Melatonin Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Western Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
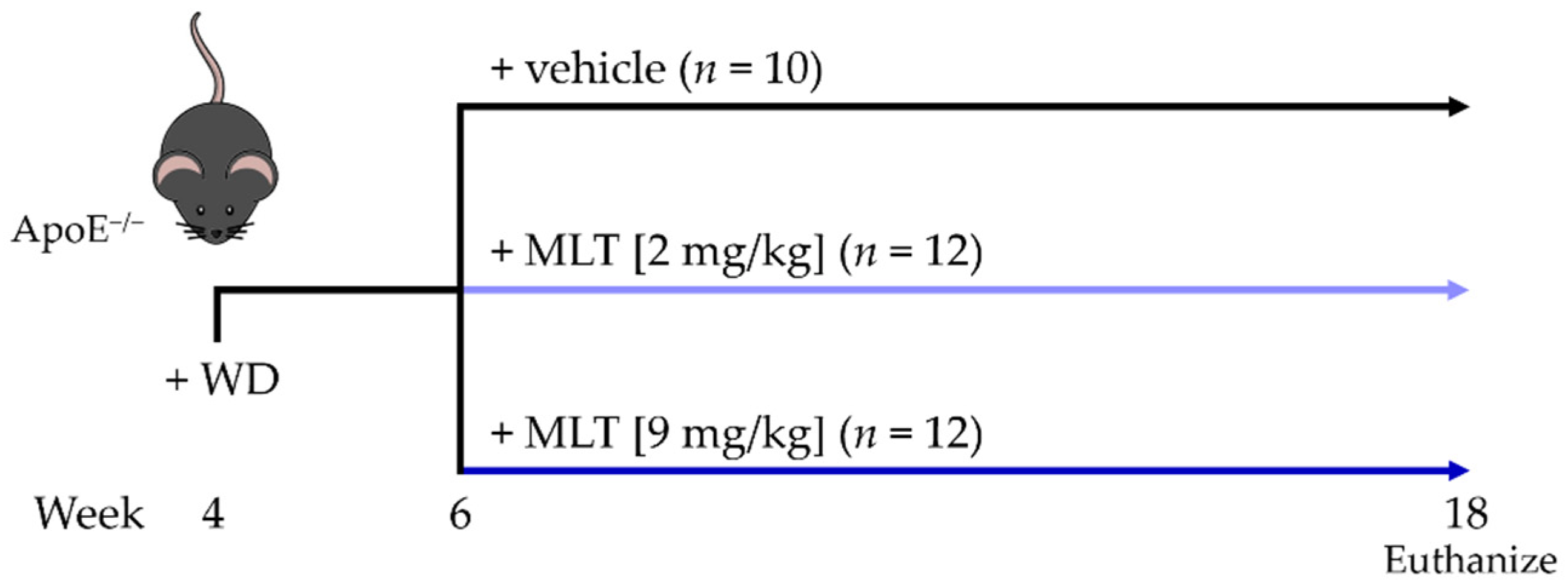
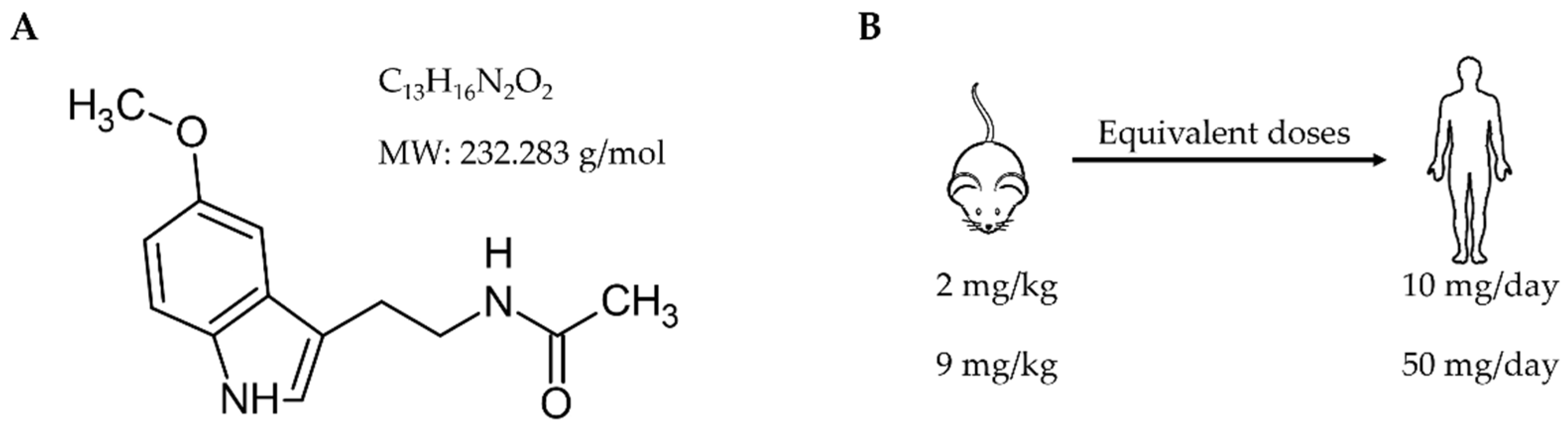
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Plasma and Hepatic–Lipid Profile
2.3. White Blood Cell (WBC) Count
2.4. Plasma ELISA
2.5. Plasma Antioxidant Capacity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
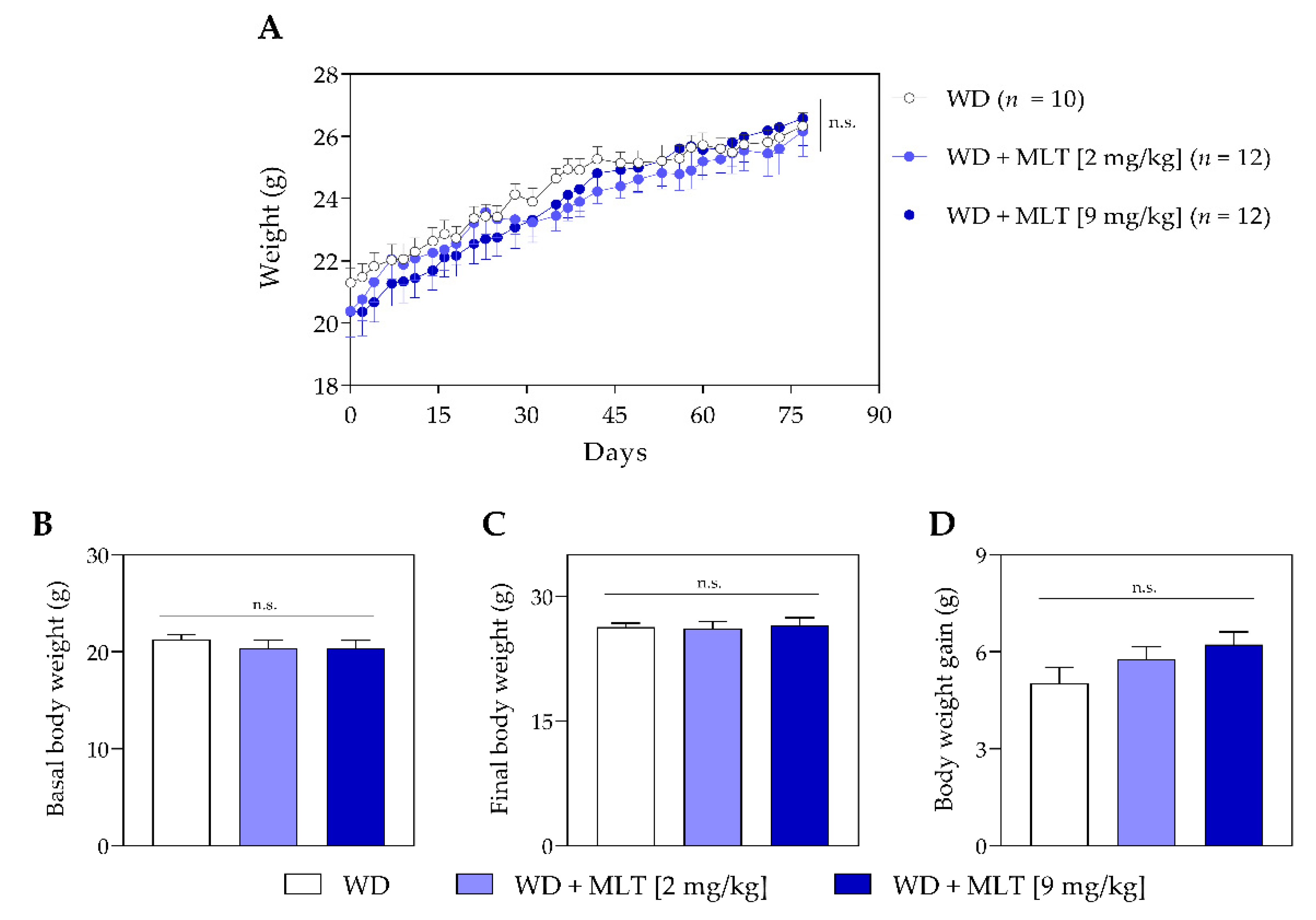
3.1. Melatonin Does Not Alter the Body Weight of Mice
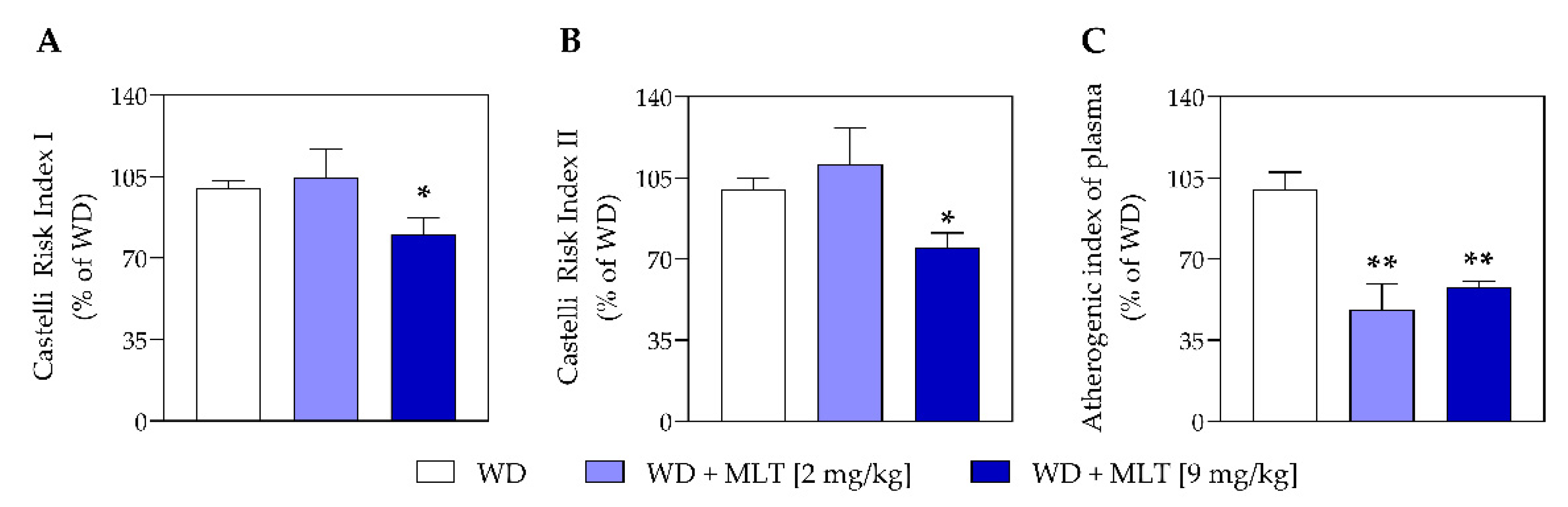
3.2. MLT Improves the Plasmatic Lipid Profile and Reduces the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
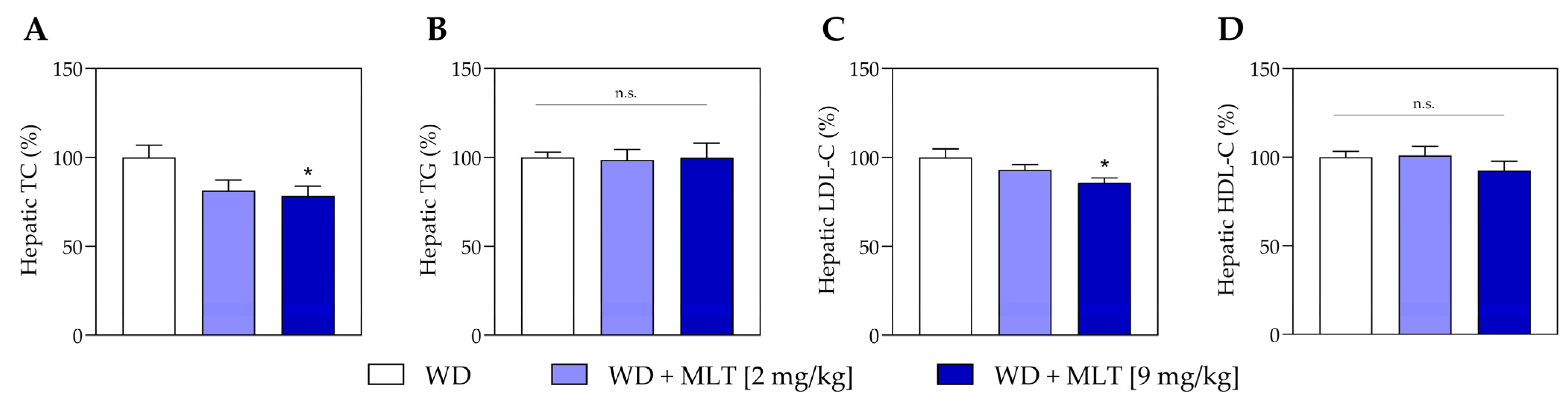
3.3. MLT Treatment Decreases Hepatic Lipids
3.4. MLT Reduces Lymphocytosis
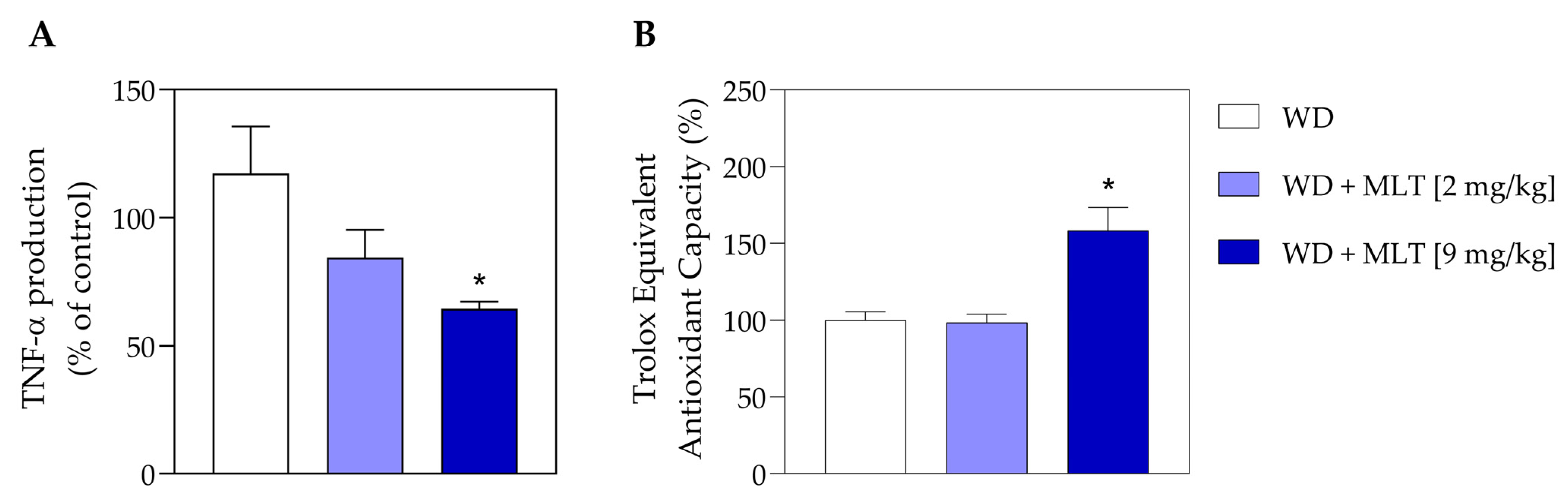
3.5. MLT Reduces the Number of TNF Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Improves the Antioxidant Capacity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.M.; Castelli, W.P.; Levy, D. Cholesterol and mortality: 30 years of follow-up from the Framingham study. JAMA 1987, 257, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Raman, G.; Vishwanathan, R.; Jacques, P.F.; Johnson, E.J. Dietary cholesterol and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Bonapace, S.; Byrne, C. Does high LDL-cholesterol cause cardiovascular disease? Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinick, T.; Duly, E. Hyperlipidemia: Overview; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bardagjy, A.S.; Steinberg, F.M. Relationship between HDL functional characteristics and cardiovascular health and potential impact of dietary patterns: A narrative review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criqui, M.H.; Golomb, B.A. Epidemiologic aspects of lipid abnormalities. Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 48s–57s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpınar, O.; Bozkurt, A.; Acartürk, E.; Seydaoğlu, G. A new index (CHOLINDEX) in detecting coronary artery disease risk. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2013, 13, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Loprinzi, P.D. Atherogenic Index of Plasma and Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Predict Mortality Risk Better Than Individual Cholesterol Risk Factors, Among an Older Adult Population. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiásová, M.; Frohlich, J.; Sedová, M.; Cheung, M.C.; Brown, B.G. Cholesterol esterification and atherogenic index of plasma correlate with lipoprotein size and findings on coronary angiography. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Shi, G.; Xue, S.; Lu, W. The atherogenic index of plasma is a strong and independent predictor for coronary artery disease in the Chinese Han population. Medicine 2017, 96, e8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olamoyegun, M.A.; Oluyombo, R.; Asaolu, S.O. Evaluation of dyslipidemia, lipid ratios, and atherogenic index as cardiovascular risk factors among semi-urban dwellers in Nigeria. Ann. Afr. Med. 2016, 15, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.; Pintó, X.; Muñoz, A.; Zúñiga, M.; Rubiés-Prat, J.; Pallardo, L.F.; Masana, L.; Mangas, A.; Hernández-Mijares, A.; González-Santos, P.; et al. Lipoprotein ratios: Physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular prevention. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hadaegh, F.; Khalili, D.; Ghasemi, A.; Tohidi, M.; Sheikholeslami, F.; Azizi, F. Triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol ratio is an independent predictor for coronary heart disease in a population of Iranian men. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, V.; Johnson, B.D.; Zineh, I.; Rogers, W.J.; Vido, D.; Marroquin, O.C.; Bairey-Merz, C.N.; Sopko, G. The TG/HDL cholesterol ratio predicts all cause mortality in women with suspected myocardial ischemia a report from the Women’s ischemia syndrome evaluation (WISE). Am. Heart J. 2009, 157, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoluci, M.C.; Quadros, A.S.; Sarmento-Leite, R.; Schaan, B.D. Insulin resistance and triglyceride/HDLc index are associated with coronary artery disease. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madjid, M.; Fatemi, O. Components of the complete blood count as risk predictors for coronary heart disease: In-depth review and update. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2013, 40, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubler, M.J.; Kennedy, A.J. Role of lipids in the metabolism and activation of immune cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, S.; Chan, Y.; Paltser, G.; Truong, D.; Tsui, H.; Bahrami, J.; Dorfman, R.; Wang, Y.; Zielenski, J.; Mastronardi, F.; et al. Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keusch, G.T. The history of nutrition: Malnutrition, infection and immunity. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 336S–340S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Ward, A.; Treasure, J.; Peakman, M. T lymphocyte subpopulations in anorexia nervosa and refeeding. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 82, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maysami, S.; Haley, M.J.; Gorenkova, N.; Krishnan, S.; McColl, B.W.; Lawrence, C.B. Prolonged diet-induced obesity in mice modifies the inflammatory response and leads to worse outcome after stroke. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaldivar, F.; McMurray, R.; Nemet, D.; Galassetti, P.; Mills, P.; Cooper, D. Body fat and circulating leukocytes in children. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois-Deruy, E.; Peugnet, V.; Turkieh, A.; Pinet, F. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourino-Alvarez, L.; Sastre-Oliva, T.; Corbacho-Alonso, N.; Barderas, M.G. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. In Importance of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant System in Health and Disease; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J. Physiology and pharmacology of melatonin in relation to biological rhythms. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Q.; Fichna, J.; Bashashati, M.; Li, Y.-Y.; Storr, M. Distribution, function and physiological role of melatonin in the lower gut. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2011, 17, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Melatonin: Buffering the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8638–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.A.R. Effect of melatonin on cholesterol absorption in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.; Tang, P. Effect of melatonin on the maintenance of cholesterol homeostasis in the rat. Endocr. Res. 1995, 21, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.; Nelson, B.; Obianime, W.A. Beneficial effects of melatonin and alpha lipoic acid on lopinavir/ritonavir-induced alterations in lipid and glucose levels in male albino rats. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 85, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Allagui, M.S.; Hachani, R.; Saidi, S.; Feriani, A.; Murat, J.C.; Kacem, K. Pleiotropic protective roles of melatonin against aluminium-induced toxicity in rats. General. Physiol. Biophys. 2015, 34, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi-Sartang, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Mazloom, Z. Effects of melatonin supplementation on blood lipid concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Díaz-Sánchez, M.; Sarmiento-Soto, H.; Medrano-Campillo, P.; Martínez-López, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Guerrero, J.M.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Melatonin reduces inflammatory response in peripheral T helper lymphocytes from relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Naji, L.; Fernández-Santos, J.M.; Martín-Lacave, I.; Guerrero, J.M.; Calvo, J.R. Beneficial pleiotropic actions of melatonin in an experimental model of septic shock in mice: Regulation of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokine network, protection against oxidative damage and anti-apoptotic effects. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Dehpour, A.R.; Shirooie, S.; Silva, A.S.; Baldi, A.; Khan, H.; Daglia, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of Melatonin: A mechanistic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, M.F.; Utami, S.B.; Fulyani, F.; Kresnoadi, E.; Wicaksono, S.A. Melatonin prevented the elevation of leukocyte count and the decreased of hematocrit levels in burn-induced Wistar Rats. Bali Med. J. 2021, 10, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, M.; Makhlouf, K.; Ghattassi, K.; Graja, A.; Ferchichi, S.; Kallel, C.; Houda, M.; Souissi, N.; Hammouda, O. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise attenuate muscle damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation during intense short term effort in the following day in teenage athletes. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalelioglu, T.; Genc, A.; Karamustafalioglu, N.; Emul, M. Assessment of cardiovascular risk via atherogenic indices in patients with bipolar disorder manic episode and alterations with treatment. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2017, 11, S473–S475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Sasso, G.; Schlage, W.K.; Boué, S.; Veljkovic, E.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J. The Apoe−/− mouse model: A suitable model to study cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and harm reduction. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, M.B.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated LDL cholesterol and increased risk of myocardial infarction and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in individuals aged 70–100 years: A contemporary primary prevention cohort. Lancet 2020, 396, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.J.; Probstfield, J.L.; Garrison, R.J.; Neaton, J.D.; Castelli, W.P.; Knoke, J.D.; Jacobs Jr, D.R.; Bangdiwala, S.; Tyroler, H.A. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 1989, 79, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Fernandez, A.; Banerjee, R.; Thomaides-Brears, H.; Telford, A.; Sanyal, A.; Neubauer, S.; Nichols, T.E.; Raman, B.; McCracken, C.; Petersen, S.E. Liver disease is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes-a UK Biobank study. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Song, Y.L.; Xu, J.M.; Gan, H.Z. Melatonin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver induced by high-fat diet in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Huang, F.-f.; Qu, S. Melatonin: A potential intervention for hepatic steatosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, A.; Foroozanfard, F.; Kavossian, E.; Aghadavod, E.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Reiter, R.J.; Eftekhar, T.; Asemi, Z. Effects of melatonin administration on mental health parameters, metabolic and genetic profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 250, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Celinski, K.; Konturek, P.; Konturek, S.; Slomka, M. The effects of L-tryptophan and melatonin on selected biochemical parameters in patients with steatohepatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agil, A.; Navarro-Alarcón, M.; Ruiz, R.; Abuhamadah, S.; El-Mir, M.Y.; Vázquez, G.F. Beneficial effects of melatonin on obesity and lipid profile in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 50, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendawy, A.K.; El-Toukhey, N.E.S.; AbdEl-Rahman, S.S.; Ahmed, H.H. Ameliorating effect of melatonin against nicotine induced lung and heart toxicity in rats (retracted). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35628–35641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Niu, S.; Ni, L.; Di, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, C. Cigarette smoke exposure impairs lipid metabolism by decreasing low-density lipoprotein receptor expression in hepatocytes. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebaid, H.; Bashandy, S.A.; Abdel-Mageed, A.M.; Al-Tamimi, J.; Hassan, I.; Alhazza, I.M. Folic acid and melatonin mitigate diabetic nephropathy in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; McFadden, J.W.; Yang, G.; Zhu, H.; Lian, H.; Fu, T.; Sun, Y.; Gao, T.; Li, M. Effect of melatonin on visceral fat deposition, lipid metabolism and hepatic lipo-metabolic gene expression in male rats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Bhatnagar, M.; Tyagi, S.; Delhi, N. Atherogenic index of plasma, castelli risk index and atherogenic coefficient-new parameters in assessing cardiovascular risk. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Quispe, R.; Elshazly, M.B.; Zhao, D.; Toth, P.P.; Puri, R.; Virani, S.S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Martin, S.S.; Jones, S.R.; Michos, E.D. Total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratio discordance with LDL-cholesterol and non-HDL-cholesterol and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in primary prevention: The ARIC study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.T.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Xie, X. Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP): A novel predictive indicator for the coronary artery disease in postmenopausal women. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; López-González, A.; Utrilla, J.C.; Fernández-Santos, J.M.; Martínez-López, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Guerrero, J.M.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Melatonin controls experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by altering the T effector/regulatory balance. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 50, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Mamun-Or-Rashid, A.N.M.; Lucy, T.T.; Pramanik, M.K.; Sil, B.K.; Mukerjee, N.; Tagde, P.; Yagi, M.; Yonei, Y. Potential Therapeutic Approach of Melatonin against Omicron and Some Other Variants of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2022, 27, 6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Salari, A.A.; Abedi, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Amani, M. Melatonin treatment improves cognitive deficits by altering inflammatory and neurotrophic factors in the hippocampus of obese mice. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 254, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obayashi, K.; Saeki, K.; Kurumatani, N. Higher melatonin secretion is associated with lower leukocyte and platelet counts in the general elderly population: The HEIJO-KYO cohort. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurhaluk, N.; Sliuta, A.; Kyriienko, S.; Winklewski, P.J. Melatonin restores white blood cell count, diminishes glycated haemoglobin level and prevents liver, kidney and muscle oxidative stress in mice exposed to acute ethanol intoxication. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepka, M.; Szwejser, E.; Pijanowski, L.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.L.; Chadzinska, M. A role for melatonin in maintaining the pro-and anti-inflammatory balance by influencing leukocyte migration and apoptosis in carp. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Campillo, P.; Sarmiento-Soto, H.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Álvarez-Ríos, A.I.; Guerrero, J.M.; Rodríguez-Prieto, I.; Castillo-Palma, M.J.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory effect of melatonin on the T-cell response in peripheral blood from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.B.; Moll, T.; El-Kalay, M.; Kohne, C.; Soo Hoo, W.; Encinas, J.; Carlo, D.J. Th1/Th2 cells in inflammatory disease states: Therapeutic implications. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2004, 4, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, L.; Rezzani, R.; Facchetti, L.; Favero, G.; Franco, C.; Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Badawi, R.D.; Guindani, M.; Seo, Y.; Pampaloni, M. Beneficial effects of melatonin on apolipoprotein-E knockout mice by morphological and 18F-FDG PET/CT assessments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Asghari Jafarabadi, M.; Heidari, L.; Nikbakht, R.; Babaahmadi Rezaei, H.; Karandish, M. Effects of melatonin and/or magnesium supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Hosseini, A.; Aghamollaei, H.; Fasihi-Ramandi, M.; Alishiri, G.; Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Hassanpour, K.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.-R.; Farnoosh, G. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress status in the mild and moderate SARS-CoV-2 infected patients: Impact of melatonin as a medicinal supplement. Z. Naturforsch. C 2022, 77, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, E.N.; Tukmagi, H.A.; Haydar, F.; Allami, H.C. Melatonin improves erythropoietin hyporesponsiveness via suppression of inflammation. Rev. Recent. Clin. Trials 2019, 14, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.S.; Teixeira, L.G.; Aguilar, E.C.; Matoso, R.O.; Soares, F.L.; Ferreira, A.V.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I. Differences in adipose tissue inflammation and oxidative status in C57BL/6 and ApoE−/− mice fed high fat diet. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Dietary regulation of oxidative stress in chronic metabolic diseases. Foods 2021, 10, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahbouni, M.; López, M.D.S.; Molina-Carballo, A.; De Haro, T.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A.; Fernández-Ortiz, M.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin treatment reduces oxidative damage and normalizes plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients suffering from Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy: A pilot study in three children. Molecules 2017, 22, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, A.L.; Ortiz, G.G.; Pacheco-Moises, F.P.; Mireles-Ramírez, M.A.; Bitzer-Quintero, O.K.; Delgado-Lara, D.L.; Ramírez-Jirano, L.J.; Velázquez-Brizuela, I.E. Efficacy of melatonin on serum pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Paolorossi, F.; Tancini, G.; Barni, S.; Ardizzoia, A.; Brivio, F.; Zubelewicz, B.; Chatikhine, V. Is there a role for melatonin in the treatment of neoplastic cachexia? Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.; Cecon, E.; Markus, R.P.; Ferreira, Z.S. Effect of TNF-α on the melatonin synthetic pathway in the rat pineal gland: Basis for a ‘feedback’of the immune response on circadian timing. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, G.N.; Cardoso, E.C.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.M.; Markus, R.P. Injury switches melatonin production source from endocrine (pineal) to paracrine (phagocytes)–melatonin in human colostrum and colostrum phagocytes. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, G.N.; Cardoso, E.C.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.M.; Markus, R.P. Pineal melatonin and the innate immune response: The TNF-α increase after cesarean section suppresses nocturnal melatonin production. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, E.K.; Fernandes, P.A.; Marçola, M.; Cruz-Machado, S.d.S.; Markus, R.P. Long-lasting priming of endothelial cells by plasma melatonin levels. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, C.E. T helper cell subsets: Diversification of the field. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2250218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Fang, J.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Agostini, M.; Bernassola, F.; Bove, P.; Candi, E.; Rovella, V.; Sica, G. Macrophage polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biochemical Parameter | WD (mg/dL) | WD + MLT (2 mg/kg) (% of Control) | p-Value | WD + MLT (9 mg/kg) (% of Control) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 506.10 ± 12.34 | 106.20 ± 8.81 | 0.548 | 87.12 ± 6.59 | 0.151 |
| TG | 99.38 ± 0.72 | 110.80 ± 14.89 | 0.706 | 105.20 ± 9.37 | 0.683 |
| LDL-C | 373.20 ± 36.81 | 112.20 ± 12.10 | 0.643 | 75.43 ± 4.39 | 0.008 |
| HDL-C | 113.70 ± 33.59 | 103.40 ± 5.41 | 0.548 | 111.00 ± 11.16 | 0.691 |
| Cells (×103/µL) | WD | MLT (2 mg/kg) | MLT (9 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leukocytes | 1.49 ± 0.21 | 1.14 ± 0.16 | 0.74 ± 0.15 * |
| Lymphocytes | 0.99 ± 0.18 | 0.76 ± 0.14 | 0.43 ± 0.13 * |
| Monocytes | 0.069 ± 0.024 | 0.067 ± 0.021 | 0.062 ± 0.032 |
| Granulocytes | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Sánchez, G.; Álvarez-López, A.I.; Ponce-España, E.; Álvarez-Ríos, A.I.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrillo-Vico, A.; Cruz-Chamorro, I. Melatonin Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Western Diet. Nutraceuticals 2024, 4, 260-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4020016
Santos-Sánchez G, Álvarez-López AI, Ponce-España E, Álvarez-Ríos AI, Lardone PJ, Carrillo-Vico A, Cruz-Chamorro I. Melatonin Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Western Diet. Nutraceuticals. 2024; 4(2):260-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Sánchez, Guillermo, Ana Isabel Álvarez-López, Eduardo Ponce-España, Ana Isabel Álvarez-Ríos, Patricia Judith Lardone, Antonio Carrillo-Vico, and Ivan Cruz-Chamorro. 2024. "Melatonin Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Western Diet" Nutraceuticals 4, no. 2: 260-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4020016
APA StyleSantos-Sánchez, G., Álvarez-López, A. I., Ponce-España, E., Álvarez-Ríos, A. I., Lardone, P. J., Carrillo-Vico, A., & Cruz-Chamorro, I. (2024). Melatonin Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Western Diet. Nutraceuticals, 4(2), 260-272. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4020016











