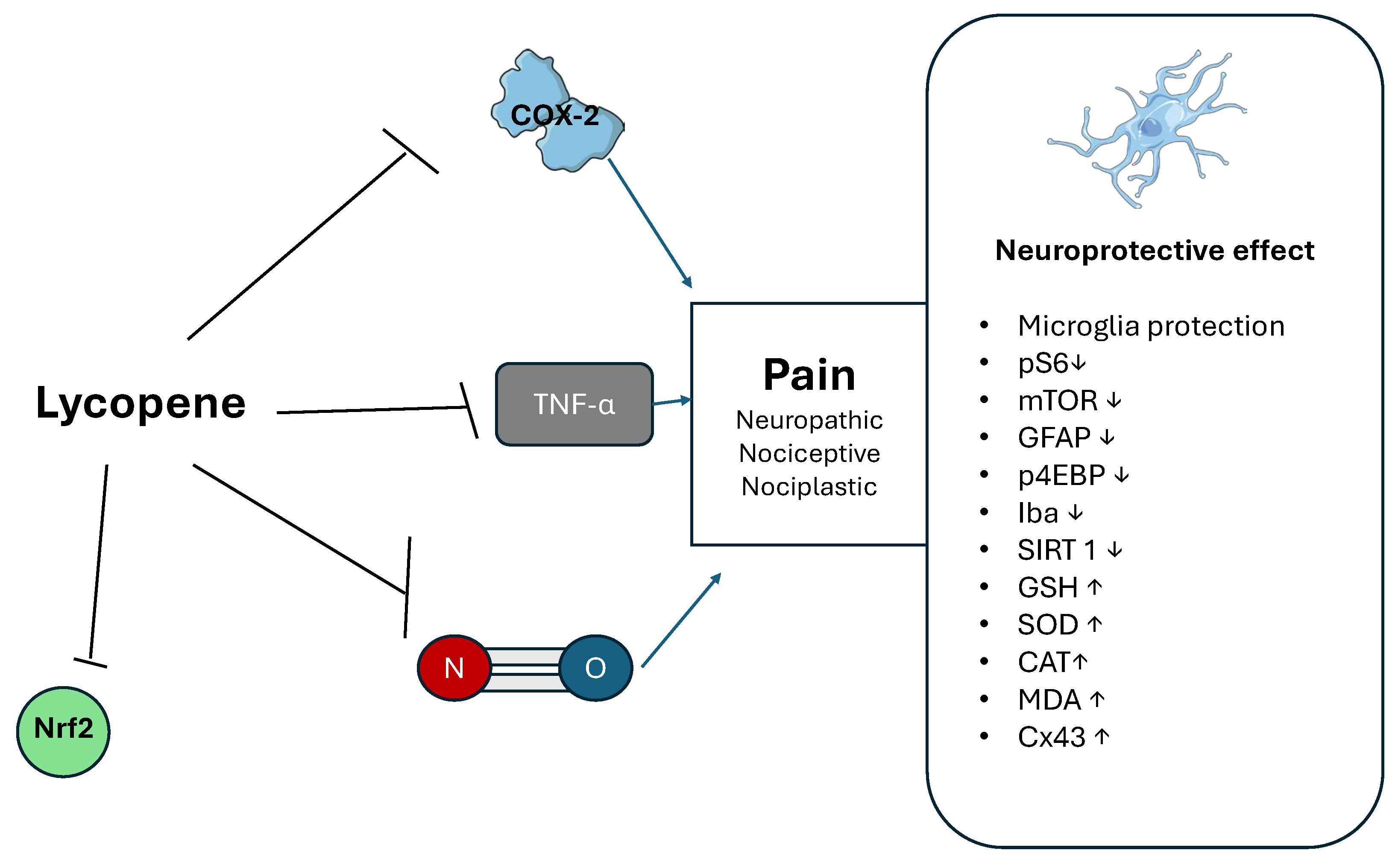
3.1. Lycopene
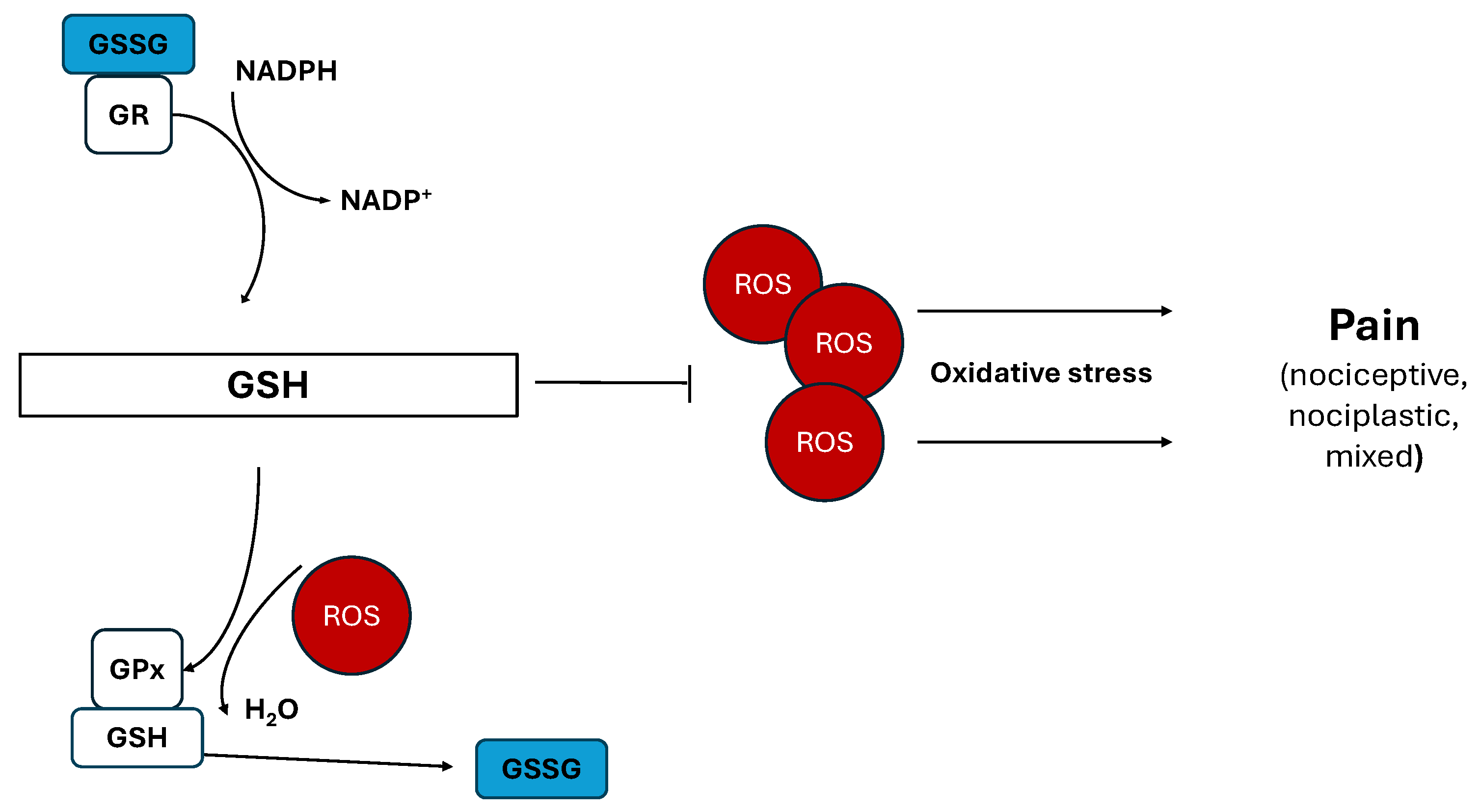
3.2. Glutathione
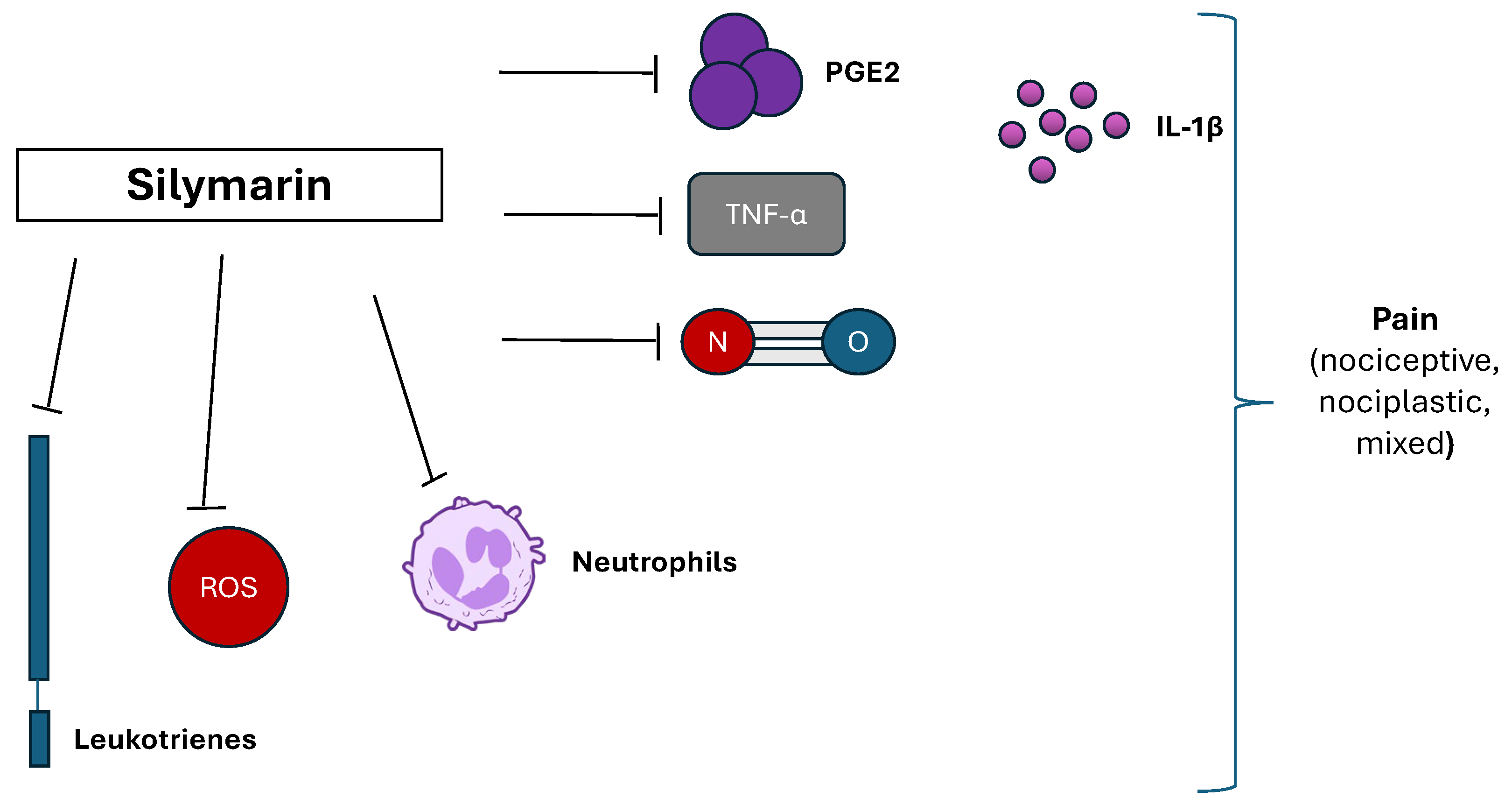
3.3. Silymarin
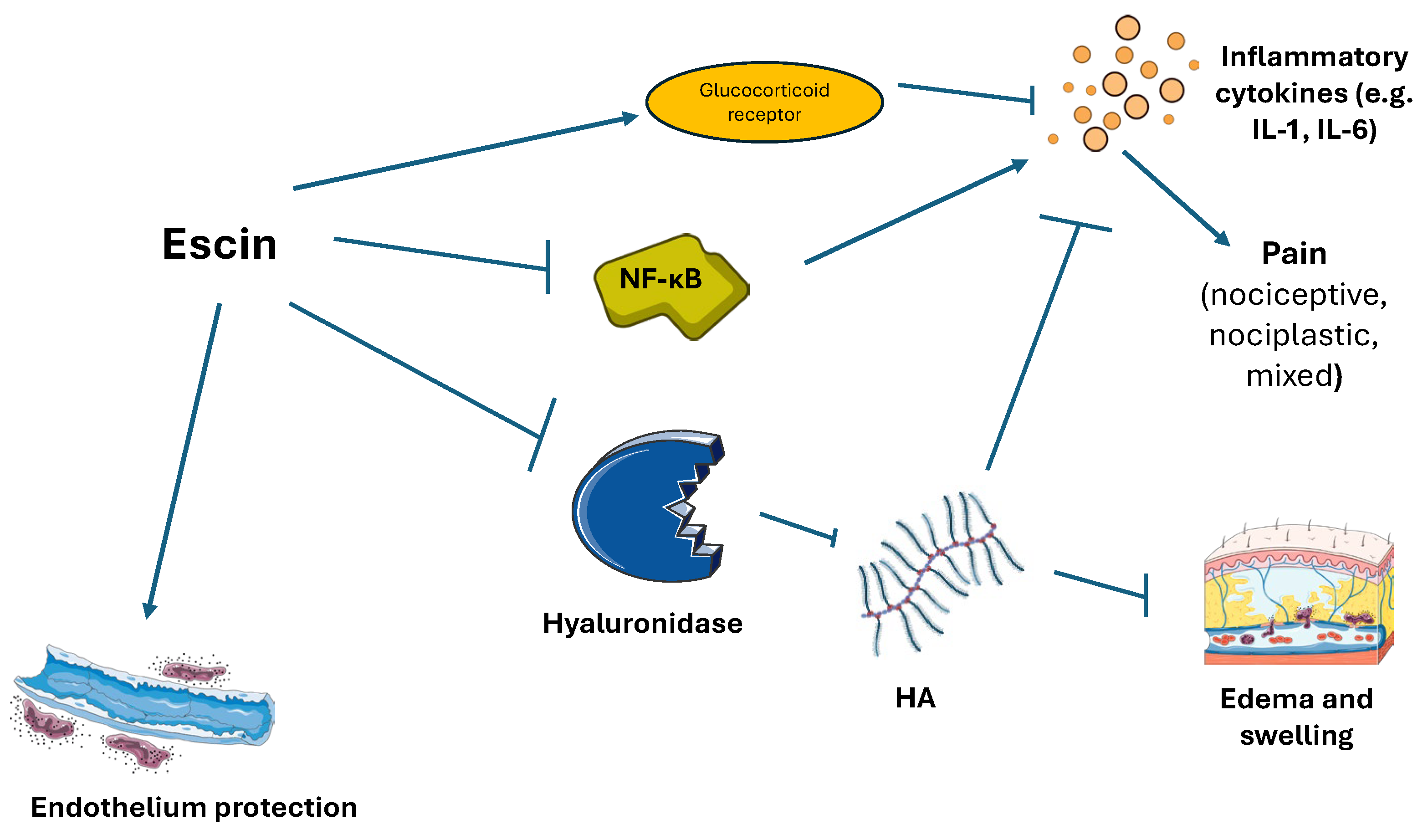
3.4. Escin (Aesculus hippocastanum)
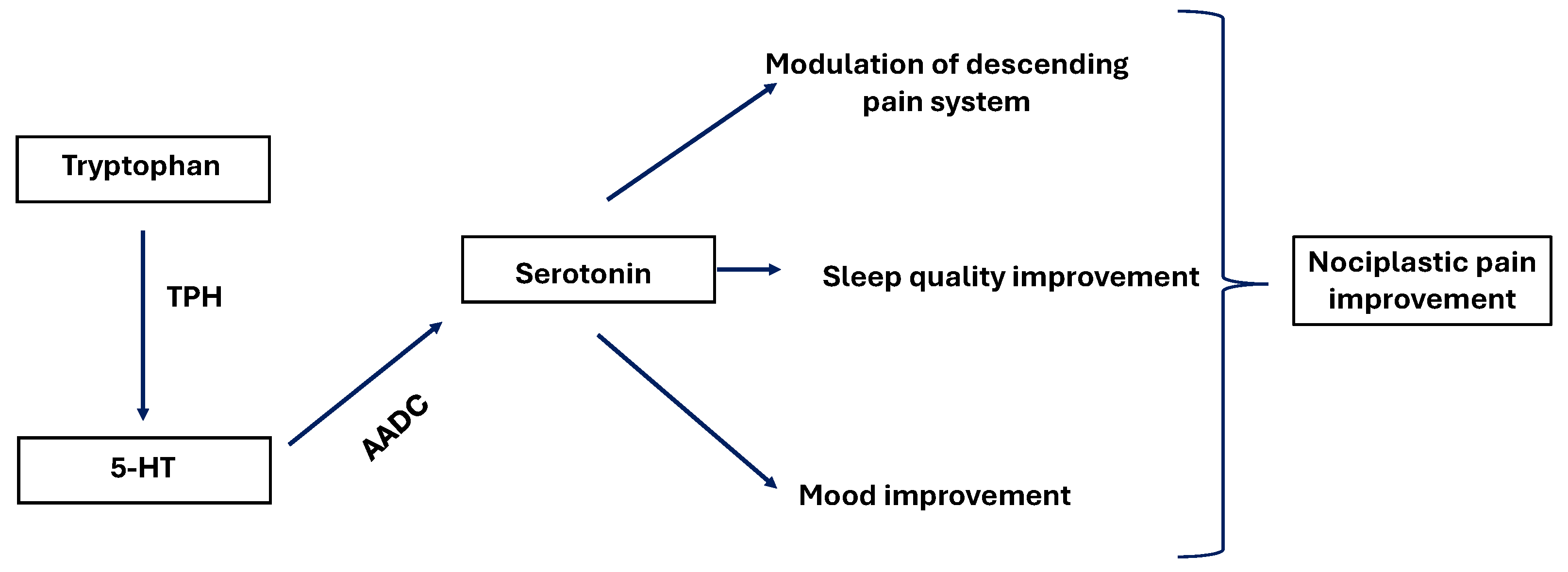
3.5. Tryptophan
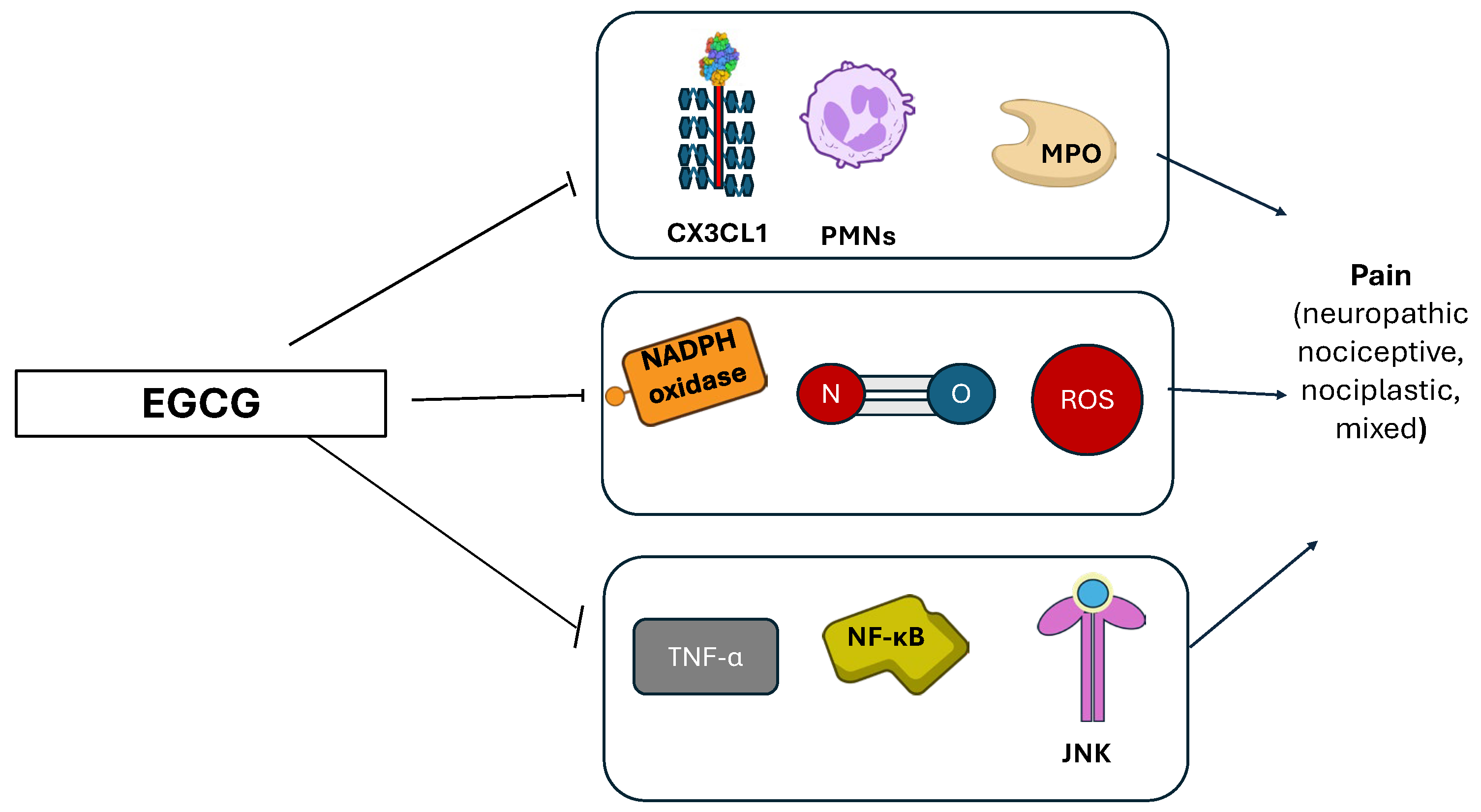
3.6. Green Tea (Camellia sinensis)
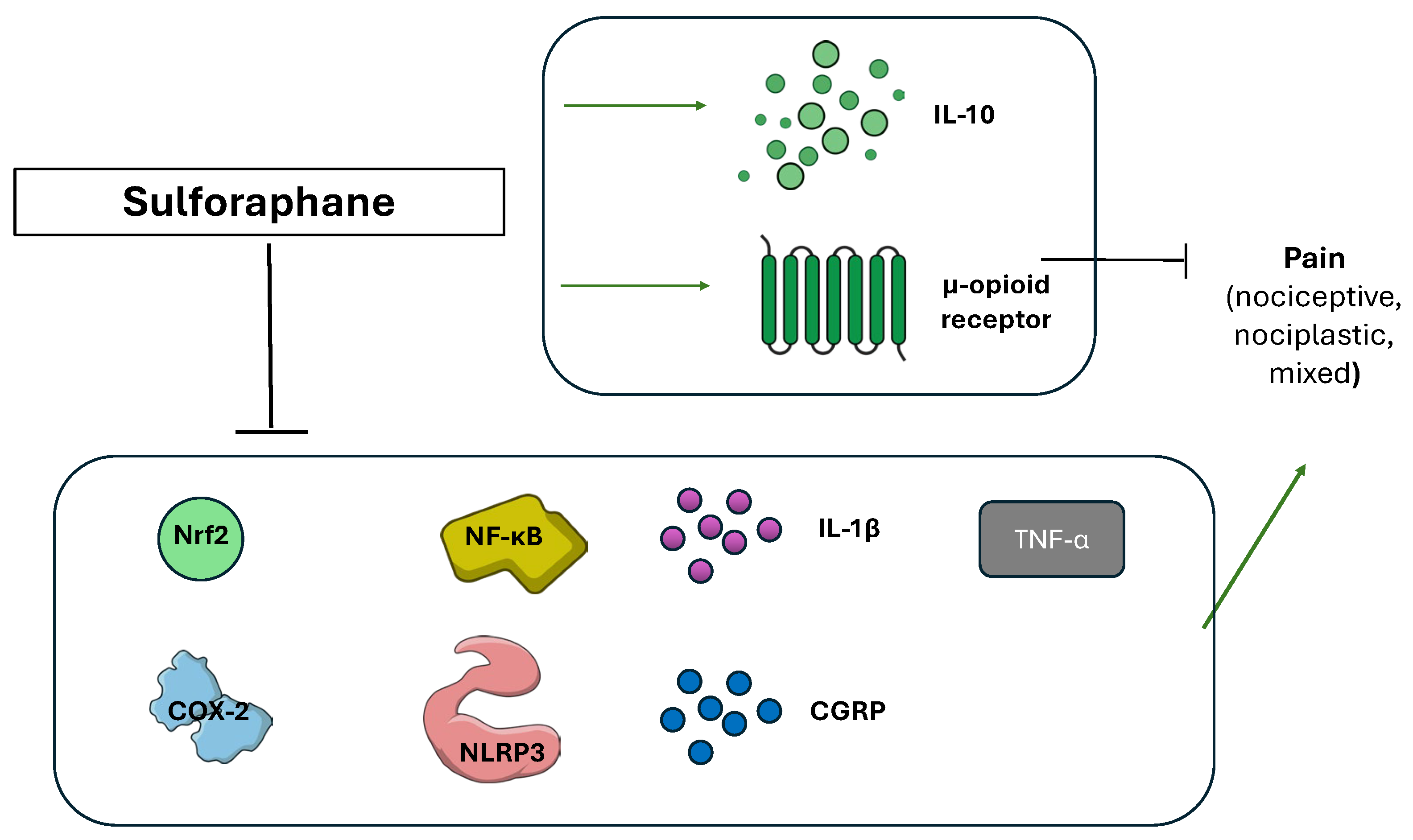
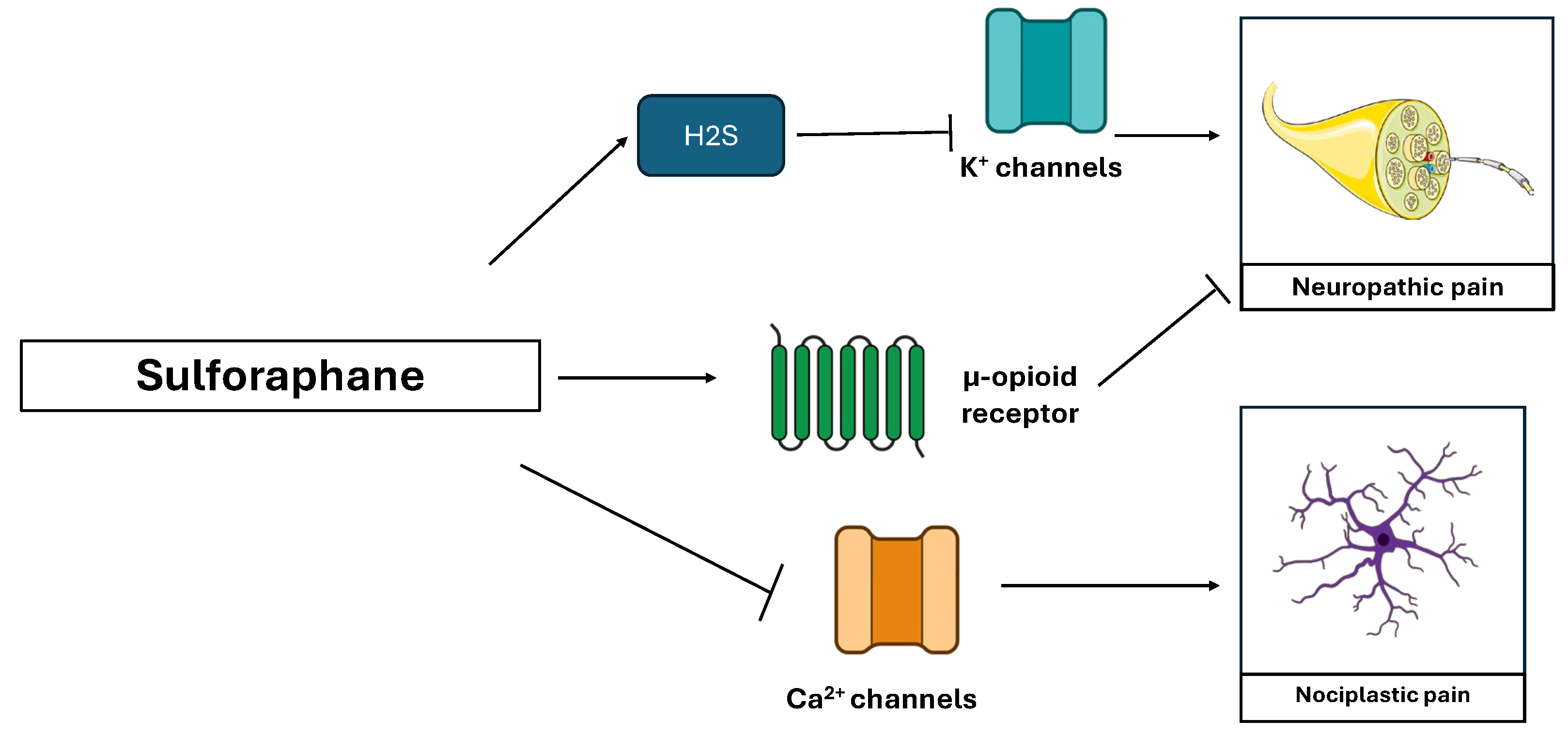
3.7. Sulforaphane (Brassica oleracea)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IASP International Association for the Study of Pain-Terminology. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/terminology/ (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- IASP High Impact Chronic Pain-International Association for the Study of Pain. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/fact-sheets/high-impact-chronic-pain/#:~:text=Chronic-pain-is-a-major,than-three-months-%5B2%5D (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Series Chronic Pain 1 Chronic Pain: An Update on Burden, Best Practices, and New Advances. Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcianò, G.; Vocca, C.; Evangelista, M.; Palleria, C.; Muraca, L.; Galati, C.; Monea, F.; Sportiello, L.; Sarro, G.D.; Capuano, A.; et al. The Pharmacological Treatment of Chronic Pain: From Guidelines to Daily Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Arif, A.W.; Bhan, C.; Kumar, D.; Malik, M.B.; Sayyed, Z.; Akhtar, K.H.; Ahmad, M.Q. Managing Chronic Pain in the Elderly: An Overview of the Recent Therapeutic Advancements. Cureus 2018, 10, e3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, G.; Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R.; Scherrer, G. Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 41, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.O.; Christie, R.; Harris, E.; Penning, J.; Mcvicar, J. Tramadol and Tapentadol: Clinical and Pharmacologic Review. Available online: https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/tramadol-and-tapentadol-clinical-and-pharmacologic-review/ (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Rodrigues-Amorim, D.; Olivares, J.M.; Spuch, C.; Rivera-Baltanás, T. A Systematic Review of Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Duloxetine. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 554899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, H.; Friedrich, C.M.; Cole, P.; Eccleston, C.; Serfaty, M.; Stewart, G.; White, S.; Moore, R.A.; Phillippo, D.; Pincus, T. Antidepressants for Pain Management in Adults with Chronic Pain: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD014682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urits, I.; Li, N.; Berardino, K.; Artounian, K.A.; Bandi, P.; Jung, J.W.; Kaye, R.J.; Manchikanti, L.; Kaye, A.M.; Simopoulos, T.; et al. The Use of Antineuropathic Medications for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 34, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, B.W.; Backes, D.; Bindels, P.J.E. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy Pharmacotherapy for Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: Current and Future Options Pharmacotherapy for Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: Current and Future Options. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, M.S.; Selph, S.S.; Buckley, D.I.; Holmes, R.S.; Mauer, K.; Ramirez, S.; Hsu, F.C.; Dana, T.; Fu, R.; Chou, R. Nonopioid Pharmacologic Treatments for Chronic Pain; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, A.; Ing, J.; Hsu, E. Opioid-Related Side Effects and Management. Cancer Treat. Res. 2021, 182, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpaa, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain in Adults: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Updated NeuPSig Recommendations. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muanda, F.T.; Weir, M.A.; Ahmadi, F.; Sontrop, J.M.; Cowan, A.; Fleet, J.L.; Blake, P.G.; Garg, A.X. Higher-Dose Gabapentinoids and the Risk of Adverse Events in Older Adults With CKD: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 98–107.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thour, A.; Marwaha, R. Amitriptyline. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- García-Rayado, G.; Navarro, M.; Lanas, A. NSAID Induced Gastrointestinal Damage and Designing GI-Sparing NSAIDs. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, N.; Pollack, C.; Butkerait, P. Adverse Drug Reactions and Drug-Drug Interactions with over-the-Counter NSAIDs. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcianò, G.; Muraca, L.; Rania, V.; Gallelli, L. Ibuprofen in the Management of Viral Infections: The Lesson of COVID-19 for Its Use in a Clinical Setting. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 63, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Nagpal, M.; Singh, I.; Singh, M.; Dhingra, G.A.; Huanbutta, K.; Dheer, D.; Sharma, A.; Sangnim, T. A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceuticals: Therapy Support and Formulation Challenges. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, G.; Marcianò, G.; Viola, P.; Palleria, C.; Pisani, D.; Rania, V.; Casarella, A.; Astorina, A.; Scarpa, A.; Esposito, M.; et al. Nutraceuticals for Peripheral Vestibular Pathology: Properties, Usefulness, Future Perspectives and Medico-Legal Aspects. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIA Drolessano-Società Italiana Di Andrologia. Available online: https://www.siabc.it/drolessano (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Sebastiani, F.; Alterio, C.D.; Vocca, C.; Gallelli, L.; Palumbo, F.; Cai, T.; Palmieri, A. Effectiveness of Silymarin, Sulforaphane, Lycopene, Green Tea, Tryptophan, Glutathione, and Escin on Human Health: A Narrative Review. Uro 2023, 3, 208–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, B.; Bai, Y.; Miao, T.; Rui, L.; Zhang, H.; Xia, B.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Lycopene in Protection against Obesity and Diabetes: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancak, M.; Altintas, D.; Balaban, Y.; Caliskan, U.K. Evidence-Based Herbal Treatments in Liver Diseases. Hepatol. Forum. 2024, 5, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašková, J.; Kočan, L.; Vaško, L.; Perjési, P. Glutathione-Related Enzymes and Proteins: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcianò, G.; Vocca, C.; Dıraçoglu, D.; Özda, R.; Gallelli, L. Escin’ s Action on Bradykinin Pathway: Advantageous Clinical Properties for an Unknown Mechanism? Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.M.; Akter, S.; Lin, C.-N.; Nazzal, S. Sulforaphane as an Anticancer Molecule: Mechanisms of Action, Synergistic Effects, Enhancement of Drug Safety, and Delivery Systems. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2020, 43, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.; Rashidi, N.; Nurgali, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolites in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Goto, S.; Monira, P.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Green Tea. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Mitra, D.; Das, P.K.; Oana, A.; Mon, E.; Janmeda, P.; Martorell, M.; Iriti, M.; Ibrayeva, M.; Sharifi-rad, J.; et al. Camellia Sinensis: Insights on Its Molecular Mechanisms of Action towards Nutraceutical, Anticancer Potential and Other Therapeutic Applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Sharma, S.; Chopra, K. Lycopene Attenuates Thermal Hyperalgesia in a Diabetic Mouse Model of Neuropathic Pain. Eur. J. Pain. 2008, 12, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Morioka, N.; Kitamura, T.; Fujii, S.; Miyauchi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Hisaoka-nakashima, K.; Nakata, Y. Lycopene Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain by Upregulating Spinal Astrocytic Connexin 43 Expression. Life Sci. 2016, 155, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, L.; He, S.; Ren, H.; Zhou, N.; Hu, Z. Lycopene Alleviates Disc Degeneration under Oxidative Stress through the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 51, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Xie, H. Effect of Lycopene on Pain Facilitation and the SIRT1 / mTOR Pathway in the Dorsal Horn of Burn Injury Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 889, 173365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Castro, L.; Fang, C.; Castro, M.; Sherali, S.; White, S.; Wang, R.; Neugebauer, V. Bioactive Compounds for Neuropathic Pain: An Update on Preclinical Studies and Future Perspectives. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 104, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.; Tyagi, N. Potential Contribution of Antioxidant Mechanism in the Defensive Effect of Lycopene Against Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation Induced Behavioral, Biochemical and Histopathological Modification in Wistar Rats. Drug Res. 2016, 66, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Huang, Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Lycopene in Spinal Cord Injury in Rats via Antioxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 642, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, G.; Fong, T.H.; Tzu, N.H.; Lin, K.H.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. A Potent Antioxidant, Lycopene, Affords Neuroprotection Against Microglia Activation and Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. In Vivo 2004, 18, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bacanli, M.; Basaran, N.; Basaran, A.A. Lycopene: Is It Beneficial to Human Health as an Antioxidant? Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 14, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grether-Beck, S.; Marini, A.; Jaenicke, T.; Stahl, W.; Krutmann, J. Molecular Evidence That Oral Supplementation with Lycopene or Lutein Protects Human Skin against Ultraviolet Radiation: Results from a Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Miyauchi, T.; Kitamura, S.; Iwata, H.; Hata, H.; Ujiie, H. Carotenoderma Due to Lycopenemia: A Case Report and Evaluation of Lycopene Deposition in the Skin. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaping, Z.; Wenli, Y.; Weile, H.; Ying, Y. Anti-Inflammatory and Anticoagulant Activities of Lycopene in Mice. Nutr. Res. 2003, 23, 1591–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, M.; Hua, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H. Combination of Autophagy and NFE2L2 / NRF2 Activation as a Treatment Approach for Neuropathic Pain. Autophagy 2021, 17, 4062–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, T.; Arab, M.G.L.; Santos, G.S.; Alkass, N.; Andrade, M.A.P.; Lana, J.F.S.D. The Protective Role of Glutathione in Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 15, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richie, J.P.; Nichenametla, S.; Neidig, W.; Calcagnotto, A.; Haley, J.S.; Schell, T.D.; Muscat, J.E. Randomized Controlled Trial of Oral Glutathione Supplementation on Body Stores of Glutathione. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Sinha, I.; Calcagnotto, A.; Trushin, N.; Haley, J.S.; Schell, T.D.; Richie, J.P. Oral Supplementation with Liposomal Glutathione Elevates Body Stores of Glutathione and Markers of Immune Function. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handog, E.B.; Datuin, M.S.L.; Singzon, I.A. An Open-Label, Single-Arm Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Preparation of Glutathione as a Skin-Lightening Agent in Filipino Women. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, F.V.; Rezaee, R.; Sazegara, H.; Hashemzaei, M.; Karimi, G. Effects of Silymarin on Neuropathic Pain and Formalin—Induced Nociception in Mice. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 715–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zugravu, G.S.; Pintilescu, C.; Cumpat, C.; Miron, S.D.; Miron, A. Silymarin Supplementation in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Outcomes of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, M.E.; Elieh-Ali-Komi, D.; Goudarzi, F.; Mohammadi-Noori, E.; Assar, S.; Shavandi, M.; Kiani, A.; Elahi, H. Effects of Silymarin as Adjuvant Drug on Serum Levels of CTRP3, Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (CCP), and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (Hs-CRP) in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2024, 13, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, V.; Delghandi, P.S.; Moallem, S.A.; Karimi, G. Safety and Toxicity of Silymarin, the Major Constituent of Milk Thistle Extract: An Updated Review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L. Escin: A Review of Its Anti-Edematous, Antiinflammatory, and Venotonic Properties. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L.; Cione, E.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Glucocorticoid-Like Activity of Escin: A New Mechanism for an Old Drug. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-Q.; Xu, S.-Q.; Cheng, J.; Cao, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.-P.; Huang, Y.-J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.-M. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of External Use of Escin on Cutaneous Inflammation: Possible Involvement of Glucocorticoids Receptor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, H.; Segesser, B.; Bulitta, M.; Wetzel, D.; Bertram, S. Efficacy and Tolerability of Escin/Diethylamine Salicylate Combination Gels in Patients with Blunt Injuries of the Extremities. Int. J. Sports Med. 2001, 22, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, D.; Menke, W.; Dieter, R.; Smasal, V.; Giannetti, B.; Bulitta, M. Escin/Diethylammonium Salicylate/Heparin Combination Gels for the Topical Treatment of Acute Impact Injuries: A Randomised, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Multicentre Study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2002, 36, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Wei, G. Ameliorative Effects of Escin on Neuropathic Pain Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury of Sciatic Nerve. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Belcaro, G.; Cesarone, M.R.; Feragalli, B.; Cotellese, R.; Dugall, M.; Scipione, C.; Scipione, V.; Maione, C.; Maramaldi, G.; et al. A Sport Cream (Harpago-Boswellia-Ginger-Escin) for Localized Neck/Shoulder Pain. Minerva Med. 2021, 112, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AIFA—Ricerca Farmaco. Available online: https://medicinali.aifa.gov.it/it/#/it/dettaglio/0000006586 (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Pittler, M.H.; Ernst, E. Horse Chestnut Seed Extract for Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD003230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Fanni, T.; Szab, Á. Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado Division of Workers’ Compensation. Chronic Pain Disorder Medical Treatment Guideline; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network-Management of Chronic Pain. Available online: https://www.sign.ac.uk/our-guidelines/management-of-chronic-pain/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Binvignat, M.; Emond, P.; Mifsud, F.; Miao, B.; Courties, A.; Lefèvre, A.; Maheu, E.; Crema, M.D.; Klatzmann, D.; Kloppenburg, M.; et al. Serum Tryptophan Metabolites Are Associated with Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis and Pain: Results from the DIGICOD Cohort. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Bär, K.-J.; Karmann, A.J.; Wagner, G.; Lautenbacher, S. Facial Expressions of Pain: The Role of the Serotonergic System. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.B. Pain and Tryptophan. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 53, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, V.; Secchettin, E.; Castellani, C.; Martini, A.; Mazzocchi, E.; Picelli, A.; Polati, E.; Donadello, K.; Valenti, M.T.; Dalle Carbonare, L. Comparison between Acupuncture and Nutraceutical Treatment with Migratens ® in Patients with Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselló Aubach, L.; Fornós Roca, X.; Fernández Álvarez, M.E. Effects of Coenzyme Q10, Tryptophan, and Magnesium Supplementation on Fatigue in Patients with Fibromyalgia—A Randomized Trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2025, 22, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiger, A.N.; Penzel, T.; Fietze, I. Chronic Pain Management and Sleep Disorders. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, H.; Flores, S.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Paul, T.; Argueta, E.D.d.e.; Nwosu, M.; Sherpa, P.L.; Ramirez, M.R.D.d.e.; Falla, D.A.R.; Natera, D.; et al. Neuropsychiatric Factors Involved in the Development of Fibromyalgia: A Literature Review. OROAJ 2023, 22, 01–09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Side Effects of Amino Acid Supplements. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Effects and Side Effects Associated with the Non-Nutritional Use of Tryptophan by Humans. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2236S–2244S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullano, S.A.; Marcianò, G.; Bianco, M.G.; Oliva, G.; Rania, V.; Vocca, C.; Cione, E.; De Sarro, G.; Gallelli, L.; Romeo, P.; et al. FT-IR Analysis of Structural Changes in Ketoprofen Lysine Salt and KiOil Caused by a Pulsed Magnetic Field. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashempur, M.H.; Sadrneshin, S.; Mosavat, S.H.; Ashraf, A. Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) for Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Open-Label Active-Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimonte, S.; Cascella, M.; Schiavone, V.; Mehrabi-Kermani, F.; Cuomo, A. The Roles of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: An Update on Preclinical in Vivo Studies and Future Perspectives. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmat, A.; Hussein, M.S. Green Tea Extract for Mild-to-Moderate Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy A Randomized Controlled Trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Chiu, J.-P.; Hsu, C.-H. Therapeutic Effect of High-Dose Green Tea Extract on Weight Reduction: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, F.; Shouval, D. Hepatotoxicity of Herbal and Dietary Supplements: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS); Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the Safety of Green Tea Catechins. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papini, J.Z.B.; de Assis Esteves, B.; de Souza Oliveira, V.G.; Abdalla, H.B.; Cereda, C.M.S.; de Araújo, D.R.; Tofoli, G.R. Analgesic Effect of Sulforaphane: A New Application for Poloxamer-Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels. Gels 2024, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Sulforaphane in Chronic Constriction Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain Mice. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.S. Nrf2 and NF- κ B Modulation by Sulforaphane Counteracts Multiple Manifestations of Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats and High Glucose-Induced Changes. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2011, 8, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, C.; Fang, X.; Zhan, G.; Huang, N.; Gao, J.; Xu, H.; Orlando, G. Role of Keap1-Nrf2 Signaling in Anhedonia Symptoms in a Rat Model of Chronic Neuropathic Pain: Improvement with Sulforaphane. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, A.; Chamorro, P.A.F.; Riego, G.; Leánez, S.; Pol, O. Treatment with Sulforaphane Produces Antinociception and Improves Morphine Effects during Inflammatory Pain in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 363, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, E.; Testai, L.; Micheli, L.; Trallori, E.; Citi, V.; Martelli, A.; Rosalinda, G.; Renato, D.N.; Vincenzo, I.; Ghelardini, C.; et al. Effect of Glucoraphanin and Sulforaphane against Chemotherapy—Induced Neuropathic Pain: Kv7 Potassium Channels Modulation by H 2 S Release in Vivo. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadarrama-Enríquez, O.; Moreno-Pérez, G.; González-Trujano, M.E.; Ángeles-López, G.; Ventura-Martínez, R.; Díaz-Reval, I.; Cano-Martínez, A.; Pellicer, F.; Baenas, N.; Moreno, D.; et al. Antinociceptive and Antiedema Effects Produced in Rats by Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica Sprouts Involving Sulforaphane. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 3217–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, G.; Lin, Z.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Xia, X.; Ma, X.; Zou, F.; et al. Sulforaphane Delays Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Nucleus Pulposus. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 3626091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Díaz, I.-Y.; González-Trujano, M.E.; Martínez-Vargas, D.; Moreno-Pérez, G.F.; Hernandez-Leon, A.; Narváez-González, H.F.; Ventura-Martínez, R.; Pellicer, F.; López-Muñoz, F.J. Pharmacological Interactions of Sulforaphane and Gabapentin in a Murine Fibromyalgia-like Pain Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 184, 117929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Rodrigues, J.F.; Silva, E.; Silva, C.; França Muniz, T.; de Aquino, A.F.; Neuza da Silva Nina, L.; Fialho Sousa, N.C.; Nascimento da Silva, L.C.; de Souza, B.G.G.F.; da Penha, T.A.; et al. Sulforaphane Modulates Joint Inflammation in a Murine Model of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Mono-Arthritis. Molecules 2018, 23, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElKhalifa, D.; Al-Ziftawi, N.; Awaisu, A.; Alali, F.; Khalil, A. Efficacy and Tolerability of Sulforaphane in the Therapeutic Management of Cancers: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1251895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Dou, C.; Hu, L.; Du, G.; Wei, G. Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism of Escin against Neuropathic Pain: A Network Pharmacology Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2023, 16, 3734861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, K.; Shepherd, A.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Haroutounian, S. Neuropathic Pain: Central vs. Peripher. Mechanisms. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.L.; Miller, R.E. Molecular Pathogenesis of OA Pain_ Past, Present, and Future. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2024, 32, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharz, E.J.; Szántó, S.; Ivanova Goycheva, M.; Petronijević, M.; Šimnovec, K.; Domżalski, M.; Gallelli, L.; Kamenov, Z.; Konstantynowicz, J.; Radunović, G.; et al. Endorsement by Central European Experts of the Revised ESCEO Algorithm for the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Chronic Pain (Primary and Secondary) in over 16s: Assessment of All Chronic Pain and Management of Chronic Primary Pain. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng193 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- GVR Nutraceuticals Market Size & Trends-Grand View Research. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/nutraceuticals-market (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Cole, J.A.; Gonçalves-Bradley, D.C.; Alqahtani, M.; Barry, H.E.; Cadogan, C.; Rankin, A.; Patterson, S.M.; Kerse, N.; Cardwell, C.R.; Ryan, C.; et al. Interventions to Improve the Appropriate Use of Polypharmacy for Older People. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 11, CD008165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vocca, C.; Siniscalchi, A.; Rania, V.; Galati, C.; Marcianò, G.; Palleria, C.; Catarisano, L.; Gareri, I.; Leuzzi, M.; Muraca, L.; et al. The Risk of Drug Interactions in Older Primary Care Patients after Hospital Discharge: The Role of Drug Reconciliation. Geriatrics 2023, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova-Gueorguieva, E.S.; Getov, I.N.; Ivanov, K.V.; Ivanova, S.D.; Gueorguiev, S.R.; Getova, V.I.; Mihaylova, A.A.; Madzharov, V.G.; Staynova, R.A. Regulatory Requirements for Food Supplements in the European Union and Bulgaria. Folia Medica 2019, 61, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Sawarkar, S.; Doshi, G.; Pimple, P.; Shah, J.; Bana, T. Chapter Twenty One—Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Nutraceuticals. In Industrial Application of Functional Foods, Ingredients and Nutraceuticals; Anandharamakrishnan, C., Subramanian, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 725–783. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2001/83/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 November 2001 on the Community Code Relating to Medicinal Products for Human Use. 2001, Volume 311. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/directive-200183ec_en?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R. Therapeutic Efficacy of Palmitoylethanolamide and Its New Formulations in Synergy with Different Antioxidant Molecules Present in Diets. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Giorgi, V.; Di Lascio, S.; Fornasari, D. Acetyl-L-Carnitine in Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.C.; McKenna, M.C. L-Carnitine and Acetyl-L-Carnitine Roles and Neuroprotection in Developing Brain. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogacci, F.; Rizzo, M.; Krogager, C.; Kennedy, C.; Georges, C.M.G.; Knežević, T.; Liberopoulos, E.; Vallée, A.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Wenstedt, E.F.E.; et al. Safety Evaluation of A-lipoic Acid Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Placebo-controlled Clinical Studies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baicus, C.; Purcarea, A.; von Elm, E.; Delcea, C.; Furtunescu, F.L. Alpha-Lipoic Acid for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 2024, CD012967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artukoglu, B.B.; Beyer, C.; Zuloff-Shani, A.; Brener, E.; Bloch, M.H. Efficacy of Palmitoylethanolamide for Pain: A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician 2017, 20, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Shavandi, M.; Yazdani, Y.; Asar, S.; Mohammadi, A. The Effect of Oral Administration of Silymarin on Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-1ß in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Iran. J. Immunol. 2022, 19, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, S.; Arcuri, E.; Santoni, A. Opioid-Induced Tolerance and Hyperalgesia. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Muley, M.M.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Microglia-Independent Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Male and Female Mice. Pain 2022, 163, e1129–e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.L.; Lim, M.; Doshi, T.L. Targeting Cytokines for Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Scand. J. Pain 2017, 17, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coraggio, V.; Guida, F.; Boccella, S.; Scafuro, M.; Paino, S.; Romano, D.; Maione, S.; Luongo, L. Neuroimmune-Driven Neuropathic Pain Establishment: A Focus on Gender Differences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound/Nutraceutical | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|
| Lycopene | TNF-α and NO inhibition. | [33] |
| COX-2 inhibition | [33] | |
| Restoring the expression of Cx 43 | [34] | |
| Modulation on Nrf2 and autophagy modulation | [35] | |
| Reduced glial activation. A decrease in the expression of markers like pS6, mTOR, GFAP, p4EBP, Iba 1 and SIRT 1. | [36] | |
| A reduction in thermal and cold hyperalgesia, an increase in CAT, GSH, SOD, MDA levels and signs of histopathological nerve damage, a reduction in cell apoptosis. | [37] | |
| Neuroprotective effect on microglia | [40] | |
| Silymarin | Inhibition of PGE2, leukotrienes, NO, cytokines production IL 1-β and TNF-α reduction, and neutrophils infiltration. Silymarin is also a scavenger, and this may account for its beneficial properties. | [50] |
| Reduced glutathione | Antioxidant effects | [45] |
| Escin | Glucocorticoid like activity with inhibition of NF-κB and hyaluronidase | [55] |
| Action on bradykinin pathway | [28] | |
| Antioxidant effect and endothelium protection | [54,93] | |
| Downregulation of TNF and IL1ß, TLR4, NF-κB, GFAP and NGF. | [59] | |
| Targeting of MMP9, SRC, PTGS 2, and MAPK 1, PKC, the T-cell receptors signaling pathway, TRP channels, and TNF. | [54,93] | |
| Tryptophan | Improvement of pain related dysfunction including mood disorders and insomnia, acting on serotonin pathway. | [69] |
| Green tea | Inhibition of PMNs, NADPH-oxidase, myeloperoxidase, and to favor scavenging of superoxide anions. | [77] |
| Inhibition of nNOS/NO; CX3CL1, JNK, and NF-κB; TNF-α. | [77] | |
| Sulforaphane | Inhibition of Nrf 2, IL-1β, TNFα, COX-2, NLRP 3, NF-κB and CGRP | [82] |
| An increase in IL-10 | [88,89] | |
| An increase in μ opioid receptor expression | [83] | |
| Inhibition of the release of H2S and of potassium Kv7 channels activation | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcianò, G.; Rania, V.; Vocca, C.; Palleria, C.; Crudo, M.; Evangelista, M.; Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Caroleo, M.C.; Gallelli, L.; Srečec, S. The Role and Safety of Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals as Adjuvant Treatments for Pain Management: A Narrative Review. Nutraceuticals 2025, 5, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5040038
Marcianò G, Rania V, Vocca C, Palleria C, Crudo M, Evangelista M, Abrego-Guandique DM, Caroleo MC, Gallelli L, Srečec S. The Role and Safety of Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals as Adjuvant Treatments for Pain Management: A Narrative Review. Nutraceuticals. 2025; 5(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcianò, Gianmarco, Vincenzo Rania, Cristina Vocca, Caterina Palleria, Michele Crudo, Maurizio Evangelista, Diana Marisol Abrego-Guandique, Maria Cristina Caroleo, Luca Gallelli, and Siniša Srečec. 2025. "The Role and Safety of Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals as Adjuvant Treatments for Pain Management: A Narrative Review" Nutraceuticals 5, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5040038
APA StyleMarcianò, G., Rania, V., Vocca, C., Palleria, C., Crudo, M., Evangelista, M., Abrego-Guandique, D. M., Caroleo, M. C., Gallelli, L., & Srečec, S. (2025). The Role and Safety of Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals as Adjuvant Treatments for Pain Management: A Narrative Review. Nutraceuticals, 5(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals5040038








